Chapter 2 Origin of Chordates
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Protostomes
Blastopore becomes mouth
Spiral Cleavage
Schizocoelic Coelom
Determinant Cells
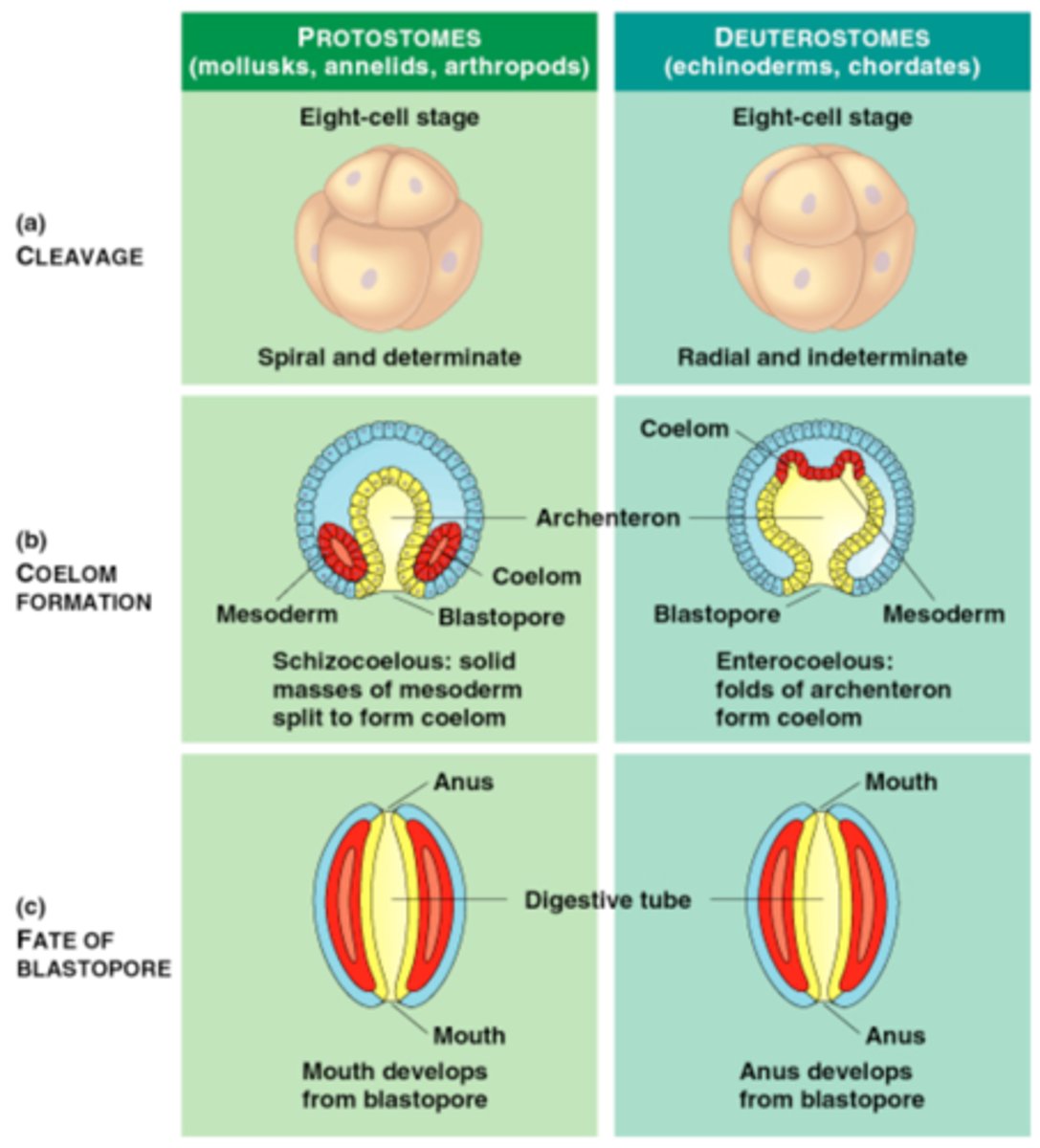
Deuterostomes
Blastopore becomes anus
Radial Cleavage
Entercoelic Coelom
Indeterminate Cell
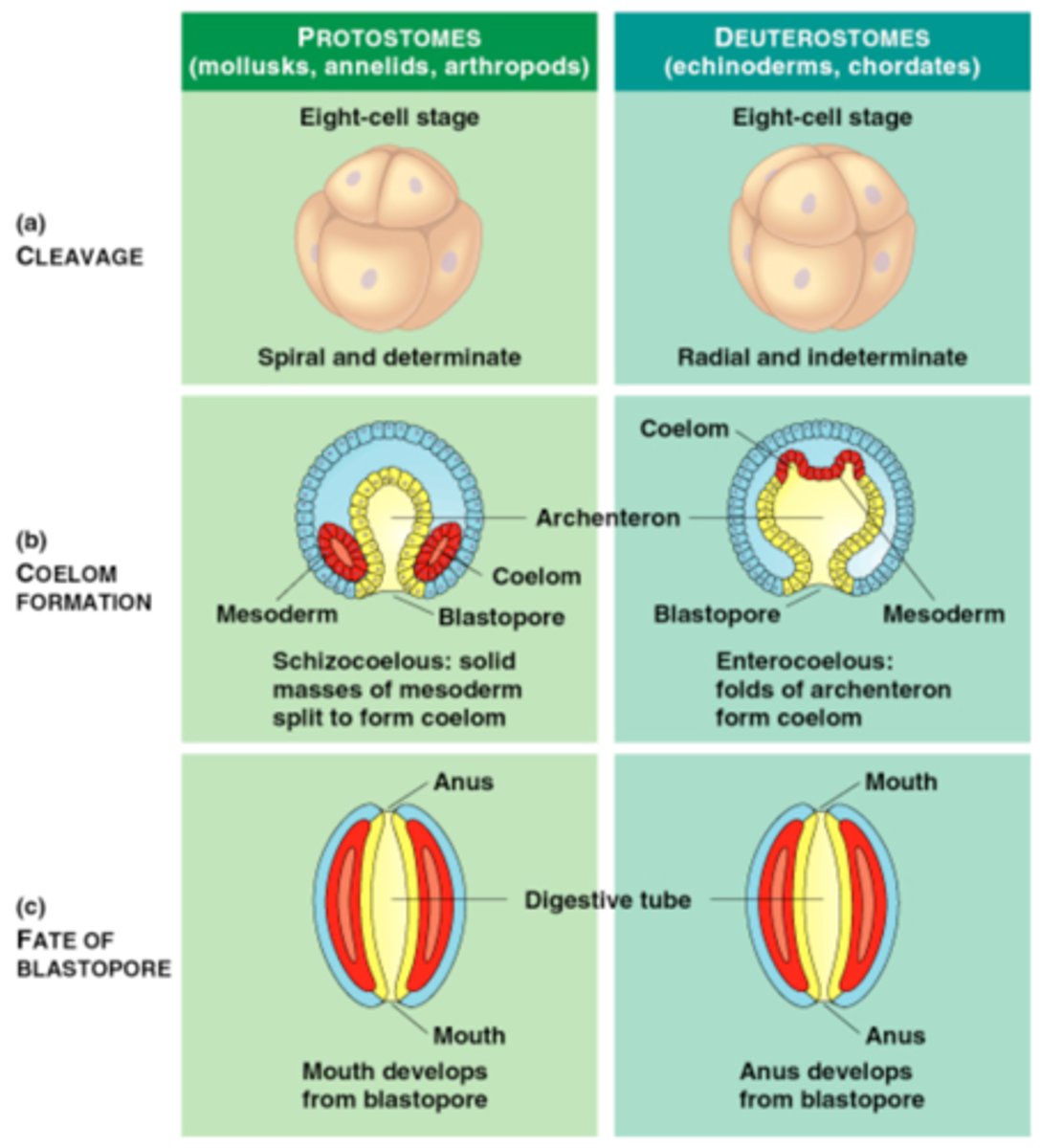
Blastocyst
An early stage of embryo described as a 'ball of cells'
Cleavage
The division of cells from the egg/zygote
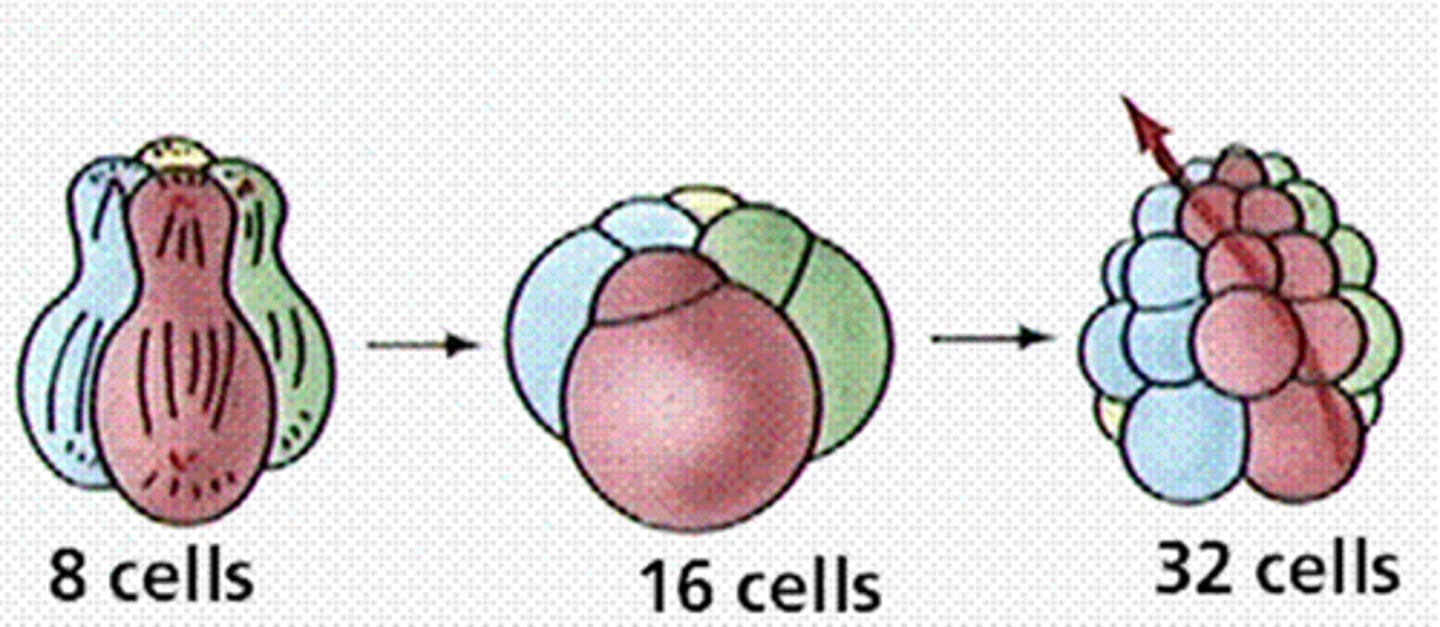
Radial Cleavage
cells are aligned as they divide
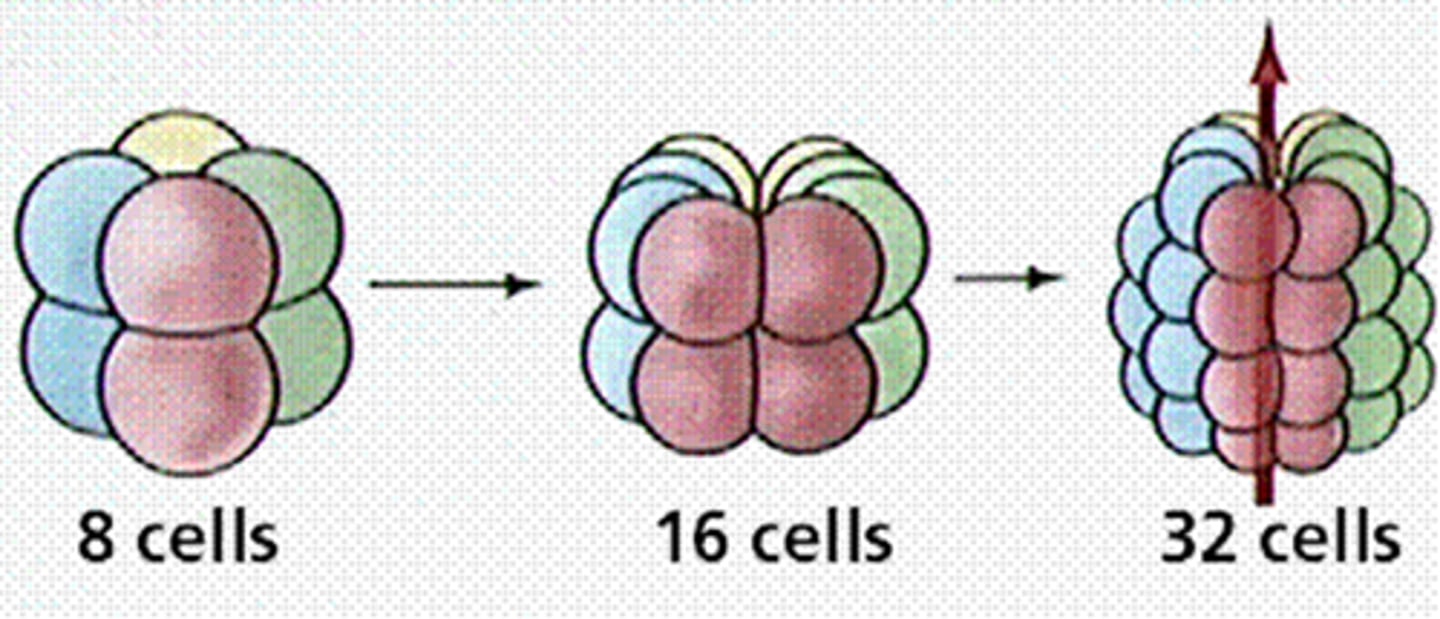
Spiral cleavage
cells are offset from each other
Gastrulation
Cells growing inward (invagination) to form the gut.
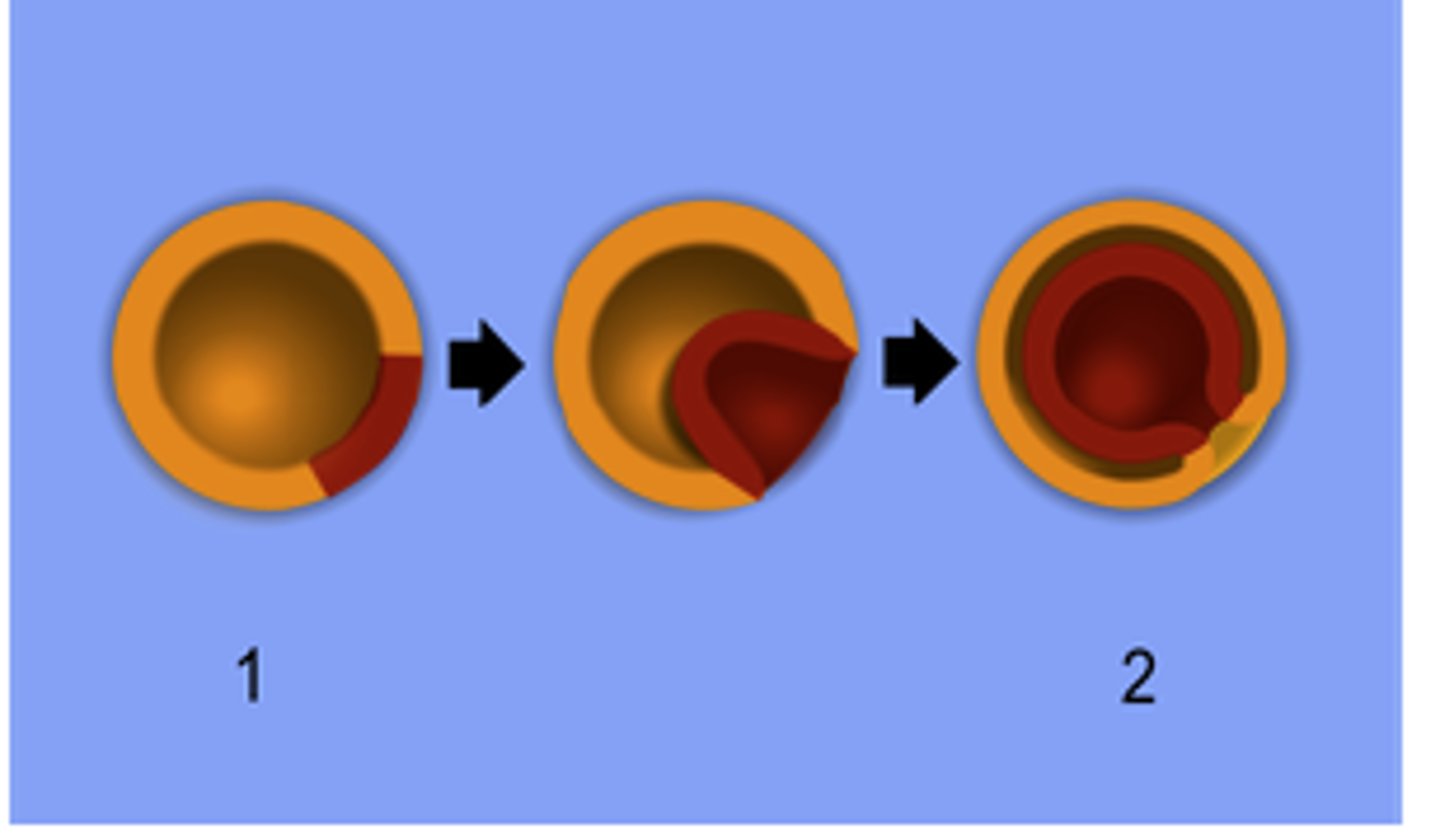
Blastopore
The first opening into the indentation of gastrulation.
In protostomes, what does the blastopore become?
The mouth.
In deuterostomes, what does the blastopore become?
The anus.
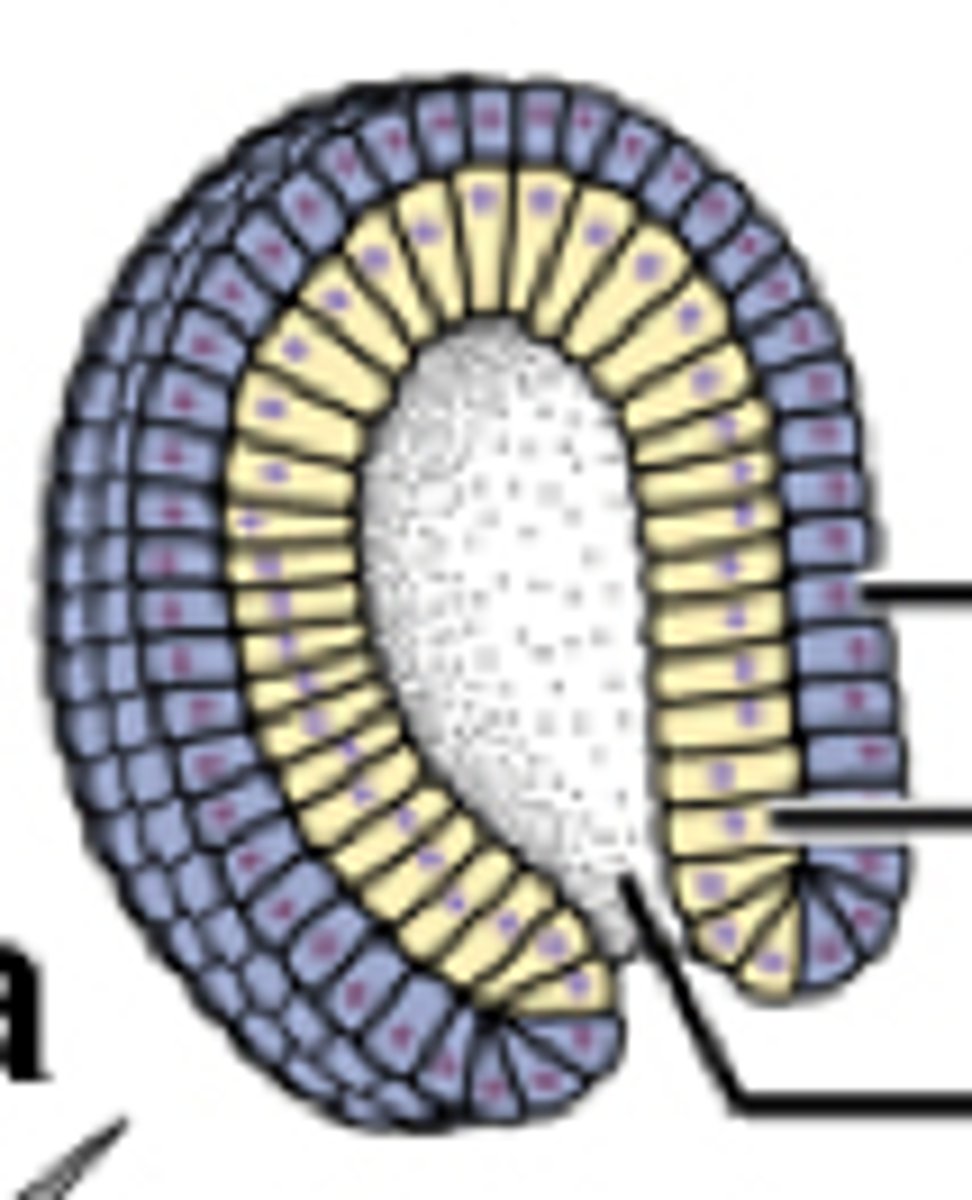
What are the three primary germ layers formed after gastrulation?
Ectoderm
Endoderm
Mesoderm
Ectoderm
outer layer
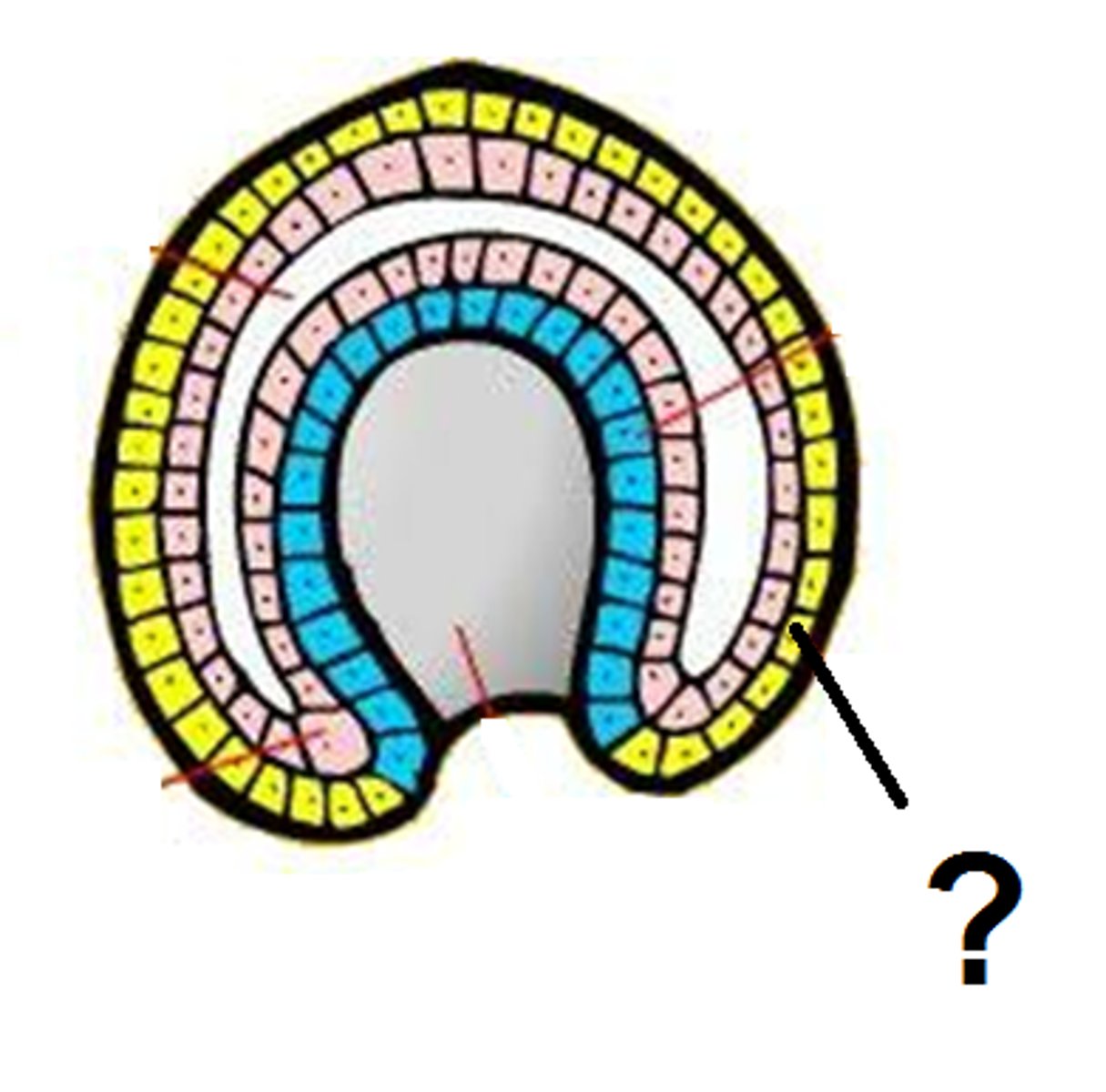
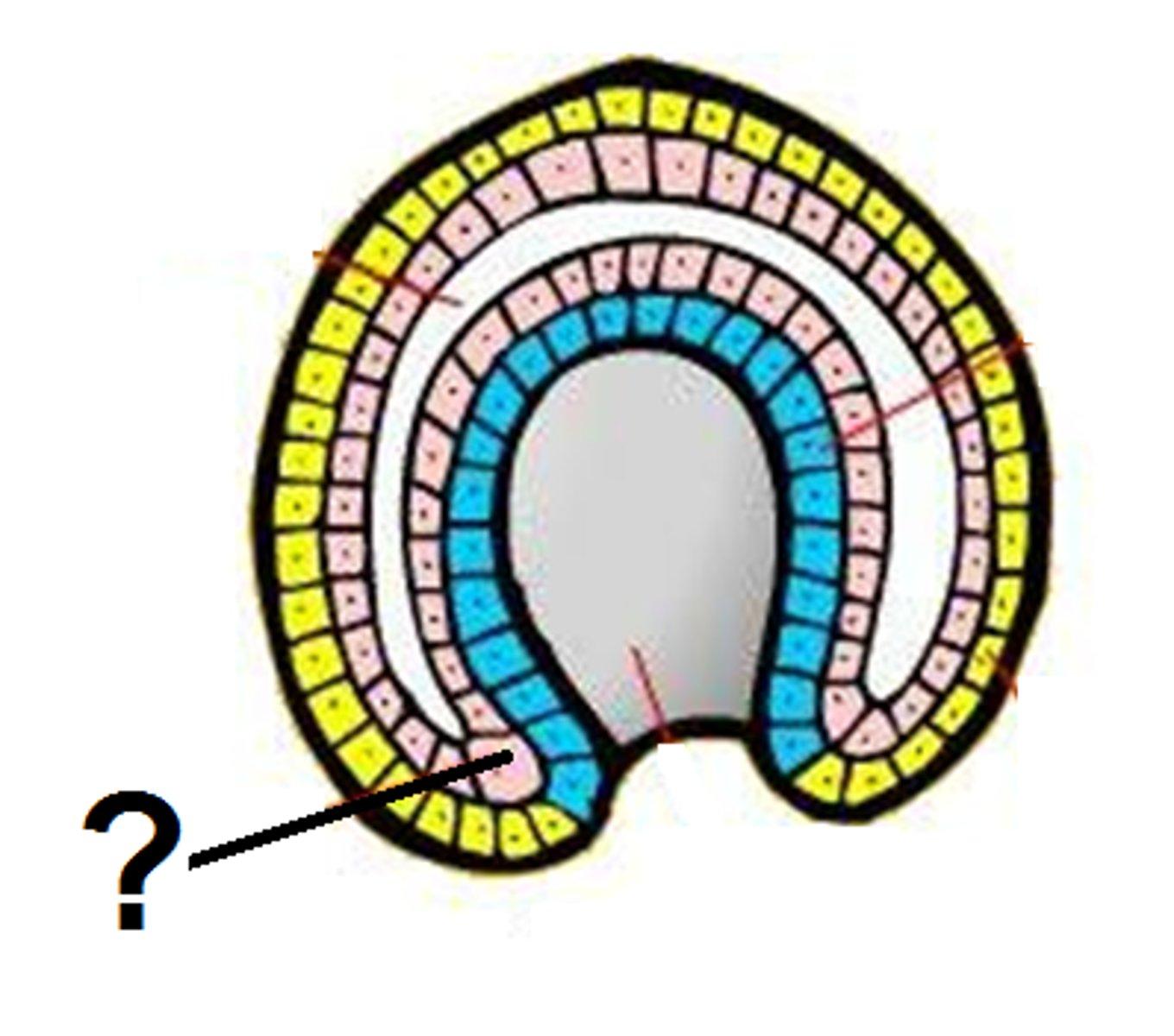
Endoderm
inner layer that forms the lining of the gut
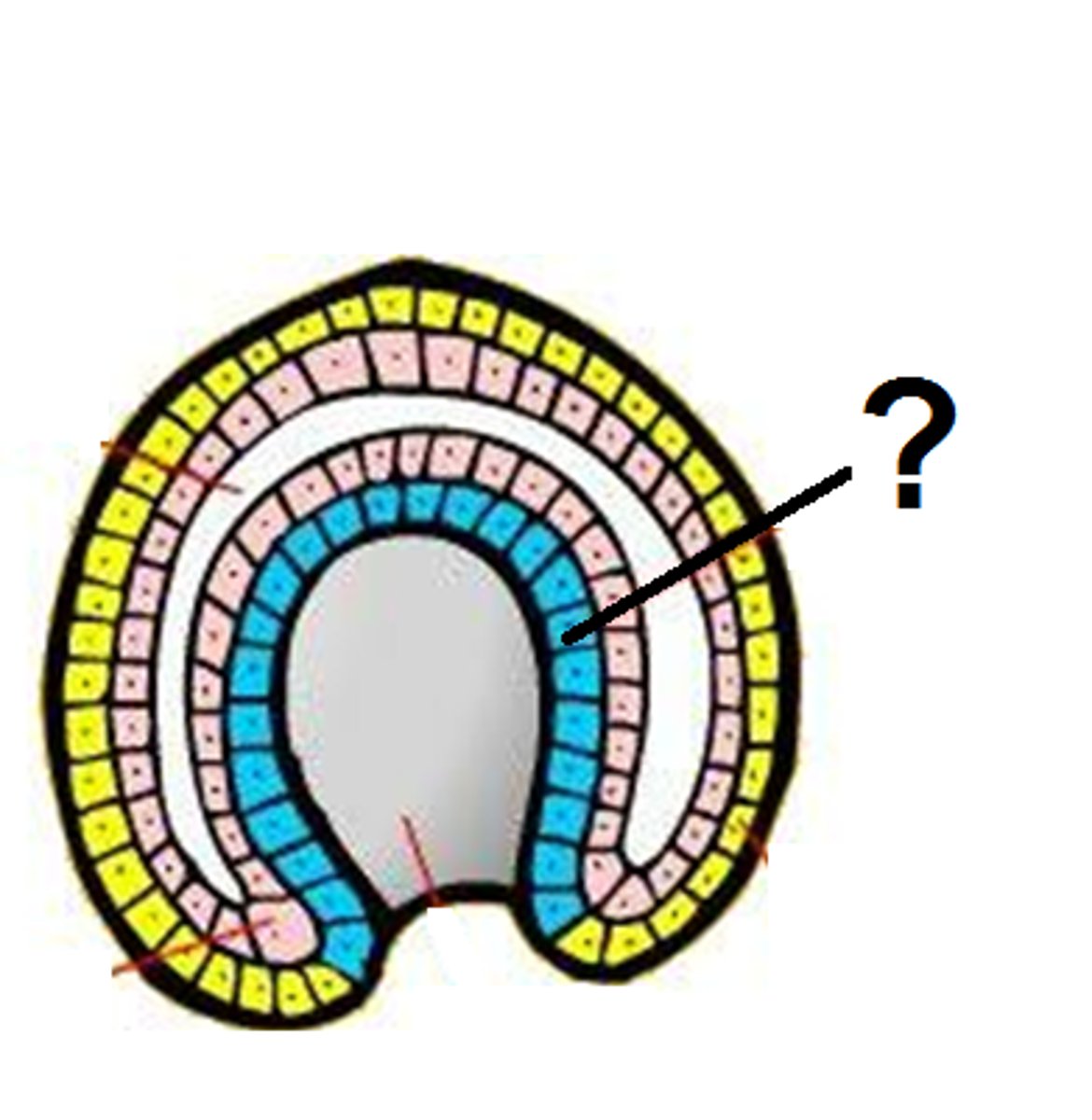
Mesoderm
middle layer between the ectoderm and endoderm
Coelom
internal body cavity.
Schizocoelom
body cavity made from solid mass of mesodermal cells splitting
Enterocoelom
body cavity forming from the outpocketing of the gut that pinches off
What is the notochord?
A slender rod that forms from mesoderm, dorsal to the coelom and ventral of the nerve cord.
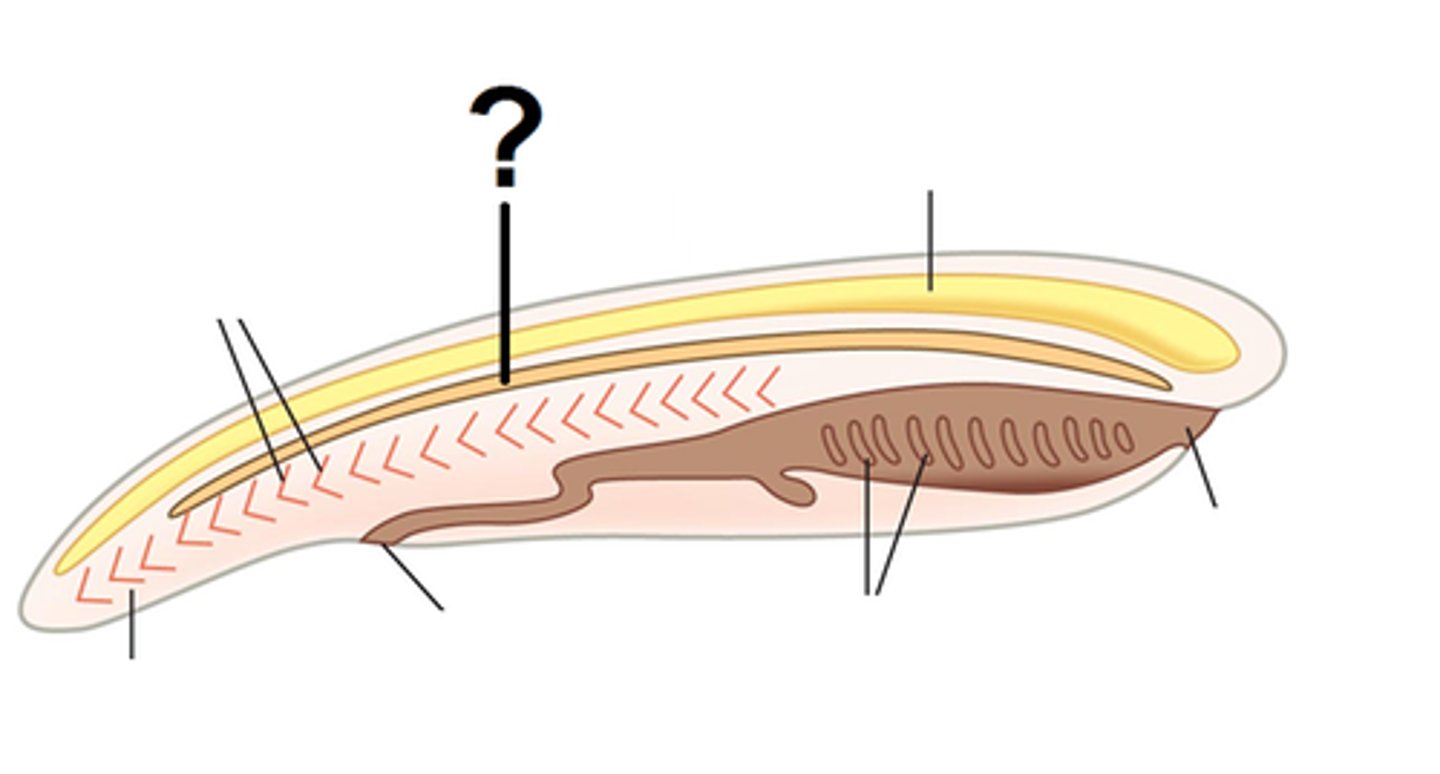
hydrostatic organ
outer fibrous sheath encloses incompressible fluid (prevents axial compression)
Pharyngeal Slits
In the pharynx, used for Filter feeding and in some cases, respiration.
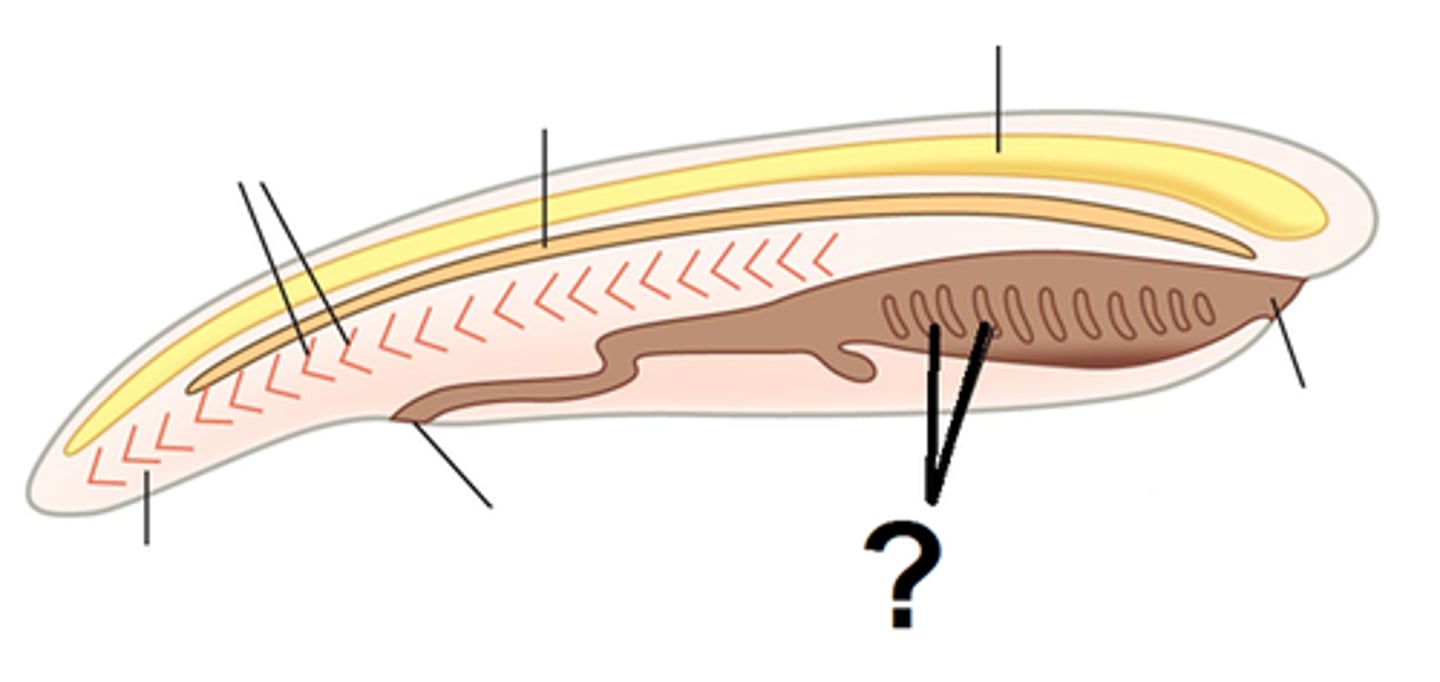
Dorsal hollow nerve cord
Formed by invagination of the ectoderm into the neural plate, it will form the CNS (Central Nervous System)
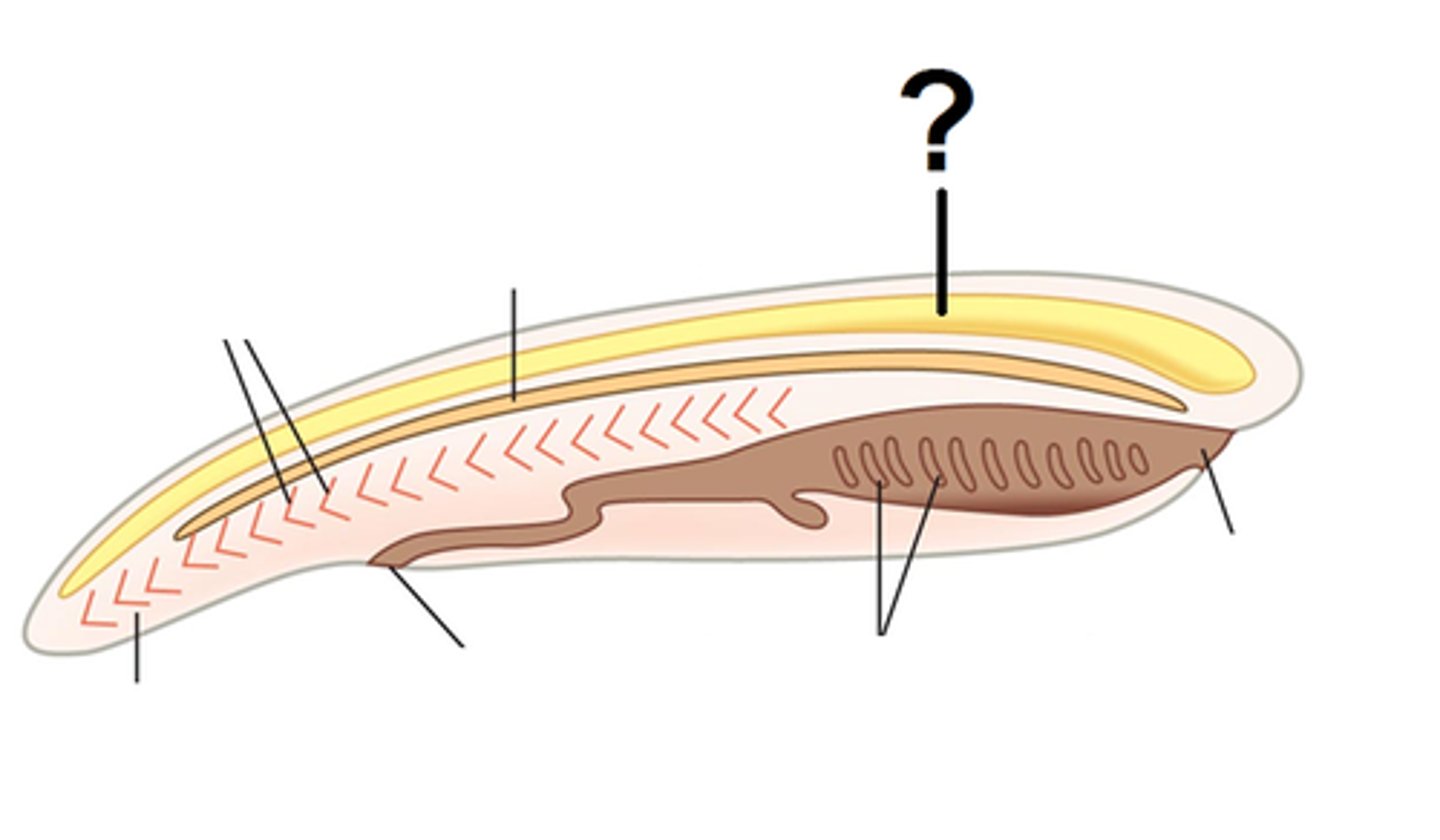
Endostyle
A glandular groove in the floor of the pharynx used in filter feeding.
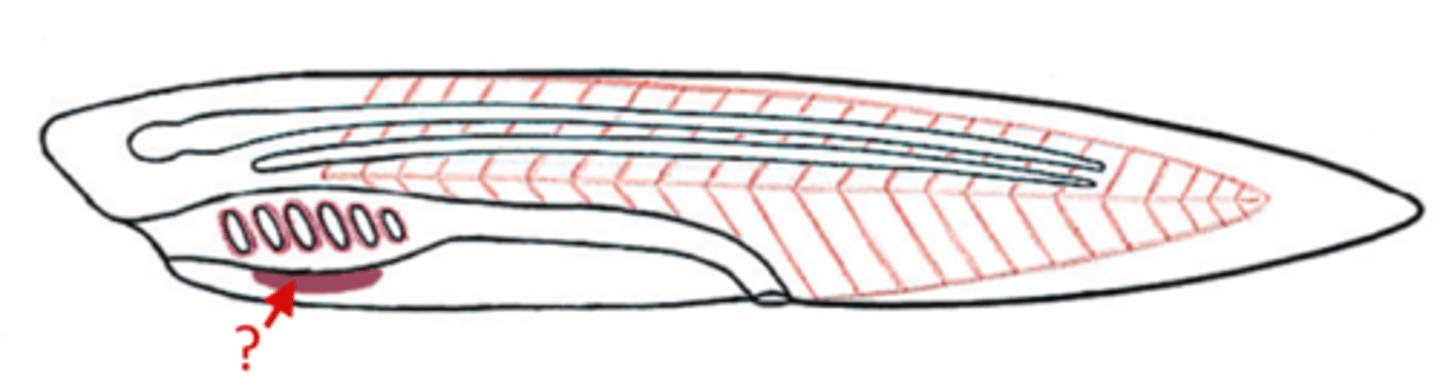
Thyroid gland
produces thyroid hormones and calcitonin
What are the Endostyle and the Thyroid Gland both involved in?
iodine metabolism
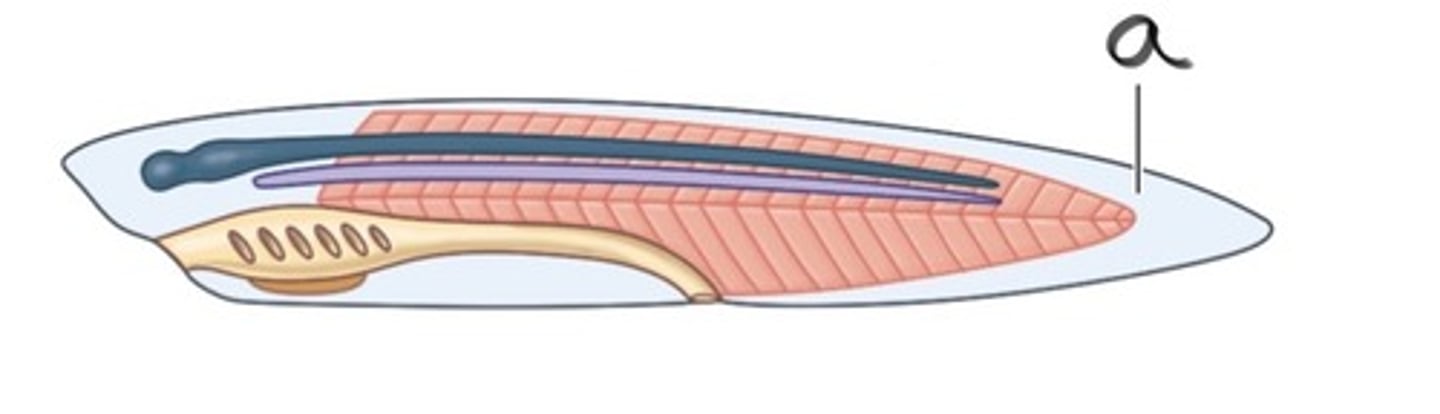
Postanal tail
A posterior elongation of the body extending beyond the anus.
larval stage of Protochordates
pelagic (residing in open water between the surface and the bottom)
Planktonic
riding from place to place primarily in currents and tides rather than their own efforts
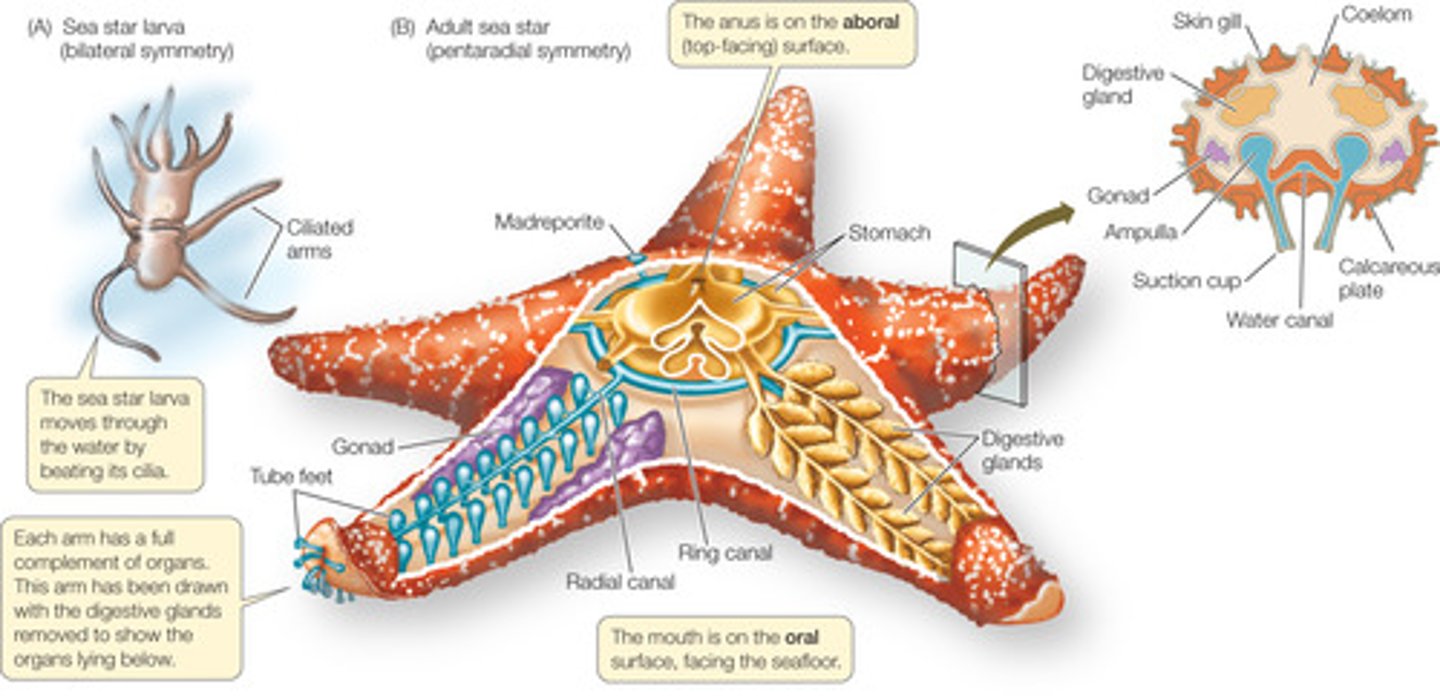
Phylum Echinodermata
Includes sea star (starfish), sea urchin, sand dollar, sea cucumber, sea lily
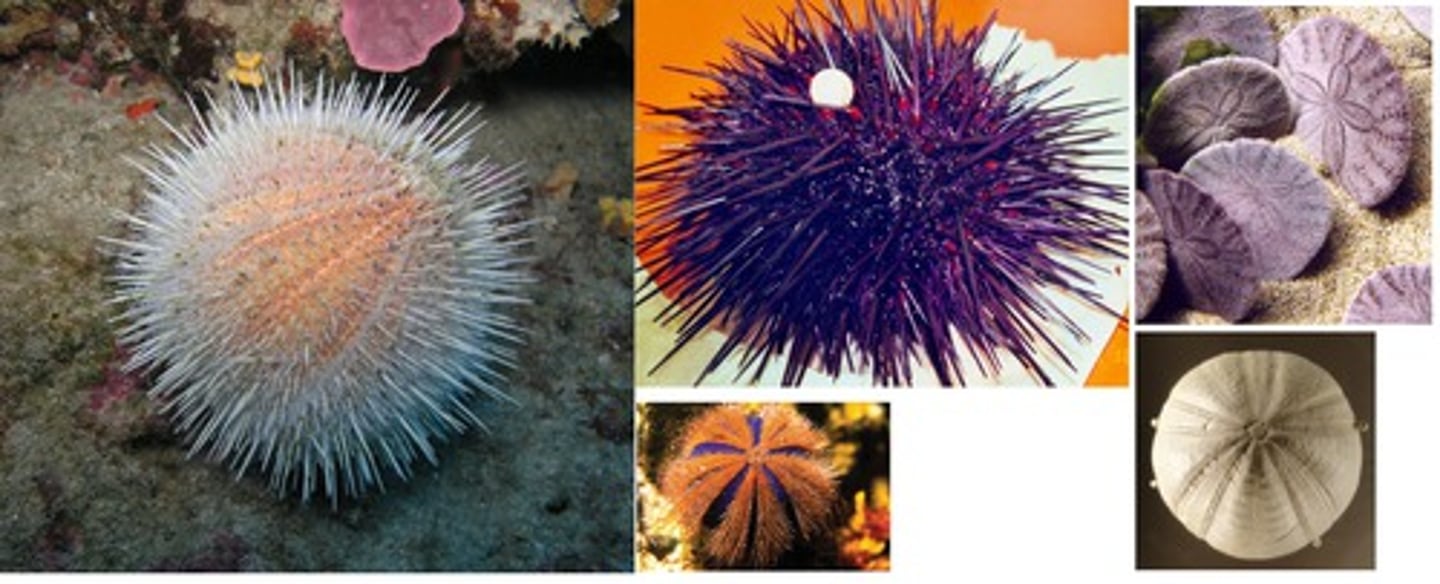

Phylum Echinodermata Characteristics
Unsegmented adult body
Endoskeleton of calcium carbonate
No head or brain, but has a nerve ring
Pentaradial symmetry
Sex Organs of Protochordates
dioecious (Sperate sex organs) or monoecious (Have both sex organs)
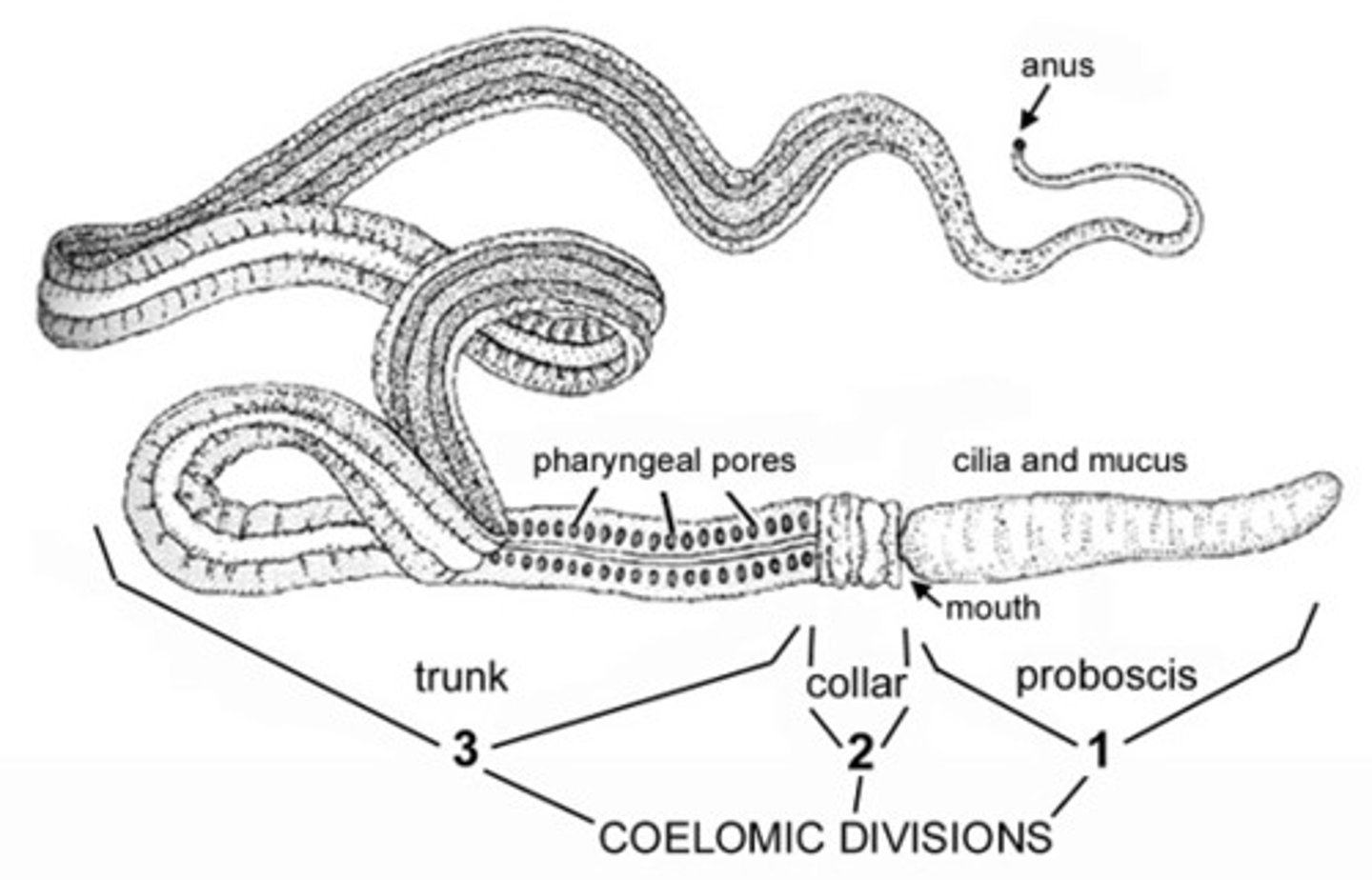
Phylum Hemichordata
half chordate or marine benthic "worms"
benthic
living on or within a marine substrate
What are the two major classes of Hemichordata?
Enteropneusta (acorn worms) and Pterobranchia.
What is the larval stage of hemichordates called?
Tornaria larva.
Hemichordates similarities to echinoderm characteristics
Tornaria larva of hemichordata resembles auricularia larva of echinoderms
Hemichordates similarities to chordate characteristics
Pharyngeal slits and Dorsal nerve cord in collar region invaginated into deeper collar chord
Class Enteropneusta
acorn worms, under Phylum Hemichordata
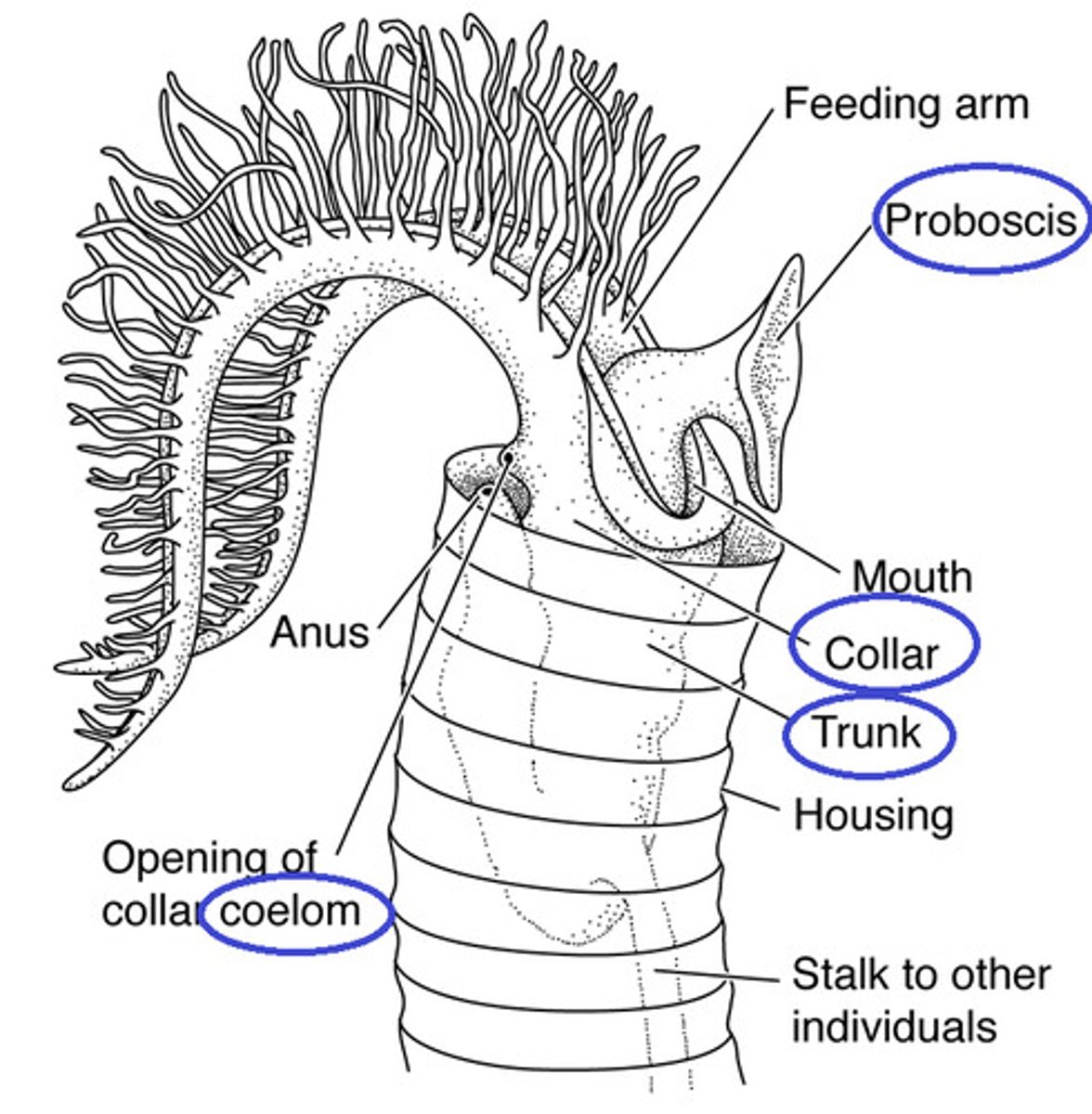
Class Pterobranchia
tube worms, under Phylum Hemichordata that may have evolved from acorn worms
Patterning
specifying general regions of an embryo which determines where body parts are positioned
Patterning in Chordates
The reverse of those in all other animals, including hemichordates (i.e., ventral gene action in non-chordates is dorsal in chordates
Cephalochordata
A subphylum of chordates that includes Burrowing filter feeders.
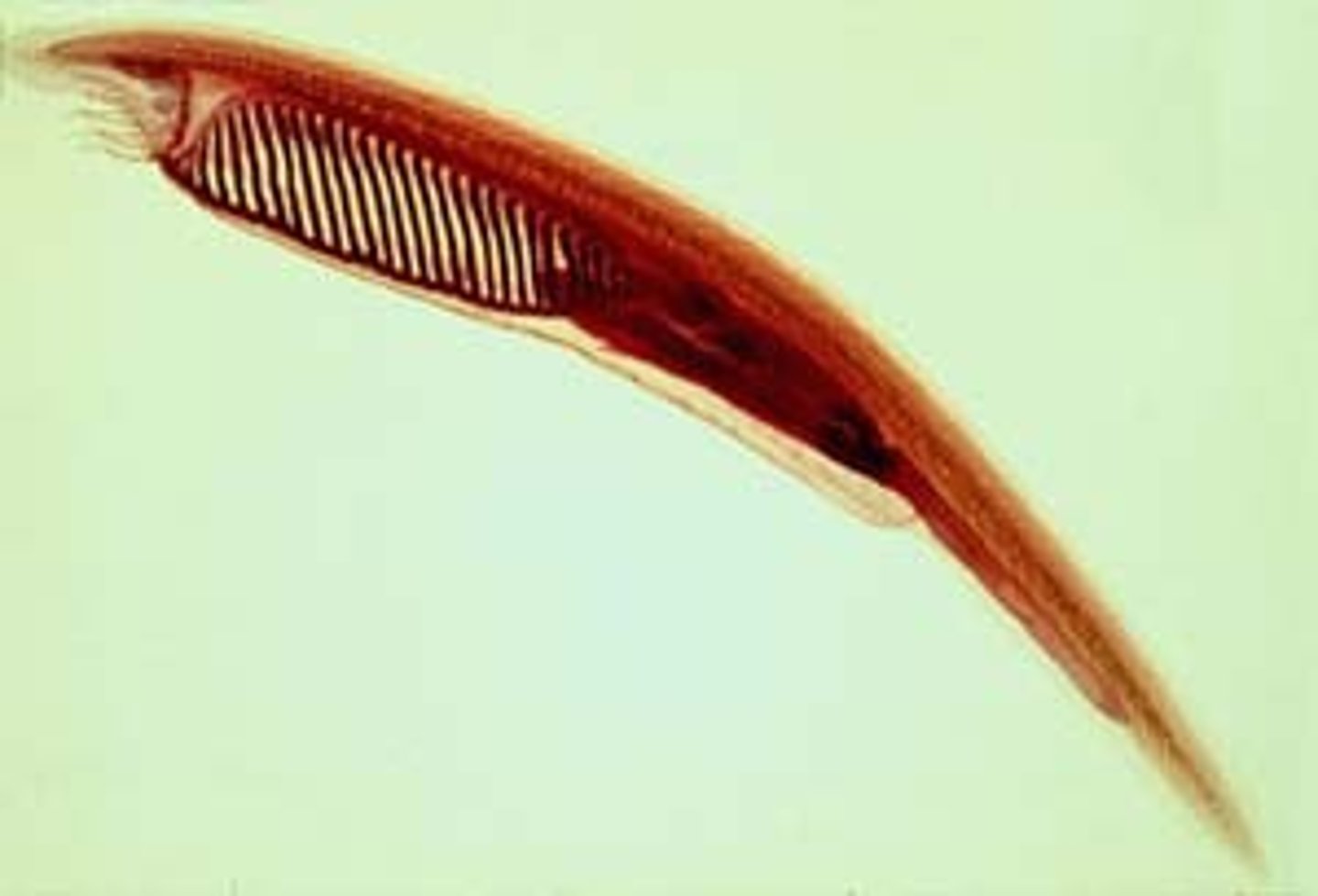
oral hood
supports food-processing equipment of Cephalochordata, including the wheel organ, ciliated tracts that sweep food into the mouth
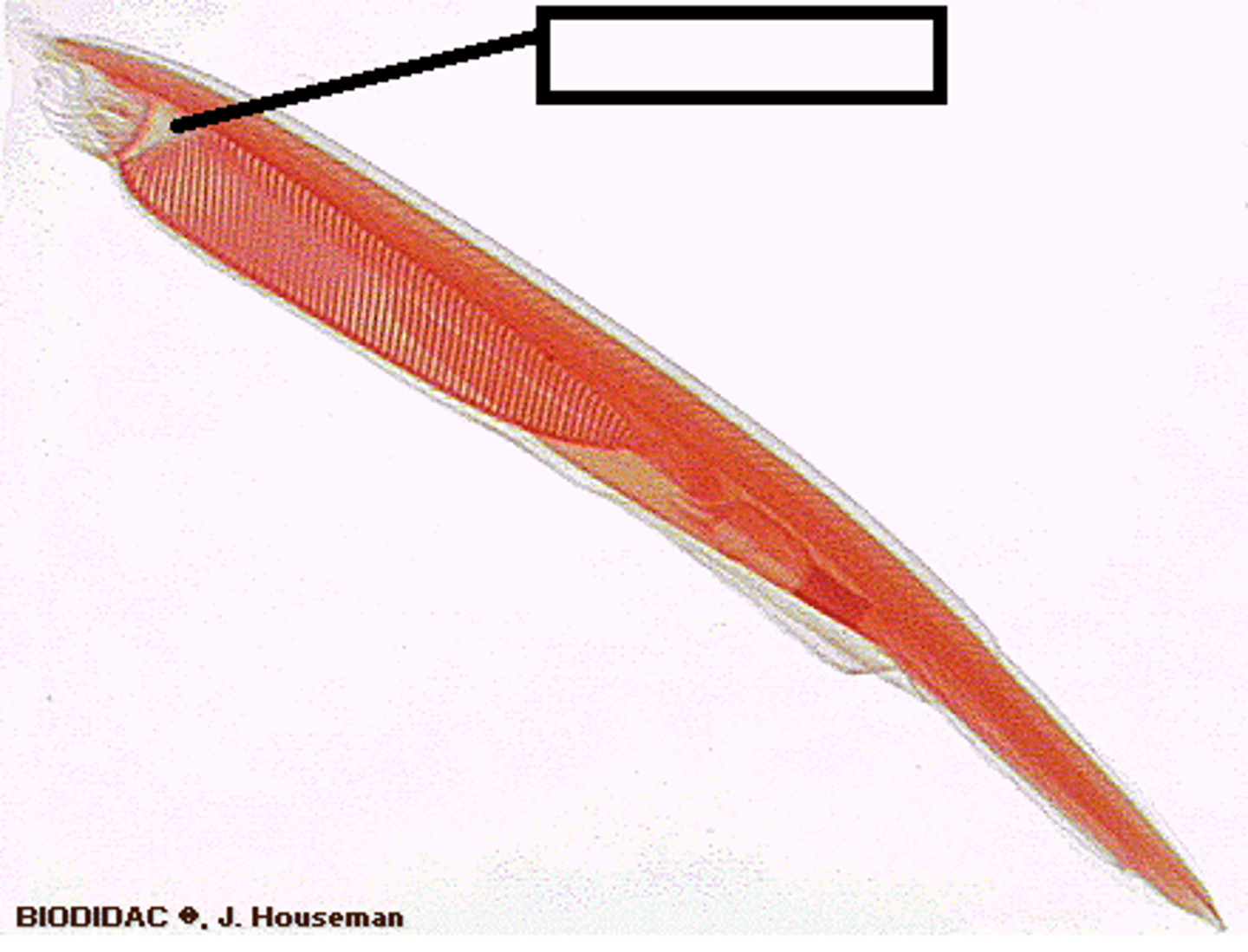
What are cephalochordates also known as?
Amphioxus or lancelets.
Hatschek's pit or groove
a ciliated invagination that secretes mucus to help collect food particles in Cephalochordatas
Urochordates
Subphylum of Chordata with simple, saclike body (as adults)
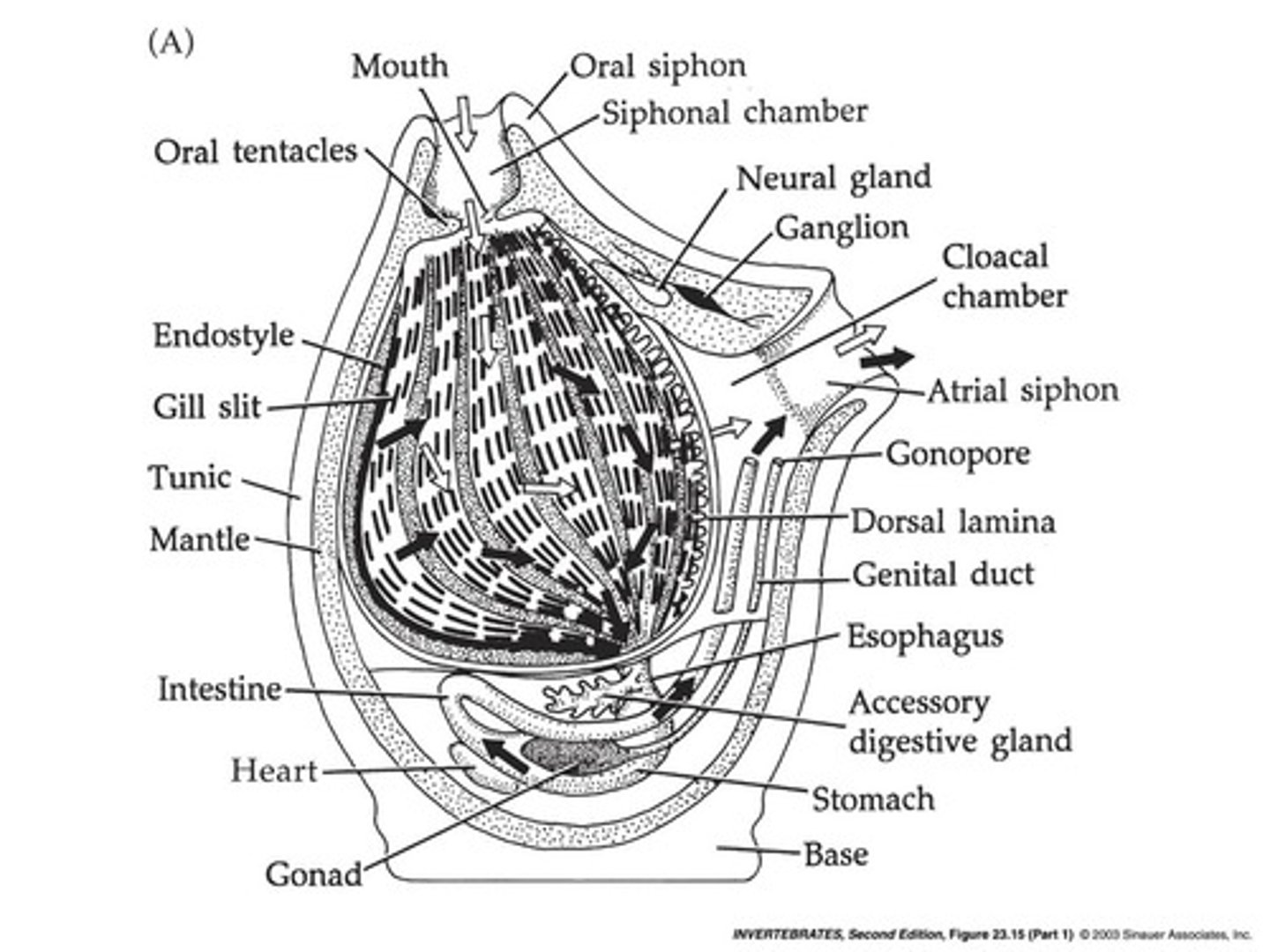
What are Urochordates also known as?
tunicates
What is the outer body covering of urochordates called?
Tunic or test.
What are the two classes of Urochordata?
Ascidiacea (sea squirts) and Larvacea (Appendicularia).
Annelid Chordate theory
Chordates evolved from from annelids or arthropods
Auricularian hypothesis
The hypothesis that chordates evolved from echinoderms.
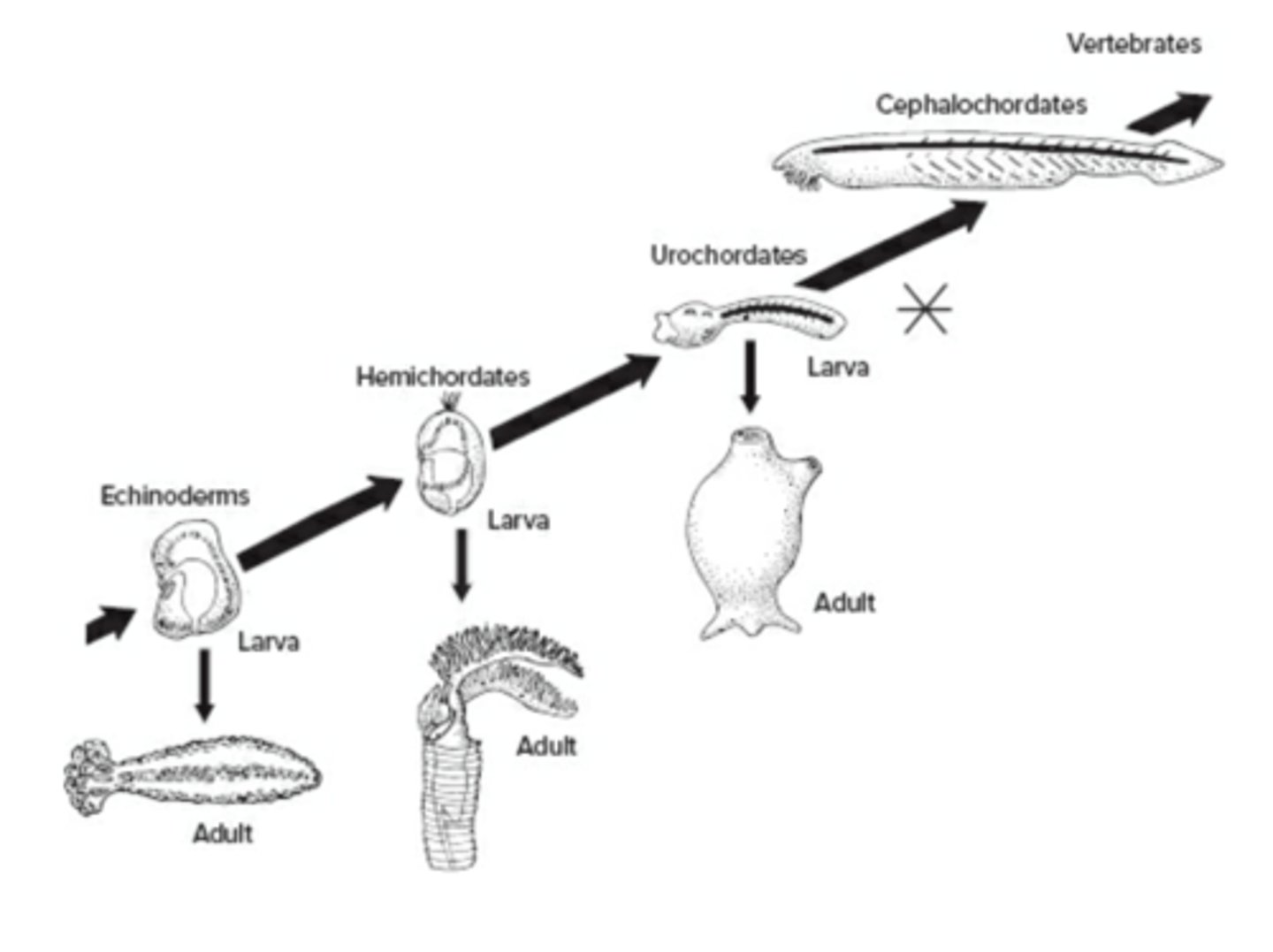
What is the hypothesis regarding the evolution of chordates?
They may have evolved from echinoderms (auricularian hypothesis) or from annelids or arthropods.
What is the fate of the pharyngeal arches in chordates?
They become ventral, unlike in hemichordates where they were dorsal.
What are the three groups included in protochordates?
Hemichordata, cephalochordates, and urochordates.
What is the significance of Hatschek's pit in cephalochordates?
It is a ciliated invagination that secretes mucus to help collect food particles.
What distinguishes the larval stage of protochordates?
It is pelagic and usually planktonic, while the adult stage is benthic.