4 - investigating foodborne diseases and controlling food spoilage
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
List 3 levels that microbes can be observed as
single cells
colonies
populations
Define selective culture media
media that selects for a particular group of bacteria, only allowing them to grow (gram positive or negative)
Give an example of selective culture media
MacConkey agar selects for gram negative bacteria
Define differential culture media
media that differentiates between bacteria based on their ability to perform certain biochemical functions. Indicated by changes in media colour
Give an example of differential culture media
mannitol salt agar
How do microbial populations grow?
exponentially
How is bacterial growth calculated?
2^n where n = number of generations
Define generation doubling time
the time taken for the population to double
List 3 methods of detecting foodborne pathogens
direct counts using chambers
plate count
selective media
Give one advantage of direct cell counts
quick, cheap and easy
Give 2 disadvantages of direct cell counts
its sometimes hard to distinguish between alive and dead cultures
used to be thought that cells were alive if culturable
How do you perform a plate count?
perform several dilutions of innoculum until 30-300 discrete colonies are countable
Give two methods of testing water sampling
total plate counting
using indicators
Discuss total plate counting with water samples
estimate the total number of colony forming units per weight of solid or volume of liquid
Define microbial indicators
microorganisms that indicate the potential presence of pathogenic bacteria
Microbial indicator criteria: sources
should be suitable for analysis of many water sources
Microbial indicator criteria: presence
should be present wherever enteric pathogens are present
Microbial indicator criteria: survival
should survive longer than the hardest enteric pathogen
Microbial indicator criteria: reproduction
shouldn’t reproduce in contaminated water
Microbial indicator criteria: harm
should be harmless to humans
Microbial indicator criteria: relationship
its level in the contaminated water should have a direct relationship to the degree of faecal pollution
Microbial indicator criteria: assay
the assay for identifying indicator should be specific
Microbial indicator criteria: testing method
the testing method should be easy to perform
What’s the most probable number method (MPN)?
a statistical technique used to estimate the concentration of microorganisms in a sample when direct counting is not feasible
What are coliforms?
bacteria that possess β-galactosidase to produce acids and gases
What are the 3 steps of the MPN test
presumptive test
confirmatory test
completed test
What does the presumptive test do?
samples water for the presence of coliform organisms
List 3 mediums that can be used for presumptive testing
lactose broth
MacConkey broth
Lauryl tryptose broth
What is the main principle of presumtive testing?
water sample is added to a lactose broth
if coliforms are present they will metabolise the lactose present in the broth with β-galactosidase and gas bubbles will appear
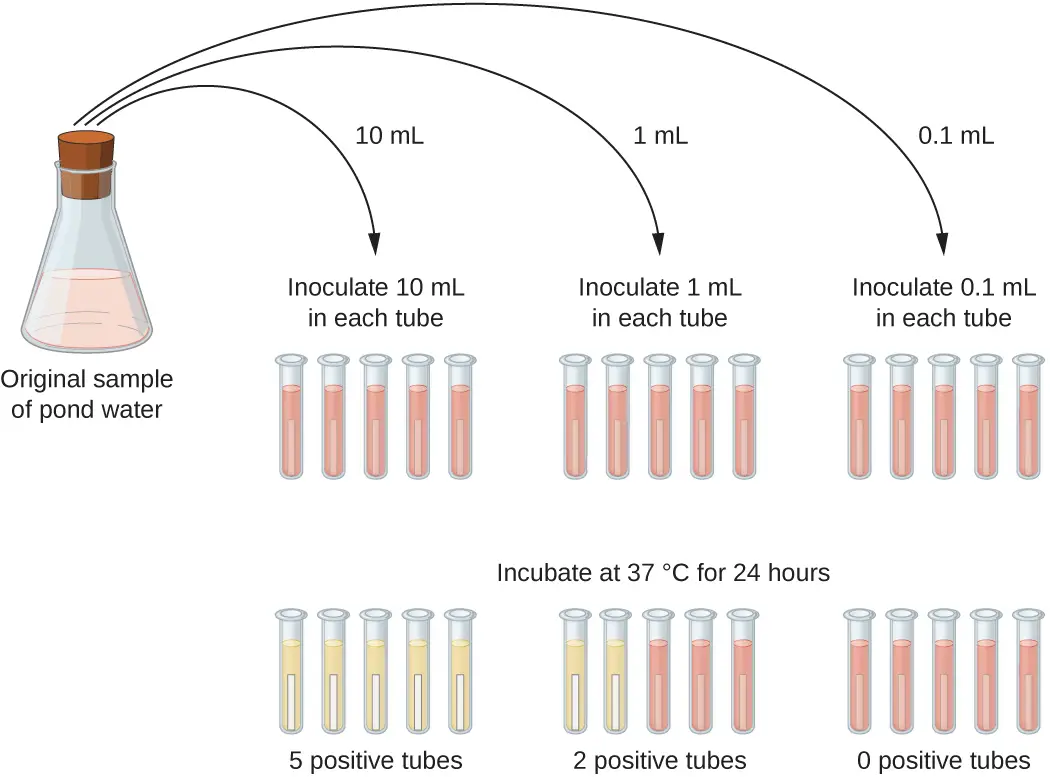
Presumptive test on untreated water: 3 steps
take 5 tubes of double strength and 10 tubes of single strength medium
add 10ml of water to 5 tubes
add 1ml to 5 tubes
add 0.1ml to 5 tubes
incubate at 37°C for 24 hours
compare the number of tubes giving a positive reaction to a standard chart and record the MPN of bacteria present
Presumptive test on treated water: 3 steps
take 5 tubes of double strength (50ml) and 1 tube of single strength medium
add 50ml of water to 1 tube
add 10ml to 5 tubes
incubate at 37°C for 24 hours
compare the number of tubes giving a positive reaction to a standard chart and record the MPN of bacteria present
What happens if the presumptive test is negative?
no further testing is performed and the water source is considered microbiologically safe
What happens if the presumptive test is posititive?
a confirmatory test is performed
Give 3 advantages of MPN
ease of interpretation
sample toxins are diluted
effective method of analysing highly turbid samples like mud that can’t easily done by membrane filtration
Give 3 disadvantages of MPN
takes a long time to get results
requires more equipment
greater probability of false positives
How is membrane filtration performed? (3 steps)
water sample is filtered through a membrane filter (0.45μm)
membrane filter is removed and placed in a plate containing appropriate medium
plate is incubated for 24 hours
Give 3 advantages of membrane filter technique
lower total cost than MPN
easily reproducible
single step results are often possible
Give 2 disadvantages of membrane filter technique
high populations of background bacteria cause overgrowth
metals and phenols can adhere to filter
Louis Pasteur (2 points)
established modern era of food microbiology in 1857
his work in the 1860s proved that heat could be used to control spoilage organisms in wines and beers
List 3 food prevention methods
low/high temp
radiation
chemical based preservation
Climate change link to water borne diseases: extreme weather events
increased rainfall, floods, and storms can overwhelm treatment systems leading to contamination
Climate change link to water borne diseases: temperature rise
warmer temperatures accelerate the replication of water borne pathogens
Climate change link to water borne diseases: flooding impact
heavy rain can flush pathogens from land into water sources, leading to outbreaks (leptospirosis)
Give an example of water borne diseases being affected by climate change
vibrio infections in the Baltic region are linked to rising sea surface temperatures
Climate change link to food borne diseases: heat
higher ambient temperatures increase the survival and replication rates of pathogens like Shigella and Campylobacter
Climate change link to food borne diseases: contamination pathways
extreme weather and warmer temperatures can disrupt food storage, handling, and distribution, increasing risk of contamination
Climate change link to food borne diseases: seasonal variations
pathogens like Campylobacter show increased activity during warmer months, linked to behavioral changes in food consumption and preparation
List 4 adaptation strategies to climate sensitive diseases
better surveillance
improved food safety regulations
waste management
community and education