Exam #3- Systemic Lupus Erythematous
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
4 types of lupus
- Discoid Lupus Erythematosus
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- Drug-Induced
- Neonatal
Discoid Lupus
- cutaneous
- always limited to skin
- rash on face, neck, scalp
- does not generally involve internal organs
- can evolve to systemic lupus
- 10% of all lupus cases
Systemic Lupus
- more severe form
- multi-system: affects skin, joints, almost any organ/body system
- 70% of all lupus cases
- 50% of cases have a major organ affected (kidneys, stomach, heart, lungs)
- flare (active) and remission (fewer symptoms)
Drug-Induced Lupus
- occurs after use of certain prescribed drugs
- symptoms usually fade when drug is stopped
- hydralazine hydrochloride (antihypertensive) & procainamide hydrochloride ( antiarrhythmic)
4% of patients who take drug get this
Neonatal Lupus
- rare condition
- associated w/ rash appearing within 1st several weeks of life
- not systemic
- may persist for 6 months
2 most common drugs that can cause drug-induced lupus
- hydralazine hydrochloride (antihypertensive)
- procainamide hydrochloride ( antiarrhythmic)
Epidemiology of Systemic Lupus
- 10-15x more frequent in women than men (link with estrogen)
- 2-3x more prevalent among people of color (west African< African American)
- highest mortality rate in pts w/ progressive renal involvement/CNS disease
- 2 most frequent causes of death are renal failure & infectious complications
Signs & Symptoms of Systemic Lupus (General)
- elevated anti-dsDNA & anti-ribosomal P antibodies
- reduced levels of complement & leukopenia
- damage by immune complexes to renal system
- Wide range of manifestations
- ↑Infections if on immunesuppresents
Immunologic Manifestations of SLE
- B lymphs: state of spontaneous B lymphocyte hyperactivity—leads to uncontrolled production of a wide variety of antibodies to host and exogenous antigens
-T lymphs: lack of or reduced generalized suppressor T cell function and hyperproduction of helper T cells occurs
- dendritic cells also involved in pathogenesis
- loss of tolerance to nuclear antigens, deposition of immune complexes (hallmark of SLE) in tissues, and multi-organ involvement
- production of multiple autoantibodies (no autoantibody = not SLE)
- monocyte phagocyte system unable to eliminate all immune complexes —> accumulate in blood circulation -> deposited in tissues
Diagnostic Evaluation of SLE (histological, renal, hematological)
- histologic changes (vasculitis)
- renal: proliferative glomerulonephritis and membranous nephritis
- hematologic findings (moderate anemia, lymphocytopenia, thrombocytopenia)
Laboratory evaluation of antinuclear antibodies
ANAs have no organ or species specificity and are capable of cross-reacting with nuclear material from humans or various animal tissues
-31.7% of all normal individuals were ANA positive at 1:40 dilution; Negative cutoff titer of 1:160
- antigens recognized are mainly proteins, protein macromolecular complexes, protein-nucleic acid complexes, and nucleic acids
- Anti-dsDNA antibodies are the only autoantibodies that may be used to monitor disease activity of SLE
Etiology of Lupus
Cause is unclear
Development of autoantibodies in SLE due to defective B cell tolerance for self antigens
Known to occur in families-- 10% of lupus patients have a parent or sibling with it but No identified gene or genes yet
environmental triggering associated: UV light, smoking
Gut microbes: Antibiotics can remove gut bacteria—may trigger lupus - sulfa drugs, tetracycline-related, and penicillin-related
Vitamins found to modulate lupus onset or flares:
Vitamin D, Vitamin A, and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids
Cutaneous Symptoms
butterfly rash worsened by UV (65% of patients get this) ; can extend to trunk and arms
alopecia
Raynaud phenomenon (1/3 of patients)
Urticaria, angioedema, nonthrombocytopenic purpura, scale formation, ulcerations of oral and genital mucous membranes
Renal and lymphatic Symptoms
Complement mediated injury to the renal system—high levels of immune complexes
Renal disease progression is unpredictable
Acute and chronic glomerulonephritis possible
Lymphoadenopathy - enlargement of peripheral and axial lymph nodes
GI and Serositis Symptoms
Non-specific GI issues common
Inflammation of the mesothelium (thin layer of connective tissue enclosing the body cavity)
sterile peritonitis (abdomen), pleuritis (lungs) , or pericarditis (membrane around heart); frequently accompanied by severe pain
inflammation of tissue with no infection
antibiotics will not help
Cardiopulmonary and Musculoskeletal Symptoms
Inflammation of myocardium can produce persistent tachycardia —> congestive heart failure
occult diffusion and obstructive abnormalities in high proportion of SLE patients
Characteristic arthritis—transient and peripheral polyarthritis, symmetrical involvement of small and large joints
Chronic can result in disability and deformity
10%--rheumatoid like hand deformities
25%-- osteonecrosis
Neuropsychiatric Symptoms
Develop secondary to involvement of central and peripheral nervous systems
Disturbances of mental function: mild confusion, memory deficiency and impairment of orientation and perception
psychiatric disturbances like hypomania, delirium, and schizophrenia possible
Late-Onset Lupus
Can occur: at any age, gender, or race
Average age: 62; women 8x more than men; primarily in Caucasian
Symptoms relatively mild—mimic other diseases—makes it hard to diagnose
DIagnostic: Hemostatic testing
Lupus anticoagulants—inhibitor or prothrombin activator—often see thrombosis instead of bleeding
Antiphospholipid antibodies –20%
Circulating anticoagulants may cause false positive for syphilis
Prolonged prothrombin time (PT) and partial thromboplastin time (PTT)
Diagnostic : serological
High levels of anti-DNA antibodies
Reduced complement levels
Presence of complement breakdown products of C3 (C3d and C3b)
Marked increase in igG (hyperviscosity syndrome or renal tubular acidosis)
Serum cryoglobulins of mixed IgG-IgM type—levels correlate with severity of SLE
ANA classification (5)
Antibodies to DNA
Antibodies to centromere
Antibodies to histone
Antibodies to nonhistone proteins
Antibodies to nucleolar antigens
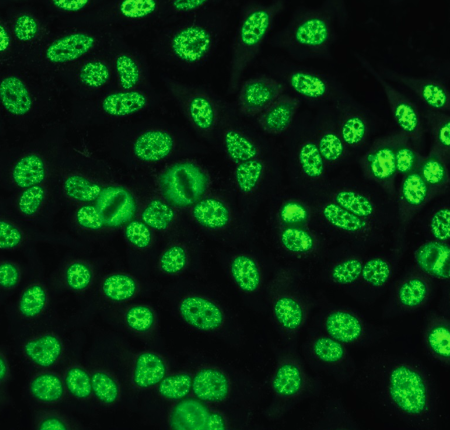
Homogeneous or Diffused
Characterizes anti-DNA nucleoprotein antibodies
nDNA, dsDNA, ssDNA, DNP, or histones
High titers: SLE
Low titers: SLE, RA Sjogren syndrome, mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD)
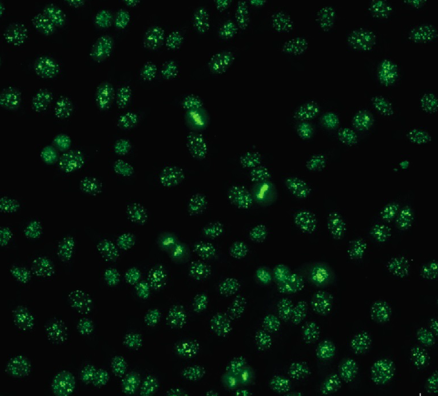
Speckled Pattern
Detected against saline extractable nuclear antigens
anti-RNP, anti-Sm
Anti-Sm: highly specific for SLE
Anti-RNP: SLE, RA, Sjogrens, PSS, MCTD, dermatomyositis
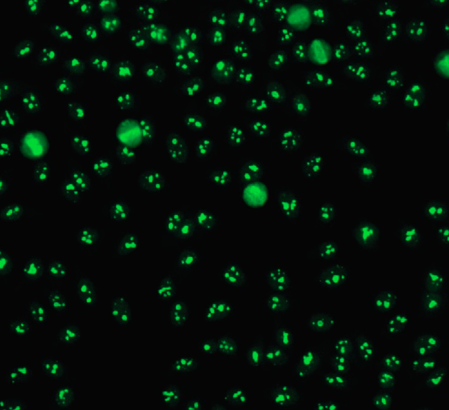
Nucleolar Pattern
Reflects an antibody to nucleolar RNA (4-6S RNP)
Present in approx. 50% of patients with scleroderma, Sjögrens, and SLE. Also seen in Raynaud phenomenon
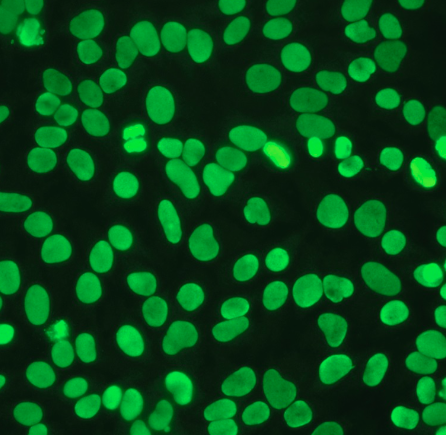
Centromere
Anticentromere antibody reacts with centromeric chromatin
Highly selected for CREST variant of PSS
Found infrequently in SLE, MCTD, PSS
- CREST: variant of systemic sclerosis haracterized by Calcinosis, Raynaud phenomenon, Esophageal motility abnormalities, Sclerodactyly, and Telangectasis