MCAT Biology
1/761
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
762 Terms
Cell Theory
Four Tenets:
1. All living things are composed of cells
2. The cell is the basic functional unit of life
3. Cells arise only from preexisting cells
4. Cells carry genetic information in the form of DNA
Cytosol
Allows for diffusion of molecules throughout the cell.
Genetic Material of the Nucleus
DNA contains coding regions called genes. Linear DNA is wound around organizing proteins known as histones, and further wound into chromosomes.
Nucleolus
-Subsection of the nucleus
-Where ribosomal RNA is synthesized
-The darker spot that is 25% of the nucleus
Mitochondria
Power plant of the cell. Two layers, inner and outer membrane. The outer membrane is a barrier between the cytosol and the inner environment of the mitochondria. The inner membrane, made up of infoldings called cristae, contains the molecules and enzymes necessary for the electron transport chain. The intermembrane space separates them, creating a matrix between them.
The pumping of protons from the matrix to the intermembrane space creates a proton-motive force that generates ATP via protons flowing through and turning ATP synthase (oxidative phosphorylation). The mitochondria is semiautonomous, meaning they replicate independently of the the nucleus via binary fission.
They can kill the cell via release of enzymes that aid in apoptosis.
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)
Interconnected membranes that are actually contiguous with the nuclear envelope. It is folding into complex structures with a central lumen. The Rough ER is studded with ribosomes that permit translation of proteins destined for secretion into the lumen.
Golgi Apparatus
Stacked membrane-bound sacs that are transferred from the ER via vesicles. The Golgi modifies the products via addition of various groups. It modifies cellular products thought the introduction of signal sequences, which help direct the delivery of product to a specific cellular location. Can also send to lysosomes for degredation
Exocytosis
Used in secretion, when the secretory vesicle merges with the cell membrane and its contents.
Cytoskeleton
Provides structure to the cell and helps it to maintain its shape. It also provides a conduit for transport of material around the cell.
Microfilaments
Solid polymerized rods of actin organized into bundles and networks that are resistant to compression and fracture. They assist in cytokinesis and cleavage furrow. Present in muscle
Microtubules
Hollow polymers of tubulin proteins that provide a primary pathway along which motor proteins like kinesin and dynein carry vesicles. Makes cilia and flagella. Also makes centrioles
Cilia
Projections of the cell that are primarily involved in movement of materials along the surface of a cell. They are made of microtubules and an example is respiratory cilia.
9 + 2 Structure
Used in flagella and cilia. Nine pairs of microtubules, with two in the center.
Centrioles
Found in a region of the cell called the centrosome. They are the organization centers for microtubules and are structured as nine triplets of microtubules with a hollow center. They migrate to opposite poles of the dividing cell and organize the mitotic spindle. They attach via kinetochores to the chromosomes.
Intermediate Filaments
Include keratin (hair, nails, skin) and desmin. They are involved in cell-cell adhesion, or maintenance of the overall integrity of the cytoskeleton. They can withstand a large amount of tension, adding rigidity to the cell structure. They help anchor other organelles!
Epithelial Tissue and Basement Membrane
Cover the body and lines its cavities. Involved in protection, absorption, secretion, and sensation. They are tightly joined to each other and to an underlying layer of connective tissue known as the basement membrane.
Simple Epithelia
One layer of cells
Stratified Epithelia
Multiple layers of cells
Pseudostratified Epithelia
Appear to have multiple layers due to difference in cell height, but are really one layer.
Cuboidal, Columnar, and Squamous Cells
Cuboidal: cube-shaped
Columnar: Long and thin
Squamous: flat, scale-like
Connective Tissue
Supports the body and provides framework for the epithelial cells to carry out their functions. Main contributors to the stroma, or support structure. Examples are bone, cartilage, tendons, ligaments, adipose tissue, and blood. They help to form the extracellular matrix.
Nucleoid Region
Where prokaryotes keep their genetic material - organized into a single circular DNA molecule, which is stored here
Archaea
Single-celled organisms that contain genes and several metabolic pathways that are more similar to eukaryotes. There are extremophiles, found mostly in harsh environments. They mostly use alternative sources of energy, such as photosynthetic, or chemosynthetic.
Bacteria
Contain a cell membrane and cytoplasm, and some have flagella or fimbriae. They work with humans as mutualistic symbiotes, for example with the human gut producing Vitamin K and biotin. Pathogens or parasites will provide no advantage to the host, and cause disease.
Cocci
Spherical bacteria.
Bacilli
Rod-shaped bacteria.
Spirilli
Spiral-shaped bacteria.
Obligate Aerobes
Bacteria that require oxygen for metabolism.
Anaerobes
Bacteria that use either fermentation or some other form of cellular metabolism that does not require oxygen.
Obligate Anaerobes
Cannot survive in an oxygen-containing environment.
Facultative Anaerobes
Toggle between metabolic processes. Can do aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
Aerotolerant Anaerobes
Unable to use oxygen for metabolism but are not harmed by its presence
Prokaryotic Cell Structure
Major difference is that there is a lack of a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. They do have ribosomes. They are single celled.
Cell Wall
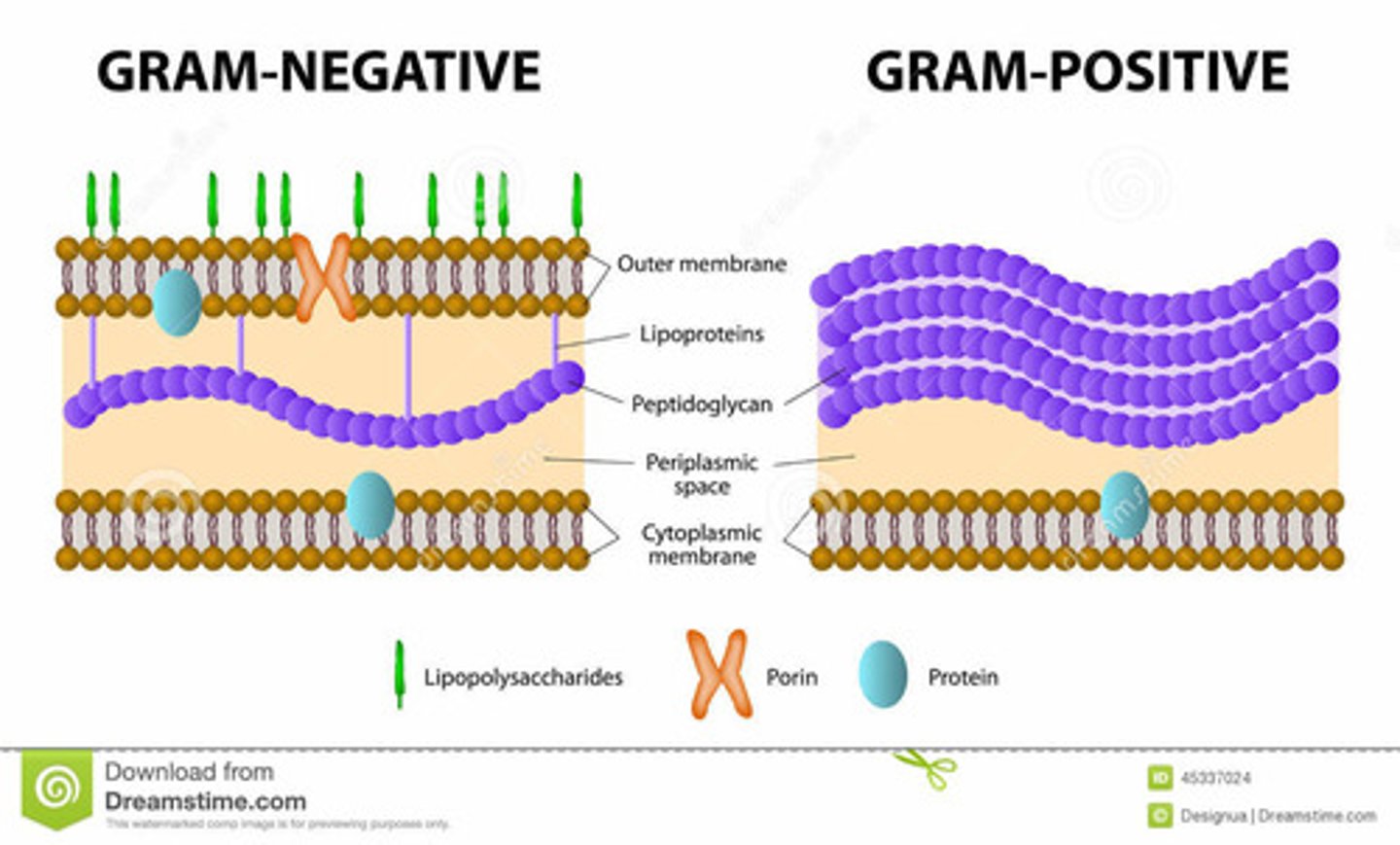
Outer barrier of the cell. Provides structure and controls the movement of solutes into and out of the bacterium. This maintains concentration gradients relative to the environment. Two types: gram positive and gram negative.
Gram Positive Bacteria
What color is it?
Is there a thick or think cell wall (peptidoglycan)?
What does the cell membrane contain?
purple
thick layer of peptidoglycan (aa + sugar)
It aids a pathogen by providing protection from a host organism's immune system.
It also contains lipoteichoic acid
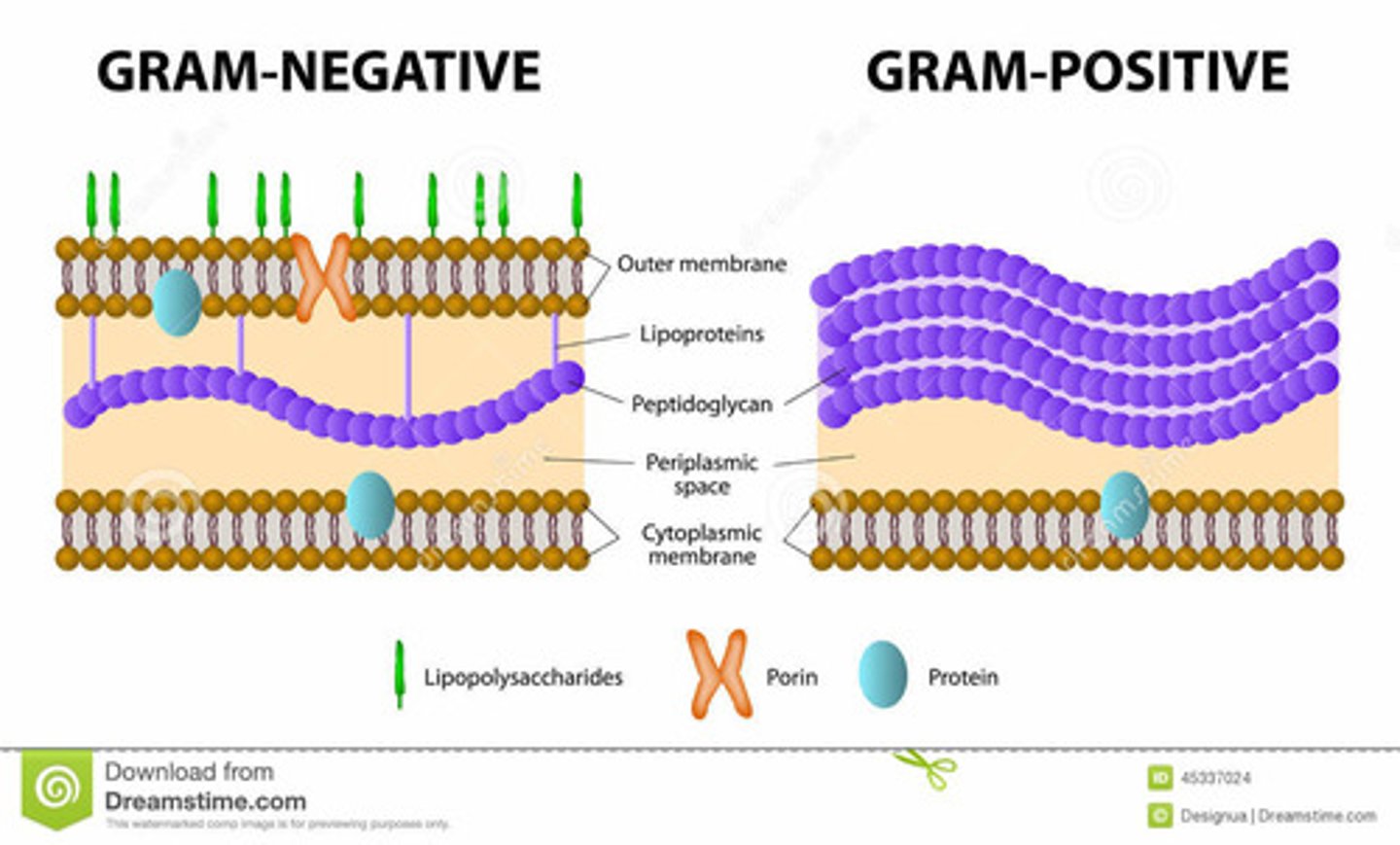
Cell Membrane
Next layer of the prokaryotic cell. It is composed of phospholipids.
Envelope
The cell wall and cell membrane together.
Eukaryotic Cells
Contain a true nucleus enclosed in a membrane.
Prokaryotic Cells
Do not contain a nucleus.
Organelles
Suspended in semifluid cytosol. In eukaryotic cells they are membrane bound, allowing for compartmentalization of functions. The membranes are made of a phospholipid bilayer, surfaces are hydrophilic, they interact with the environment.
Nucleus
Genetic material is encoded in DNA, organized in chromosomes. This DNA provides all the genetic material needed for replication of the cell. It is surrounded by the nuclear membrane or envelope, which forms a double membrane. Nuclear pores allow for selective exchange of material between cytoplasm and the nucleus.
Nuclear Membrane
Contains nuclear pores that allow for selective 2-way exchange of material between the cytoplasm and the nucleolus
Lysosomes
Membrane-bound structures containing hydrolytic enzymes that are capable of breaking down many different substrates, including those ingested by endocytosis and cellular waste products.
The enzymes are sequestered to protect the cell, releasing these enzymes causes autolysis, resulting in apoptosis...in this case, the released enzymes directly lead to cell degradation.
Peroxisomes
Contain hydrogen peroxide. It breaks down long chain fatty acids via beta oxidation. They help in the synthesis of phospholipids.
Actin
Subunit of microfilaments, used with ATP to generate force for movement by interacting with myosin for muscle contraction.
Flagella
Structures involved in the movement of the cell itself, such as the movement of sperm cells through the reproductive tract.
Bacterial Flagella
Used for propulsion. Triggered via chemotaxis which is the movement to or from a chemical stimuli. Made of a filament, hollow structure of flagellin anchored by a basal body, and a hook, which connects the filament and the basal body to increase torque.
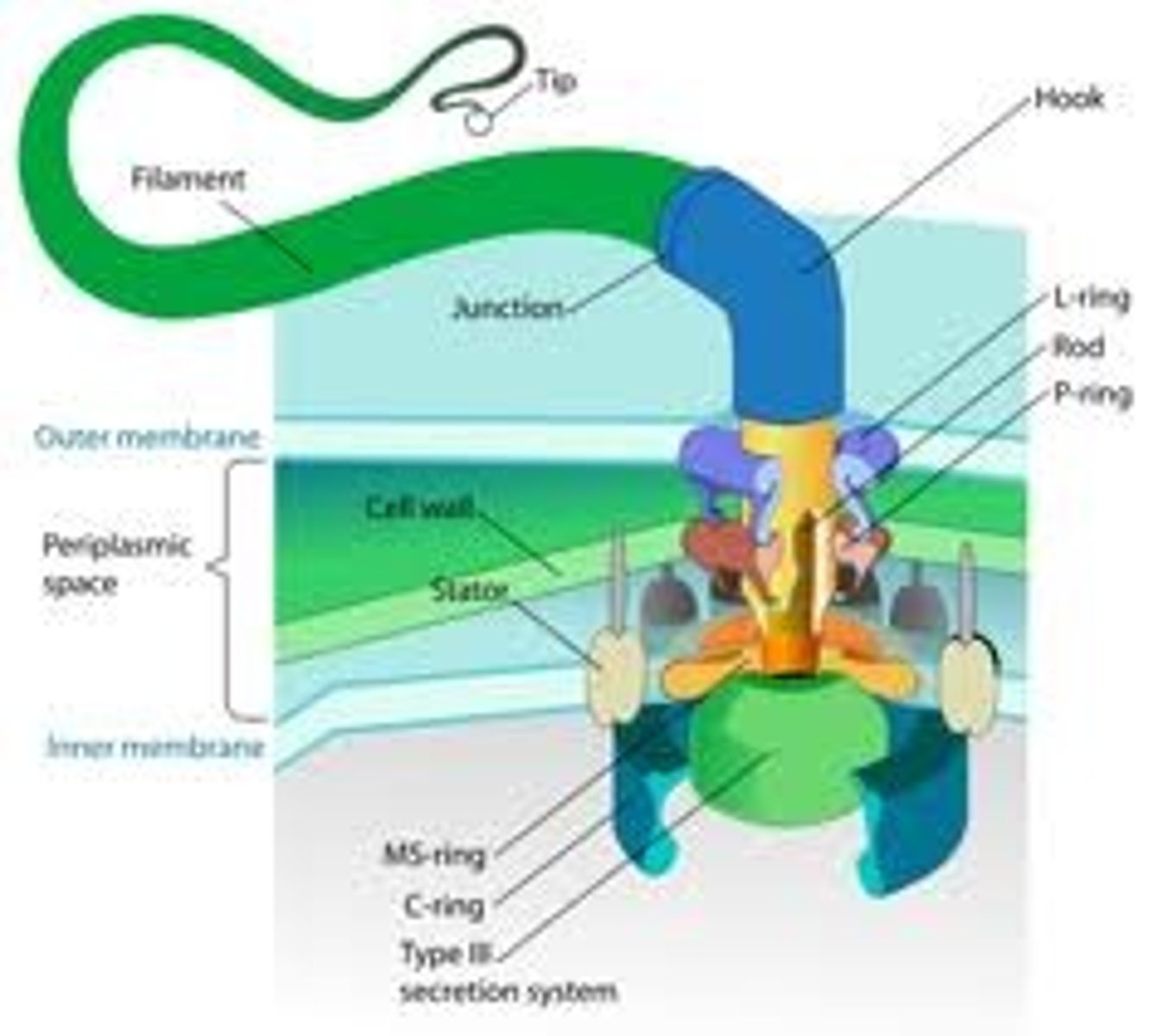
Plasmids
Small circular structures of DNA acquired from external sources. They carry DNA that is not necessary for survival of the prokaryote, but may confer an advantage such as antibiotic resistance.
Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic ribosome
Prokaryotes have a 30 S and 50 S ribosome
Euk have 40 and 60s ribosome
Generation of ATP (in bacteria)
Done via the cell membrane where ETC lies.
Gram Negative Bacteria
What color is it?
Is there a thick or think cell wall (peptidoglycan)?
What does the cell membrane contain?
Appears pink
Thin cell wall
phospholipids and lipopolysaccharides (elicit a stronger immune response)
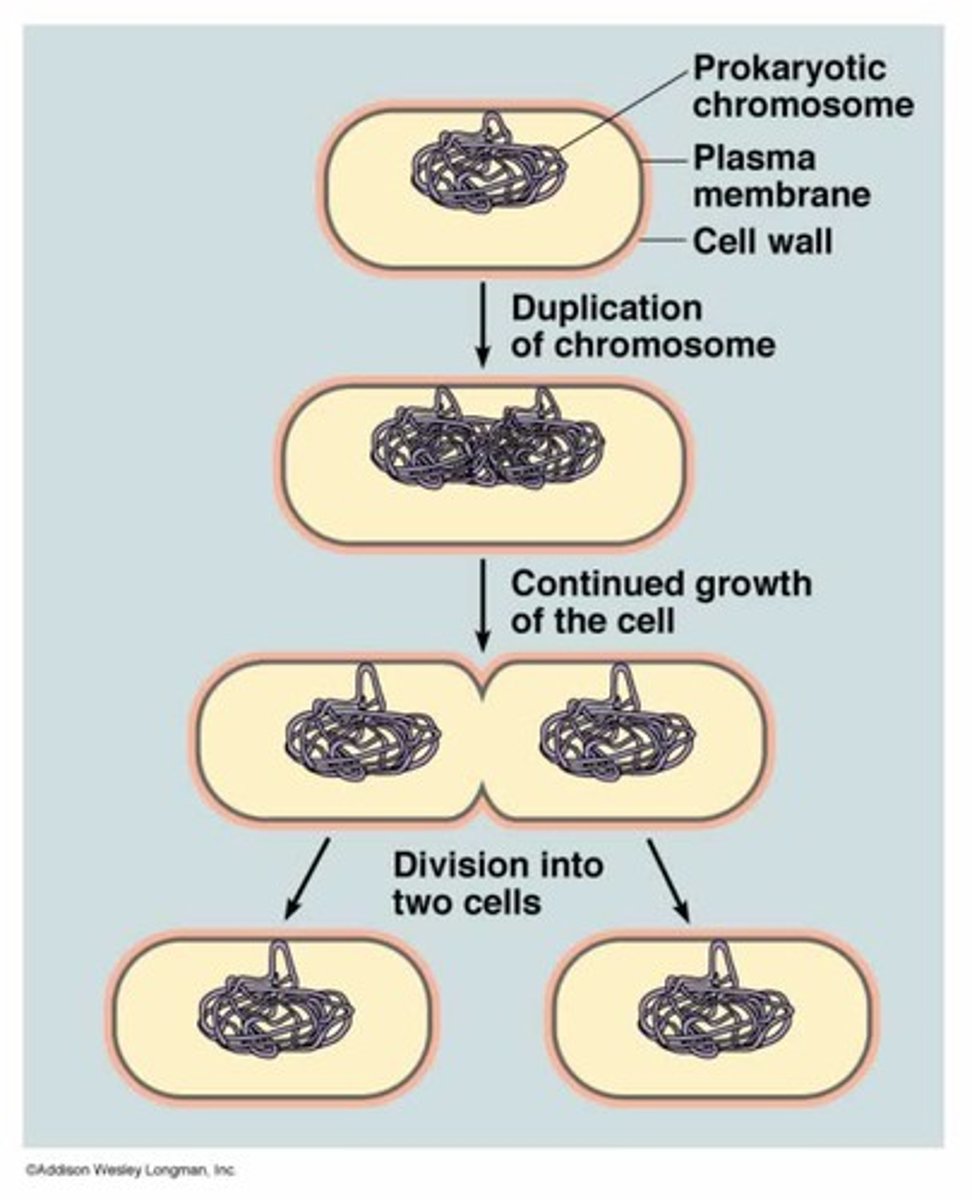
Binary Fission
Simple form of asexual reproduction in prokaryotes. Chromosome attaches to the cell wall and replicates while the cell continues to grow in size.
Genetic Recombination
Plasmids will carry genes that impart some benefit on the bacteria or carry virulence factors that increase how pathogenic it is. .
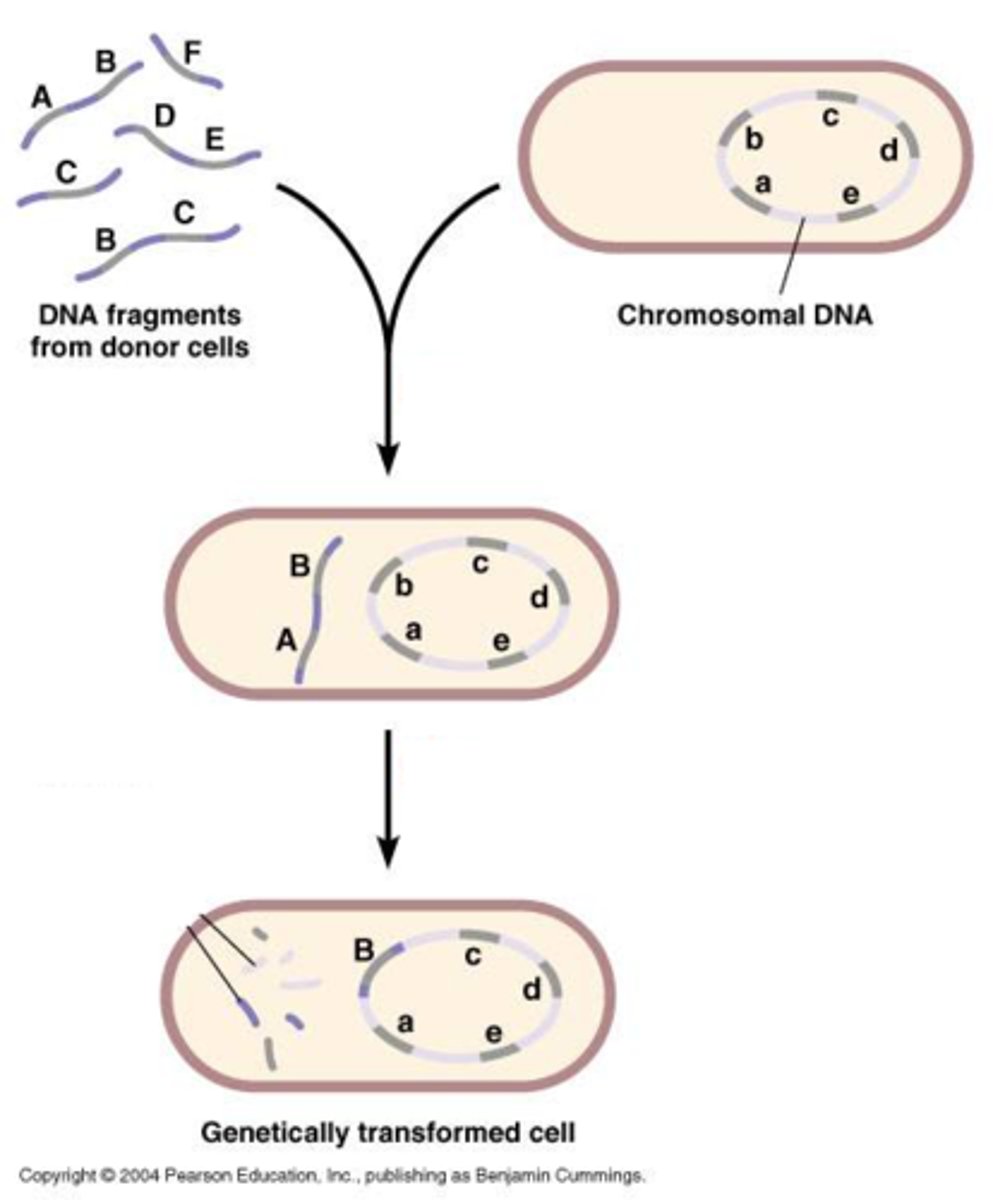
Transformation
Integration of foreign genetic material into the host genome.
Conjugation
Bacterial sexual reproduction. Two bacteria form a conjugation bridge, made from the sex pili and sex factors (plasmids containing necessary genes), that allows for transfer of materials. Donor male (+) to the recipient female (-). Unidirectional.
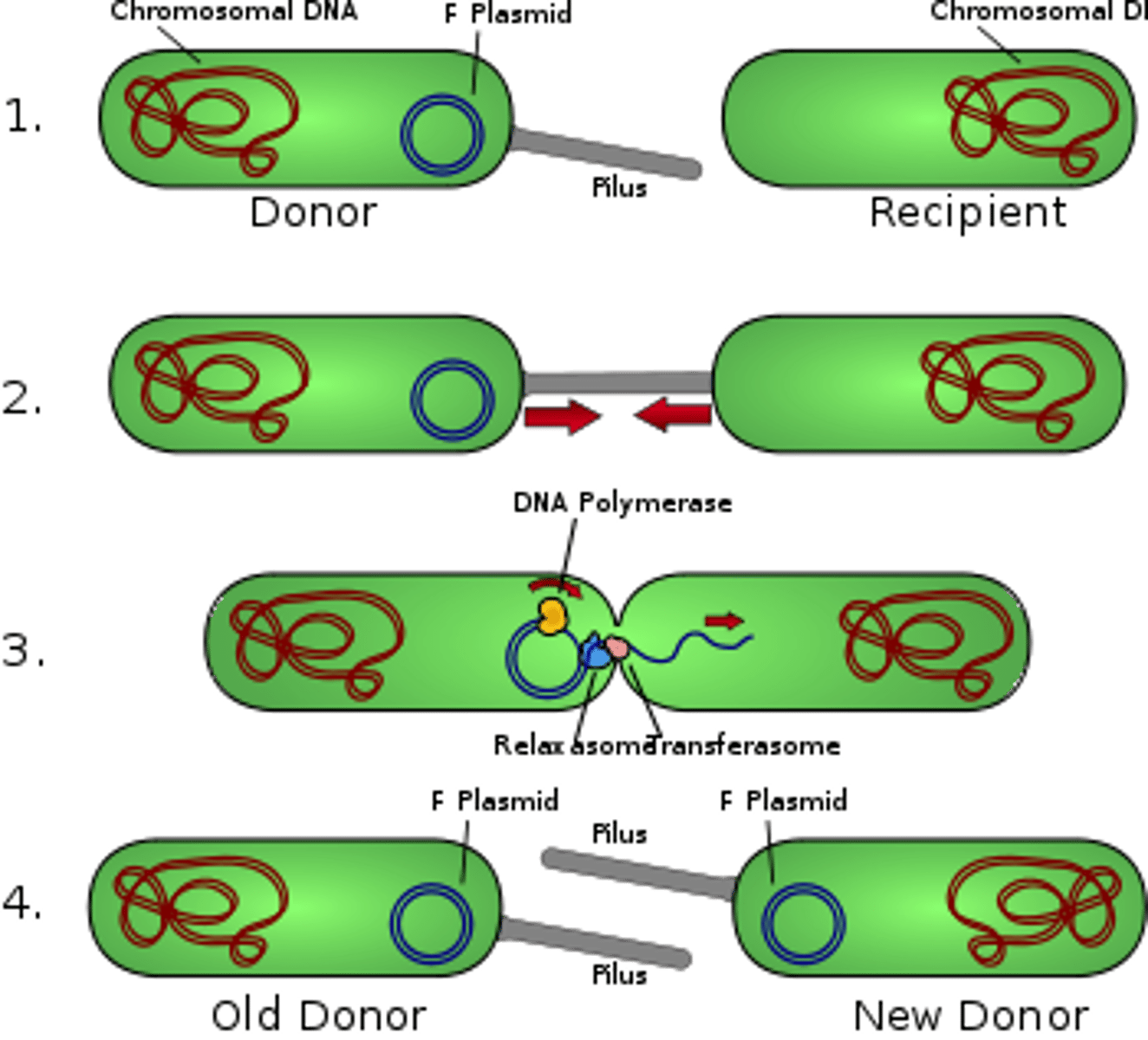
Sex Factor F
Best studied sex factor is the Fertility factor. F+ cells with it, F- without it. F+ cell replicates its F factor, donates it to the recipient, and makes it an F+ factor. Then they can copy and transfer genetic material via conjugation; great for sharing antibiotic resistance or virulence factors.
Hfr
High frequency of recombination. Incomplete transfer of genetic information to the female recipient - sex pilus bridge breaks before the whole DNA sequence can be transferred. Sex factor often incorporates itself into host genome so in conjugation, host genome bits also are transferred.
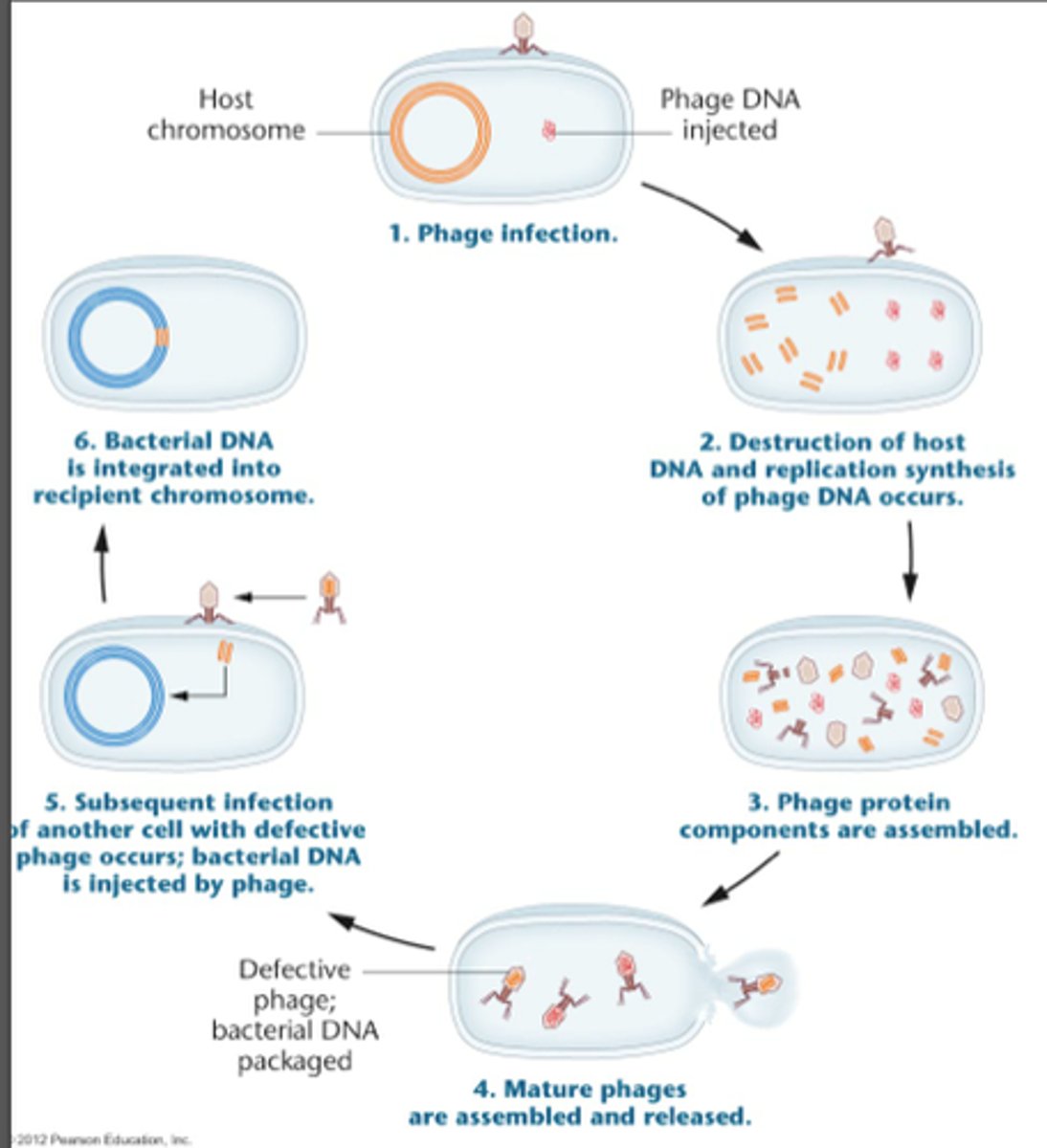
Transduction
Requires a vector, or a virus that carries genetic material from one bacteria to the other. Bacteriophages can trap a segment of host DNA during assembly, it can then release it in another infection later on.
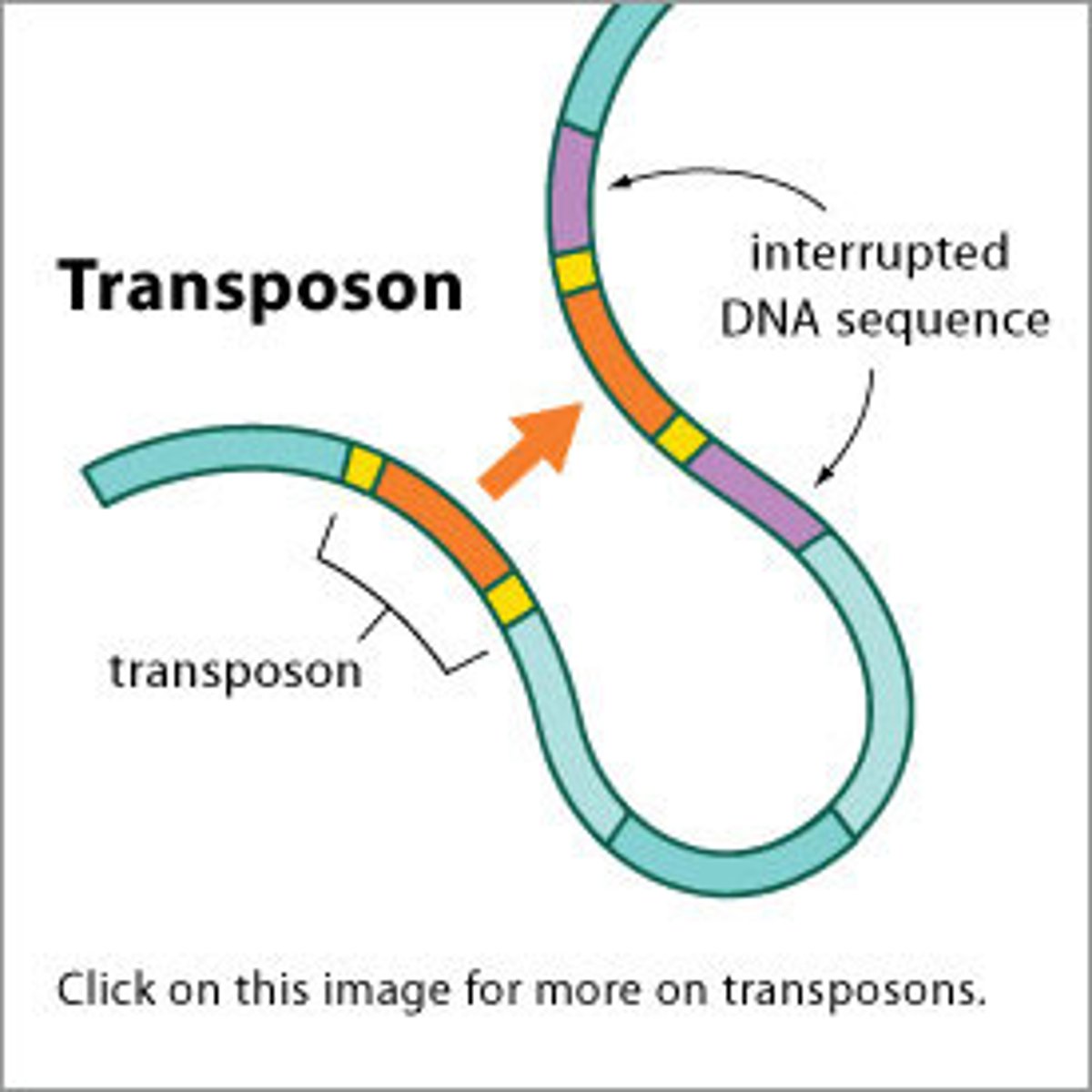
Transposons
Genetic element capable of inserting and removing themselves from the genome.
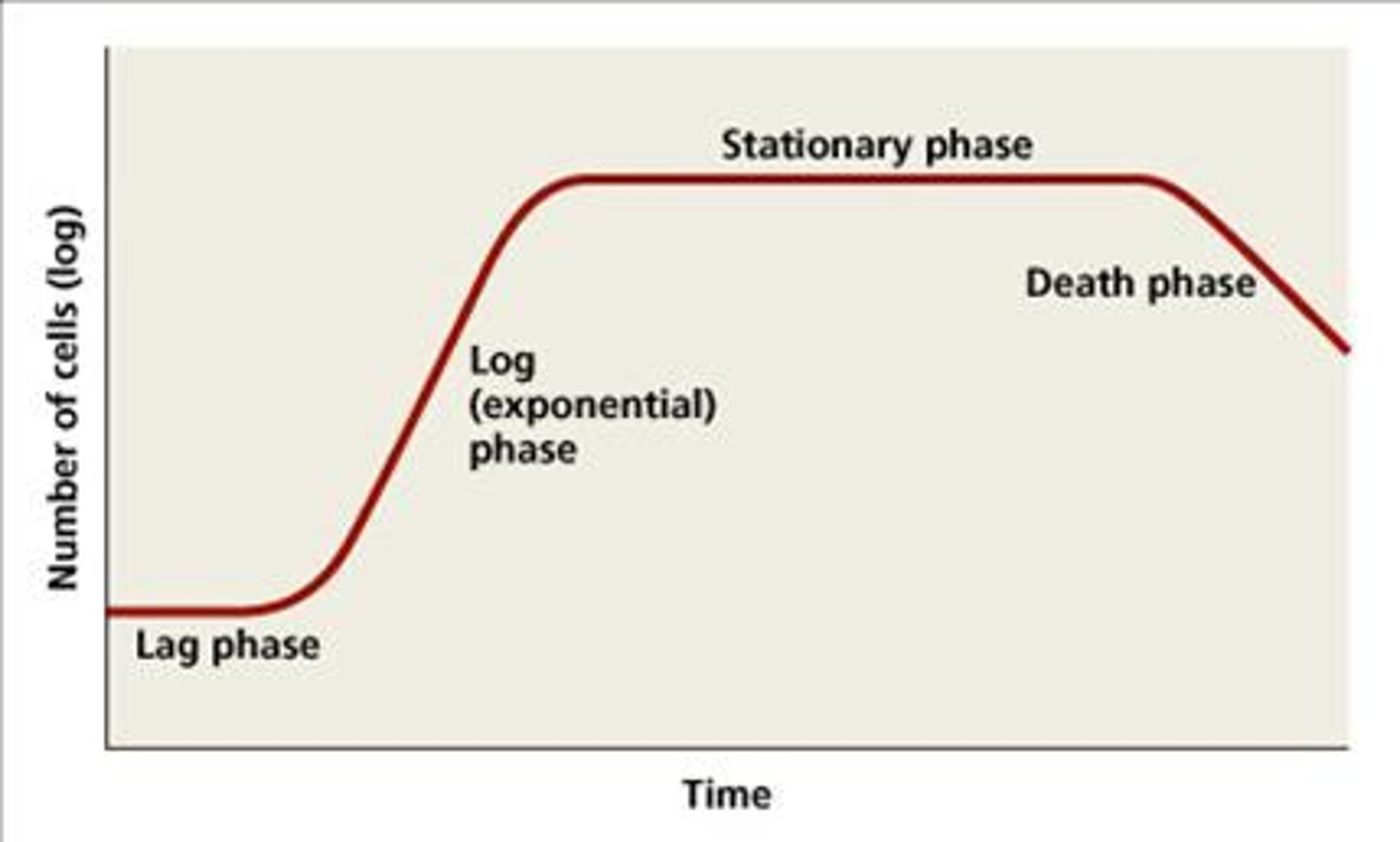
Phases of Bacterial Growth
Lag phase: Adaptation to the new local conditions of the environment.
Log phase: Adaptation, growth increase, increase in bacterial colony.
Stationary phase: Reduction of resources slows reproduction. Characterized by flat top of curve
Death phase: Lack of ability to support the number of bacteria. Decline in number.
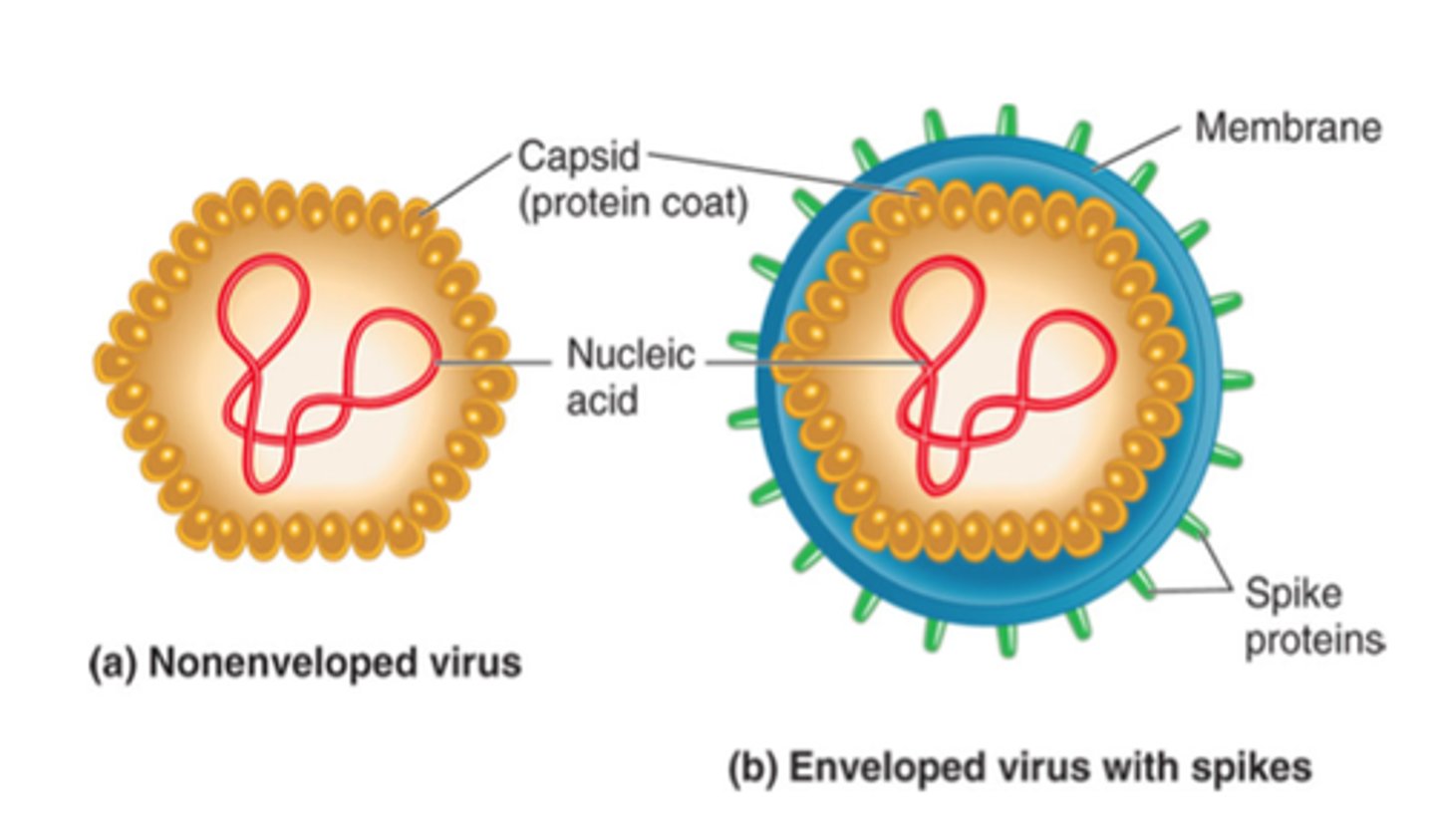
Viral Structure
Composed of genetic material, protein coat, and envelope containing lipids. Genetic info is either circular or linear, single or double stranded, and either made of DNA or RNA. The protein coat is the capsid. Envelope will surround the capsid and is made of phospholipids that are sensitive to heat, detergents, and desiccation.
Viral Host Cell
Where the virus must express and replicate genetic information, because they do not have their own ribosomes. It helps to produce the viral product, virions (viral progeny).
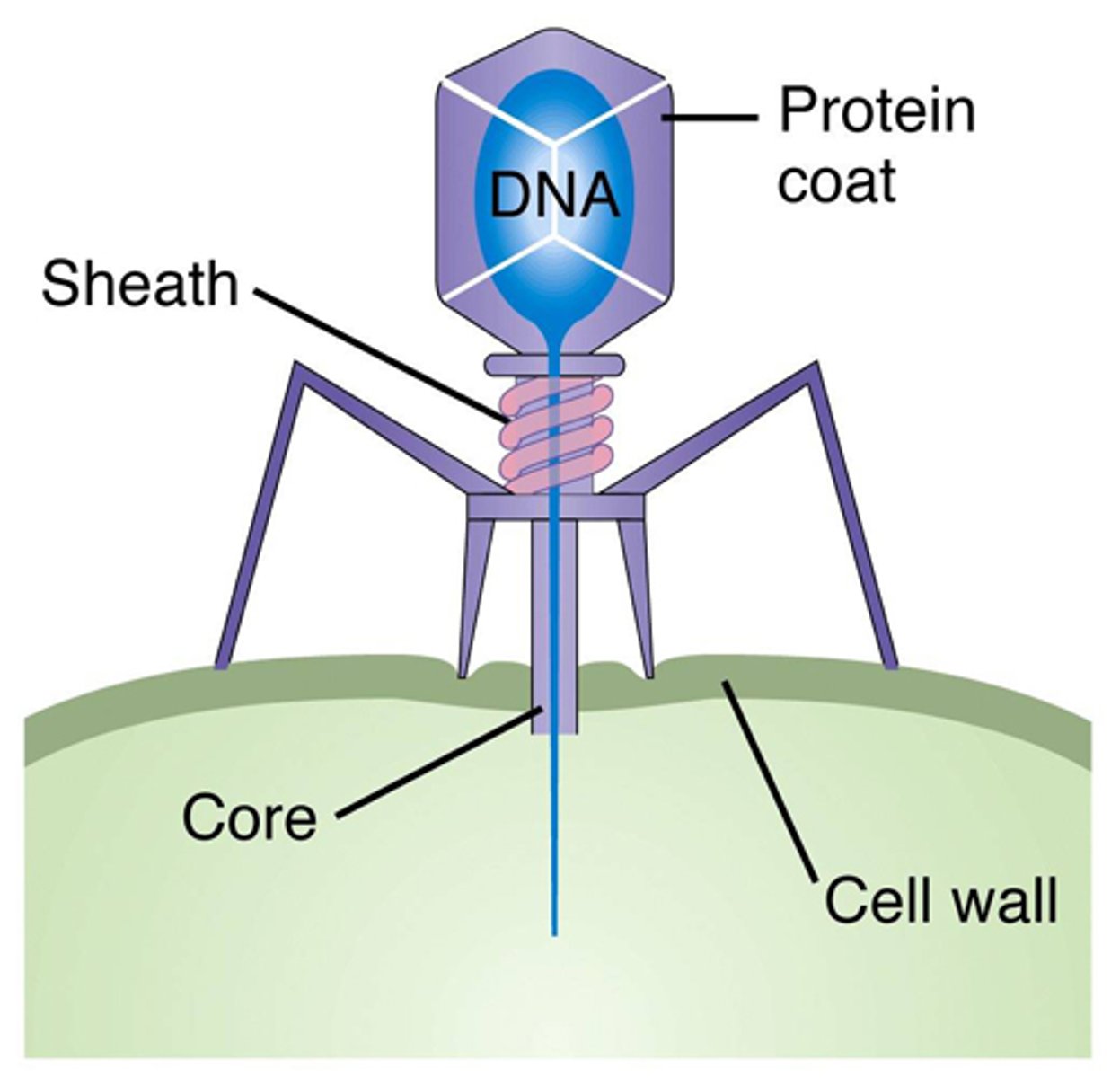
Bacteriophages
Viruses that specifically target bacteria. They only inject genetic material via a tail sheath. The tail fibers help with connection to the host cell.
Viral Genome
ssDNA, dsDNA, dsRNA, or ssRNA. ssRNA is either positive sense or negative sense.
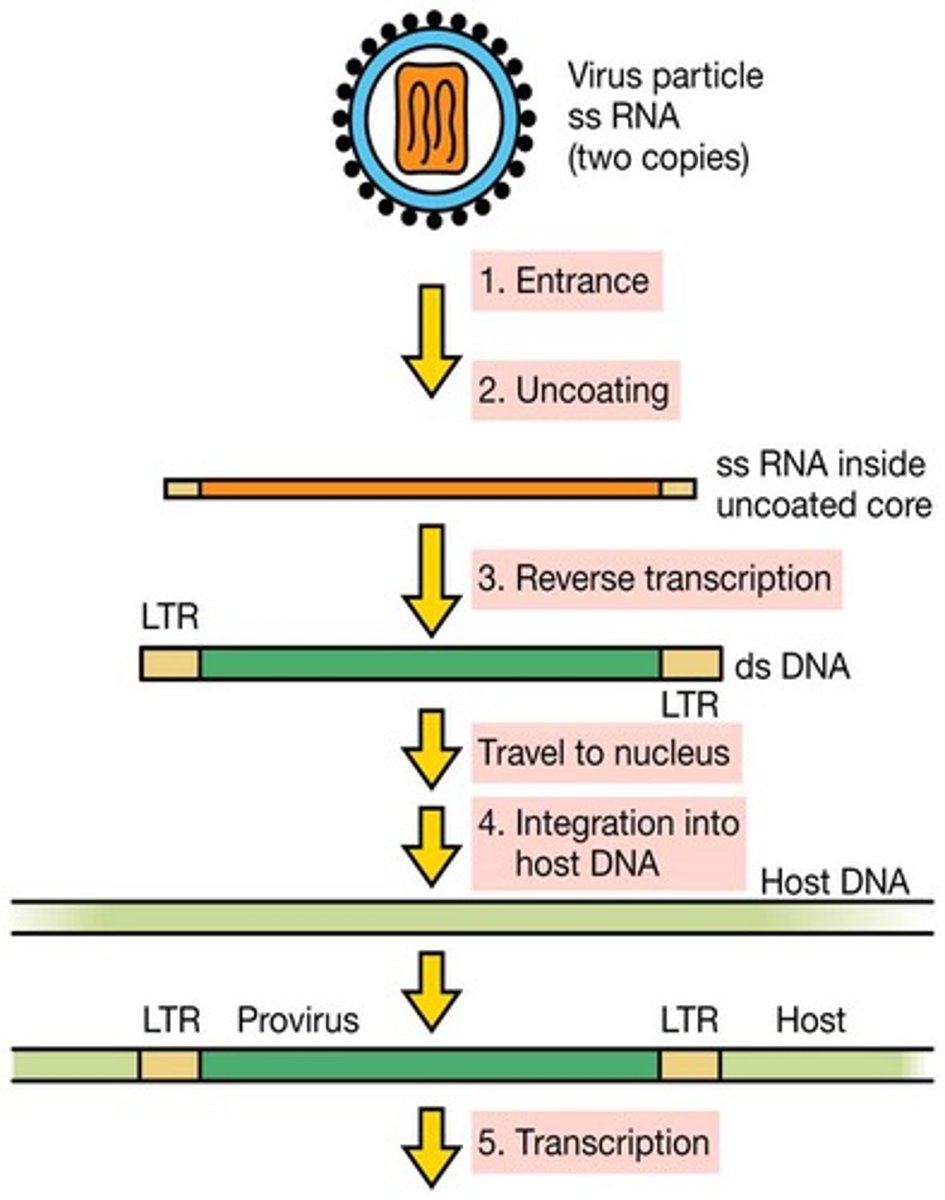
Retroviruses
Enveloped, ssRNA viruses that carry reverse transcriptase in order to synthesize dsDNA from single-stranded RNA (two rounds of reverse transcription). The DNA then integrates into the host cell genome and acts as if it were the host cell's own DNA. An example is HIV.
Viral Life Cycle
1. Infection: Bind to receptors, fusion, entry of virion. Bacteriophage only inserts genetic material.
2. Translation and Progeny Assembly: Translation must occur in order for a virus to reproduce. DNA viruses go to the nucleus, +RNA viruses stay in the cytoplasm, -RNA needs synthesis of the +RNA via RNA replicase for translations. Proteins are created and packaging then occurs.
3. Progeny Release: Released via initiation of cell death or lysing due to a large number of virions. It can also be released via extrusion, or fusing with its plasma membrane and budding essentially. Can also leave by extrusion, where the virus fuses with the plasma membrane and forms a vesicle.
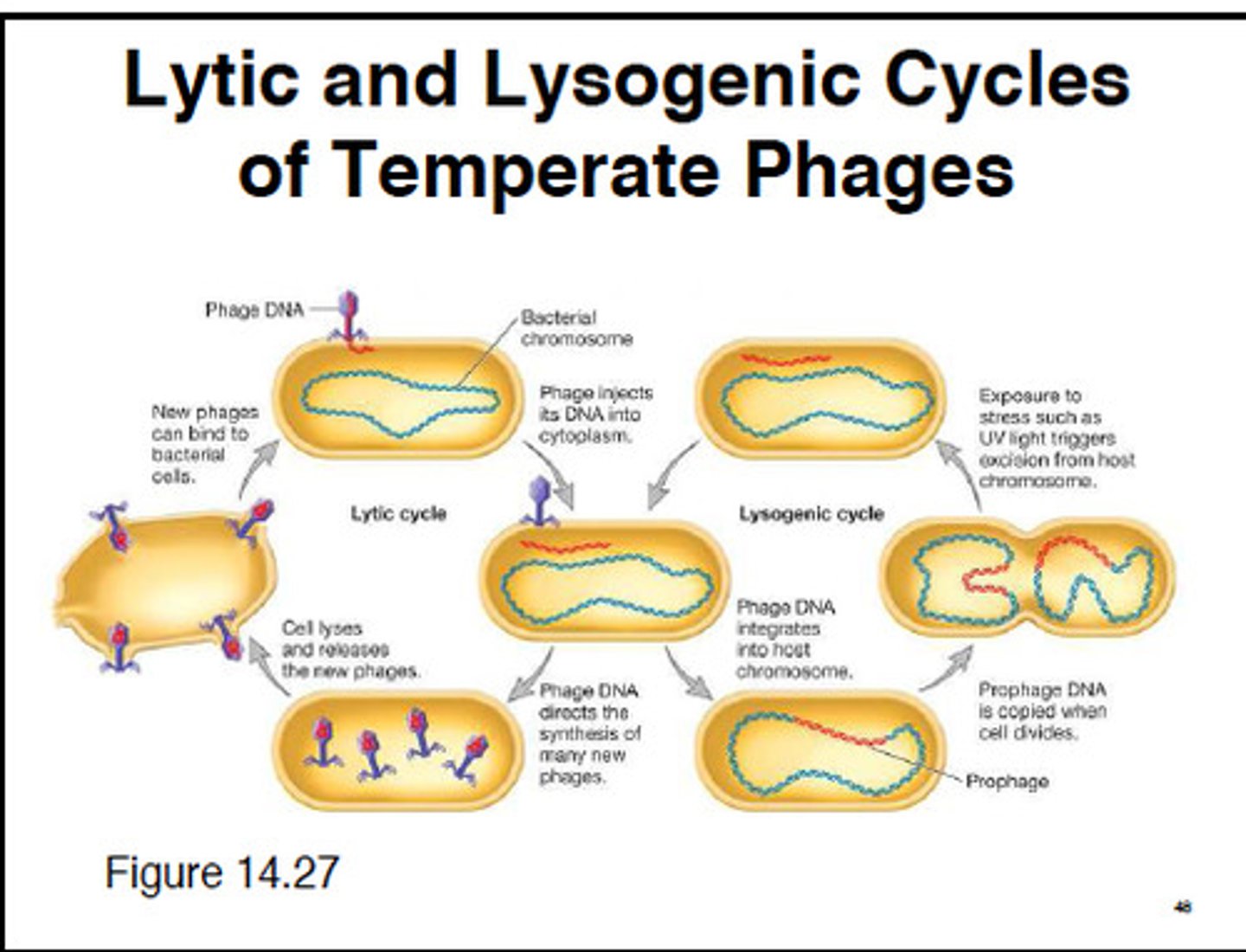
Lytic Cycle
Bacteriophage makes maximal use of the cell's machinery with little regard for the survival of the host cell. the bacteria are termed virulent.
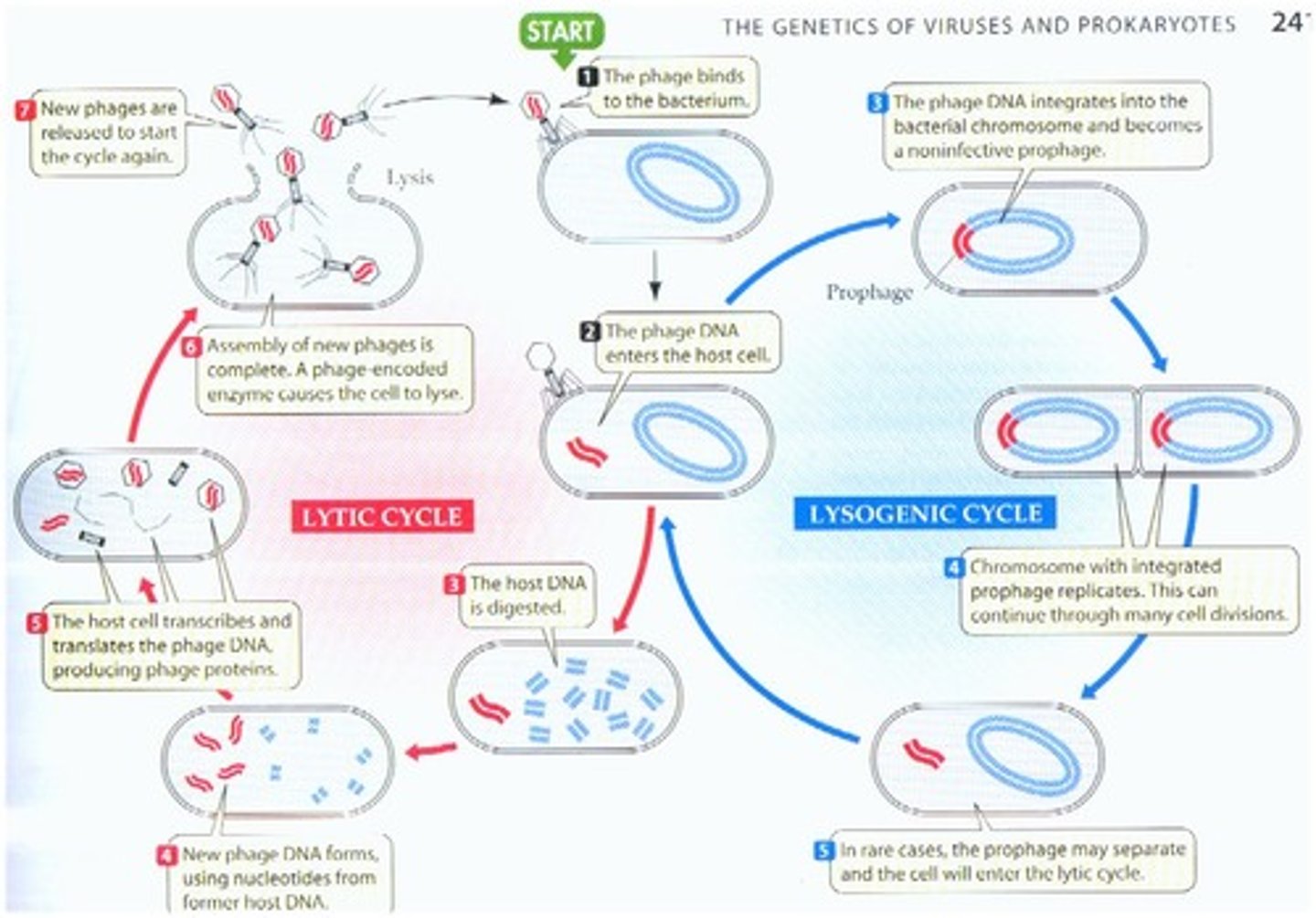
Lysogenic Cycle
Integration into the genome as a provirus or prophage. Environmental factors will revert the provirus back to a lytic cycle.
Superinfection
Simultaneous infection, usually prevented by lysogenic cycles. Infection with one strain of phage generally makes it harder for the bacterium to be infected with other phages.
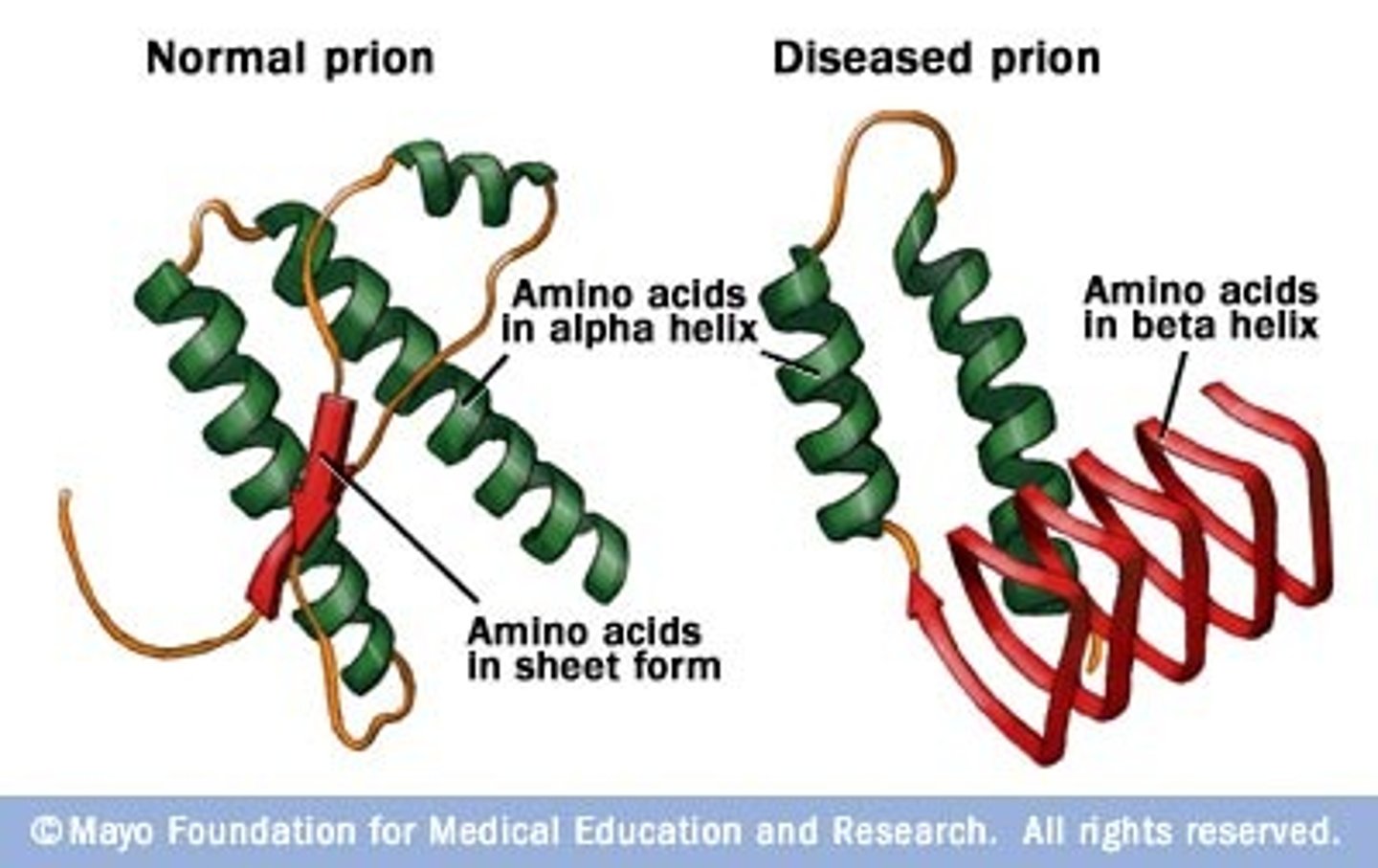
Prions
Infectious proteins that are nonliving things. Cause disease via misfolding other proteins, usually causing the change from an alpha helical structure to a beta helical structure. Protein aggregates form and cell function is reduced. Mad cow disease!!
Viroids
Small plant pathogens that consist of a very short, circular, single-stranded RNA. They silence genes in the PLANT genome. HDV (hepatitis D virus) is an example of a human viroid. Although alone HDV is harmless, when coinfected with hepatitis B, HDV is able to exert its silencing function on human hepatocytes (liver cell).
Episomes
Episomes are a subset of plasmids that are capable of integrating into the genome of the bacterium
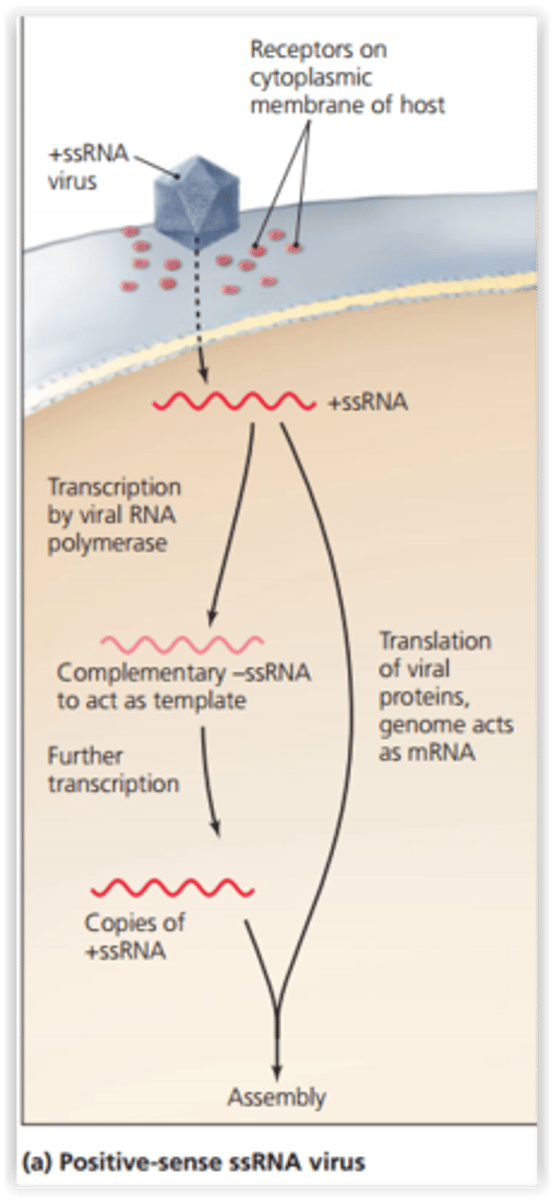
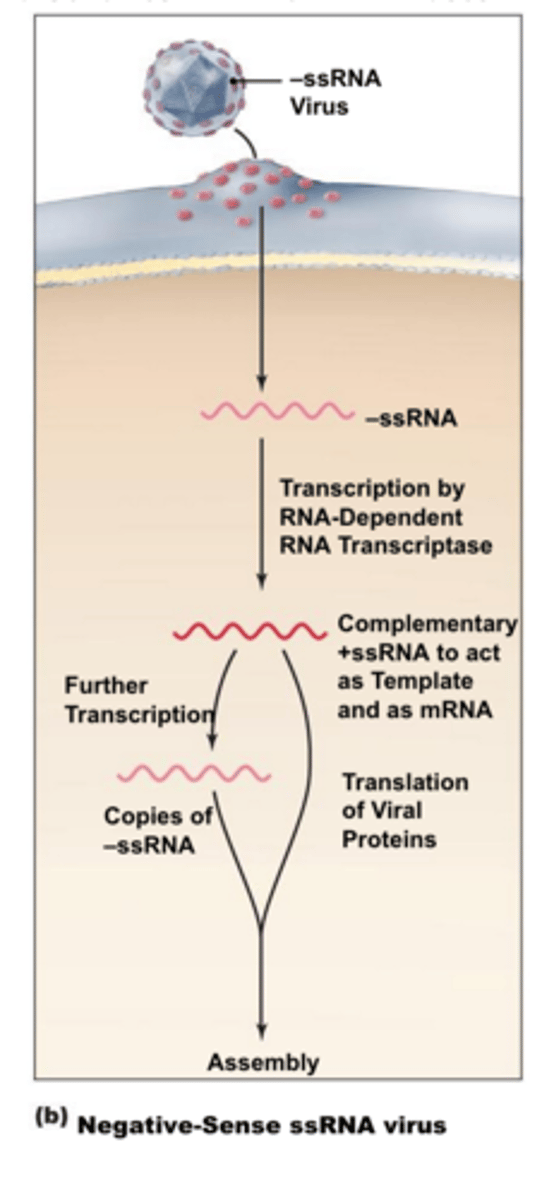
Positive Sense Viruses
Implies that the genome may be directly translated to functional proteins by the ribosomes of the host cell, just like mRNA.
Negative Sense Viruses
These viruses require synthesis of an RNA strand that is complementary to the negative sense RNA strand, which can then be used as a template for protein synthesis. These viruses must carry an RNA replicase in the virion to ensure that this synthesis occurs.
Apoptosis
Release of ETC enzymes
Autolysis
Release of lysosome enzymes
Endosomes
transport, package and sort materials to and from membrane. Can send vesicles to:
1. Cell membrane for recycling
2. Lysosome for degradation
3. Golgi for transport or modification
Smooth Endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth ER lacks ribosomes and is used for lipid synthesis and detoxification of drugs and poisons. It also transports proteins from the RER to the Golgi Apparatus.
HIV life cycle
1. Proteins on the envelope bind to CD4 and CR5 on cell surface
2. Virus fuses with cell and empties content into cytoplasm
3. Reverse transcriptase converts RNA to DNA, making errors to generate diversity
4. Integrase inserts virus's DNA into host DNA
5. RNA polymerase converts DNA into RNA, ribosomes make proteins
6. Budding virus particle
7. Mature virus
Parenchyma
Epithelial tissue constitute the parenchyma in most organs, meaning they are functional parts of the organ (i.e. hepatocytes of the liver, nephron of the kidneys). They are often polarized, one side faces the lumen, the other interacts with blood vessels and structural cells.
Anaphase
Centromeres split, each chromatid has its own distinct centromere
chromatids separate-via shortening of the kinetochore fibers.
Anaphase I
Disjunction - each chromosome of paternal origin separates from its homologue of maternal origin (either chromosome can end up in either daughter cell).
The separating of the two homologous chromosomes is referred to as segregation.
This explains mendels law of segregation
Anaphase II
Centromeres divide,
sister chromatids pulled to opposite poles.
Carriers
females with a disease-causing X allele that do not exhibit the disease.
Cell Cycle
A series of specific phases in which the cell grows, synthesizes DNA, and divides.
Chromatin
less Condensed form of chromosomes during interphase. Makes DNA available to RNA polymerase for transcription.
Corona Radiata
Lies outside of the zona pellucida. Is a layer of cells that adhered to the oocyte during ovulation. Meiosis II is triggered when a sperm penetrates the corona radiata and zona pellucida via acrosomal enzymes.
Crossing Over
homologous chromosomes break at synapsis, (called chiasma)
pieces of DNA are exchanged = recombination of genes.
Genetic diversity!
Cyclins and Cyclin-Dependent Kinases
Molecules responsible for the cell cycle, via fluctuating levels of cyclin. Cyclins bind CDK to activate them —> activated CDK-cyclin complex phosphorylates transcription factors.
These then promise transcription of genes required for the next stage of the cell cycle.
Cytokinesis
Separation of the cytoplasm/organelles -> daughter survive on own
Diploid
(2n) contain two copies of each chromosome, 46
roles of NS?
When penis is flaccid, norepinephrine from Sympathetic NS is present.
When sexual stimulation is present, the Parasympathetic NS causes release of NO which causes Corpora Cavernosa/Spongiosum in penis to fill with blood=erection
Ejaculation meatus=contraction of muscle to expel sperm. The SNS is stimulated and norepinephrine is released which causes contraction and release of semen into urethra of penis. Sympathetic NS causes ejaculation, PNS causes erection!!
Female Sexual Development
Ovaries are also under FSH and LH control. They produce estrogen and progesterone.
Estrogens are secreted in response to FSH
—> the making/maintenance of reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. In embryo, they develop the repro. tract. In adults, E initially thickens the uterine lining (endometrium).
Progesterone is secreted by the corpus luteum (remnant follicle that remains after ovulation) in response to LH. Involved in development and maintenance of the endometrium. End of 1st trimester, it's supplied by placenta.
Fertilization
Sperm cell penetrates the layers with acrosomal enzymes, triggering meiosis II. This indicates another meiotic division creating the mature ovum and another polar body.
Follicle Stimulating Hormone
In males, it triggers sperm maturation via Sertoli cell stimulation.
In females, FSH causes estrogen to be produced
Follicular Phase
Begins when menstrual flow, shedding of the uterine lining, begins.
GnRH secretion from the hypothalamus increases in response to decreased estrogen and progesterone.
Both FSH and LH increase in secretion —> development of follicles occurs
—> follicles produce estrogen, which (negative feedback) causes the decline of GnRH, FSH, and LH.
Estrogen regrows the ENDOMETRIAL LINING, vascularizing and glandularizing the decidua (uterine lining forming maternal part of placenta).
G0 Stage
Normal cell/no division offshoot of G1 phase. Cell is simply living and serving its function.
G1 Stage
Create organelles - energy/protein production
increasing size.
governed by restriction points.
G1/S Checkpoint
DNA good enough for synthesis? p53 protein is the main control here. Known as the Restriction Point
G2 Stage
Cell passes through another quality control checkpoint to ensure DNA replicated correctly so error isnt passed down through M phase to progeny cells.