Bio Exam
1/153
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
154 Terms
Microscope
zooms in on what the naked eye can’t see
3 parts of cell theory
all living things are composed of one or more cells, cells are the basic unit of life, and all cells come from other pre-existing cells
Who invented the microscope
Hans and Zacharias Janssen (brothers)
electron microscope
obtaining high resolution images of biological and non-biological specimens
SEM
detailed surface scan (3d)
TEM
through the specimen
light microscope
an instrument that uses light, magnifying lenses, and an eyepiece to examine objects too small to be seen by the naked eye.
light vs electron microscope
one can be alive and the other cant be alive but you get a higher resolution image
field of view
how much you're able to see of a magnified sample at a specific magnification level
total magnification
take the power of the objective (4X, 10X, 40x) and multiply by the power of the eyepiece, usually 10X.
estimate size of organell
a few nanometers to several micrometers, depending on the specific organelle and organism, with most falling within the range of 0.5 - 10 micrometers
nucleus
a membrane-bound organelle within a cell that serves as the control center, stores DNA, metabolism
nucleolus
to synthesize and process ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and assemble ribosomes
nuclear pore
a protein-lined channel in the nuclear envelope that regulates the transportation of molecules between the nucleus and the cytoplasm
nucleur membrane
serves to separate the chromosomes from the cell's cytoplasm and other contents
cell membrane
provides protection for a cell
cell wall
(only plants) layer that surrounds some cell types, found immediately outside the cell membrane
cytoskeleton
a structure that helps cells maintain their shape and internal organization,
cytopalsm
to act as the gel-like fluid inside a cell, holding organelles in place and facilitating the movement of molecules within the cell
cytosol
provide structural support to the cell organelles
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
makes lipids, phospholipids as in plasma membranes, and steroids, found in liver (Detox)
rough endoplasmic reticulum
makes and process proteins, is located within the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells, often near the nucleus
golgi appartaus
transport, sorting and modification of both protein and lipid (packaging center) positioned near the nucleus and close to the (ER)
ribosomes
makes proteins (into a chain of amino acids, which then fold to form proteins) found near cytoplasm or RER
lysosomes
garbage disposal (breaks down waste) found in cytoplasm of animals
preixoslomes
Carrying out oxidative reactions using molecular oxygen. They generate hydrogen peroxide, which they use for destroying the excess by means of the catalase they contain. (acting as a cellular detoxification center) (cell cytoplasm)
vacoule
In animal cells, generally small and help get rid of waste products. In plant cells, help maintain water balance
vesiscle
A small sac formed by a membrane and filled with liquid, ER and Golgi apparatus
centrioles
organizing centers for microtubules within a cell, near nucleus in animal cells
chloroplast
carry out photosynthesis, and receives sunlight for plant
mitochondria
powerhouse of cell- provides usable energy for the cell
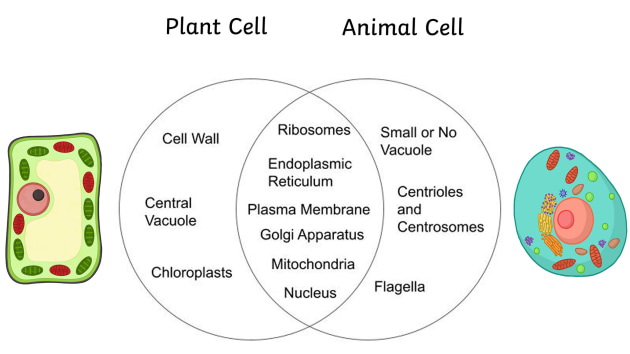
plant vs animal cell
plant cells have a cell wall, chloroplasts, and a large central vacuole, while animal cells lack these structures, instead having centrioles and lysosomes which are typically absent in plant cells
prokaroyic vs eukarotic
Prokaryotic cells (bacteria) lack a nuclear envelope; eukaryotic cells have a nucleus in which the genetic material is separated from the cytoplasm.
where cellular respiration takes place
in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells
C6H12O6 + 6O2 --> 6CO2 + 6H2O + Chemical Energy (in ATP)
where photosynthesis takes place
in the chloroplasts of plant cells
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
cell membrane
regulates the transport of materials entering and exiting the cell.
phospholipid
a hydrophilic "head" with a phosphate group and two hydrophobic "tails" made up of fatty acids, typically connected by a glycerol backbone
cholesterol
to stabilize the interactions between the phospholipids and prevent the membrane from getting too fluid or too flexible.
transmembrane protein
serve as channels or gates that facilitate the entry and exit of molecules and across the cell membranes.
peripheral proteins
support communication, enzymes, and molecule transfer and on surface of cell membrane
integral proteins
channeling or transporting molecules across the membrane and found in plasma membrane
glycoproteins
allow white blood cells to move around the body, initiate immune responses, and identify other cells and are found in cell membrane
glycolipids
to maintain the stability of the cell membrane and to facilitate cellular recognition
fluid mosaic model
describes the main characteristics of the plasma membrane because fluid and has many parts
extracellular matrix
A large network of proteins and other molecules that surround, support, and give structure to cells and tissues in the body
transport proteins
acts as doors to the cell, helping certain molecules pass back and forth across the plasma membrane
polar heads
contact the fluid inside and outside of the cell hydrophillic (water loving)
non polar tails
hydrophobic (water-fearing) part of the molecule, causing them to face inwards within the membrane, away from the aqueous environment, and essentially creating a barrier that prevents water-soluble substances from easily passing through the cell membrane
channel proteins
a protein that allows the transport of specific substances across a cell membrane
carrier proteins
bind specific molecules to be transported on one side of the membrane
passive transport
a naturally occurring phenomenon and does not require the cell to expend energy to accomplish the movement
active transport
the movement of molecules or ions across a cell membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration—against the concentration gradient.
ATP
nucleoside triphosphate, consisting of a nitrogenous base (adenine), a ribose sugar, and three serially bonded phosphate groups.
diffusion
moving of substances by the natural movement of their particles.
osmosis
water diffusion
tonicity
the capability of a solution to modify the volume of cells by altering their water content (hyper, hypo)
isotonic
same amount inside and out of cell
dynamic
relationships existing between organisms, their physiology, and their environment
equilibrium
the balance of particles in a cell
hypotonic
water outside so rushes inside
hypertonic
water inside cell so rushed outside
turgid
normal state of plants
flacid
wilting state of plants
lyse
explosion of animal cell
animal and plants cells in diffrent solutions
iso is normal for plants and hypo is normal for plants
with/down concentration gradient
passive transport - diffusion
up//\against concentration gradient
active transport - uses energy
solution
mixture of solute and solvent
solvent
what there is more of (ex:water)
solute
what there is less of (ex: salt)
plasmolysis
a process involving a plant cell losing water content and therefore contracting and shrinking its cytoplasm and plasma membrane away from the inside of its cell wall.
Exocytosis
exists the cell (the process by which cells take in substances from outside of the cell by engulfing them in a vesicle.)
endocytosis
enters the cell (the process by which cells take in substances from outside of the cell by engulfing them in a vesicle)
pinocytosis
a process by which the cell takes in the fluids along with dissolved small molecules
phagocytosis
The process by which a phagocyte (a type of white blood cell) surrounds and destroys foreign substances (such as bacteria) and removes dead cells.
Sodium/Potassium pump
active transporters that use energy, such as ATP, to. For every three sodium ions pumped out of the cell transports two potassium ions inside the cell.
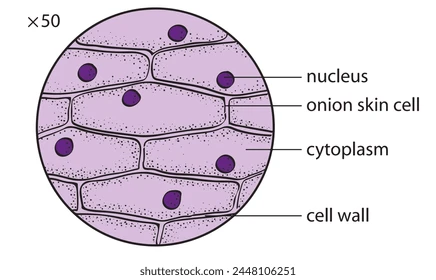
organelles found in onion root tip cells
nucleus, cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, large vacuole, mitochondria, and ribosomes
Active Transport vs Passive Transport
requires energy vs natural movement
Organic compounds
compound containing carbon
monomers
a molecule that can be bonded to other identical molecules to form a polymer.
dehydration reaction
chemical reaction that involves the loss of water to bond monomers.
hydrolysis reactions
chemical reaction that involves the gain of water to separate polymers
carbohydrates
a macromolecule that is part of the 4 main groups of life, sugar molecules, body main fuel source
lipids
not a macromolecule that is part of the 4 main groups of life, fatty compounds, storing energy
protiens
a macromolecule that is part of the 4 main groups of life, made of amino acids, help make new cells and repair them
nucleic acids
a macromolecule that is part of the 4 main groups of life, large biomolecules, storage of DNA
fatty acids
amino acids
nucleotides
peptide bonds
when two amino acids are positioned so that carboxyl/group of one is adjacent to amino groip of another they can be joined by denaturation with removal of water
polypeptides
polymer of amino acids protein biologically functioned molecule made up of one or mode polypeptides folded and coiled into specific 3D structure
saccharides
sugar molecule
monosachrides
simplest carbohydrate (sugar) CH20
disachradies
a type of carbohydrate that consists of two monosaccharides linked together
polysacchrides
long chains of carbohydrate molecules, composed of several smaller monosaccharides
glucose
the main sugar found in your blood. It is your body's primary source of energy
fructose
sugar found naturally in fruits, fruit juices, some vegetables and honey
sucrose
a disaccharide consisting of glucose and fructose, commonly found in sugarcane and sugar beets
amylose
a polysaccharide made of α-D-glucose units, bonded to each other through α(1→4) glycosidic bonds (in starch)
starch
polymer of glucose monomers, as granules within cells