CVM - Lecture 6: The circulatory system
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
1. tunica externa (aka adventitia)
2. tunica media
3. tunica interna (aka intima)
4. Smooth muscle
5. Internal elastic membrane/lamina
6. Vasa vasorum
7. external elastic membrane
8. Nervi vasorum
9. Endothelium
10. Elastic fibre
Fill the blanks
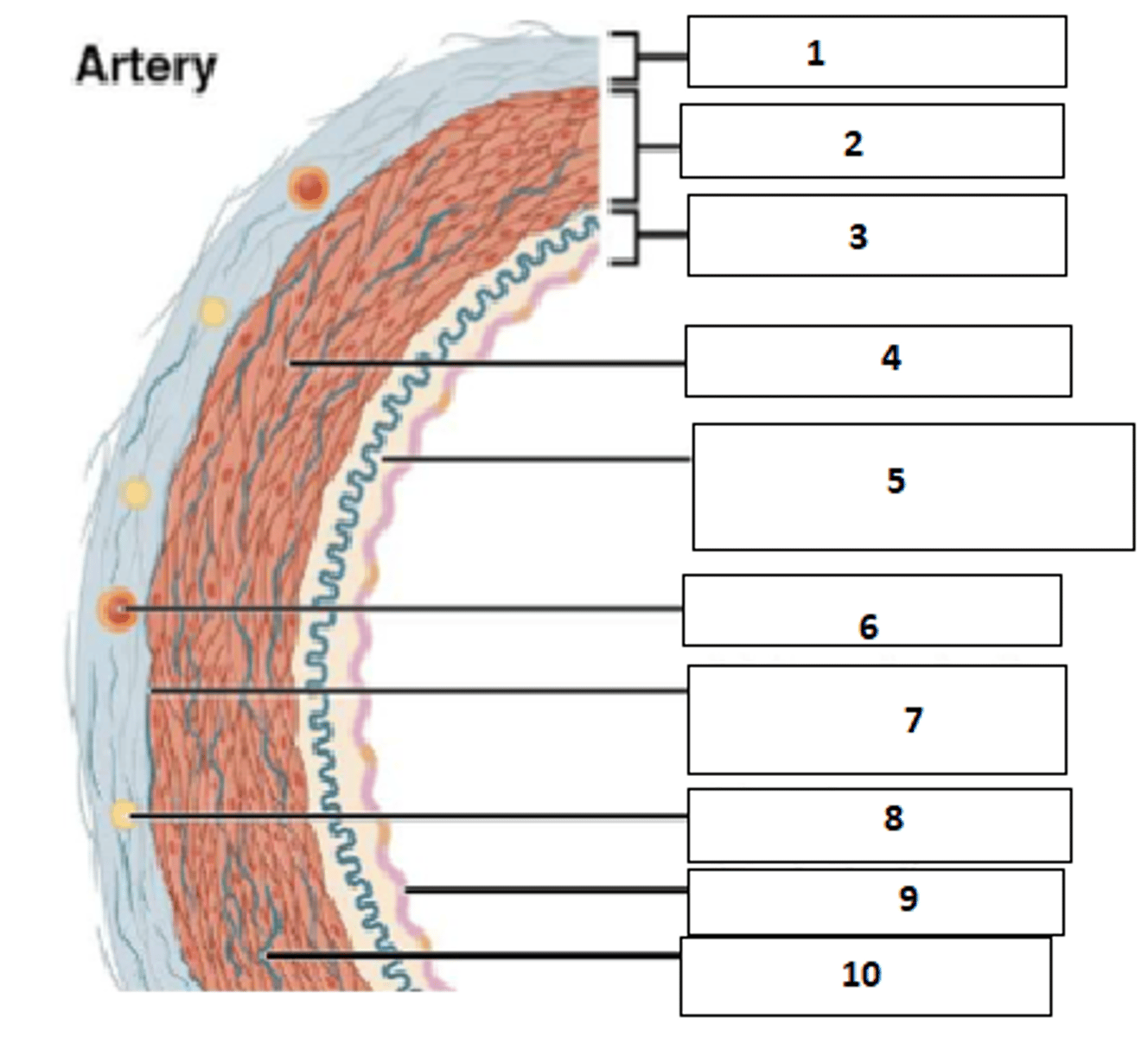
1. tunica externa (aka adventitia)
2. tunica media
3. tunica interna (aka intima)
4. vasa vasorum
5. smooth muscle
6. endothelium
Fill the blanks
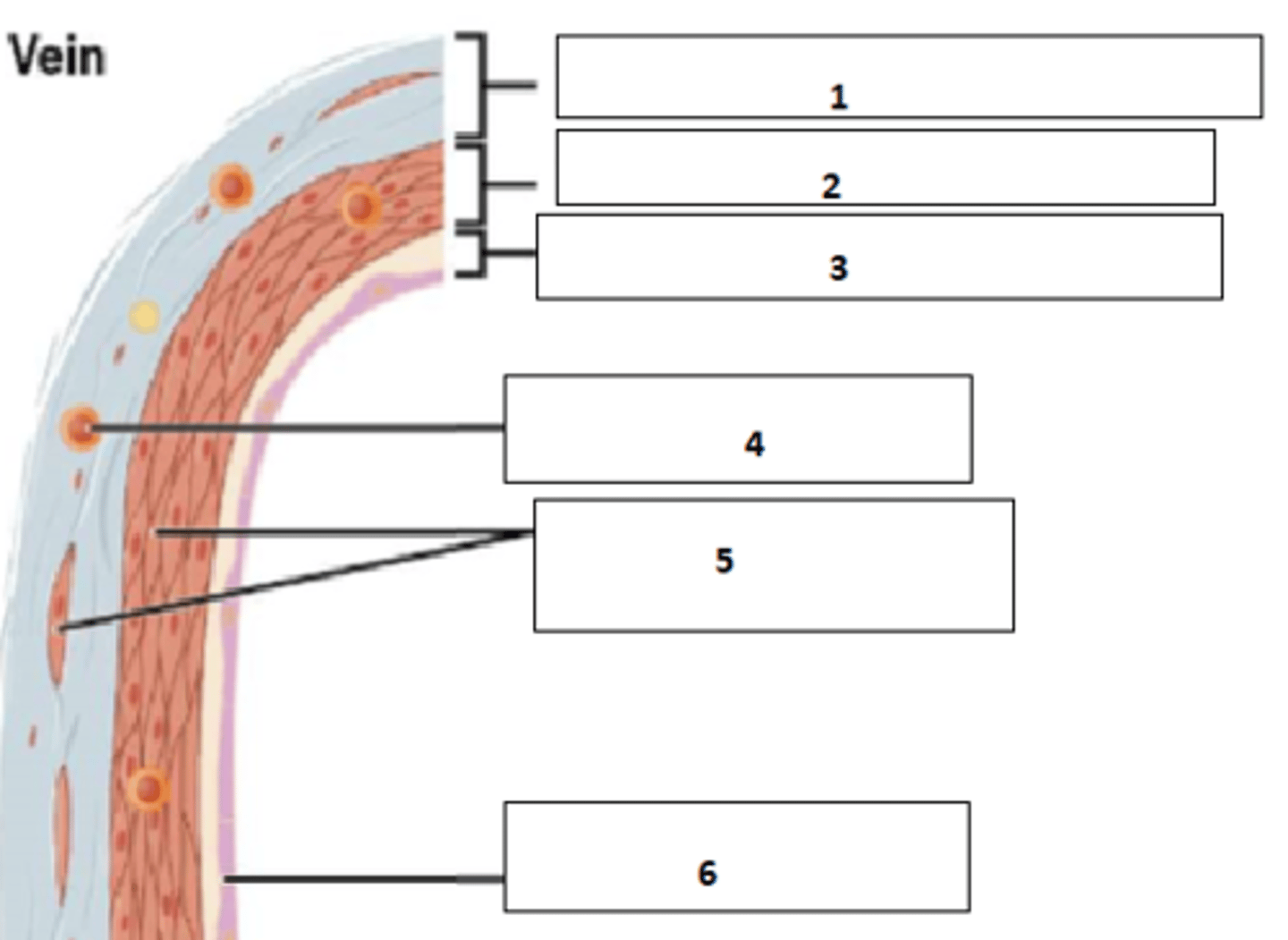
Top: vein
Bottom: artery
Which is which?
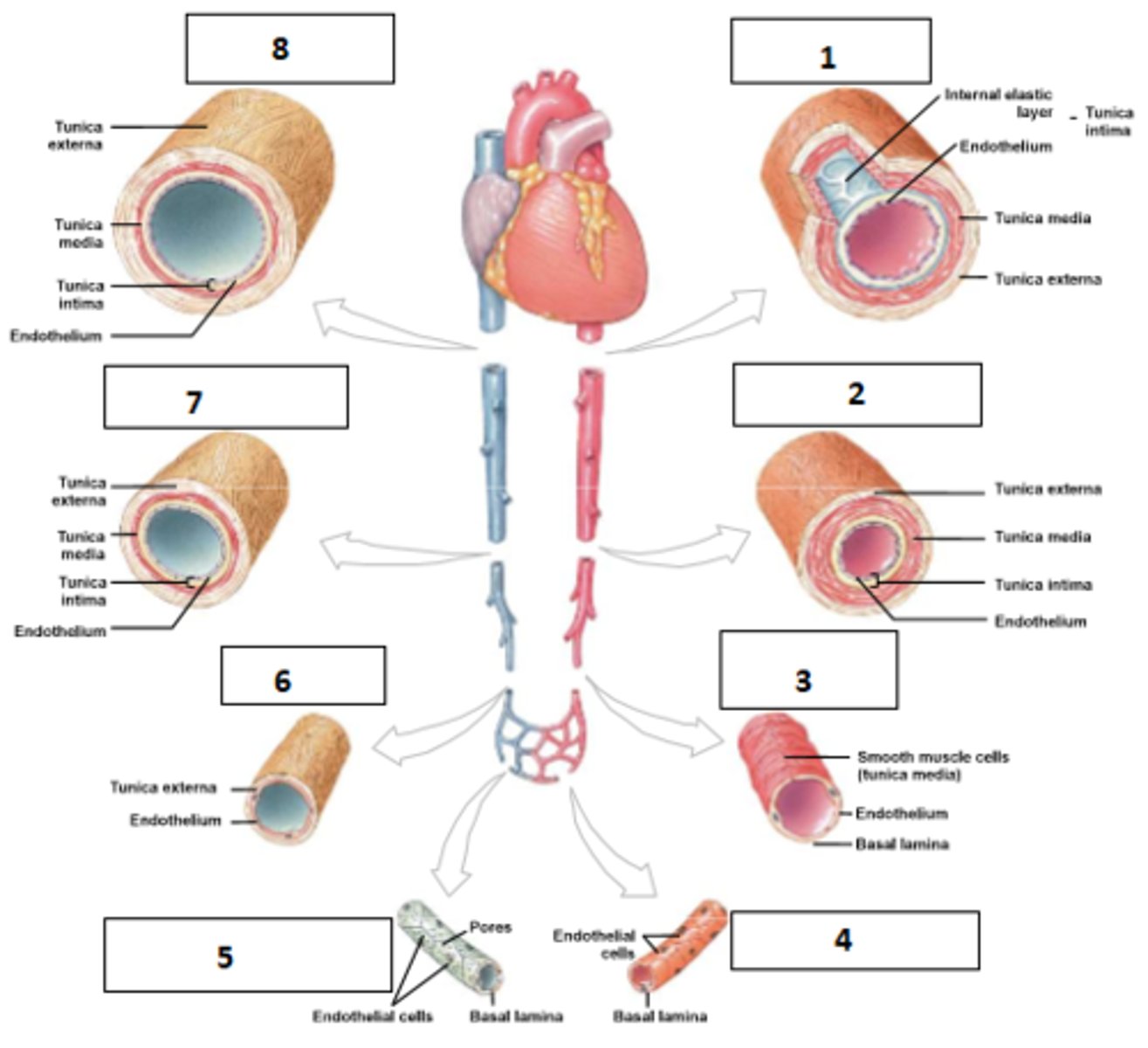
1. elastic artery
2. muscular artery
3. arteriole
4. continuous capillary
5. fenestrated capillary and sinusoids
6. venule
7. medium-sized vein
8. large vein
Name the vessels
- connective tissue: loose weave of collagen and elastic fibres
- contains nerves and lymphatics
- vasa vasorum in large vessels: tiny vessels that supply all of the big vessel's tissue
Describe the makeup of the tunica externa/adventitia
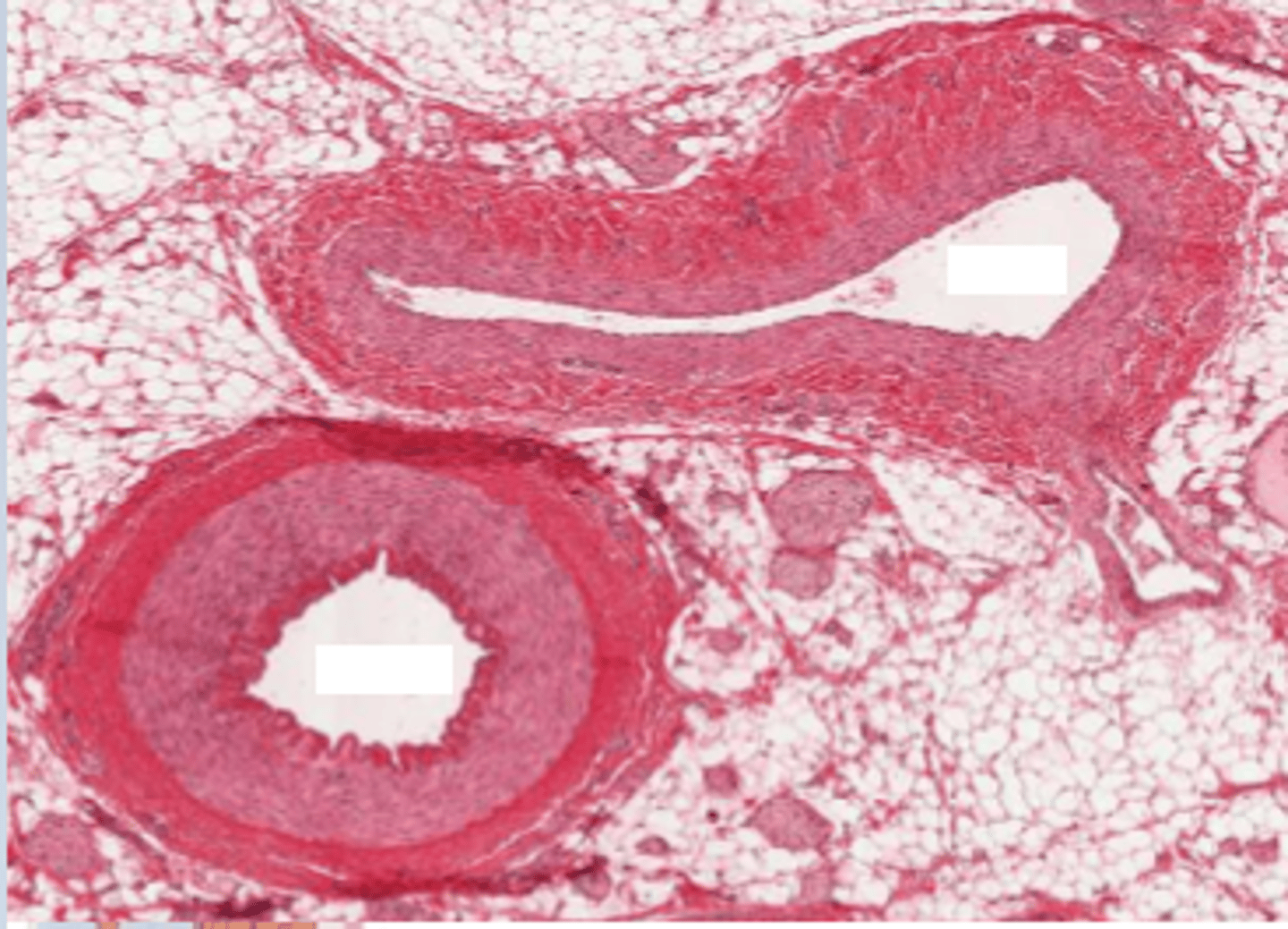
vas vasis (aka vasum vasi/vasus vasi) (Latin singular of vasa vasorum)
Name the structure with the blue star
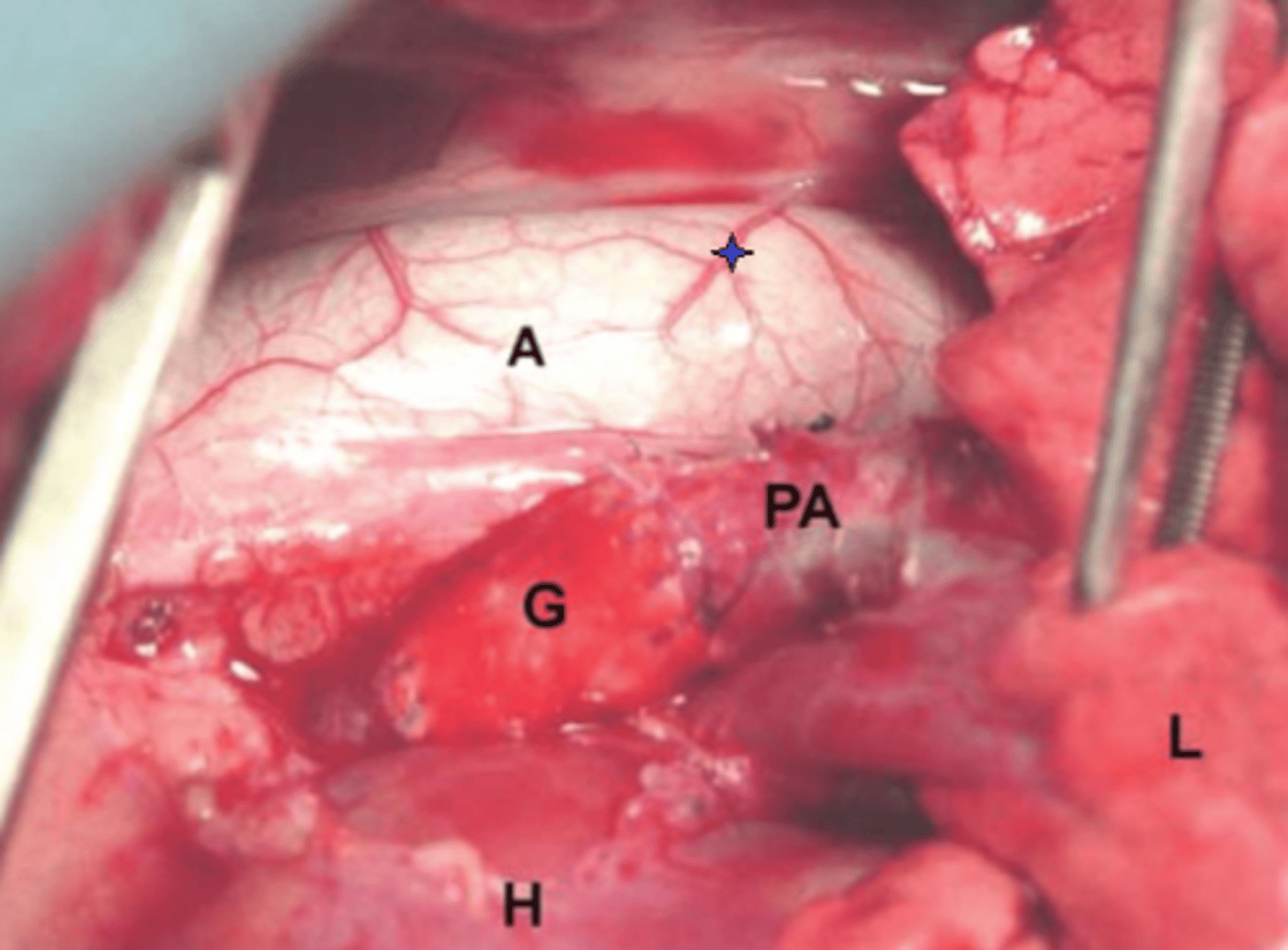
- smooth muscle and loose connective tissue
- in arteries: band of elastic tissue around periphery "external elastic membrane"
Describe the tissue makeup of the tunica media
- mostly sympathetic control
- some blood vessels have parasympathetic input (face viscera, PSS important in sexual arousal)
Describe the innervation of blood vessels
- Constrict and decrease diameter
- Stabilise vessel against increased pressure
How can sympathetic tone influence blood vessels?
- In arteries: Outer membrane: internal elastic membrane
- Some connective tissue with elastin
- Endothelium providing smooth luminal surface
Describe the tissue makeup of the tunica intima/interna
Artery: present - standard
Arteriole: present - standard
Capillary: present - standard
Venule: present - standard
Vein: present - standard
Describe the amount/presence of endothelium in each of the following vessels: artery, arteriole, capillary, venule, vein
Artery: Large amount
Arteriole: none
Capillary: none
Venule: none
Vein: Fair amount
Describe the amount/presence of elastic tissue in each of the following vessels: artery, arteriole, capillary, venule, vein
Artery: large amount
Arteriole: fair amount
Capillary: none
Venule: none
Vein: fair amount
Describe the amount/presence of smooth muscle in each of the following vessels: artery, arteriole, capillary, venule, vein
Artery: fair amount
Arteriole: none
Capillary: none
Venule: fair amount
Vein: fair amount
Describe the amount/presence of fibrous tissue in each of the following vessels: artery, arteriole, capillary, venule, vein
- Elastic/conducting
- Muscular/distributing
What are the two main types of arteries?
- largest: 1cm - 2.5cm
- closest to heart
- thick walls but wide lumen
- A lot of elastin to withstand pressure
- smooth muscle opposes stretch rather than constricting vessel diameter
What are the main features of elastic arteries?
- distal to elastic arteries
- distribute blood among organ systems
- thinner than elastic: diameter = 0.3mm-1cm
- thickest relative tunica media with a lot of smooth muscle
- capable of vasodilation and vasoconstriction to modulate blood pressure and flow
What are the main features of muscular arteries?
- Minimal or no tunica externa
- most distal of artery system from heart
- 10micrometers - 3mm
- as little as single cell layer of smooth muscle
- vasoactive with strong influence over BP
What are the main features of the arteriole?
- membrane potential of smooth muscle
- chemical ligands
- mechanical stimuli (myogenic mechanism)
Which 3 factors modulate vascular smooth muscle tone?
~-40mV
What is the approximate smooth muscle membrane potential?
- Cl-
- K+
- Ca2+
Which ions control smooth muscle depolarisation/repolarisation?
Voltage gated L-type calcium channels (voltage-gated K+ channels provide a braking action)
Which channels cause vascular constriction?
K+ channels (and inhibition of VGLCa2+ channels)
Which channels cause vascular relaxation?
- epinephrine
- norepinephrine
- endothelin-1
- Angiotensin II
- Vasopressin (ADH)
- thromboaxane
Name 6 ligands that cause vasoconstriction
alpha-adrenergic receptors - vasoconstriction
What type of sympathetic receptor is present in the viscera (splanchnic circulation), arterioles of the skin, and salivary glands? What happens when they are stimulated?
beta-1 and beta-2 adrenergic receptors - vasodilation
What type of sympathetic receptor is present in the coronary and muscle arterioles
- stretch-induced contraction in large arteries and large arterioles
- pressure induced contraction in terminal resistance arterioles
Describe the myogenic mechanism for vascular smooth muscle tone
- only endothelium and basement membrane - no tunica media or externa
- 8-10 micrometer diameter
- site of gas nutrient, and waste exchange
Describe the layers of the capillary
1. continuous capillary
2. fenestrated capillary
3. sinusoid (capillary)
Fill the blanks
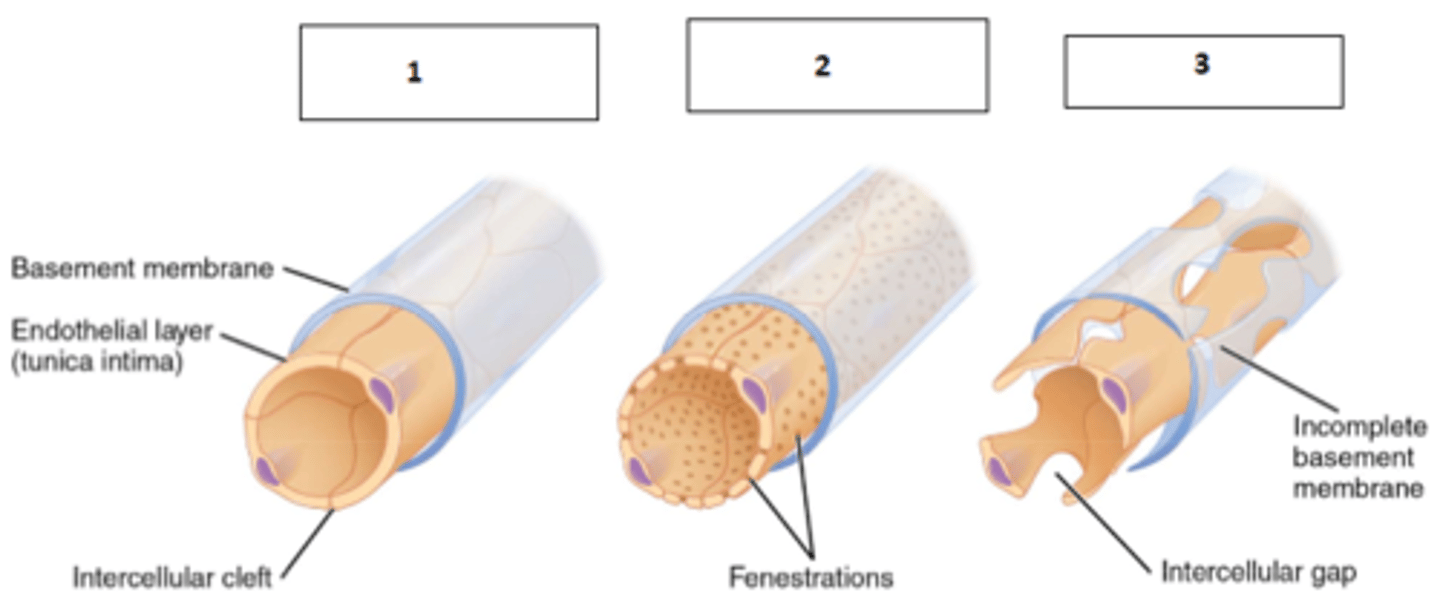
- very leaky
- allow passage of larger molecules
- present in liver, bone marrow, lymphoid tissues and some endocrine organs
- may have large irregular lumen
Describe the main characteristics of sinusoids
- fenstrations (pores
- allow passage of solute and in some cases small proteins
- easy uptake of filtration
Describe the main characteristics of fenestrated capillaries
- most common type
- allow passage of only water, small solutes and lipid soluble substances
- may allow be almost completely impermeable (BBB)
Describe the main characteristics of continuous capillaries
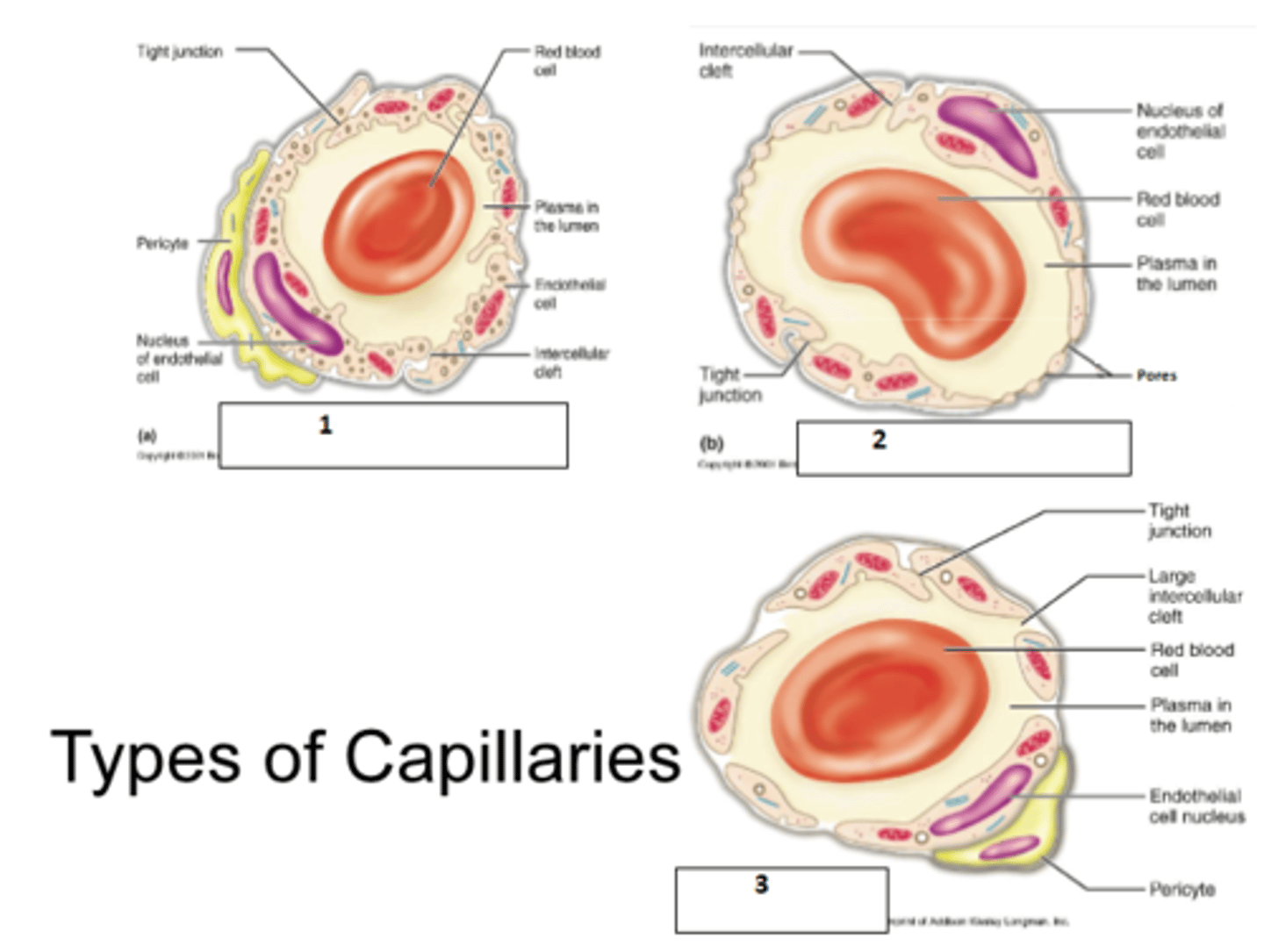
1. continuous
2. fenestrated
3. sinusoid
Name the types of capillaries
arteriole → capillaries → venule
What is microcirculation?
vasomotor nerves and local chemical conditions
How is microcirculation controlled?
1. metarteriole
2. thoroughfare channel
3. precapillary sphincter
Fill the blanks
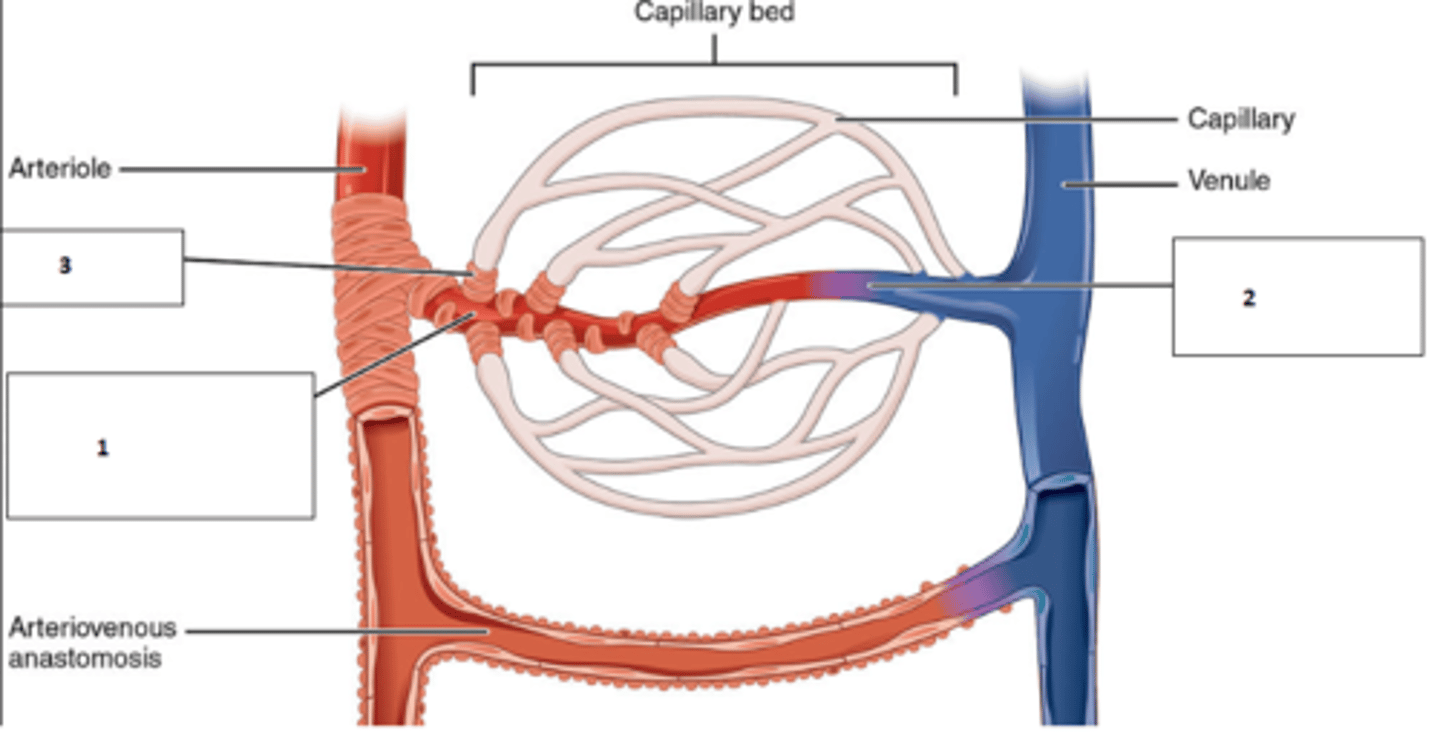
The precapillary sphincters can shut and let blood bypass the capillary bed to get blood flow straight from the metarteriole to the thoroughfare channel into the venule. When precapillary sphincters are open, capillary bed is perfused
Basicly, how does the metarteriole thoroughfare channel shunt work?
- smallest branch of venous system which drains capillary bed
- 8-100 microns
- largest of this group may have 1-2 cell layer of smooth muscle
Describe the main features of venules
- contain tunica externa, media, and interna
- low pressure
- valves prevent back-flow
- muscle pumping promotes venous return (eg calf muscle)
- act as blood reservoir and may hold up to 65% of blood in capacitance veins
Describe the main features of veins
Muscles contract and squeeze the walls of the vein. Valves prevent blood from flowing inferiorly, so it drains up to the heart
Describe how the calf muscles drain the veins of the posterior leg (small saphenous etc)
A connection between peripheral veins that is more proximal than the capillary bed eg: palmar arches
What is an anastomosis?
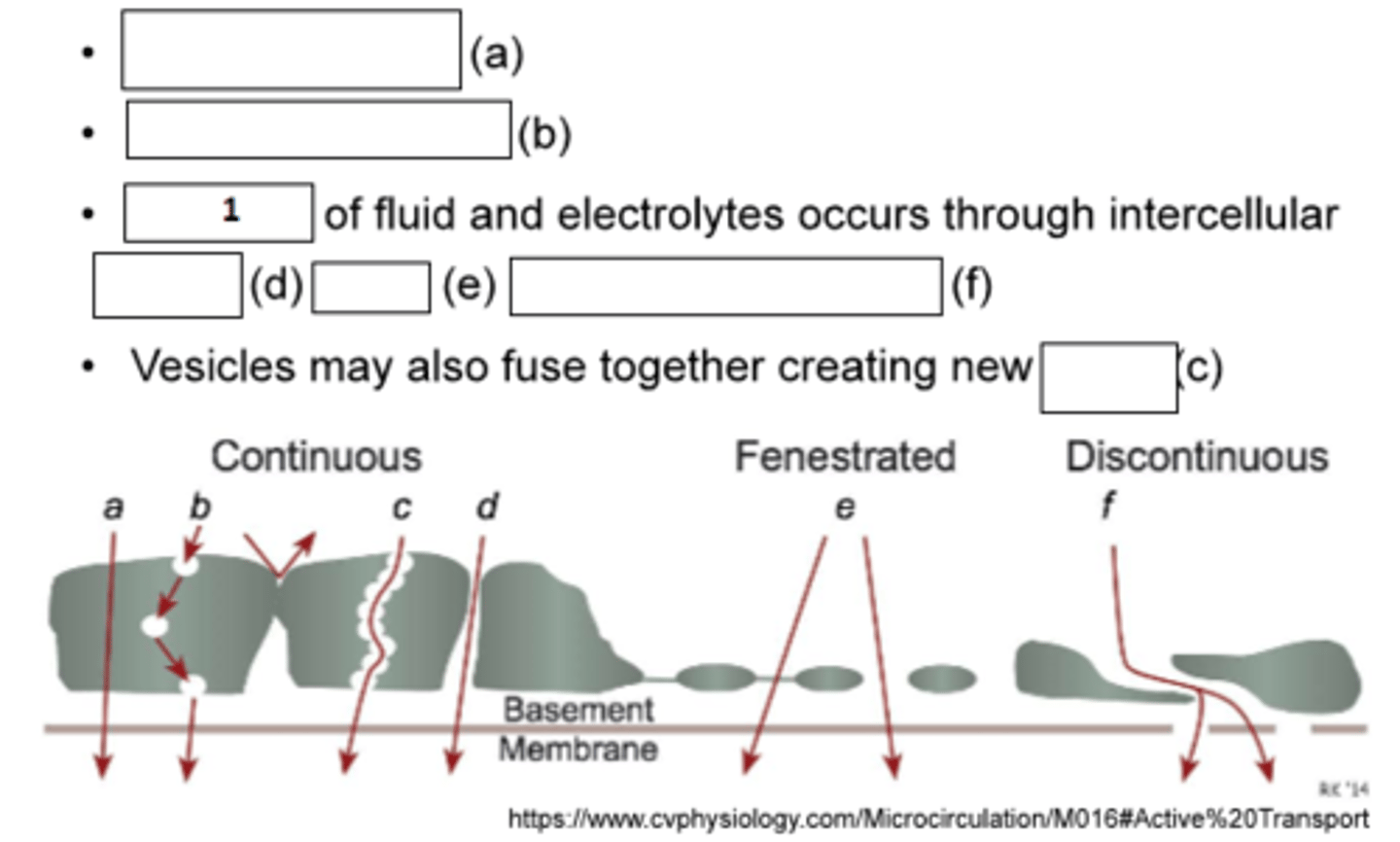
1. Bulk flow
a. active transport
b. vesicular transport
c. pores
d. clefts
e. pores
f. intercellular gaps
Fill the blanks
1. capillary hydrostatic pressure (HPcap)
2. plasma oncotic (colloidal osmotic) pressure (OPcap)
3. interstitial hydrostatic pressure (HPif)
4. interstitial oncotic (colloidal osmotic) pressure (OPif)
Name the 4 starling forces
positive
Is the net pressure at the arteriole end positive or negative?
negative
Is the net pressure at the venule end positive or negative?
NFP = (HPcap-HPif)-(OPcap-OPif)
(Colloidal osmotic pressure to be listed as a positive value)
Give a formula for Net filtration pressure (NFP) (Own version is fine as long)
capillary hydrostatic pressure
What is the main starling force that changes between the arteriole and venule end and allows for a circulation?
It is drained by lymph
What happens to excess fluid ininterstitium?
How many walls of a vessels are a