6.1 - regulation of the composition of body fluids
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
recap of kidneys & homeostasis of body fluid conc
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
how are body fluid concs maintained?

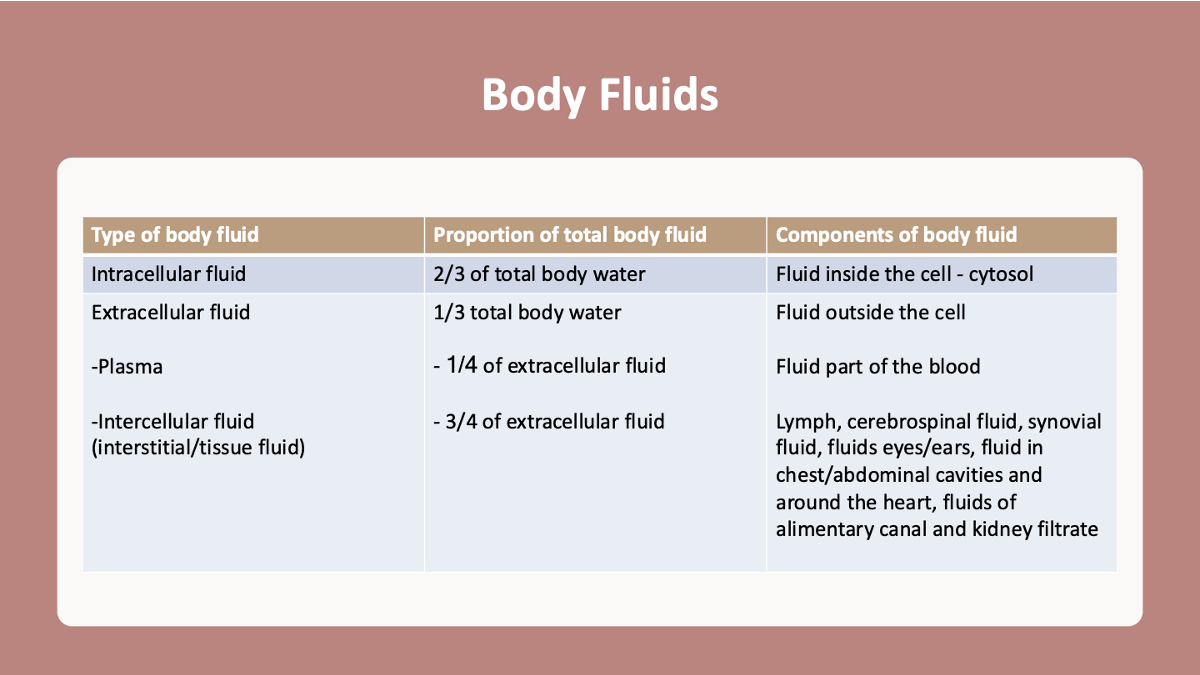
explain the proportions of total body fluid of different bodily fluids & include the components of each body fluid
total volume = approx 42L - approx 60% of body weight
intracellular fluid/cytosol compartment = approx 28L
extracellular fluid compartment = approx 14L
intravascular fluid (plasma) = approx 3L
interstitial fluid = approx 10.5L
Transcellular fluid = approx 0.5L
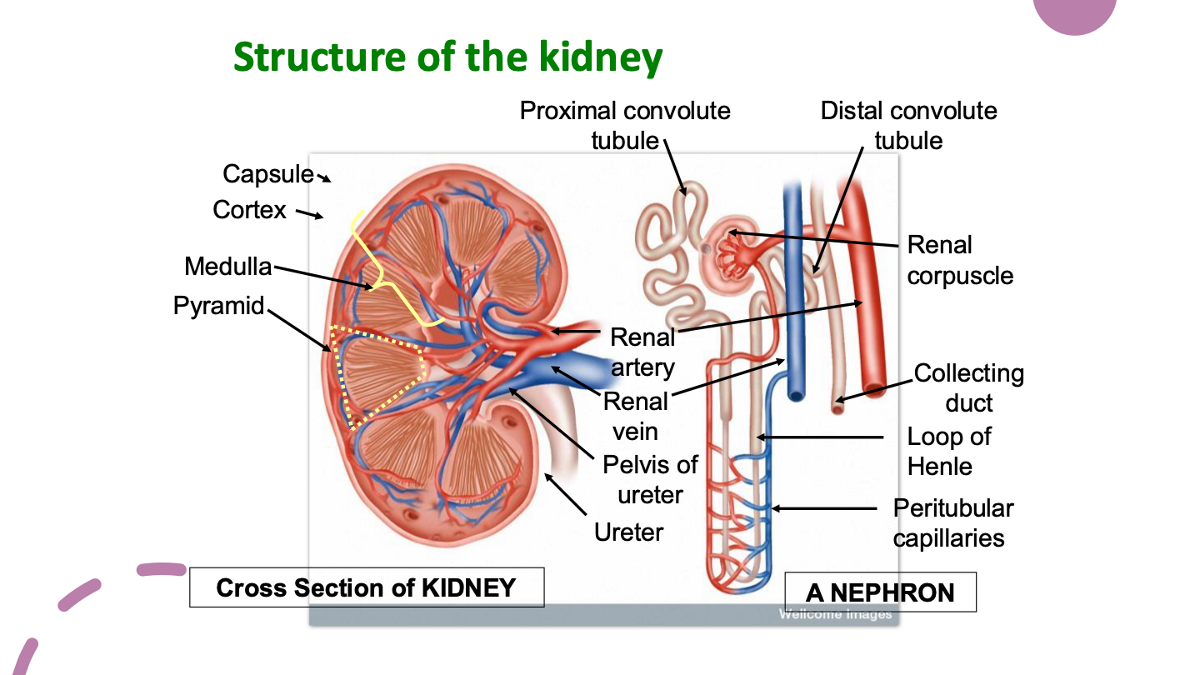
identify the parts of the kidney & a nephron
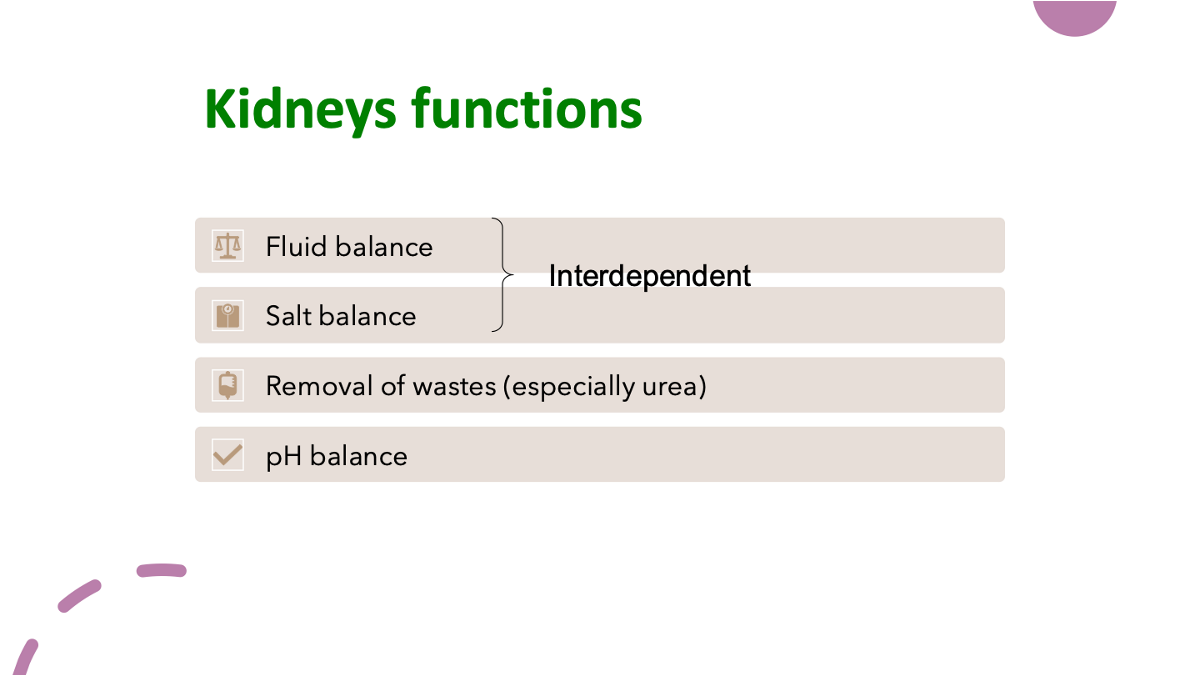
what are the functions of a kidney
identify the 3 steps of urine formation
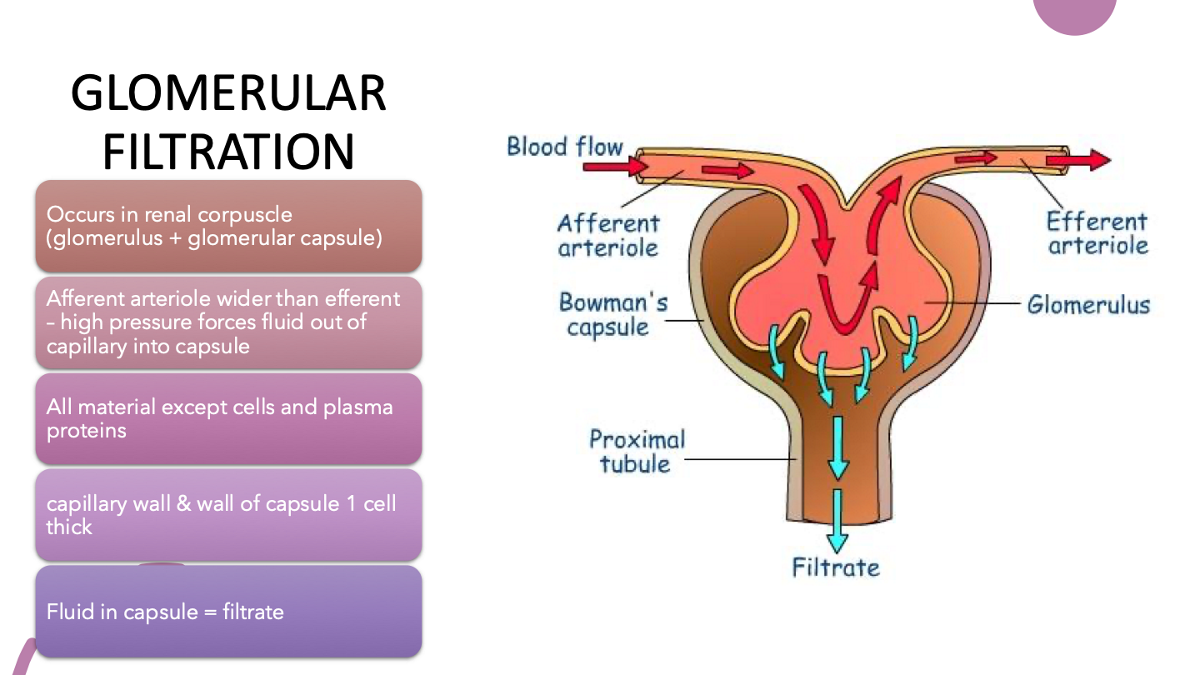
glomerular filtration
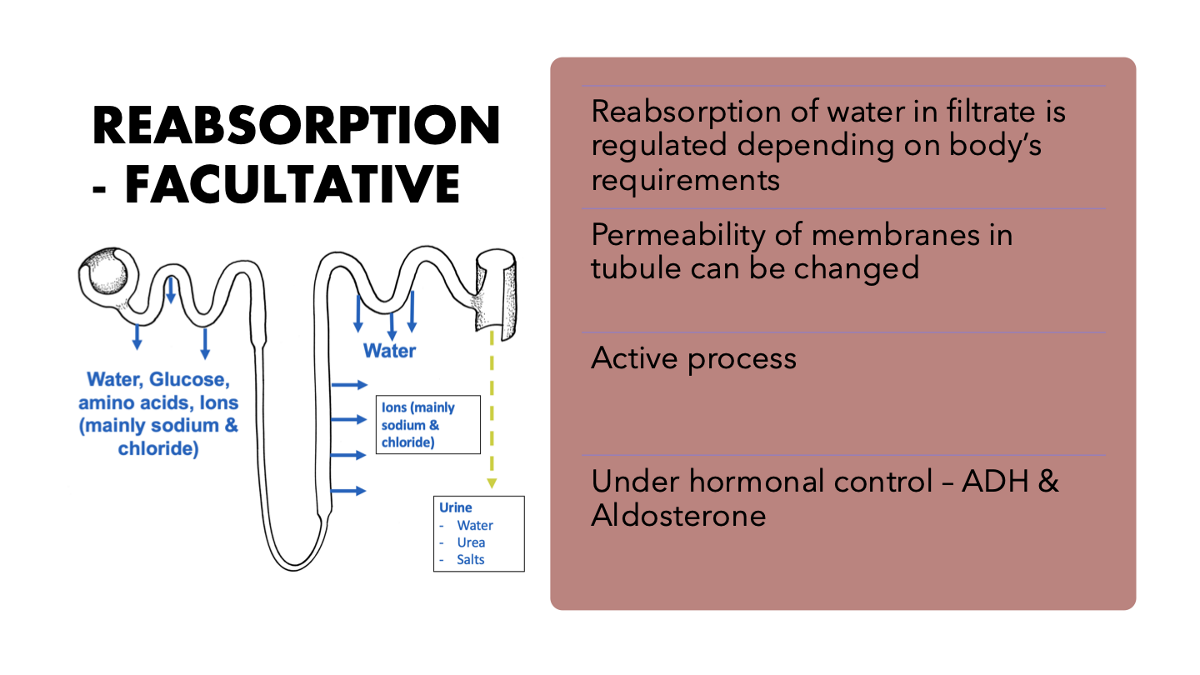
selective reabsorption
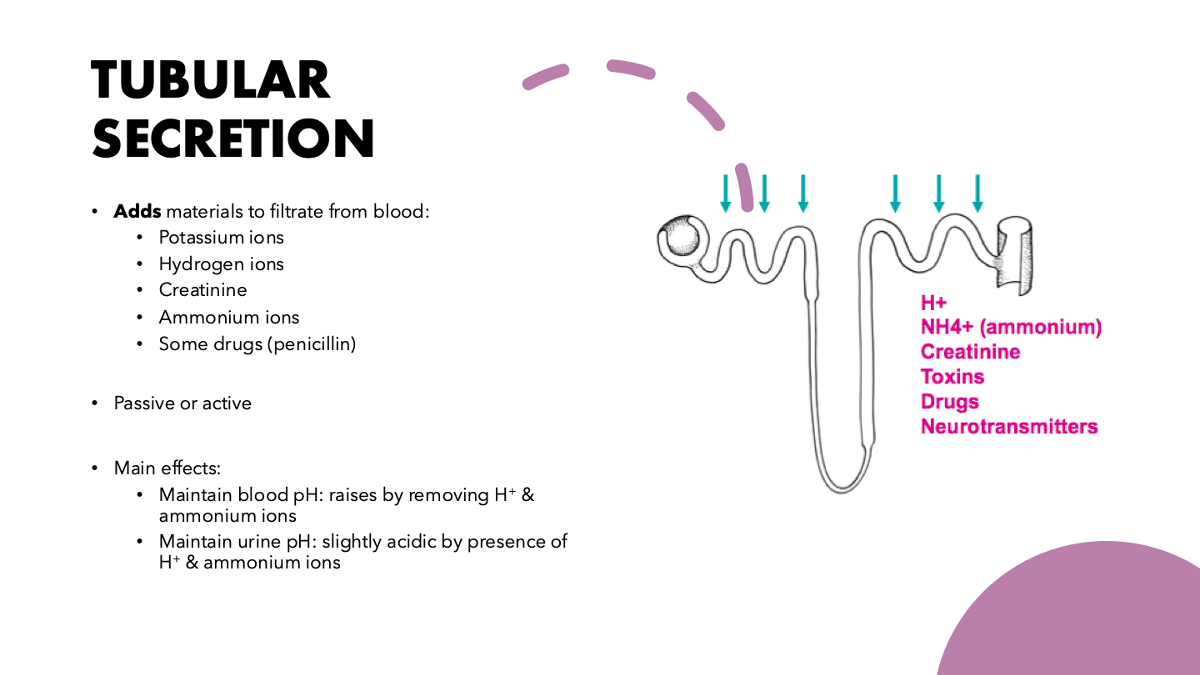
tubular secretion
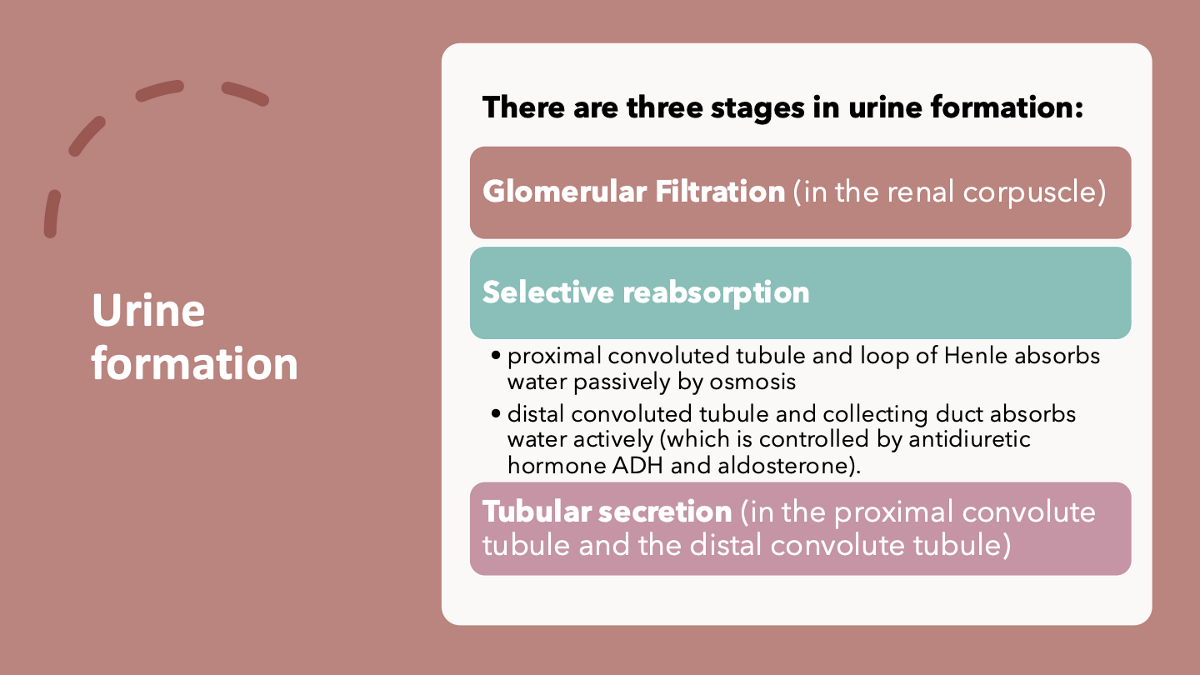
explain glomerular filtration
explain selective reabsorption

explain facultative reabsorption
explain tubular secretion
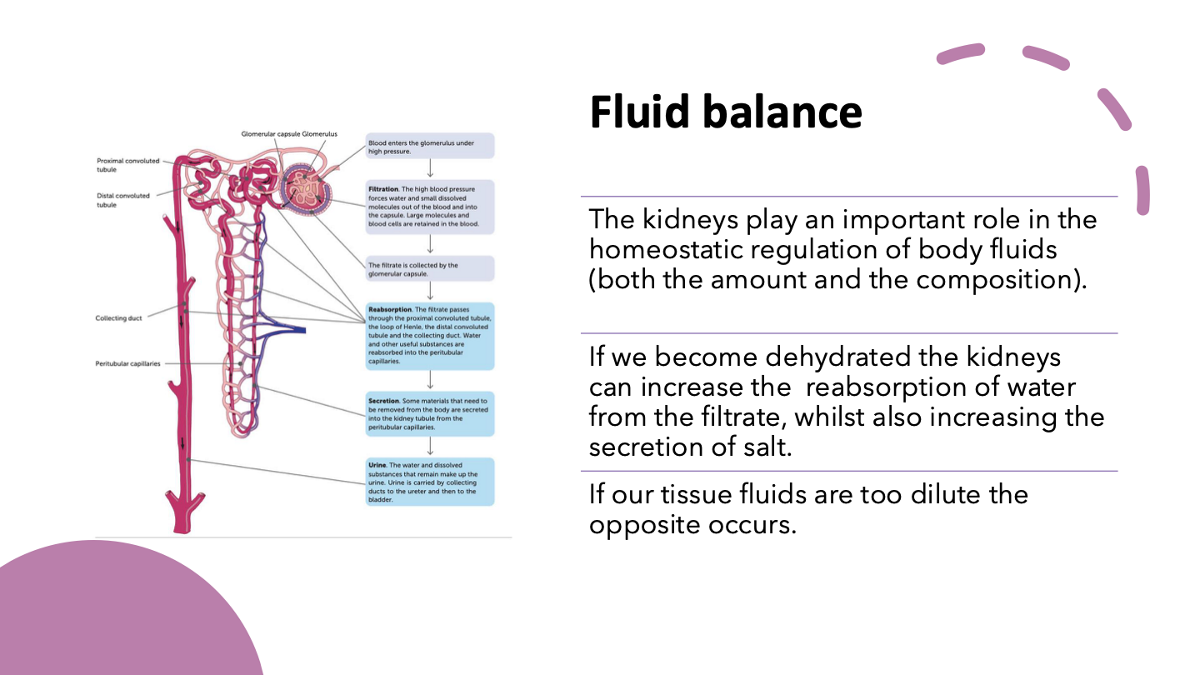
explain the kidney’s role in fluid balance
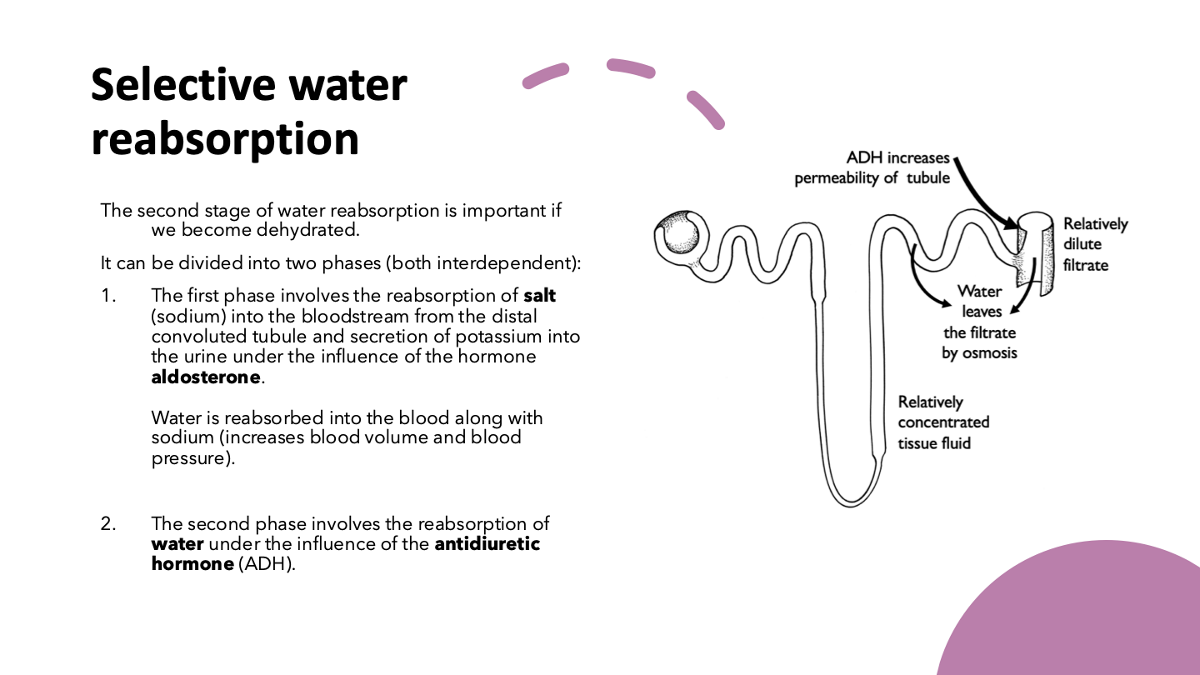
explain selective water reabsorption relating to dehydration & using key words: salt, aldosterone, water & antidiuretic hormone
define osmotic pressure
The tendency of a solution to take in the pure solvent
define osmotic conc
The concentration of solutes; also known as osmolarity
define & explain dehydration
Excessive loss of water and accompanying salts from the body; results when the body loses more uid than it takes in
occurs when there is insufficient water in the body. If untreated, it can be fatal as the body cannot carry out essential functions.
define & explain water intoxication
A potentially life-threatening condition caused by drinking too much water when the amount of salt (and other electrolytes) in the body is low; commonly caused by long bouts of intensive exercise during which electrolytes are not replenished and large amounts of water are consumed
Drinking excessive amounts of water can lead to water intoxication. The body fluids become too dilute and the cells swell due to osmosis.
define metabolic water
Water formed as a by-product of cellular respiration