4 + 5- custom trays + final impressions
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
why do you block out undercuts when making custom trays
triad shrinks as it sets, therefore the custom tray would be locked/stocked after curing is the undercuts are not blocked out
2 types of techniques when making custom trays
wash: triad directly applied to tissues
spaced: baseplate wax applied to tissues before triad
which custom tray technique is better
spaced b/c there’s less pressure on the tissue → less likely to distort hyperplastic/non-attached tissues + create pain on non-resilient tissues
when is spaced technique less necessary
on primary stress bearing areas
ex: thicker mucosa, cortical bone. attached gingiva
where on the maxilla is spacing less necessary
primary bearing area: horizontal portion of hard palate
secondary bearing area: residual ridge
where on the mandible is spacing less necessary
primary bearing areas: buccal shelf + retromolar pad
secondary bearing areas: crest of residual ridge
where on the maxilla is spacing more necessary
rugae area
medial palatal suture
incisive papilla
sharp spiny processes
torus
advantage of spaced technique
all undercuts will be automatically blocked out
what makes triad shrink when it cured
due to polymerization of a network of urethane dimethylmethacrylate + absence of methylmethacrylate
what component of triad makes it light curable
Camphoroquinone that reacts to light in a range of 400-500 nm
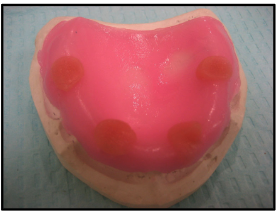
why do you need to put these balls here before putting on the triad
balls create vertical stops to maintain a uniform amount of space between the typodont + trays
how long do you cure the triad
7 min total
what is the 1st step of the 2nd appt
custom trays are placed in pt’s mouth + assessed for support, stability, retention
when should the custom tray be adjusted
if there are any over-extensions, to relieve any frenum, and sharp edges that cause pain to pt
5 objectives of an impression
provide retention
provide stability
provide support
provide esthetics for the lips
maintain health of oral tissues
R S S E H
definition of support
resistance to vertical components of mastication + occlusal forces applied in the direction of the basal seat
definition of retention
resistance to removal in a direction opposite that of its insertion
definition of stability
quality of a denture to be firm, steady, and constant in position when horizontal forces are applied to it
2 primary areas of support
maxilla: horizontal segment of the palate
mandible: buccal shelf + posterior ridges
secondary areas of support
crest of the ridge of max + mand
3 components of retention
adhesion: physical attraction of unlike particles
cohesion: physical attraction of like materials
peripheral seal + atmospheric pressure
adhesion depends on what
close adaptation of the denture + size of the bearing area
cohesion depends on what
interfacial surface tension: resistance to separation to a fill of liquid
mechanical locking into undercuts: must be handled carefully as to not creat sore spots + abraded tissue
what’s the only way to capture a peripheral seal
border molding
6 factors that are required for stability
good retention
non-interfering occlusion: if occlusion is off, stability will be off (Bilateral Balanced Occlusion)
proper tooth arrangement: best if teeth are placed on the ridge
proper form an contour of the polished surfaces
proper orientation of the occlusal plane.
good control + coordination of the patient’s musculature
what material is used for border molding in clinic
compound sticks
what material is used for border molding in preclin
VPS (vinylpolysiloxane)
what are compound sticks made of
40% natural resins (thermoplastic properties)
7% waxes (thermoplastic properties)
3% stearic acid (lubricant + plasticizer)
50% fillers + pigments
what are the 3 types of compound sticks + their working temps
soft green: 122-124 F
gray: 128-130 F
red: 130-132 F
what’s the sequence of maxillary structures in border molding
labial vestibule
buccal vestibule (one side then the other)
posterior palatal seal
what’s the sequence of mandibular structures in border molding
sublingual crescent area
mylohyoid area (one side then the other)
retromylohyoid area (one side then the other)
buccal vestibule (one side then the other)
labial vestibule
how to get functional border molding of the max +mand labial vestibule
ask pt to overtly move the lips by saying “Ouh! Ah! E!”
how to do manual manipulation of muscles for border molding of the max labial vestibule
pt cannot understand instructions: mental impairment or language barrier
muscular disability: Parkinson’s disease or tardive dyskinesia
how to get functional border molding of the max + mand buccal vestibule
ask pt to do fish face
how to do manual manipulation of muscles for border molding of the buccinator of max + mand buccal vestibule
cheek is:
elevated
pulled downward, outward, inward, forward for orbicularis oris action, backward for buccinator action
how to get functional border molding of the coronoid process of max buccal vestibule
ask pt to move mandible side to side
how to get functional border molding of the pterygo-mandibular raphe of PPS
ask pt to open as wide as possible
how to locate the 3 landmarks of the posterior palatal seal (PPS)
anterior outline: press gently against hard palate w/ ball burnisher + work backward until displaceable tissue is located
depth: press burnisher against soft tissue to approximate amount of displacement
posterior outline (vibrating line): based on movement of soft palate muscles + fovae palatinae
how to get functional border molding of vibrating line of PPS
ask pt to say long “ah” or do valsava maneuver
how to get functional border molding of the masseter of the mand buccal vestibule
hold down custom tray + instructing pt to close
how to get functional border molding of sublingual crescent area of the alveololingual sulcus
anterior lingual flange length: ask pt to protrude the tongue out as it activates the genioglossus muscle, which raises sublingual fold
anterior lingual flange thickness: push tongue against front part of the palate
how to get functional border molding of mylohyoid area of the alveololingual sulcus
ask pt to move tongue to opposite cheek + push tongue against front part of palate
how to get functional border molding of retromylohyoid area of the alveololingual sulcus
ask pt to open wide ppterygomandibular raphe to be brought forward
thrust tongue out so superior constrictor of pharynx pushes mylohyoid muscle
ask pt to close → downward pressure on mandible activate medial pterygoids push against retromylohyoid curtains distal end of lingual flange
s
summarize all the movements the pt must do to capture border molding of the alveololingual sulcus
tongue out
tongue to front part of palate
tongue to R + L cheeks
open wide
close