Physics Chapter Exam 1
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
What is unrelated?
two items that are not associated
What is directly related or proportional?
Two items that are associated such that when one item increases, the other increases.
Example: Smoking and the likelihood of cardiovascular disease. Generally, people who smoke are most likely to have cardiovascular disease.
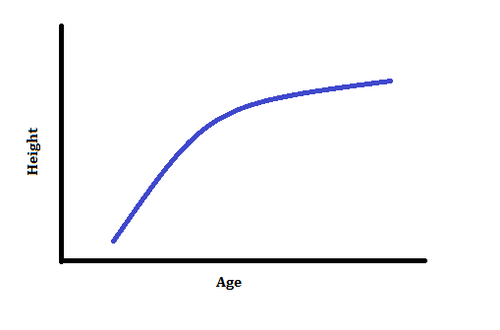
What is inversely related, or inversely proportional?
Two items are inversely related, meaning that when one item increases, the other decreases.
Example: Cholesterol level and longevity. As cholesterol levels increase, life span generally decreases.
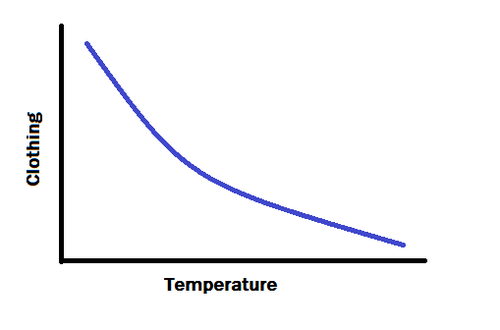
What is a reciprocal relationship?
When two numbers with a reciprocal relationship are multiplied together, the result is one.
This is a special form of inverse relationship. Reciprocal numbers are inverse because when one increases, the other decreases.
Example: What is the reciprocal of 20 =1/20 (exact “flip” that keeps a balance)
If one goes up, the other goes down exactly enough to keep the product the same.
What type of wave is a sound wave?
A sound wave is a mechanical, longitudinal wave.
Mechanical → It(particles) needs a medium (like air, tissue, water) to travel. It can’t move through a vacuum.
Longitudinal → The particles of the medium move back and forth in the same direction as the wave travels.
This creates alternating areas of compression (particles close together, high pressure) and rarefaction (particles spread apart, low pressure).
What are acoustic propagation properties?
The effects of the medium upon the sound wave mean that the sound wave may travel differently through different media(how sound behaves as it travels through the body)
What are biological effects?
The effects of the sound wave upon the biologic tissue through which it passes (changes that sound waves can cause in the body’s tissues when they travel through them.)
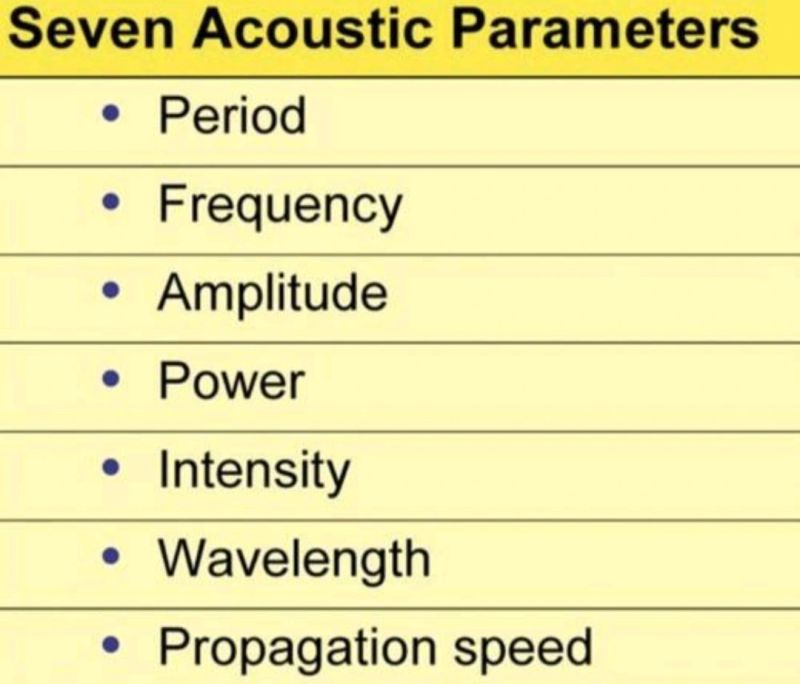
What are the acoustic parameters?
Period
Frequency
Amplitude
Power
Intensity
Wavelength
Propagation Speed
Memory Trick: “Please Find A Perfect Ice Water Pitcher.”
Acoustic parameters are used to describe the features of sound waves
What is oscillation?
back-and-forth or repeating movement
All of the following are true for sound waves except
a. They are acoustic
b. They are pressure waves
c. they are transverse
d. they move energy
c. they are transverse
sound waves are longitudinal!
What are the acoustic variables that identify a sound wave?
Pressure: Concentration of force in an area. Units: Pascals (Pa)
Density: Concentration of mass in a volume. Units: kg/cm3
Distance: Measure of particle motions: Units: cm, feet, mile
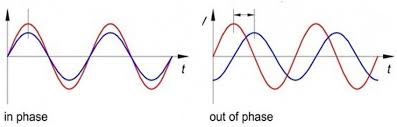
What are In-Phase and Out-of-Phase Waves?
In-phase: A pair of waves is in-phase when their peaks (maximum values) occur at the same time and at the same location. (even though they are not at the same peak)
Out-of-phase: When two waves are out of phase, their peaks occur at different times, and so do their troughs.
What is interference?
It is what happens when two or more sound waves meet each other.
Waves lose their individual characteristics at that moment and combine to make a single wave. Either
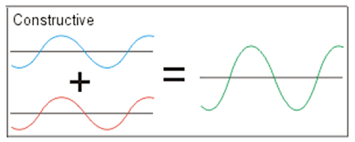
What is Constructive interference?
When two in-phase waves (peaks and troughs occur at the same time)
combine to make a stronger wave (amplitude increases).
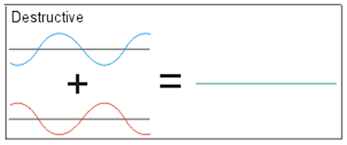
What is Destructive Interference?
When two out-of-phase waves (when peaks and troughs occur at different locations and times) combine. They weaken and cancel out entirely. Amplitude decreases.
How do you best describe sound waves?
A series of compressions(squeezed together, high density) and rarefactions(regions where the particles are spread apart, low density)
What is Attenuation?
Sound waves weaken as they propagate(traveling through the tissue) g
The farther the sound travels, the greater the attenuation
Distance + Attenuation=Directly related
If the distance increases, the attenuation increases
What are the 3 bigness?
Intensity
power
amplitude
Attenuation= the decrease in the three bigness
What is period?
The period is the time it takes for one cycle of a wave to occur.
What is frequency?
The number of cycles a wave completes per second.
Attenuation is measured in?
Decibels
What is Specular and Difusse?
They are the 2 forms of reflection
Specular: When the boundary is smooth,large, and sound is reflected in only one direction in an organized manner(produces strong mirror-like echoes). Example:Liver Capsule, Diaphragm, blood vessel wall, muscle fascia.
Diffuse(backscatter): Occurs at irregular or small surfaces, causing weaker echoes that scatter in many directions

Scattering
Is the random redirection of sound in many directions. Sound scatters
Which Acoustic Parameters have potential biologic affects?
The 3 bigness A
I-Intensity
P-power
A-Amplitude
Attenuation is measured in?
Decibels (dB)
Attenuation is determined(to decide, define, or set the outcome) by what two factors?
Path Length-The deeper the tissue, the more sound is going to attenuate(weakening of sound beam)
Frequency-the frequency of the sound beam
What 3 processes contribute(to play a role, add to, or influence) to attenuation?
Reflection
Scattering
Absorption
Together, the 3 processes explain why deeper tissues look darker(less echo strength because the beam keeps losing energy. They describe how ultrasound beam losses its strength as it travels
The weakening of amplitude as the sound wave travels is ?
Attenuation and its measured in dB
The 3 bigness-the decrease in amplitude
How are distance and attenuation related?
Directly Related(or Proportional)
If the distance increases, the attenuation increases
“The farther sound travels, the weaker it gets”
How is frequency and attenuation related?
If frequency increases, attenuation increases
Attenuation in lung tissue, bone, and air is ______attenuation in soft tissue
Greater than
Bone: Much higher attenuation than soft tissue.
Bone absorbs and reflects strongly, so little sound passes through.
That’s why bone shadows appear on ultrasound.
(absorbs & reflects, causes shadows).
Lung: Much higher attenuation than soft tissue.
Full of air pockets → sound scatters a lot, very little gets through.
Air: Extremely high attenuation (practically blocks ultrasound).
That’s why we can’t image air-filled structures well (like the stomach full of gas)
Soft tissue = where ultrasound works best (why most imaging is done here).
Lung = bad for ultrasound (scattering from tiny air pockets).
Bone = bad for ultrasound (absorbs & reflects, causes shadows).
Air = worst, basically blocks the beam.
What is reflection?
As sound waves strike a boundary a boundary a portion of the waves’ energy may be redirected or reflected back to the sound source
Two forms of reflection?
2 forms of reflection created in soft tissue
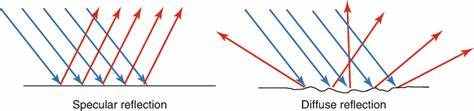
Specular: occurs when the boundary is smooth, large, and sound is reflected in only one direction. (organized)
Examples: Mirror a large flat surface: liver capsule, diaphragm, blood vessel wall, muscle fascia.
Diffuse (Backscatter): Occurs at irregular or small surfaces, causing weaker echoes that scatter in many directions (disorganized). The echoes that return to the probe are weaker compared to a mirror specular reflection
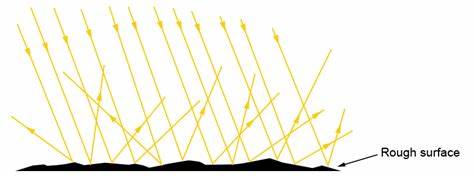
What is scattering ?
Random redirection of sound in many directions instead of bouncing straight back
Scattering is when a sound wave (or any wave) hits a small object or rough surface and bounces off in many directions instead of one straight direction.
Example: Lung tissue – alveoli scatter sound because they’re tiny air-filled sacs
When ultrasound hits them, most of the sound is scattered because air strongly reflects sound
Scattering is disorganized and chaotic
Is frequency directly related to scattering?
Yes
Low frequency → less scattering, penetrates deeper.
High frequency → more scattering, better resolution but less penetration.
Frequency | Wavelength | Scattering | Penetration | Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Low | Long | Low | Deep | Low |
High | Short | High | Shallow | High |
Human hearing in Hertz?
Range: 20 Hz – 20,000 Hz (20 kHz)
Anything above 20 kHz cannot be heard by humans.
Human hearing → thousands of Hz (kHz)
Ultrasound Hz?
Ultrasound
Uses sound waves above 20 kHz
Medical ultrasound typically uses 1–20 MHz (1 million to 20 million Hz)
Much higher than human hearing → can’t be heard by the ear.
Ultrasound → millions of Hz (MHz)
Think: “Ultra = way beyond what we hear.”
What is Rayleigh Scattering?
A special form of scattering that occurs when the structure's dimensions are much smaller than the beam's wavelength.
Rayleigh scattering is organized. (waves are predictable and uniform)
Example: Red blood cells (Tiny compared to ultrasound wavelength
They scatter the sound → this is how Doppler detects blood flow.)
Rayleigh scattering is directly related to frequency
R.L scattering increases dramatically with increasing frequency
Happens when the structure is much smaller than the wavelength of the sound wave.
Absorption:
It is the largest component of attenuation
Absorption causes attenuation to occur the most
When the sound wave loses energy as it passes through tissue, that energy is turned into heat.(related to Bio-effects=tissue heating)
Absorption is directly related to frequency.
Higher frequency → more absorption
Lower frequency → less absorption
Absorption = sound energy disappears as heat inside tissue.
Incidence:
The angle at which the wave strikes the boundary
In ultrasound, it usually refers to the angle between the ultrasound beam and the surface of the tissue.
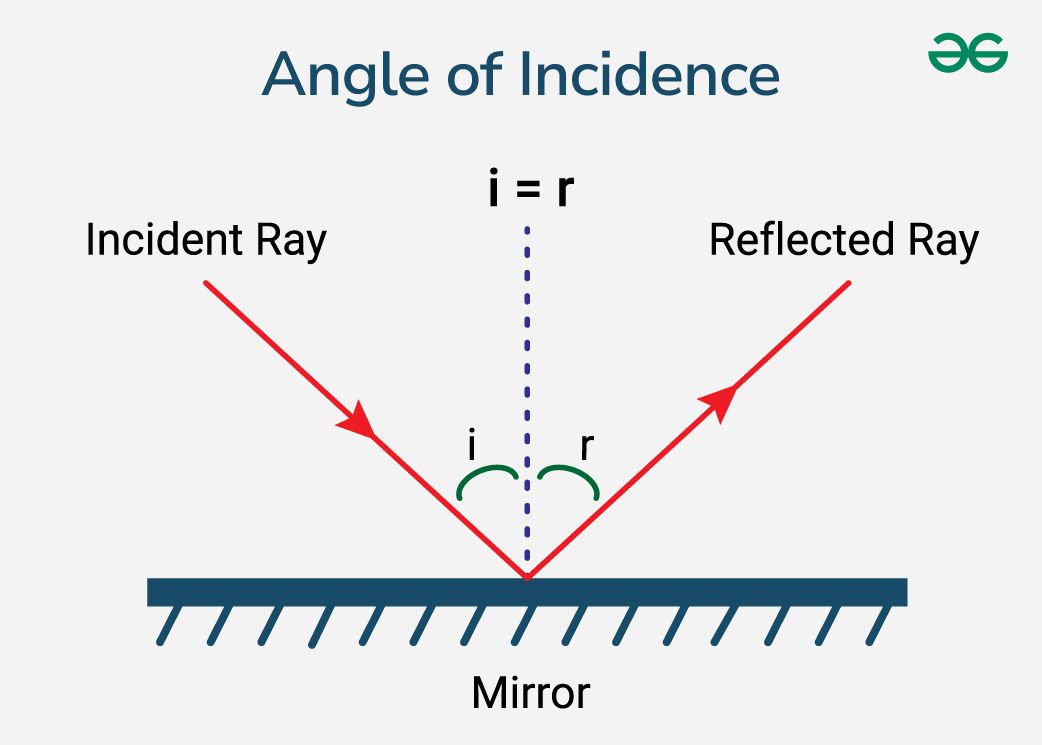
Normal incidence
Incidence sound beam strikes at exactly 90 degrees
Synonyms: Right Angle, 90 degrees, perpendicular, orthogonal
Oblique incidence
Incidence occurs when the incident sound beam strikes the boundary at any angle other than 90 degrees:
Synonyms: Incidence not equal to 90 degrees, not a right angle, non-perpendicular
Period
The time it takes a wave to vibrate a single cycle.
Units: microsecond(us) units of time
Determined: by the sound, not by the medium
Adjustable: NO