Neuroanatomy - NEUR 3400 Chapter 7
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Central Nervous System (CNS)
brain and spinal cord - integrative function
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
cranial and spinal nerves - sensory and motor function
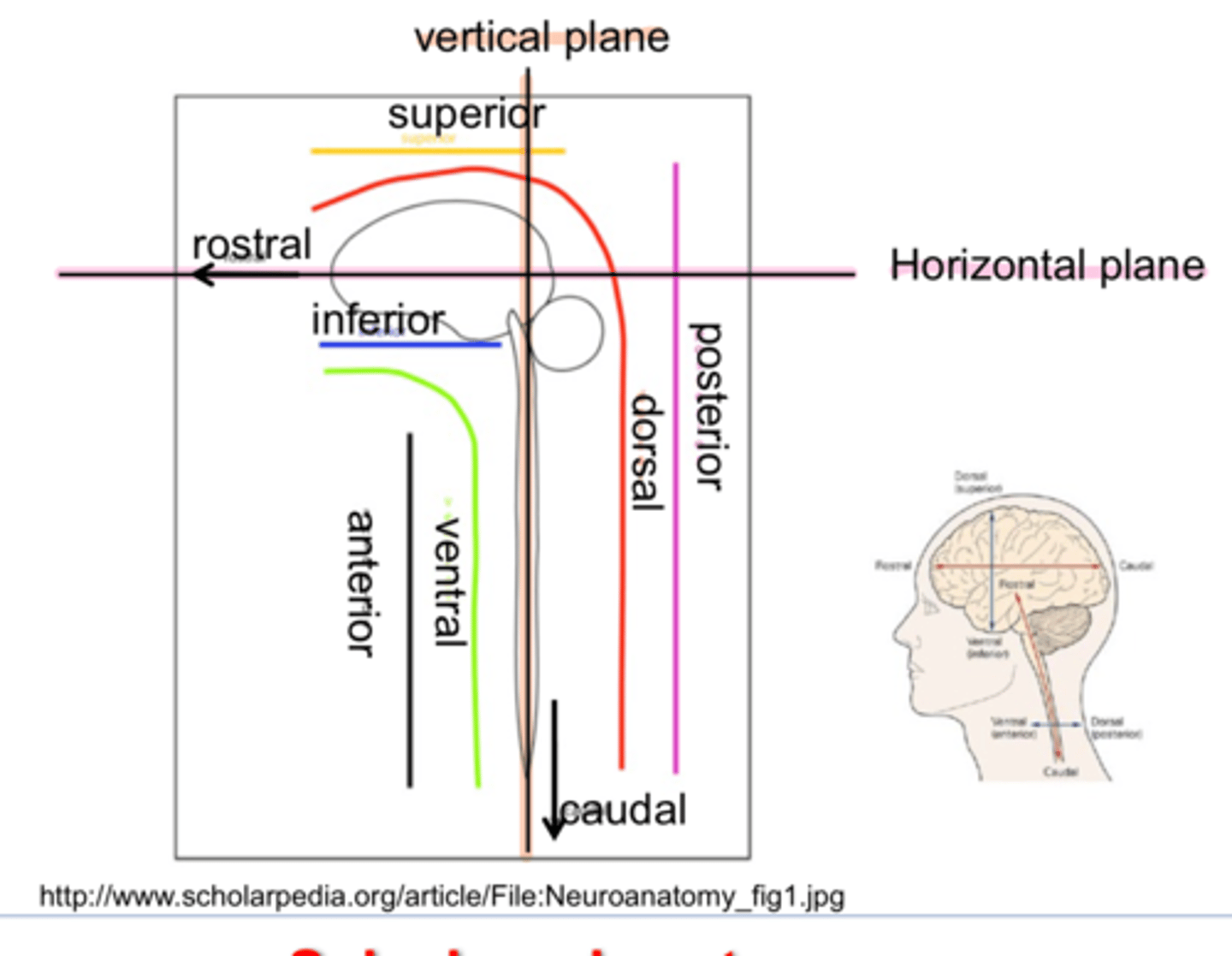
orientation in the CNS
Rostral/Caudal
Ventral/Dorsal
- Anterior/Posterior
- Superior/Inferior
Afferent/Efferent
- Afferent -> Incoming sensory information
- Efferent -> Outgoing motor information
Contralateral/Ipsilateral
- Contralateral -> opposite side
- Ipsilateral -> same side
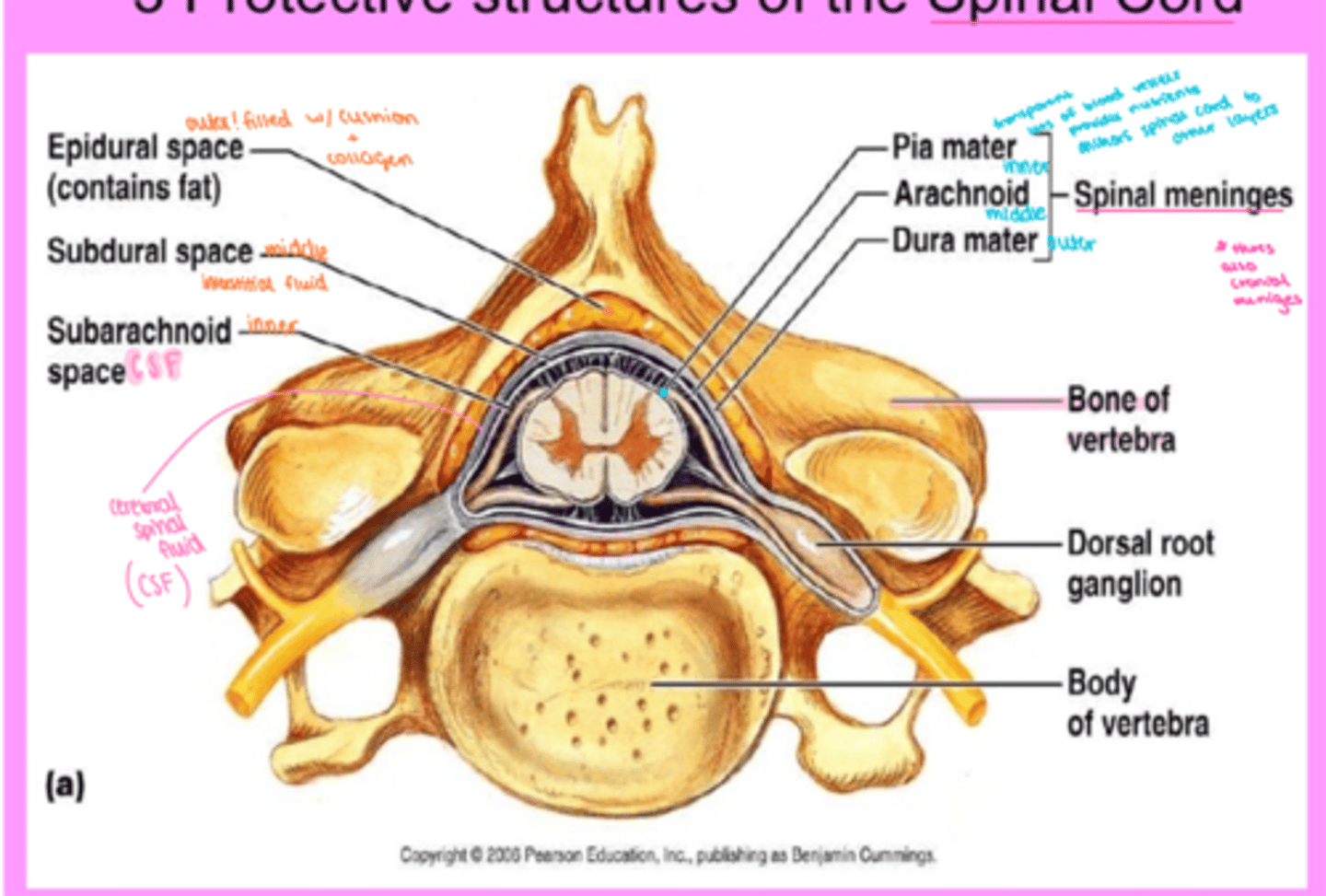
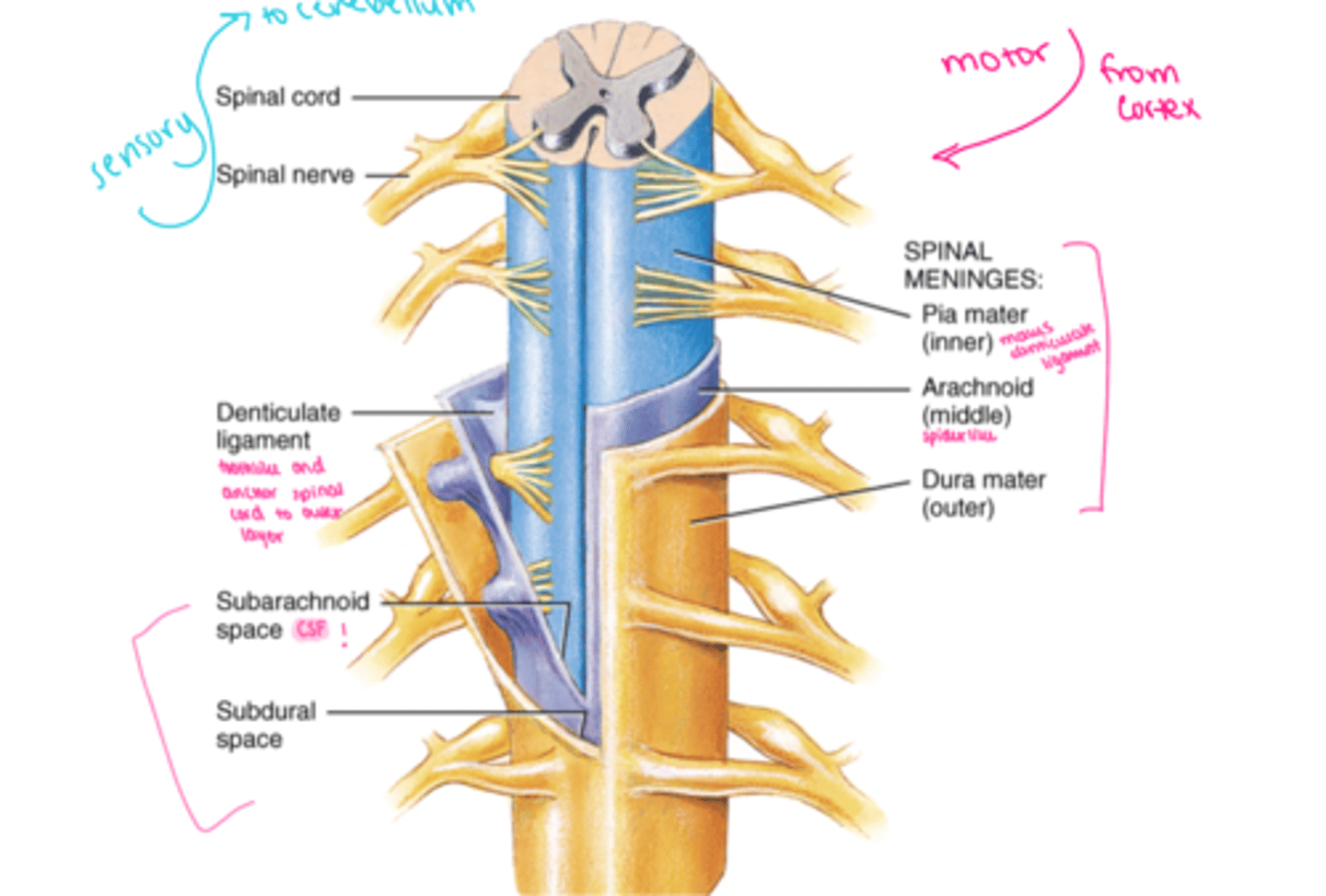
spinal cord anatomy
bony structures = vertebral column = spinal cord
three layers of meninges :
a. dura mater outer
b. arachnoid middle - spiderlike elastic collagen
c. pia mater inner - lots of blood vesicles
denticulate ligament - extension of pia mater - tooth like
spaces :
a. epidural - outer
b. subdural - middle
c. subarachnoid - inner - CSF
3 protective structures of the spinal cord
1) Vertebral Column
2) Meninges
3) Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
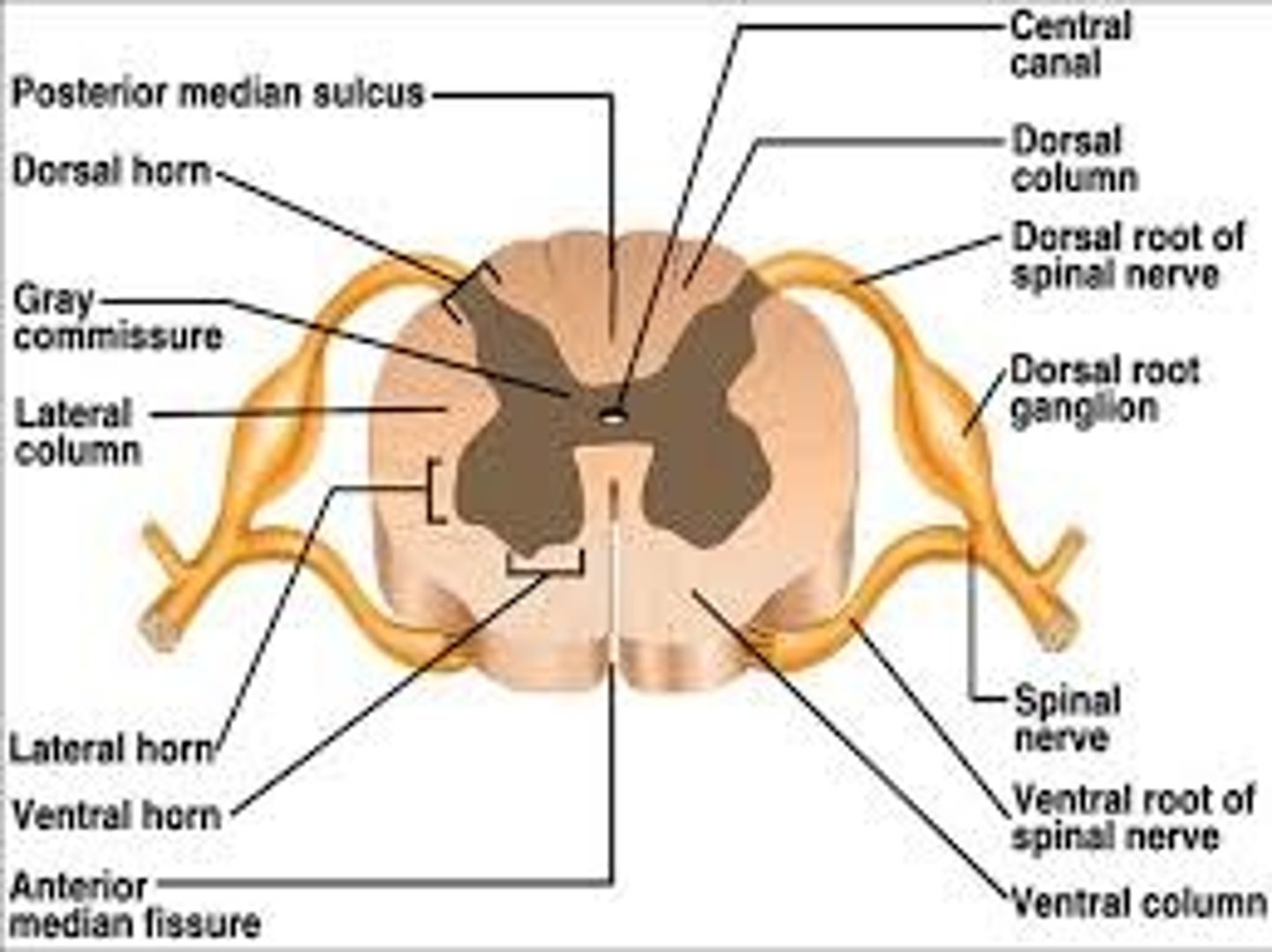
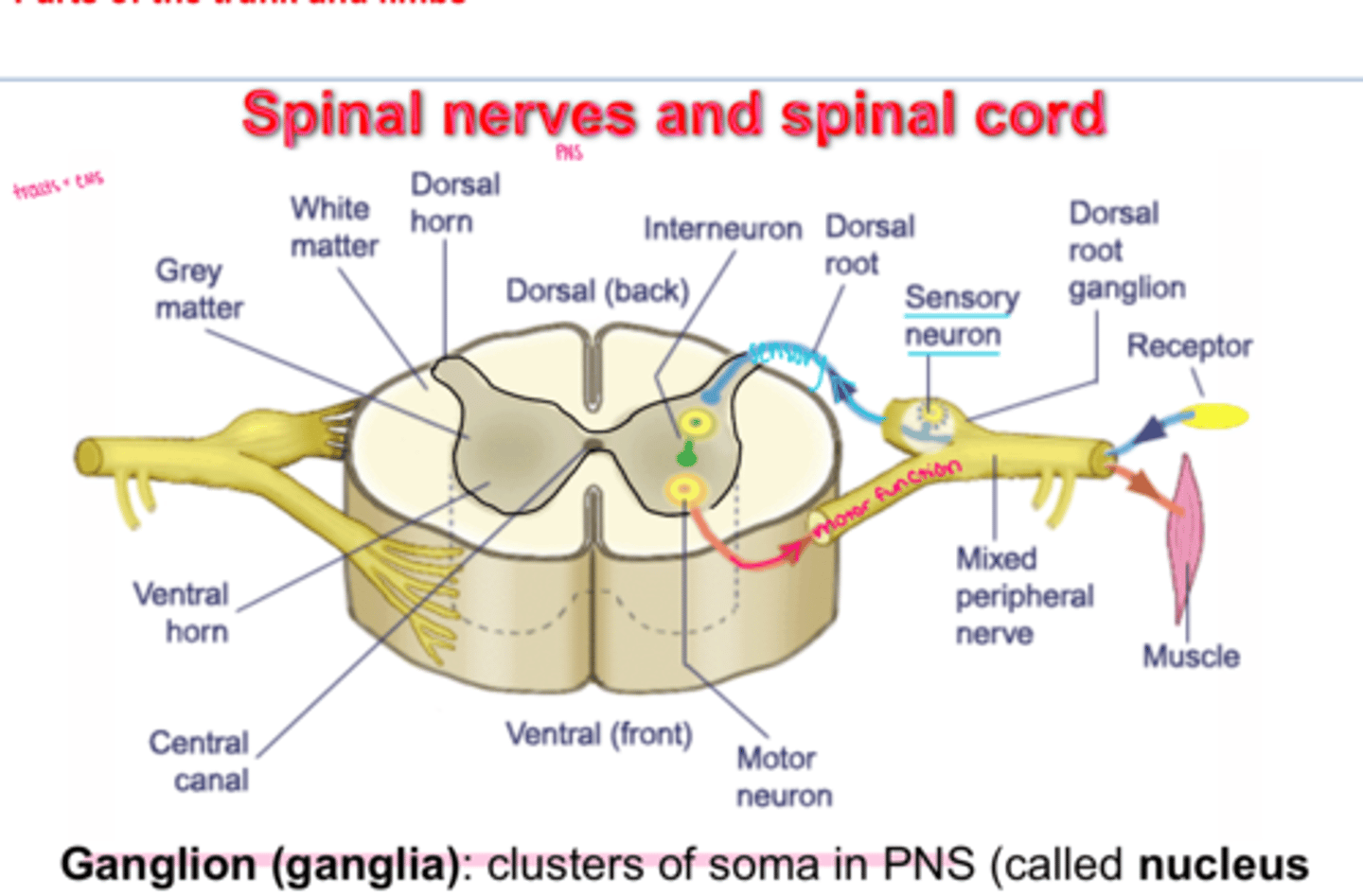
internal anatomy of the spinal cord
gray matter = cell bodies, dendrites, and parts of axons
white matter = axons myelinated
central canal = CSF
spinal cord ascending and descending tracts
- ascending tracts are sensory axons that carry impulses upwards toward the brain
- descending tracts contain motor axons that conduct impulses downward, away from brain
tracts are bundles of axons in CNS
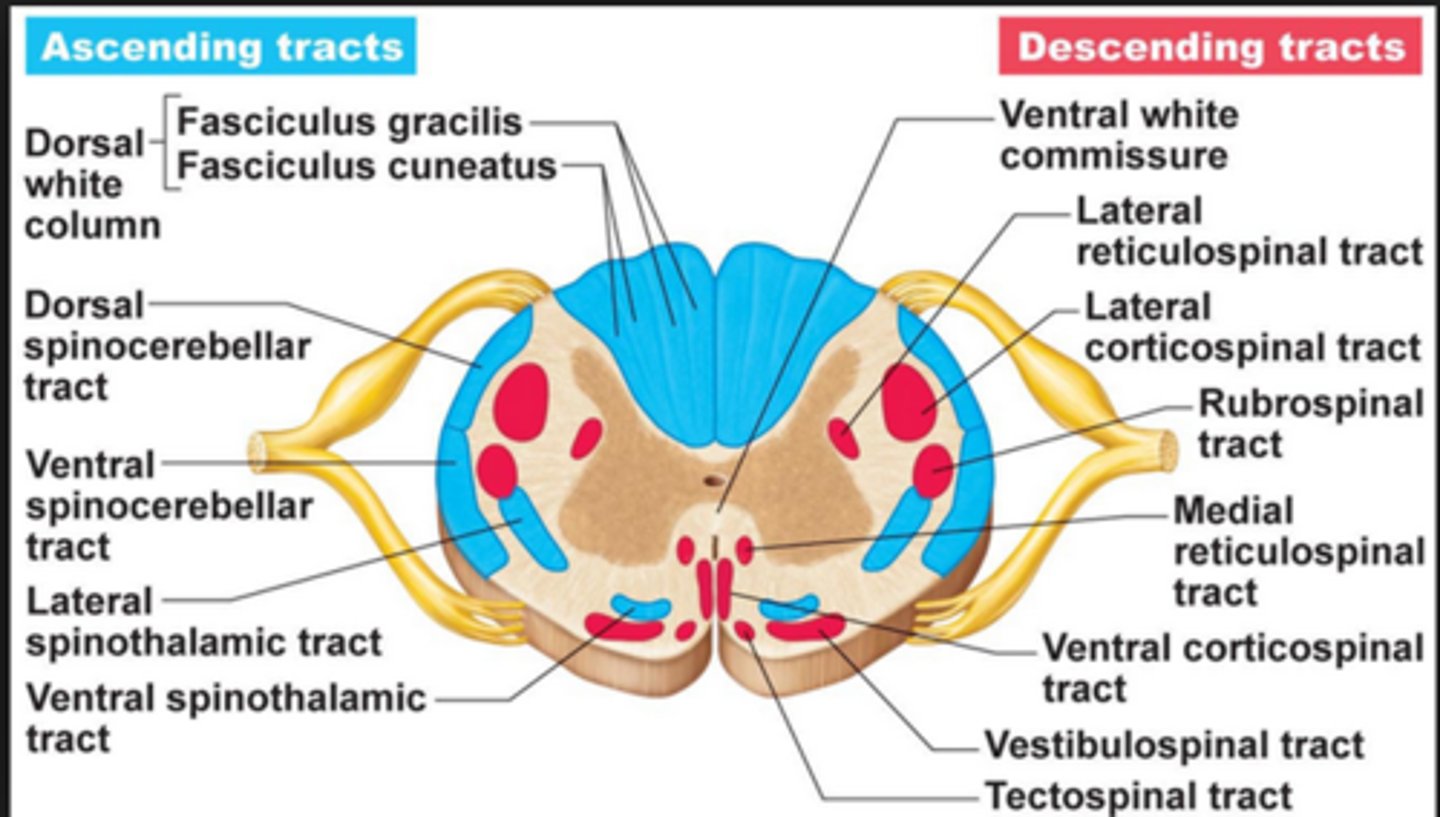
gross anatomy of the spinal cord
About 18 inches (45 cm) long
1/2 inch (14 mm) wide
Ends between vertebrae L1 and L2
Bilateral symmetry
two enlargements = cervical and lumbar
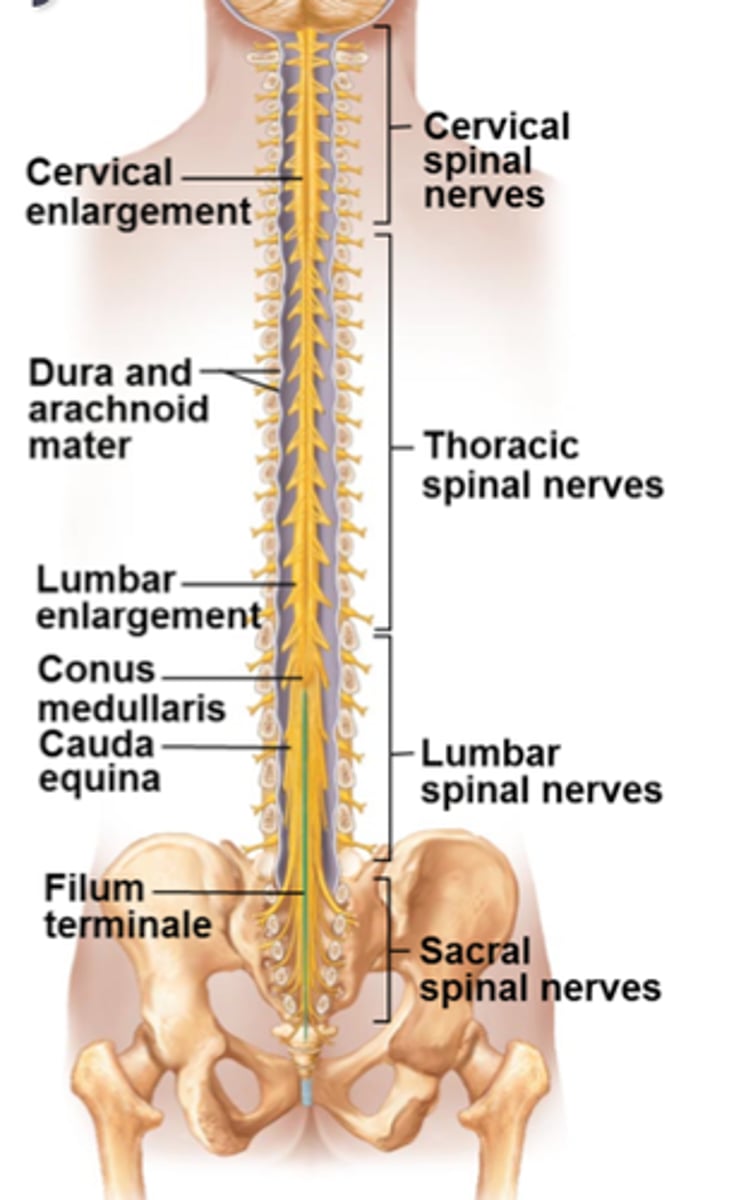
What are the two enlargements of the spinal cord?
cervical and lumbar enlargements
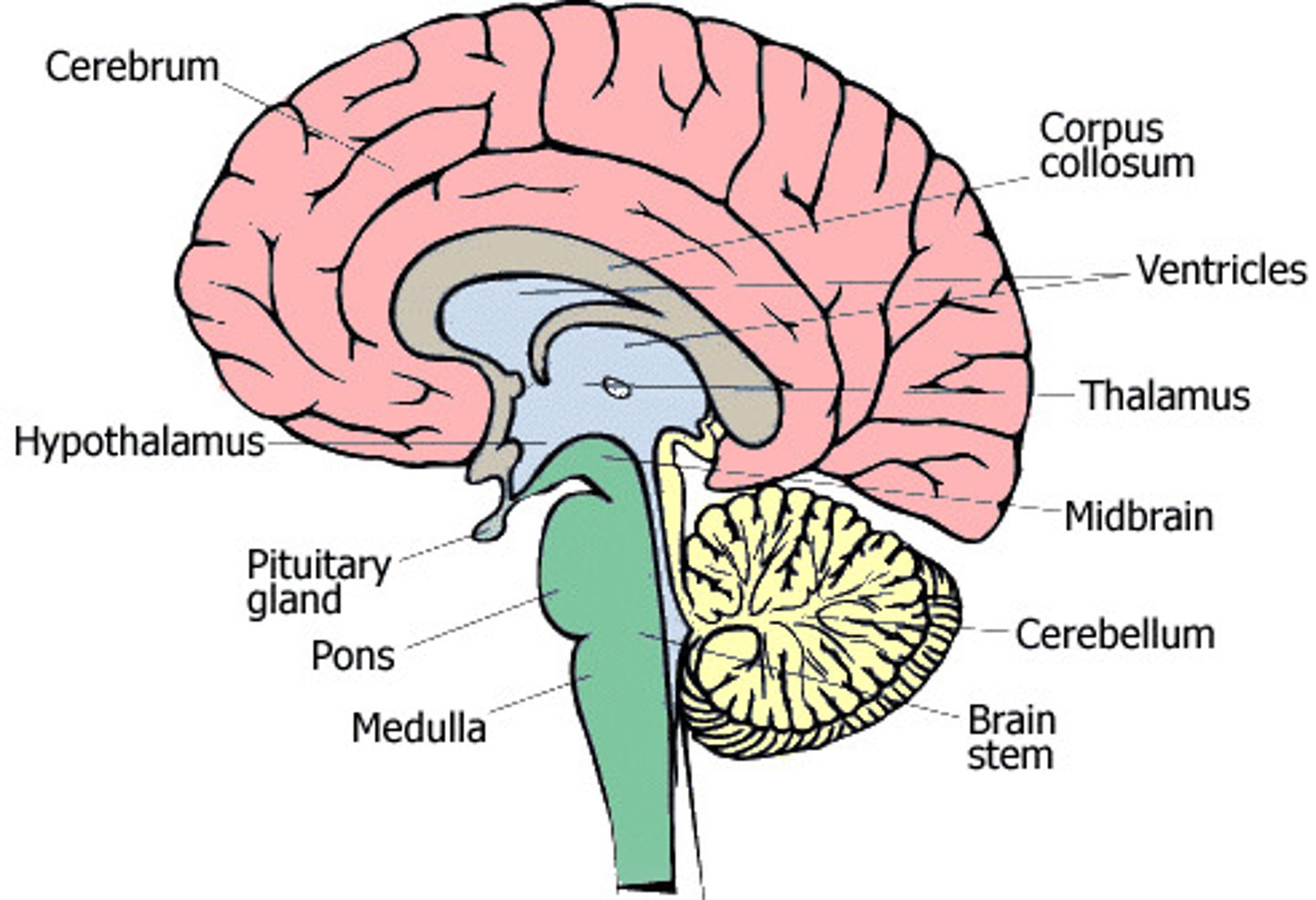
major regions of the brain
cerebrum, diencephalon, brainstem, cerebellum
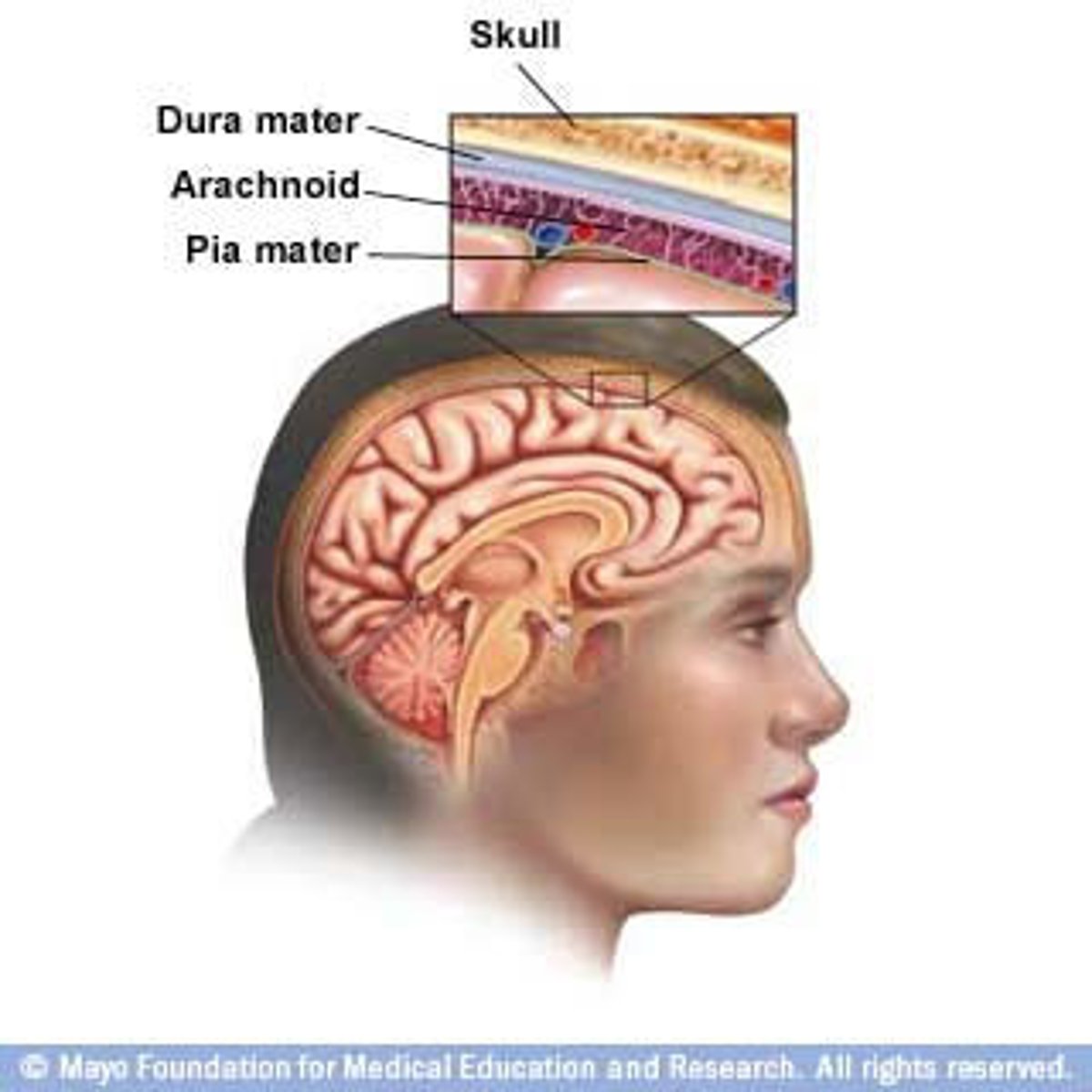
protective structures of the brain
cranium = bony skull
cranial meninges:
a. duramater
b. arachnoid mater
c. pia mater
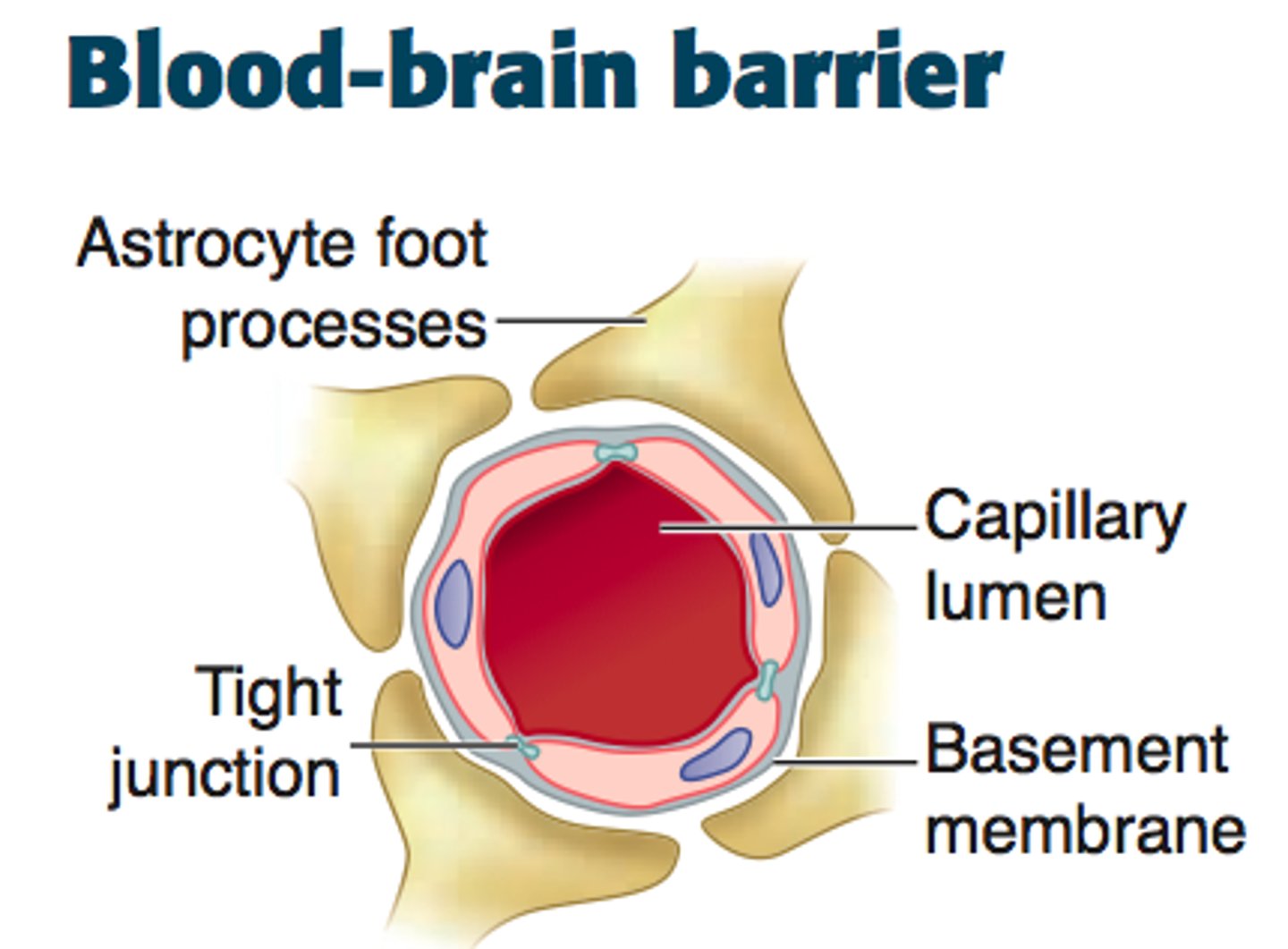
blood brain barrier - made up of astrocytes
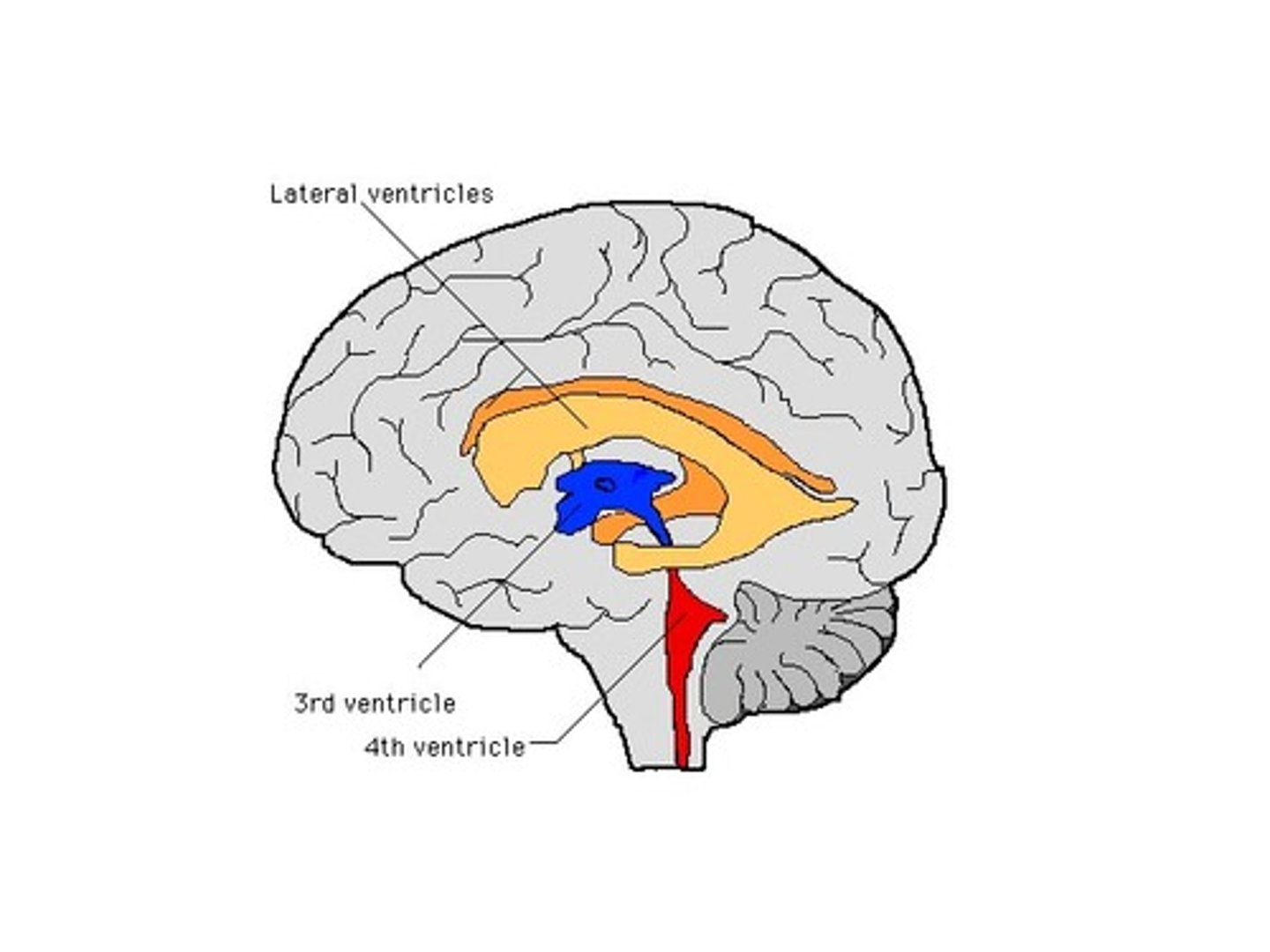
ventricles of the brain
canals in the brain that contain cerebrospinal fluid
lateral ventricles - cerebral hemispheres
third ventricle - diencephalon
cerebral aqueduct - midbraon
fourth ventricle - brain stem and cerebellum
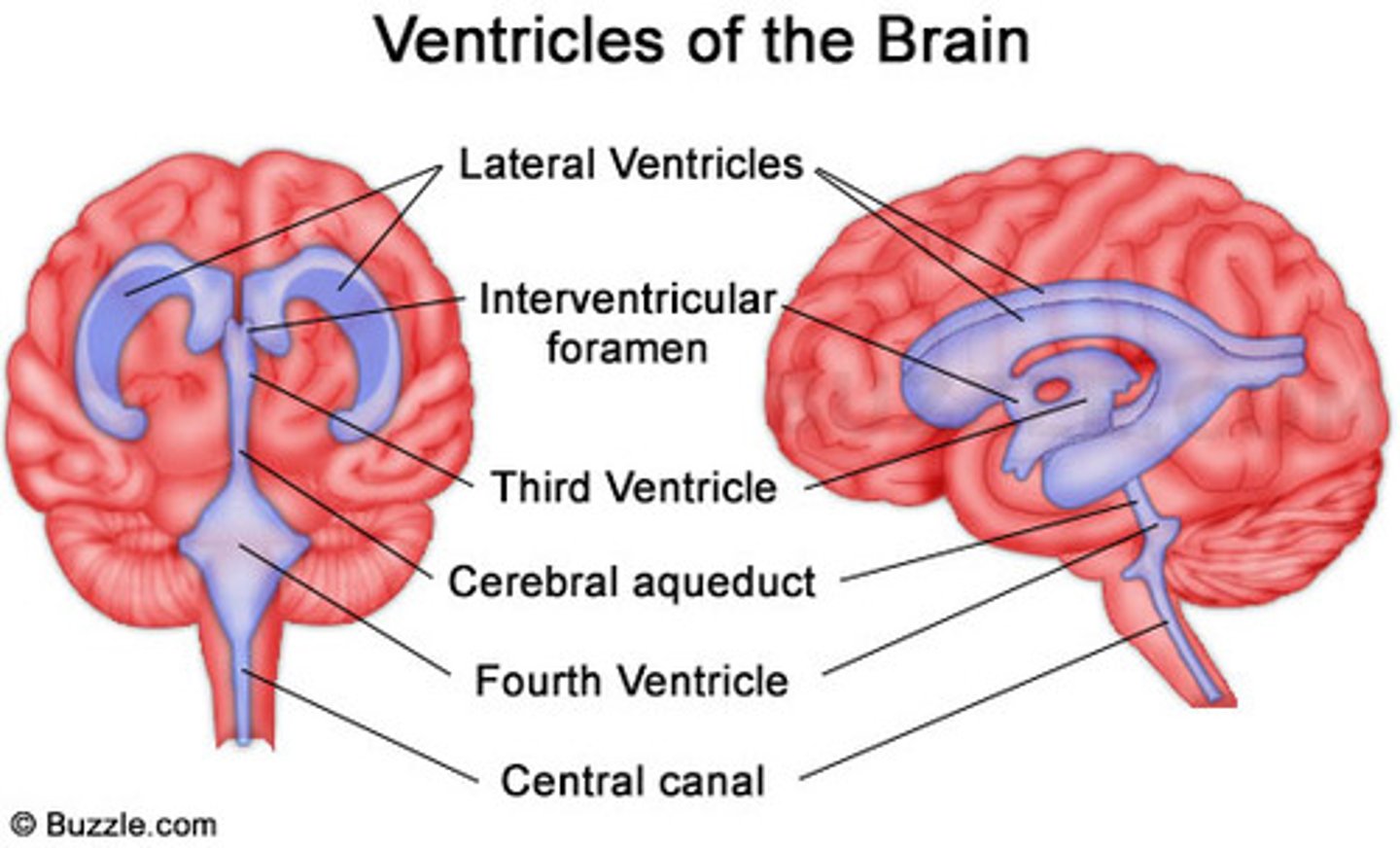
lateral ventricles of brain
ventricles found in each cerebral hemisphere
third ventricle of brain
Most central brain ventricle, ventral to the lateral ventricle, with the mesencephalic duct found inside it
in the diencephalon
cerebral aqueduct
a narrow tube interconnecting the third and fourth ventricles of the brain, located in the center of the mesencephalon
midbrain!
fourth ventricle of brain
The choroid plexus is located within this brain ventricle, found regionally under the cerebellum
brain stem and cerebellum!
What cells product most CSF?
ependymal cells
Blood Brain Barrier (BBB)
physiological barrier between the circulatory system and the central nervous system that establishes a privileged blood supply, restricting the flow of substances into the CNS
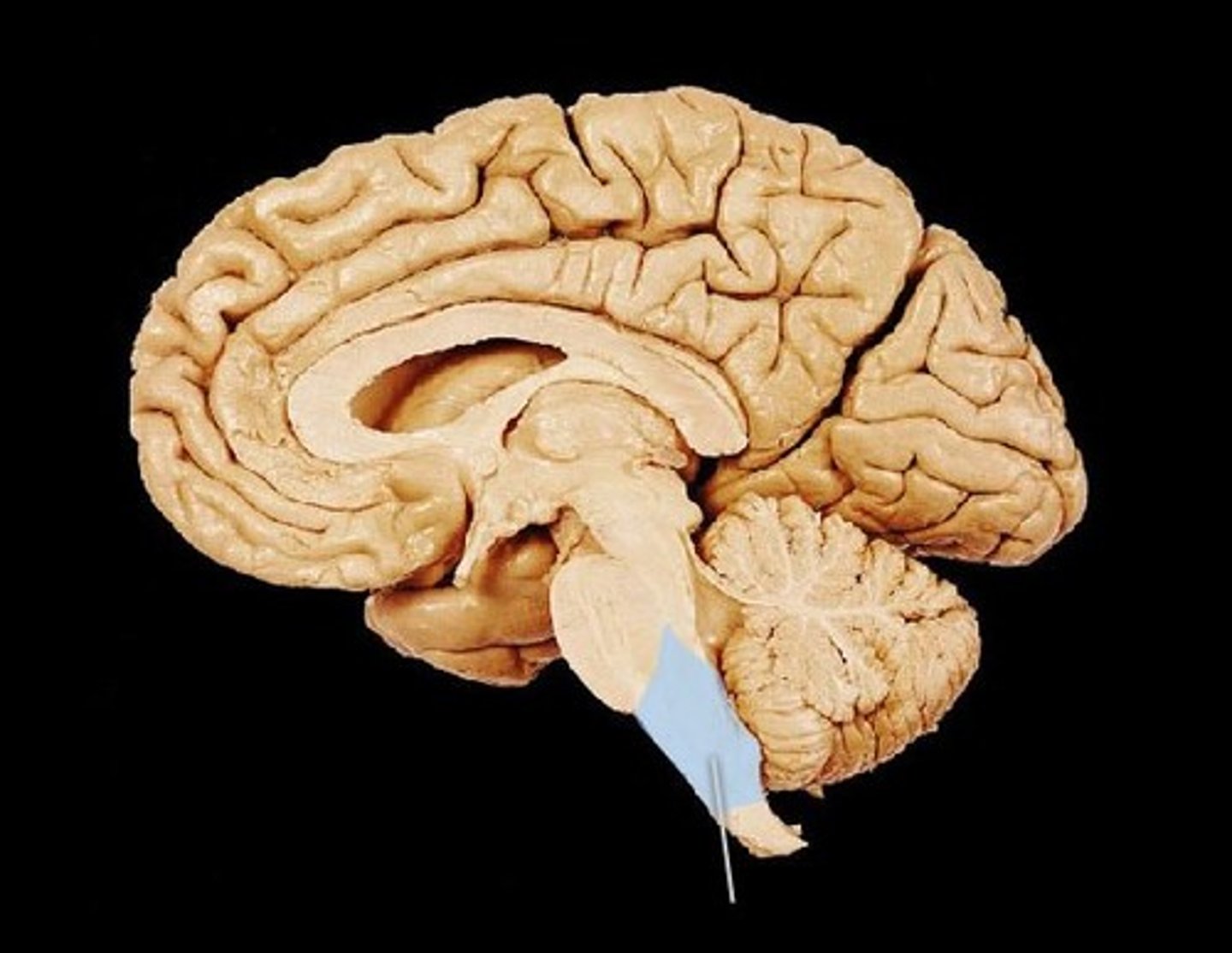
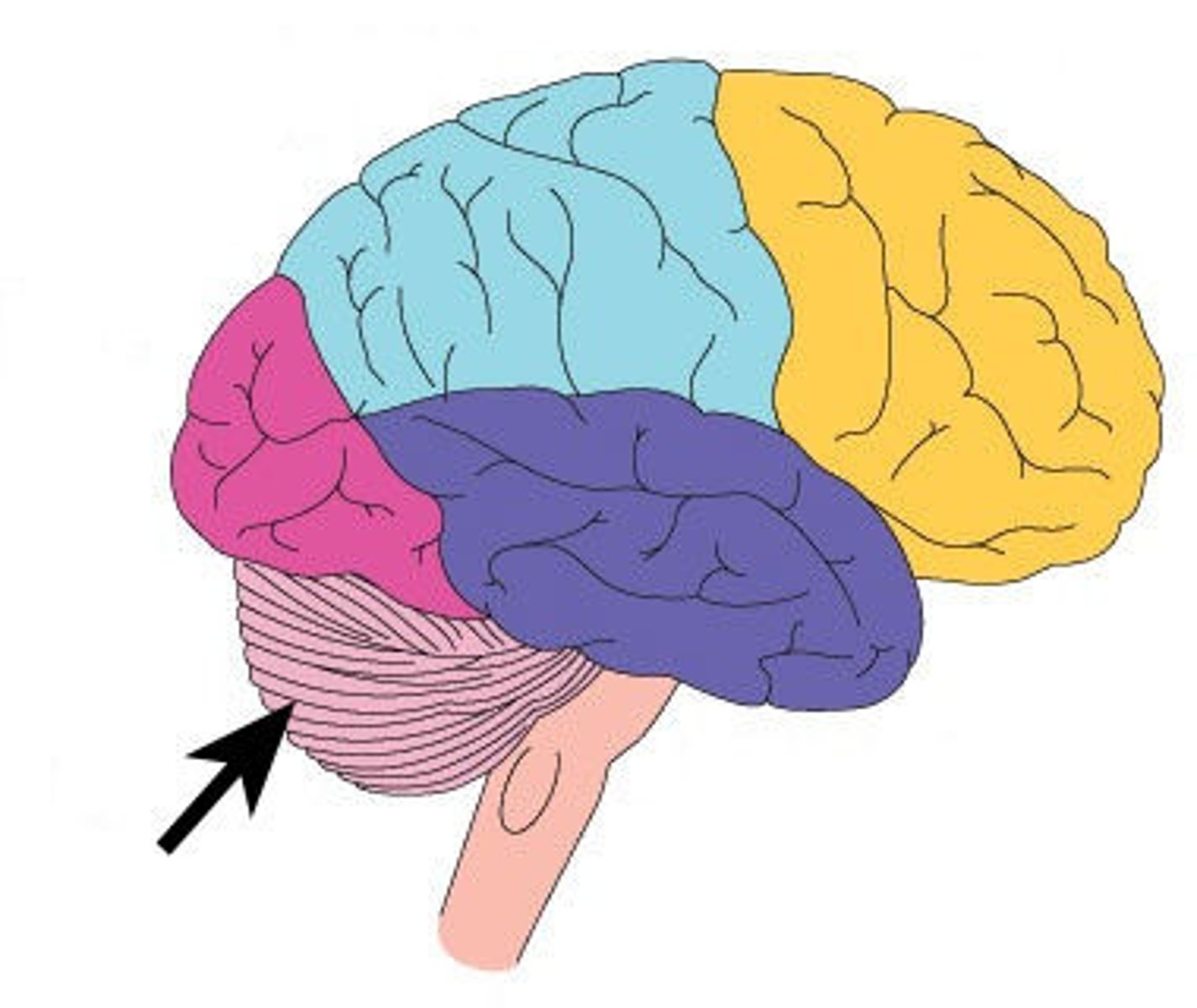
brain stem
medulla oblongata
pons
midbrain
houses cranial nerves 3-12 (10 pairs)
midbran aquaduct
fourth ventricle
medulla oblongata
Part of the brainstem that controls vital life-sustaining functions such as heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure, and digestion.
cardiovascular and respiratory centers
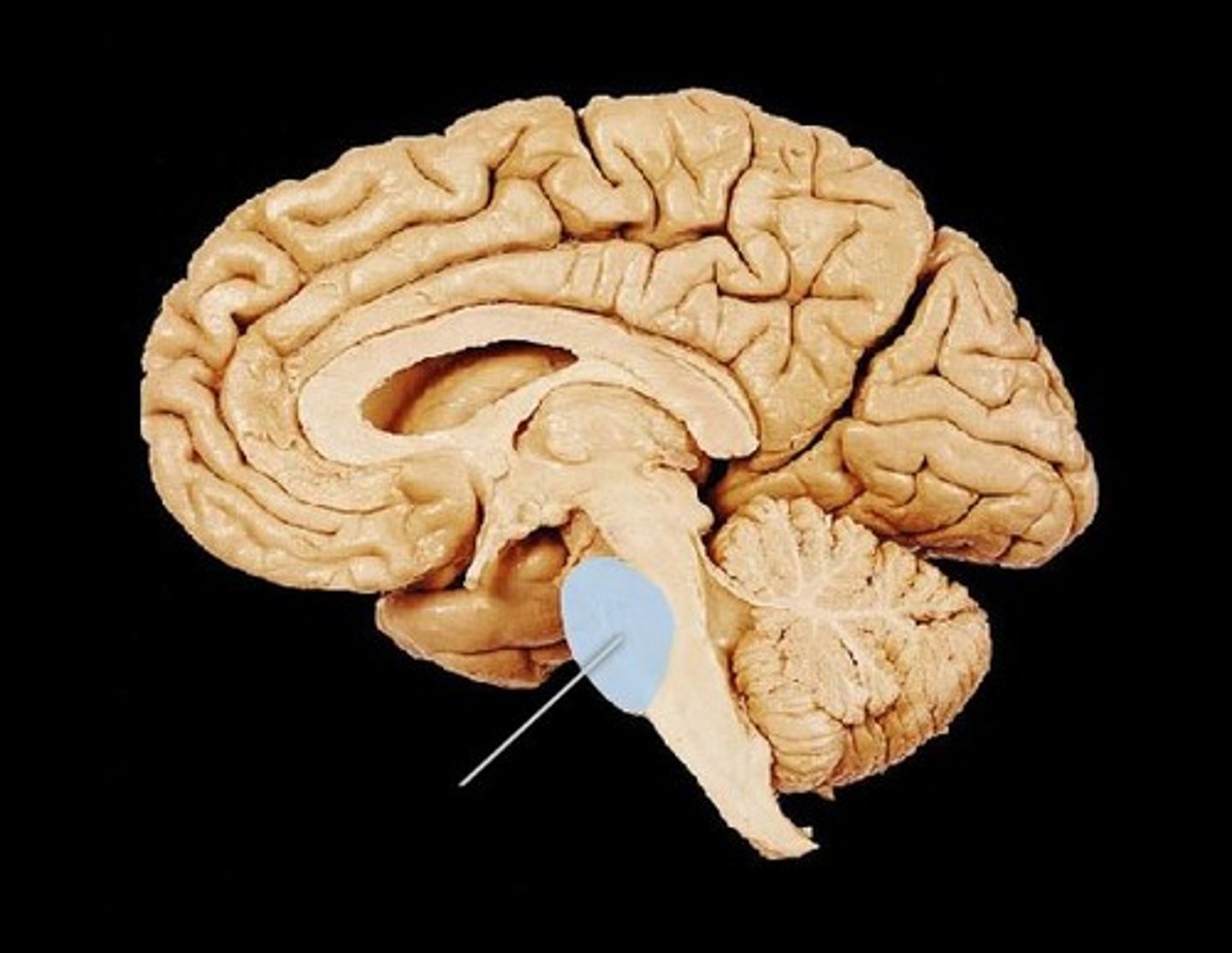
pons
A brain structure that relays information from the cerebellum to the rest of the brain
midbrain
A small part of the brain above the pons that integrates sensory information and relays it upward.
dopamine
control of movement and motivation
substantial nigra
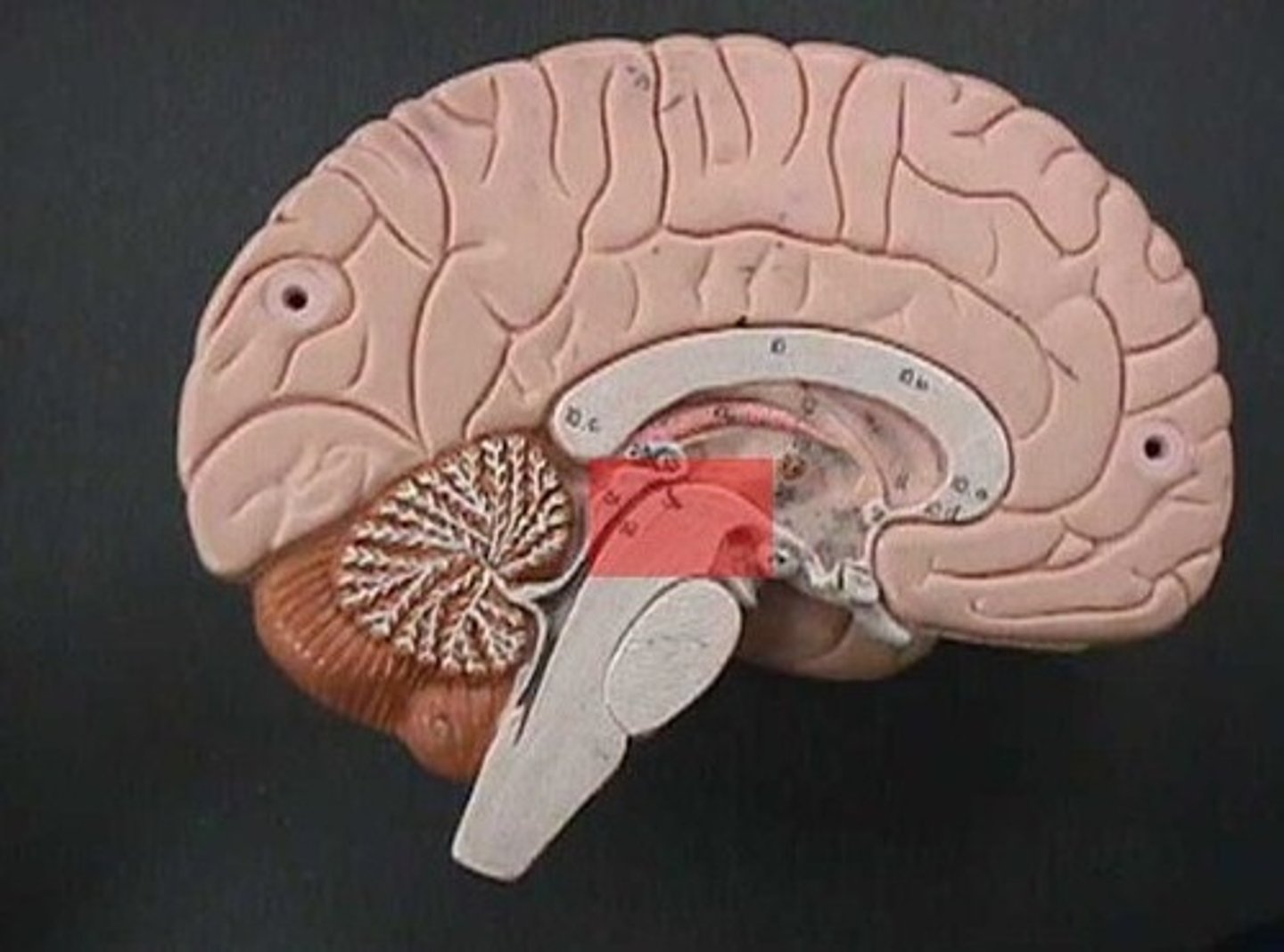
cerebellum
gray matter = cell bodies outside
white matter = tracts inside
functions = coordinate movements, balance, learning
fourth ventricle
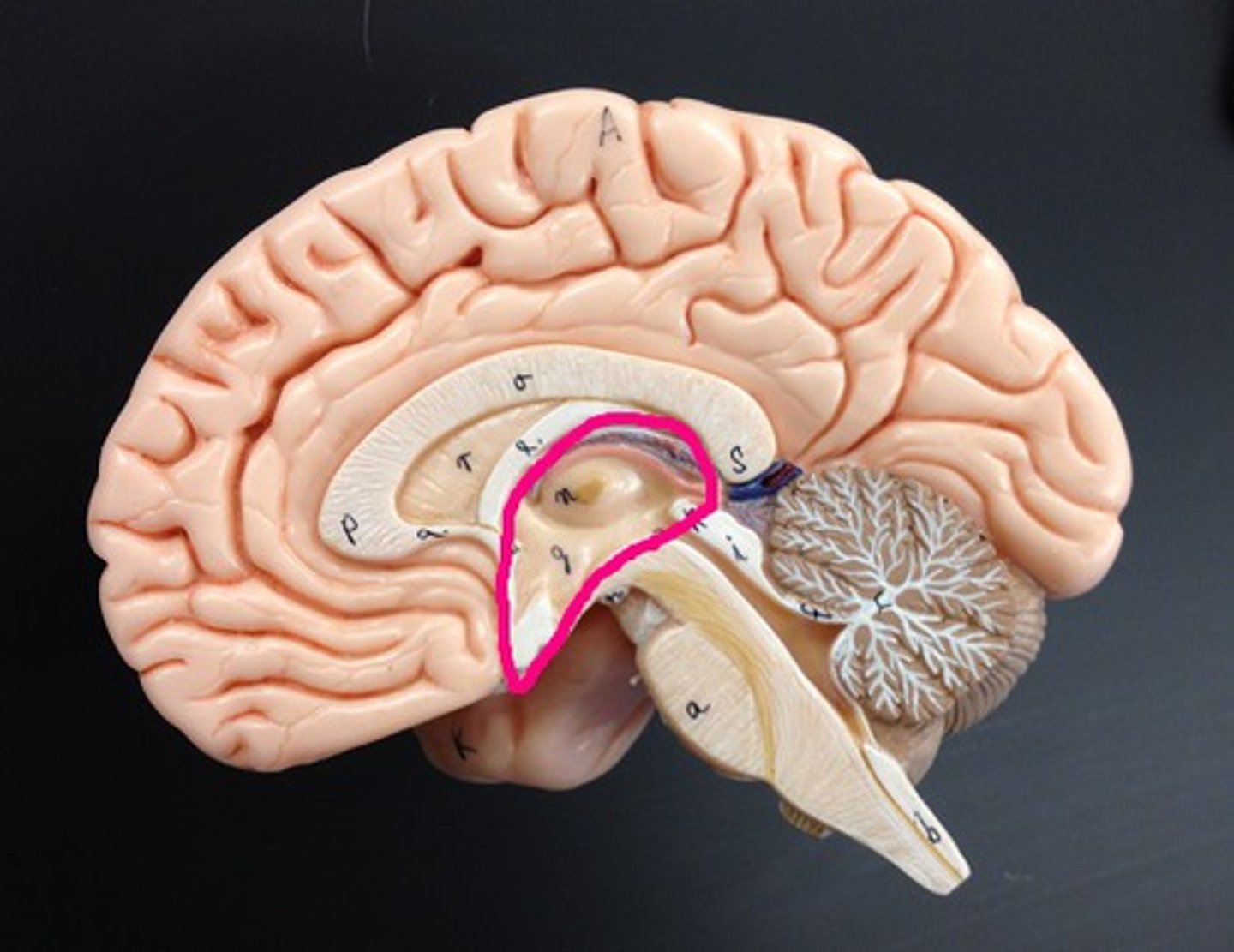
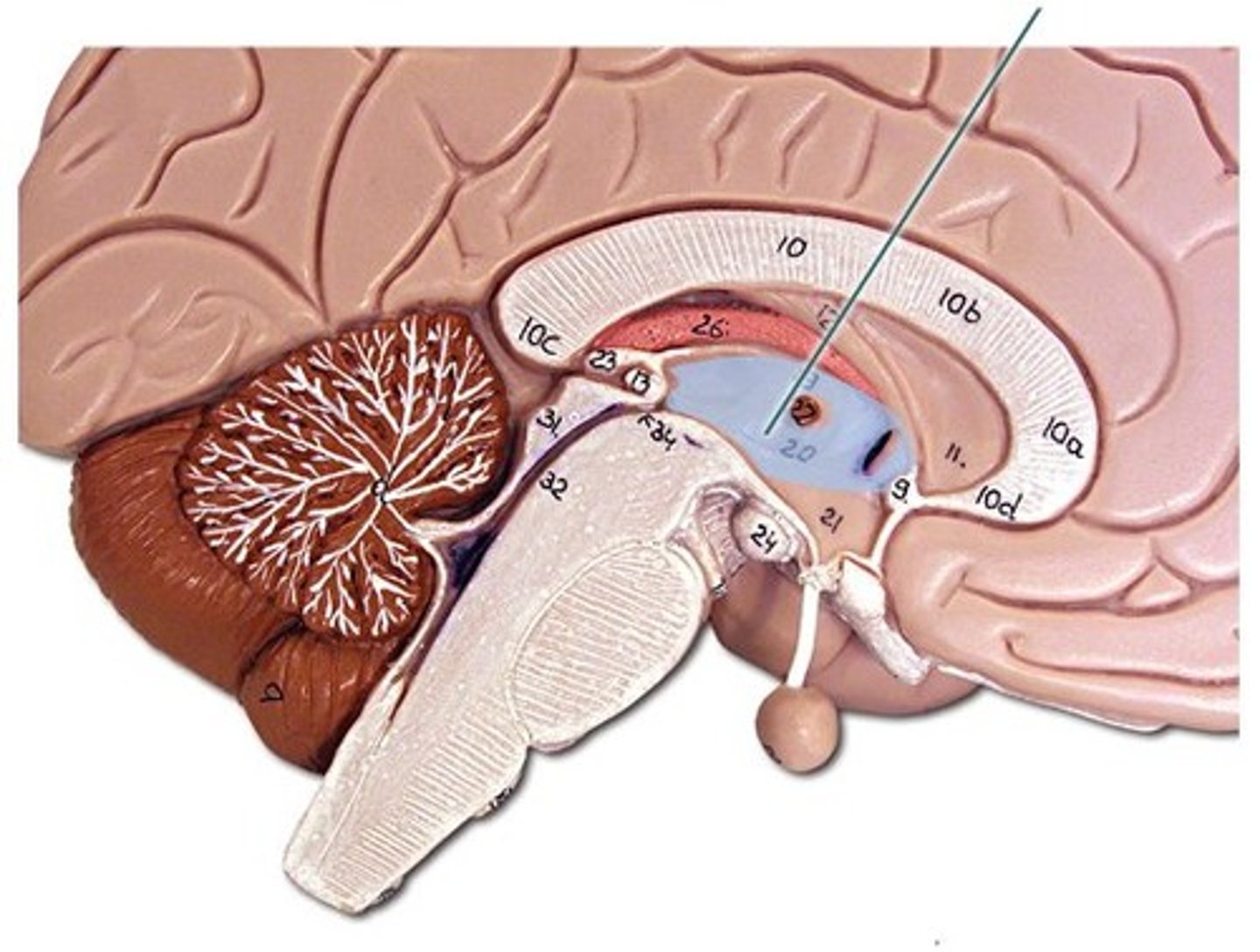
diencephalon
thalamus
hypothalamus
epithalamus
third ventricle
Thalamus
the brain's sensory control center, located on top of the brainstem; it directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla
Hypothalamus
a neural structure lying below the thalamus; directs eating, drinking, body temperature; helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, and is linked to emotion
autonomic function
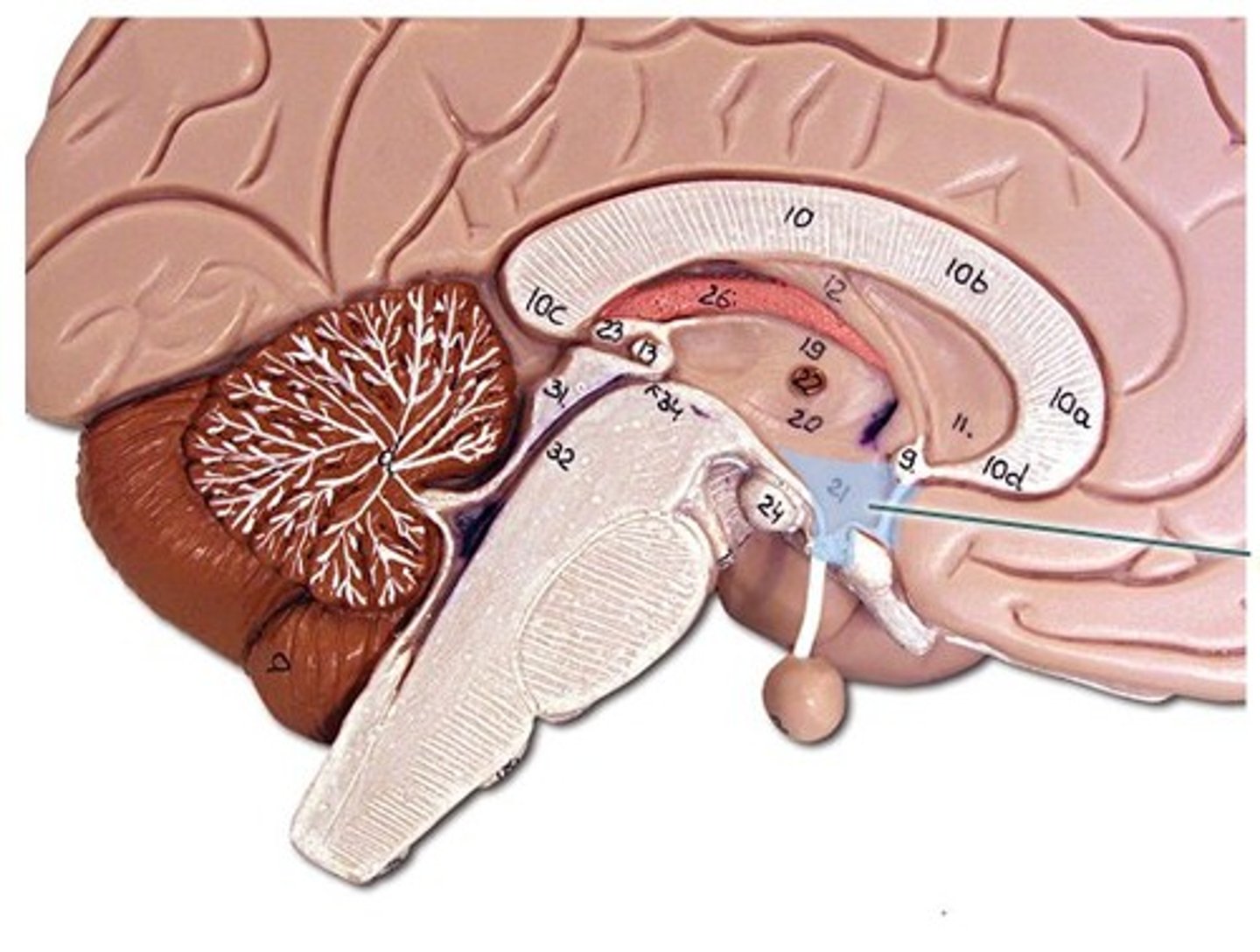
epithalamus
Contains pineal body. Involved in olfactory senses and sleep/wake cycle
no BBB
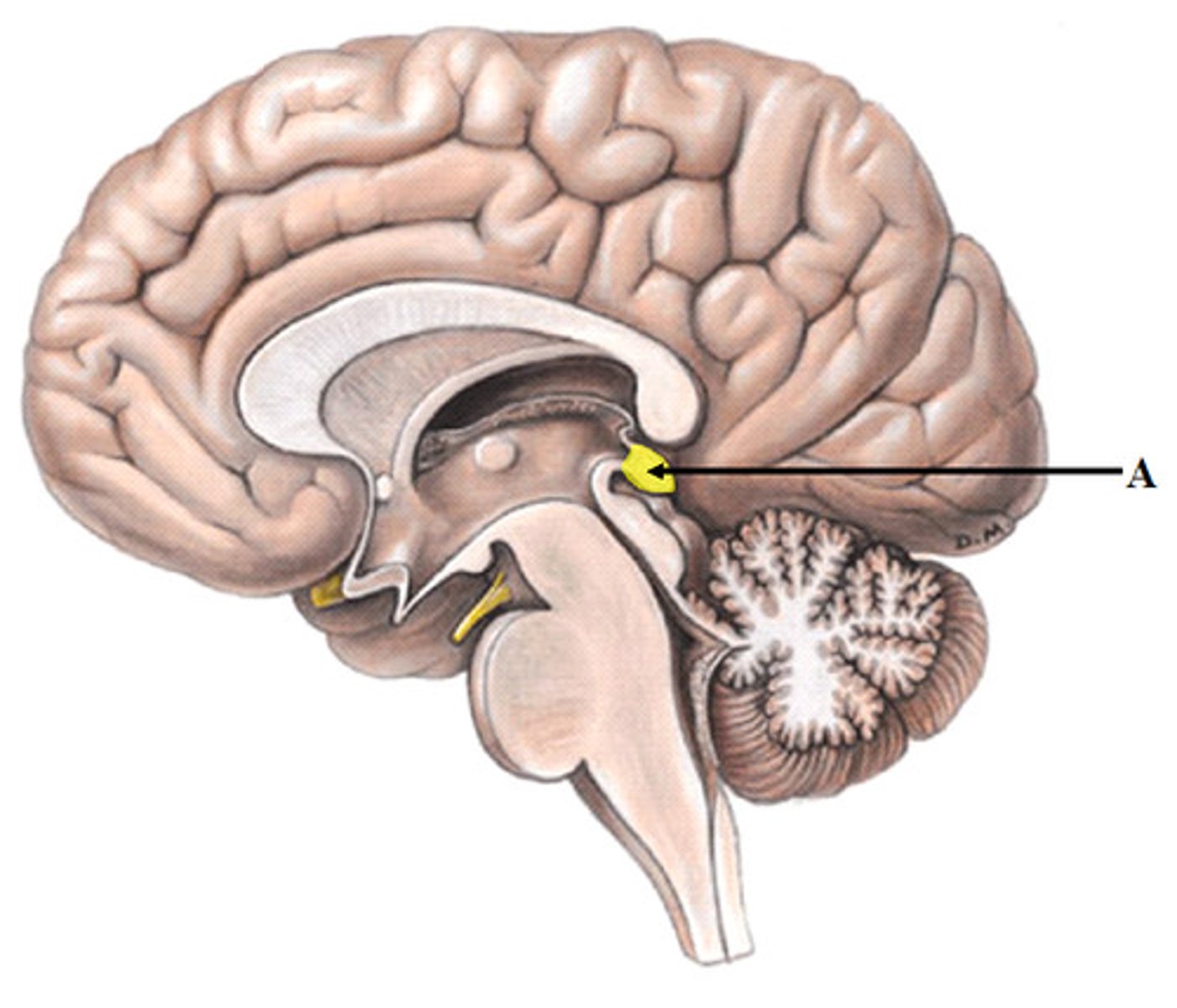
Cerebrum
cerebral cortex
cerebral tract
gyri = ridges
sulci = shallow grooves
fissures = deep grooves, valleys
lateral ventricles
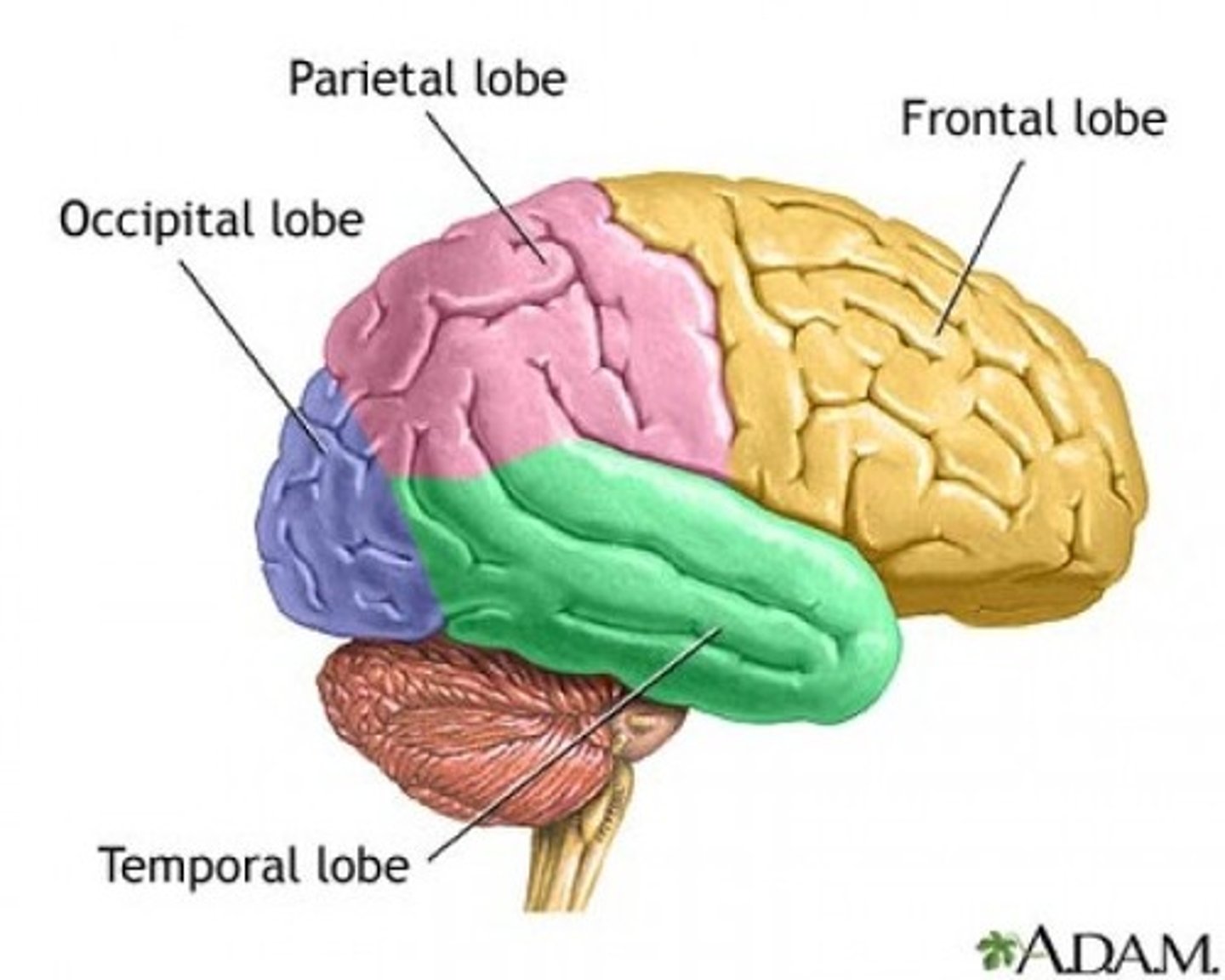
Cerebrum (four lobes)
frontal
parietal
temporal
occipital
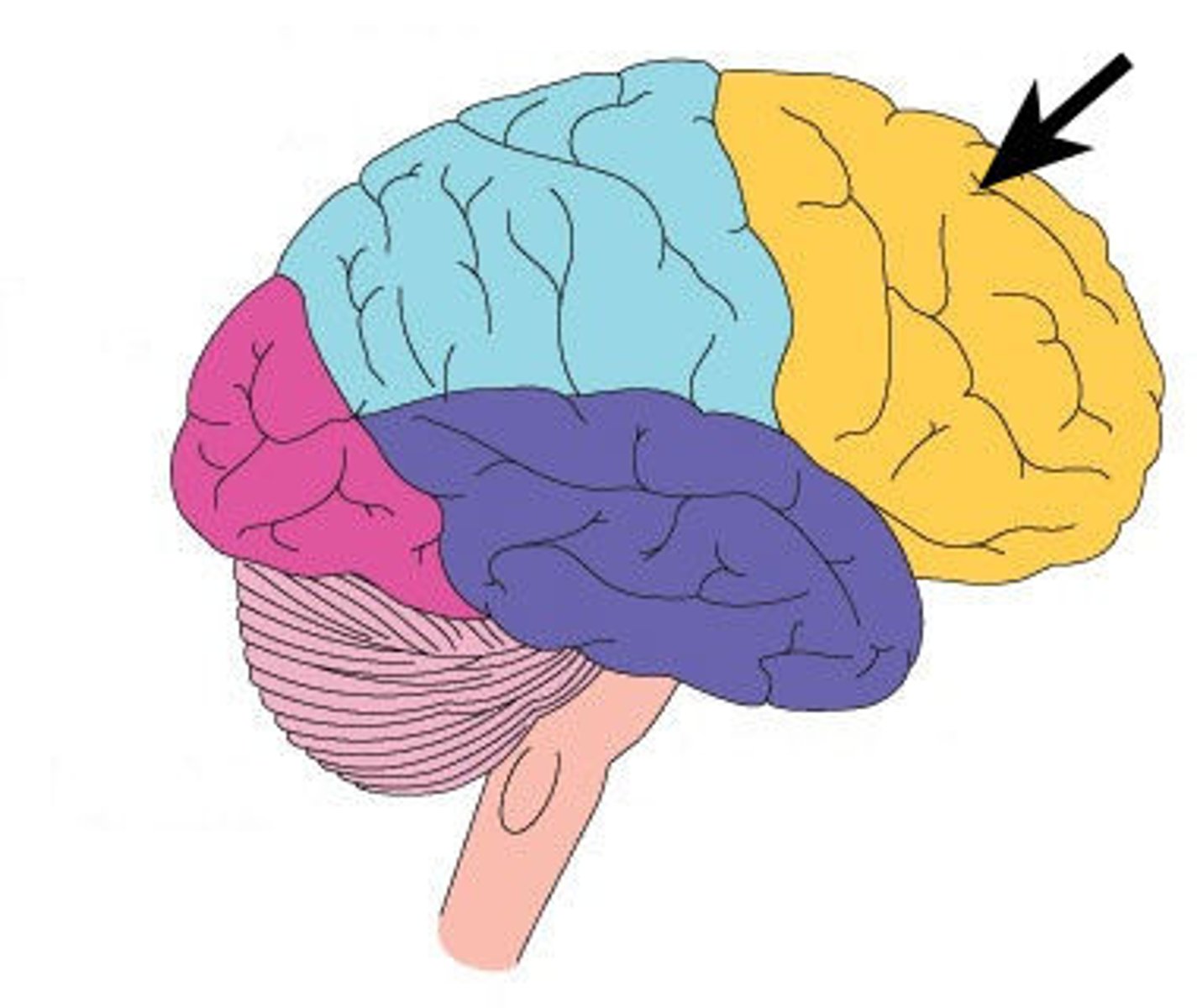
frontal lobe
mainly for motor thinking
high cognition
frontal association area
motor cortex
brocas area
parietal lobe
speech
somatosensory association
somatosensory cortex
taste
reading
wernickes area!
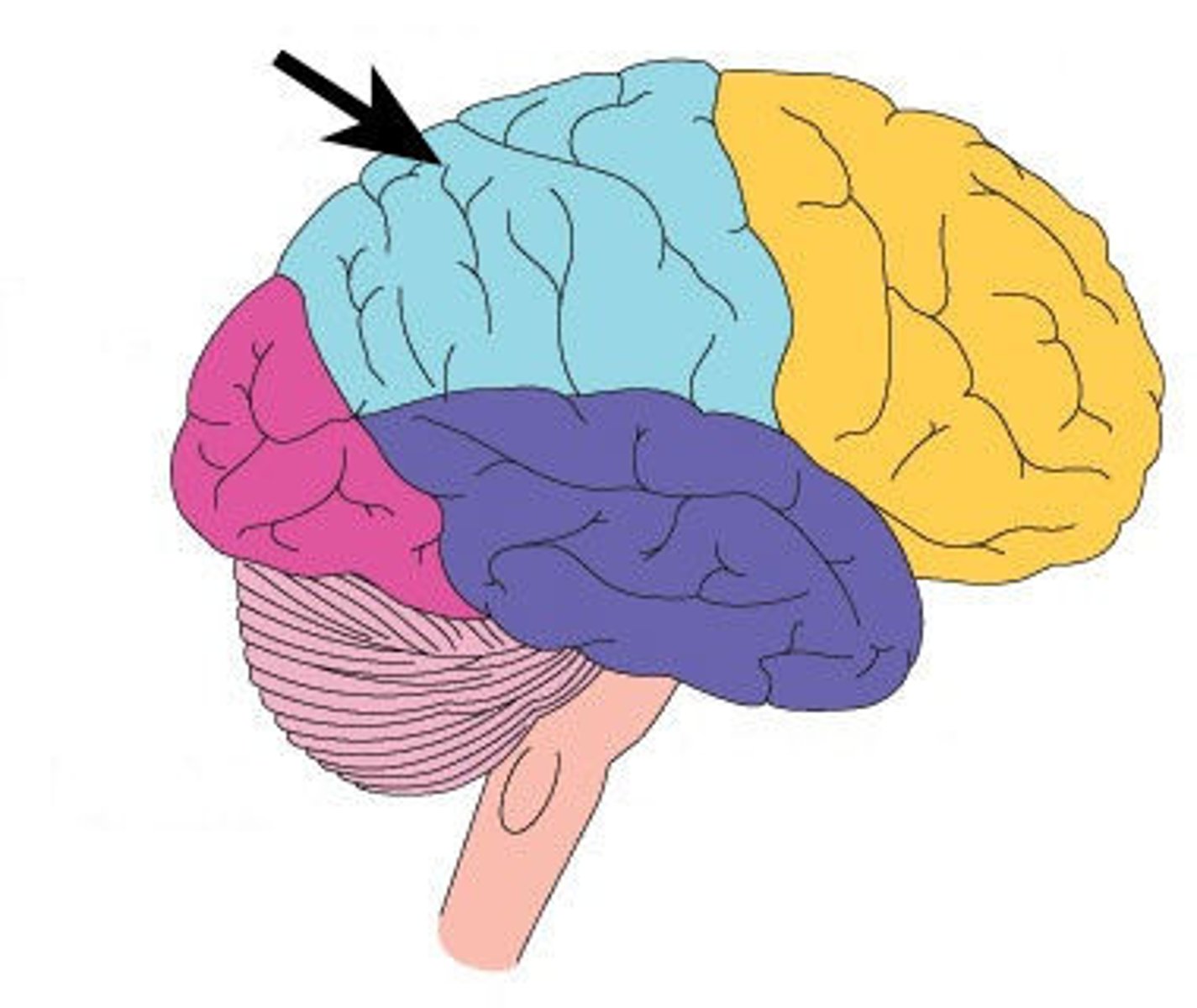
temporal lobe
smell
hearing
auditory association area
hippocampus
memory
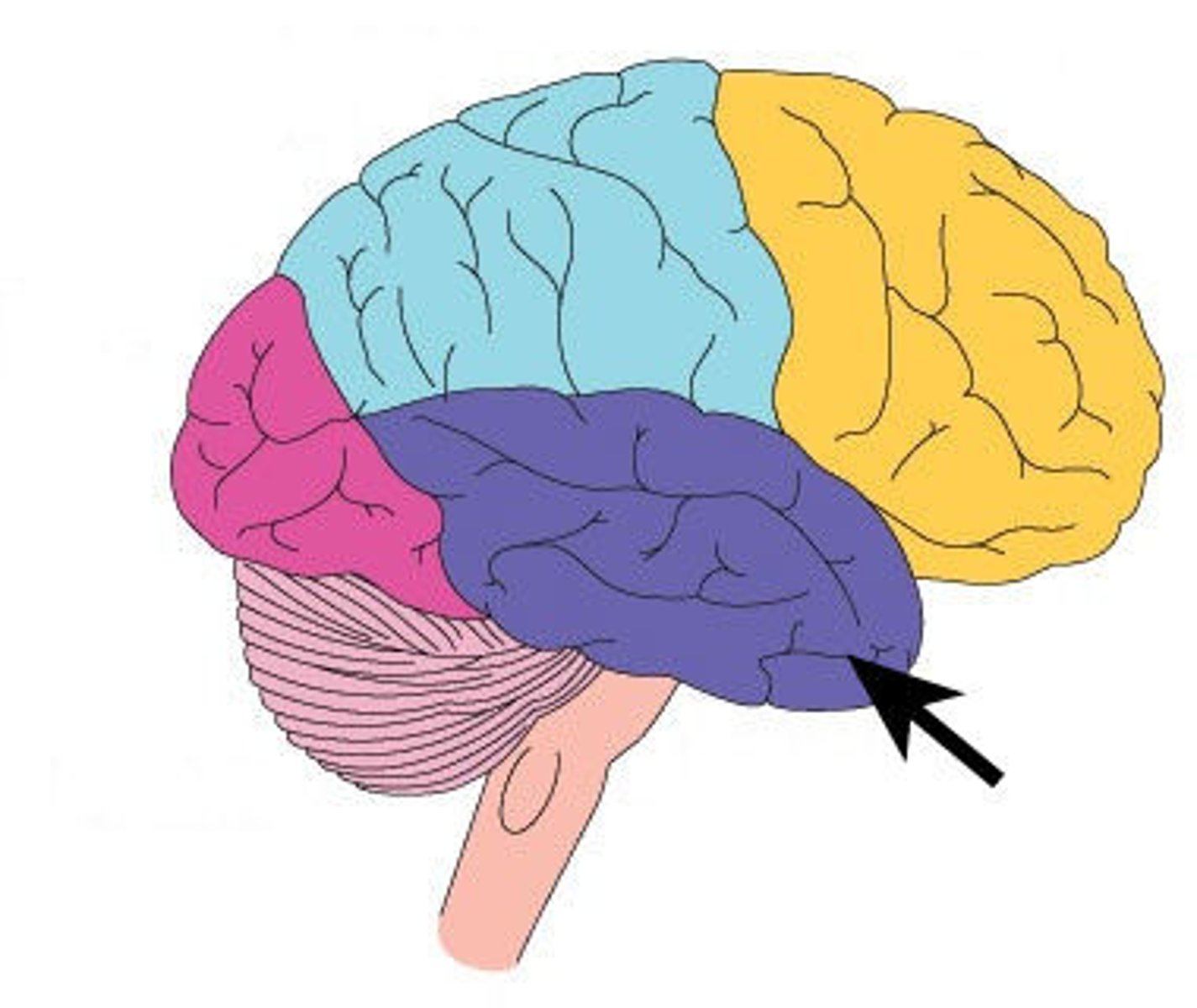
occipital lobe
visual association area
vision
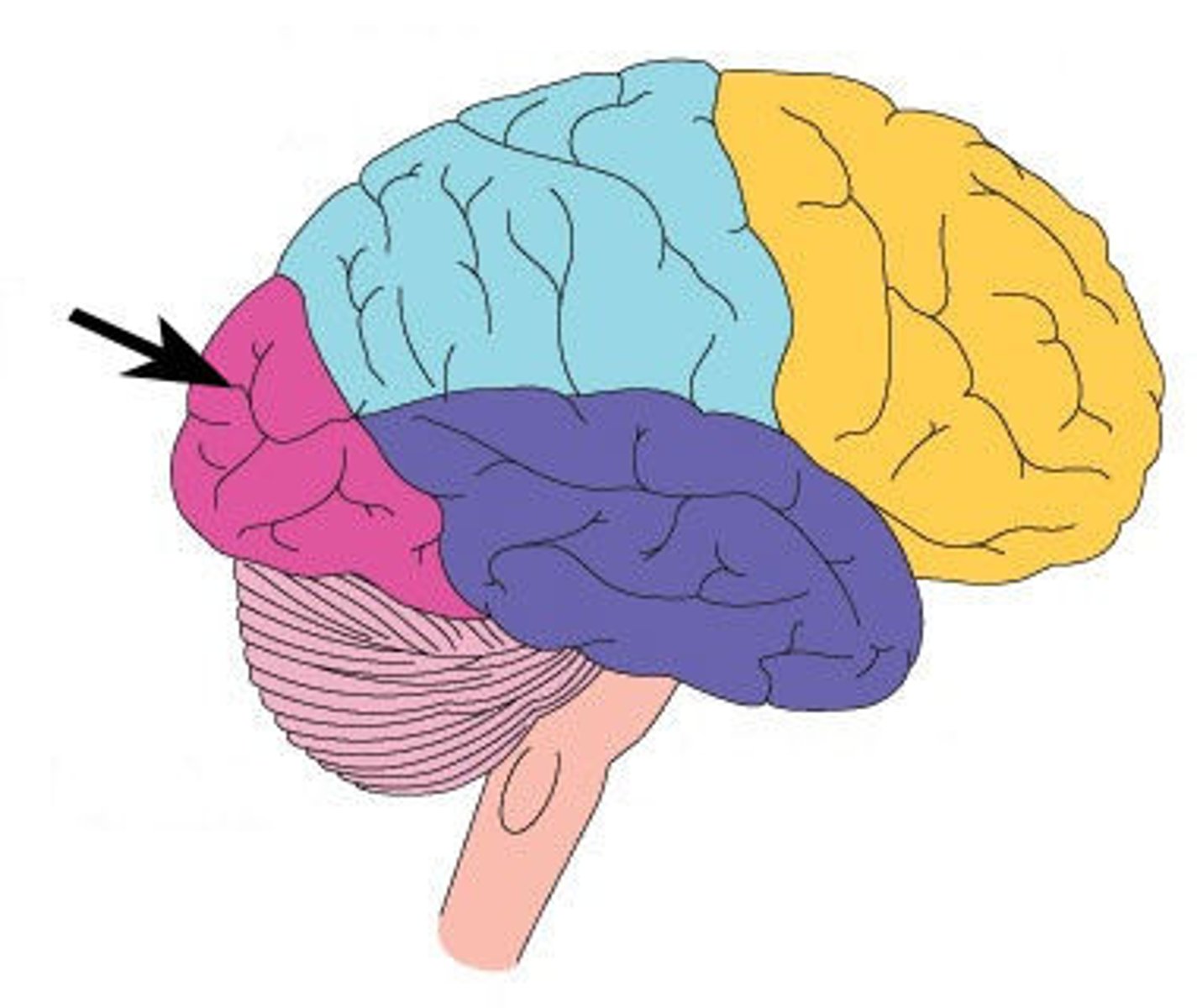
basal nuclei (cluster of neurons in CNS)
control initiation or termination of movement and thought
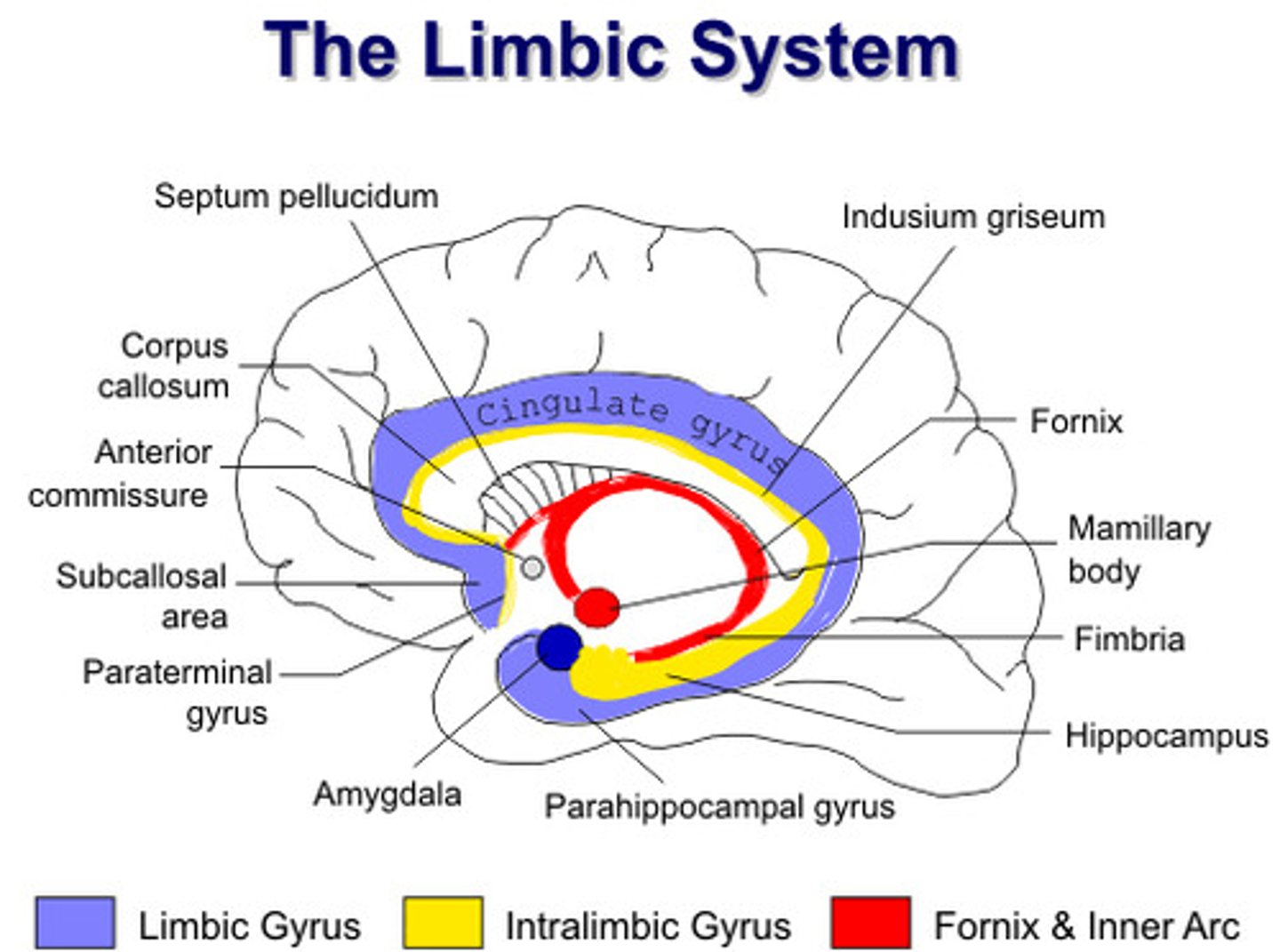
limbic system
neural system located below the cerebral hemispheres; associated with emotions and drives
hypothamalus
amygydala
spinal cord has
a core of gray matter surrounded by white matter.
gray matter inside
white matter outside
brain has
gray matter outside
white matter inside
spinal nerves
31 pairs of nerves arising from the spinal cord
cervical
thoracic
lumbar
sacral
coccygeal
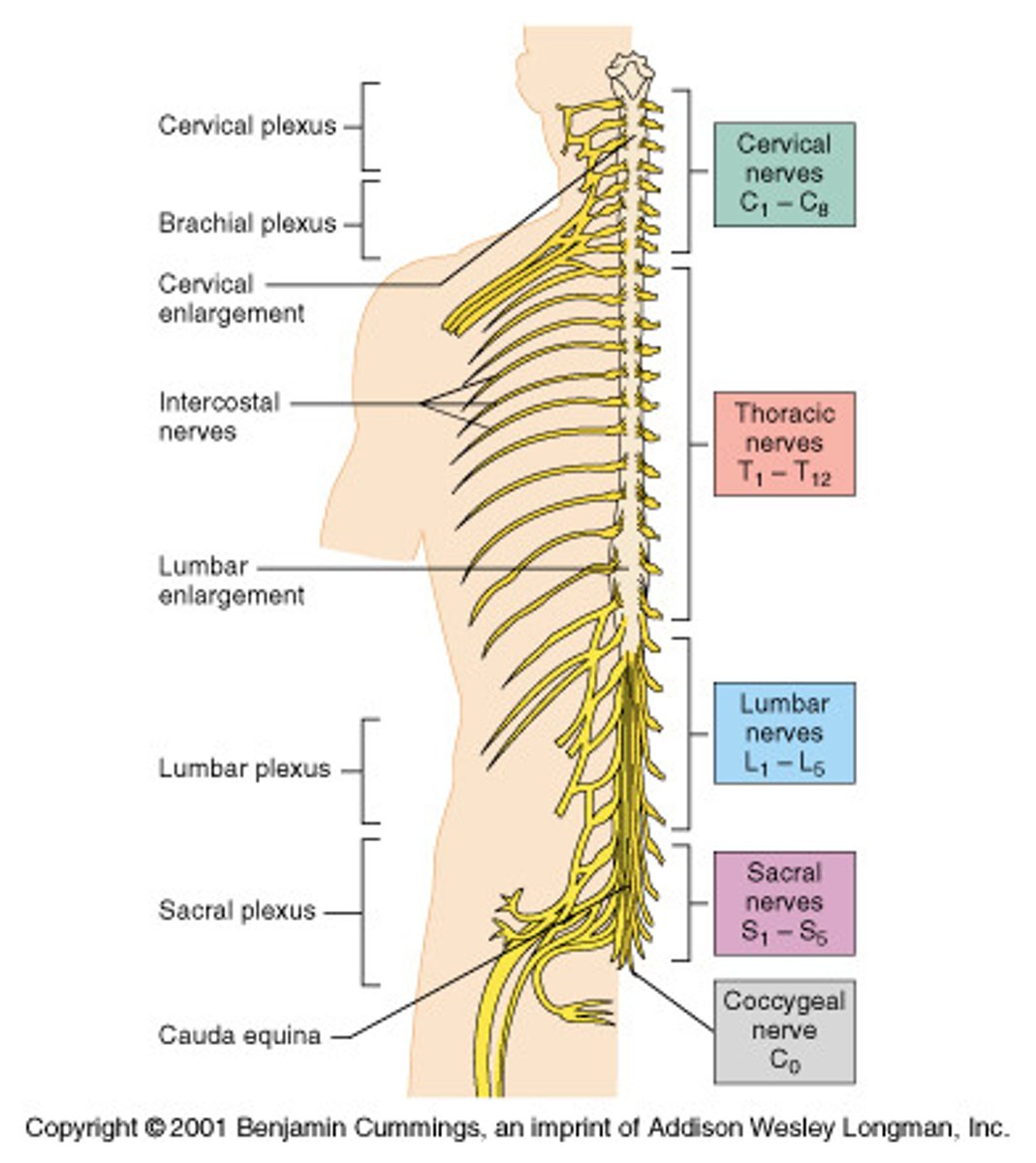
cervical nerves
C1-C8 8 pairs
thoracic nerves
T1-T12 12 pairs
lumbar nerves
L1-L5 5 pairs
sacral nerves
S1-S5 5 pairs
coccygeal nerves
1 pair (Co1)
ganglia
clusters of soma in PNS
dorsal
sensory
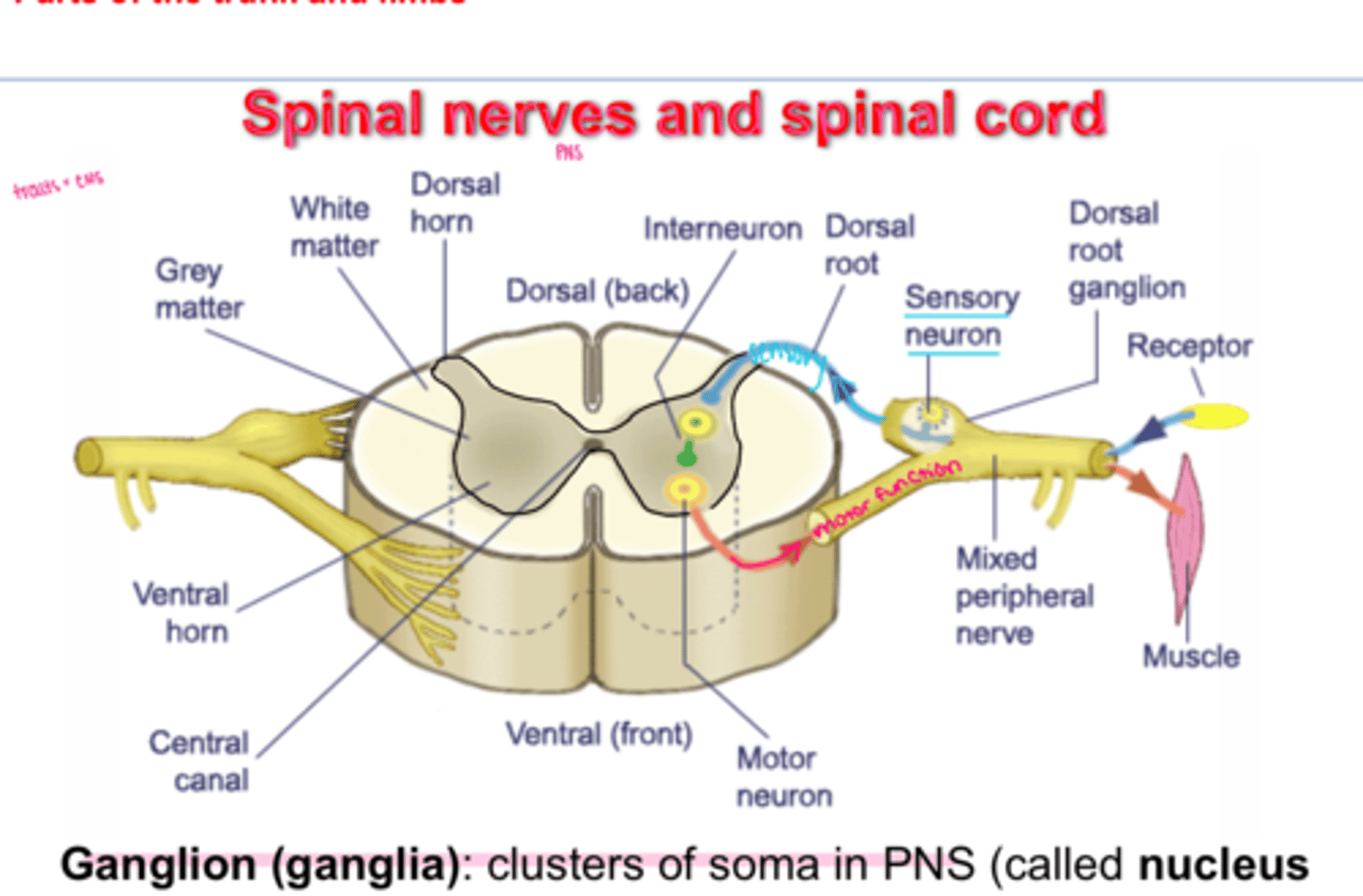
ventral
motor
plexuses
Formed from groups of nerves that join together to do a common function after they have left the spinal cord
Cervical Plexus (C1-C5)
supplies neck and phrenic nerve to the diaphragm
phrenic nerves C3-C5
innervate the diaphragm
Brachial Plexus (C5-T1)
supplies shoulders and upper limbs
5 nerves :
radial (C5-T1)
median (C5-T1)
ulnar (C8-T1)
axillary (C5-T1)
musculocuntaneous (C5-C6)
long thoracic nerve (C5-C7)
radial nerve
Nerve that runs along the thumb side of the arm and the back of the hand
median nerve
Sensory-motor nerve that is smaller than the ulnar and radial nerves and that, with its branches, supplies the arm and hand.
thumb side of hand
ulnar nerve
Sensory-motor nerve that, with its branches, affects the little-finger side of the arm and palm of the hand.
pinky side of hand
axillary nerve
deltoid and teres minor
shoulder
musculocutaneous nerve
anterior upper lateral forearm
long thoracic nerve
scapula
Lumbar Plexus (L1-L4)
Femoral nerve:
- motor to anterior muscles of thigh na dot pectineus, iliacus
- skin of anterior and medial thigh via anterior femoral cutaneous branch
- Skin of medial leg & foot, hip & knee joints via saphenous branch
Sacral Plexus (L4-S4)
L4-S4
supplies the buttocks, perineum, and lower limbs
longest nerve - sciatic nerve!
sciatic nerve
nerve extending from the base of the spine down the thigh, lower leg, and foot
largest and longest nerve
injuries to sciatic nerve
sciatica = pain from buttock down posterior and lateral of leg
injury = herniated disc, dislocated hip, arthritis
injuries to brachial plexus
* C5-C8, T1
-some say is the most common shoulder injury
ulnar nerve palsy
median and ulnar nerve palsy
radial nerve palsy
reflex
a simple, automatic response to a sensory stimulus, such as the knee-jerk response
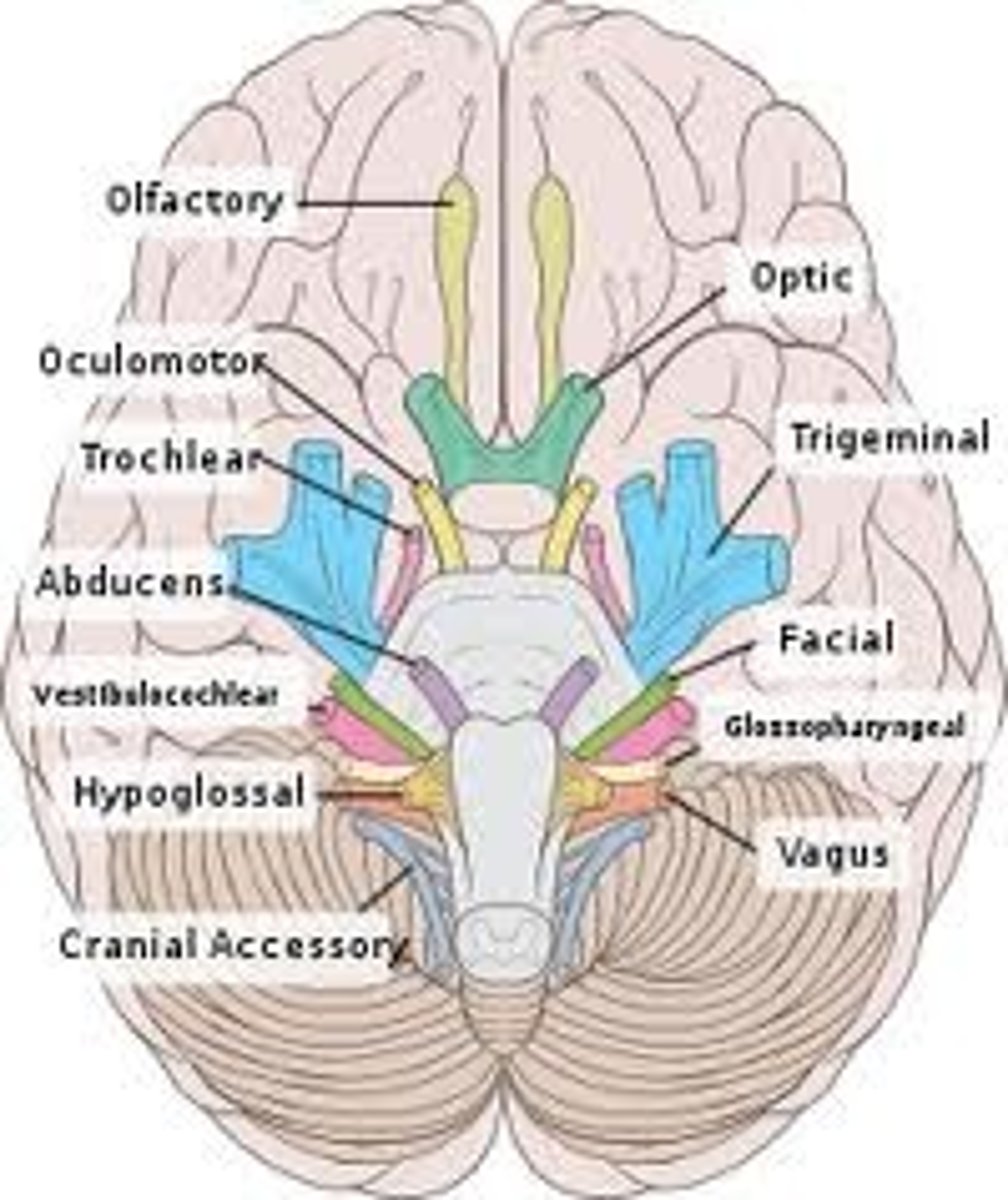
cranial nerves
12 pairs of nerves that carry messages to and from the brain
PNS!
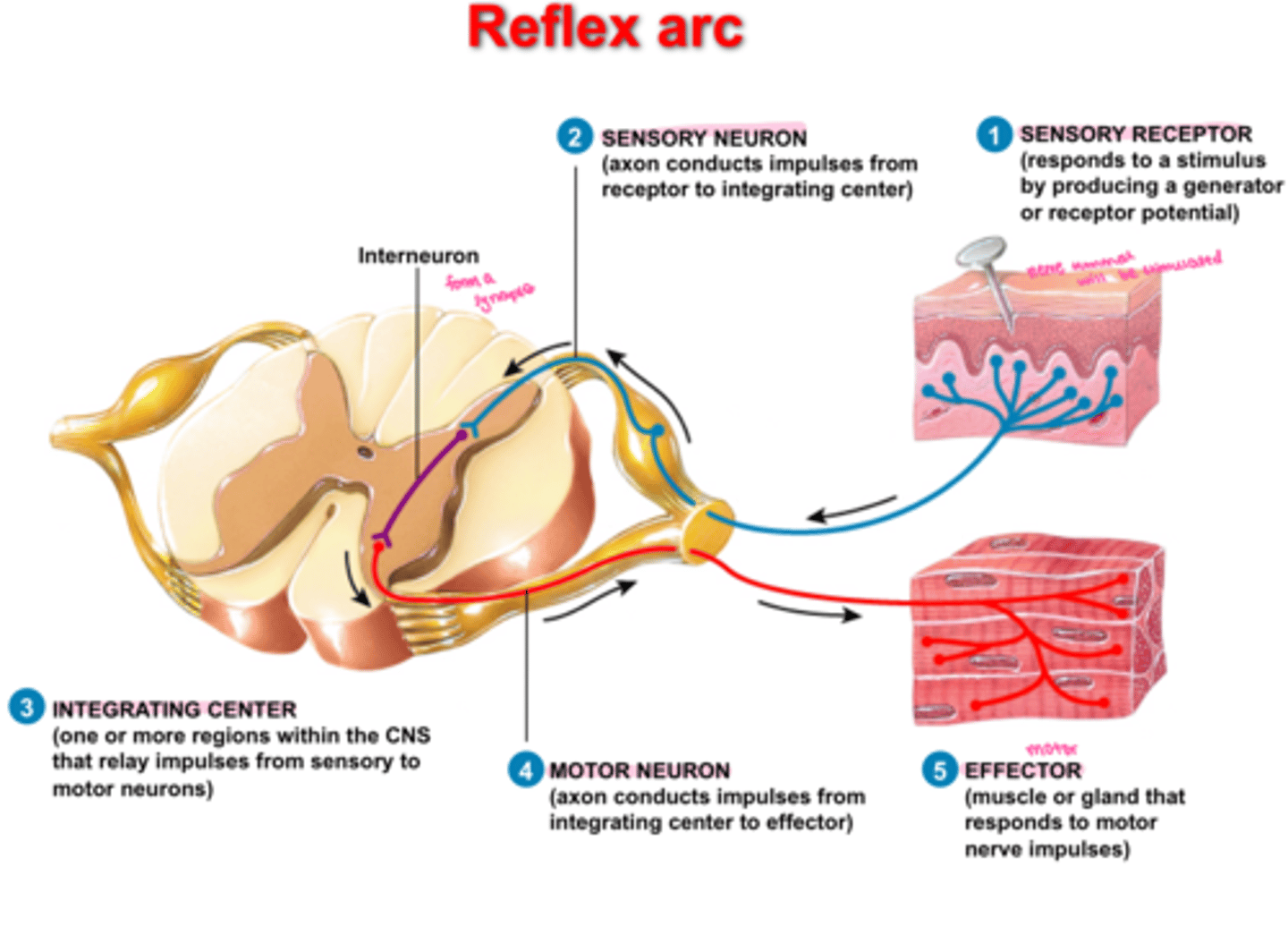
reflex arc
the nerve pathway involved in a reflex action including at its simplest a sensory nerve and a motor nerve with a synapse between.
A relatively direct connection between a sensory neuron and a motor neuron that allows an extremely rapid response to a stimulus, often without conscious brain involvement.
stretch reflex
muscle contraction in response to stretching within the muscle
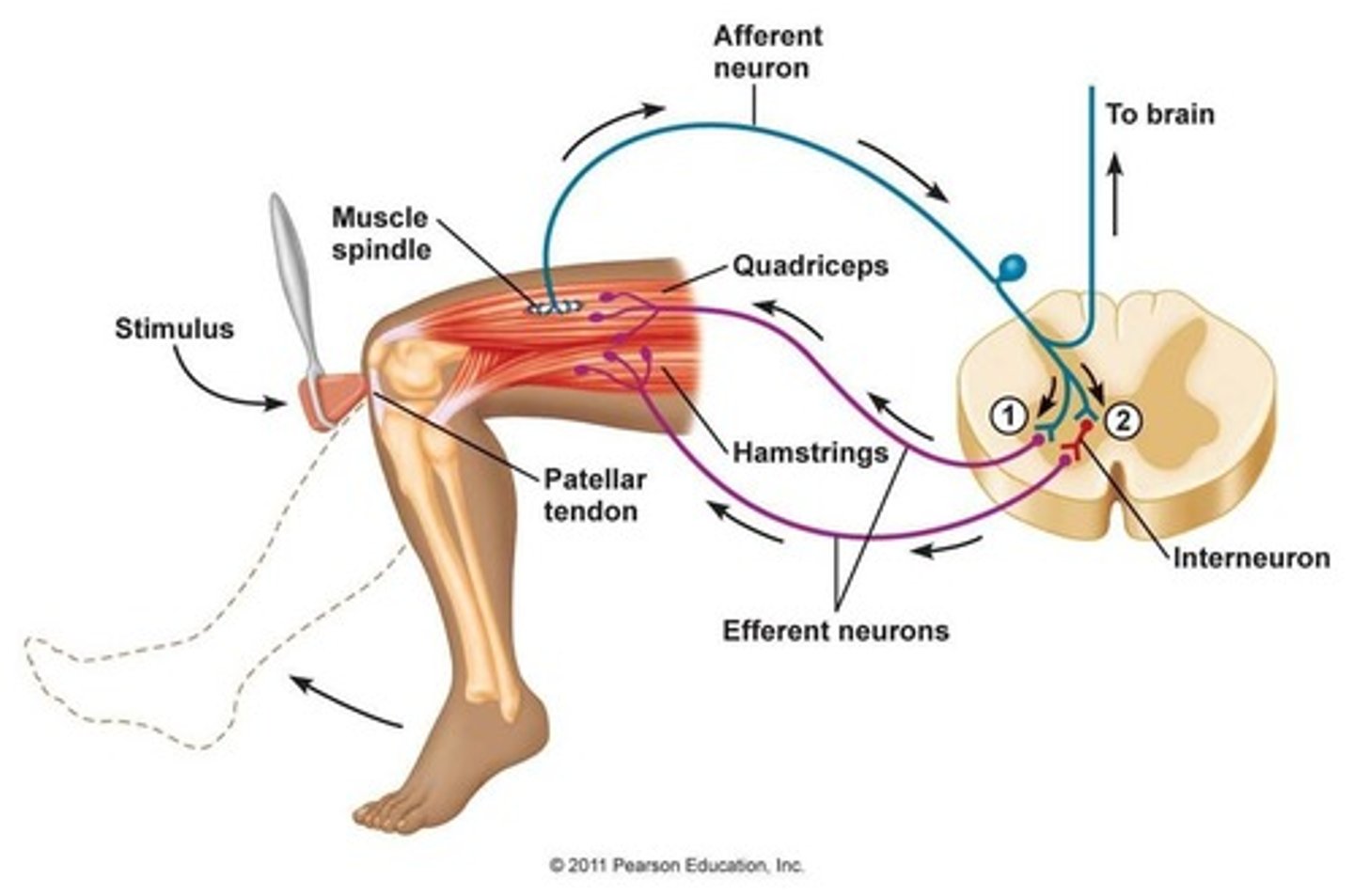
monosynaptic
-single synapse between sensory neuron that received and motor neuron responds
-e.g. knee jerk
ipsilateral
on the same side of the body
Contralateral
on the opposite side of the body
reciprocal
contraction of one muscle and relaxation of its antagonists