LAM: Exam 3
1/71
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
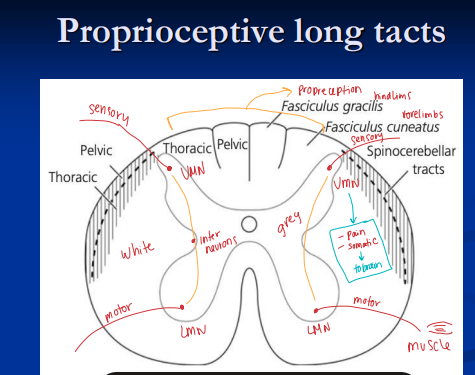
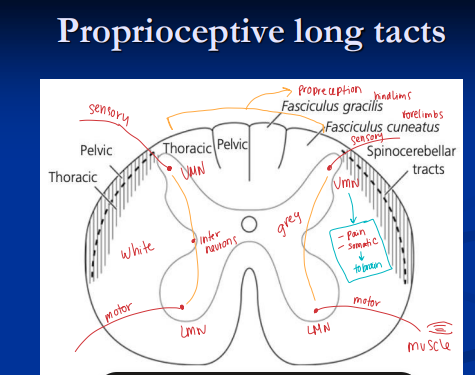
Neurological Localization of PNS and Spinal Cord Disease
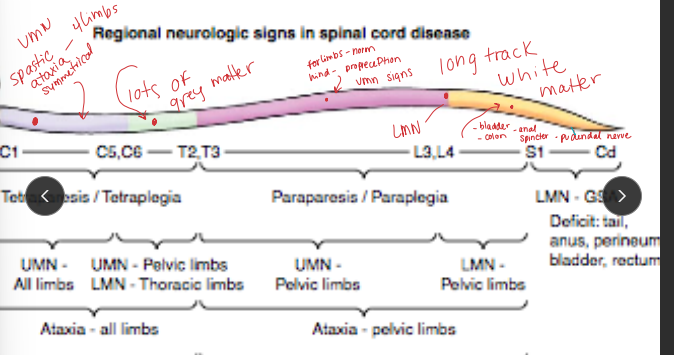
Spinal cord: Gait abnormalities w/ absence of intracranial signs
gait deficits, spastic paresis, ataxia, Flaccid paresis & muscle atrophy, proprioceptive deficits
Cervical: Head normal, both fore & hindlimbs abnormal
Below T2: Head/neck/forelimbs normal, hindlimbs abnormal
If tetraparesis w/o brain signs → lesion localizes to C1–T2
White matter lesions (long tracts): spastic paresis, ataxia caudal to lesion
sensory information from the body to the brain (ascending tracts) and motor commands from the brain to the muscles and glands (descending tracts).
Gray matter lesions (LMN): flaccid paresis, muscle atrophy (focal/segmental)
Peripheral n.: flaccid paresis, focal atrophy, sensory loss in one limb
Motor unit
consisting of a single motor neuron (nerve cell) and all the individual skeletal muscle fibers it innervates
Localization of Brain Disease
Cerebrum- Forebrain: depression, disorientation, nervousness, hyperexcitability, compulsive walking/circling, head pressing, maniacal behavior, seizures, cortical blindness
Consciousness, awareness, behavior change, intellect, voluntary motor control (UMN)
Brainstem: Alterations in consciousness & arousal - no brain signs
obtunded, stupor, coma, cranial nerve deficits, head tilt, leaning/listing, resting nystagmus, spastic paresis, ataxia, vestibular ataxia
motion, vestibular input
Cerebellum: attention tremor, coordination & motor activity(rate/range/speed/force)
Dysmetria/hypermetria(all 4 legs), Truncal sway, Intention tremor of head, Loss of menace response, Disequilibrium or paradoxical vestibular syndrome
motor activity, arousal (RAS), aranial nerve nuclei, vestibular & somatic motor integration
Cranial N.: Head abnormal, limbs/trunk normal
Diffuse Brain: Head + limbs abnormal
Cerebrospinal Fluid Analysis
Collection sites:
Lumbosacral: Standing horse
Needle enters ventral subarachnoid space through conus medullaris (S4–S5)
Collect from dorsal subarachnoid space
Atlanto-occipital: Recumbent under GA
Midline insertion between atlas wings and nuchal crest
Atlanto-axial: Standing, lateral approach
Evaluation:
Colour: Clear, colorless
WBC: 0–4, mononuclear
IgG index = (CSF IgG / serum IgG) × (serum albumin / CSF albumin) → intrathecal IgG production
Total protein: < 90 mg/dL
Albumin quotient = (CSF albumin / serum albumin) × 100 → BBB integrity
Ab testing:
Viral: EHV-1, WNV, EEV, WEV
Protozoal: EPM
Diagnostic Imaging of the Nervous System
Radiography/myelography: vertebral alignment, compression
CT/MRI: brain, cervical spine
Electromyography: LMN dz vs myopathy
Electroencephalography: cerebral electrical activity
Auditory brainstem evoked response: hearing & brainstem lesions
Cell bodies: ventral gray horn (spinal cord) or brainstem nuclei
Axons: form ventral spinal roots & motor cranial nerves
Why: directly cause muscle contraction (motor unit)
what are the clinical signs of peripheral nerve injuries or neuropathies in a horse?
lameness, poor coordination (ataxia), and weakness, which can be severe enough to prevent weight bearing.
muscle wasting (atrophy), drooping or paralysis of facial features like the lip or ear, gait abnormalities like goose-stepping or toe-dragging, and a lack of sensation in affected areas.
Cranial Nerves
I Olfactory: Smell (sensory)
II Optic: Vision (sensory)
III Oculomotor: Eye movement, parasympathetic to ciliary muscle
IV Trochlear: Dorsal oblique muscle
V Trigeminal: Mastication, facial sensation
VI Abducens: Lateral rectus & retractor bulbi
VII Facial: Facial expression, salivation, lacrimation, taste
VIII Vestibulocochlear: Balance & hearing, head position
IX Glossopharyngeal: Pharynx, salivation, taste
X Vagus: Pharynx, larynx, parasympathetic to thorax & abdomen
XI Spinal Accessory: Neck & pharyngeal muscles
XII Hypoglossal: Tongue movement
Adult Seizures
Et: Uncontrolled synchronous discharge of cerebral cortical neurons
CS Specific to cerebral cortex
Types:
Primary: trauma, infection, toxins, developmental
Secondary: hepatic/renal, glucose/Na/Ca disturbances, hyperthermia, hypoxia/ischemia
Idiopathic: Sporadic adult idiopathic epilepsy (all breeds)
Cs:
Focal(partial/localized/absence): facial/limb twitching, compulsive circling, self-mutilation
Gen: loss of consciousness, recumbency, tonic-clonic activity, post-ictal blindness/depression
Epilepsy: recurrent seizures, non-progressive cerebral cortical disease
Tx: Diagnosis & treatment of underlying dz #1!!! protect the head, Padding, Diazepam (short/ER), Phenobarbital (Long term) Levetiracetam (Keppra), Bromides, Gaba
Management: Loading dose, maintenance dose, daily dose for recurrent seizures
Juvenile Idiopathic Epilepsy
inheritable
Sig: Arabian foal syndrome, start ~ <6m
Cs: post-ictal depression: most common, disorientation, blindness, trauma
Dx: CS, history and breeding
Tx: Diazepam acutely, phenobarbital 1y (maintenance), supportive care, self limiting with age, don’t breed
Lavender Foal Syndrome
coat color dilution lethal
Et: Autosomal recessive, lethal
Sig: Egyptian Arabians w/ color dilution (lavender/pink/purple)
Cs: inability to stand @ birth, seizures, CNS signs, death
Tx: Euthanasia
Cerebellar Abiotrophy
inheritable
Et: Autosomal recessive
Sig: Arabians, 6m
Cs: symmetric hypermetria/dysmetria(4 limbs), spasticity, truncal sway, intention tremor, absent menace
Dt: genetic testing
Tx: euthanasia, no treatment
Seizure Disorders in Foals
Neonatal encephalopathy; due to perinatal oxygen
deprivation = most common!!!!
metabolite/electrolyte disturbances, bacterial meningitis, congenital defects(Arabians), older foals: trauma
Cerebellar Abiotrophy, Lavender Foal Syndrome,Juvenile Idiopathic Epilepsy
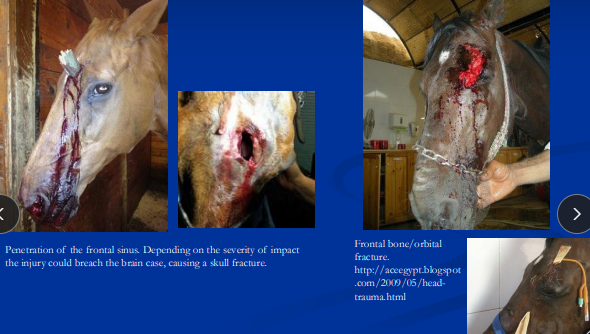
Cranial Trauma
Common injury: direct impact
Et: edema #1!!**, ↑ ICP, herniation
severe/uncontrolled edema: cerebral and/or cerebellar herniation
Cs: Depression, recumbency w/ stupor or coma, vestibular signs, blood/CSF from ears/nose = fracture, abnormal pupils, head tilt
Frontal/parietal/orbital: concussion, contusion, hemorrhage, brain parenchyma disruption
Petrous temporal/occipital: very common - young by flipping over backwards
vestibular dysfunction, facial paralysis, bleeding from ears, optic nerve damage
Poll injuries: hyperextension of neck, basilar fractures = fractures/b-sphenoid & b-occipital bone separation = intracranial hemorrhage & severe brain injury, guttural pouch hemorrhage, tearing optic nerve: blindness
Rupture/avulsion of ventral straight mm &/or fracture at base of brain
Dt: rads, CT, MRI, endoscopy
Tx: Stabilize airway / padding, IV catheter, Mannitol/furosemide (not w/ hemorrhage), hypertonic saline, hyperventilation (foals), Sx for fragments, monitor BP
poor prognosis → hemorrhage in CSF, recumbence, seizures, coma, fixed pupils, erratic breathing
Metabolic and Hepatic Encephalopathy
Very common!
Et: hepatic failure, hyperammonemia, renal failure, uremia(head pressing), glucose/Na/Ca imbalance, hypercalcemia, Theiler’s dz, hyperlipemia, Plant Alkaloids toxicity, cholangiohepatitis, chronic hepatitis, mycotoxins
Cs: behavior changes, seizures
Tx: dextrose fluids, dietary modifications, lactulose, neomycin, metronidazole

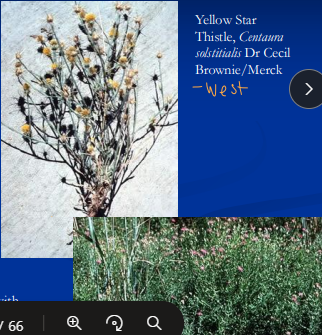
Nigropallidal encephalomalacia
Neuro toxins
Et: Repin toxin in Yellow Star Thistle & Russian Knapweed
necrosis of substantia nigra & globus pallidus: UMN → throat, tongue
Cs: facial dystonia, “sardonic grin,” inability to eat/swallow, dunks head into bucket for water
necropsy: neuronal cell bodies in midbrain
Tx: Euthanasia
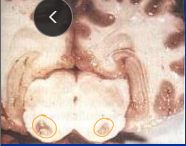

Locoism: acquired polysaccharide storage disease
Neuro toxins
Et: Oxytropis/Astragalus spp
endophytic fungus produces → Swainsonine causes lysosomal storage dz
Intracytoplasmic vacuolization of cells
Cs: ataxia, alternating somnolence/excitability, intention tremor, flaccid lips, dysphagia
young, herd problem
Px: permanent deficits, ill thrift
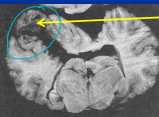
Leukoencephalomalacia: mycotoxin Moldy Corn Poisoning
Neuro toxins
Et: Fusarium verticilloides (fumonisin B1),
liquefactive necrosis of cerebral hemispheres and liver damage
Cs: rapid progressive signs, ataxia, blindness, seizures, agitation, death
Dt: toxin in feed
Tx: Euthanasia
Sorghum Toxicosis
Neuro toxins
Et: Sudan/Johnson grasses, sorghum hybrids
cyanide compounds or lathyrogens
Axonal degeneration in spinal tracts, dorsal roots, cerebellar peduncles
Cs: Hindlimb ataxia, urinary retention, cystitis
Often outbreaks/herd problem
Tx: remove source, manage bladder/cystitis
Bacterial Infections of the Nervous System
Brain Abscess: young horses
Et: head trauma, hematogenous spread (S equi zooepidemicus/equi), extension from sinus/middle ear & tooth abscess
Cs: brain signs, depression, circling, blindness, seizures, CN deficits, head pressing
Dt: inflammlatory leukogram, CSF (↑ neutrophils, protein), imaging
Tx: high-dose antibiotics (penicillin, sulfa), NSAIDs, DMSO, drain, seizure (phenobarbital)
Px: guarded-poor
Spinal Abscess:
Et: Strangles (Strep equi), septicemia in foals
extradural, vertebral body
Cs: spinal cord compression, progressive paresis/ataxia
Meningitis
Et: rare complication of neonatal septicemia or local extension
neuroborelliosis(lyme)
Sleeping sickness
Alpha Virus Encephalidities
Et: Mosquito-borne→birds, seasonal, viral
Horses dead end host
EEE: SE US, severe, high mortality, poor Px
very common
WEE: western US, rare
less common
VEE: FAD→regulated, South/Central America, zoonotic, severe
horses = major amplifiers
Cs: high fever, rapid progressive encephalopathy→ recumbence
incubation 1-3w
Dt: IgM ELISA (MAC-ELISA), CSF neutrophilia
Tx: supportive, core vax → prevention
x3 in 1st year, then annually
Combo w/ tetanus
West Nile Virus
mosquito-borne encephalomyelitis virus, seasonal
Et: Endemic in north america, polioencephalomyelitis
gray matter of brainstem, spinal cord
Cs: weakness, stumbling, recumbence, muscle fasciculations, CN deficits, blinking, twitching muzzle
Dt: IgM ELISA
Tx: supportive, sling support, core inactivated vax: protective
Px: 30% mortality, worse if recumbent
Rabies
fatal viral encephalomyelitis → saliva
DDX MUST be considered for any undiagnosed encephalopathy
Et: zoonotic, raccoon(#1), skunk, fox, bat
bite causes virus ascends nerves, varies from days to long incubation
typical bites: muzzle/face/distal limbs
Cs: paralytic (ascending paraparesis), encephalopathic (“furious/dumb”), terminal hyperesthesia, self-mutilation, recumbency → death
Dt: DFA on brain postmortem(brainstem & cerebellum), limit exposure: gloves/wash hands
no antemortem test
NOTIFY PUBLIC HEALTH OFFICALS!!
Tx: Euthanasia, core killed vax → x2 @ 6/7m & annual
prevention is key!
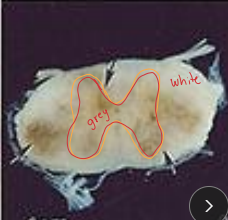
Equine Protozoal Myeloencephalitis (EPM)
The most common infectious equine CNS disease
brainstem & spinal cord most common
Et: Sarcocystis neurona, opossum** → horse dead end host
sporocysts in contaminated feed/water
focal/multifocal gray + white lesions → hemorrhage, and necrosis
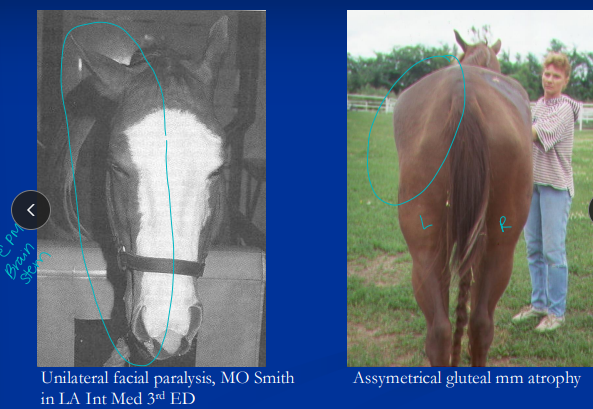
Cs: asymmetrical ataxia(side of lesion), focal muscle atrophy w/ ± cranial nerve defects: facial paralysis, dysphagia, LMN signs(spastic hind limbs), CN 5(facial paralysis)
Dt: rule-outs, serology, CSF ELISA, necropsy (definitive)
+ serum titer = exposure
S neurona antibodies in serum & CSF: both positive = EPM
Tx: ponazuril, diclazuril, sulfadiazine/pyrimethamine(cheap)
best outcome when tx early!
Px: 60% improve, 20% full recovery, relapses common
Spinal Cord Trauma
White matter (long tracts): spastic paresis & ataxia behind lesion
Gray matter (LMNs): flaccid paresis & atrophy, focal/segmental
Et: edema, vertebral fracture, cord impingement
cervical spine from young horses → flipping over, pulling back
dens/atlas & thoracolumbar fractures: young
Cs: paresis, ataxia(disrupts long tracts)*, hypalgesia: diminished sensitivity or response to normally painful stimuli
Stable = standing Unstable= down
no brain signs, tetraparesis localizes to C1-T2
Tx: Non fracture/stable: DMSO, corticosteroids, NSAIDs, stall rest, Sx(unstable fractures)
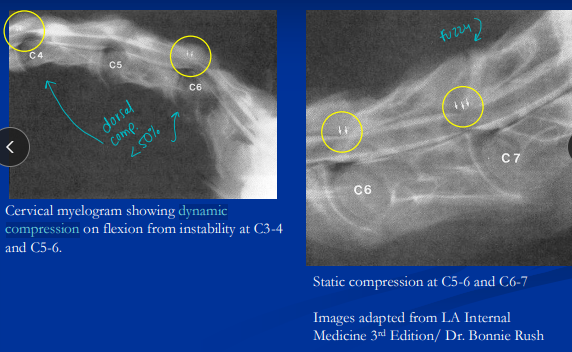
Cervical Stenotic Myelopathy (CSM)
“Wobbler Syndrome” → young, rapidly growing foals
OC: Developmental disease of growing cartilage
Et: Abnormal vertebral growth/development (osteochondrosis OC), Instability/malformation with cord compression
Most common non-infectious neuro dz of horses!!
Abnormal growth & development = cervical cord compression & tetraparesis & spastic ataxia
cervical: Osteochondritis dissecans (OCD) of facet joints &/or Physeal dysplasia
Types:
Type I (Dynamic instability/high): C3-C6, intermittent, young horses
Type II (Static compression/low): C5-T1, constant, older horses
present @ 2-5 yrs
Cs: young Clumsy → BAR, stumbling, falling, poor performance, UMN + proprioception defects, spastic tetraparesis, hindlib ataxia(more severe)
Dt: rads, sagittal ratios, myelography, CT/MRI
Tx: reduce growth rate, Vit E supp, steroids, DMSO, Interbody fusion Sx “bagby”(type I), Dorsal laminectomy (type II)
Occipito-Atlanto-Axial Malformations (OAAM)
Stenosis/cervical spinal cord compression!
Et: Congenital defect
Cord compression at birth
Sig: Arabians, QH, Drafts
Cs: spastic tetraparesis & ataxia: from birth some a bit older, limited cervical ROM (cannot extend neck)
Dt: imaging(cervical), history, PE
Tx: euthanasia
Equine Neuroaxonal Dystrophy (eNAD) and Equine Degenerative Myelopathy (EDM)
Et: Dev degenerative dz of spinal proprioceptive tracts( ALL 4 limbs)
Vit E deficiency (mare or foal)
had no access to green grass/quality hay
Sig: 6-24m, QH
Cs: Symmetric ataxia @ 6-24m , clumsy young horse
Generally no CS(eNAD), CS showing (EDM)
Dt: exclusion, history of Vit. E deficiency, histopathology postmortem
Normal vitals, labs, CSF, cervical imaging
Tx: Vit E supp (prevents progression, not reversal)
Equine Herpesvirus-1 Myeloencephalopathy (EHM)
Herpes, reportable!, effects white matter
Et: Neurotropic EHV-1 strains → acute ataxia & sacral signs & abortion
Latent virus: resp dz, cell-associated viremia in CNS, endothelial infection
Vasculitis in thoracolumbar & sacral cord: edema, hemorrhage, infarction
Sig: Adults >3y, event/comingling/stress outbreaks
Cs: Acute onset hindlimb ataxia, urinary retention, bladder paralysis, tail/anal tone loss, penile prolapse, fever
RARE: encephalopathy/brainstem/CN signs
Dx: ↑ protein, pleocytosis, xanthochromia-yellow (CSF tap); PCR(nasal/blood), paired sera (4x titer rise), IHC(necropsy)
Tx: NSAIDs, steroids, DMSO, antivirals (valacyclovir @ risk), biosecurity, quarantine, vax (resp only; not protective for CNS dz)
Px: 40% mortality, residual deficits
Post-Anesthetic Myelomalacia
Et: dorsal recumbent anesthesia
ischemic injury to lumbosacral spinal cord gray matter
Sig: young draft horses after Sx
Cs: Fail to rise, bilateral hindlimb paresis, paralysis
Ddx: Type I PSSM (draft breeds), Post-anesthetic myopathies/neuropathies (treatable)
Px: poor, don’t recover
Vestibular Disease
Vest. system: Maintain posture, muscle tone & equilibrium, Orientation of head
Et: trauma, infection, petrosal fractures, temporohyoid osteoarthropathy, otitis media-interna
Central: medulla, pons, cerebellum
Peripheral: CN VIII; common in horses → temporal bone
CN VII & VIII run close together, lesions may effect both
Facial paralysis very common
Cs: Head tilt, leaning, falling, rolling, resting horizontal fast nystagmus
Signs ipsilateral(same side) to lesion
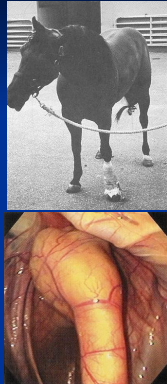
Temporohyoid Osteoarthropathy
Et: otitis media, guttural pouch dz, cribbing, idiopathic degen
Bony proliferation, sclerosis, fusion of temporohyoid articulation
Stenosis of ear canal, obliteration of tympanic bulla
Cs: mastication pain, head rubbing, head shaking
spontaneous fracture(due to fusion): acute vestibular signs + facial paralysis
Dt: endoscopy, radios, CT
Tx: anti-inflam, antibiotics, protect cornea, ceratohyoidectomy Sx→ prevent fracture
Otitis Media–Interna
Cs: vestibular dz, facial paralysis,
Extension beyond inner ear: osteomyelitis calivrium, subdural abscess, meningitis → lead to CNS signs
Dt: tympanocentesis, cytology/culture, rads/CT/MRI
Tx: aggressive antibiotics, anti-inflammation → less severe
Pharyngeal & Laryngeal Neuropathies
Pharyngeal:
Et: guttural pouch mycosis, trauma (surgery, fractures), neoplasia
Cs: dysphagia, feed in nostrils, weight loss
Laryngeal:
Et: Idiopathic left laryngeal hemiplegia, recurrent laryngeal nerve injury: (perivascular injection of NSAIDS) or lead poisoning (polyneuritis)
Cs: abnormal whinny, inspiratory noise, obx
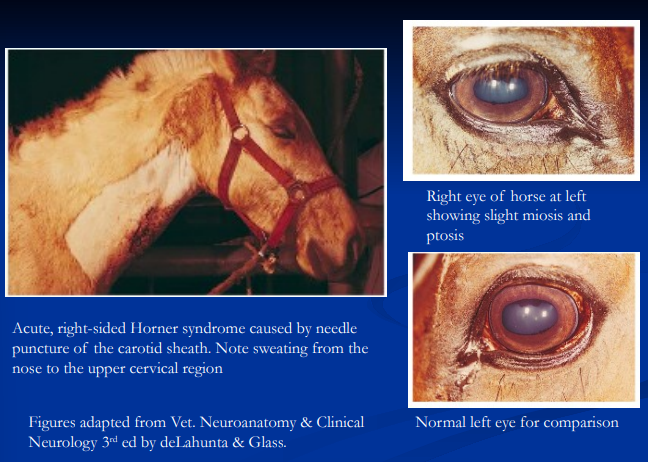
Horner Syndrome
Et: cranial trauma, guttural pouch disease, cervical injections, SC injury, brachial plexus injury, thoracic trauma/mass
disruption of Sympathetic pathway dz to head/neck
Cs: Ptosis, enophthalmos, 3rd eyelid prolapse, miosis, focal sweating (distribution helps localize lesion)
Neuropathic (Photic) Head Shaking
Et: trigeminal (CN V ophthalmic branch) hyperesthesia
exposure to light or environmental stimuli
Cs: head shaking, sneezing, rubbing, snorting
progressive
Dx: r/o other head shaking issues
Tx: Nose nets, UV masks, cyproheptadine, carbamazepine, euthanasia(many cases are debilitating)
Polyneuritis Equi (Cauda Equina Neuritis)
Et: Immune-mediated
chronic granulomatous inflam, fibrosis of cauda equina nerve roots
Cs: hyperesthesia around rump/tail, tail rubbing!!, flaccid bladder (overflow incontinence), urine scald, fecal retention, tail paralysis/atrophy, perineal anesthesia, penile prolapse/anesthesia
Tx: no cure, corticosteroids(temp effect), catheterization, manual rectal emptying, nursing care, euthanasia
Stringhalt
characteristic gait abnormality spasmodic hyper-flexion of one or both hind limbs!
Et: peripheral axonal degeneration of peroneal nerve
Sporadic: usually unilateral, often after hock injury
Epidemic: herd outbreaks, bilateral, Plant tox: flatweed, false dandelion, cheeseweed
Cs: spasmodic hyperflexion of hindlimbs
Tx: tenectomy of lateral digital extensor → sporadic
remove from pasture → epidemic
Dysautonomia (Equine Grass Sickness)
generalized GI motility disorder
Et: enteric nervous system, ANS ganglia degeneration
idiopathic, C botulinum type C toxin
Sig: pastured horses, UK
Cs: Dysphagia, gastric dilation, reflux, impaction, SI ileus, colonic impaction, death
Px: fatal

Traumatic Peripheral Nerve Injuries
Et:
Facial nerve: base of ear or halter injury under anesthesia
Suprascapular nerve: harness/collar injury
Sweeney
Radial nerve: trauma, fracture, anesthesia
Brachial plexus: root avulsion, limb paralysis
Femoral nerve: anesthesia, pelvic/femur fracture
Obturator nerve: dystocia, pelvic fracture
Sciatic/peroneal nerve: IM injection in foals, pelvic trauma, anesthesia
Tx: Sx, time, anti-inflam, corticosteroids, slings/splints, hydrotherapy, eye care (lubricants, tarsorrhaphy)
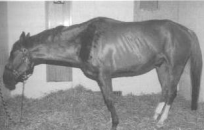
Equine Motor Neuron Disease
Et: Vit E deficiency, poor hay, no pasture, stabled
degeneration of LMNs in cord & brainstem
Cs: weakness, trembling, recumbency, weight loss, muscle atrophy, base-narrow stance, dropped head, elevated tailhead
Dt: low serum Vit E, muscle biopsy (sacrocaudalis), retinal lesions
Tx: Vit E supp, pasture access
Px: guarded
Botulism
Et: C botulinum toxin (types B, A, C) blocks NMJ
Forage: ingested contaminated feed, silage, carcasses
many horses effected/herd issue
Wound: rare
Toxoinfectious: foals ingest spores and toxin produced in gut
“Shaker foal” → endemic areas
Cs: weakness, dysphagia, generalized paresis, recumbency, resp failure, flaccid paralysis!
signs occur 1-17d after ingestion/exposure!!
Dt: toxin ID (mouse bioassay on feed/poop)
Tx: Antitoxin, toxoid vax → prevention
good if remain standing
Tetanus
Clostridium tetani in wounds/conditions that favor anaerobic growth
spinal cord and brainstem, UMN w/ renshaw cells
CS: generalized muscle rigidity, vague stiffness, muscle spasms “sawhorse”, prolapsed 3rd eyelid, sensitive to touch/sound
End stage: respiratory failure
TX: wound debridement & antibiotics, antitoxin, acepromazine, quite place w/ low light, supportive care
Core vax: tetanus, revaccinate w/ injury or sx if vaccine was >6m ago
give toxoid and antitoxin together
UA
Looks like Beer
Consistency: Turbid/viscous
Ca carbonate & mucus
Colour: Yellow–brown color
Pigments: hemoglobin, myoglobin, bilirubin, plant pigments, drugs
Bld: kidney, bladder, urethra
Dz: NSAID injury, neoplasia, cystitis, idiopathic hemorrhage
USG: 1.025–1.060
Isosthenuria = 1.008–1.017
pH: alkaline
7.5–9
Absent: glucose, protein, bacteria, casts
Acute Renal Failure
Et: >70–80% nephron loss & Isosthenuria in the face of azotemia!!
Pre-renal: ↓ renal perfusion from hypovolemia/fluid defect, shock, dehydration
Physiologic oliguria, reversible
Renal (intrinsic): ischemic injury =Hypoxia, toxic injury
Commonly acute tubular nephrosis
shock, SIRS/endotoxemia, sepsis, NSAIDs, aminoglycosides, tetracyclines, myoglobin (rhabdomyolysis), hemoglobin, cantharidin (blister beetles), vit D/K3, acorns, heavy metals
renal ischemia is a major predisposition for
toxic injury
Cs: Depression, edema, encephalopathy
Dt: azotemia, ↓ Na, ↓ Cl, ↑ K, isosthenuria, aciduria, ↑ GGT:Cr, casts
Tx: Fluids!! (until Cr stabilizes), diuretics (furosemide) until CK drop
Monitor: urine output, lytes, creatinine, PU/PD will persist during recovery
Goal: convert oliguria → polyuria
can’t concentrate urine, &/or creatinine
remains elevated, there is chronic renal disease
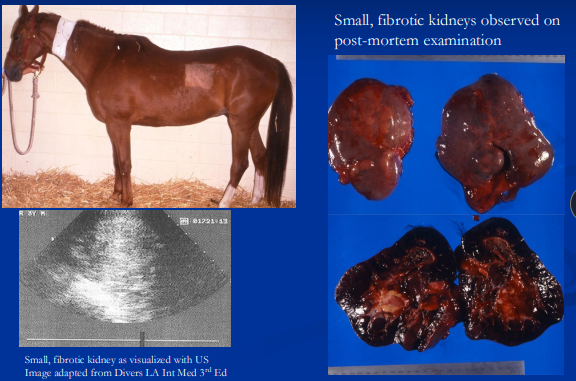
Chronic Kidney Disease
Irreversible, progressive
Et: >70–80% nephron loss = renal failure and compensatory hypertrophy, reduced nephrotic mass
Congenital: agenesis, dysplasia, polycystic kidney
Sig: Young horses (1–5 yrs) @ birth, poor BCS, rough coat
Acquired: chronic interstitial nephritis (#1), infiltrative diseases (LSA, neoplasia), glomerulonephropathy → hypoalbuminemia and edema
Cs: Gradual weight loss, poor appetite, rough coat, PU/PD, edema, dental tartar
Dt: azotemia, isosthenuria,↓ Na, ↓ Cl, ↑ K, metabolic acidosis, small fibrotic kidneys, ± ↑ Ca
Tx: Hydration, salt, grass hay (↓ Ca), palatable concentrate, add fat, lyte balance, tx acidosis
Px: poor
Renal Tubular Acidosis
Et: Tubular dysfunction → bicarb loss → hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis
Cs: depression, weakness, inappetence
No azotemia
Tx: bicarb + KCl
Pyelonephritis
Et: ascending or hematogenous: Uncommon
R equi, strangles, lepto, septic foals
Cs: fever, depression, pyuria, bacteriuria, hematuria
Dt: leukocytosis, ↑ fibrinogen,
UA, culture, US, endoscopy, lepto PCR
Tx: antibiotics based on culture
Cystitis (Lower UTI)
Et: secondary to bladder stones, paralysis, incompetent sphincter (mares), catheter, abnormal flow
mares more prone, iatrogenic w/ catheters
Cs: stranguria, pollakiuria, incontinence, hematuria
Dt: >10 WBC/hpf or >20 bacteria/hpf, culture, endoscopy
Tx: based on culture: TMS, ampicillin, ceftiofur, penicillin
Urolithiasis
Types:
Ca carbonate: #1, yellow spiculated
Ca phosphate: Grey-white, smooth
Sites: kidney, ureter, bladder, urethra
some: spontaneous develop in bladder, CKD
Renal Calculi: originates from renal pelvis → hydronephrosis, abdominal pain
Sig: males > females
Cs: pain, hematuria, obstruction, CKD
Dt: US, rectal, endoscopy
Tx: lithotripsy, cystotomy, nephrectomy if unilateral,
↑ water, add salt, avoid alfalfa, reduce calcium intake
Control of Bladder Micturition
Pontine micturition center in brainstem controls:
Filling/storage: inhibits detrusor, parasympathetic LMNs, closes sphincters
Voiding: contracts detrusor, relaxes sphincters
Ascending: sensory
Descending: UMN
Neurogenic Bladder
Et: Polyneuritis equi, EHV-1, sorghum toxicity, EPM, neoplasia, spinal trauma
UMN spastic bladder long tracts: lesion above sacral segments
Cs: spastic bladder, open internal sphincter, and spastic urethralis → dysynergia(detrussor & urethralis), intermittent incontinence
LMN Flaccid bladder: lesion in sacral cord/nerves
Cs: flaccid, distended bladder, overflow incontinence, loss of perineal reflex
Tx: Manual evacuation, catheter, Bethanechol (stimulate detrusor), Phenoxybenzamine (relax sphincter), Dantrolene (relax urethralis), Phenazopyridine (mucosal analgesic)
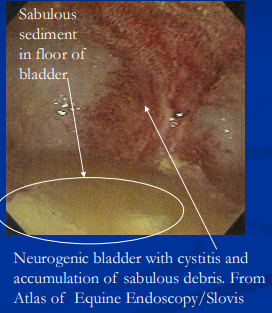
Px: risk of sabulous cystitis from Ca carbonate buildup
sabulous cystitis: accumulation of sediment in floor of bladder
Detrusor Atony & Idiopathic Sabulous Cystitis
Mares, idiopathic
retention of urine & accumulation of sabulous debris = ultimately resulting in detrussor atony
Et: neuro dysfunction, pain = urine retention , idiopathic in geldings w/ sabulous cystitis
Cs: Flaccid bladder
Tx: flush bladder, antibiotics, Bethanechol (stimulate detrusor), Phenoxybenzamine (relax sphincter)
Px: fair, chronic
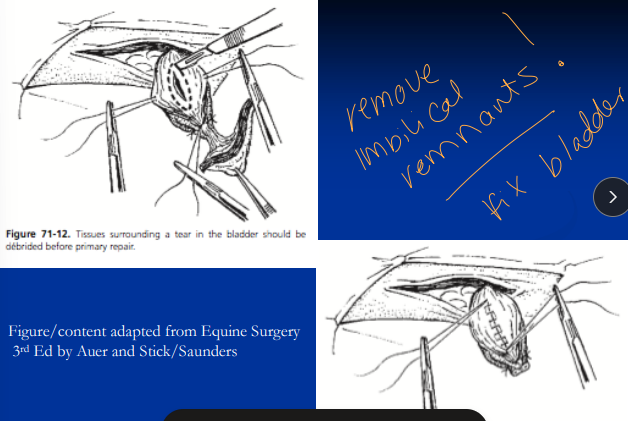
Uroperitoneum
Et:
Foals: Ruptured bladder(most common), urachal tear(dorsal), ureter, hospital aquirred
Adults RARE: trauma, dystocia, obstruction(males)
Sm: dorsal tears: medically managed, LG: SX repair
Dt: azotemia, ↓ Na, ↓ Cl, ↑ K, met. acidosis, peritoneal Cr > serum Cr, US, abdominocentesis
Tx: 09% NaCl + dextrose/bicarb (#1), Sx→ stabilize first
avoid K fluids
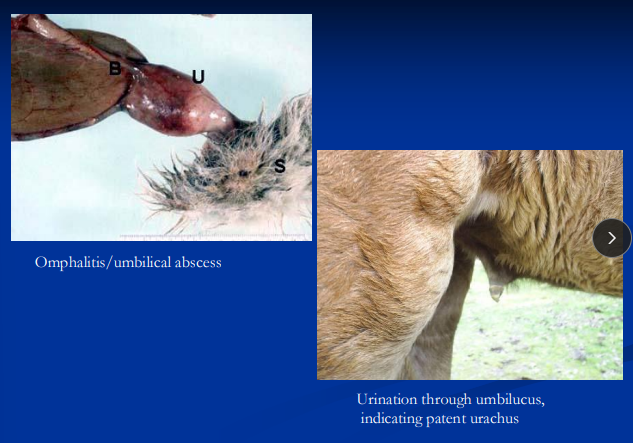
Omphalitis
infection of the umbilical stump, the remnant of the umbilical cord left after birth
Et: failure passive transfer, ascending infection through urachus, arteries, vein
Cs: umbilical inflam, patent urachus, abscess, uroperitoneum
Dt: palpation + US for signs of infection!
Tx: antibiotics, Sx removal of infected/leaky remnants
Parturient & Urethral Injuries
Et: bladder rupture, urethral incompetence/laceration, detrusor injury, bladder prolapse→ urethra or cervical tear
Sig: Mares
Tx: catheter, Sx, Bethanechol (stimulate detrusor),
Male Dorsal Urethral Hemorrhage
Et: Defect in dorsal urethral mucosa communicating with corpus spongiosum
Cs: hemospermia &/or expulsion of blood at end of urination
blood staining on canon/pasterns
Tx: perineal urethrotomy/transect bulbospongiosum
heals by 2° intention, relieves pressure
Polyuria & Polydipsia
Et: renal failure, PPID(cushings), psychogenic(wet stall), corticosteroids, α2 agonists, diuretics
Cs: r/o renal issues 1st
PU: >25 L/day urine
PD: >50 L/day water
Dt: water deprivation test (psychogenic: primary) very common
Urinary Neoplasia
Et:
Kidney: renal cell carcinoma (old), nephroblastoma (young)
Bladder: SCC, TCC, adenoma
Urethra/external genitalia: SCC, sarcoid, melanoma
Dt: rectal exam, US, biopsy
Tx: nephrectomy if unilateral
Castration Surgical Planning Considerations
Why: Stop stud behaviour, genetic soft cull, Dz of testis or spermatic cord
When: 1.5–2 years
Sx at 1.5–2 years allows MS dev under testosterone
Older stallions have learned behaviour persists + more complications
Risks: Hemorrhage, preputial/scrotal swelling, septic funiculitis, schirrhous cord, septic peritonitis, hydrocele, omental prolapse, visceration or eventration
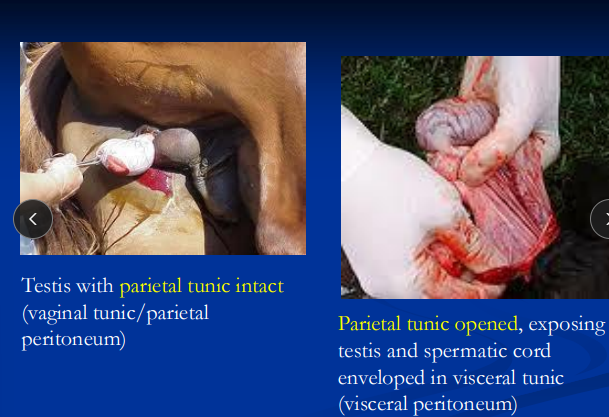
Pre and Post Op Considerations for Castration
Pre-Op: make sure you have the RIGHT horse
Tetanus Vax: Must be current
Give tetanus toxoid if uncertain
Confirm two testes in scrotum; no inguinal hernia
Rx: ± Penicillin(clostridial), flunixin
Ventral scrotum incision, no ligatures
Nut to nut : emasculators
Op:
Closed: Young with small cords
Open: Most common
Recombinant R lateral: xylazine (sedation), ketamine (induction)
Better control, safety, hemostasis BUT risk & $$ of GA
Standing: alpha-2 + butorphanol (sedation), local to testicles & cords
Avoids GA, cheaper BUT bad for movement, bleeding, poor behaviour, ponies, donkeys, mules, small testes
Post-Op:
Incisions left open for drainage
Confine 24 hrs, then exercise twice daily for 2w
reduce edema and promote drainage
Routine Castration
Position:
R Lateral recumbency: upper hindlimb pulled forward & secured
Remove halter, pad, cover eyes
Standing: Wrap tail
Insise:
Compress testes into scrotum
10 cm incision over each testis, parallel to median raphe, 2 cm from midline
Exteriorize: via ventral scrotal incisions
Closed: Tunic not opened and strip fascia around cord proximally
Open: Open vaginal tunic, split mesorchium
Cut: Apply emasculator “nut to nut”
Open: Crush vessels, then vas deferens, cremaster, tunic separately
Close: Incisions left open for drainage
second intention healing
Testicular Descent
Normally occurs by 1m
Testis initially behind kidneys
Gubernaculum testis: connects testis to scrotum
Testis enlarges → regresses → descends via inguinal canal
Gubernaculum contracts, pulling testis into scrotum
Inguinal extension of GT
becomes proper lig of testis, lig of tail of epididymis, scrotal lig
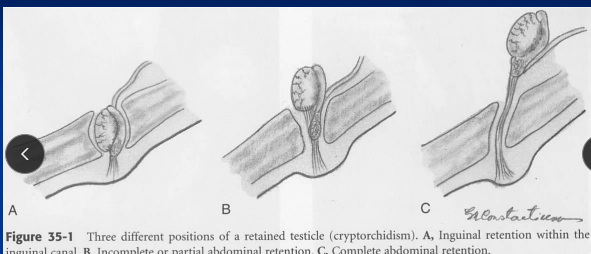
Cryptorchidism
Et: Failure of, one > both, testicles to descend into scrotum
Inguinal: testis in inguinal canal
Incomplete abdominal: epididymis in canal, testis just inside internal ring
Complete abdominal: both epididymis & testis retained in abdomen
Sig: Percherons, Saddlebreds, QH
TB are RARE
Cs: late descent at 2-3y, absent testes, stallion-like behavior, unclear castration history
produce testosterone, no sperm from retained testes
Dt: Palpation, US, high testosterone/estrogen, hCG stim, Laparoscopy (definitive)
Tx: castration: inguinal (most common)
Cryptorchid Castration
Inguinal approach (#1):
GA, dorsal recumbency
Incise over superficial ring
Locate inverted vaginal process and exteriorize
Para-inguinal: incomplete abdominal retention
Considered safer than inguinal
Abdominal: complete abdominal retention
Laparoscopic: Minimally invasive option
Parturition in Mares
Gestation: 320-365 days
avg 340, generally are constant year to year
premature if <320d
Stage 1: 4-24h
Discomfort, restlessness
Stage 2: delivery within 20 min
Rupture of chorioallantois (water breaks)
Prolonged = dystocia and birth asphyxia risk
Stage 3: <3 hrs
Expulsion of fetal membranes
Neonatal Behavior and Vitals
Behavior: precocious, BAR, teat seeking
Sternal in 10 min
Abnormal = Not sternal by 10 min
Standing by 1 hr
Abnormal = Not attempting to rise by 20 min or standing by 1 hr
Suckling by 2 hrs
Abnormal = Weak suckle reflex at 10 min
Sleep ~50% of time, stretches then teat seeks
HR: 80–120
RR: 40–60
Abnormal = not breathing in 30 sec
Temp: 99–102°F
Diet: Consume 25%+ BW in milk/day
Feces: Pass meconium at 12–24 hrs
Neonatal Septicemia
Et: FPT → bacterial dissemination
Bacti enter umbilicus, MM, GIT, lack of colostrum
Cs: neonatal weakness, organ failure, sepsis, dropped ears, fever Prolonged CRT, weak pilse, cold limbs
major cause of neonatal death
Tx: Correct FPT, Antibiotics, Resp Support, Cardio Support, Nutrition, Seizure Management, Umbilical Care, Enviro Management
Treat ASAP
Px:Poor
Peripartum Asphyxia (Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy)
Et: oxygen deprivation “dummy foals”
Prenatal: placental insufficiency, fescue tox, bacterial, torsion
Parturient: birth asphyxia
Postnatal: immature lungs, aspiration, rib fractures
Cs: neonatal weakness, disoriented, no suckle reflex, seizures, coma, brain edema
Tx: Correct FPT, Antibiotics, Resp Support, Cardio Support, Nutrition, Seizure Management, Umbilical Care, Enviro Management
Px: Good if full-term
Prematurity/Dysmaturity
Et: Placental insufficiency, placentitis, fescue toxicosis late pregnancy(placenta edema), late abortion
Premature: < 320 days
Dysmature: signs of immaturity despite normal gestation
Cs: neonatal weakness, abnormal ossification (carpal/cuboidal bones), tendon laxity, respiratory issues, domed head, floppy ears, silky hair coat
Tx: Correct FPT, Antibiotics, Resp Support, Cardio Support, Nutrition, Seizure Management, Umbilical Care, Enviro Management
Px: Fair to Poor
Placentitis
Ascending bacterial infection in 3rd trimester
Mare not very sick
CS: Vaginal discharge, premature udder development, premature lactation(colostrum lost)
death, abortion, premature, Premature placental detachment, prenatal septicemia
Foals hypoxemic in utero, high rish for asphyxia : small weak foals
high risk for FPT
Fescue toxicosis
Mares ingest tall fescue pasture in late pregnancy
Ergots Alkaloids induce the endocrine dysfunction and negative effects on preg/lactation
CS: placental edema and insufficiency, hypogalactia(low milk supply) & lack of udder development!
Take mare off pasture >30d before gestation
Supportive & Intensive Care for Neonates
Correcting FPT: colostrum within 12hrs (15–2L in divided feedings), plasma transfusion after 12hrs (gut closure)
Goal is IgG >800 mg/dL by 24 hrs
Measure plasma IgG w/in 24h, test colostrum
Antibiotics: Ceftiofur (mild), beta-lactam + aminoglycoside (severe)
Broad spectrum (G-) for E coli, streptococci, anaerobes
Resp Support: insufflation (septic/recumbent), continuous (premature/asphyxiated)
Cardiovascular Support: use arterial blood gas analysis
Fluids: boluses (20 ml/kg), maintenance 100 ml/kg/day
Correct electrolytes & glucose
Pressors (dopamine/dobutamine): hypotensive
Nutrition: Mare’s milk (#1), goat’s milk, replacer, pan feed, NG tube, TPN
Goal is 15–25% BW milk/day, gain 1–3 lbs/day
Dextrose, AA, lipids
Seizure Management: diazepam/midazolam, phenobarbital, mannitol/furosemide (cerebral edema)
Umbilical Care: palpate, US; daily antibiotics or Sx removal
Omphalitis/omphalophlebitis common in weak foals
Enviro: padded stall, keep sternal and rotate hourly, ophthalmic care to prevent corneal ulcers