Food and Milk Sanitation
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
Food Sanitation
Practices involved in protecting food from risk of contamination, harmful bacteria, poisons, and foreign bodies.
Contamination
The presence of harmful substances in the food.
Cross Contamination
Occurs when microorganisms are transferred from one surface or food to another.
Food
Any substance whether simple, mixed or compounded that is used as food, drink, confectionery or condiments.
Food Safety
Overall quality of food fit for consumption.
Food Infection
Microbial infection resulting from ingestion of contaminated foods.
Food Intoxication
Type of illness caused by toxins produced by certain bacteria.
Food Spoilage
Means the original nutritional value, texture, flavor of the food are damaged, making it harmful to people and unsuitable to eat.
Foodborne Illness
A disease carried or transmitted to people by food.
Foodborne Outbreak
An incident in which two or more people experience the same illness after eating the same food.
Time-Temperature Abuse
Food that has been exposed to temperature favorable to the growth of foodborne microorganisms.
Potentially Hazardous Foods
Food in which microorganisms can grow rapidly; often moist, high protein, slightly acidic.
Personal Hygiene
Sanitary health habits that include keeping the body, hair, teeth, clothes and washing hands regularly.
Temperature Danger Zone
Temperature range (41⁰F - 140⁰F) where foodborne bacteria grow and reproduce.
Biological Contaminants
A microbial contaminant that may cause a foodborne illness (bacteria, viruses, fungi, parasites, biological toxins).
Physical Contaminants
Any foreign object that accidentally finds its way into food.
Chemical Contaminants
A chemical substance that can cause foodborne illness.
Main Causes of Food Borne Illness
Cross-Contamination, Time-Temperature Abuse, Poor Personal Hygiene.
Hand to Food Contamination
Occurs when contaminated hands handle cooked or ready-to-eat foods.
Food to Food Contamination
When harmful organisms from one food contaminate other foods.
Equipment to Food Contamination
Occurs because the equipment or utensils were not properly cleaned and sanitized between each use.
Preventing Biological Contaminants
Purchase foods only from reputable suppliers, maintain good personal hygiene, and clean and sanitize equipment.
Preventing Physical Contaminants
Wear hair restraints, avoid jewelry, and clean can openers regularly.
Preventing Chemical Contaminants
Teach employees how to use chemicals and store them in original containers.
Proper Handwashing
Critical for preventing contamination and ensuring food safety.
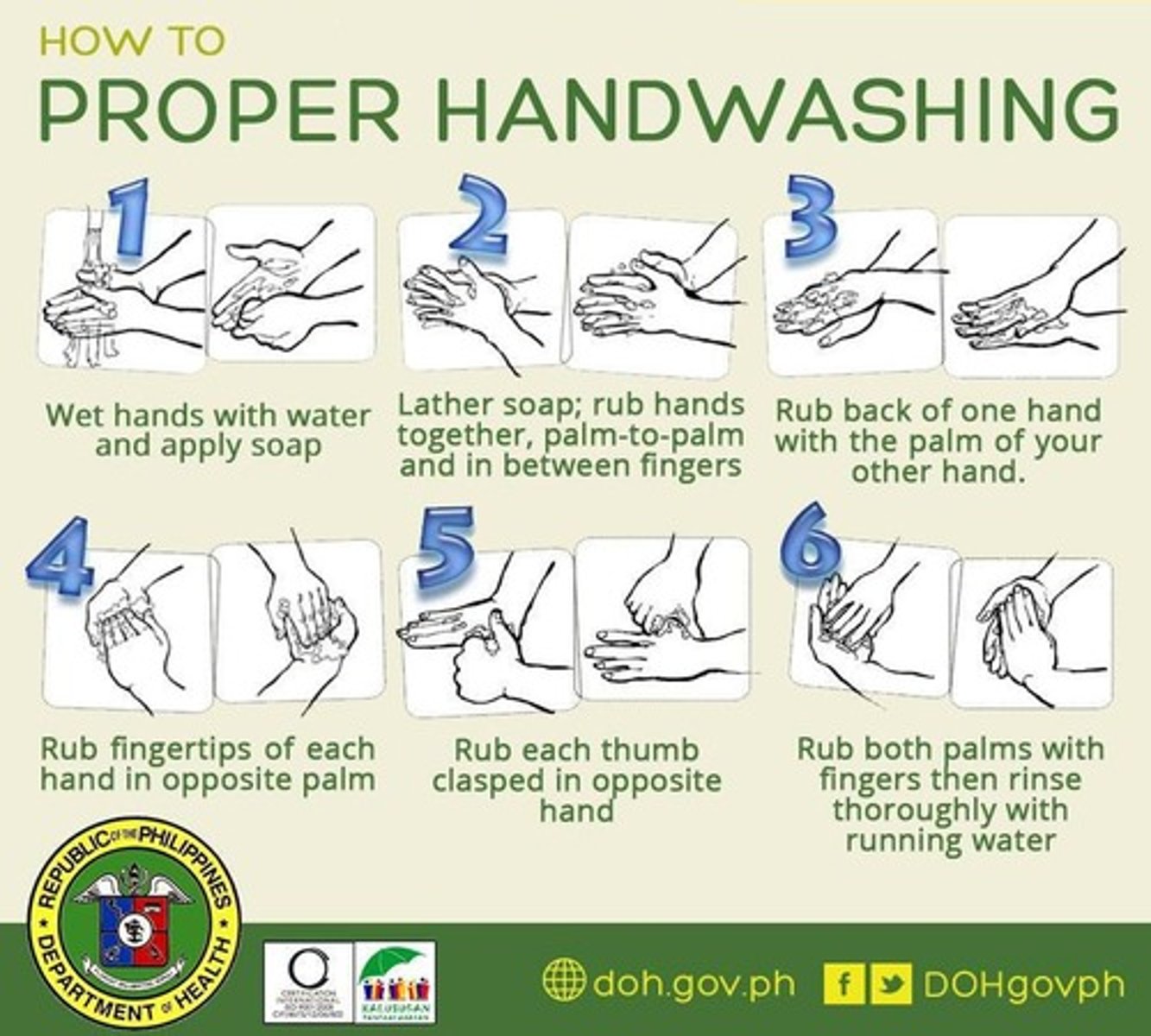
Temperature Abuse
Foods that have not been to a safe temperature or kept at the proper temperature.
Psychrophilic bacteria
Spoilage organisms that grow within the temperature range of 32°F (0°C) - 70°F (21°C).
Mesophilic bacteria
Bacteria that grow at temperatures of 70°F (21°C) - 110°F (43°C).
Thermophilic bacteria
Bacteria that grow best above 110°F (43°C).
Poor Personal Hygiene
Linked to numerous outbreaks of food poisoning; food handlers can contaminate food.
Carrier
A person who harbors and may pass on harmful bacteria without showing signs of illness.
Route of Contamination
Bacteria found in feces, urine, nose, mouth, hair, and cuts can be transferred to hands and food.
Good Personal Hygiene Basics
Includes taking a bath daily, wearing appropriate attire, and observing proper hand washing procedures.
Food Preservation
Techniques that allow food to be kept for extended periods without losing nutritional quality.
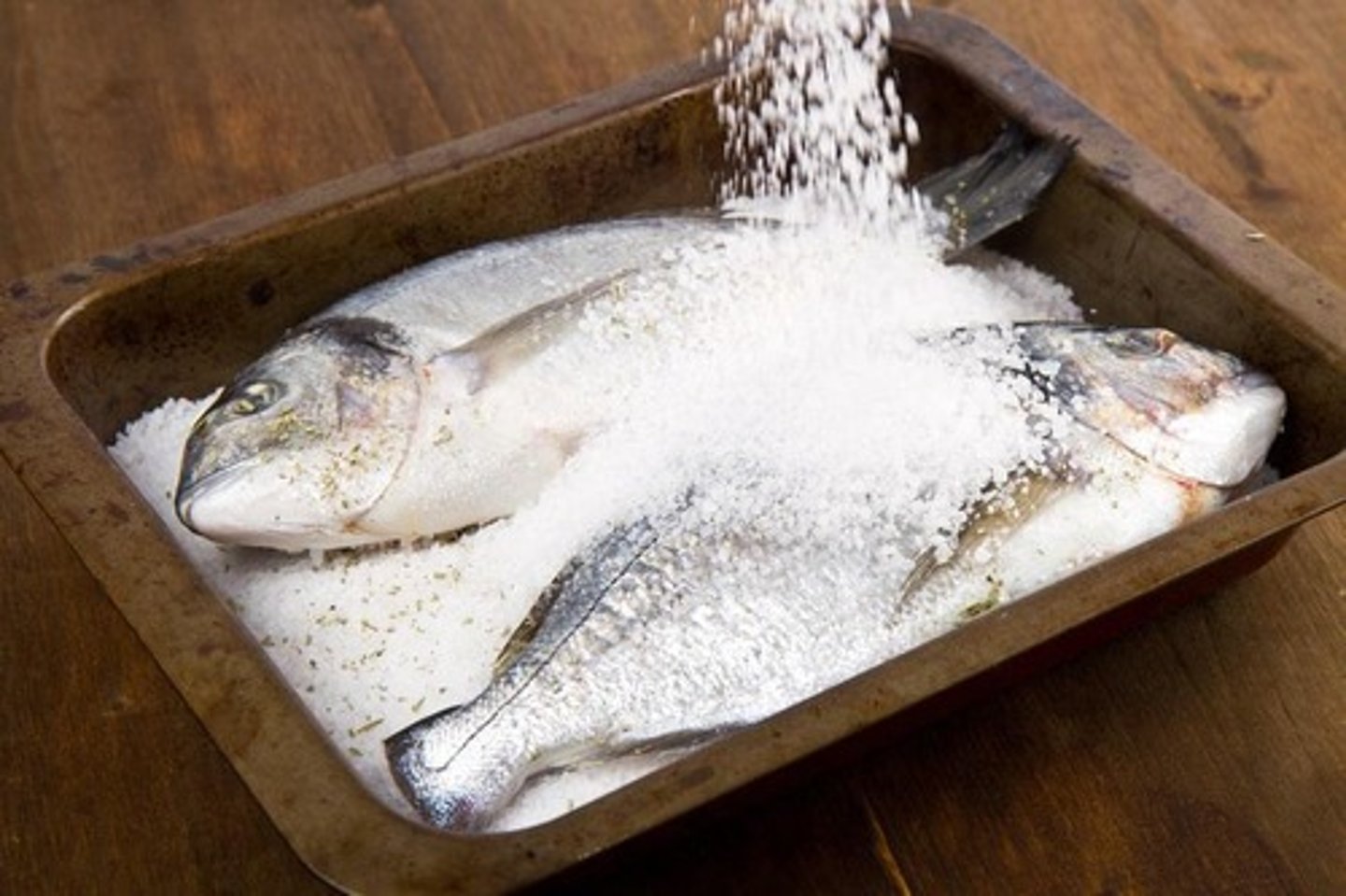
Salting
Preserves food by drawing water out, preventing bacteria from growing.

Curing
An ancient food preservation technique that reduces water activity to prevent bacterial growth.
Refrigeration
Preserves food by slowing down the growth and reproduction of microorganisms.

Freezing
A commonly used process for preserving a wide range of food by stopping microbial growth.

Sugaring
Draws water from microbes, dehydrating and killing them to prevent spoilage.
Pickling
Preserving food in an edible, antimicrobial liquid, classified into chemical and fermentation pickling.
Canning
Involves cooking food, sealing it in sterile containers, and boiling to kill remaining bacteria.

Heating
An effective way of preserving food by killing harmful pathogens at high temperatures.
Burial
Preserves food by burying it below the frost line, utilizing cool temperatures and soil conditions.
Botulism
A bacterial intoxication caused by a neurotoxin, leading to dizziness and difficulty in breathing.
Campylobacteriosis
A bacterial infection requiring strict air for growth, causing diarrhea and abdominal pain.
E-Coli Infection
A bacterial intoxication that can cause bloody diarrhea and kidney failure.
Listeriosis
A bacterial infection from undercooked foods, causing headaches and confusion, dangerous for pregnant women.
Salmonellosis
Bacterial infection caused by fecal contamination.
Symptoms of Salmonellosis
Stomach cramps, diarrhea, headache, nausea, fever, vomiting.
Prevention of Salmonellosis
Good personal hygiene, avoid cross contamination, cook all meat carefully.
Shigellosis
Bacterial infection characterized by diarrhea and fever.
Symptoms of Shigellosis
Diarrhea, fever, abdominal cramps, dehydration.
Prevention of Shigellosis
Good personal hygiene, avoid cross contamination, use clean water, control flies, cook foods properly.
Food Sources of Shigellosis
Foods prepared by human contacts, salads, ready to eat meats.
Staphylococcal Illness
Bacterial intoxication leading to nausea and vomiting.
Symptoms of Staphylococcal Illness
Nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, headaches.
Food Sources of Staphylococcal Illness
Foods prepared by human contacts, leftovers, eggs, potato salad, salad dressings.
Hepatitis A Virus
Virus causing fever, fatigue, headache, nausea, and jaundice.
Prevention of Hepatitis A Virus
Handle foods properly, cook at recommended temperature, avoid raw seafoods.
Norwalk Virus
Virus causing nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain.
Prevention of Norwalk Virus
Cook foods to proper temperature, practice good personal hygiene.
Rota Virus
Virus leading to severe diarrhea among infants and children.
Symptoms of Rota Virus
Vomiting, low grade fever, watery diarrhea.
Anisakis
Parasite associated with foodborne infection from fish.
Symptoms of Anisakis Infection
Vomiting, abdominal pain, coughing, sharp pain, fever.
Food Sources of Anisakis
Raw undercooked seafoods, bottom feeding fish.
Cyclospora
Parasite causing infections in the small intestines.
Symptoms of Cyclospora Infection
Watery diarrhea, loss of appetite, bloating, stomach cramps.
Giardiasis
Parasite caused by Giardia doudenalis.
Symptoms of Giardiasis
Diarrhea, stomach cramps, nausea.
Trichinosis
Parasite caused by Trichiniella spiralis.
Symptoms of Trichinosis
Nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, fever, swelling of tissues.
Molds
Fungi that cause food spoilage and produce toxins.
Yeast
Fungi that can cause food spoilage, evidenced by bubbles and alcoholic smell.
Food Allergens
Cause the immune system to overreact, leading to hives and difficulty breathing.
Ciguatoxins
Toxins from contaminated tropical reef fish causing nausea and dizziness.
Scombrotoxin
Called 'histamine' poisoning, caused by eating food high in a chemical compound called 'histamine' which is produced by certain bacteria.
Symptoms of Scombrotoxin
Dizziness, burning sensation, facial rash, shortness of breath, peppery taste in the mouth.
Typhoid
A bacterial infection that can lead to a high fever, diarrhea, and vomiting caused by bacteria, Salmonella typhi.
Dysentery
A type of gastroenteritis that results in diarrhea with blood, transmitted by ingestion of unpasteurized milk or dairy products from tuberculous cows.
Bovine Tuberculosis
Caused by Mycobacterium, transmitted through unclean hands of milkers or contaminated animal products.
Diphtheria
An infection caused by the bacterium Corynebacterium diphtheriae, causing a thick covering in the back of the throat.
Septic Sore Throat
An acute, toxin, streptococcus infection of the throat producing fever, tonsillitis, and other serious effects.
Brucellosis
Consumption of raw milk and cheese made from raw milk is the major source of infection in man.
Q-Fever
A worldwide disease with acute and chronic stages caused by the bacteria Coxiella Burnetii.
Essential of Milk Sanitation
Includes healthy cows, clean and healthy workers, clean environment, separate milk room, proper design of equipment, effective sanitation, prompt cooling, and pasteurization.
Total Count Test
Determining the number of organisms which will grow on agar.
Butterfat Test
Determines whether the cream content is up to standard.
Chemical Test of Milk
Made when milk is suspected to contain preservatives.
Pasteurization
The application of heat to milk for the purpose of destroying disease-producing organisms.
Types of Pasteurization
Includes Holding or Vat Pasteurization, High Temperature Short Time Pasteurization, and Flash Pasteurization.
Sterilization
Attained by ultra high temperature but not high enough to destroy important nutrients in milk.
Grade A Milk
Has the lowest bacteria count and is grade sold in retail stores.
Ordinary Milk
Contains 8.25% solids non-fat like protein, lactose & minerals which are not fats and 3% of milk fat.
Raw Milk
Fresh, unpasteurized milk straight from the cow.
Chocolate Milk
Made by adding chocolate or cocoa and sweetener to 2% milk.
Nonfat Dry Milk
Obtained by removing water from pasteurized skim milk.
Fortified Milk
The addition of one or more vitamins, minerals, or proteins not already present in a food.
Buttermilk
Made by adding a special bacterial culture to milk to produce desirable acidity, body, flavor, and aroma.
Sweetened Condensed Milk
Prepared like evaporated milk, but with added sugar.