Emotional Learning - Limbic System and Goal Directed Behaviour
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
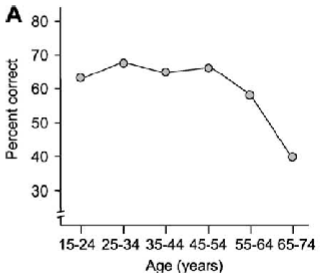
Normal, age-related cognitive decline
Many, but not all, cognitive function decline with age
Spatial memory is one of these
Spatial navigation task - finding objects in a maze (museum)
How does the hippocampus age
Does not appear to get smaller
Although evidence is mixed
Retains the same number of neurons
Functional connectivity is impaired
LTP does not last as long, and is not as strong
Impaired retrieval of spatial maps
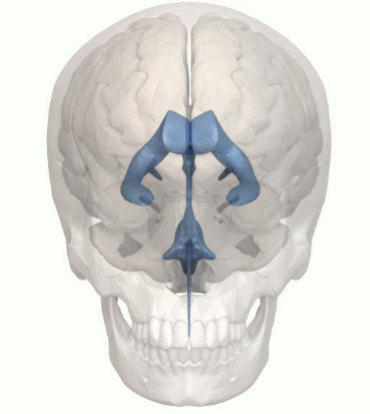
What structure does this image show?
Ventricles
Ventricular System
Ventricles filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Produced by ependymal cells which line ventricles
Shock absorber
Nutrient supply
Waste flush
approximately 125 mL at any one time and approx., 500 mL produced per day.
Common signs of Alzheimer’s Disease
Memory loss
Poor judgement leading to bad decisions
Loss of spontaneity and sense of initiative
Repeating questions
Trouble handling money and handling bills
Wandering and getting lost
Losing things or misplacing them in odd places
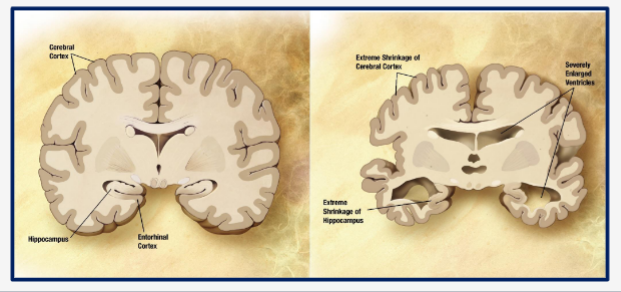
Alzheimer’s Disease
Loss of neurons in various brain regions
Particularly the hippocampus, and cerebral cortex
Alzheimer’s: Cause and Treatment
Accumulation of misfolded proteins in certain brain regions
Cholinergic nuclei, hippocampus and frontal cortex
Beta-amyloid (amyloid plaques)
Tau (neurofibrillary tangles)
Accumulation is toxic - mechanisms unclear
Some genetic risk
Memantine - slows excitotoxicity
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors - mitigates loss of Ach
Brain cholinergic system
Key nuclei:
Basal forebrain
Brainstem tegmentum
Project across the brain
Cortex
Hippocampus
Thalamus
Neuromodulatory functions:
Memory
cognition
arousal
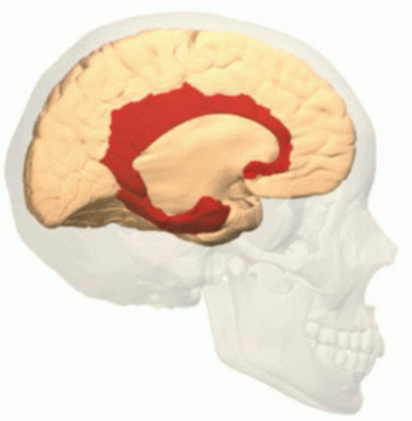
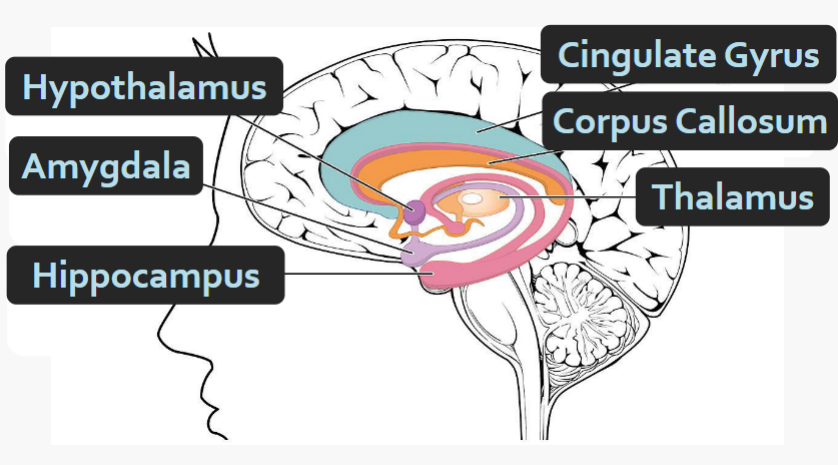
What structure is shown in the image?
The Limbic System
Components of the limbic system
Hippocampus
Amygdala
Hypothalamus
Fornix
Thalamus
Mamillary Bodies
(Cingulate gyrus)
(Orbitofrontal cortex)
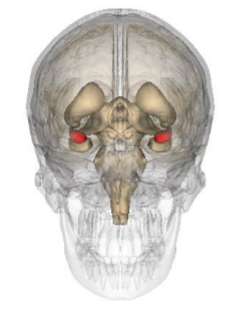
What structure is shown by the image?
The Amygdala
What does the amygdala do?
Salience, vigilance
Amygdalofugal pathway to/from the thalamus
Stimulation results in fear + aggression
Recognising fear in other people
Learning about cues
best understood in fear/danger
(more than just fear)
Amygdala - Clinical
Anxiety disorders
Hyperactive
Hypervigilance (PTSD)
Bilateral lesions - Kluwer-Bucy Syndrome (very rare)
Reduced fear/docility
Visual agnosia
Pica
Hyperorality and hypersexuality
Normally caused by surgical complications or HSV
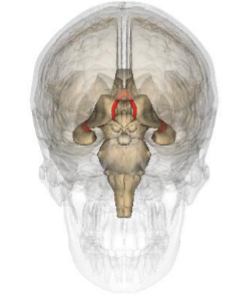
What structure is represented by this image?
The Fornix
What does the fornix do?
Hippocampal output
Connect left and right hemispheres
Helps the hippocampus function
Damage is rare
Looks like hippocampal damage
Anterograde amnesia
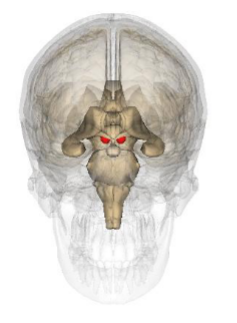
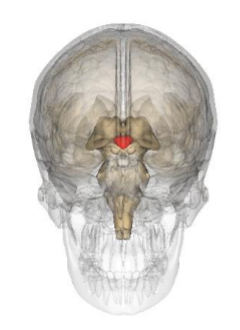
What structure is represented by this image?
Mammillary Bodies
Korsakoff’s Syndrome
Irreversible damage to the medial thymus and mammillary bodies
Most common cause is vitamin B1 deficiency
chronic alcoholism
Unable to absorb vitamin B1 (thiamine)
Direct toxicity of alcohol
Anterograde and retrograde amnesia
Confabulation
Little to no recovery
precise role for mammillary bodies in learning and memory
Which structure is represented by this image?
The Hypothalamus
What does the Hypothalamus do?
Start of a physiological output from the brain
Hypothalamus-Pituitary Adrenal (HPA axis)
Hormonal outputs - especially stress hormones
Also wired into the brainstem, autonomic system
Thermoregulation
Hunger, thirst etc.
The rest of the limbic system is trying to persuade the hypothalamus to do what the limbic system wants
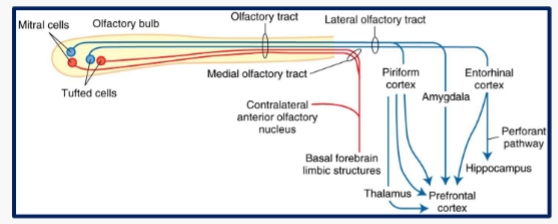
Olfactory Pathways
Don’t really go through the thalamus
Connect to limbic/memory systems - is a very powerful memory cue
Pavlovian (Classical) Conditioning
Hungry dog → Bell → Dog food
Hungry dog salivating (unconditioned response) → dog food (unconditioned stimulus)
Amygdala and classical conditioning
Amygdala is important for learning conditioned clues
Best understood role is learning about danger and fear
Probably important for all cues, not just fear-inducing
Learning about danger is really important
Extinction of Classical Conditioning
Learning about cues in our environment, that predict serious danger, is very important, and normal
This learning is very strong
Learning is when those cues are not associated with danger takes time
This ‘forgetting’ is new learning
The old memory is not ‘lost’
New memory is ‘stronger’, more salient
Post-traumatic stress disorder
Associated with significant trauma
risk of death or serious harm
Sufferer ‘re-experiences’ trauma
triggered by reminders, or reminders of reminders
conditioned stimuli
Is normal for a few weeks, becomes PTSD if it persists
Hyperarousal, hypervigilance (‘on edge’)
Avoidance
Emotional numbing
What is different in PTSD?
Functional neuroimaging
Amygdala
Hyperactive
Prefrontal cortex
Hypoactive
Smaller
Hippocampus
Smaller?
Impaired function
Patients exhibit behavioural signs of all of these
PTSD causes and treatments
Associated with significant trauma
Can be treated by Cognitive Behaviour Therapy
Exposure therapy using triggers
New learning takes time
Pharmaceutical treatment also common (SSRIs)
Life mood
Reduce physiological expression of anxiety
Sufferer often knows something is wrong
Prefrontal cortex