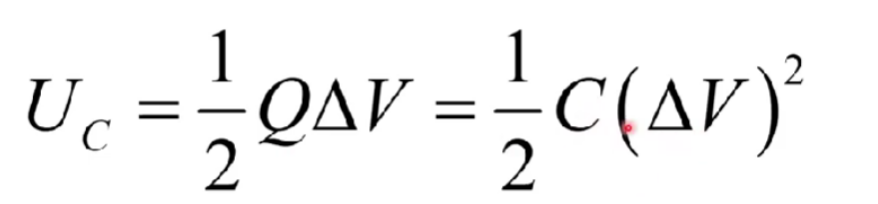surviving physics 2
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Thermodynamics
the exchange and conversion of heat energy between bodies
Kinetic energy(thermal)
K=3/2 nKbT or 3/2 nRT=1/2mv²
n= number of particles
kb= maxwell boltzmann constant
R= universal gas constant
T = temperature
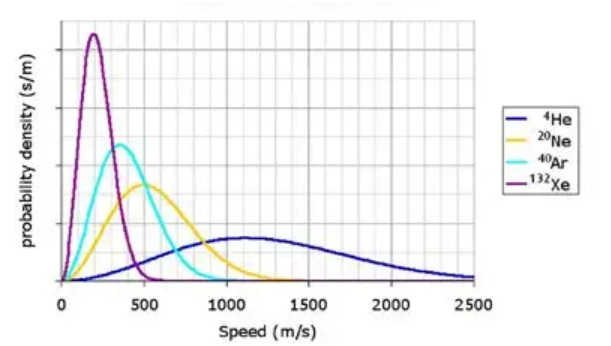
Maxwell-Bolton graph
Shows the average speed of particles throughout
Right is larger than the left, but the more scooched up it is means the more common it is
Where does thermal energy flow to
From hot to cold
How do the collisions between two gases’ molecules work
Random
Kinetic theory of gases
Gases have identical molecules unique to their certain gas
Volume is negligible
Instantaneous velocities are negligible
Density is constant at all point
Gas molecules exert pressure on container walls and collide elastically
The pressure of an ideal gas is the same everywhere
Ideal gas law
PV= NRT/Nkbt
P= Pressure
V = volume
N= number of molecules
Kb= boltzmann’s constant
T= temperature
Isochoric
Constant volume
Isothermic
Constant temperature
Isobaric
Constant pressure
Adiabatic
no heat transferred
Heating
transfer of energy into a system
Cooling
transfer of energy out of a system
Thermal equilbrium
two objects in a system/ two systems having the same temperature
Convection
heating through fluids
radioaction
heating through radioactive waves
Conduction
heating through direct contact
Internal energy(U)
Total energy of the whole system; total of each particles energy that does not have potential energy
U= Number of particles * average kinetic energy(N* Kavg)
Work on a gas
Positive during compression, negative during expansion; check same direction
W=-P(change in)V
Work by a gas
OPPOSITE DIRECTION; negative during compression, positive during expansion
Heat(Q)
thermal energy transferred from one body to another
Q = mcT
First law of thermodynamics
The change to energy is the sum of energy transferred to or from the system by heating work done of the system
U= Q + W
Insulated container
Energy does not escape
Rate of energy transfer by conduction
Q/t=kAT/L
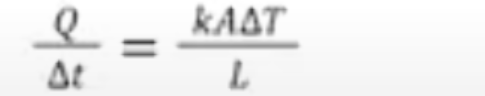
Entropy
the amount of disorder in a system; tendency of energy to spread and the unavailability of the system to do work; highest in thermal equilibrium
Constant but can increase in a closed system
Increases when molecules/thermal energy spread out more
Isolated system
Energy stays the same
Charge
scalar quantity measured in coulombs; conserved

Elementary charge
e= 1.60×10^-19 Coulombs
Value of coulomb
6.25×10^18 electrons/protons
Coulomb’s law
Force between 2 objects with charge
The two forces are in opposite directions
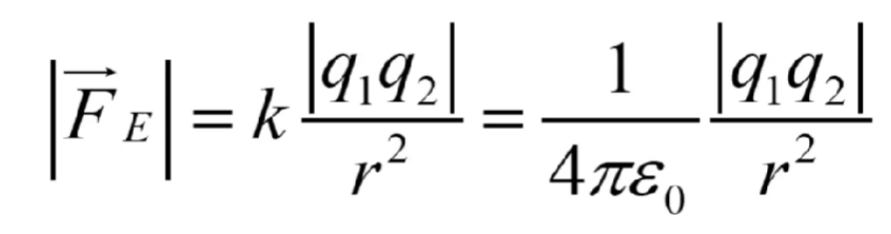
Coulomb’s constant
k= 1/4pie= 9×10^9 N*m²/c²
Electric polarization
rearrangement of electrons by an external electric field, separated by positive and negative charges
Electric permittivity
is a measurement of the degree to which a material/medium is polarized in the presence of an electric field, determined by how easily electrons can change configurations
Free space
Electric permittivity
conductor
material that does not allow electrons to move freely(metals)
insulator
material that doesn’t allow electrons to move freely(rubber, plastic, wood)
induction
charging with polarization and grounding(not touching)
transfer of charge
through WHOLE electrons friction, conduction, induction
Test charge
point charge of small magnitude that doesn’t affect an electric field nearby
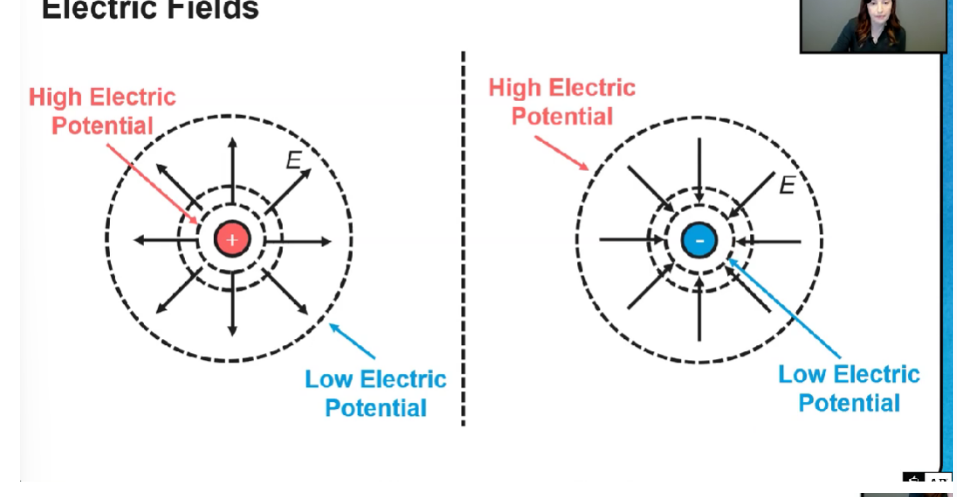
Electric field
the ratio between electric force and charge exerted on a test charge
Acts as a positive particle
Field and force in the same direction
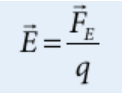
Charged particle in an electric field
Moves in a parabolic path
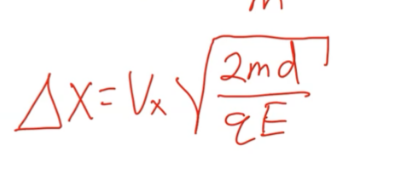
Field at the center of a solid conductor in electrostatic equilibrium
0
Electric potential energy
when the same charged particles are closer to each other PE is higher
one particle can’t have this
when there are multiple charges do it for multiple configurations
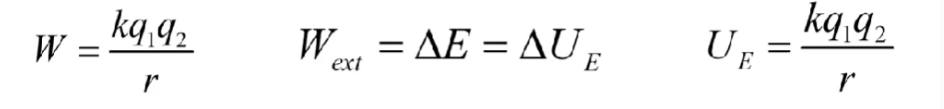
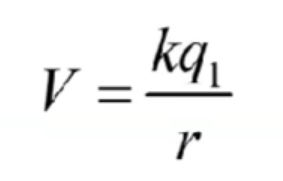
Electrical potential
Helps find potential energy if charge was placed
q1 is inital charge q2 is new
Charge flows until potential is the same
Perpendicular to the electric field
Same potential = no field or force, equilibrium
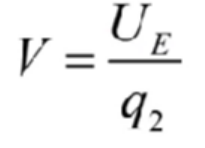
Field diagram
Closer together means higher potential for positive
Capacitors
oppositely charged parallel plates
Particles have constant acceleration in this
Electric potential energy increases with distance
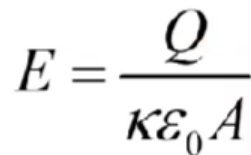
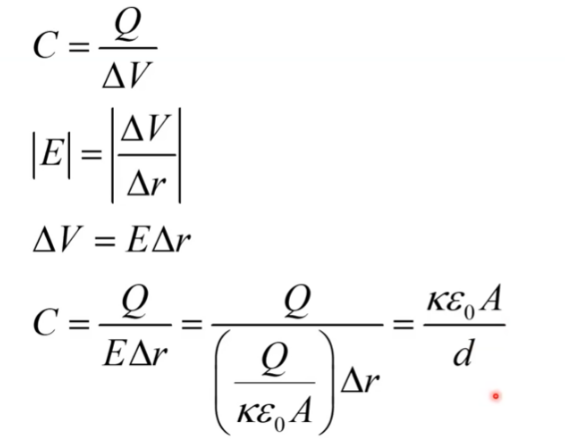
Capacitance
ability to store electric charge
Capitance PE