TEST 3 - AGRCULTURE
1/82
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
What is an example of a Monogastric nutritionist?
A specialist for one stomach animals such as hogs and horses (specify big/small)
What’s an example of a Ruminant nutritionist?
Someone who specializes in animals with four compartment stomachs such as cattle, sheep, and goats (specify big/small)
What’s a basic nutritionist?
studies the metabolism of animals, biochemical mechanisms of nutrient metabolism
What’s an applied/production nutritionist?
deals with cost effective feeding, the practical aspects
little tommy is doing a study and he is studying the effects of ionophores in blood and tissue levels of sheep, what kind of nutritionist is he?
A small ruminant nutritionist
What are the six required nutrients required for life process?
Water, carbohydrates, vitamins, fats, vitamins, and minerals
What is the single most important nutrient?
water
which nutrient primarily provides animals with energy?
carbohydrates
which nutrient is most commonly in feedstuffs?
carbohydrates
are any carbohydrates essential to the diet?
no
which nutrient gets animals fat and why?
carbohydrates because it has a high starch and sugar content
What are some carbohydrates?
monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides, polysaccharides
What are proteins made out of?
long chains of amino acids
What are the primary uses for proteins?
build lean tissue, enzymes, hormones, and metabolism
What nutrient is the most expensive of any ration and why?
protein, cottonseed meals
What are the 10 essential amino acids?
phenylamine, valine, threonine, tryptophan, isoleucine, methionine, histidine, arginine, leucine, and lysine
What do the 10 essential amino acids produce?
Nitrogen (crude protein)
What is the Kjedahl procedure?
analyzes how much crude protein is in the tested material
What is the crude protein formula?
Nitrogen x 6.25 = crude protein
Which protein is used as a source of energy? (more than carbohydrates)
Fats/lipids
What are Fats/Lipids?
esters of fatty acids and glycerol
Which nutrient is 2.25 times more energizing than carbohydrates?
Fats/Lipids
What is the soul source for essential body acids that can’t be made by the body?
Fats/Lipids
What nutrient has organic compounds needed by the body?
Vitamins
What are teh two Vitamin classifications?
fat-soluble and water-soluble
What do fat-soluble vitamins do? Which vitamins are in it?
regulate body function, Vitamins A, D, E, and K
What is Vitamin A?
Vision vitamin, and fat-soluble
What is Vitamin D?
The sun vitamin, fat-soluble
What is Vitamin E?
An antioxidant, fat-soluble
What is Vitamin K?
Blood-clotting vitamin, fat-soluble
What are the water-soluble vitamins?
C and D
What is Vitamin C?
antioxidant
What nutrient is an important part of the body’s enzyme system?
Minerals
What are the two types of minerals?
macro and micro
What’s a ration?
A particular way to eat (diet)
What does the NRC stand for? What does it do?
National Research Counsel, knows everything about nutrition requirements in animals for any stage of life
What are the phases of meat animal production?
Maintenance, Growth, and Finishing
What does TDN stand for?
Total digestible nutrients
What are feeds/feedstuffs?
Mixed substances that contain nutrients for animal needs
What does the gastrointestinal tract do?
Prepared food for digestion
What are the two types of actions for digestion?
Physical, Enzymic, and Chemical
What is physical digestive action?
chewing
what is chemical digestive action?
acid/bile
What is Enzyme digestive action?
increases the speed to breakdown chemical bonds in food
What is monogastric?
A single-stomach
What type of stomach is this?
Monogastric
What type of stomach is this?
Ruminant
What is prehension?
how an animal eats
What’s horse/cattle/sheep/pig/cat/dog prehension?
lip/tongue/upperlip/snout, lower lip/tongue/tongue
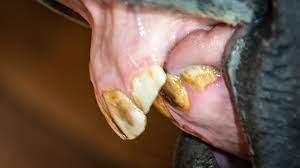
What type of dental pad is this?
Parrot Mouth
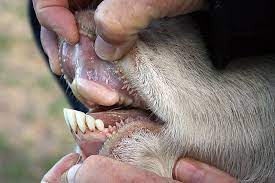
What type of dental pad is this?
Monkey Mouth
What are the steps of digestion?
Mastication, Salvation, Deglutition
What’s mastication?
chewing
What’s deglutition?
swallowing
What are the three portions of the small intestine?
Duodenum, Jejunum, Ileum
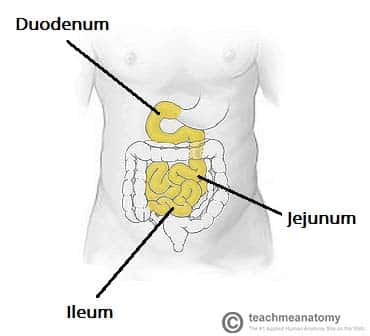
What’s this?
The small intestine
What’s the jejunum?
second largest small intestine portion, absorbs digestive products
What’s the Ileum?
The third part of the small intestine, connects to the large intestine
Does the large intestine contain villi? What about absorption?
No, and absorption is restricted.
What are the three parts of the large intestine?
cecum, colon, rectum
What are some examples of monogastric herbivores?
horses, rabbits, guinea pigs, elephant - they have a functional cecum
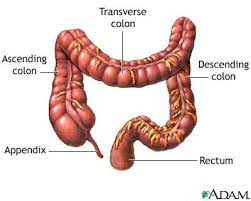
What’s this?
The large intestine.
What is micturition?
pee
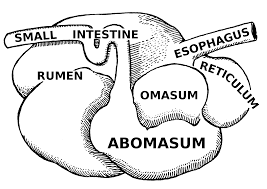
What is this?
Ruminant stomach
What are the parts of a complex stomach?
rumen, reticulum, omasum, abomasum
What are the forestomachs?
rumen, reticulum, omasum, abomasum
What’s the rumen?
stores food, is it’s own entity, in the digestive system
What’s the reticulum?
pacemaker, decides if something’s been chewed enough
What’s omasum?
part of the stomach that absorbs water and electrolytes
What’s eructation?
IMPERITIBE mechanism for ruminant, burping, will bloat if they don’t get rid of gas
What are the two types of bloating?
frothy bloat, free-gas bloat
What’s a frothy bloat?
too much concentrate, not enough roughage in diet
What’s a symptom of free-gas bloat?
blockage
What’s the fermentation process?
turns feed into energy sources
What’s coprophagy?
eating feces
What are the two feedstuff categories?
one: provides one or more of the six essential nutrients
two: improves palatability or rumen fermentation