3.2.1.1 Structure of Eukaryotic Cells
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
nucleus function
site of DNA replication and transcription, making rRNA
contains genetic code for each cell
structure of nucleus
nuclear envelope,
nuclear pores,
nucleoplasm,
chromosomes,
nucleolus
nucleoplasm
granular jelly like material in the nucleus
nuclear envelope
double membrane, contains nuclear pores
nuclear pores
found in nuclear envelope (around 3000), enables molecules to enter and leave
nucleolus
smaller sphere inside the nucleus
the site of rRNA production
makes ribosomes
chromosomes
found in nucleus,
protein bound linear DNA
golgi apparatus structure
a series of fluid filled flattened and curved sacs making cisternae
with vesicles surrounding the edges
golgi apparatus function (7)
add carbohydrates to proteins (glycoproteins),
produce secretary enzymes,
secrete carbohydrates,
transport/modify/store lipids
form lysosomes,
molecules are labelled with their final destination,
final products transported to cell surface in Golgi vesicles where they fuse with the membrane and the contents is released
lysosomes structure
vesicles/bags of digestive enzymes,
bound by single membrane,
can have 50 different enzymes
lysosomes function (4)
hydrolyse phagocytic cells,
break down dead cells (autolysis),
release enzymes to outside of cell to destroy material (exocytosis),
digest worn out organelle to be reused
mitochondria function
site of aerobic respiration, site of ATP production, DNA codes for enzymes needed in respiration
mitochondria structure
oval shaped
bound by a double membrane called the envelope
inner membrane is folded to form projections called cristae
a matrix on the inside containing all the enzymes needed for respiration
loop of mitochondria dna
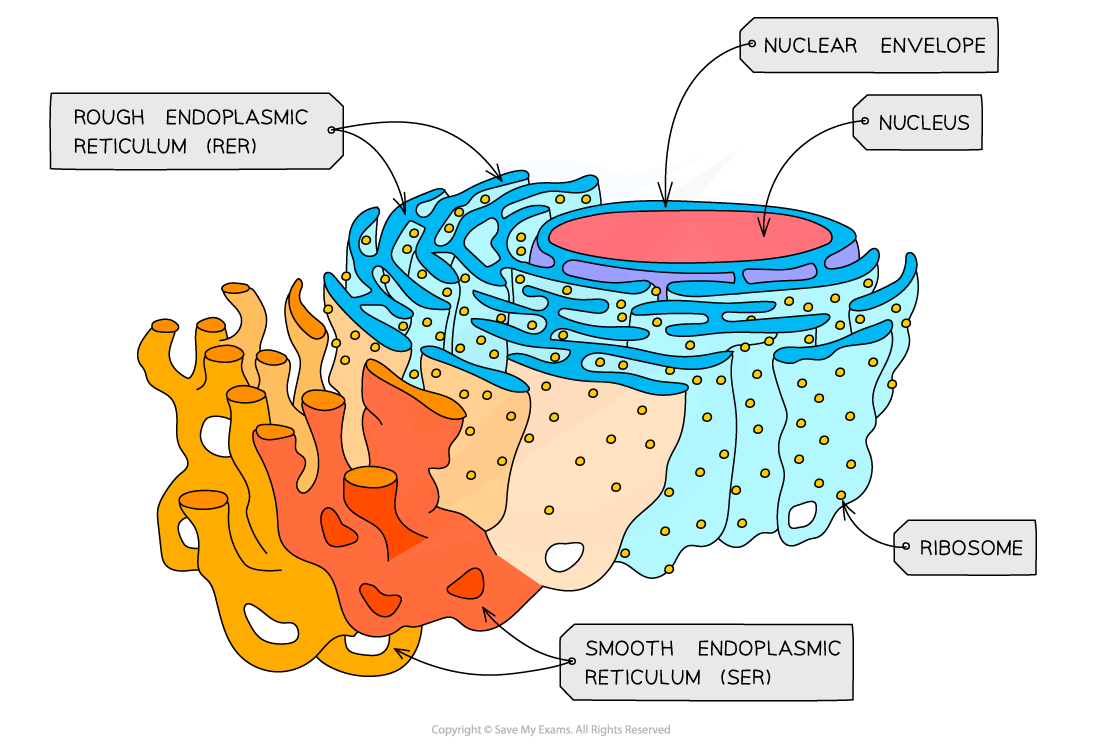
rough endoplasmic reticulum function
synthesise proteins
rough endoplasmic reticulum structure
a series of unflattened sacs
enclosed by a membrane
with ribosomes on the surface
smooth endoplasmic reticulum function
synthesis and store lipids
smooth endoplasmic reticulum structure
system of membrane bound sacs
vacuole function
make cell turgid
provide support
temporary source of sugars and amino acids
pigments may colour petals to attract pollinators
vacuole structure
filled with fluid surrounded by single membrane called a atonoplast
what are cisternae?
folded membranes found in RER and SER
xylem tissue specialisation
in plants used to transport water and mineral ions throughout the plant mechanical support
epithelial tissue specialisation
found in animals,
consist of sheets of cells line the surface of organs
often have protective of secretory function
line the alveoli in lungs and the trachea
name two structures in a eukaryotic cell that cannot be identified using an optical microscope
lysosomes
ribosomes
mitochondrion
endoplasmic reticulum
cell-surface membrane
cell wall function
provide structural strength and prevent cell bursting
cell wall structure
in plants = made of microfibrils of cellulose polysaccharide,
in algae = cellulose,
in fungi = chitin (a nitrogen containing polysaccharide)
what are plant cell walls made of?
cellulose
what are fungal cell walls made of?
chitin
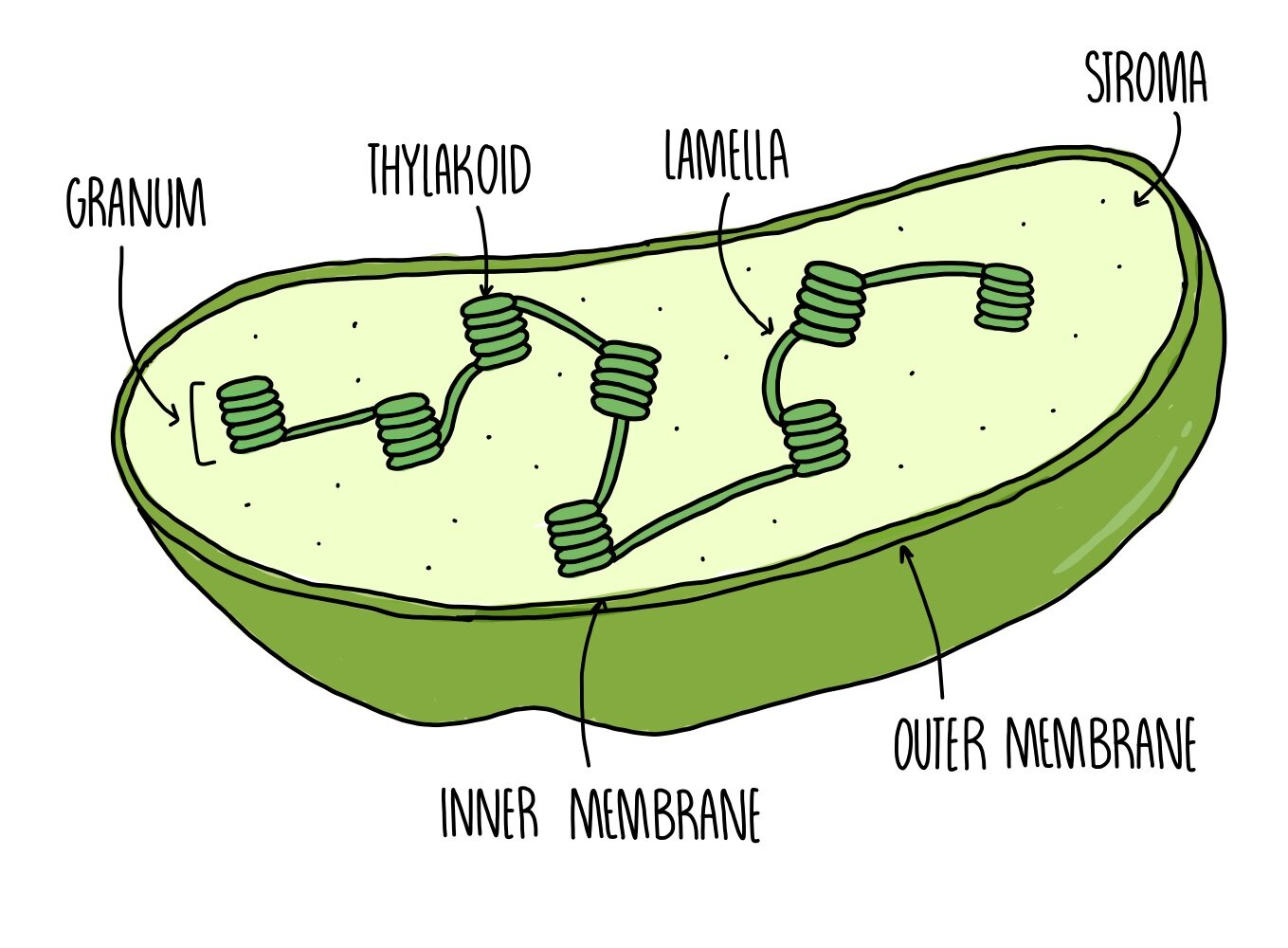
chloroplast function
site of photosynthesis (light dependent)
chloroplast structure
surrounded by a double membrane,
contains thylakoids (folded membranes embedded with pigments),
fluid filled stroma contains enzymes for photosynthesis in plants
ribosomes function
site of protein synthesis
ribosomes structure
made of two sub units of protein and rRNA,
70s = smaller ribosome found in prokaryotic cells,
80s = large ribosome found in eukaryotic cells
tissue definition
collection of similar cells that perform a specific function
explain how the nucleus, rough ER and golgi apparatus are involved in protein synthesis
nucleus- the carries instructions for protein synthesis, ribosomal synthesis occurs here rough
ER- these are covered in ribosomes, and this is where protein synthesis occurs
golgi apparatus- sorts, modifies and packages proteins into vesicles to be transported to the cell membrane
name 2 structures in plant cells that are not present in animal cells
cell wall chloroplasts