history- unit 2: Mesopotamia and ancient Egypt
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
1
New cards
Mesopotamia
A historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent.
2
New cards
Sumerians
the earliest known ancient civilization founded in the Mesopotamia region of the Fertile Crescent.
3
New cards
city-state
political organization based on the authority of a single, large city that controls outlying (surrounding) territories
4
New cards
irrigation
the act of supplying dry land with water by means of canals, ditches, pipes, and streams
5
New cards
surplus
an extra amount; more than is needed
6
New cards
Polytheism
worship many gods
7
New cards
ziggurat
temple
8
New cards
social class
aka hierarchy
9
New cards
Hierarchy
a. Rulers and priests at top
b.Wealthy landowners and merchants next
c. Artisans and farmers
d. Enslaved people at bottom
b.Wealthy landowners and merchants next
c. Artisans and farmers
d. Enslaved people at bottom
10
New cards
cuneiform
(“wedged-shaped”) First writing system developed in Mesopotamia c. 3000 BCE, originally developed to keep track of trade and property
11
New cards
Scribe
specialized workers that were trained from a young age for this job of writing
12
New cards
pictograph
symbols that represented words or phrases
13
New cards
Sargon of Akkad
(c. 2350 BCE), At first, Sumerians lived in independent city-states, Sargon conquered most of the city-states of Mesopotamia, creating the first empire* in history
14
New cards
Hammurabi’s Code
was one of the first times laws were codified (written down for all to see)
15
New cards
Assyrian Empire
-850-650 BCE, the Assyrians controlled a large empire
Advantages
16
New cards
tribute
a payment made by a weaker power to a stronger power to obtain an assurance of peace and security
17
New cards
Ashurbanipal
king who created a huge library containing more than 20,000 clay tablets (including The Epic of Gilgamesh)
18
New cards
Nile River
longest river in the world, life in Egypt centered around it, annual flooding providing both water and silt
19
New cards
silt
fine-grained soil often deposited on riverbanks during floods
20
New cards
Narmer
AKA Menes, believed by historians to have unified Upper and Lower Egypt
21
New cards
Pharaoh
rulers that were seen as gods on Earth
22
New cards
Pyramid
built as tombs so the god-kings could continue to help rule Egypt
23
New cards
Mummification
a better way to preserve bodies after death
24
New cards
Hieroglyphics
a more flexible system of writing, Pictures often represented an idea but also could represent a sound like modern alphabet
25
New cards
Papyrus
paper-like, was easier to write on compared to clay and stone
26
New cards
Rosetta Stone
made translation possible
27
New cards
Old Kingdom, Middle Kingdom, New Kingdom
1. Old Kingdom (c. 2700-2200 BCE) when most of pyramids built
2. Middle Kingdom (c. 2050-1650 BCE) when Egypt made
advances in literature, art, and architecture
3. New Kingdom (c. 1570-1070 BCE) when Egypt
conquered its neighbors and created a powerful empire
28
New cards
Hapshetsut
(c.1470 BCE) Daughter of a pharaoh who married her half-brother (Thutmose II), served as a regent for Thutmose III, Hatshepsut made herself co-ruler and really held most of the power for about 20 years, known for her great building projects and expanding Egypt’s trade with other nations
29
New cards
Thutmose III
son of Thutmose II, became the pharaoh at a young age, tried to destroy all images and writings about Hatshepsut
30
New cards
regent
person appointed to rule, usually when the monarch is too young
31
New cards
Akhenaten
(c. 1340 BCE) ,Best known for abolishing (ending) polytheism and forcing people to worship only one god
32
New cards
Ramses II
(c. 1290 BCE-1224 BCE), c. 1285 BCE, Ramses II leads the Egyptians against the Hittites in the Battle of Kadesh (he claims victory but probably a draw/tie), later makes a peace treaty with Hittite king, also known as a great builder who added huge statues of himself to temples he built, some believe he is the pharaoh from Exodus
33
New cards
Cataracts
steep rapids
Kashta, Piankhy, Shabaka
Kashta, Piankhy, Shabaka
34
New cards
Geography/Environment Challenges of Mesopotamia
-LARGE flooding problem while also struggling with a predictable water source/the SOLUTION was the creation of the irrigation systems
-located in an area with multiple surrounding civilizations, opening doors for more attacks from neighboring nations
-located in an area with multiple surrounding civilizations, opening doors for more attacks from neighboring nations
35
New cards
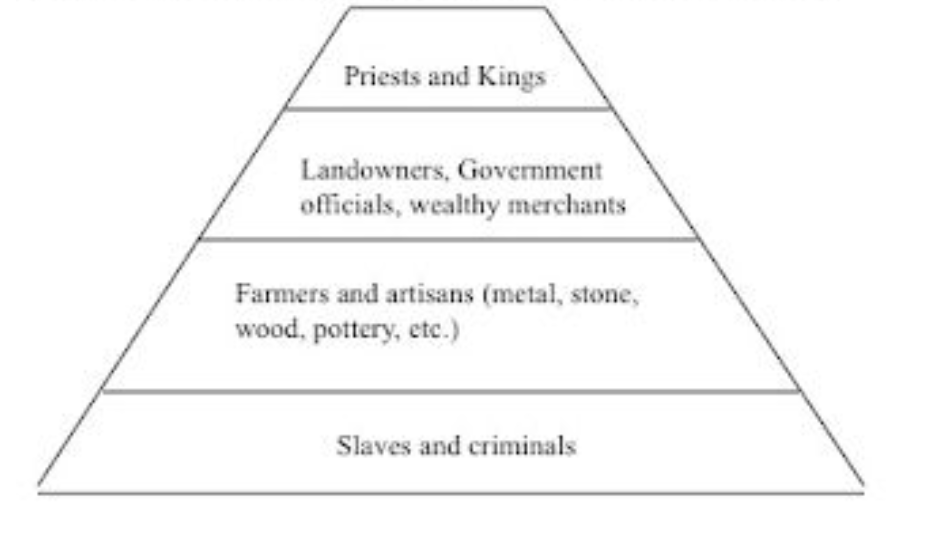
Government and Social Structure of the Sumerians
Sumer had a ruling class, upper class, middle class, working-class, and enslaved class of peoples.
36
New cards
Sumerian Religious Beliefs
FROM NOTES: Polytheistic (worship many gods), Gods needed to be pleased through sacrifices and construction of ziggurats (temples)
(from Gilgamesh reading): Enkidu said that Gilgamesh would weep if he found out. Enkidu’s body is rotting in the Underworld.
(from Gilgamesh reading): Enkidu said that Gilgamesh would weep if he found out. Enkidu’s body is rotting in the Underworld.
37
New cards
Five Characteristics of Civilization for the Sumerians
1. Rise of the Sumerian City-States
2. Organized governments developed to address these problems
3. Religion
4. Social classes (AKA hierarchy)
5.Cuneiform
2. Organized governments developed to address these problems
3. Religion
4. Social classes (AKA hierarchy)
5.Cuneiform
38
New cards
Geography/Environment Challenges of Ancient Egypt
Deserts to the east and west
Travel up the Nile was difficult
Close to the sea
Many natural barriers
Travel up the Nile was difficult
Close to the sea
Many natural barriers
39
New cards
Government and Social Structure of Ancient Egypt
Social Hierarchy
a. Pharaoh and family
b. Upper class: wealthy landowners, government officials, priests, army commanders
c. Middle class: merchants and artisans
d. Lower class: peasant farmers and laborers
e. Enslaved people at the bottom
Ruled by the pharaoh, people would follow the pharaoh’s rules bc they believed they were gods.
a. Pharaoh and family
b. Upper class: wealthy landowners, government officials, priests, army commanders
c. Middle class: merchants and artisans
d. Lower class: peasant farmers and laborers
e. Enslaved people at the bottom
Ruled by the pharaoh, people would follow the pharaoh’s rules bc they believed they were gods.
40
New cards
Egyptian Religious Beliefs
Polytheistic-believed in many gods
Believed dead people would be judged and good would be rewarded while bad will have their soul/heart devoured
Pharaohs (and eventually wealthy people) were mummified to better preserve their bodies and buried with stuff they needed for the afterlife
Believed pharaohs were gods
41
New cards
Five Characteristics of Civilization for Ancient Egypt
Advanced cities:
Many permanent structures and homes, as well as larger permanent structures like the pyramids and the temples
Organized Government:
A clear structure of leaders and rulers, including the Pharaoh at the head
Specialized workers:
Artisans, scribes, etc.
Record keeping:
HIEROGLYPHICS; they wrote stories and recorded history
Advanced Technology:
Writing system, chariots, tools and weapons, etc.
Many permanent structures and homes, as well as larger permanent structures like the pyramids and the temples
Organized Government:
A clear structure of leaders and rulers, including the Pharaoh at the head
Specialized workers:
Artisans, scribes, etc.
Record keeping:
HIEROGLYPHICS; they wrote stories and recorded history
Advanced Technology:
Writing system, chariots, tools and weapons, etc.
42
New cards
Egypt and Kush
Egyptians built forts in Kush along the Nile and considered it part of their empire
Kush heavily influenced by Egypt and adopts its religion, art, and use of hieroglyphics
c. 1070 BCE Egypt was weak so Kush stopped paying tribute
Shabaka defeated the last of the Egyptians and declares himself the first Kushite pharaoh
Kush driven out of Egypt by the Assyrians c. 660 BCE
Kush heavily influenced by Egypt and adopts its religion, art, and use of hieroglyphics
c. 1070 BCE Egypt was weak so Kush stopped paying tribute
Shabaka defeated the last of the Egyptians and declares himself the first Kushite pharaoh
Kush driven out of Egypt by the Assyrians c. 660 BCE
43
New cards
Map of the Fertile Crescent
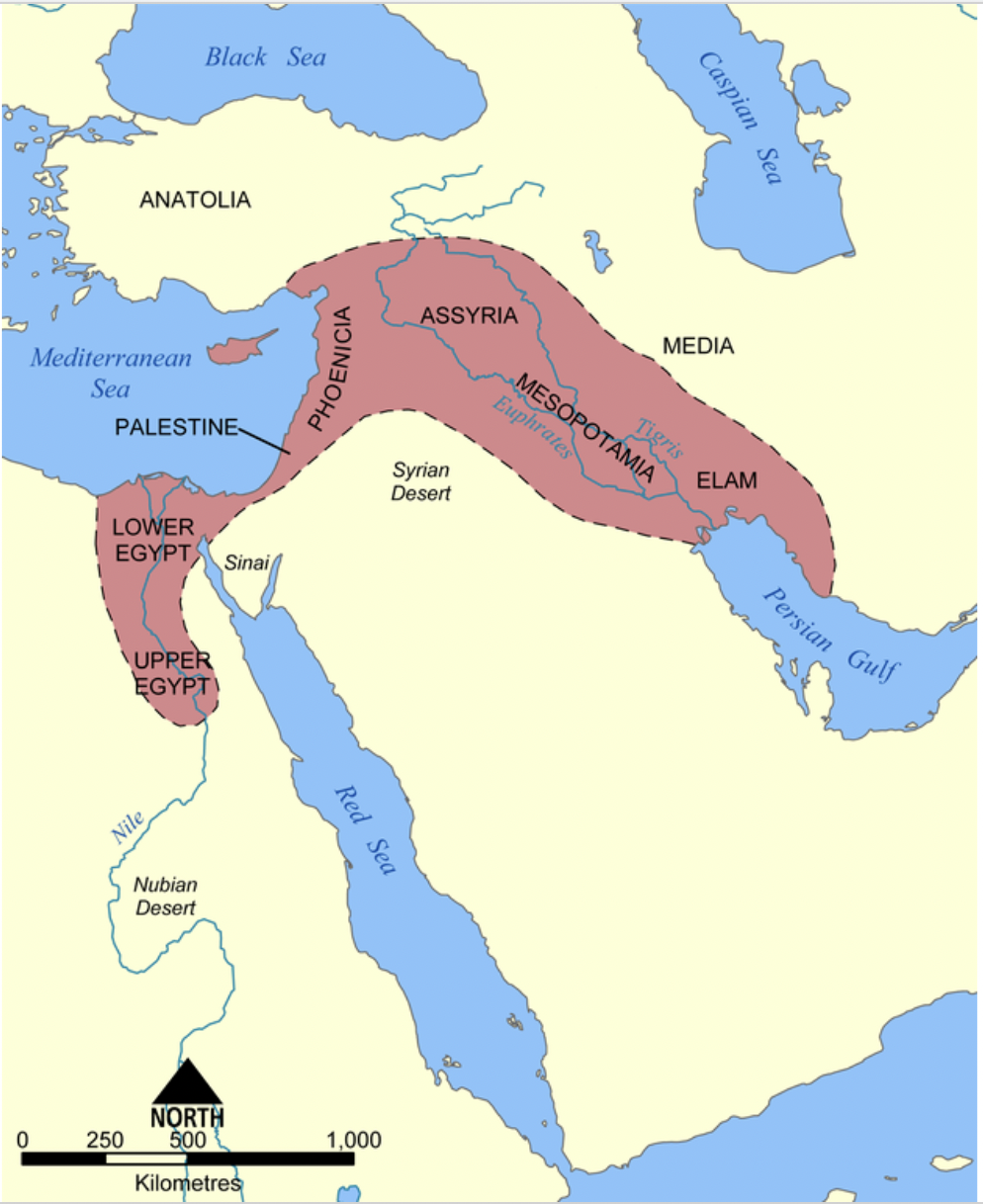
44
New cards
Modern day map