Ch. 32 - Ionizing Radiation, Nuclear Energy, & Elementary Particles
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
The current view of how matter is composed of basic units
Molecule → Atom → Nucleus → Neutron (or proton) → Quark
Environmental radiation
Natural and artificial radiation
Natural radiation
Cosmic rays & earth itself.
Artificial radiation
Medical diagnostics and manmade sources.
Ionizing radiation
Consists of photons and/or moving particles that have sufficient energy to knock an electron out of an atom or molecule, thus forming an ion.
Exposure
A measure of the ionizing radiation produced in air by x-rays or γ-rays.
Exposure (in roentgens) =
(1 / 2.58 × 10-4) q / m
RADs (radiation absorbed dose) =
The unit of absorbed dose.
One rad is = to…
0.01 J of radiant energy absorbed per 1 kg of tissue.
Absorbed dose =
energy absorbed / mass of absorbing material
1 gray = 1Gy = 1 J/kg = 100rad
Relative biological effectiveness (RBE)
Used to compare the damage produced ny different types of radiation.
RBE =
Dose of 200 -keV X-rays that produces a certain biological effect / Dose of radiation that produces the same biological effect
Biologically equivalent dose =
absorbed dose x RBE 1Sv (seivert) = 100rem
REMs (roentgen equivalent man) =
The unit of radiation dosage based on potential damage and accounts for the different health effects of different types of radiation determined by clinical studies.
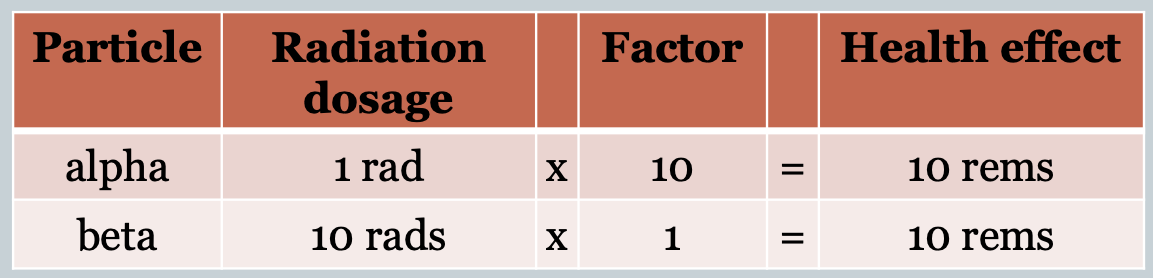
Lethal dose of radiation
> 500 rems
~50% survival chance
The average person in the US is exposed to ~ _____________ a year.
360 mrems
Nuclear reaction
Said to occur whenever the incident nucleus, particle, or photon causes a change to occur in the target nucleus.
An Induced Nuclear Transmutation Example
An alpha particle strikes an aluminum nucleus. As a result,
an unknown nucleus and a neutron are produced.
42He + 2713Al → AZX +10n
3015P

Nuclear fission
The colloquial ‘splitting of atoms’
Neutrons and massive energy are released
Applications of weaponry and energy production
Nuclear fission is the process of…
Splitting atoms of heavy elements into two or more smaller atoms.
The splitting of the atom during fission produces…
A tremendous amount of energy in the form of heat and light.
Each fissioning of an atom by one neutron can produce…
From 8-27 additional neutrons, all available for furthering reactions.
Fission chain reaction
Neutrons from one reaction start the next reaction.
Critical mass
The point at which the chain reaction becomes self-sustaining.
The amount of fissionable material’s critical mass depends on:
The shape of the material, its composition and density, and the level of purity.
Nuclear fusion
Two nuclei of very low mass can combine to generate energy.
When atoms are fused, atoms of ligher masses produce…
More energy than those of heavier masses.
Fusion vs Fission
Both release large amounts of energy.
Fission is more effective as of today.
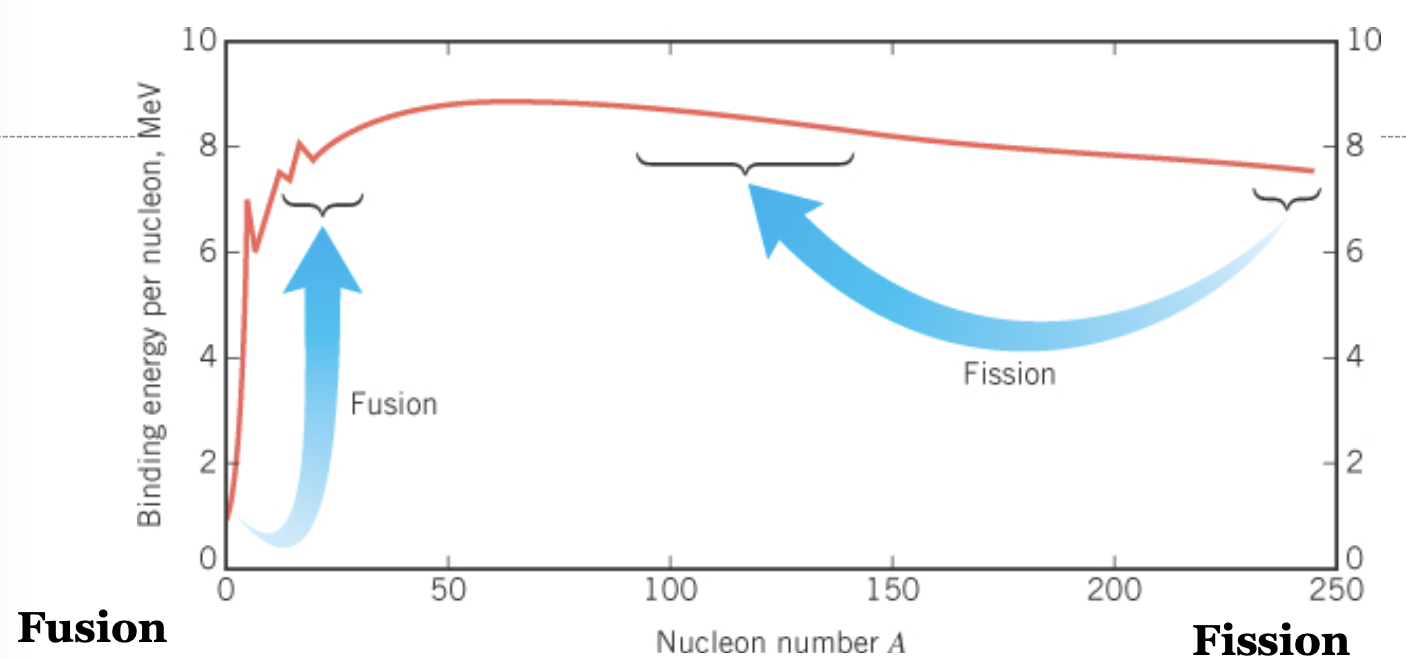
Generating fusion - how to confine the plasma?
Gravitational confinement
Magnetic confinement
Internal confinement
All stars have…
Fusion cores.
The fusion reactor
Uses massive magnetic field to control the heated plasma produced by powerful lasers.
Biological effects of Ionizing Radiation Example
Biologically equivalent doses are specified in units called ________.
a) rads
b) grays
c) rems
d) J/kg
e) roentgens
c) rems
Induced nuclear reactions Example
Determine the unknown nuclear species AZX in the following nuclear reaction:
AZX + 147N → 146C + 11H
a) 21H
b) 10n
c) γ ray
d) 42He
b) 10n
Nuclear Fission Example
The fission of 23592U can occur via many different reactions. In general, they can be written as follows:
10n + 23592U → AxZxX + AyZyY + n10n
where X and Y refer to the identities of the fission fragments and n is the number of neutrons produced. Which one or more of the following statements are true?
A) The compound nucleus that is formed to initiate the fission process is the
same, no matter what the X and Y refer to.
B) The greater the number n of neutrons produced by the reaction, the smaller
is the sum of the nucleon numbers Ax and Ay.
C) The sum of the atomic numbers Zx and Zy is the same, no matter what the X
and Y refer to.
a) A
b) A and B
c) A and C
d) B and C
e) A, B, and C
e) A, B, and C
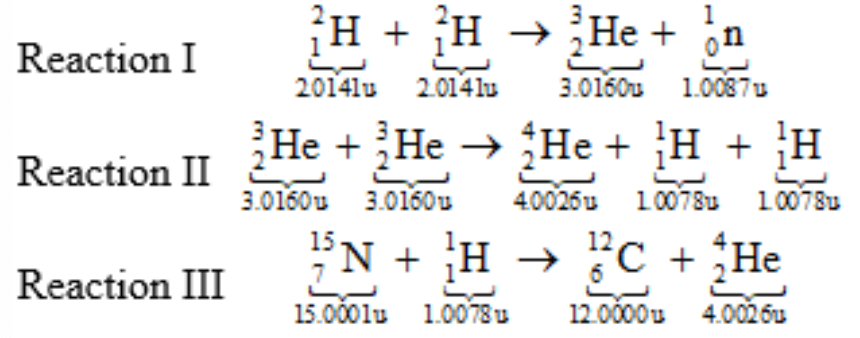
Nuclear Fusion Example
In each of the following three nuclear fusion reactions, the masses of the nuclei are given beneath each nucleus. Rank the energy produced by each reaction in descending order (greatest first).
a) I, II, III
b) I, III, II
c) II, III, I
d) II, I, III
e) III, II, I
c) II, III, I