Religion and Rituals
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Souls
Early humans believe that two entities inhabit the body. One is active during the day the other—a soul— is active during sleep and trance
animism: the belief in souls (Edward Taylor)
Animism
The belief in souls
Impersonal power or force — Manna
A sacred, impersonal force existing in the universe, so named in Melanesia and Polynesia
Impersonal power or force — the Yin and Yang
The two contrary and mutually complementary forces that together form everything that exists, as expressed in ancient Chinese philosophy
symbol of balance
Deities
The perfect and all-powerful spirit(s) that is (are) worshipped as the creator(s) and ruler(s) of the universe, often personified
Most religions include these spiritual beings:
souls
gods
demons
charms
talismans
Similarities and differences between magic and religion (James Frazer)
magic and religion can be both regarded as beliefs in supernaturals beings and powers
the practitioners of both religion and magic perform rituals
both religion and magic fulfill certain social and psychological functions
Magic
A mode of rationality or way of thinking that looks to
invisible forces to influence events, effect change in material
conditions, or present the illusion of change
supernatural practices and techniques intended to accomplish specific aims
a type of primitive science, a more optimistic view on life and existence
Religion
Human beings’ relation to that which they regard as
holy, sacred, absolute, spiritual, divine, or worthy of especial
reverence. It is also commonly regarded as consisting of the way
people deal with ultimate concerns about their lives and their
fate after death
a conciliatory view toward the supernatural, involving prayer and supplication to a high power
highly organized
large-scaled
often with a written tradition
Religion and magic reflect different world views
Religion and magic are not mutually exclusive. Most religious systems include magic practices
Magic
supernatural practices and techniques intended to accomplish specific aims
a type of primitive science, a more optimistic view on life and existence
Religion
A conciliatory view toward the supernatural,
involving prayer and supplication to a higher powerHighly organized
Large-scaled
Often with a written tradition
Ritual
A formal, symbolic act or event consisting of a series of actions performed according to a prescribed order
Effect of rituals
Through formal, stylized, and repetitive actions, rituals can
provide a way to practice a belief in a consistent form and build a community
convey and reinforce the social order and values of the practitioners
Rites of passage — a special type of ritual
Rituals marking transitions from one place, status, or stage of life to another
rites of passage can be individual or collective
Three phases of a rite of passage:
Separation: withdraw from ordinary society
Liminality: in-between phase, marked by a temporary suspension of social status and a reversal of ordinary behavior
incorporation: re-enter society with new status
An evolutionary typology (Edward Taylor)
According to the number of supernatural beings in a religion
animism: everything has a soul (1st stage)
polytheism: belief in multiple deities (2nd stage)
monotheism: belief in a single, all-powerful deity (3rd stage)
science: a new belief system (final stage)
Statistics about worl religions (Pew Research Center 2012)
5.8 billion people (84% of the world’s population in 2010 were religiously affiliated)
1.1 billion (16%) lacked any religios affiliations (people who lack religious affiliations are not necessarily atheist)
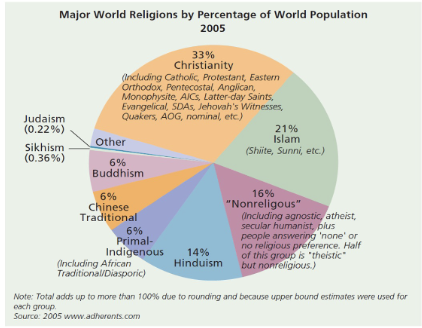
What role do religions play in people’s lives?
explaining things, providing reasons, and reducing anxiety and uncertainty
creating community
instill values and exerting social control
often intertwined with politics and economy
An organizational typology (Anthony Wallace)
According to the ways religious rituals are organized:
individualistic: each individual has a special relationship with the supernatural power
shamanistic: shamans as organizers
communal: no religios specialists
ecclesiastical: a full time priesthood
Religious pluralism in contemporary world
religious pluralism: followers of many different religions live within a society
most modern nations face the issue of accommodating religious pluralism