Psychology - Approaches
4.0(2)
4.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/74
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
1
New cards
Introspection
The first systematic experimental attempt to study the mind by breaking up conscious awareness into basic structures of thoughts, images and sensations
2
New cards
Wundt in Psychology
* Opened the first ever lab dedicated to psychological research
* His work is significant as it marked the beginning of scientific psychology
* He wanted to analyse the nature of human consciousness in controlled conditions
* His work is significant as it marked the beginning of scientific psychology
* He wanted to analyse the nature of human consciousness in controlled conditions
3
New cards
Wundt - Introspection
* Wanted to develop theories about mental processes like language and perception
* Recorded their experiences of various stimuli such as objects and sounds
* They would divide their observations into 3 categories: thoughts, images and sensations
* Recorded their experiences of various stimuli such as objects and sounds
* They would divide their observations into 3 categories: thoughts, images and sensations
4
New cards
Behavioural Approach
A way of explaining behaviour in terms of what is observable and in terms of learning
5
New cards
Classical Conditioning
Learning by association. Occurs when two stimuli are repeatedly paired together - an unconditioned stimulus and a neutral stimulus. The neural stimulus eventually produces the same response that was first produced by the unconditional stimulus alone
6
New cards
Operant Conditioning
A form of learning in which behaviour is shaped and maintained by its consequences of behaviour include reinforcement. Possible consequences of behaviour include reinforcement and punishment
7
New cards
Reinforcement
A consequence of behaviour that increases the likelihood of that behaviour being repeated
8
New cards
Pavlov - Classical Conditioning
* Learning through association when a dog associated the sound of a bell with food
* Eventually when the sound of a bell chimed dogs began salivating without food (stimulus)
* Eventually when the sound of a bell chimed dogs began salivating without food (stimulus)
9
New cards
Positive Reinforcement
Receiving a reward when a certain behaviour is performed (additional stimulus)
10
New cards
Negative Reinforcement
Occurs when you avoid something undesired and the outcome is then positive (the removal of a stimulus)
11
New cards
Punishment
An unpleasant consequence of behaviour (decreases likelihood of a behaviour)
12
New cards
Skinner - Operant Conditioning
* Experimented on rats and pigeons in specialised cages
* Every time a rat pulled a lever it was rewarded with food
* Every time a rat pulled a lever it was rewarded with food
13
New cards
Token Economy
Using operant conditioning a reward system can be created often to encourage specific behaviours
14
New cards
Social Learning Theory
A way of explaining behaviour that includes both direct and indirect reinforcement,combining learning theory with the role of cognitive factors
15
New cards
Imitation
Copying the behaviours of others
16
New cards
Identification
When an observer associates themselves with a role model and wants to be like the role model
17
New cards
Modelling
From the observer’s perspective, modelling is imitating the behaviour of a role model. From the role model’s perspective, modelling is the precise demonstration of a specific behaviour that may be imitated by an observer
18
New cards
Vicarious Reinforcement
Reinforcement which is not directly experienced but occurs through observing someone else being reinforced for a behaviour. This is a key factor in imitation
19
New cards
Mediational Processes
Cognitive factors that influence learning and come between stimulus and response
20
New cards
Bandura - Mediational Processes
* Attention - the extent to which we notice certain behaviours
* Retention - how well that behaviour is remembered
* Motor reproduction - the ability of the observer to perform the behaviour
* Motivation - the will to perform the behaviour, which is often determined by whether the behaviour is rewarded or punished
* Retention - how well that behaviour is remembered
* Motor reproduction - the ability of the observer to perform the behaviour
* Motivation - the will to perform the behaviour, which is often determined by whether the behaviour is rewarded or punished
21
New cards
Bandura - Bobo Doll (A)
* Recorded the behaviour of young children who watched an adult behave in an aggressive way towards a Bobo doll
* Children were later observed and seen to be more violent towards the doll
* Children were later observed and seen to be more violent towards the doll
22
New cards
Bandura - Bobo Doll (B)
* Showed videos to children when an adult behaved aggressively towards the Bobo doll
* One group saw the adult being praised and another told off whilst the control saw aggression with no consequence
* First group was the most aggressive then control and then the second group
* One group saw the adult being praised and another told off whilst the control saw aggression with no consequence
* First group was the most aggressive then control and then the second group
23
New cards
Cognitive Approach
This approach is focused on how our mental processes affect behaviour
24
New cards
Internal Mental Processes
‘Private’ operations of the mind such as perception and attention that mediate between stimulus and response
25
New cards
Schema
A mental framework of beliefs and expectations that influence cognitive processing. They are developed from experience
26
New cards
Inference
The process whereby cognitive psychologists draw conclusions about the way mental processes operate on the basis of observed behaviour
27
New cards
Cognitive Neuroscience
The scientific study of those biological structures that underpin cognitive processes
28
New cards
Informational Processing Approach
Suggests that information flows through the cognitive system in a sequence of stages including input, storage and retrieval. This acts as a computational model
29
New cards
Biological Approach
A perspective that emphasises the importance of physical processes in the body such as genetic inheritance and neural function
30
New cards
Biological Structure
An arrangement or organisation of parts to form an organ, system or living thing
31
New cards
Neurochemistry
Relating to chemicals in the brain that regulate psychological functioning
32
New cards
Genotype
The particular set of genes that a person possesses
33
New cards
Phenotype
The characteristics of an individual determined by both genes and the environment
34
New cards
Evolution
The changes in inherited characteristics in a biological population over successive generations
35
New cards
Nervous System
Consists of the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. Communicates using electrical signals
36
New cards
Central Nervous System
Consists of the brain and the spinal card and is the origin of all complex commands and decisions
37
New cards
Peripheral Nervous System
Sends information to the CNS from the outside world, and transmits messages from the CNS to muscles and glands in the body
38
New cards
Somatic Nervous System
Transmits information from receptor cells in the sense organs to the CNS. It also receives information from the CNS that directs muscles to act
39
New cards
Autonomic Nervous System
Transmits information to and from internal bodily organs. It is autonomic as the system operates involuntarily. It has two main divisions the sympathetic and the parasympathetic nervous system
40
New cards
Cerebral Cortex
The brain’s outer layer
41
New cards
Endocrine System
One of the body’s major information systems that instructs glands to release hormones directly into the bloodstream. These hormones are carried towards target organs in the body. Communicates via chemicals
42
New cards
Fight or Flight Response
The way an animals responds when stressed. The body becomes physiologically aroused in readiness to fight an aggressor or in some cases flee
43
New cards
Neuron
The basic building blocks of the nervous system, neurons are nerve cells that process and transmit messages through electrical and chemical impulses
44
New cards
Sensory Neurons
These carry messages from the PNS to the CNS. They have long dendrites and short axons
45
New cards
Relay Neurons
These connect the sensory neurons to the motor or other relay neurons. They have short dendrites and short axons
46
New cards
Motor Neurons
These connect the CNS to effectors such as muscles and glands. They have short dendrites and long axons
47
New cards
Dendrites
Branchlike structures which carry nerve impulses from neurons to cell body
48
New cards
Axon
Carries the impulse away from the cell body down the length of the neuron
49
New cards
Myelin Sheath
Protects the axon and speeds up the electrical transmission impulse
50
New cards
Nodes of ranvier
Speed up the transmission of the impulse by forcing it to ‘jump’ across the synapse along the axon
51
New cards
Synaptic Transmission
The process by which neighbouring neurons communicate with each other by sending chemical messages across the synapse that separates them
52
New cards
Neurotransmitter
Brain chemicals released from synactic vesicles that relay signals across the synapse from one neuron to another. Neurotransmitters cam be broadly divided into that that perform excitatory or inhibitory function
53
New cards
Excitation
When a neurotransmitter such as adrenaline, increases the positive charge of the postsynaptic neuron. This increases the likelihood that the postsynaptic neuron will pass on the electrical impulse
54
New cards
Inhibition
When a neurotransmitter such as serotonin increases the negative charge of the postsynaptic neuron. This decreases the likelihood that the postsynaptic neuron will pass on the electrical impulse
55
New cards
Acetylcholine
A transmitter found at each point where a motor neuron meets a muscle, and upon its release,it will cause muscles to contract
56
New cards
Psychodynamic Approach
A perspective that describes the different forces (dynamic) most of which are unconscious that operate on the mind and direct human behaviour and experience
57
New cards
Unconscious
The part of the mind that we are unaware of but which directs much of our behaviour
58
New cards
Id
Entirely unconscious, the Id is made up of selfish aggressive instincts that demand immediate gratification
59
New cards
Ego
The ‘reality check’ that balances the conflicting demands of the Id and the Superego
60
New cards
Super ego
The moralistic part of our personality which represents the ideal self how we ought to be
61
New cards
Defence Mechanisms
Unconscious strategies that the Ego uses to manage the conflict between the Id and the Superego
62
New cards
Psychosexual
* Oral (0-1) - focus of pleasure is the mouth and can create an oral fixation
* Anal (1-3) - focus of pleasure is the anus and can result in retentiveness or expulsivity
* Phallic (3-6) - focus of pleasure is the genital area and can result in a phallic personality
* Latency - Early conflicts are repressed
* Genital - sexual desires become conscious alongside puberty and could then find difficult to form heterosexual relationships
* Anal (1-3) - focus of pleasure is the anus and can result in retentiveness or expulsivity
* Phallic (3-6) - focus of pleasure is the genital area and can result in a phallic personality
* Latency - Early conflicts are repressed
* Genital - sexual desires become conscious alongside puberty and could then find difficult to form heterosexual relationships
63
New cards
Repression
Forcing a distressing memory out of the conscious mind
64
New cards
Denial
Refusing to acknowledge some aspect of reality
65
New cards
Displacement
Transferring feelings from true source of distressing emotion onto a substitute target
66
New cards
The Tripartite
The Id, Ego and Superego
67
New cards
Parapraxes
A ‘slip of the tongue’
68
New cards
Humanistic Psychology
An approach to understanding behaviour that emphasises the importance of subjective experience and each person’s capacity for self-determinism
69
New cards
Free Will
The notion that humans can make choices and are not determined by internal biological or external forces
70
New cards
Self-Actualisation
The desire to grow psychologically and fulfill one’s full potential - becoming what you are capable of
71
New cards
Hierarchy of Needs
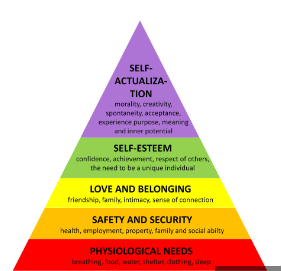
72
New cards
Congruence
The aim of Rogerian therapy, when the self-concept and ideal self are seen to broadly accord or match
73
New cards
Conditions of Worth
When a parent places limits or boundaries on their love for their children
74
New cards
Client-Centered Therapy
Reduces the gap between self-concept and the ideal self (aka counselling)
75
New cards
Debates of Approaches
* Nature Vs Nurture
* Reductionism Vs Holism
* Free will Vs Determinism
* Reductionism Vs Holism
* Free will Vs Determinism