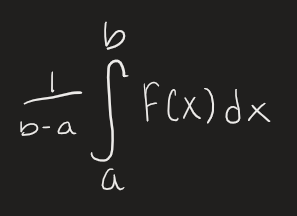BC Definitions and Some AB
1/56
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Integration By Parts
∫udv = uv -∫ [vdu]
![<p>∫udv = uv -∫ [vdu]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/7f08b332-6e85-4241-bec0-eb67c1b65eeb.jpeg)
Geometric Series
infinite series of ar^n
a= first term, r =common ratio
from n=0 to infinity of ∑ ar^n
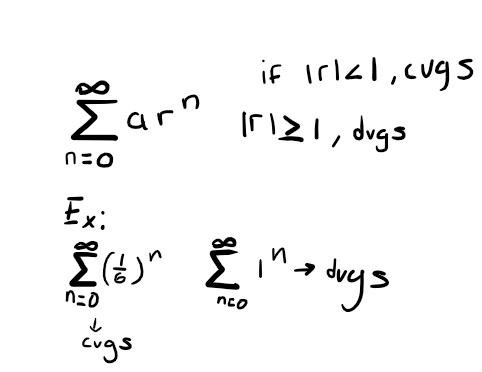
Taylor Series Formula
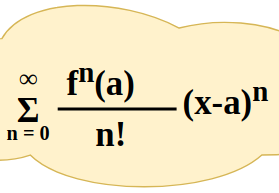
Maclaurin Series Formula
Maclaurin series is a Taylor series but not vice versa
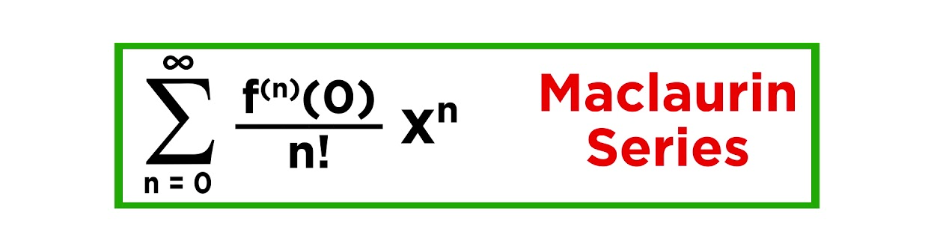
sin(x) Maclaurin Series
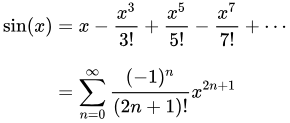
cos(x) Maclaurin Series
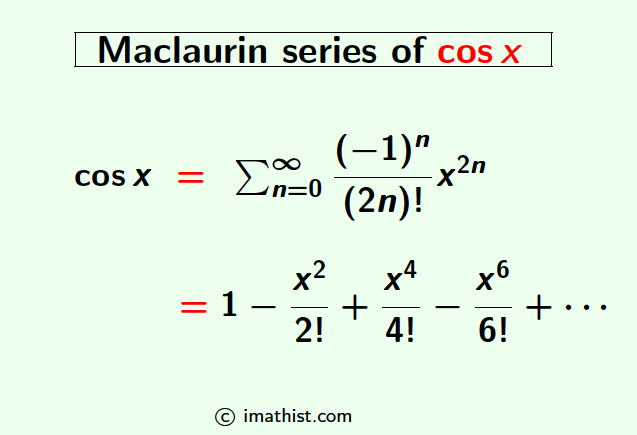
1(1+x) Maclaurin Series
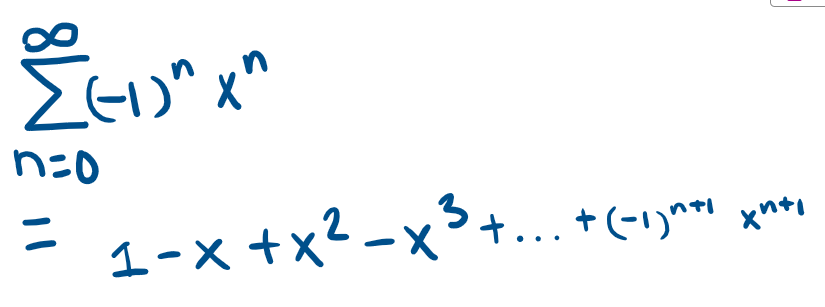
arctan(x) Maclaurin Series
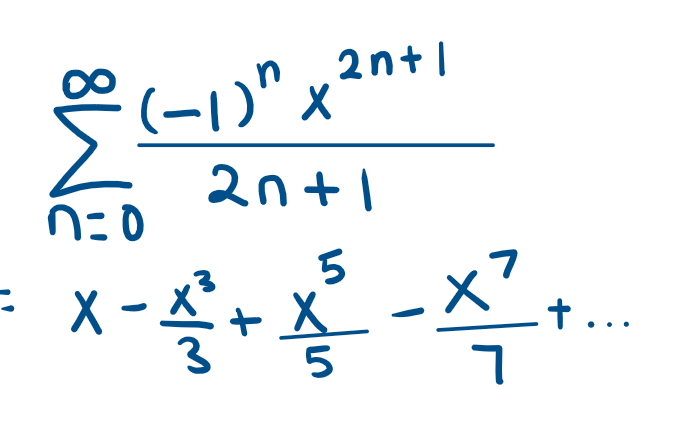
1/(1-x) Maclaurin Series
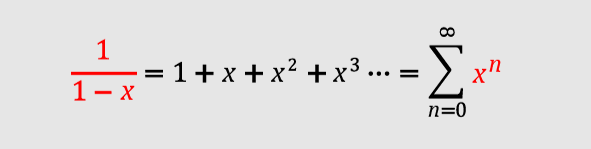
ln(1+x) Maclaurin Series
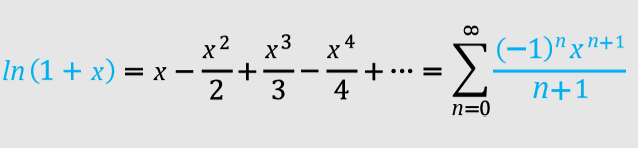
e^x Maclaurin Series
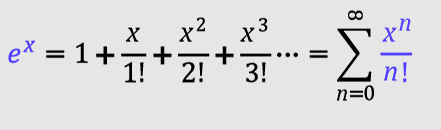
Lagrange Error Bound
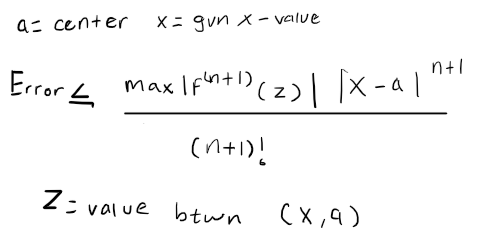
Alternating Series Error Bound
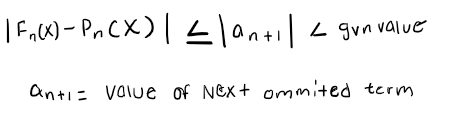
Divergence/nth term test
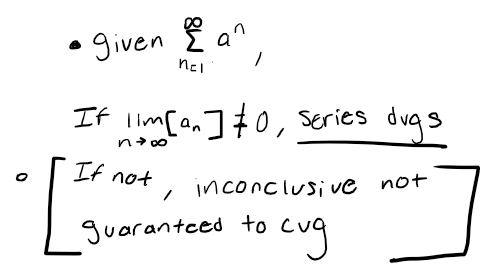
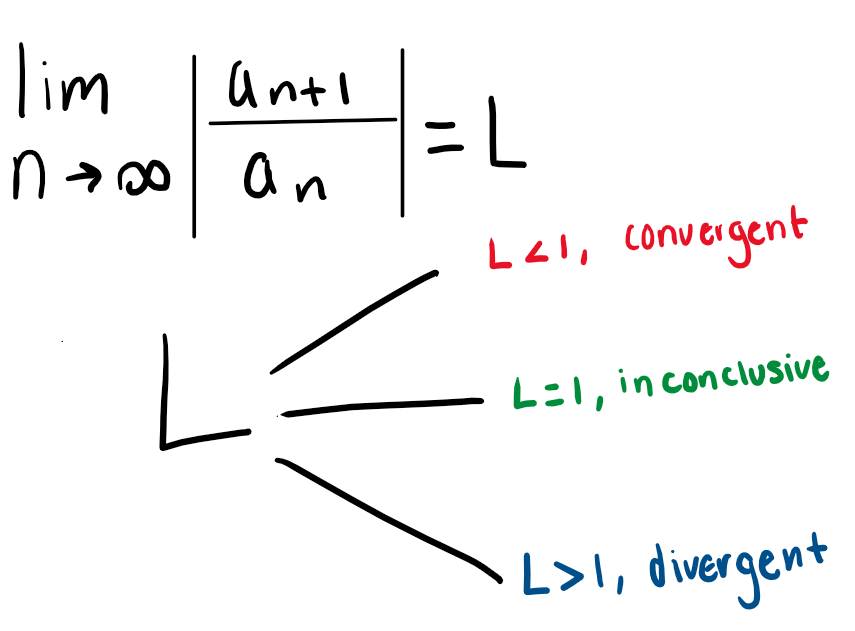
Ratio Test
nth Root Test
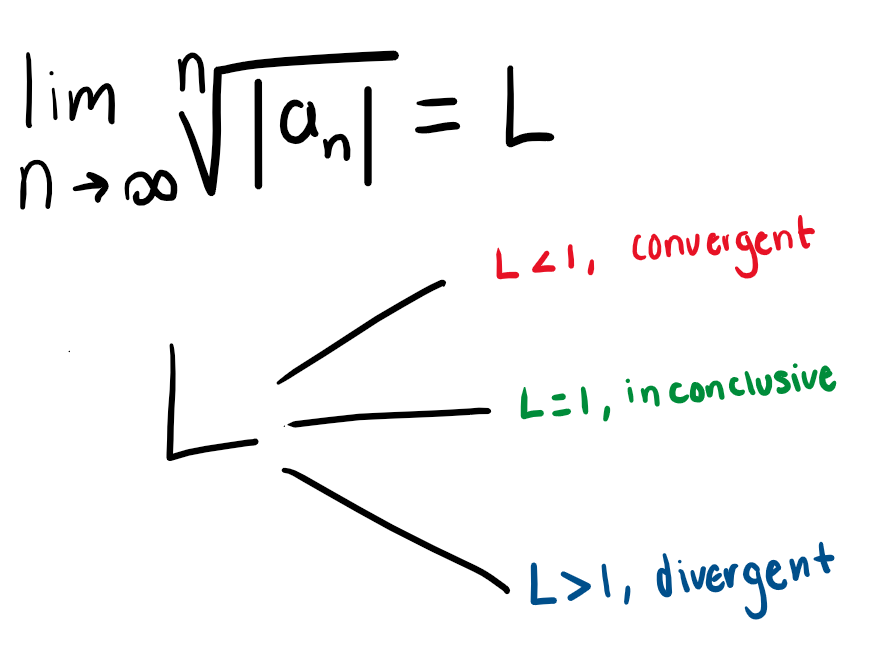
Integral Test
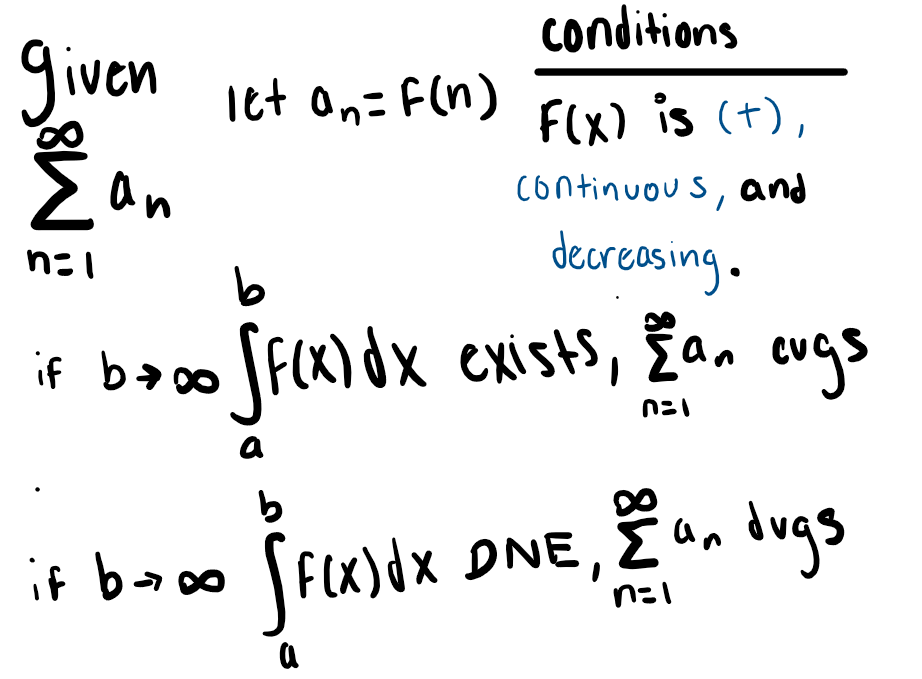
Alternating Series Test
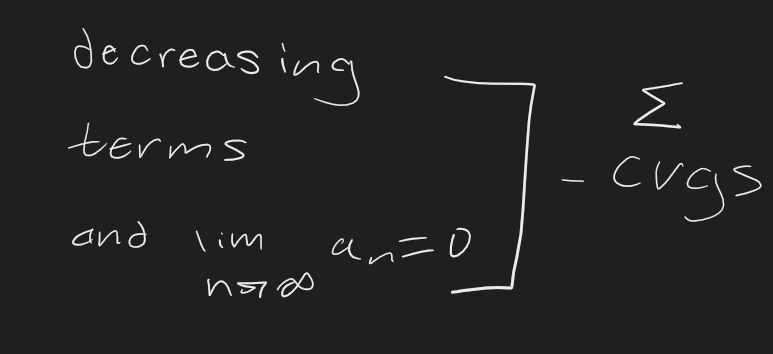
P-series Test
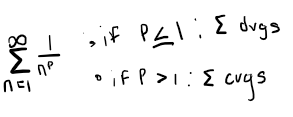
Direct Comparison Test
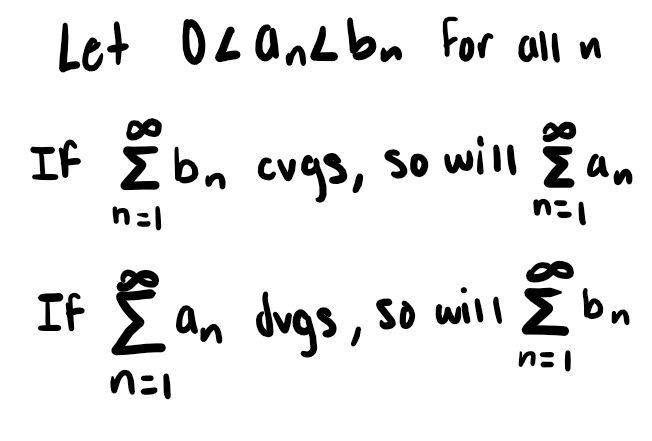
Limit Comparison Test
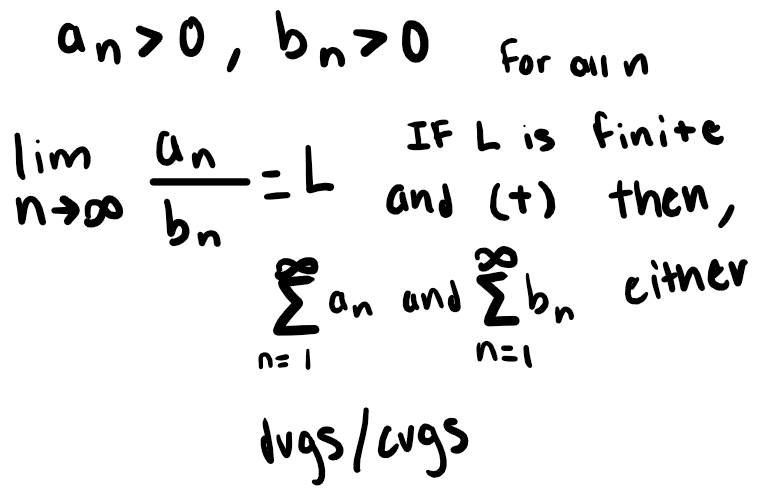
Absolute Convergence Test

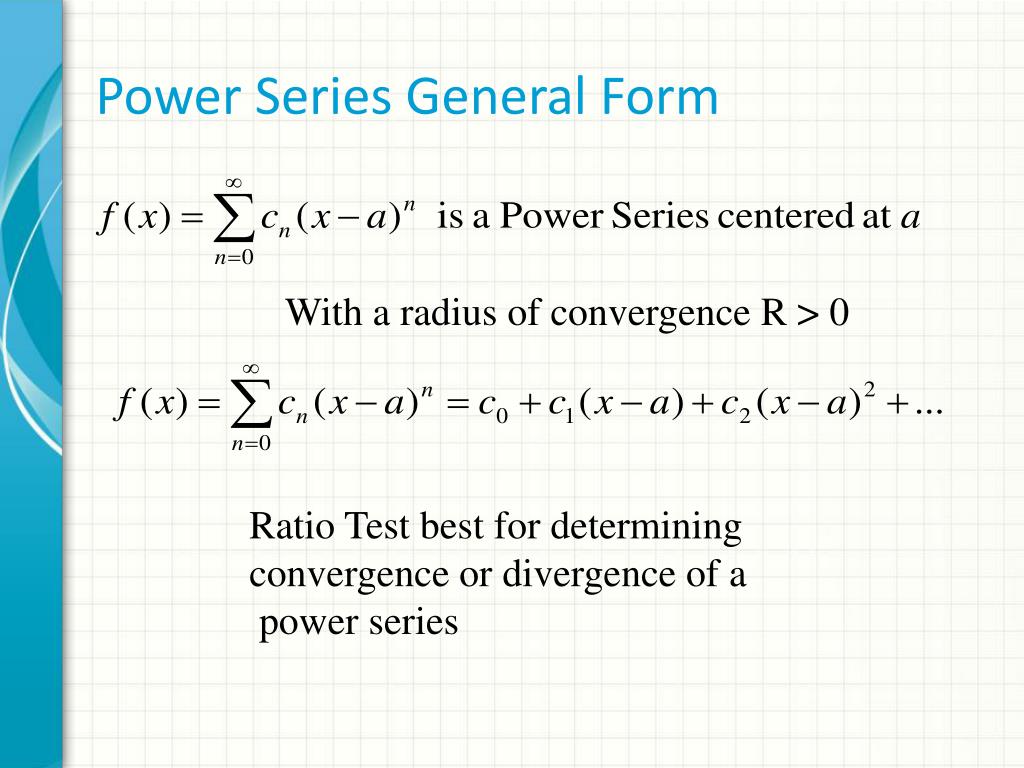
Power Series General Form
In Polar Cords what is x and y equal to?
tanθ = ?
x = rcos(θ) y= rsin(θ)
tan(θ) = y/x
Also
r² = x²+y²
θ = tan-1(y/x)
Area for Polar Curve
A = ½ ∫r²dθ
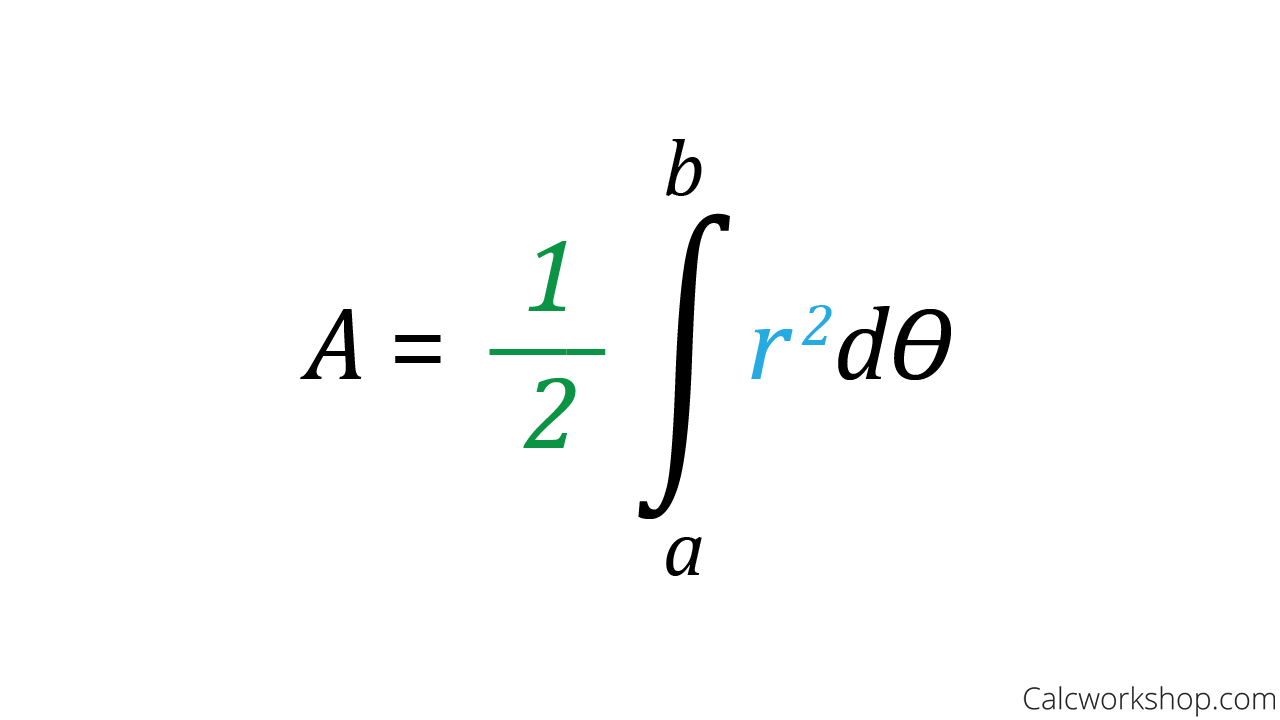
slope for a polar curve
dy/dx = (dy/dθ)/(dx/dθ)
Slope for a parametric curve
dy/dx = (dy/dt)/(dx/dt)
Second derivative of a parametric curve
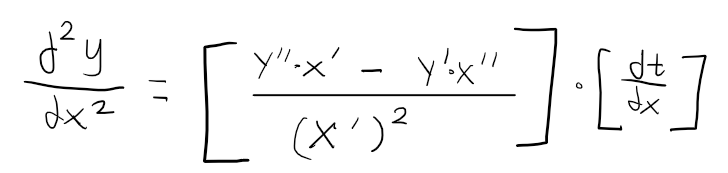
Position, Velocity and Acceleration Vectors.
P = <x(t), y(t)>
V =<x’(t), y’(t)>
A = <x’’(t), y’’(t)>
Arc Length Formula
Remember Arc length parametric terms is simply distance formula
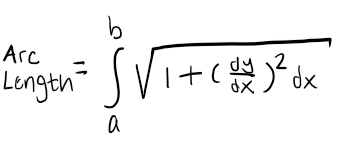
Speed Formula
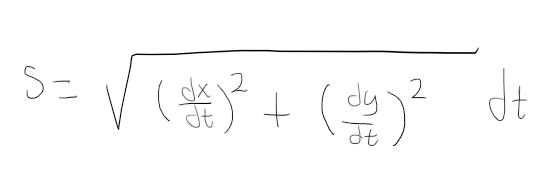
Distance Formula
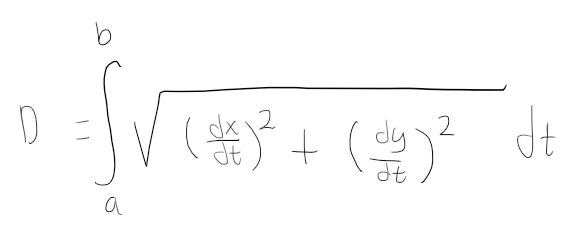
When is the Particle moving to the left and moving to the right?
Velocity = (-) , left
Velocity =(+), right
When is the particle speeding up/moving away from origin?
When Velocity and Acceleration are the same sign
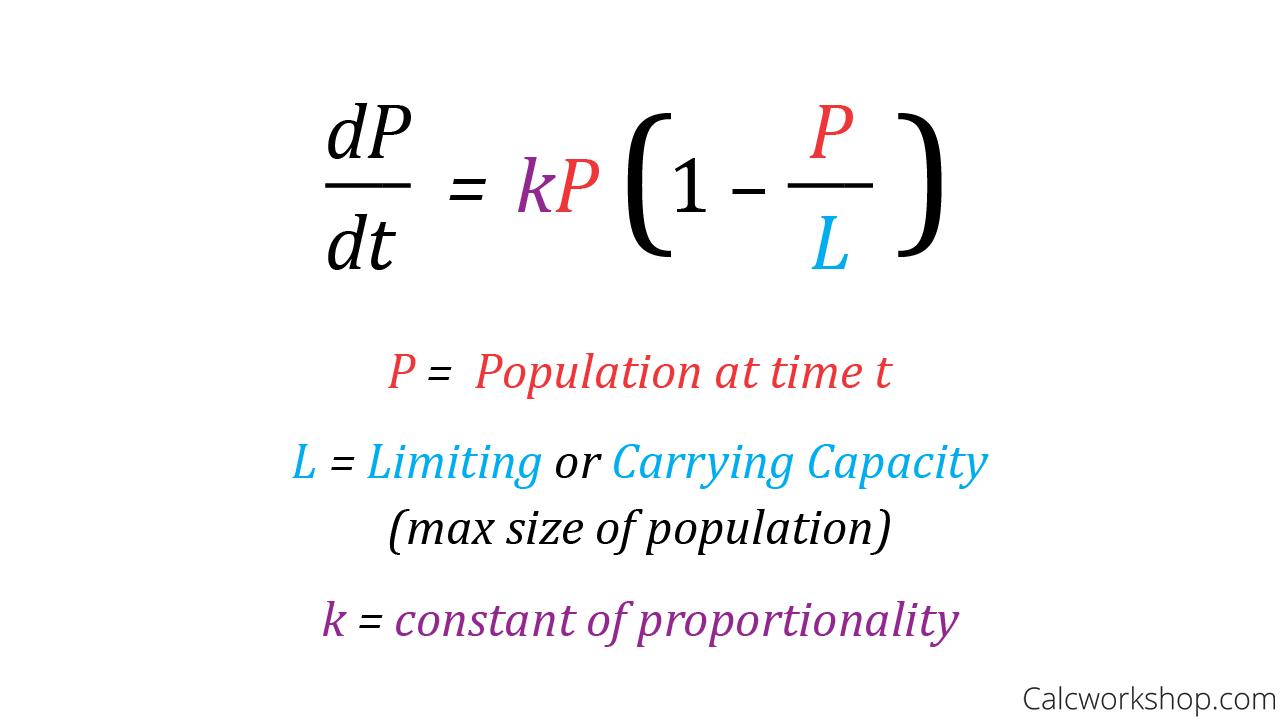
Logistic Differential Equation General Form
dp/dt = kP(1 - P/C)
P = population at time t
C = carrying capacity
k = constant
Logistic Solution Form
P = c/(1+Ae^-kt)
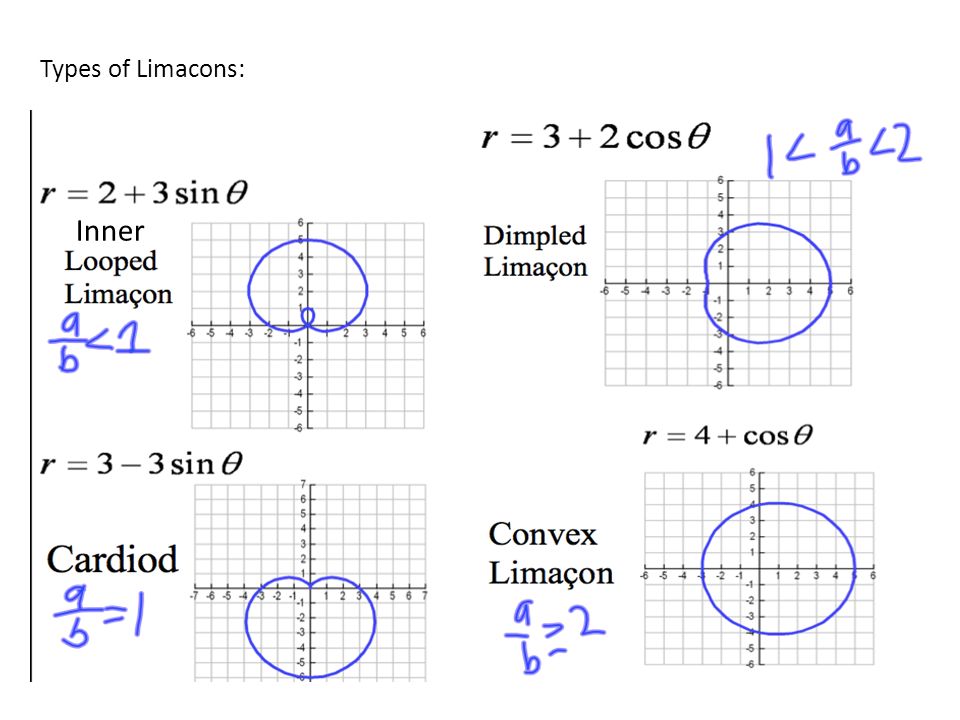
Limacons Variations and General Equation
r = a±bcosθ or r = a±bsinθ
Inner Loop
Cardioid
Dimpled
Convex
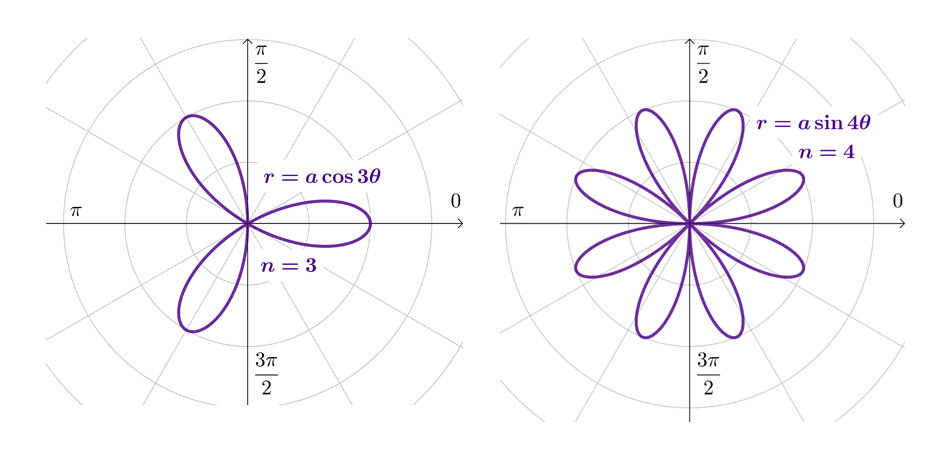
Rose Curves and General Equation
acos(nθ) or asin(nθ)
If n is odd, there are n petals
If n is even, there are 2n petals
First petal positions:
Cos curve - On the x-axis
Sin curve - First Quadrant
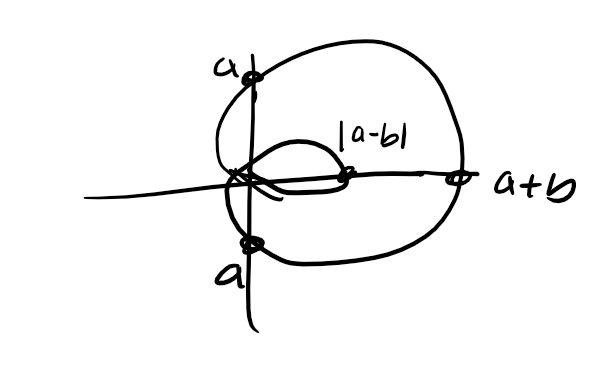
Limacon Inner Loop Points
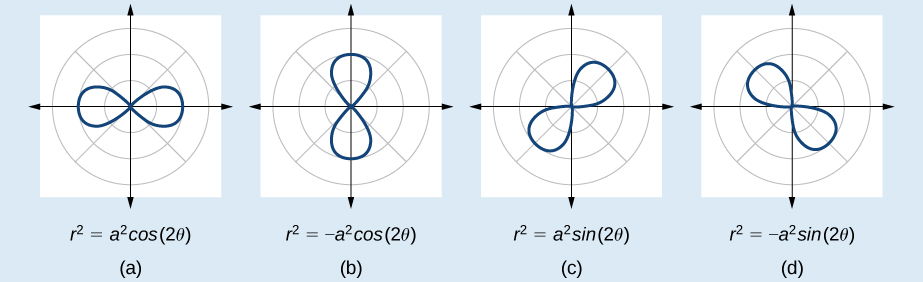
Leminiscate General Equation
r = a²sinθ or a²cosθ
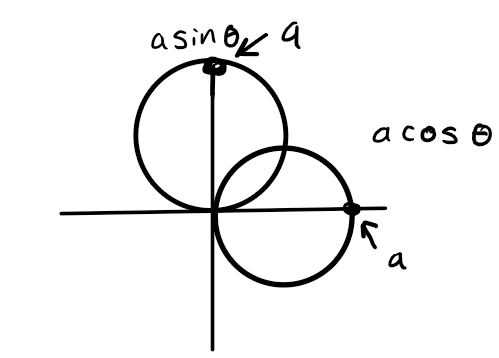
Circle General Equation
r = acosθ or asinθ
Spiral General Equation
r = θ
Infinite Sum
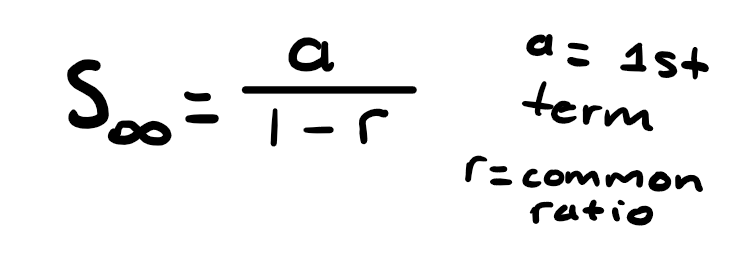
Finite sum
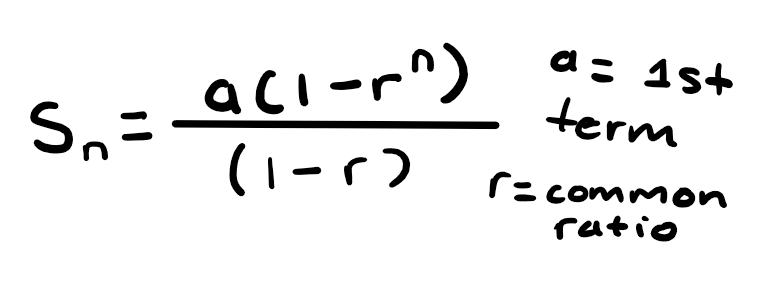
Telescoping Series
First and last term are the only remaining terms within series.
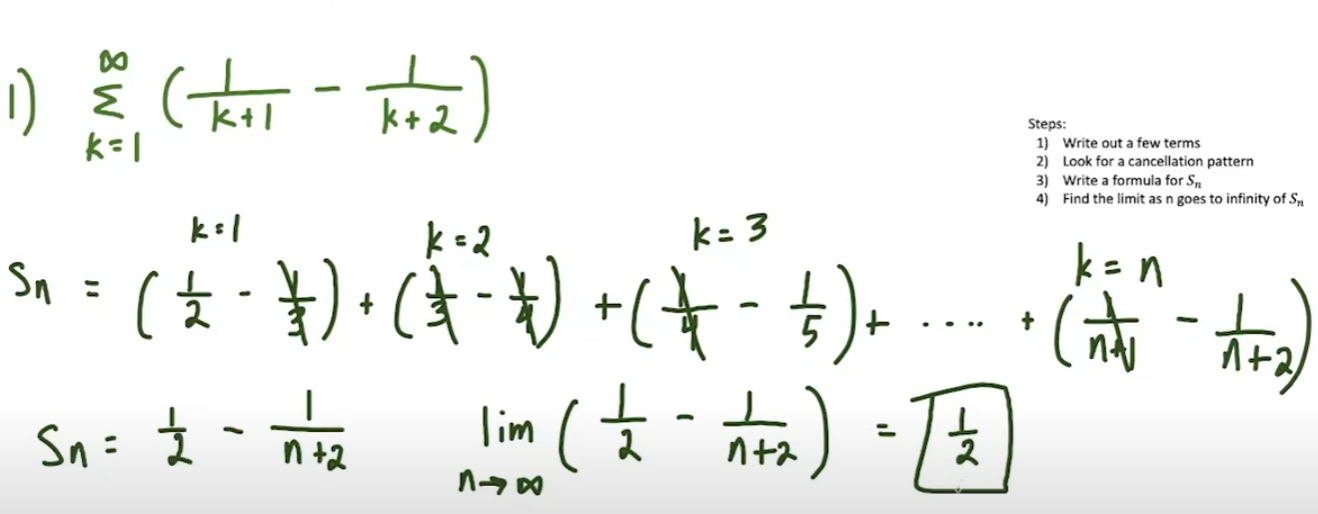
Euler’s Method

Inflection Point/POI
f’’(x) =0 or und and changes sign
Critical Point
f’(x) = 0 or und
Relative Min/Max
Min: f’ changes from (+) to (-) and f’ = 0 or und
f’ changes from (-) to (+) and f’ = 0 or und
What does concave up/down mean?
f’’ > 0 for concave up, f’’<0 for concave down
Tangent Line Eq/ Normal Line eq
Tangent Line: y-y1=m(x-x1)
Norm Line: y-y1=1/m(x-x1)
Riemann Sums
Right hand - overestimate for increasing functions and under for decreasing functions
Vice versa for Left hand
The Trapezoidal sum is the same as the average of the left and right Riemann sums (Goldilocks for estimating)
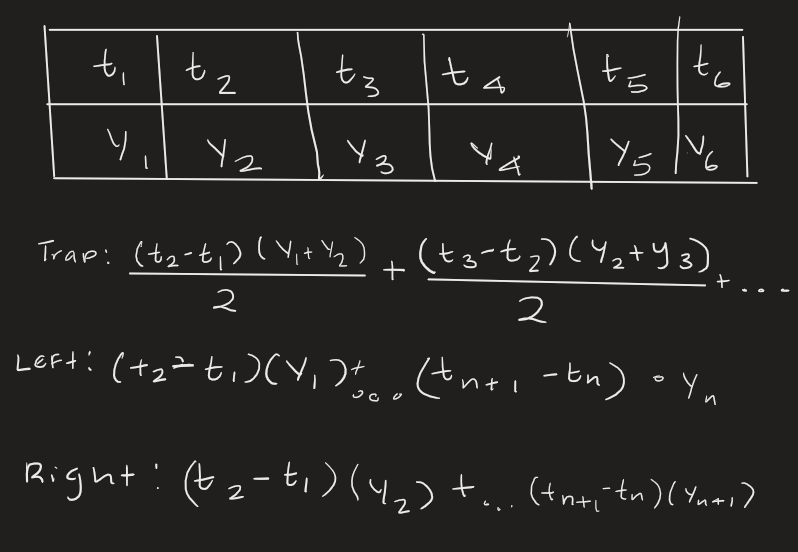
MVT
continuous on [a,b], and differentiable on open,
then exists x=c where f’(c ) =f(b)-f(a)/(b-a)
EVT
If F(x) is continuous on [a,b], then f has both an abs minimum and an abs max
IVT
If f(x) is continuous on [a,b], and k is between f(a) and f(b), and a<C<b then F(C) = k
Cross Section Volume Identities
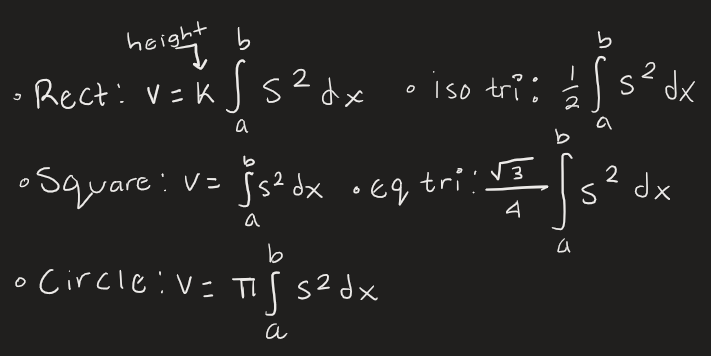
Avg Value