Chapter 14 Vocab
Hydrocarbon- a compound made of carbon and hydrogen only.
Empirical Formula- the formula that tells us the simplest ratio of the different atoms present in a molecule.
Molecular Formula- the formula that tells us the actual numbers of each type of atom in a molecule (C4H8 rather than CH2).
Structural Formula- the formula that tells us about the atoms bonded to each carbon atom in an organic molecule.
Displayed Formula- a drawing of a molecule that shows all the atoms and bonds within the molecule.
Skeletal Formula- a simplified version of the displayed formula; carbon atoms, hydrogen atoms, and C-H bonds are removed; everything else remains the same.
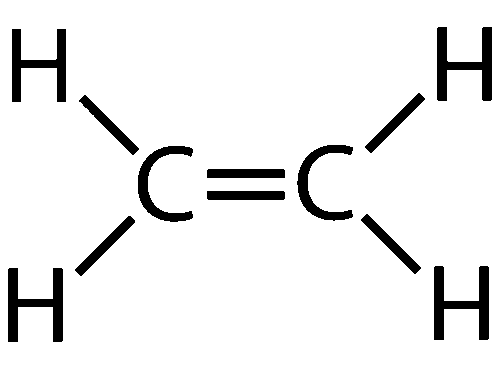
Alkenes- unsaturated hydrocarbons with a C=C bond, general formula CnH2n \n
Arenes- hydrocarbons containing one or more benzene rings general formula: C6H5–(bond).

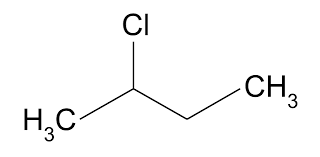
Halogenoalkanes- hydrocarbons with a —X, where X is F,Cl,Br, or I; General formula CnH(2n+1)X.
Alcohols- hydrocarbons with a hydroxy (OH) group; general formula CnH(2n+1)OH.

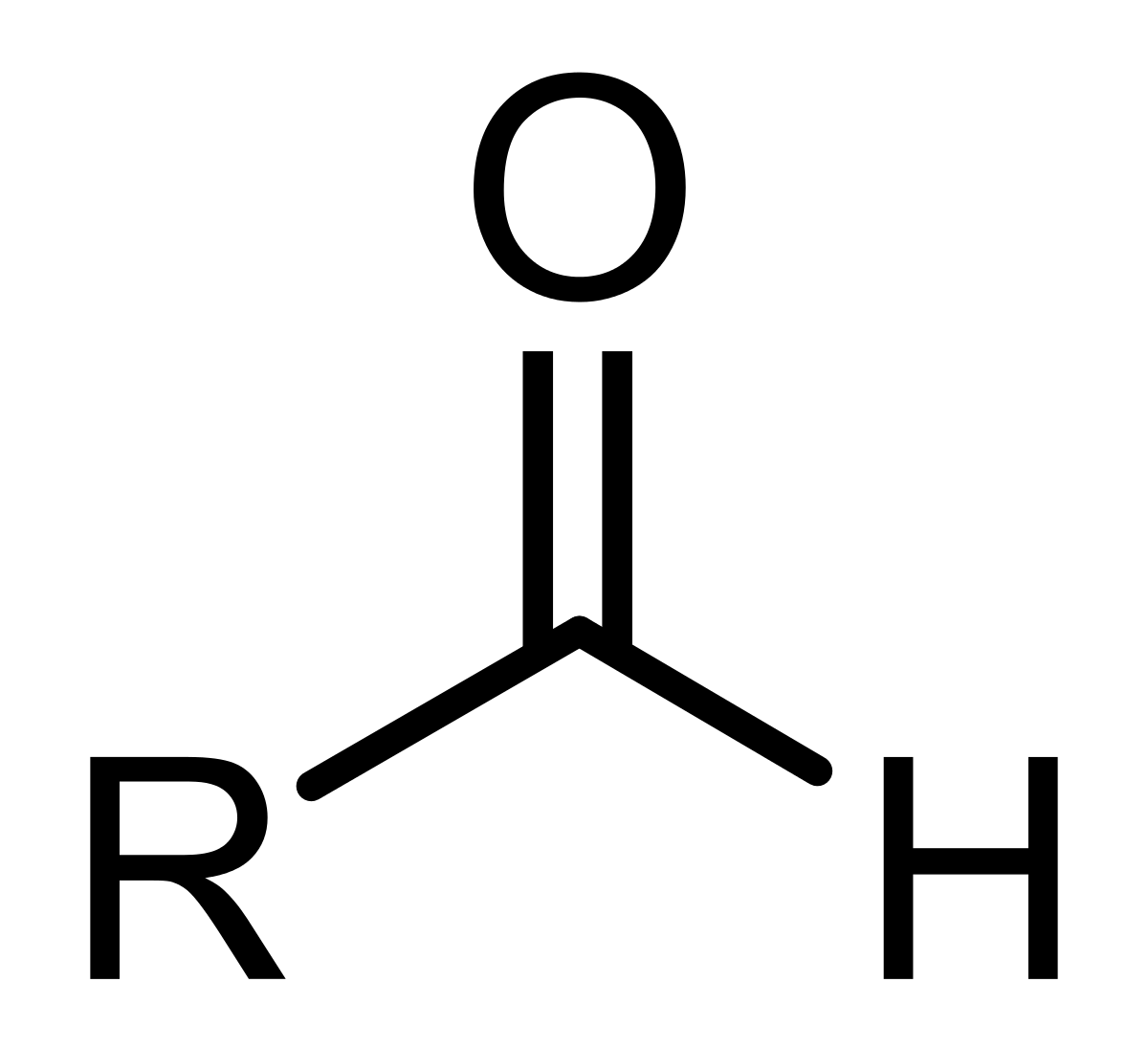
Aldehydes- hydrocarbons with —CHO; general formula CnH(2n+1)CHO.
Ketones- have C=O amidst hydrocarbon chain, general formula CnH(2n+1)COCmH(2m+1).

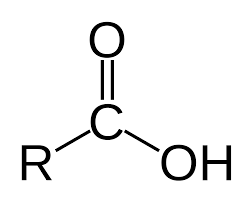
Carboxylic Acids- hydrocarbons with a —COOH; general formula CnH(2n+1)COOH.
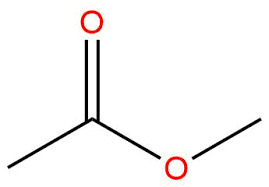
Esters- have a —COO bond amidst hydrocarbon chain; general formula CnH(2n+1)COOCmH(2m+1).
Amines- hydrocarbons with a —NH2(or NH(w/ 2 Carbon bonds) or just N(w/ 3 Carbon bonds)); general formula CnH(2n+1)NH2.
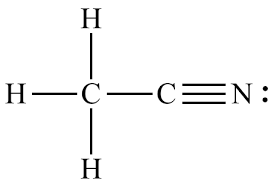
Nitriles- Hydrocarbons with a C(triple bond)N, general formula CnH(2n+1)CN.
%%Functional Group-%% An atom/ group of atoms in an organic molecule that determine the characteristic reactions of a homologous series, examples 7 to 16.
%%General Formula-%% A formula that represents a homologous series of compounds using letters and numbers; plug in any number n/m to get different compounds, listed for vocal words 7 to 16.
Alkyl Group- Alkane stem with -yl at the end.
Single Covalent Bonds- a shared pair of e- bonding 2 atoms together.
%%Sigma (σ) Bonds%%- single covalent bonds formed by “head on” overlap of atomic orbitals.
%%Pi (π) Bond%%- multiple covalent bonds involving the sideways overlap of atomic orbitals.

%%Structural Isomers%%- Compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural formulas (3 types→ position, functional group, and chain).
Position Isomerism- Functional group positions vary.

Functional Group Isomerism- Different functional groups present.
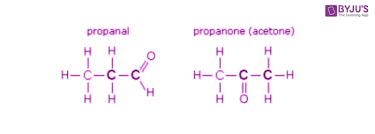
Chain Isomerism- Carbon “skeleton” structures differ; aka main C-chain differs.

%%Stereoisomerism%%- Same molecules bonded to each other except in different arrangements; two types →cis-trans and optical.
Cis-trans Isomerism- No free rotation exists, typically because of C=C.

Optical Isomerism- When 2 molecules are mirror images; sometimes called enantiomers, referenced using right-hand and left-hand analogy (b/c right and left hands are mirror images).
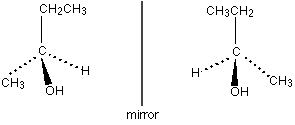
Chiral Center- atom with 4 different groups attached, allows for optical isomerism, typically marked using asterisk (*).

Homolytic Fission- Both atoms take 1e- each (HCl→H•+Cl•).
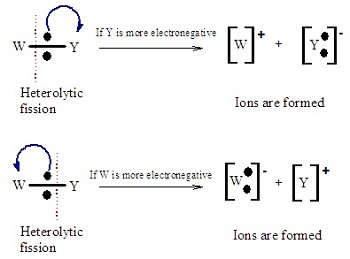
Heterolytic Fission- 1 atom takes both e-, marked using small curly arrows.
Free Radicals- Very reactive atoms/molecules that have a single unpaired e-, represented with a dot (H• and Cl•).
Initiation Step- First step in mechanism of free radical substitution of alkanes by halogens, involves the breaking of the halogen-halogen bond by UV light from the sun.

Propagation Step- radicals formed in 34 can then attack reactant molecules generating more free radicals, can happen multiple times.

Termination Step- Final step continuing from 34 and 35 where 2 free radicals react and form a molecule, ending the reaction.

Carbocation- An alkyl ion with a single positive charge on one carbon atom.

Positive Inductive Effect- Property of an alkyl group to “push” e- away from themselves (b/c of this, more alkyl groups= lower charge density).
Electrophile- Acceptor of a pair of e-, carbocations are electrophiles.
Nucleophile- Donator of a pair of e-, electron rich.
Addition Reaction- Organic reaction where 2 reactant molecules form 1 product molecule (C2H4+Br2→C2H4Br2).
Elimination Reaction- Removal of a small molecule (like H2O or HCl) from an organic molecule
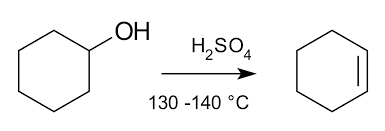
Substitution Reaction- Replacement of one atom/ group of atoms by another.

Hydrolysis- Breakdown of a compound by water, often speeded up by reacting with base/alkali.
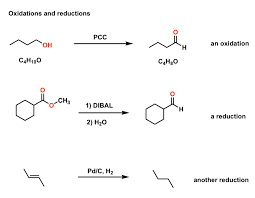
Oxidation- Addition of oxygen and/or removal of hydrogen from a molecule.
Reduction- Removal of oxygen and/or addition of hydrogen from a molecule.