2.2 Organizational structure
Introduction
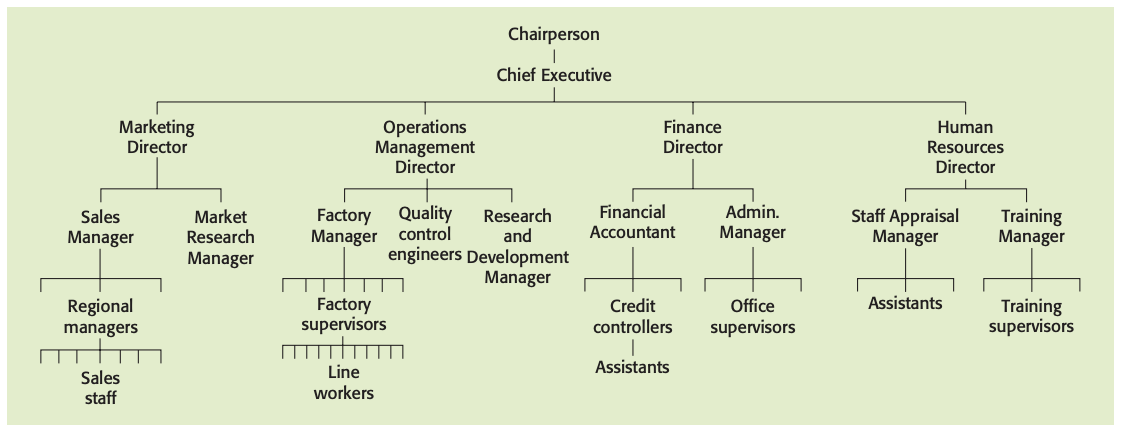
Organizational structure: internal, formal framework of a business that shows the way in which management is organized and linked together and how authority is passed through the organization.
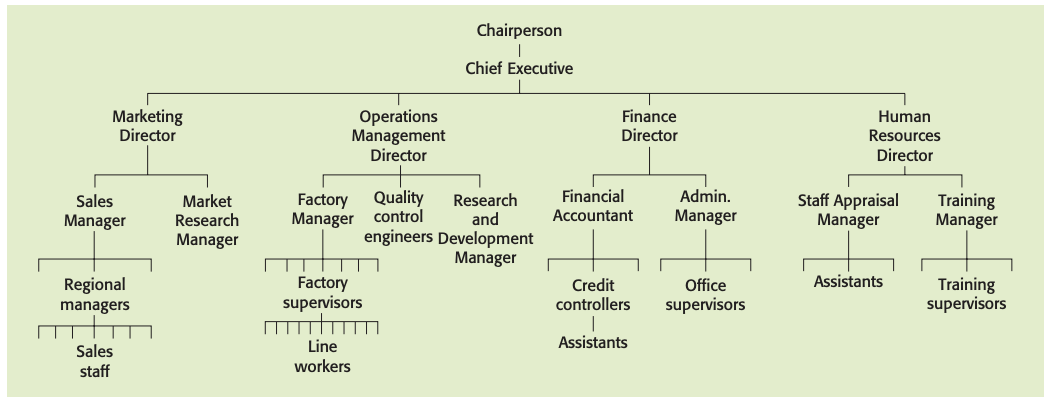
The traditional hierarchical structure
Key principles of organizational structure
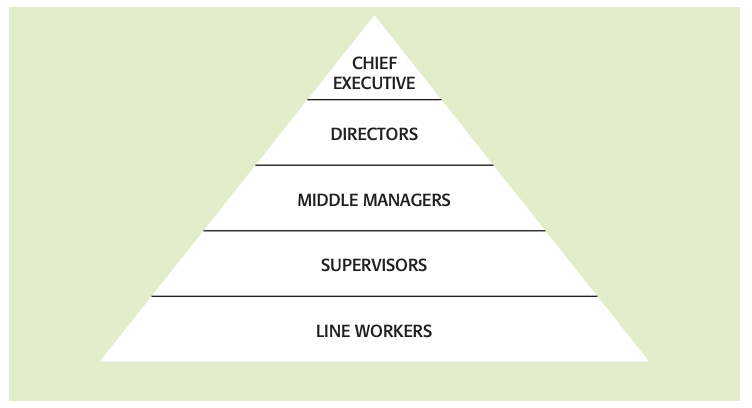
Level of hierarchy: stage of the organizational structure at which the personnel on it have equal status and authority.
Tall (vertical) structure: one with many levels of hierarchy and, usually, narrow spans of control.
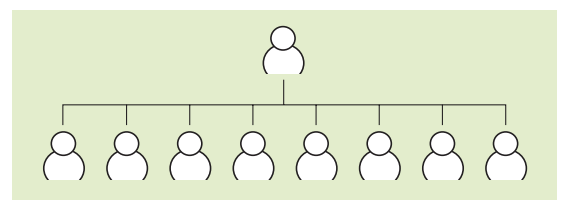
Flat (horizontal) structure: one with few levels of hierarchy and wide spans of control.
Span of control: number of subordinates reporting directly to a manager.
Chain of command: this is the route through which authority is passed down an organization from the chief executive and the board of directors.
Delegation and accountability
Delegation: passing authority down the organizational hierarchy.
Accountability: obligation of an individual to account for his/her activities and to disclose results in a transparent way.
Delayering
- Delayering: removal of one or more of the levels of hierarchy from an organizational structure.
- It leads to wider spans of control and increased delegation to subordinates.
Bureaucracy
- Bureaucracy: organizational system with standardized procedures and rules.
- It discourages initiative and enterprise as decisions are taken centrally and then put into effect by staff following set procedures and protocols.
- Max Weber (sociologist) identified the main attributes of bureaucracy as rationality and efficiency.
Centralization and decentralization
Centralization: keeping all of the important decision making powers within head office or the centre of the organization.
Decentralization: decision-making powers are passed down the organization to empower subordinates and regional/product managers.
Different types of organizational structures
Hierarchical structure: structure in which power and responsibility are clearly specified and allocated to individuals according to their standing or position in the hierarchy.
By product: organizational structure based on products that usually consists of several parallel teams a focusing on a single product or service line.
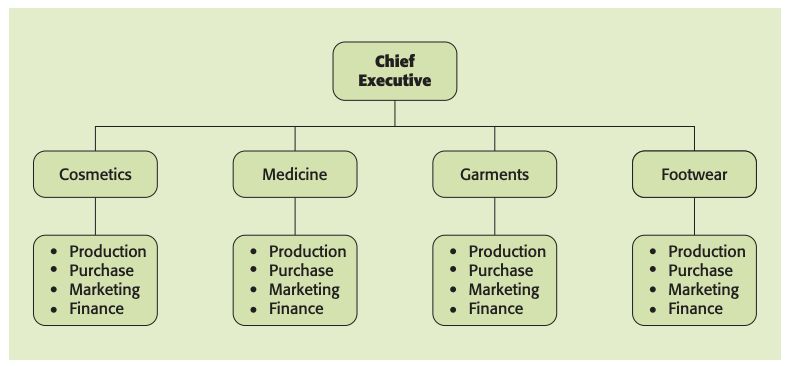
By function
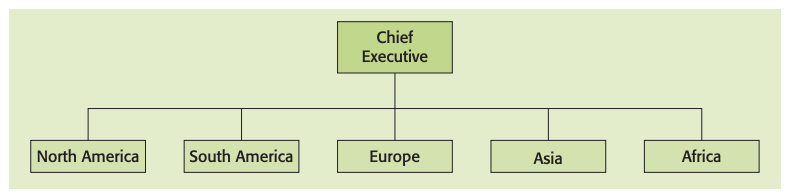
By region
Factors influencing organizational structure
- Size of the business and the number of employees.
- Style of leadership and culture of management.
- Retrenchment caused by economic recession or increased competition might lead to delayering to reduce overhead costs
- Corporate objectives
- New technologies (especially IT)
Changes in organizational structures
- There are alternative organizational structures, other than the hierarchical type, namely:
- Matrix structure: organizational structure that creates project teams that cut across traditional functional departments.
- Horizontally linked structure
- Structure primarily found in the IT and high-tech sectors
- In a horizontal structure, employees are grouped by function into three areas planning, building and running.
- This structure allows the company to respond quickly to changing market conditions and technological advances, but may not work as well for companies that produce products with a longer lifespan, or for service industries.
Communication in an organization
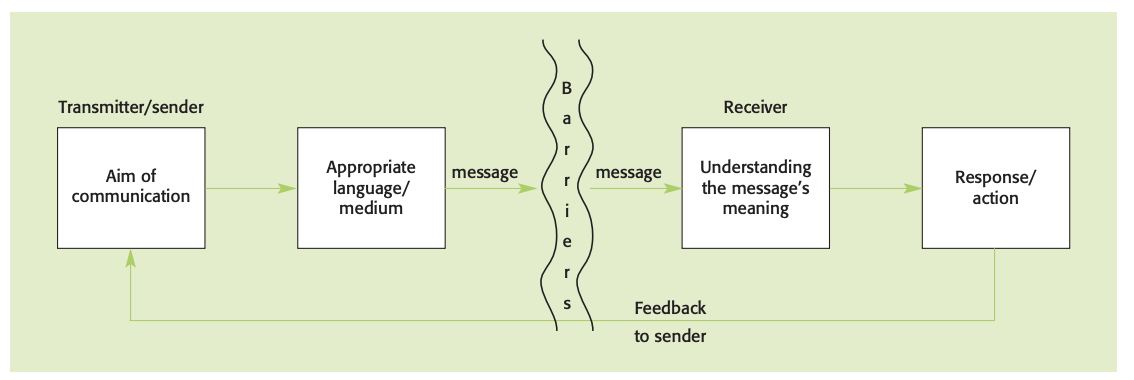
Communication is only effective if the message has been received and understood by the receiver and the sender knows that it has been understood.
Effective communication: exchange of information between people or groups, with feedback.
Key features:
Sender (or transmitter) of the message
Clear message
Appropriate medium (way in which the message is sent)
Receiver
Feedback to confirm receipt and understanding