lab practical 2
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
113 Terms
Prokaryotic cells and 2 domains
lacks a membrane bound nucleus
archae
bacteria
Eukaryotic cells and 4 domains
have a membrane bound nucleus
protista
fungi
plantae
animalia
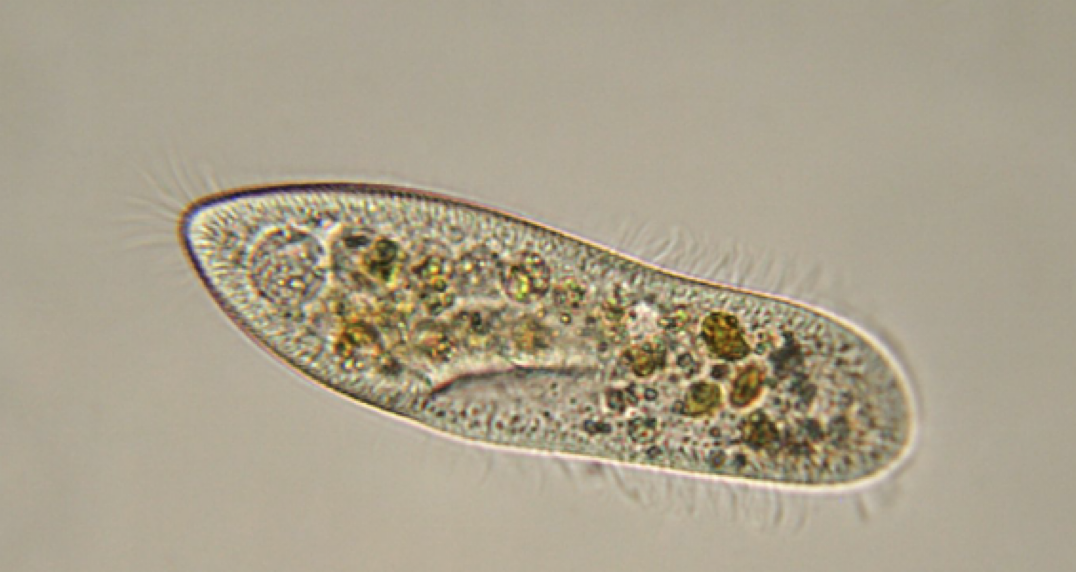
what is this?
protista
nucleus
cilia
unicellular
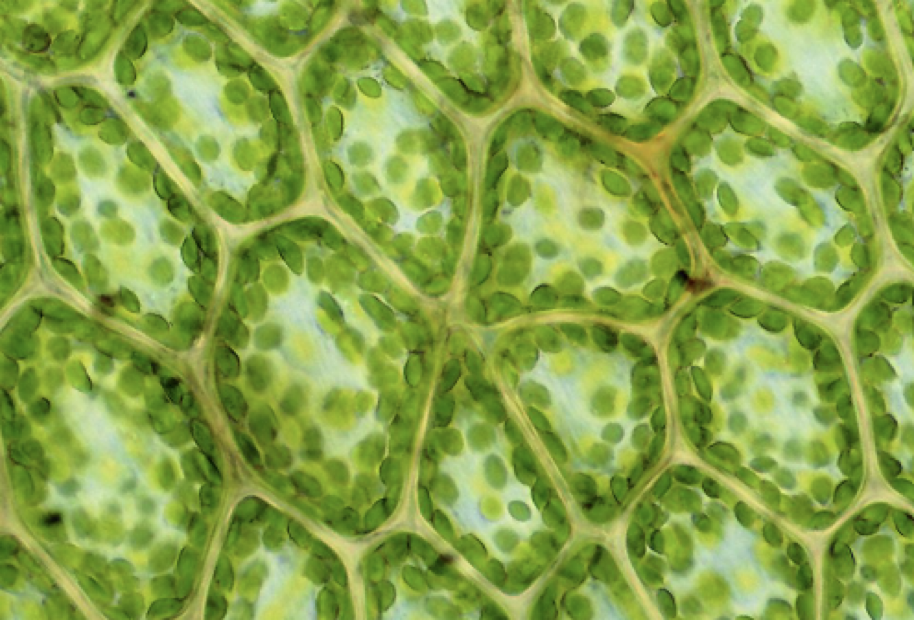

what is this
plantae
chloroplasts
cell wall
multicellular
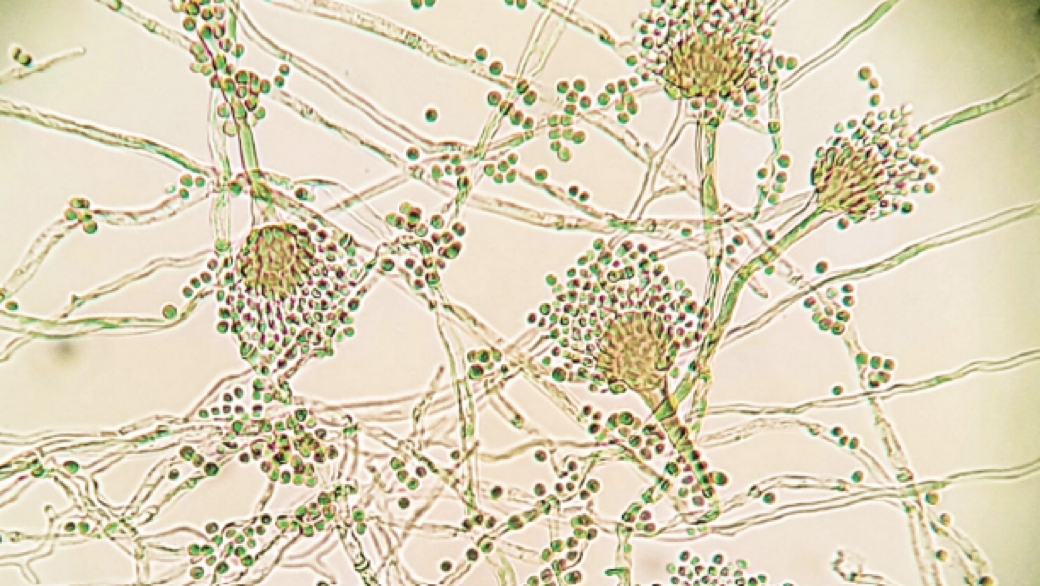
what is this
fungi
ascospores
multicellular
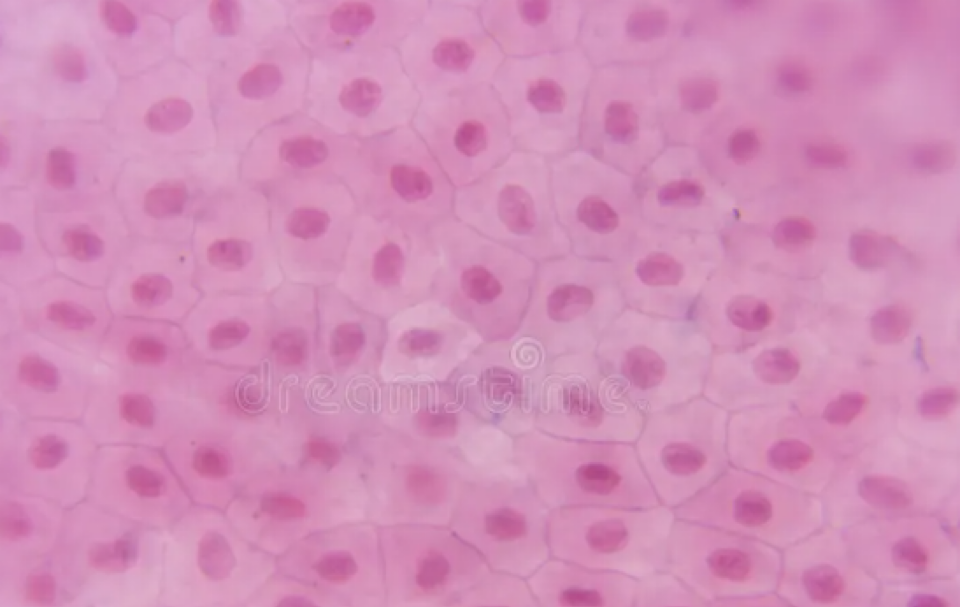
what is this
animalia
nucleus
no cell wall
multicellular
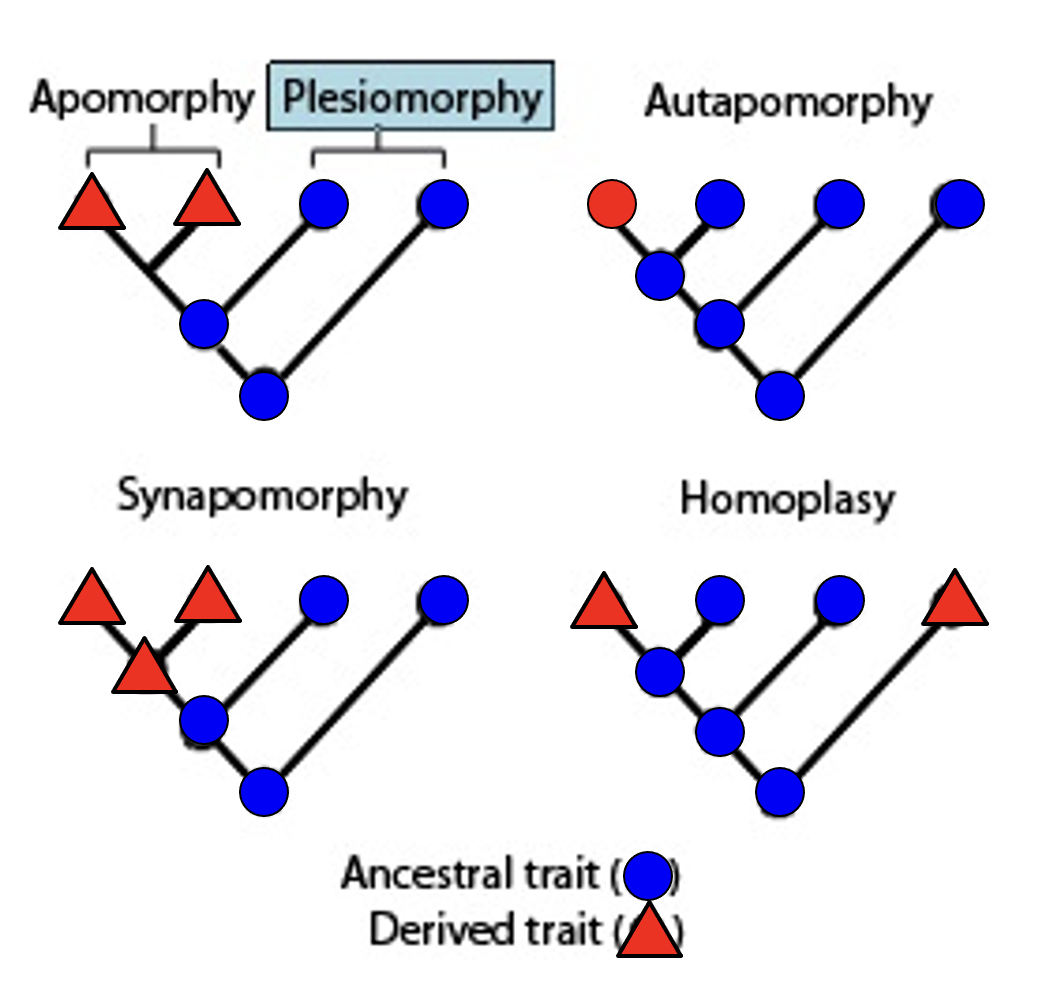
plesiomorphy
ancestral character state
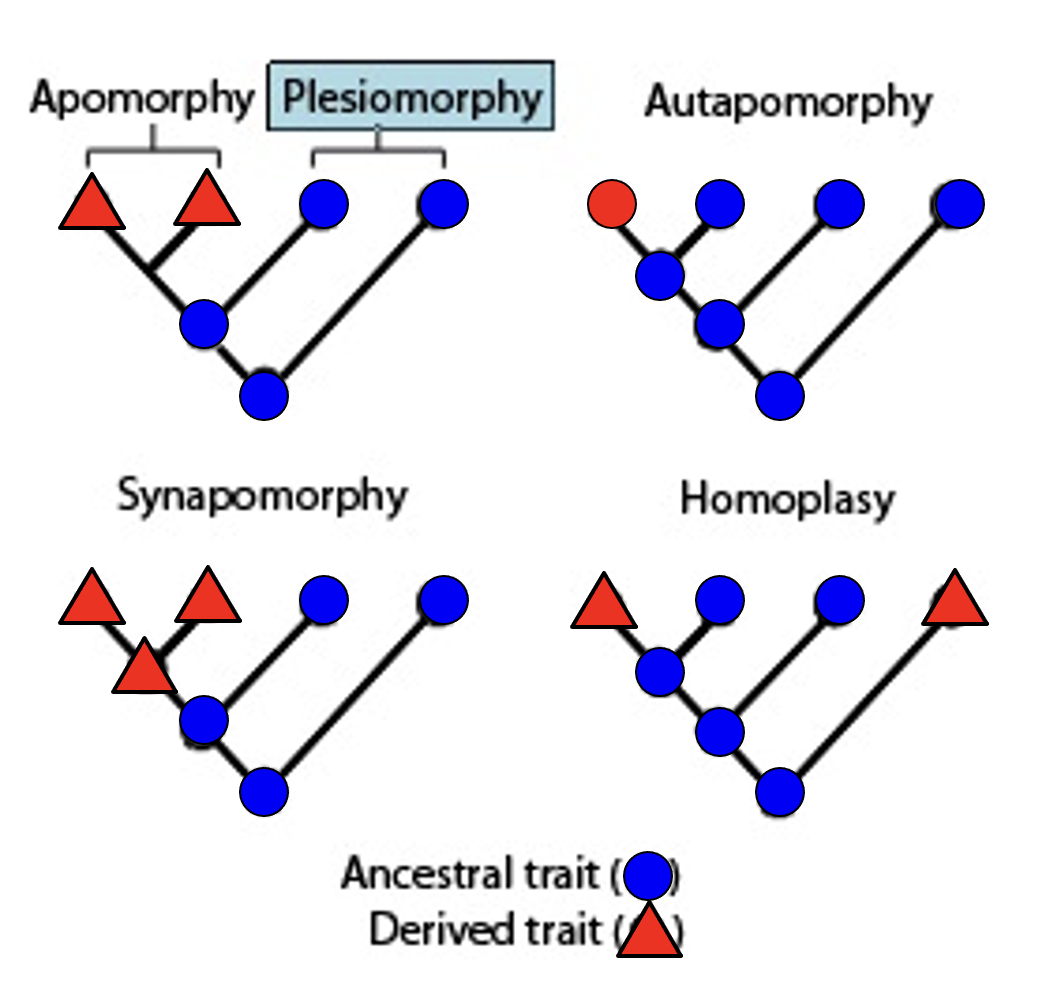
apomorphy
a new derived character state
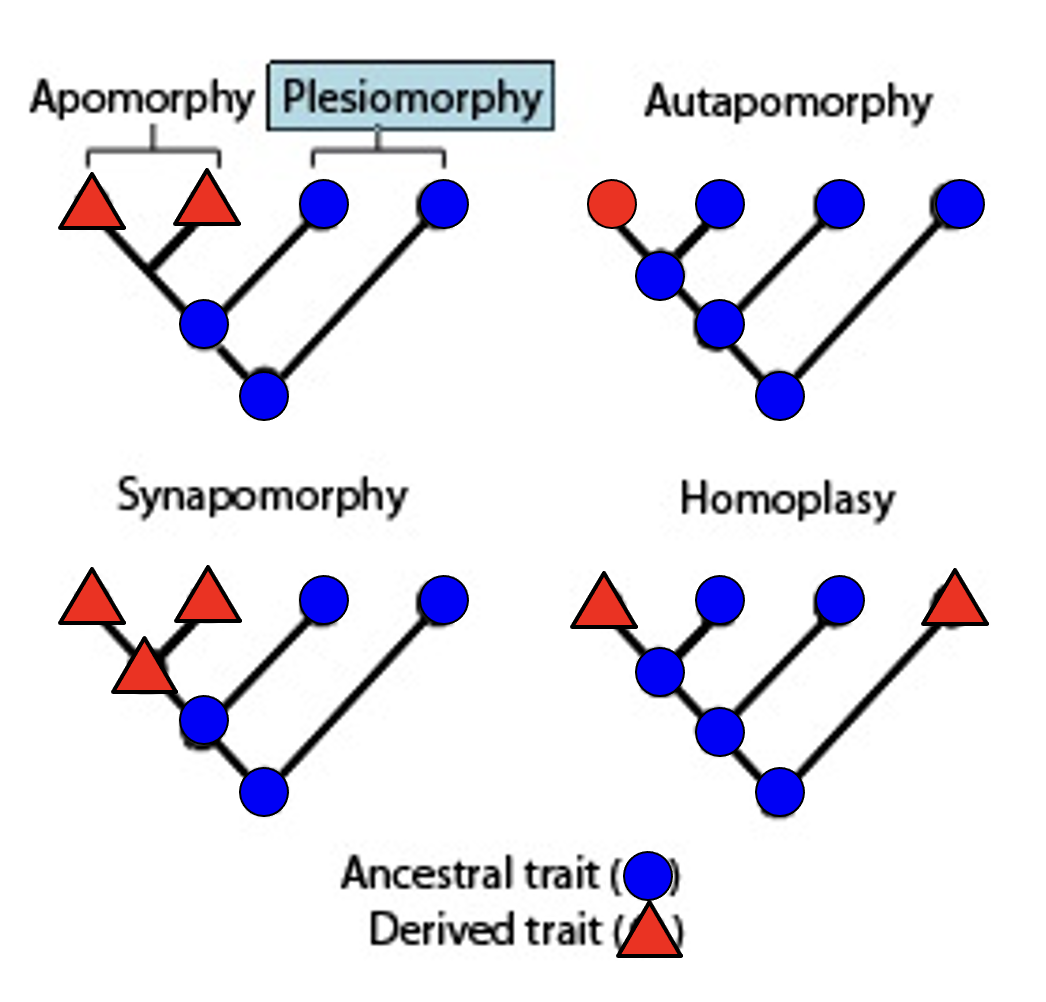
autapomorphy
derived character state that is unique to a monophyletic taxonomic group
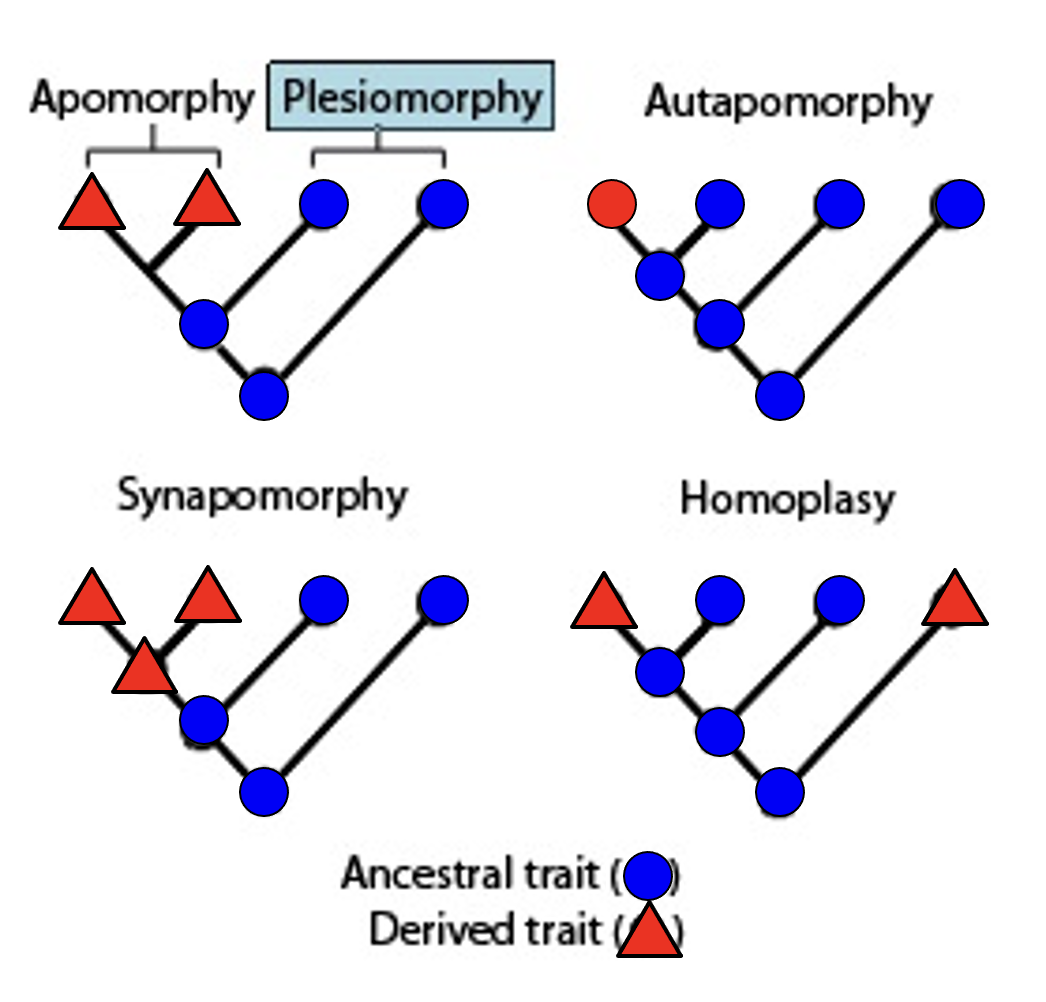
synapomorphy
a derived trait present in ancestral species and shared exclusively with its evolutionary descendants
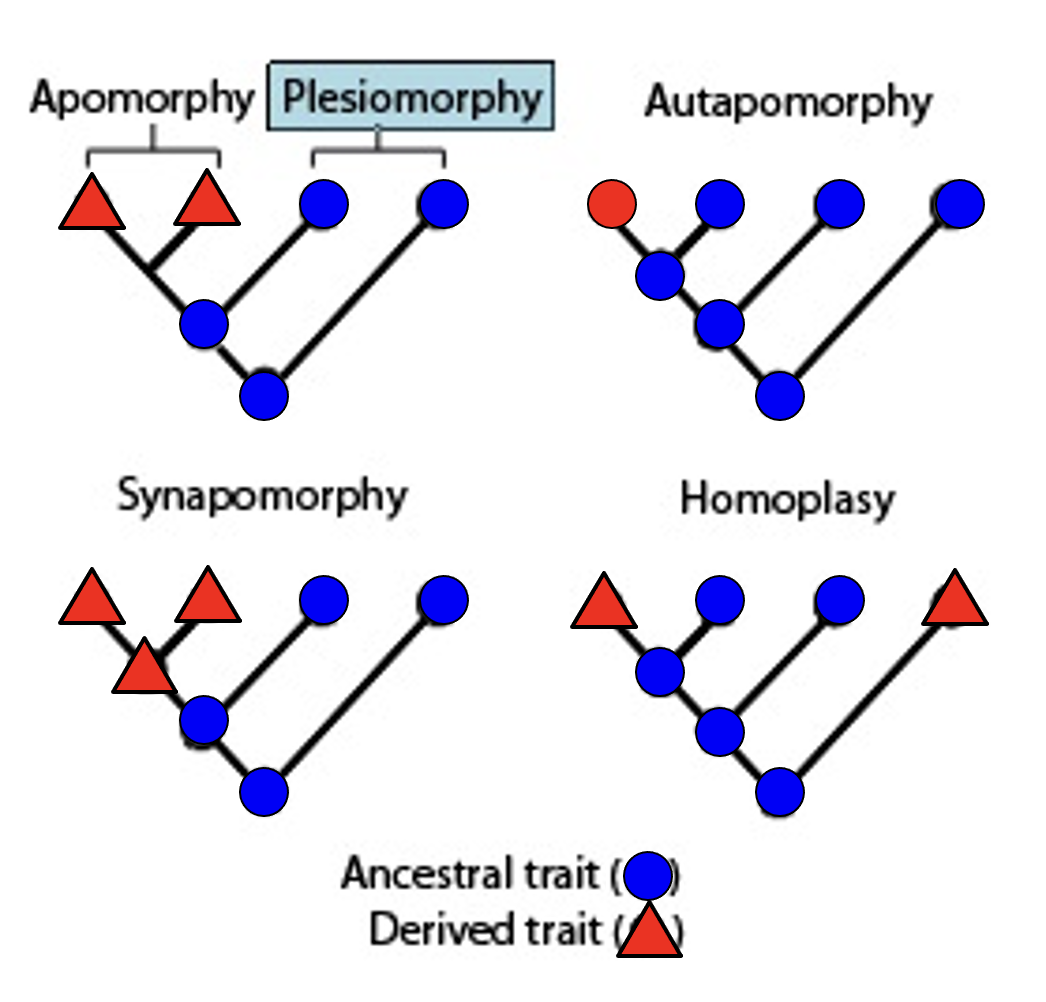
homoplasy
derived character that is shared between two or more organisms that did not arise from common ancestry
monophyletic group
a group of organisms that includes a common ancestor and all of its descendants.
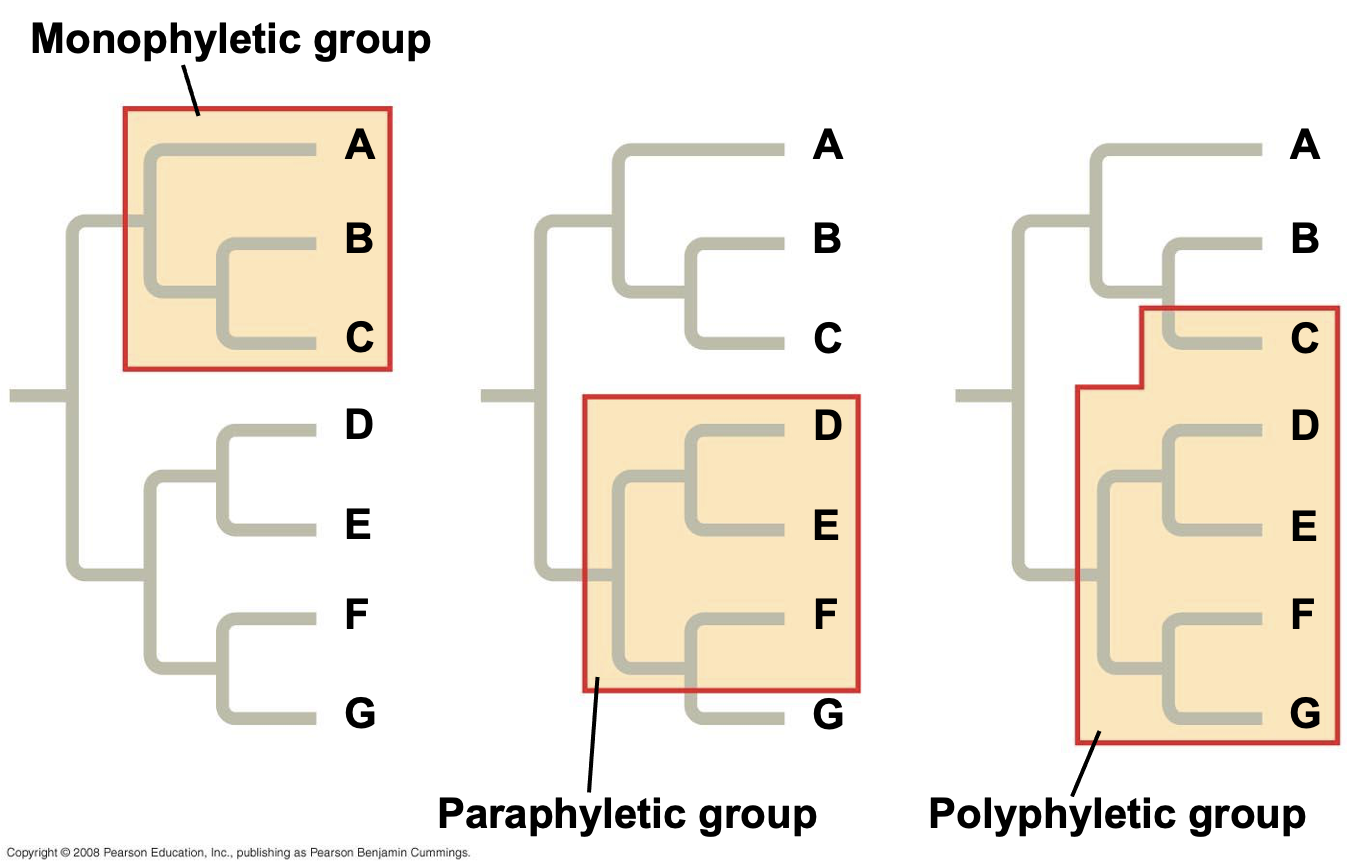
paraphyletic group
a group that includes a common ancestor and some, but not all, of its descendants
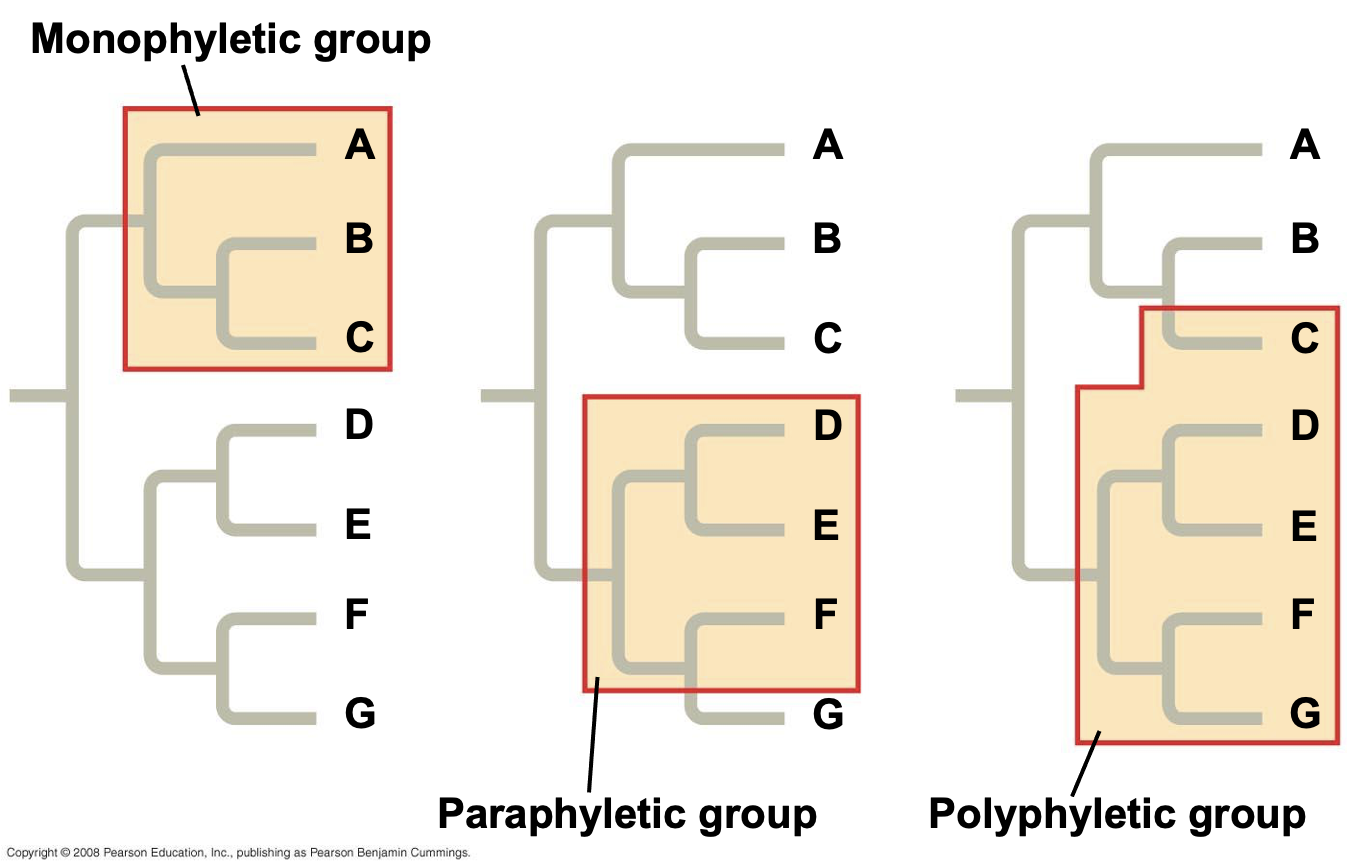
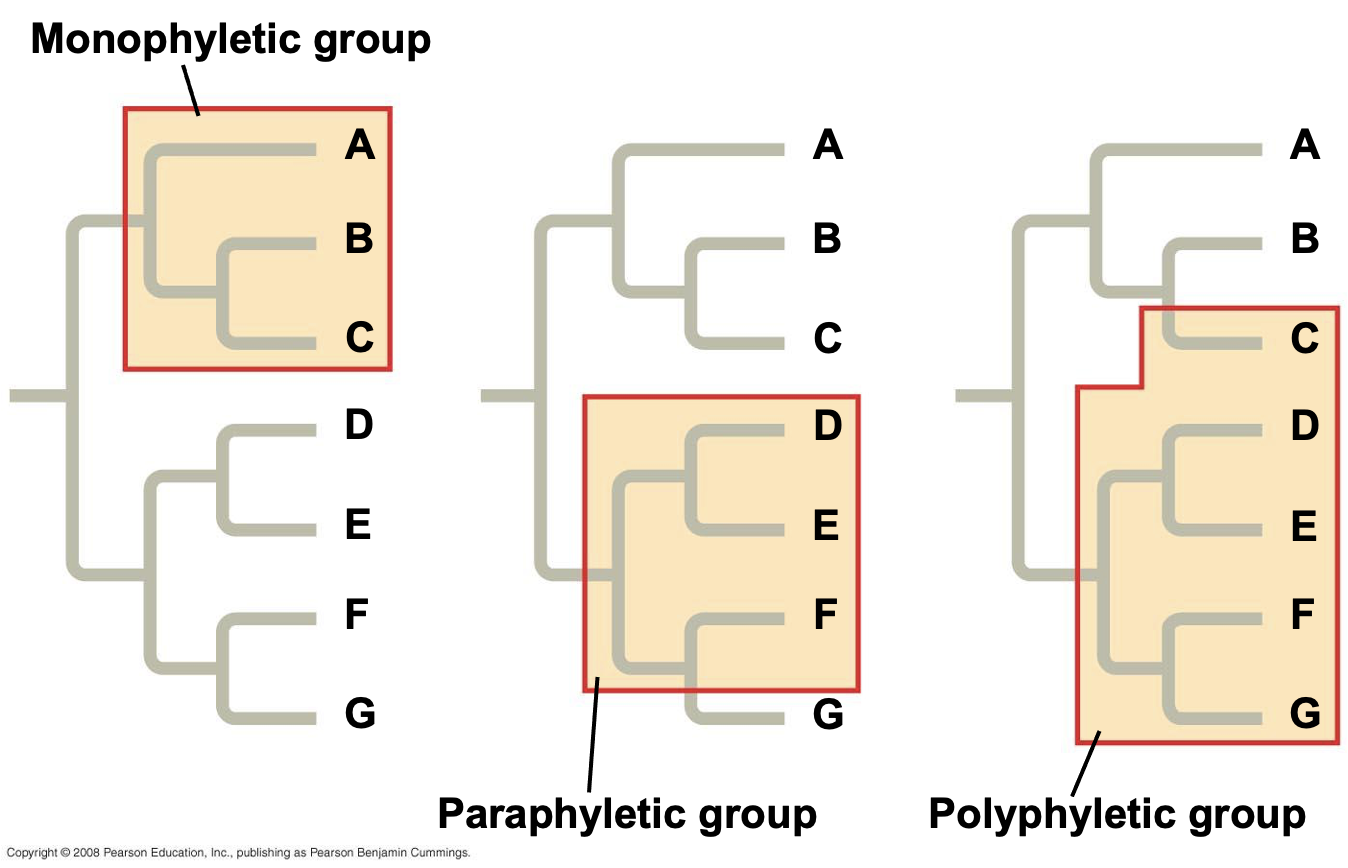
polyphyletic group
a group of organisms that share a common set of traits, but whose members do not share a recent common ancestor
5 assumptions of the hardy-weinberg principle
no natural selection
no mutation
no migration(gene flow)
no genetic drift (large population)
no sexual selection (random mating)
Hardy-weinberg model
p²+2pq+q²=1
If the frequency of the homozygous dominant genotype (AA) is 0.49, and the population is in H-W equilibrium, what is the frequency of the dominant allele?
p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1
p2 = 0.49
p2 = 0.7
If the frequency of the recessive allele (a) is 0.3, what is the frequency of the dominant allele?
p + q = 1
p + 0.3 = 1
p = 0.7
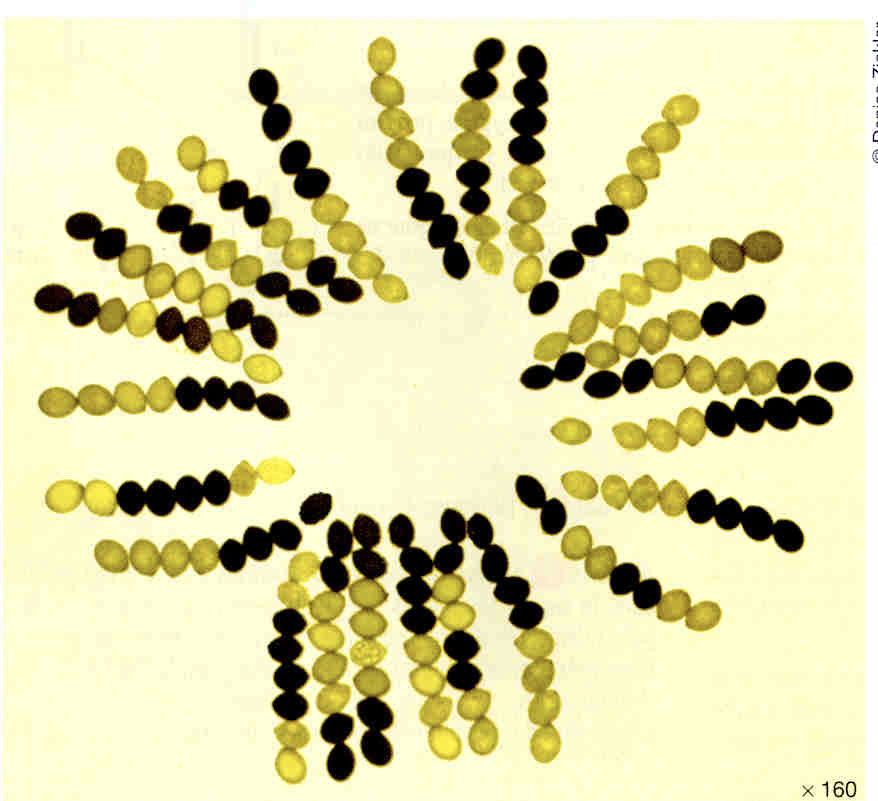
how many spores show crossing over
13 or 14
In a population of ladybugs, you find that 100 individuals have no spots (g, recessive) and 300 have spots.
Assuming the population is in H-W equilibrium, what are the frequencies for each genotype? What are the allele frequencies? How many individuals are heterozygous for the trait?
Allele frequencies:
p = 0.75
q = 0.25
Genotype frequencies:
p2 = 0.563
2pq = 0.375
q2 = 0.0625
individual counts:
GG = 225
Gg = 150
gg = 25
In a population of cats, you find that 25 individuals are feisty (c, recessive) and 50 are docile.
Assuming the population is in H-W equilibrium, what are the allele frequencies? What are the frequencies for the three genotypes? How many individuals are heterozygous for the trait?
Allele frequencies:
p = 0.67
q = 0.33
Genotype frequencies:
p2 = (0.67 x 0.67) = 0.45
2pq = 2(0.67 x 0.33) = 0.44
q2 = (0.33 x 0.33) = 0.11
individual counts:
CC = 0.45 x 75 = 33.75
Cc = 0.44 x 75 = 33
cc = 8.25
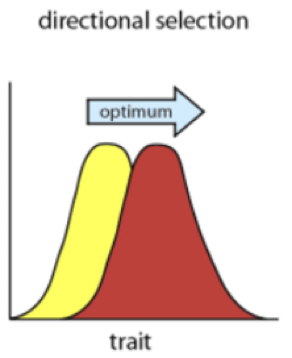
Direction selection
frequencies change to lef or right of the equilibrium
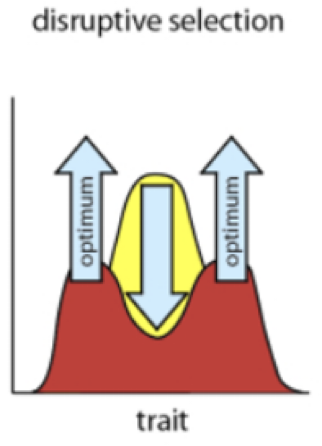
Disruptive selection
frequencies change to both sides of the equilibrium
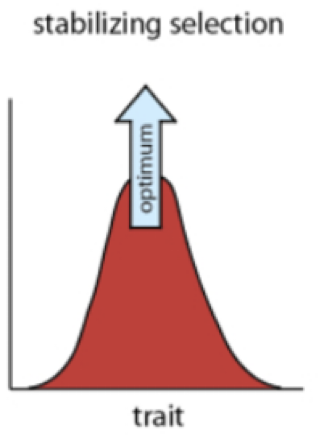
stabilizing selection
median phenotype has greatest advantage
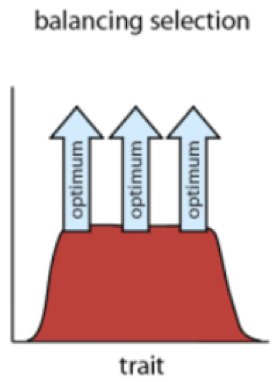
Balancing selection
multiple alleles are mantained
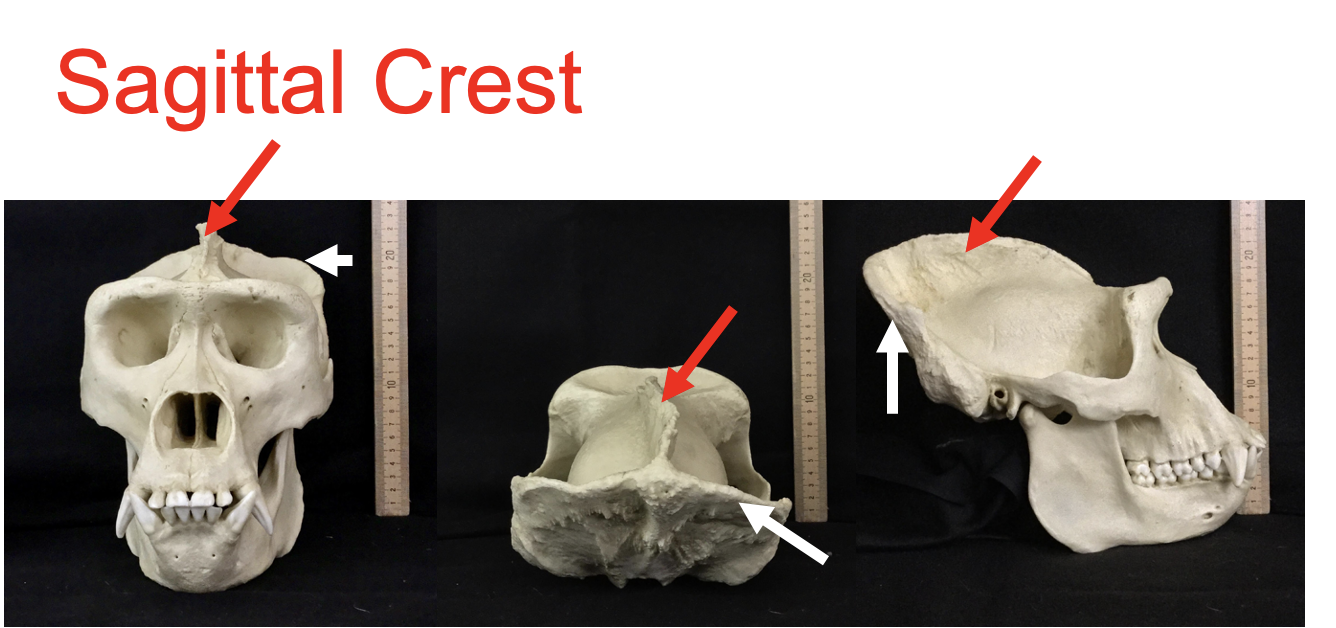
sagital crest (red)
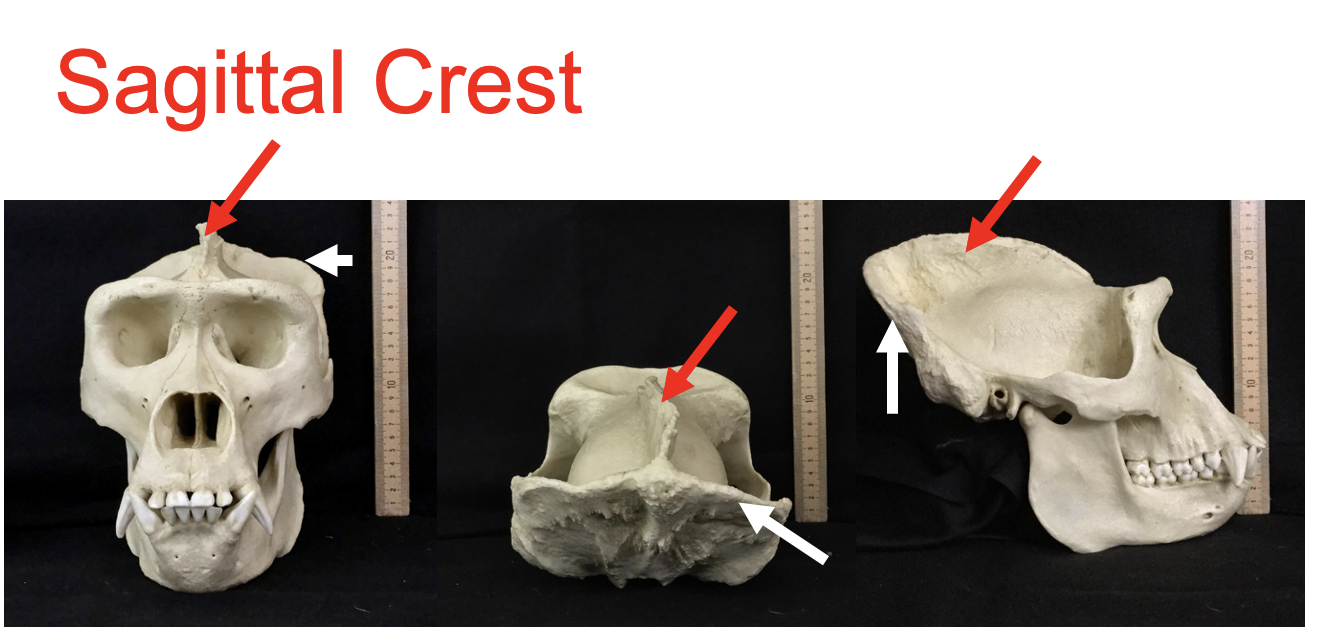
lambdoidal crest (white)
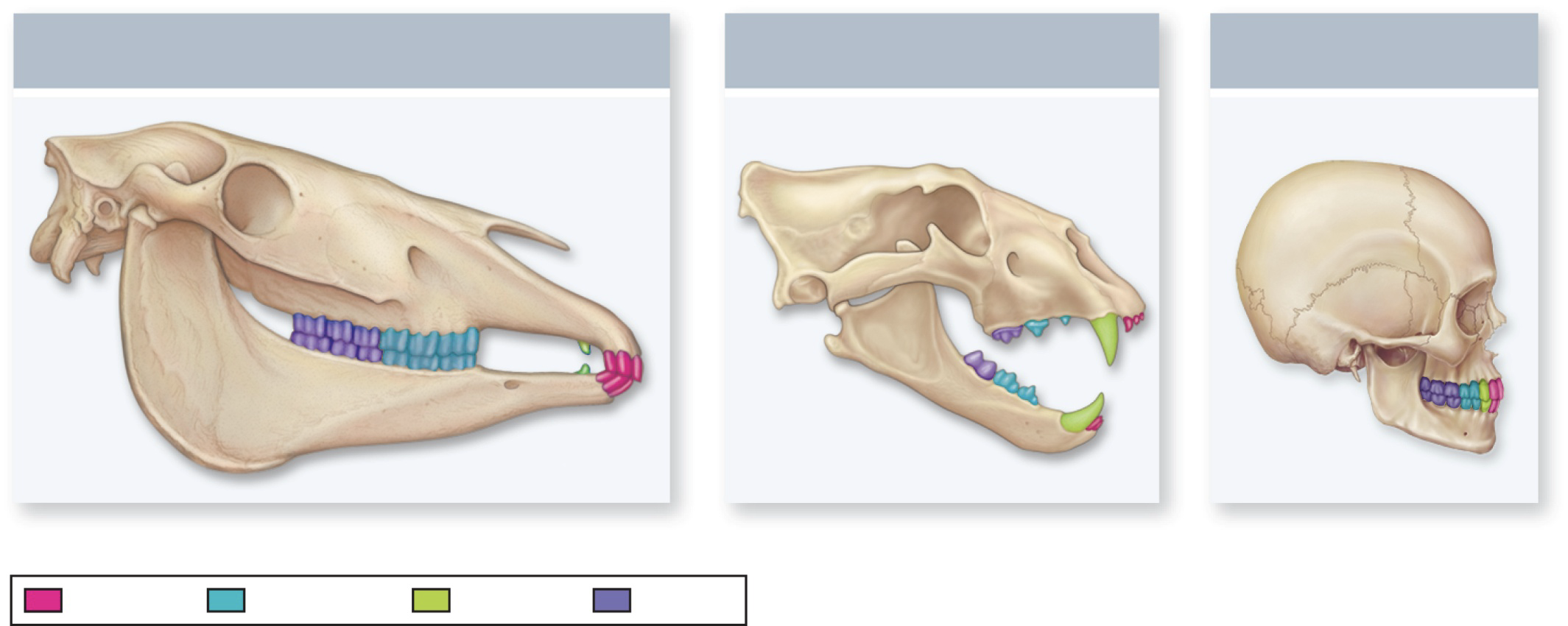
Teeth type
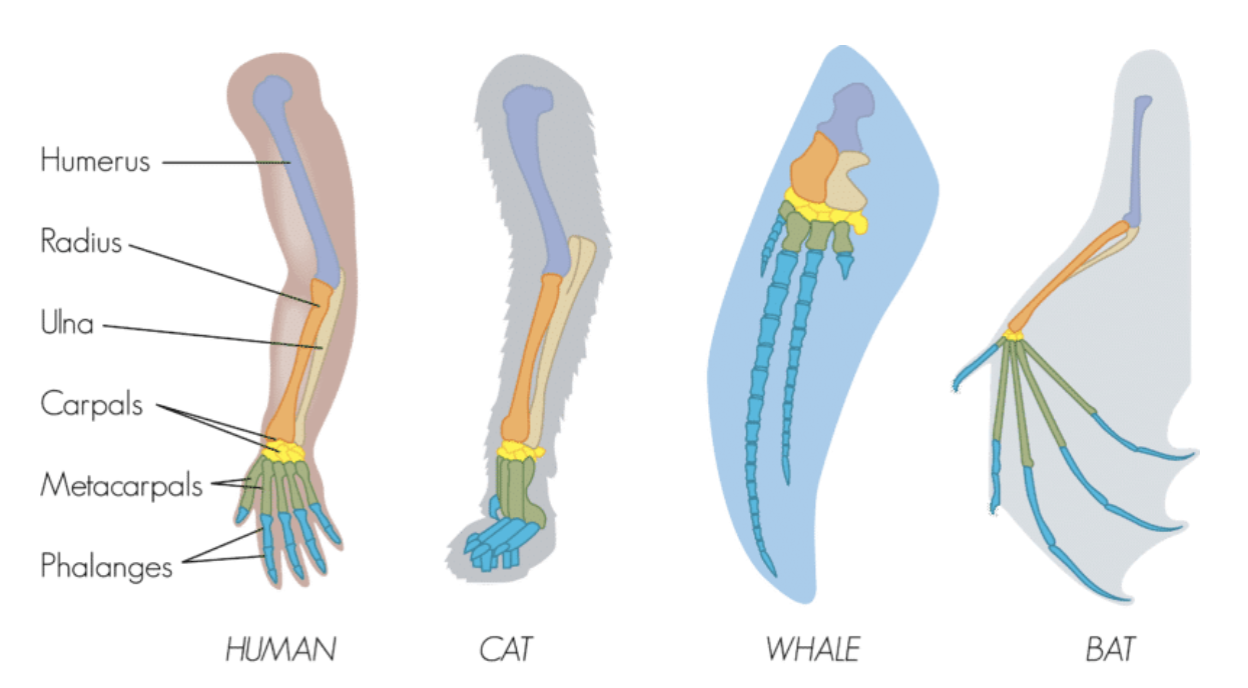
homologous structure
Control: Calculation of Standard Deviation and Standard Error and 95% Confidence Interval
t, Chi-sq, and F tables are provided for reference to significance
DF = # of groups – 1
Alpha value = 0.05 (always for this class)
Chi-sq test is used to compare….
observed vs expected values
T-test is used when we want to compare …
means amongst two samples.
ANOVA is used when we want to compare…
means among three or more samples.
Linear regression is used to…
correlate one variable against another.
Type 1 versus Type 2 Errors
Type I Error Rate (α) which is the probability of concluding two (or more) means ARE different when they actually ARE NOT different.
Type II Error Rate (β) which is the probability of concluding two (or more) means are NOT different when they actually ARE different.
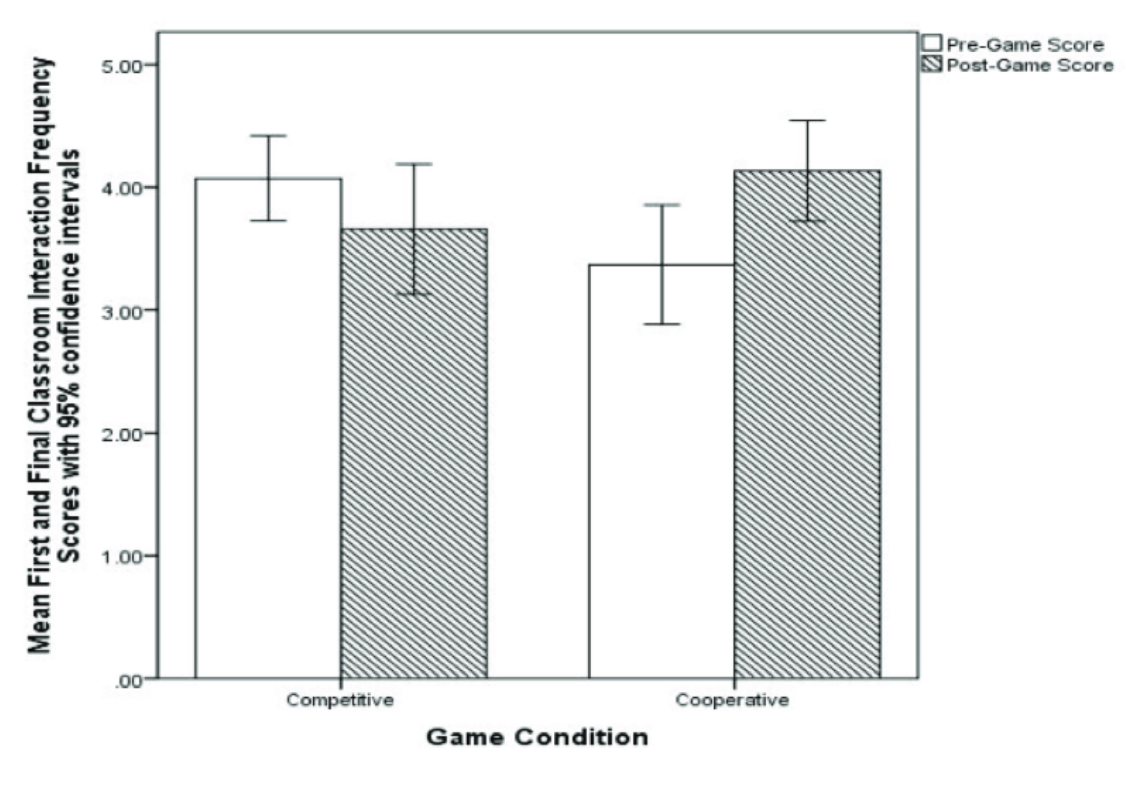
Is there a significant difference?
All overlap, NO significant difference
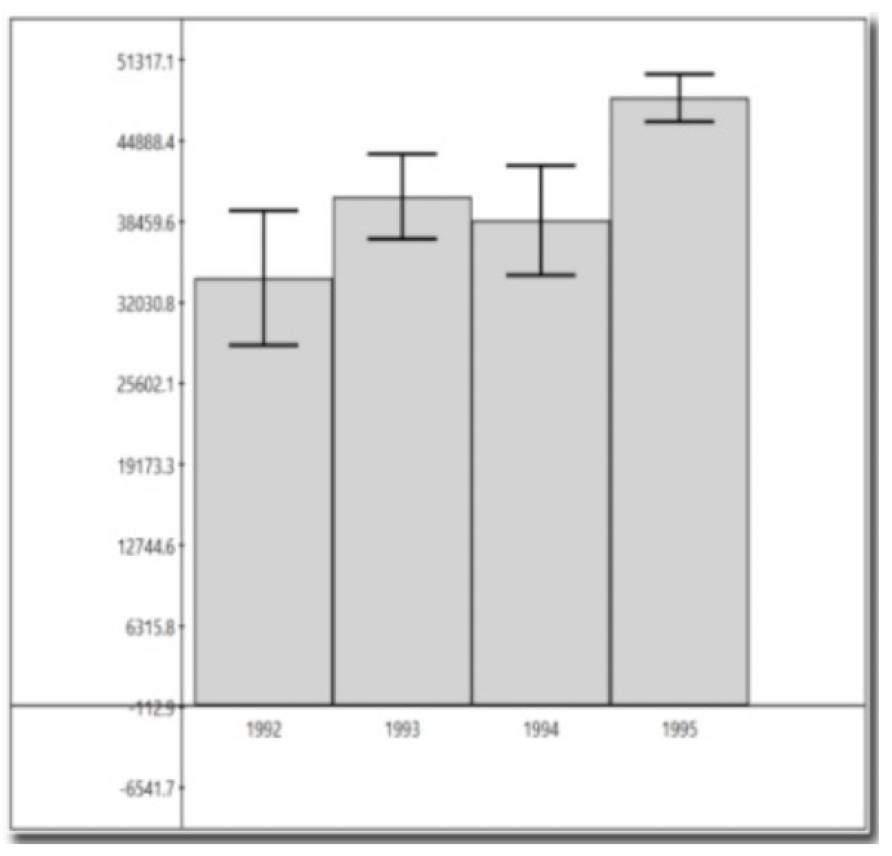
Is there a significant difference?
One group stands out (CIs don’t touch), there IS a significant difference
How to evaluate different lever systems in terms of the effectiveness of moving the load
MA= In lever length/ out lever length
In-lever length (a) = length between the fulcrum and placement of effort
Out-lever length (b) = length between the fulcrum and the placement of the load
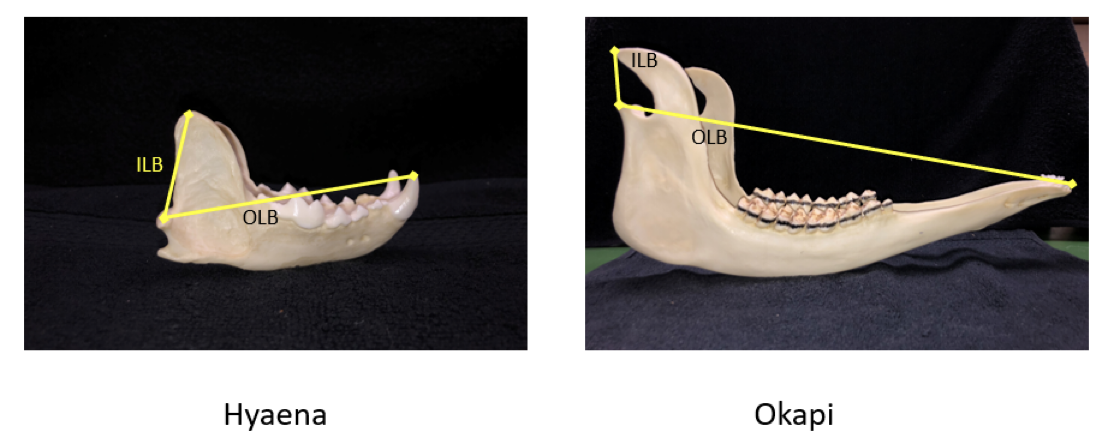
Biting measurements
Biting – temporalis muscle pulls against coronoid process to CLOSE the jaws.
ILB = In-lever Biting = Distance between the mandibular condyle and coronoid process
OLB = Out-lever Biting = Distance between the mandibular condyle and either the canines or the incisors
Chewing measurements
Chewing – masseter muscle pulls against mandibular angle to pull the jaw upward
ILC = In-lever Chewing = Distance between the Mandibular Condyle and Mandibular Angle
OLC = Out-lever Chewing = Distance between the Mandibular Condyle and midpoint of the molars or the point where molars and premolars meet.
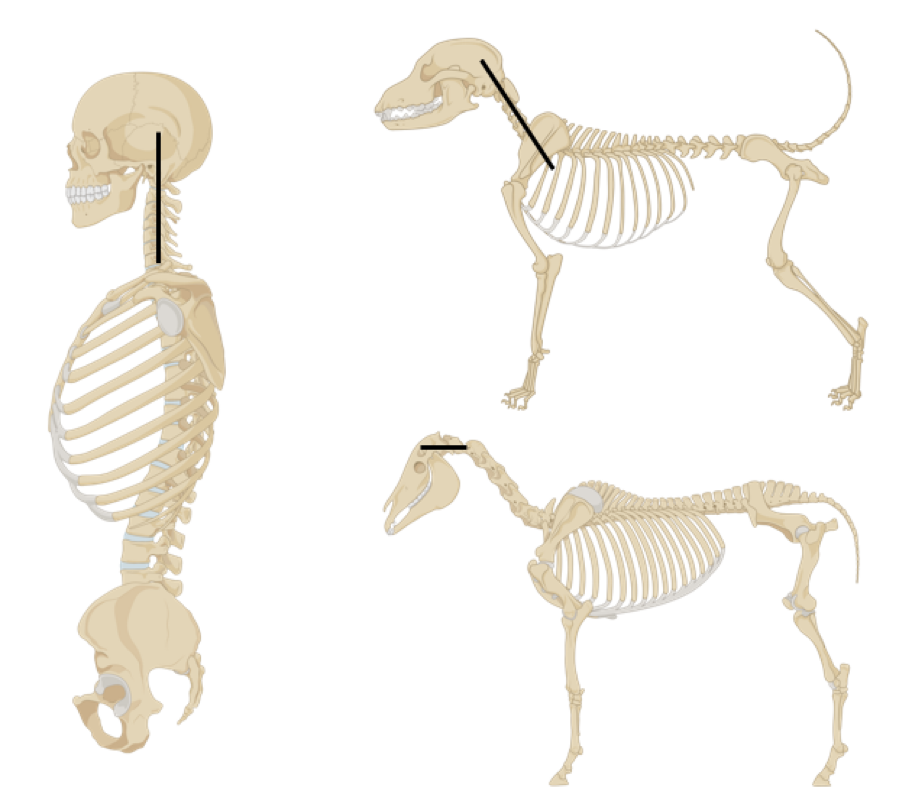
Modes of locomotion
Bipedal – walking on two limbs
Quadrupedal – walking on four limbs
Orthograde = vertical posture
Pronograde = horizontal posture
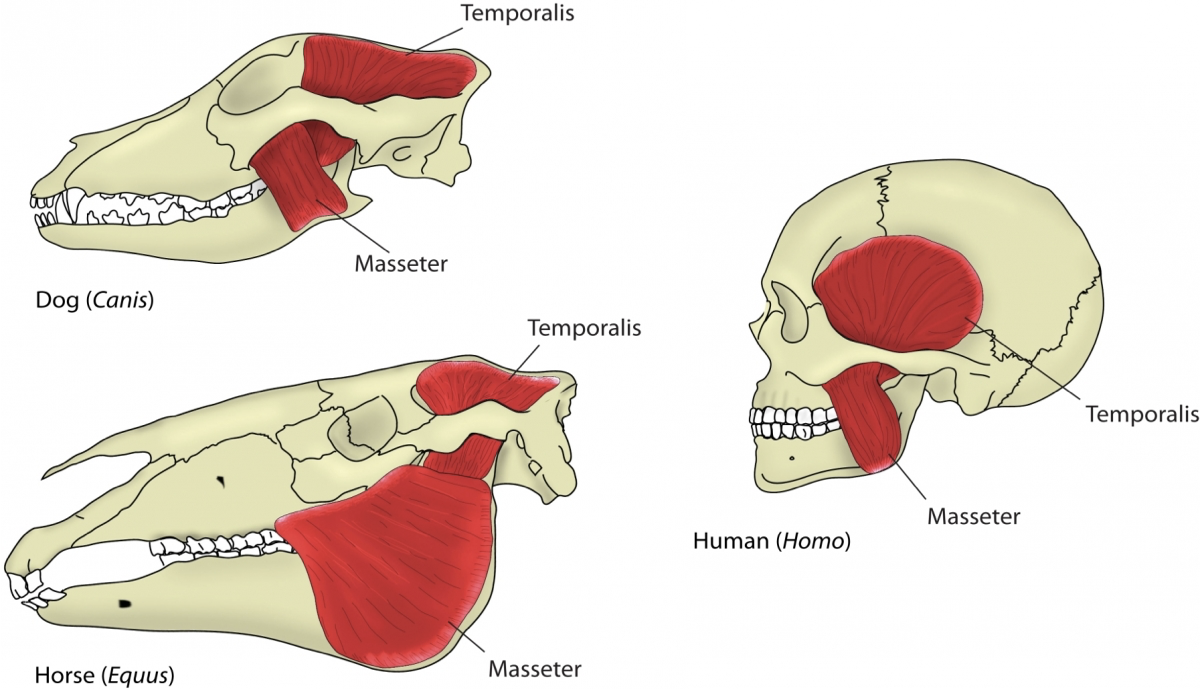
Carnivore, Herbivore, Omnivore Musculature Comparison
The major muscles that operate the jaw are the temporalis muscle and the masseter muscle. They pull against the mandible which pivots at the fulcrum provided by the mandibular condyle.
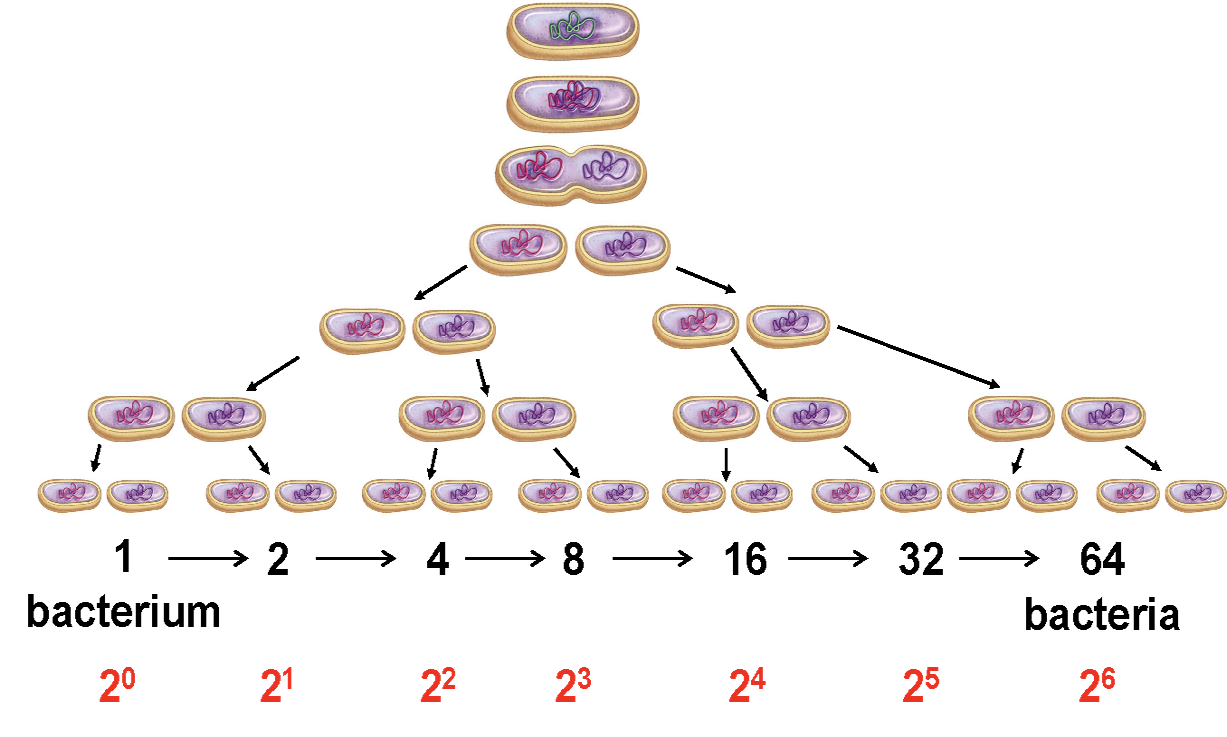
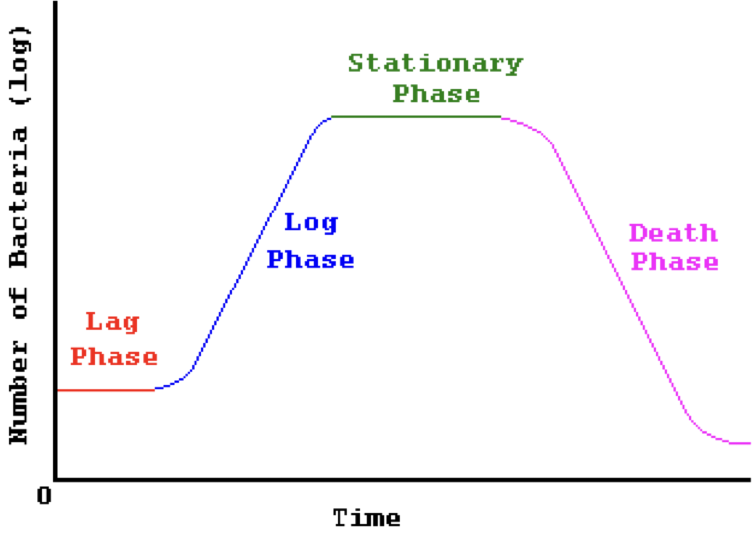
Closed-Growth System:
Environment in which NO nutrients are added and NO waste products removed.
Bacteria divide through binary fission
Doubling/generation time
= time taken to get from N to 2N
- Bacterial doubling times can range from 10 minutes to 30 days. The average doubling time is between 20-60 minutes.
- Environmental factors (e.g., temperature, pH, nutrient availability) directly impact the doubling time.
- The effects of various environmental factors on growth rate(doubling time) can be examined using a closed growth system.
Phases of a closed-growth system
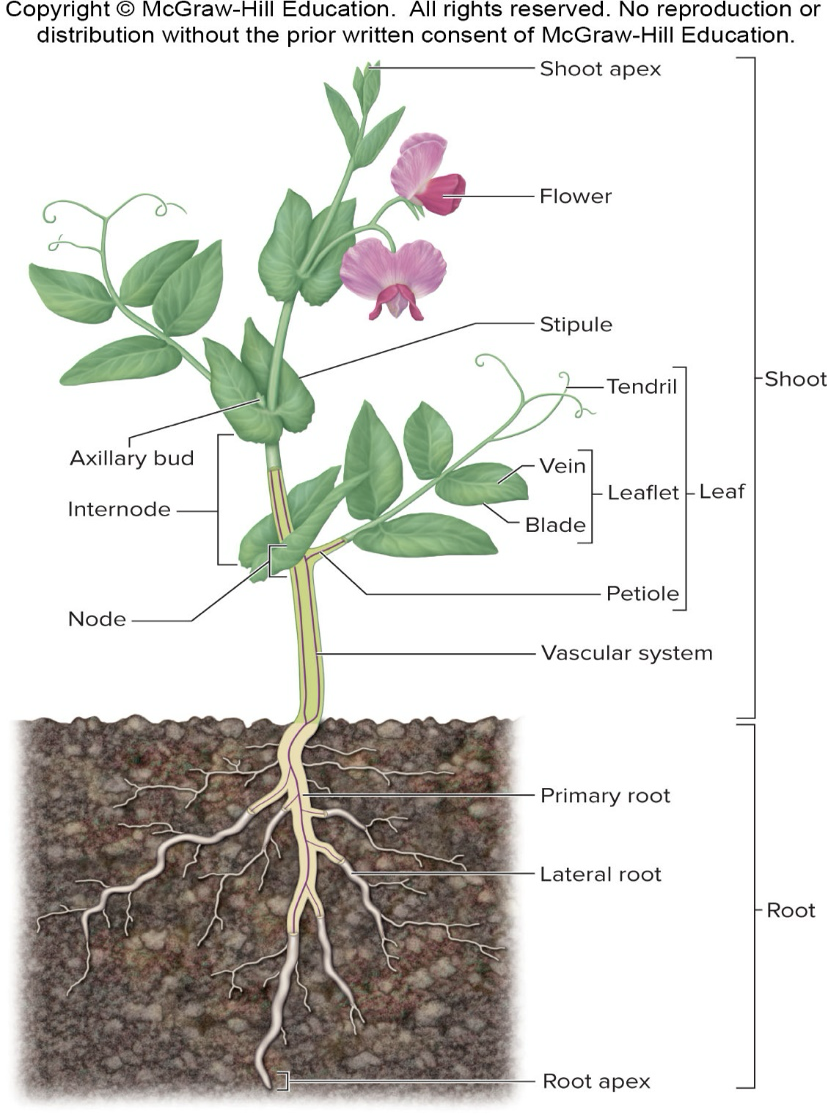
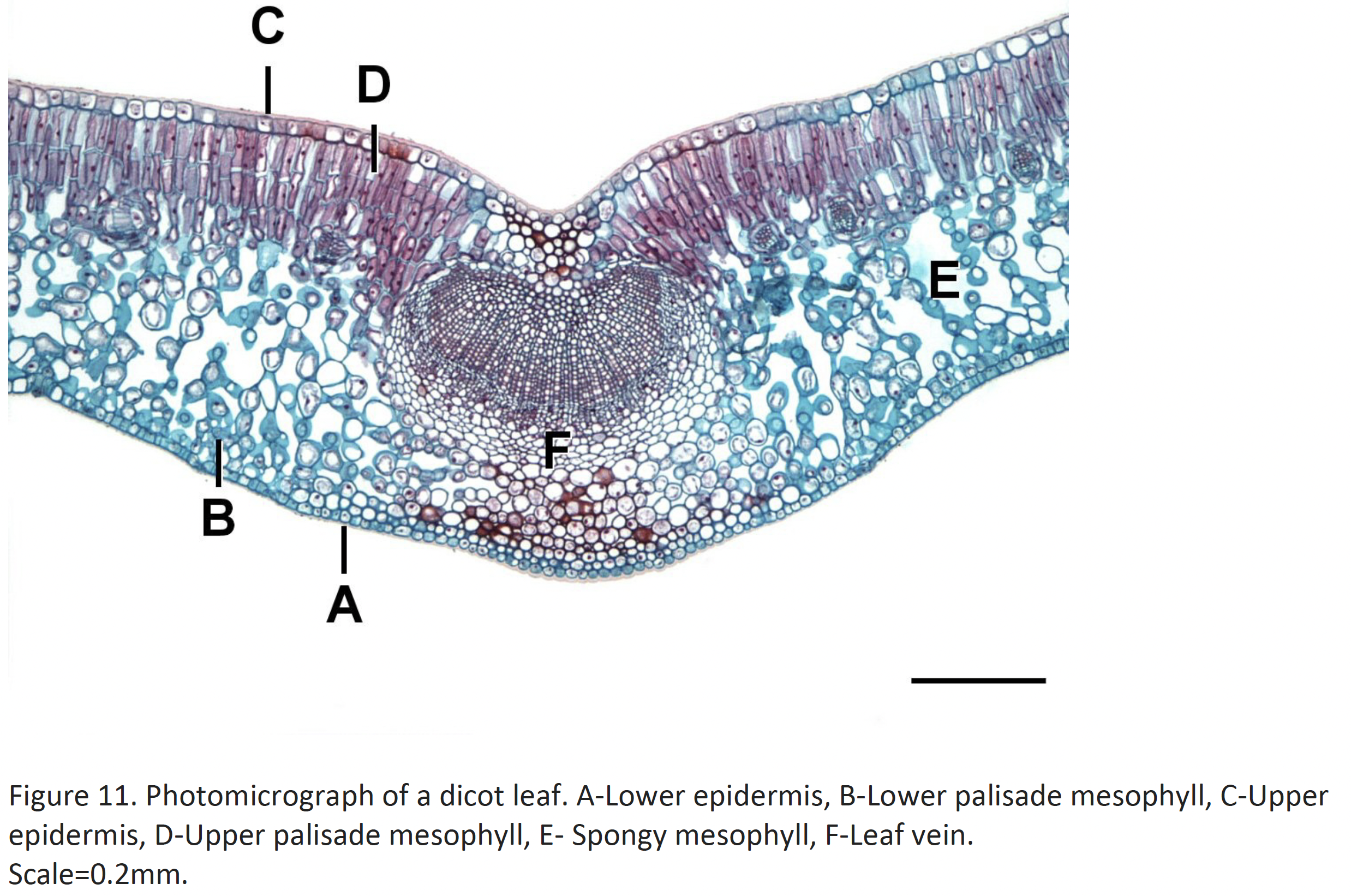
Dicot
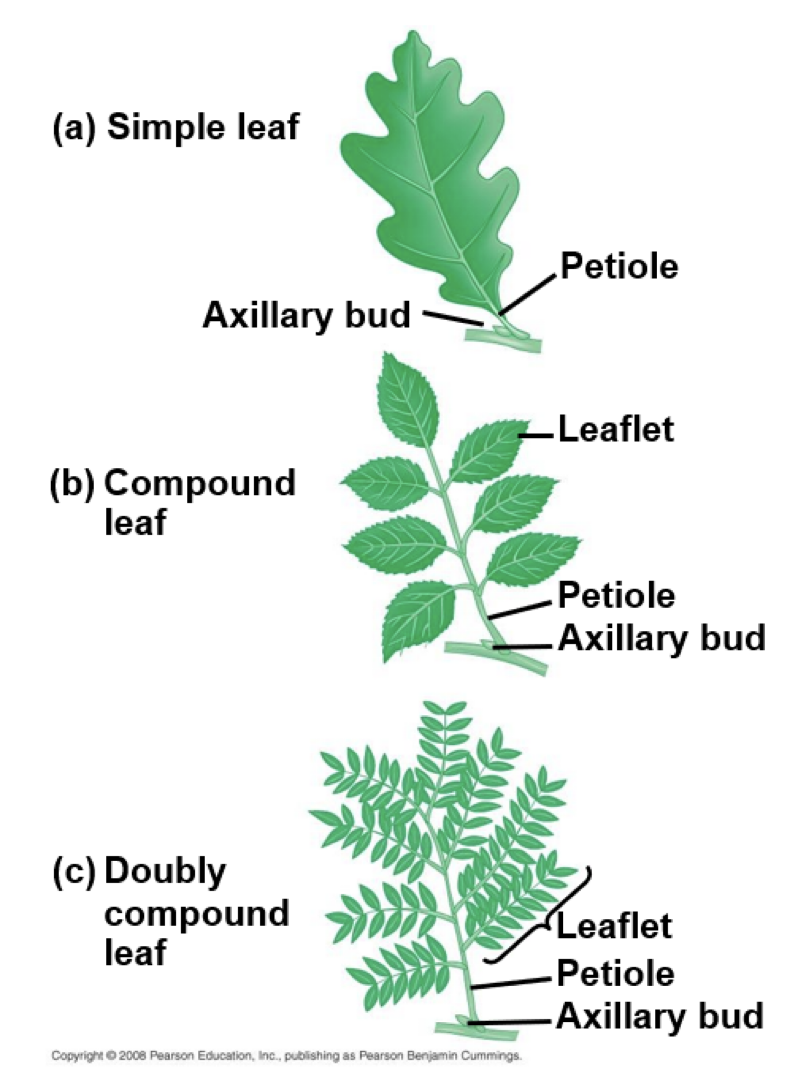
Leaf types
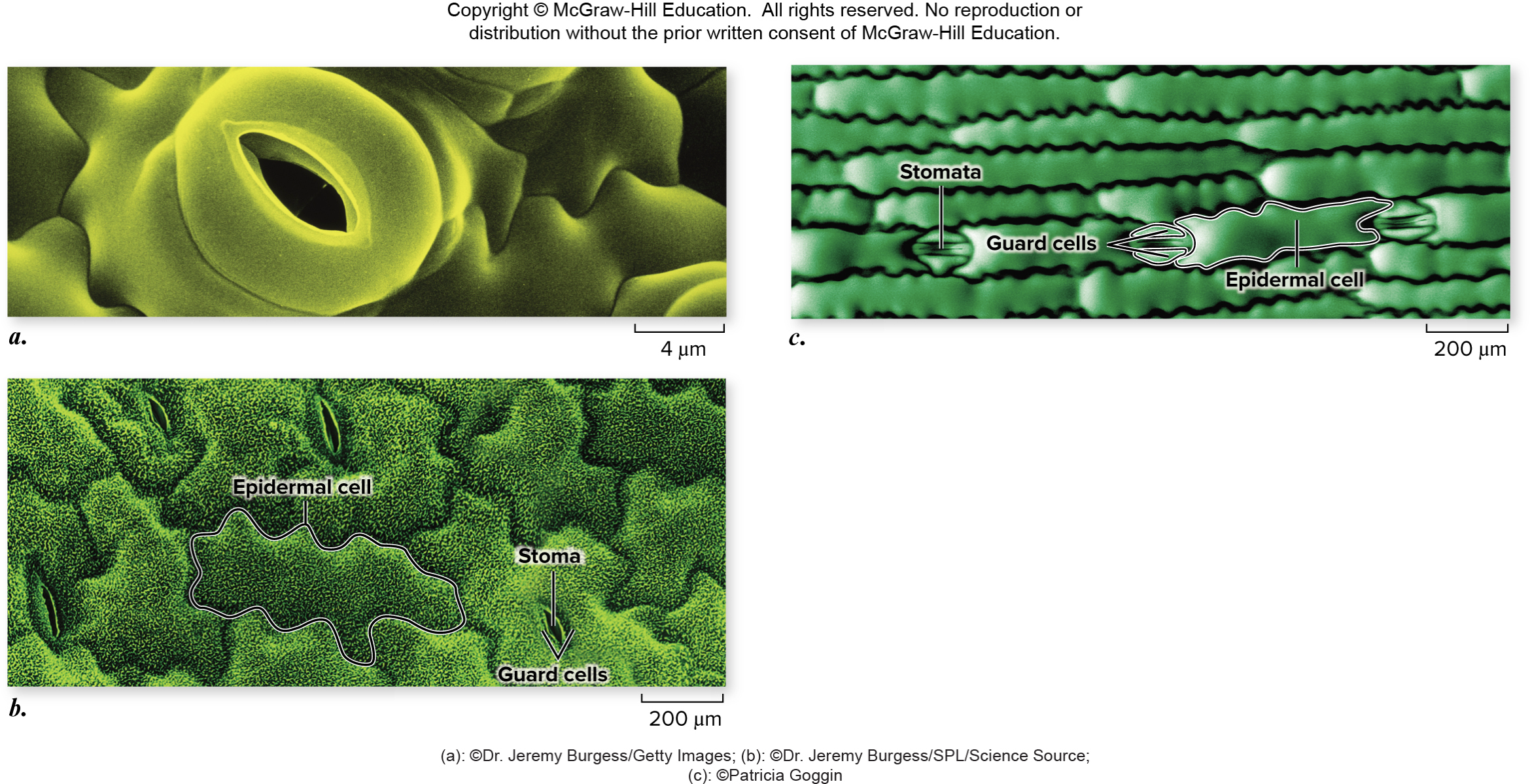
Dermal - plant tissue type
Covering of plant body for protection
Parenchyma cells
Prevent desiccation
Ground - plant tissue type
Parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma
Support and storage
Ground tissue in leaf mesophyll is primary site of photosynthesis
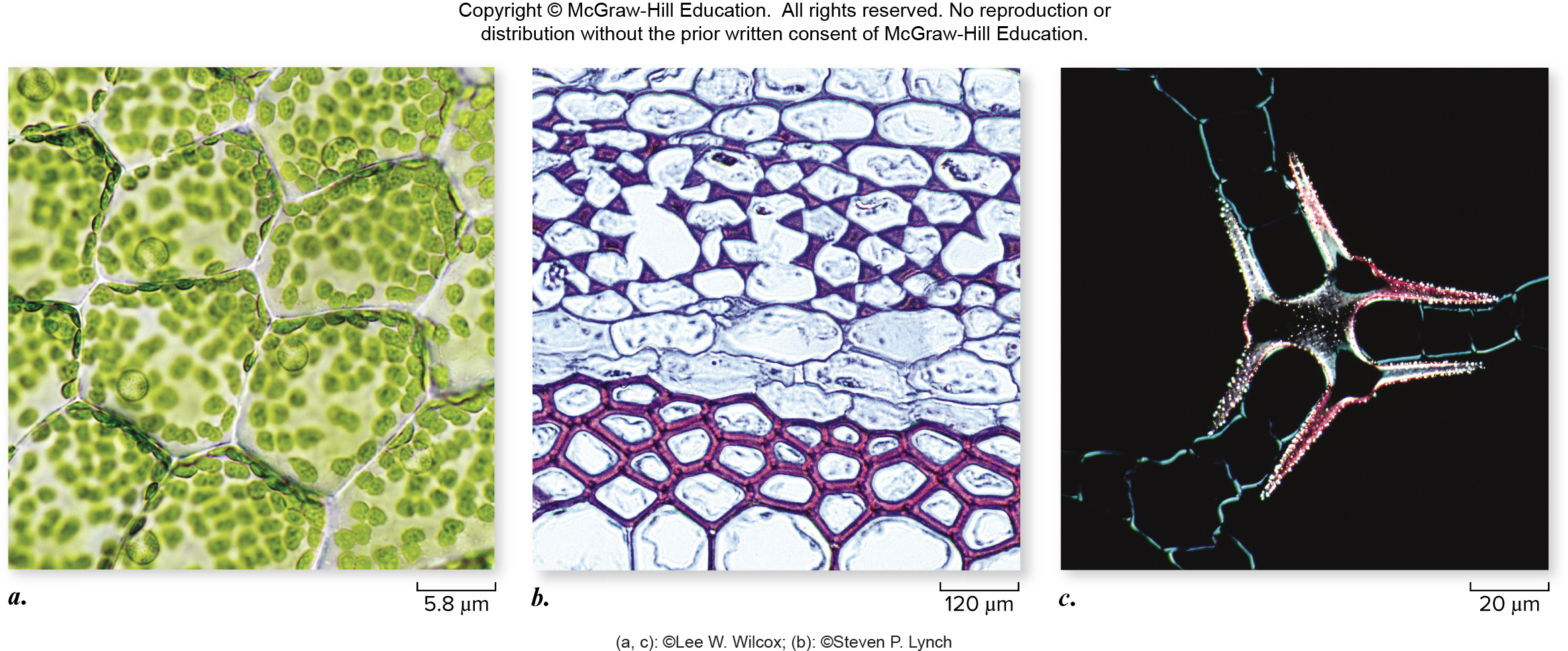
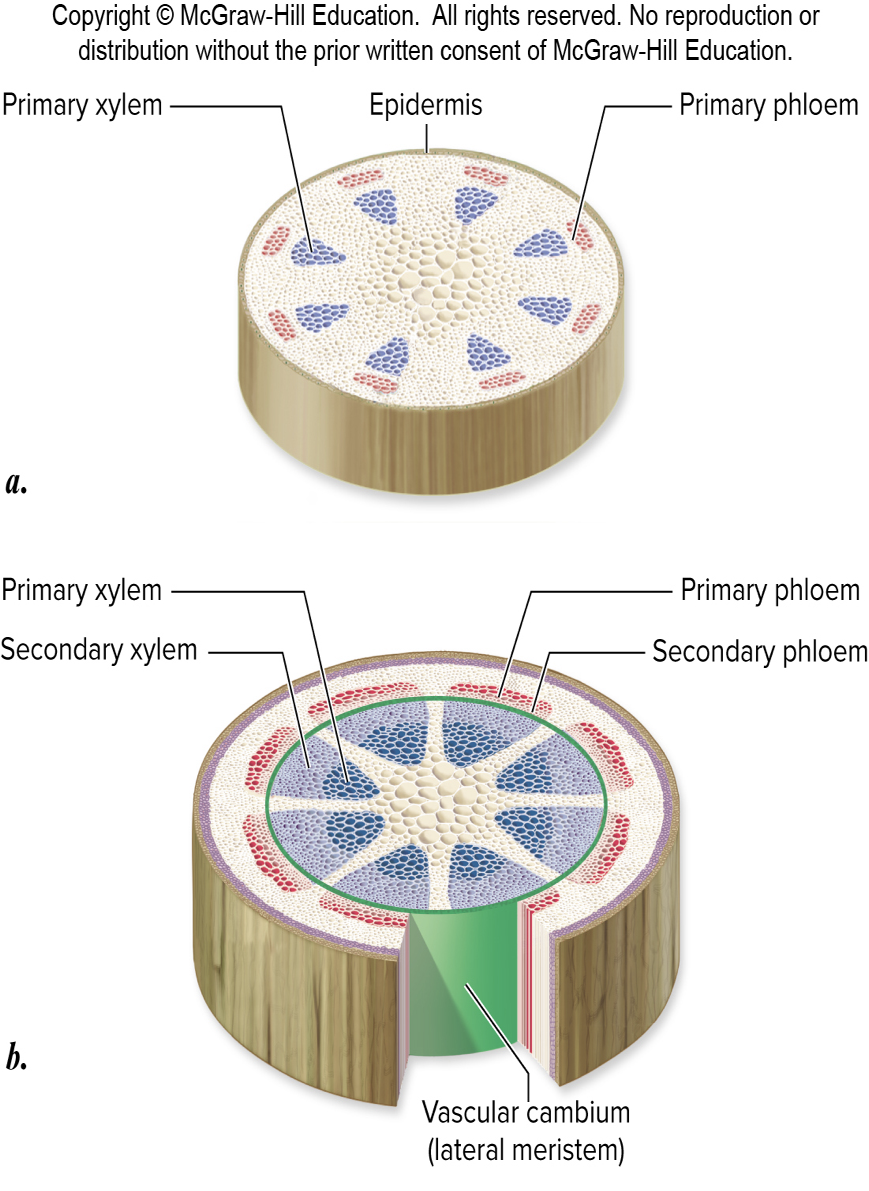
Vascular - plant tissue type
Xylem
Transport of nutrients & water from soil
Phloem
Transports products of photosynthesis & other materials around plant body
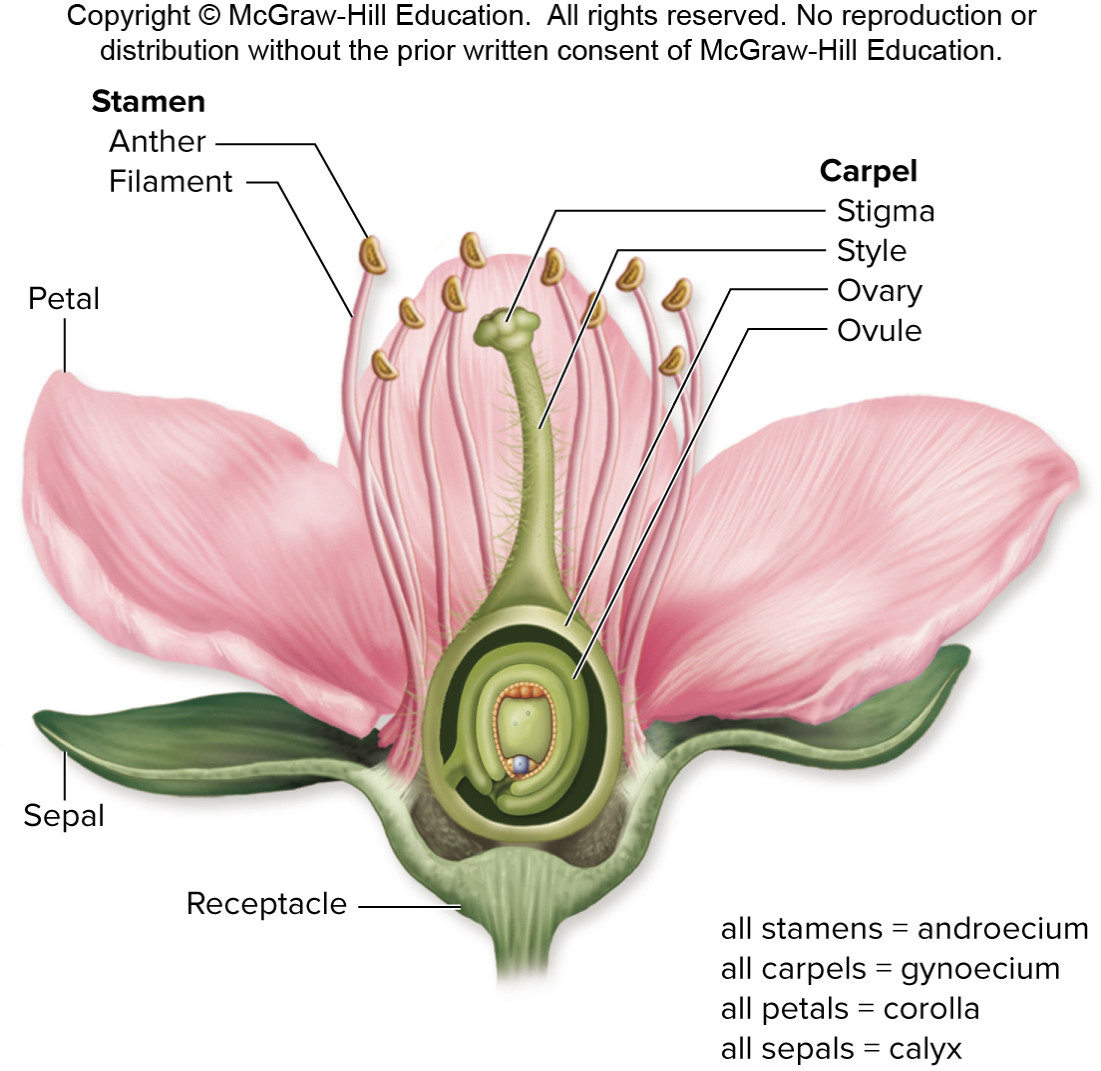
Angiosperms – Flowering Plants – Division Magnoliophyta
Flower Structure
Megasporangium
Megaspore mother cell
Produces the ovum and the polar bodies
Microsporangium
Microspore mother cell
Produces the pollen
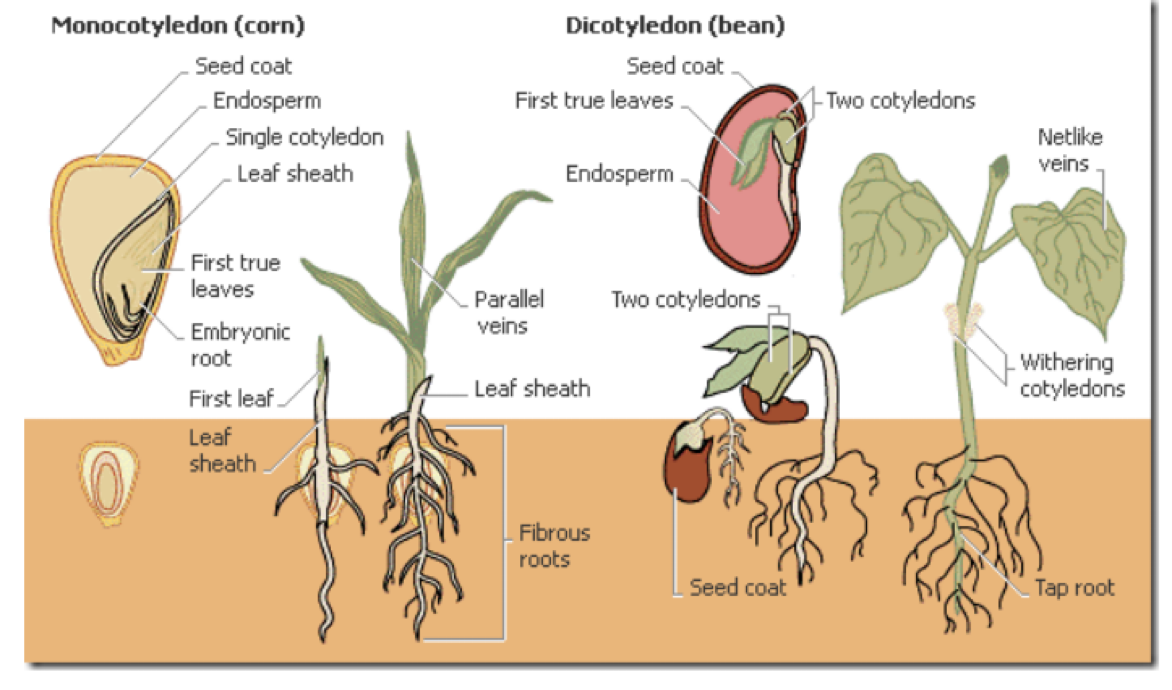
Angiosperms – Dicots versus Monocots
Dicot
2 Cotyledons
Monocots
Single Cotyledon
Eudicot or monocot
eudicot
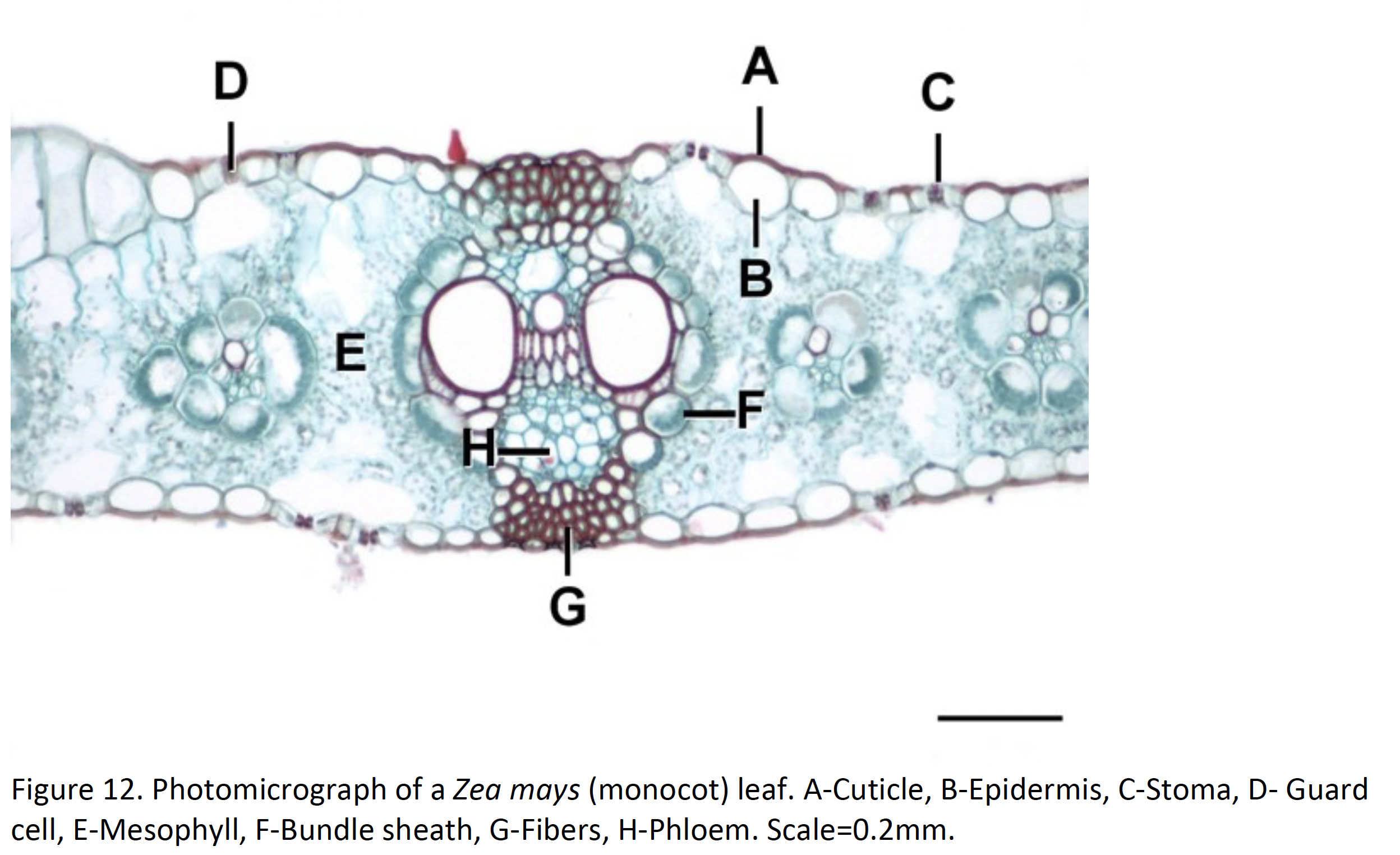
eudicot or monocot
monocot
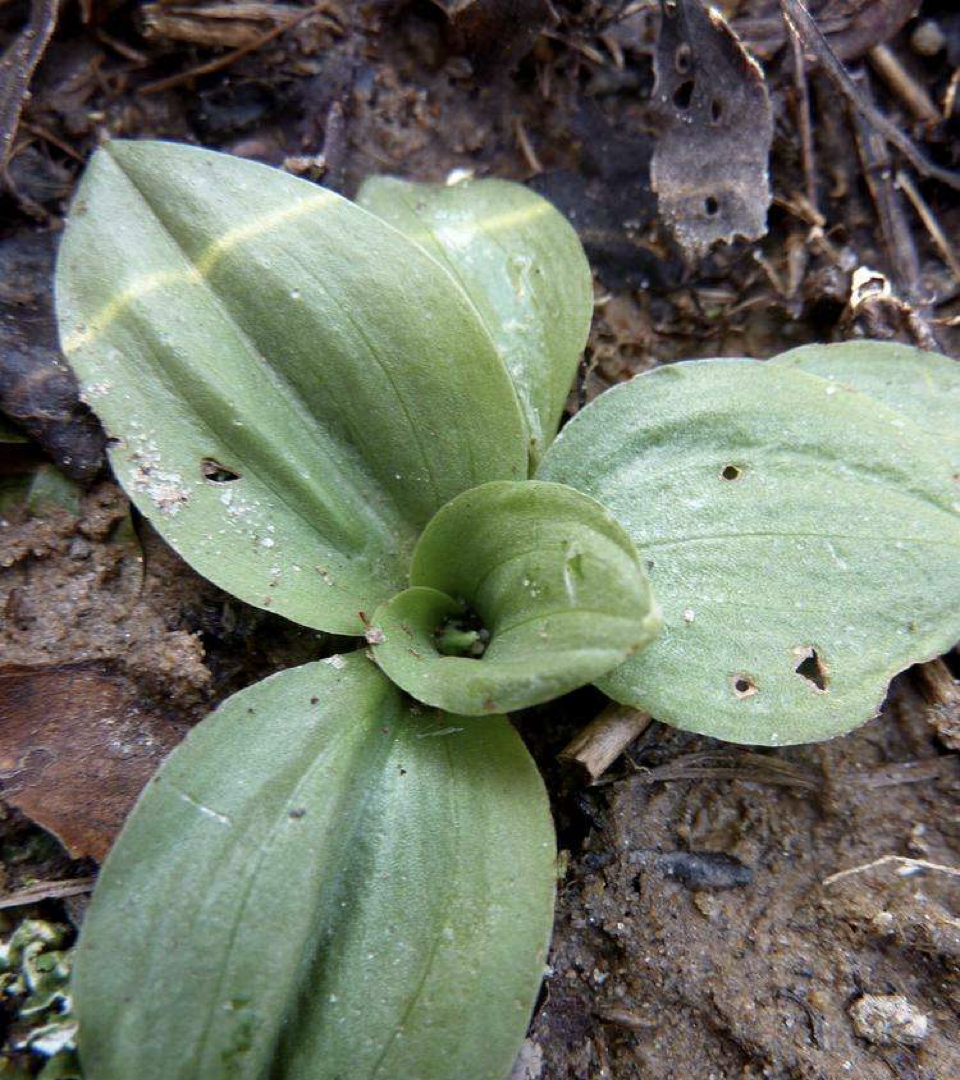

Eudicot or monocot
monocot
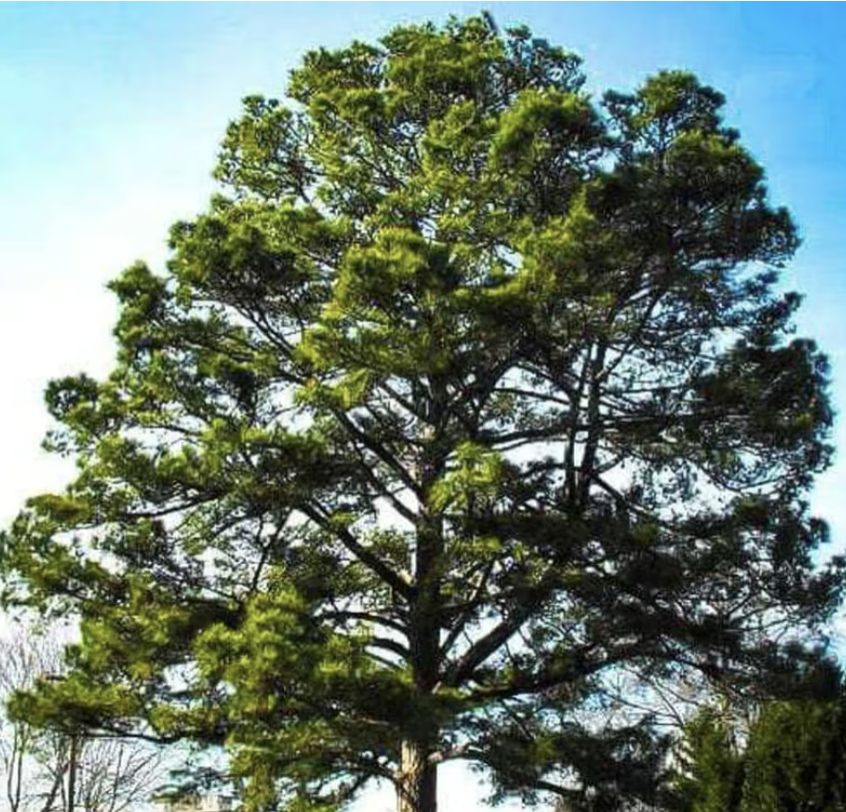

what is this?
gymnosperm
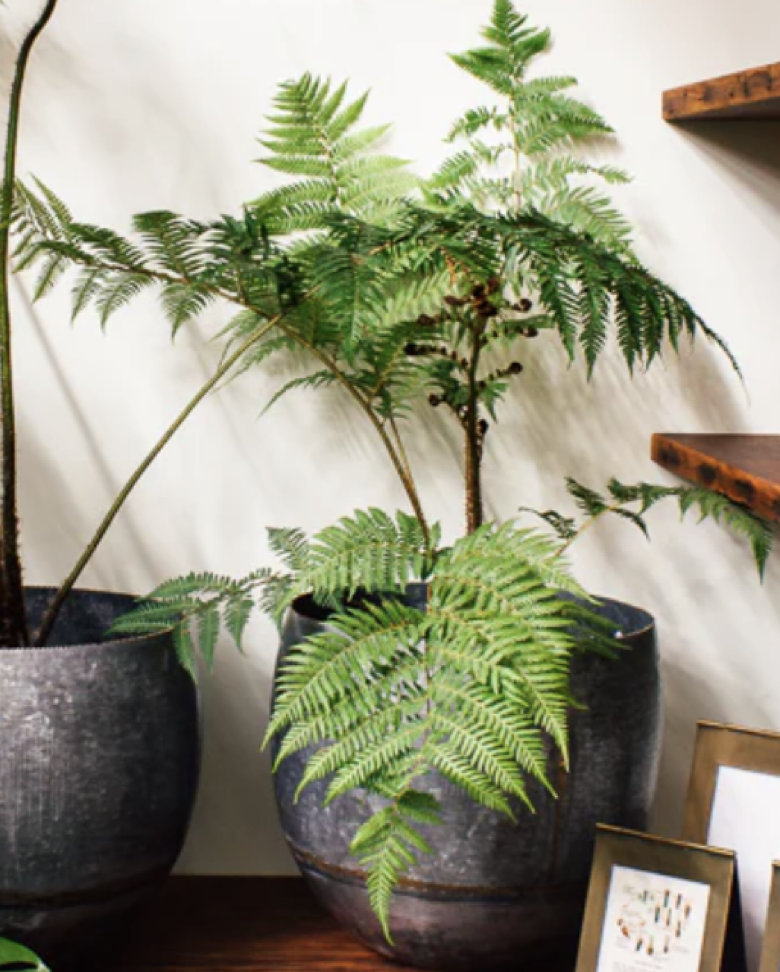

what is this?
fern
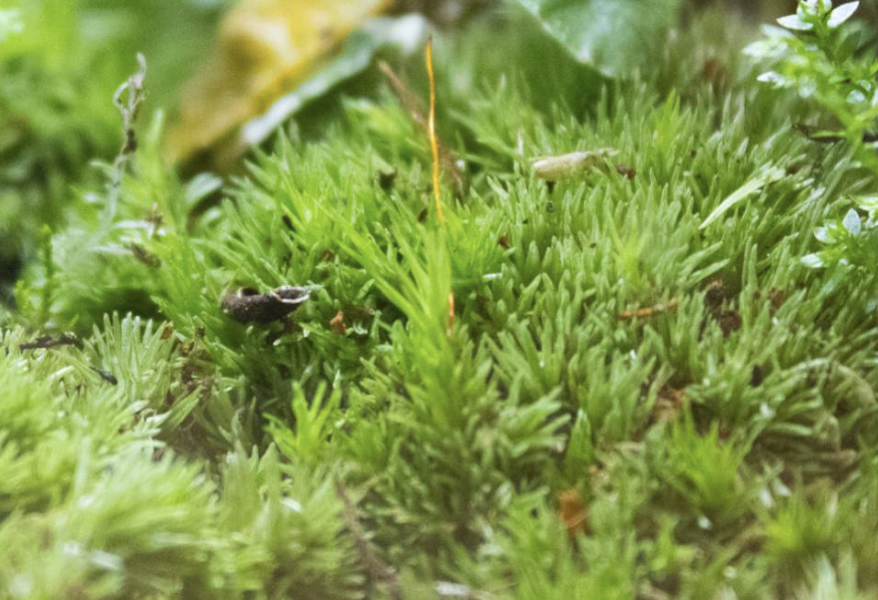

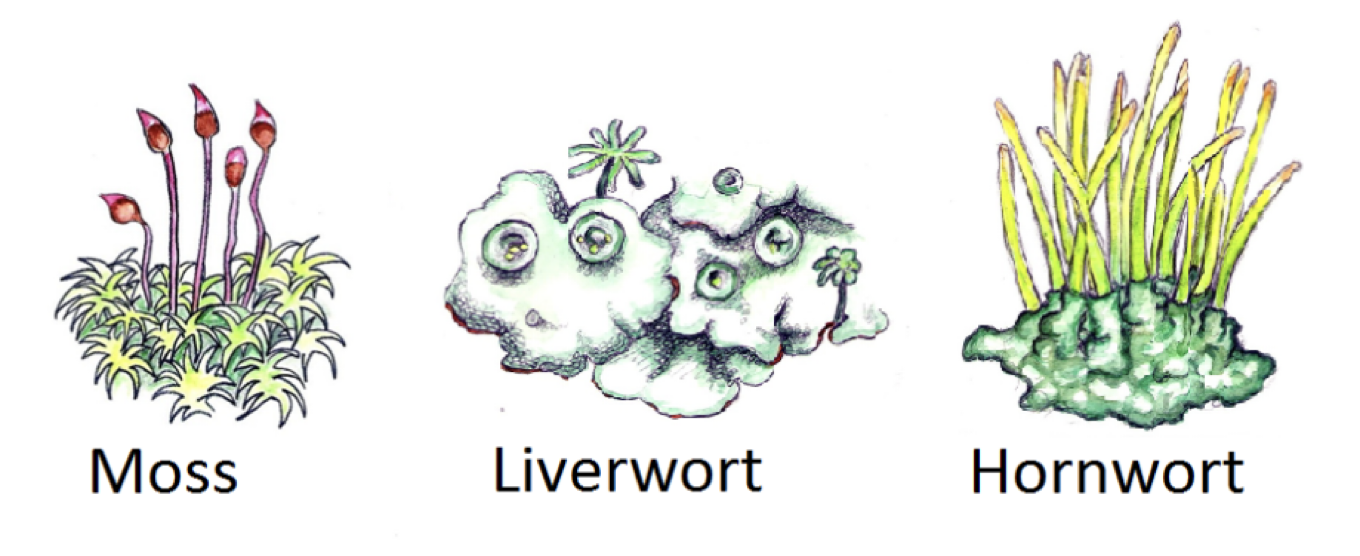
what is this
Byrophyte - moss
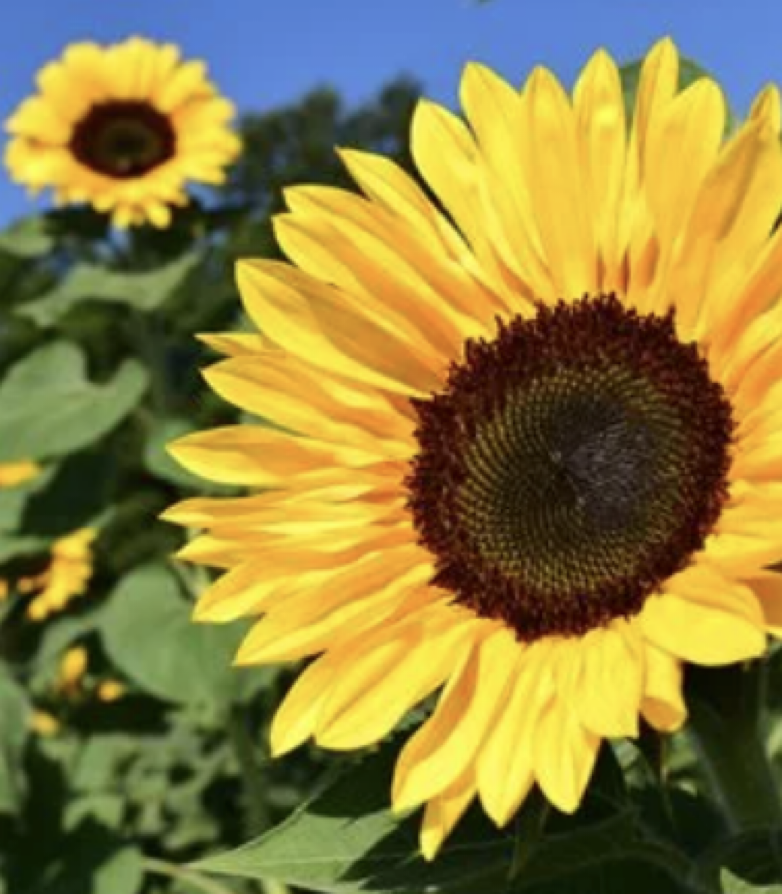

what is this
gymnosperm
Bryophytes
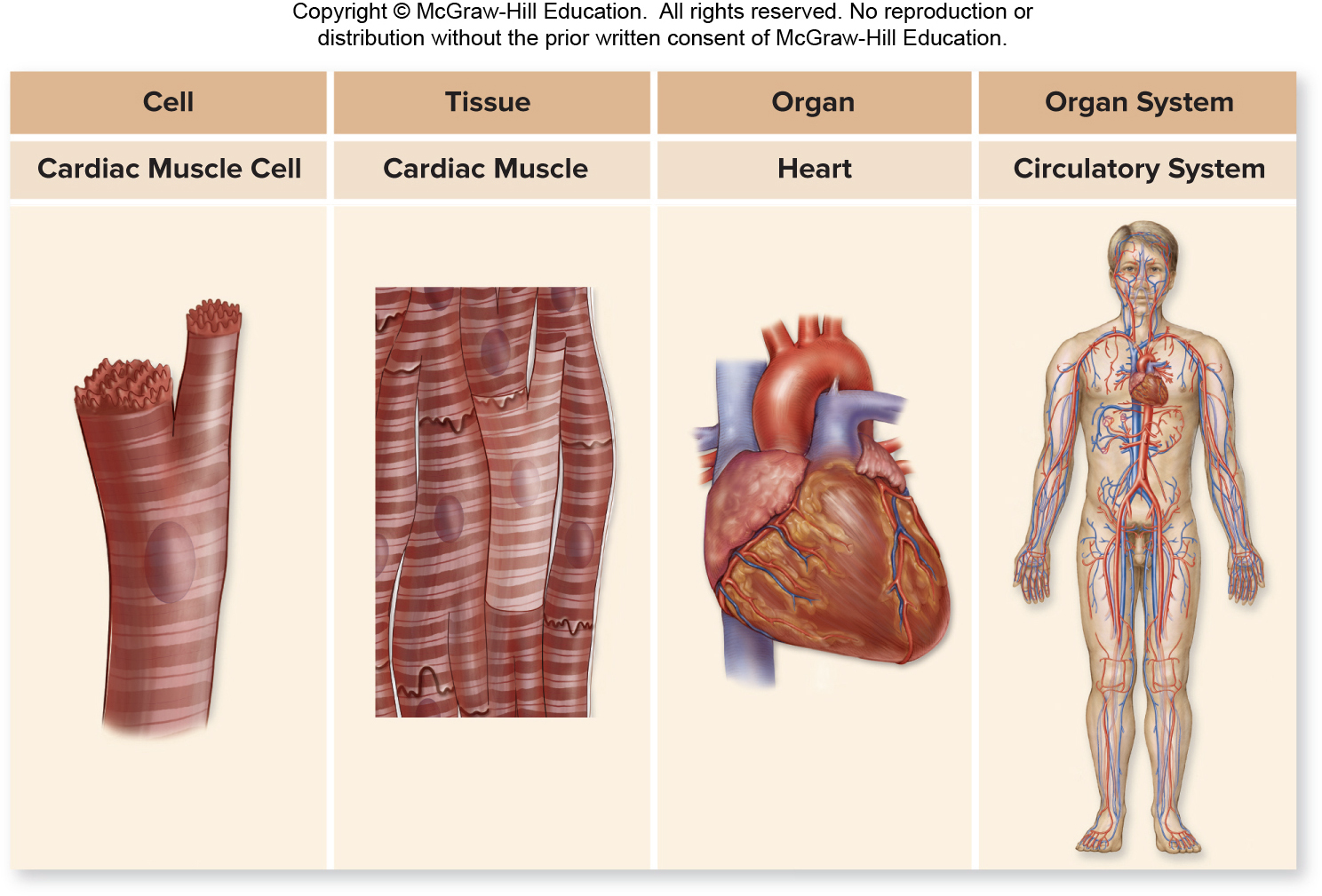
Tissues
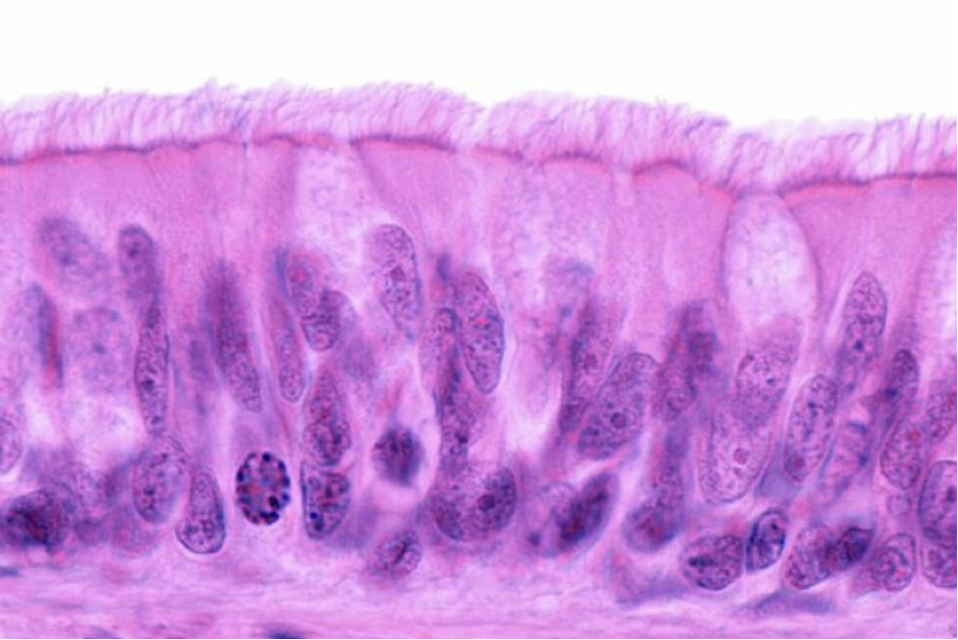
what is this
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
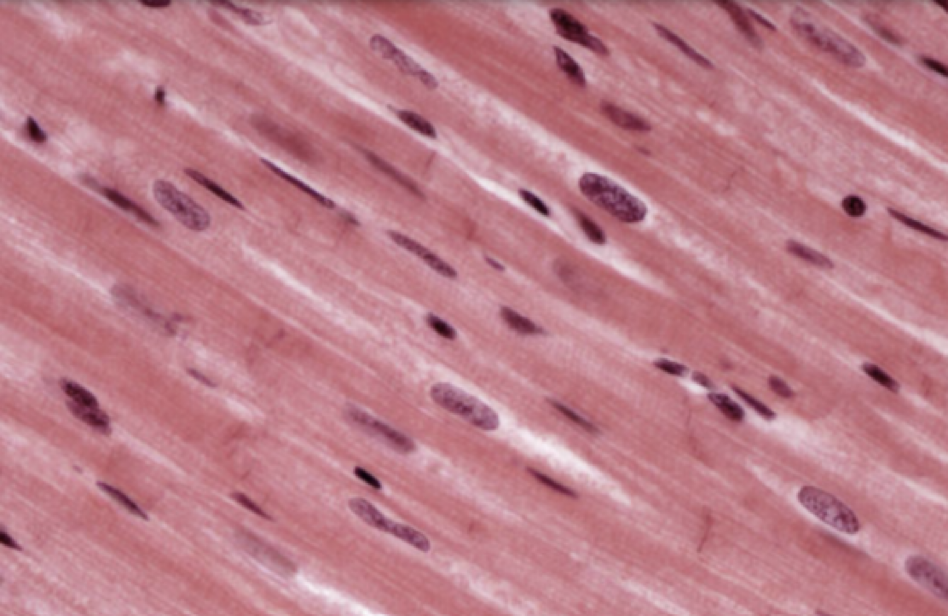
what is this
cardiac muscle
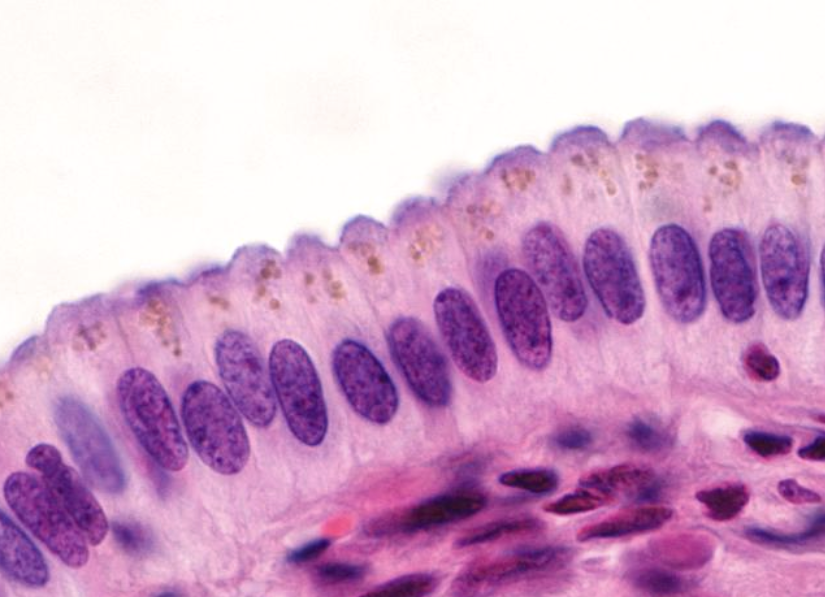
what is this
Columnar epithelium
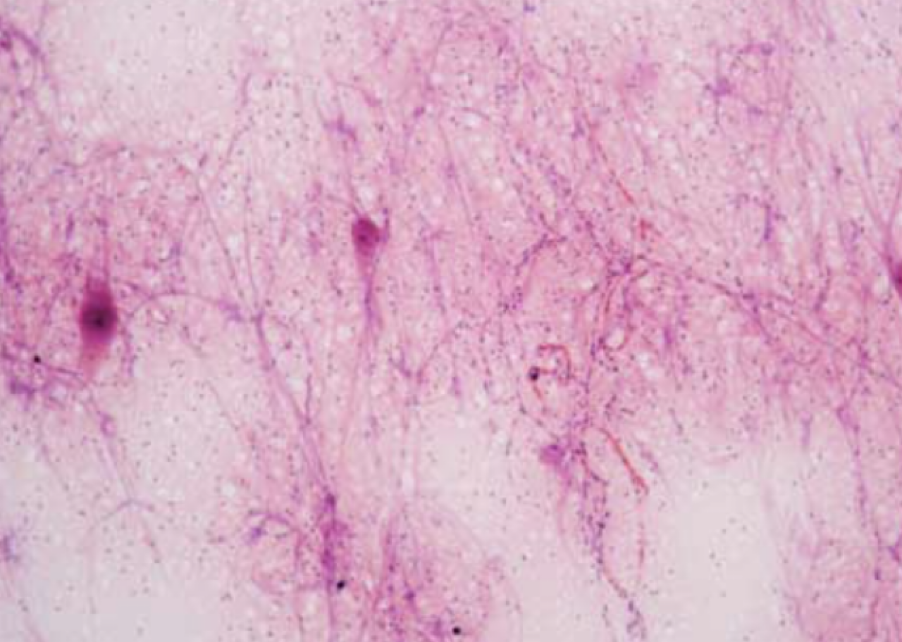
What is this
Nervous tissue
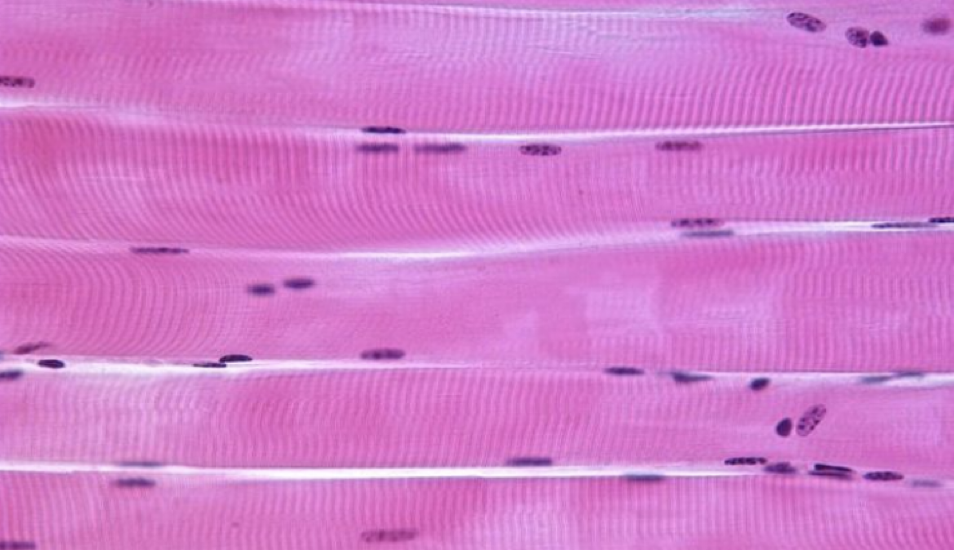
what is this
skeletal muscle
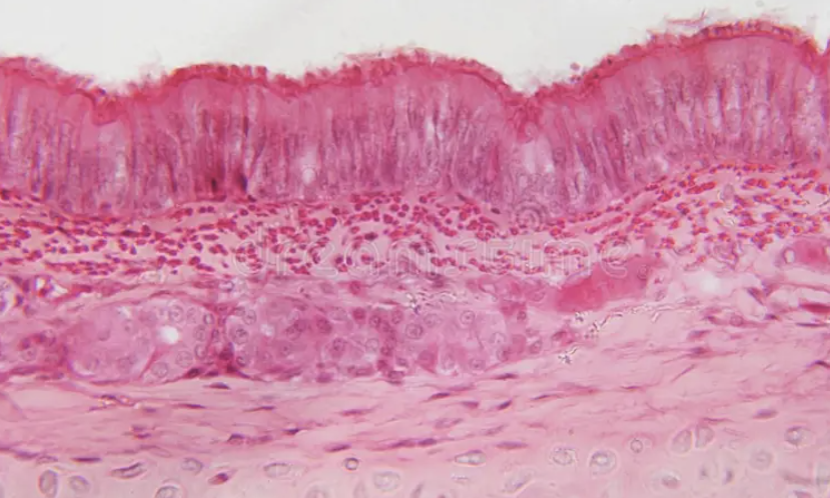
what is this
Pseudostratified squamous epithelium
several layers
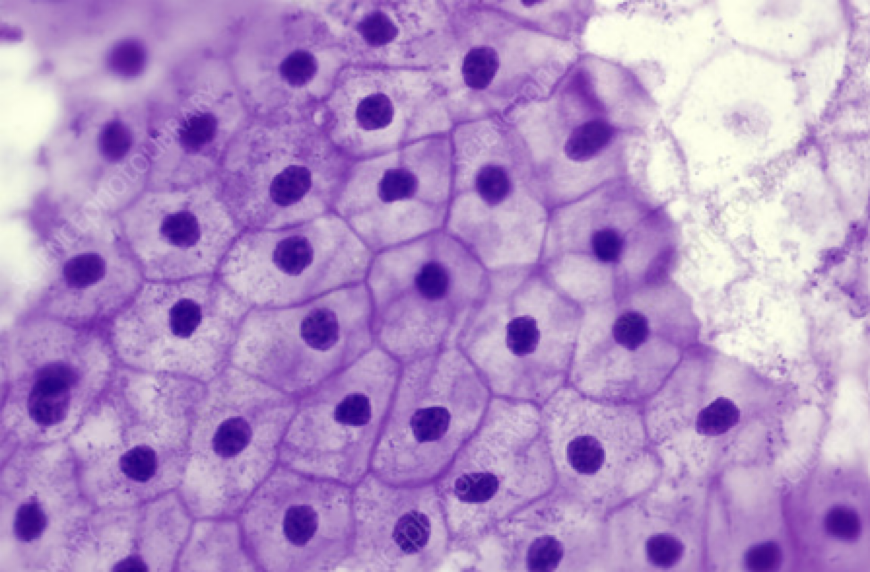
what is this
Simple squamous epithelium
Single-layer
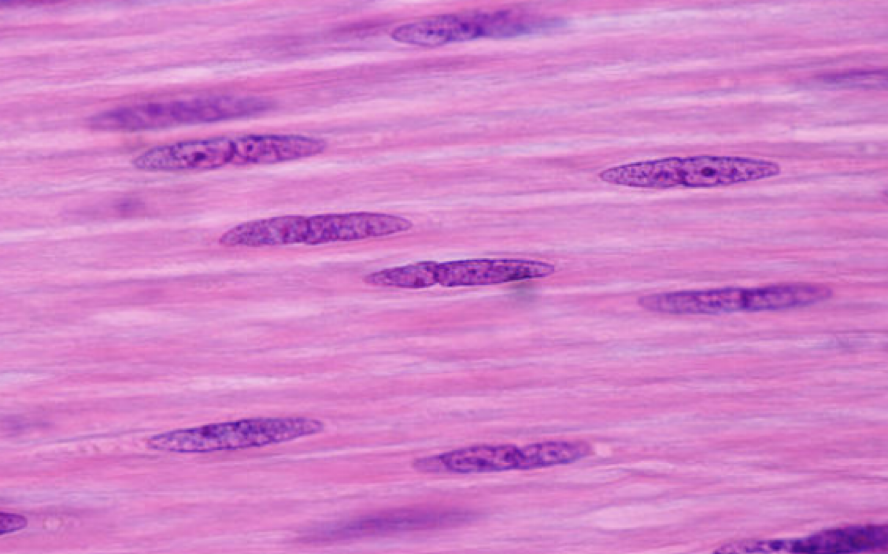
what is this
smooth muscle
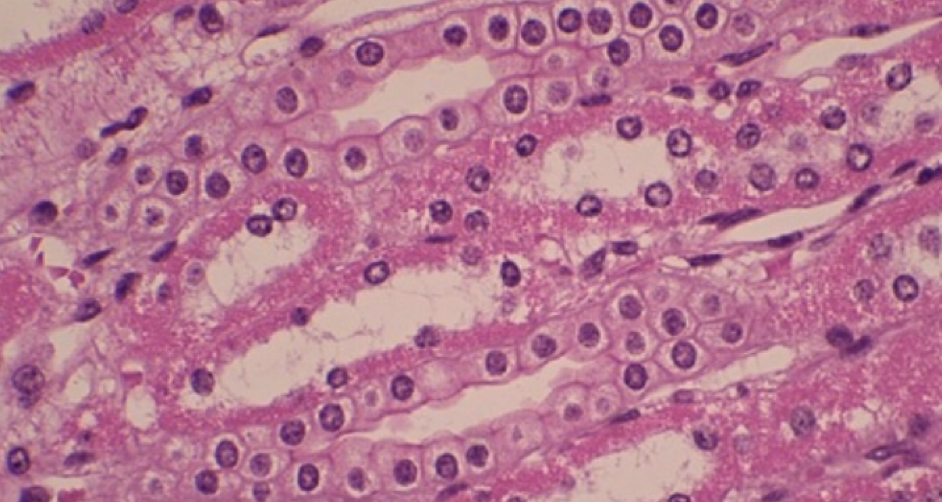
what is this
Cuboidal epithelium
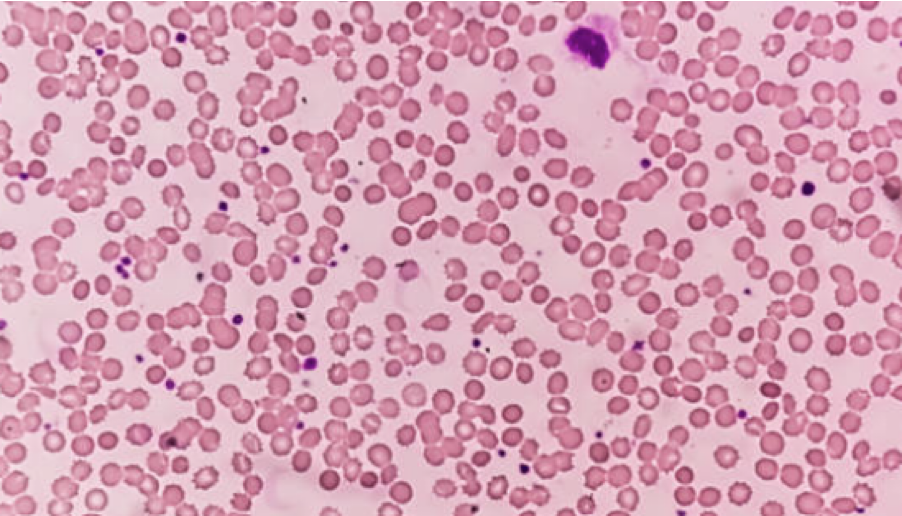
what is this
Connective Tissue: Blood
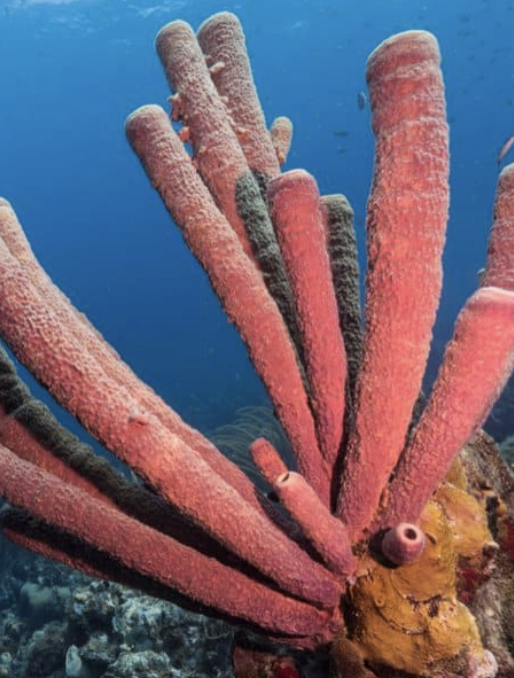

type of symmetry
asymmetrical
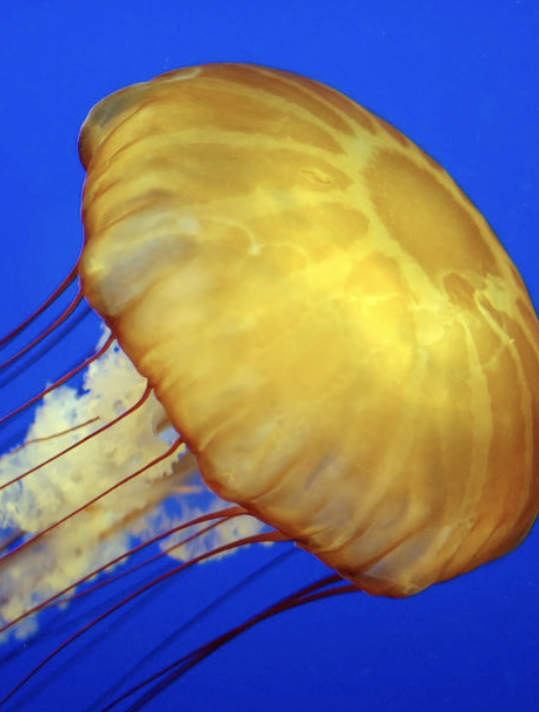

type of symmetry
radial
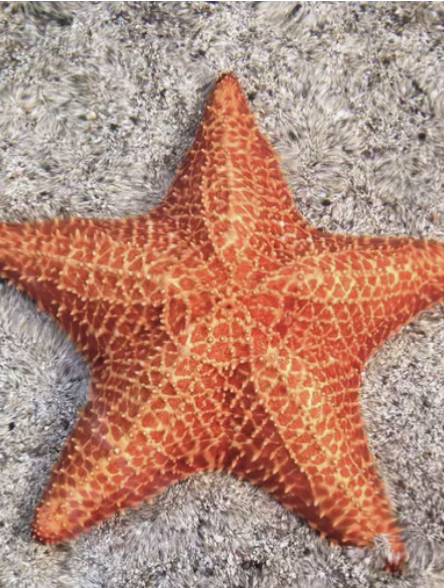

type of symmetry
pentaradial

type of symmetry
bilateral
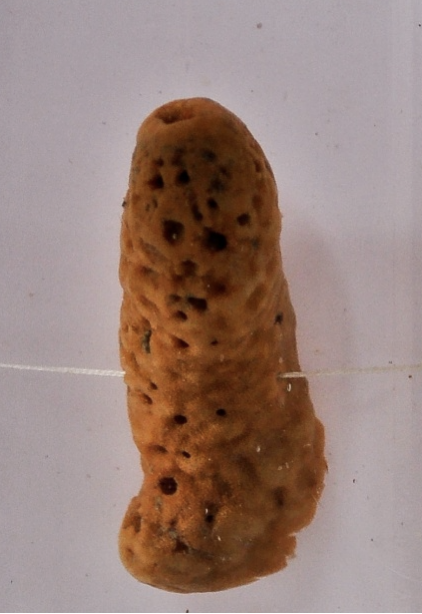
what is this
Phylum:
Porifera (sponge)
No symmetry
Simple organisms

what is this
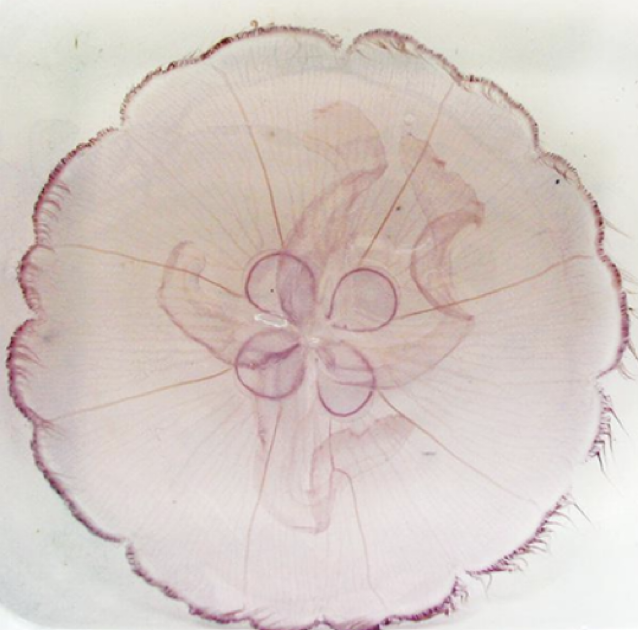
Phyla:
Cnidaris & Ctenophora (jellies, corals, and ctenophores)
Radial symmetry
Transparent
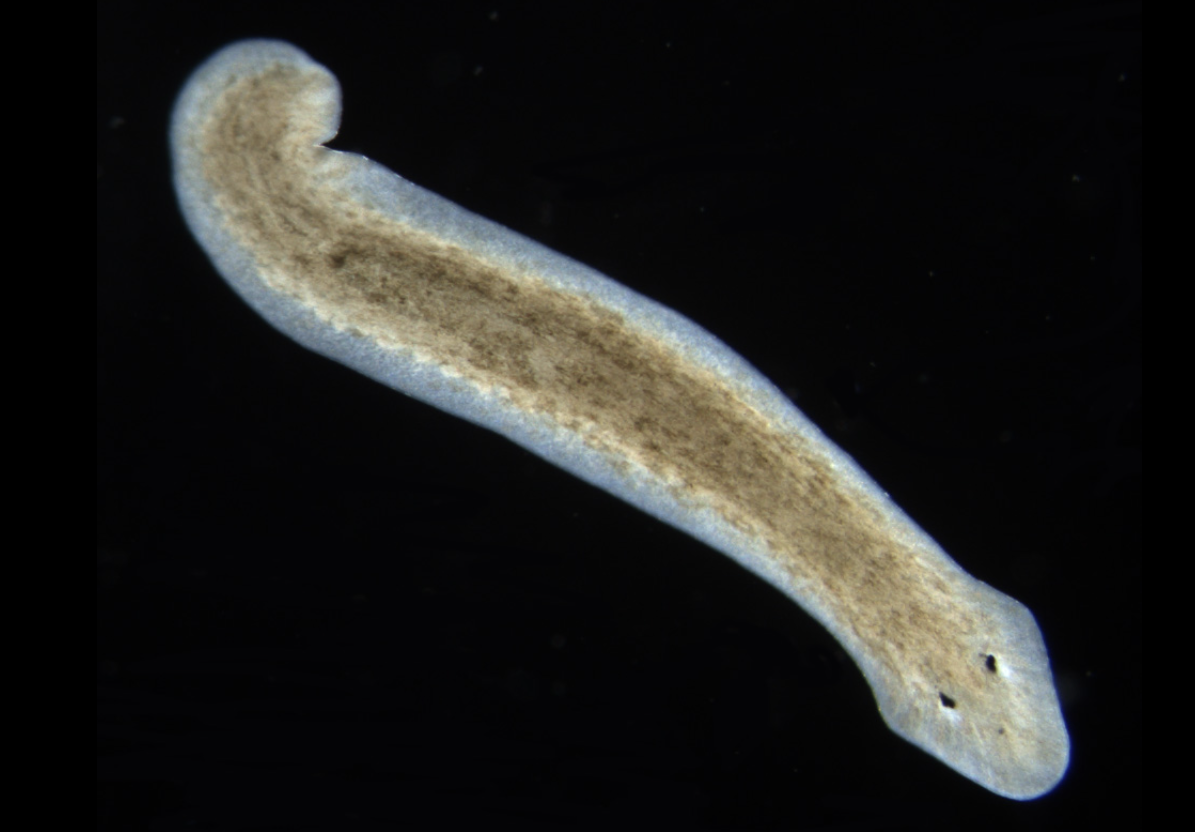
what is this
Phylum:
Platyhelminthes (Flatworms)
Flat
Have eyespots

what is this
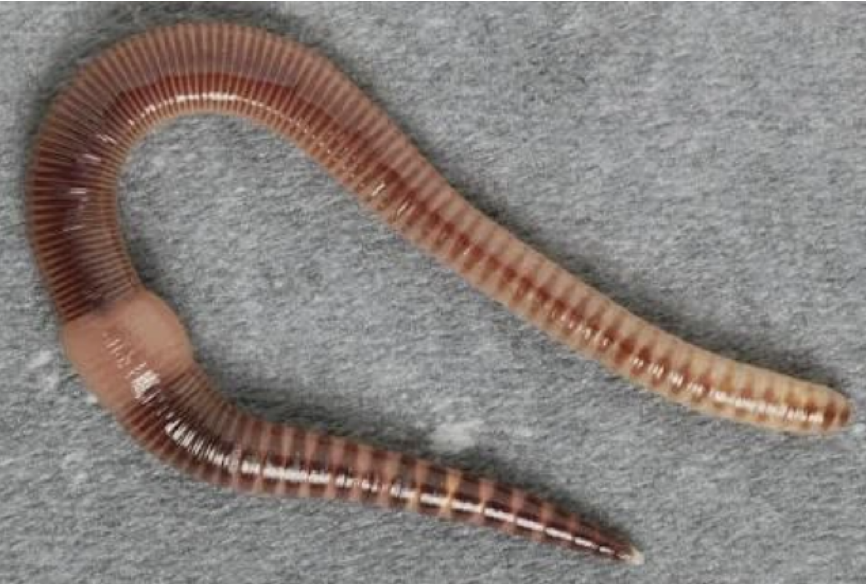
Phylum:
Annelida (Segmented worms)
Segmented
Visible Cheatea in some species

what is this
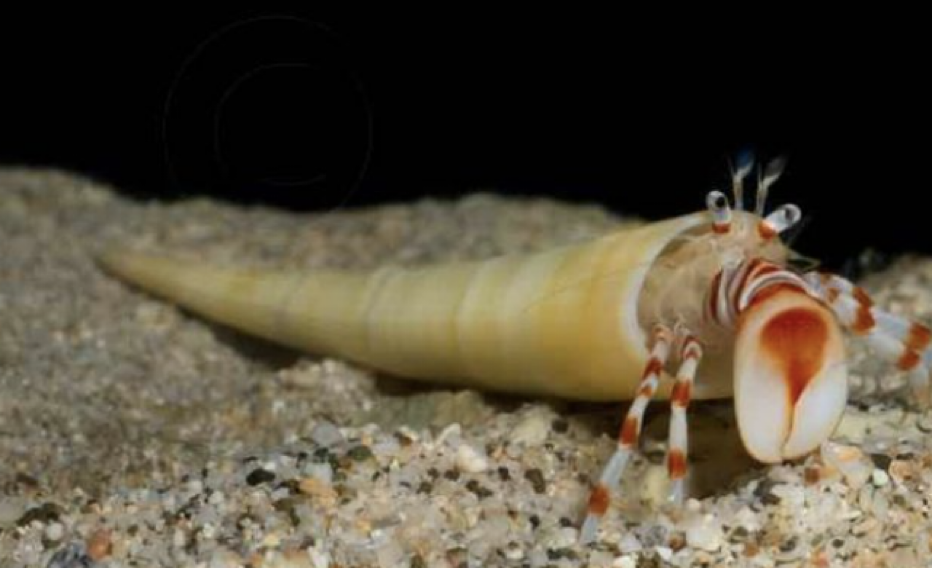
Phylum Mollusca:
Class: Scaphopoda

what is this
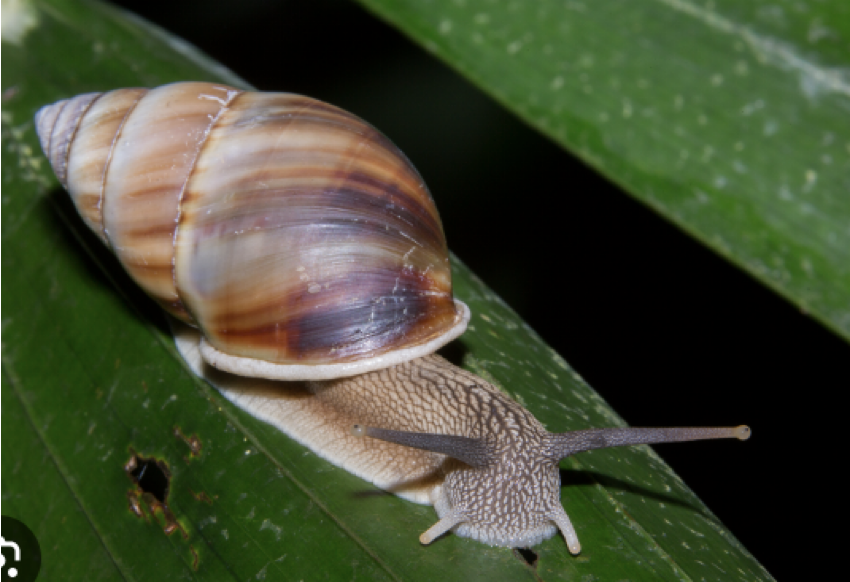
Phylum Mollusca:
Class: Gastropoda
Spiral shell (absent in some groups)
Mantle

what is this
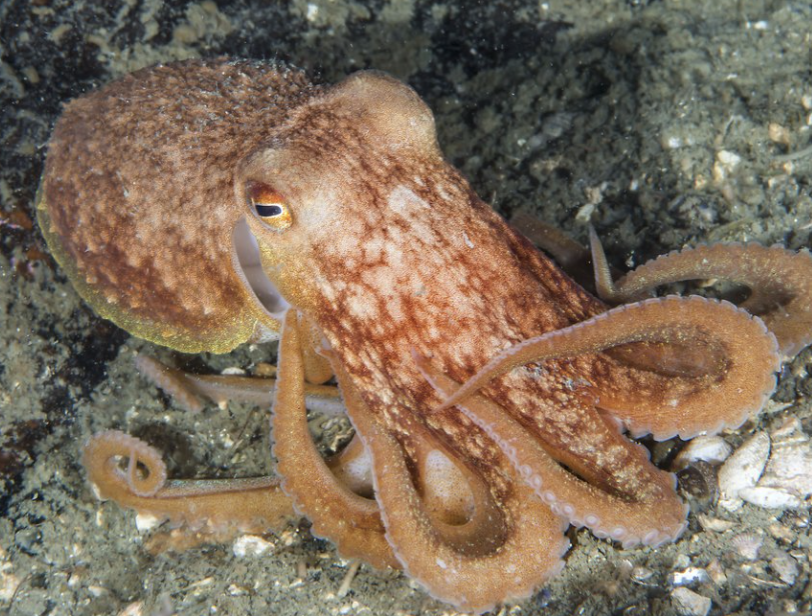
Phylum Mollusca:
Class: Cephalopoda
Large head
8 feet
Large eyes

what is this
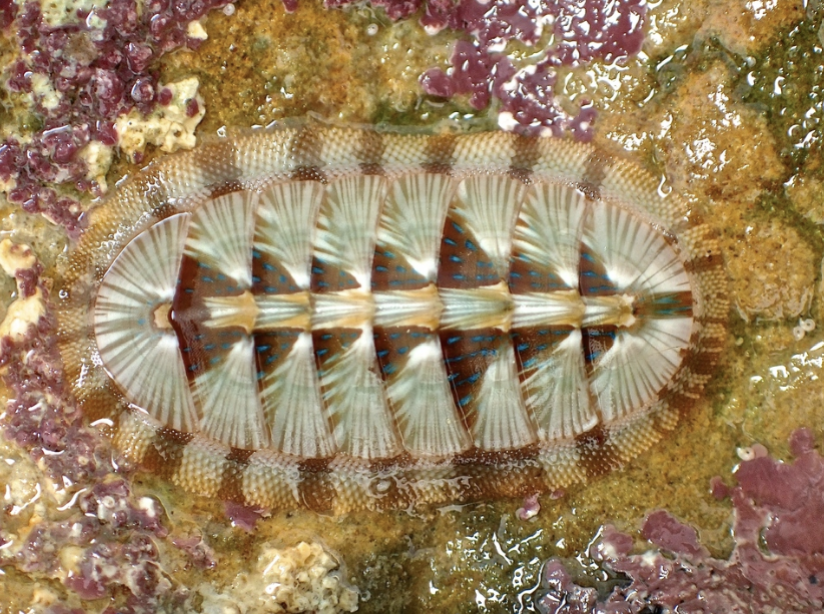
Phylum Mollusca:
Class: Polyplacopoda
Hard shells (oval)
Empty body cavity

what is this
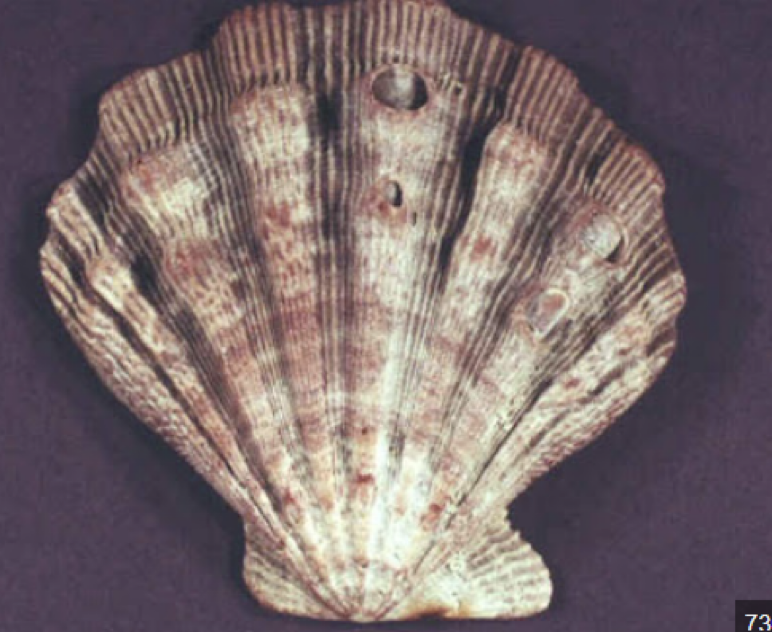
Phylum Mollusca:
Class: Bivalvia
Dual shell

what is this
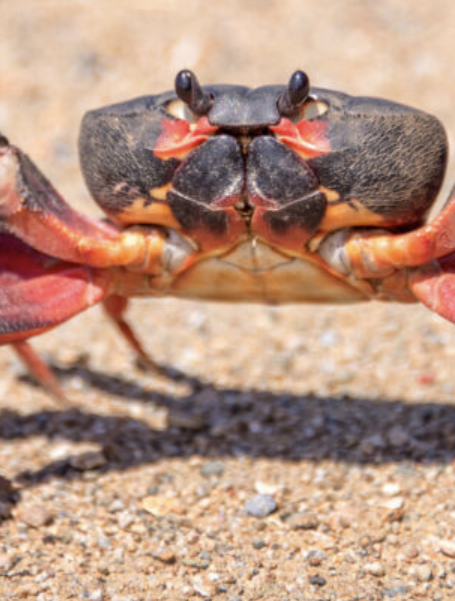
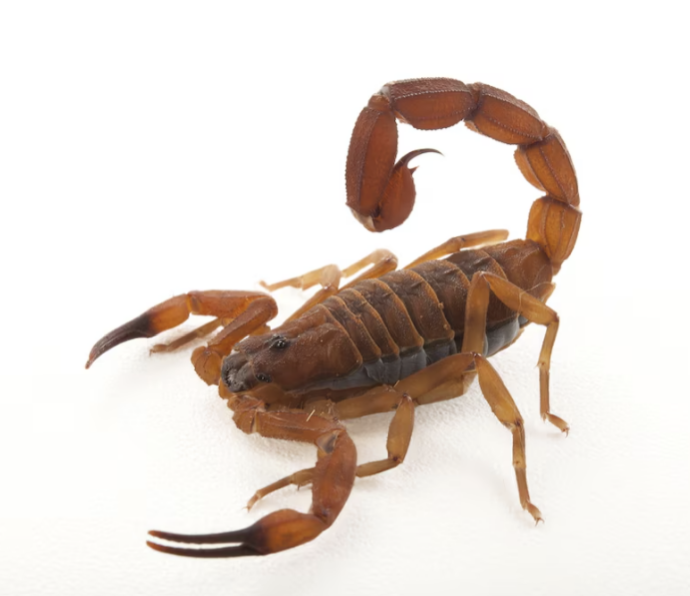
Phylum Arthropoda:
Class: Chelicerata
8 legs

what is this
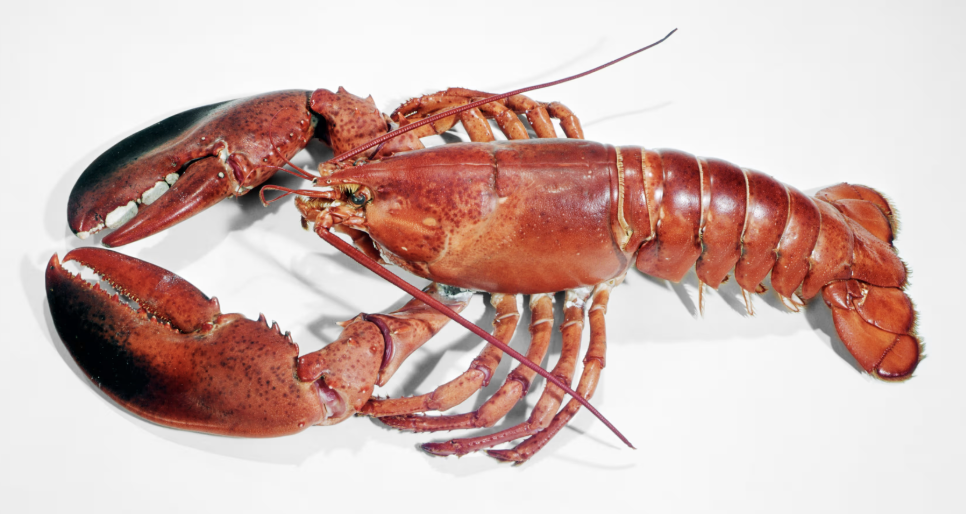
Phylum Arthropoda:
Class: Crustacea
Very clear cephalothorax
# legs vary

what is this
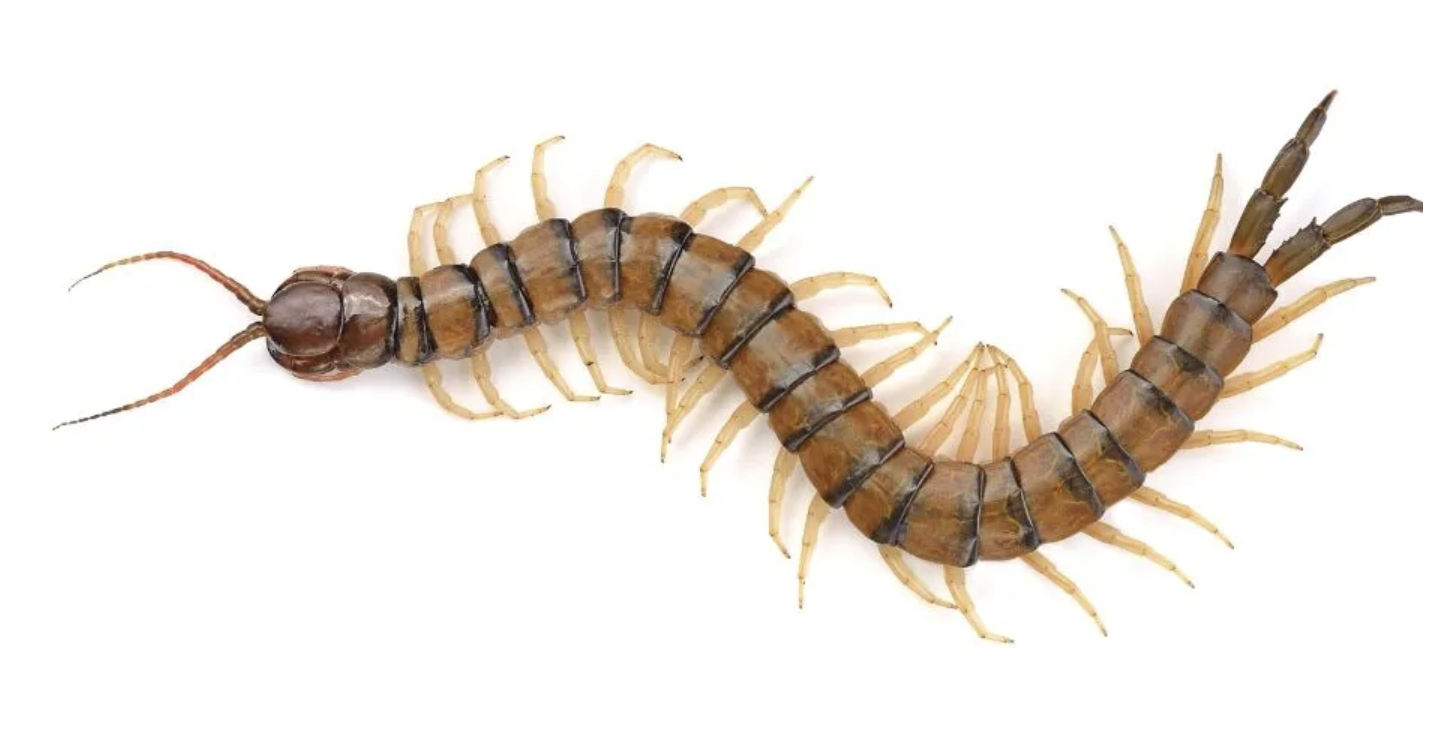
Phylum Arthropoda:
Class: Myriapoda
Hard exoskeleton
Many legs

what is this
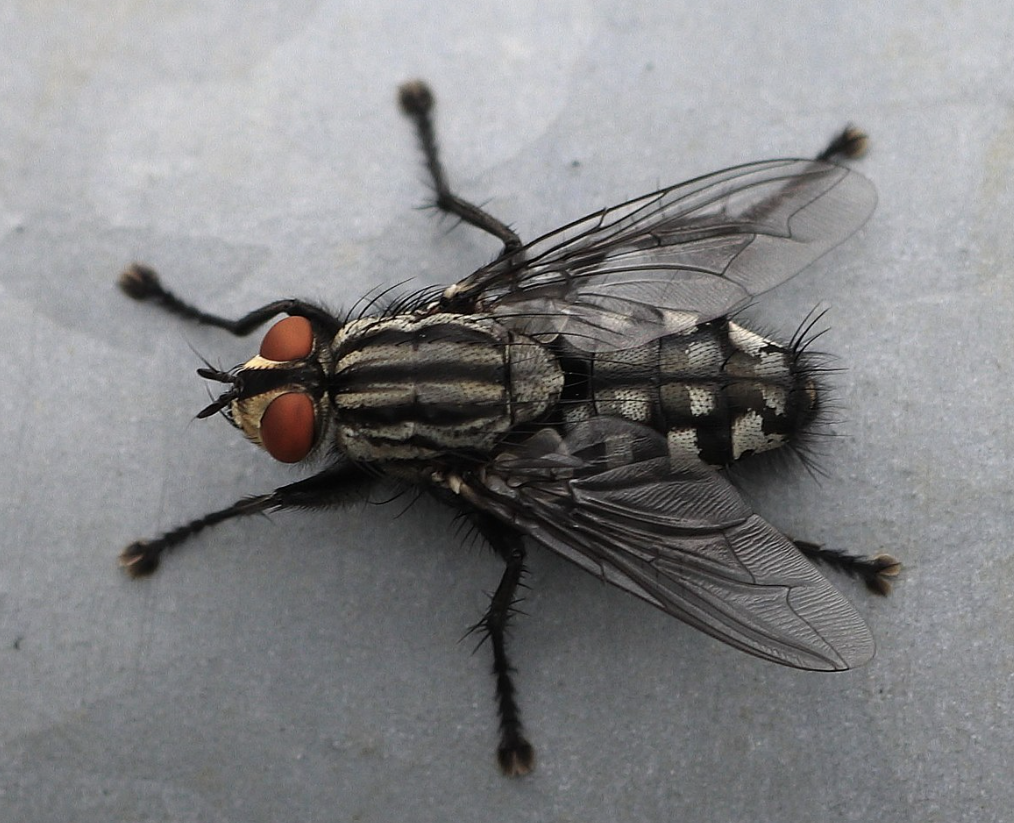
Phylum Arthropoda:
Class: Hexapoda
Head, thorax, and abdomen clearly marked
6 legs

what is this
Phylum: Nematoda
Under microscope
Transparent

what is this
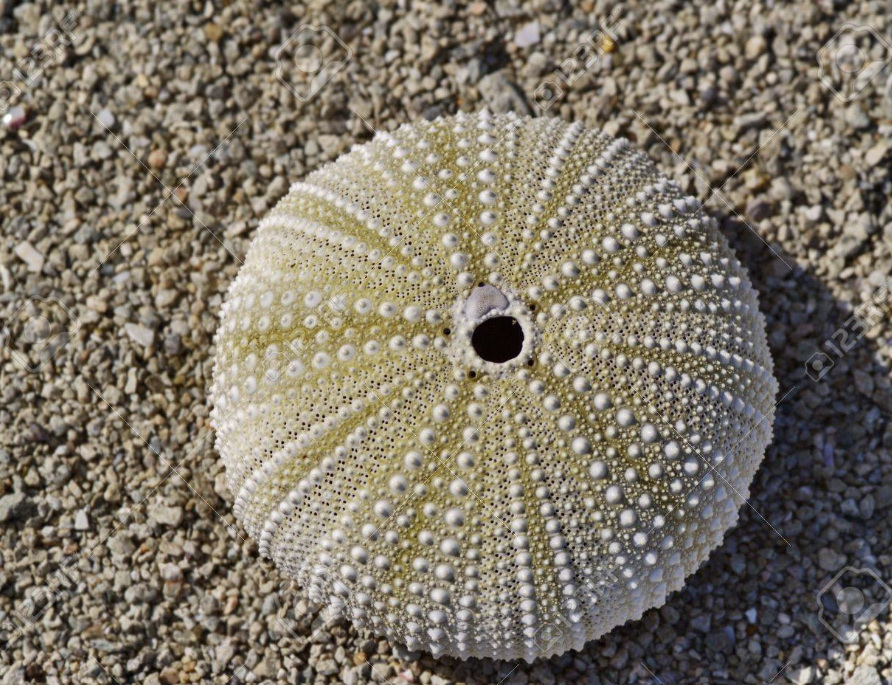
Phylum: Echinodermata
Pentaradial symmetry (only in this group)

what is this
Phylum Chordata:
Subphylum: Cephalochordata (Lancelets)

what is this
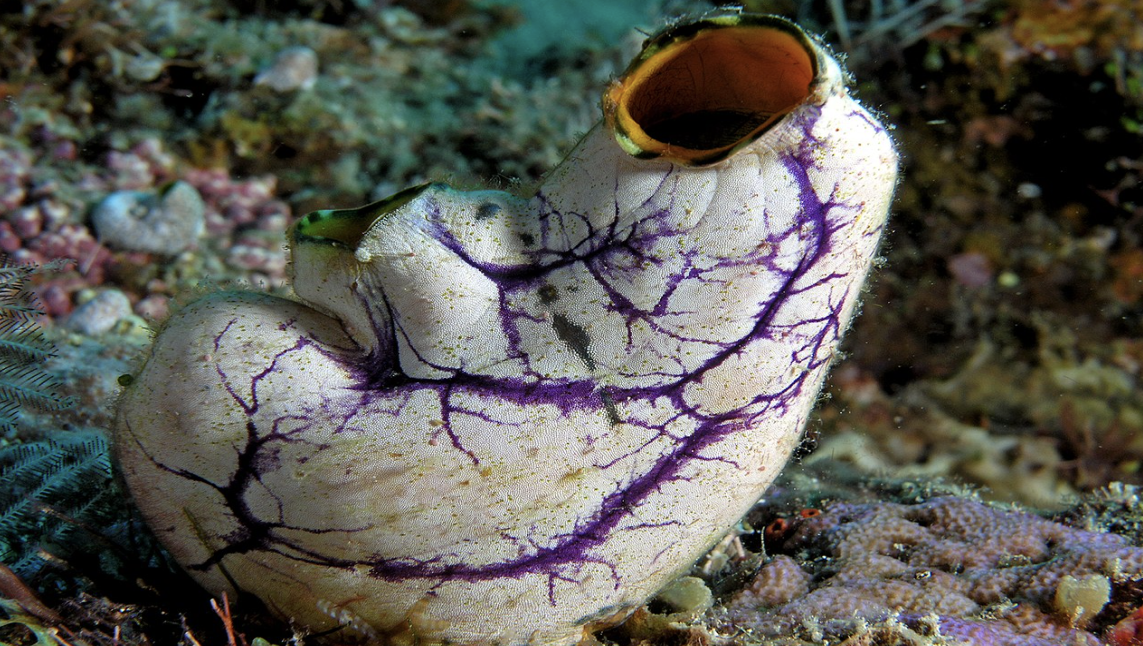
Phylum Chordata:
Subphylum: Urochordata (Tunicates)
what is this
Phylum Chordata:
Subphylum:Vertebrata
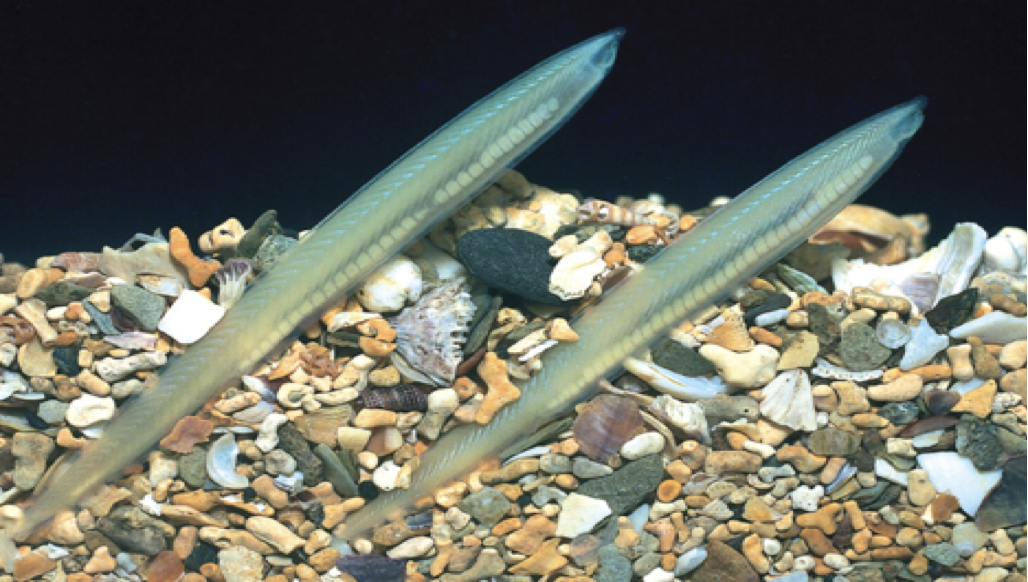
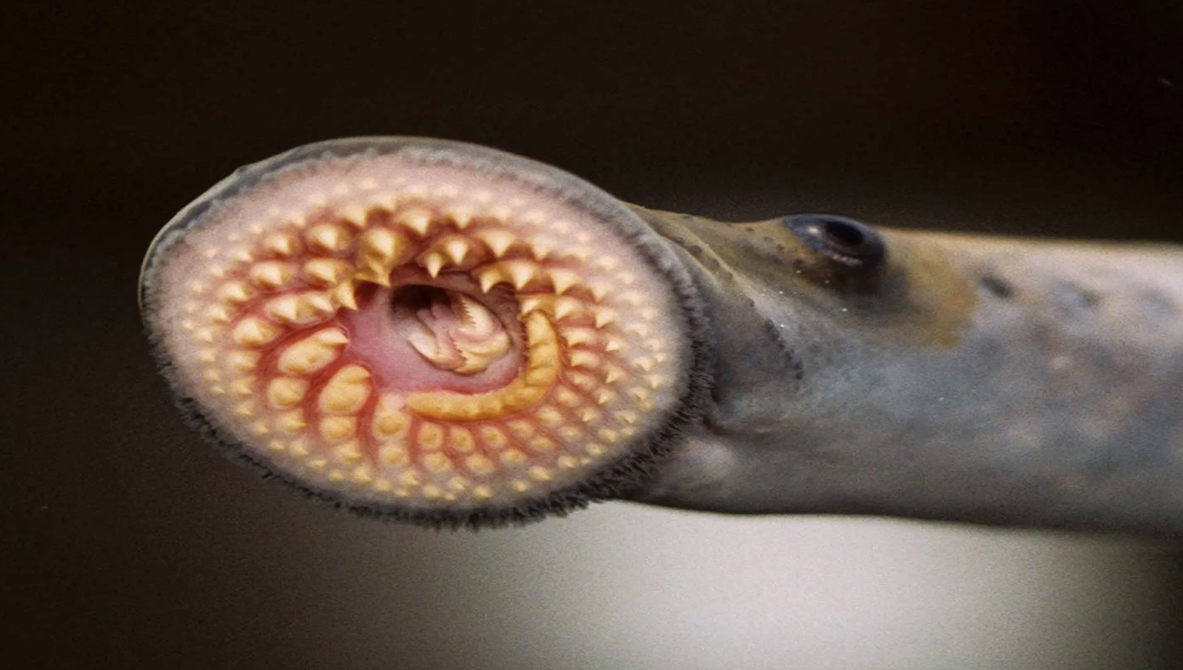
Infraphylum: Agnatha (Lampreys & Hagfishes)
Round, toothed mouths
No jaws

what is this
Subphylum:Vertebrata
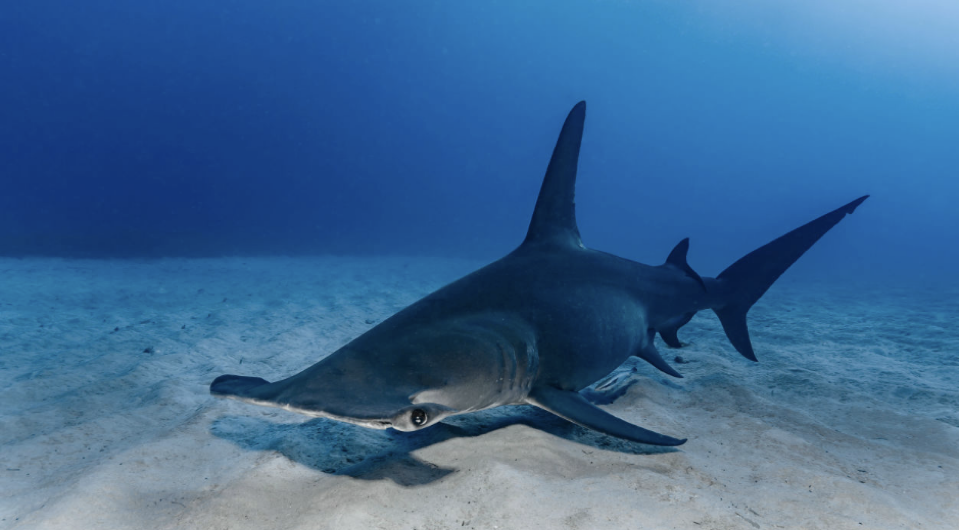
Infraphylum: Gnathostomata
Class: Chondrichthyes (Cartilogenous fish)
Shark or ray if placed in practical
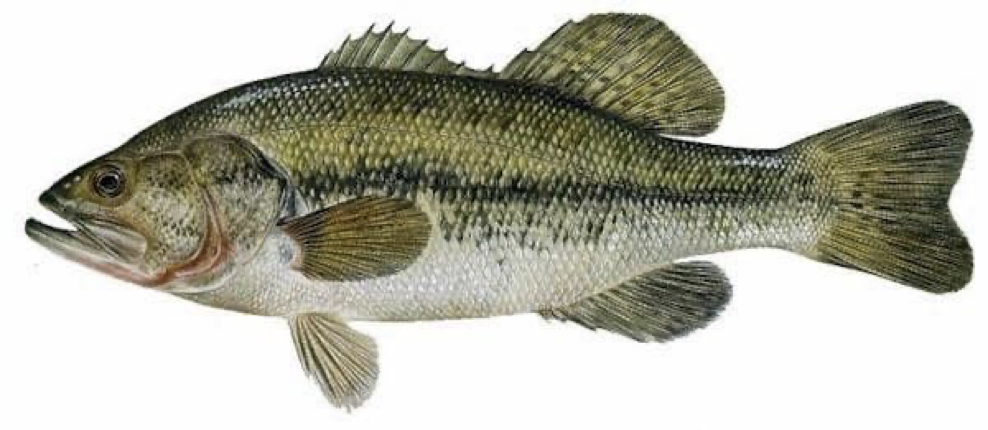

what is this
Subphylum:Vertebrata
Classes: Actinopterygii & Actinista (Ray and Lobe-finned fishes)
Any non-shark fish (excluding marine mammals- whale)

what is this
Subphylum:Vertebrata
Infraphylum: Tetrapoda
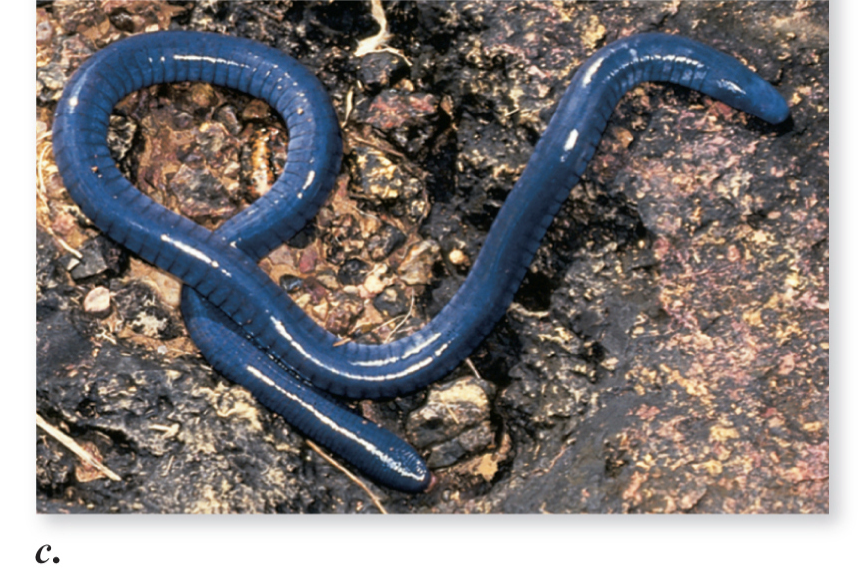
Class: Amphibia (Order Apoda)

what is this
Subphylum:Vertebrata
Infraphylum: Tetrapoda
Class: Amphibia (Order Caudata)
Rounded heads
Tail (always)
Frog-like

what is this
Subphylum:Vertebrata
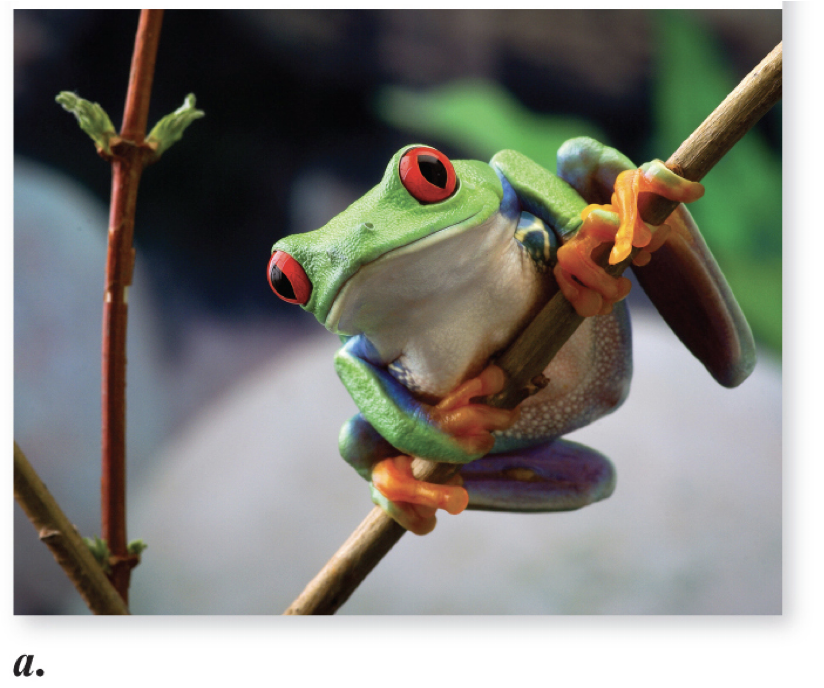
Infraphylum: Tetrapoda
Class: Amphibia (Order Anura)
Frogs and toads

what is this
Subphylum:Vertebrata
Infraphylum: Tetrapoda
Class: Amniota
Subclass: Reptilia
Dry skin
Scales visible
Snakes- only members with no legs

what is this
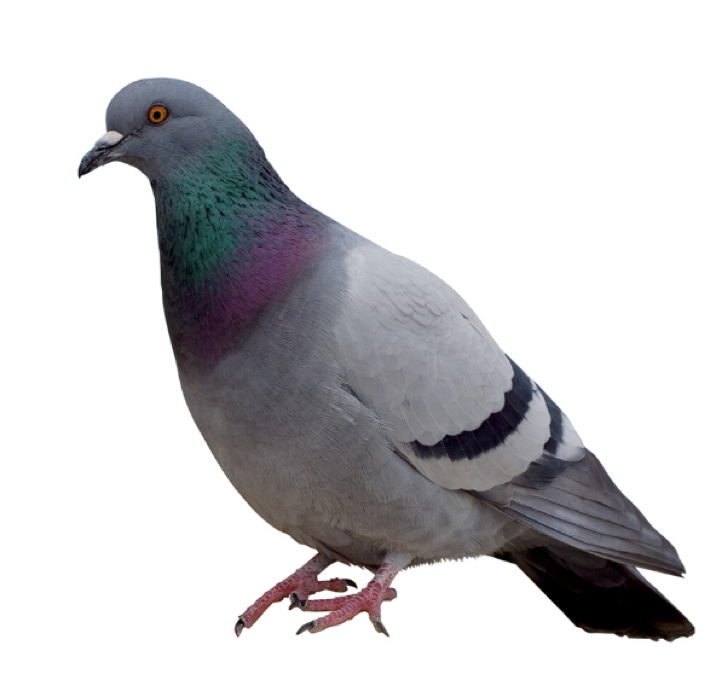
Subphylum:Vertebrata
Infraphylum: Tetrapoda
Class: Amniota
Subclass: Reptilia
Infraclass: Aves
Feathers