Chapter 19 OCHEM 2
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
amines
organic derivatives of ammonia with one or more alkyl or aryl groups bonded to the nitrogen atom.
heterocyclic amine
the nitrogen atom is apart of the aliphatic ring or aromatic
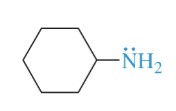
cyclohexylamine
primary amine
piperidine
secondary amine
quinuclidine
tertiary amine
Quaternary (4°) ammonium salts
have four alkyl or aryl bonds to a nitrogen atom, the nitrogen atom bears a positive charge
ethylamine
CH3CH2NH2
diisopentylamine
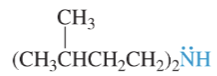
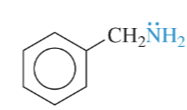
bemzylamine
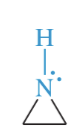
aziridine
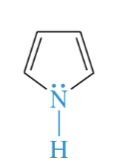
pyrrole
pyrrolidine
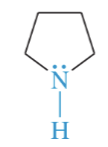
N-methyl pyrrolidine
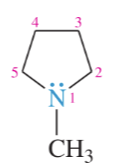
imidazole
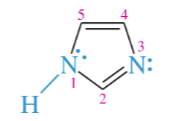
indole
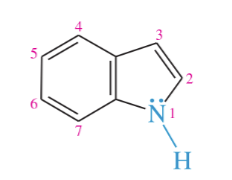
pyridine
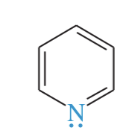
methyl pyridine
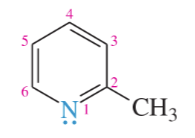
pyrimidine
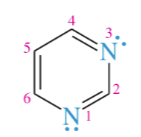
purine
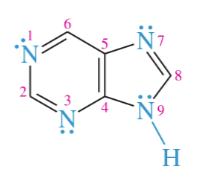
structure of amines
nitrogen in amines forms 3 sigma bonds and has 1 lone pair, with sp³
amine dipole moments
strongly polar due to hydrogen bonds and the lone pair on nitrogen
amine functions
Bronsted Lowry base and accepts a proton
amine basicity
sp < sp 2 < sp 3
amine solubility
Increasing the number of alkyl groups decreases solvation of ion, so 2° and 3° amines are similar to 1° amines in basicity
amine resonance
Any delocalization of the electron pair weakens the base
less basic than most aliphatic amines.
Aniline is
a very weak base
pyrrole is
amine salt ions
the protonated amine cation and the anion derived from the acid
amine IR N-H
3200-3500
NMR N-H
1-4
C13 N-H
30-50
amine MS
alpha cleavage
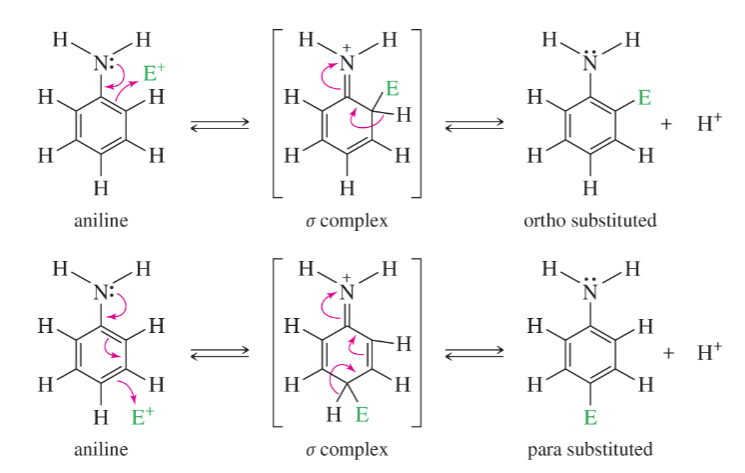
EAS Arylamines
Protonation of the amine under acidic conditions converts the group into a strong deactivator, multiple substitution is a problem
EAS Arylamines conditions
excess X2, NaHCO3
excess X2, NaHCO3
EAS Arylamines conditions
EAS w/ excess X2, NaHCO3
tri-substituted X
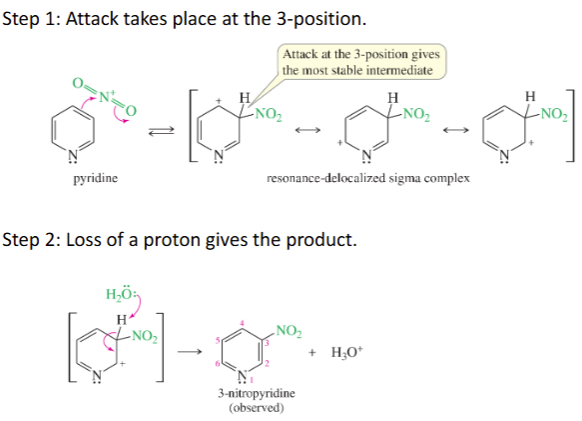
EAS of Arylamines mechanism
Step 1: Attack takes place at the 3-position.
Step 2: Loss of a proton gives the product.
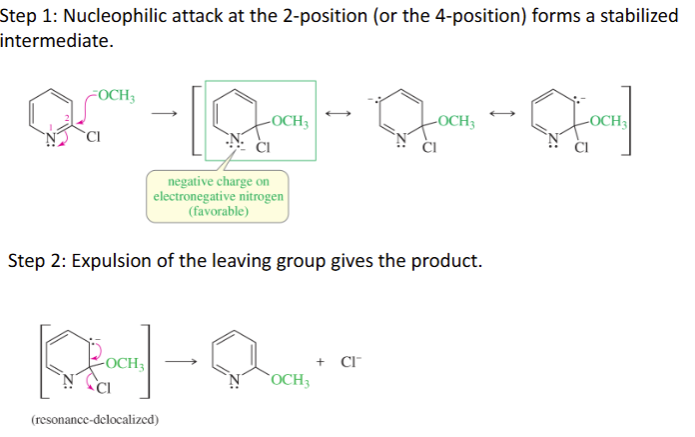
NAS of Arylamines mechanism
Step 1: Nucleophilic attack at the 2-position (or the 4-position) forms a stabilized
intermediate.
Step 2: Expulsion of the leaving group gives the product
amines + 1 alkyl halides
ammonium halides
direct alkylation
some amine molecules will react once and some twice, giving mixed results
exhaustive alkylation
A mild base (often or dilute NaOH) is added to deprotonate the intermediate alkylated amines and to neutralize
the large quantities of HX formed
Excess ammonia alkylation
10 moles of ammonia with one mole of R—X
Acylation of amines product
amide
mechanism of acylation of amines
Step 1: A nucleophile attacks the strongly electrophilic carbonyl group of the acid
chloride to form a tetrahedral intermediate.
Step 2: The tetrahedral intermediate expels chloride ion.
Step 3: Loss of a proton gives the amide
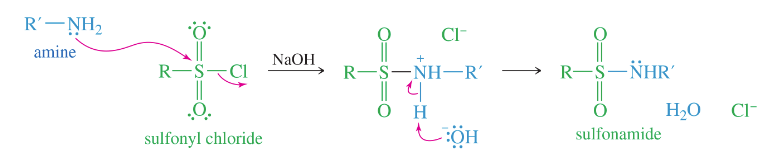
sulfonamides
amides of sulfonic acid
Hofmann elimination
the elimination of a quaternary ammonium hydroxide in a concerted E2 reaction with amine as the leaving group
Hofmann product
least substituted alkene as the major product
Zaistev product
most substituted alkene as major product
hofmann elimination primary amine product
alkene + amine
hofmann elimination secondary amine product
opened ring alkene + substitution on the nitrogen
Hofmann elimination conditions
amine + -OH under heat
amine + -OH under heat
Hofmann elimination
Zaitsev elimination conditions
sodium methoxide + amine or alkyl halide
primary amine oxidation
oxidize easily, but complex mixtures of products often result
secondary amine oxidation
are easily oxidized to hydroxylamines, side products are often
formed, however, and the yields may be low
tertiary amine oxidation
are oxidized to amine oxides with good yields
common oxidizing agents
H2O2, MCPBA, MnO4-, RCO3H
1° amine + [O]
(R—NHOH) hydroxylamine
2° amine + [O]
(R2—NOH) 2° hydroxylamine
3° amine + [O]
(R3—O-) 3° hydroxylamine
cope elimination
reaction where an amine is oxidized to an intermediate called
an “N-oxide”, which, when heated, acts as the base in an intramolecular E2 elimination reaction to give a new alkene
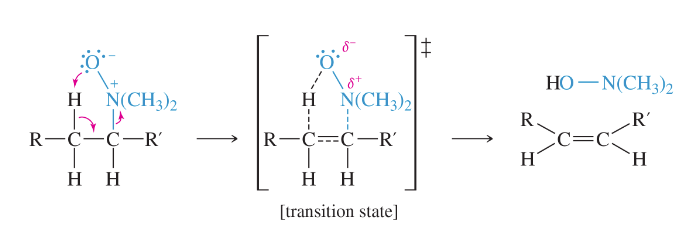
cope elimination product
least substituted product
primary amines + nitric acid (HNO2) product
dialkyldiazonium salts, that decompose into carbocations and nitrogen
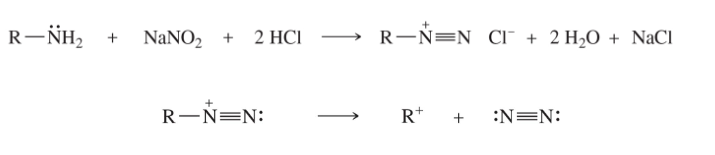
secondary amines + nitrosomium ion (N+)=O product
secondary N-nitrosoamines
Mechanism of Diazotization of primary amine
Part 1: Attack on the nitrosonium ion (a strong electrophile), followed by deprotonation, gives an N-nitrosoamine.
Part 2: A proton transfer (a tautomerism) from nitrogen to oxygen forms a hydroxy group and a second bond.
Part 3: Protonation of the hydroxy group, followed by loss of water, gives the diazonium ion.
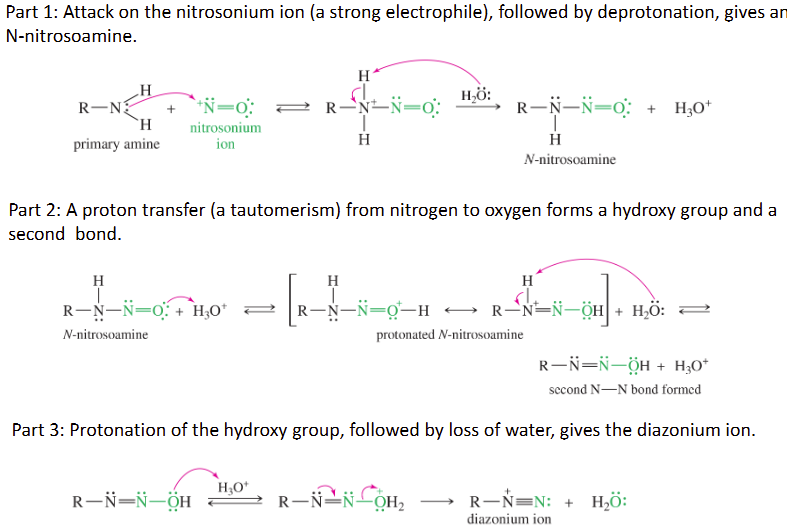
Arenediazonium salts
relatively stable in aqueous solutions around 0-10 Celsius
arene diazonium salt
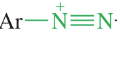
ArN2 + H3O+ warm product
phenols
ArN2 + CuCl product
aryl chlorides
ArN2 + CuBr product
aryl bromides
ArN2 + CuCN product
benzonitriles
ArN2 + HBF4 product
aryl fluorides
ArN2 + KI product
aryl iodides
ArN2 +H3PO2 product
aryl group
deamination
process of removing an amine group (NH2)
ArN2 + AR—H product
azo dyes ( Ar—N==N—Ar )
hydrolysis product
replaces the NH2 group with a hydroxide group
amine hydrolysis conditions
(1) H2SO4, heat, H2O
(1) H2SO4, heat, H2O
amine hydrolysis conditions
Sandmeyer product
replace the amine group (NH2) with Br, Cl, CN
sandmeyer conditions
(1) NaNO2. HCl (2) CuCl
(1) NaNO2. HCl (2) CuCl
sandmeyer conditions
Deamination reaction product
removal of the NH2 group on the compound
deamination reaction conditions
(1) NaNO2, HCL (2) H3PO2
(1) NaNO2, HCL (2) H3PO2
deamination reaction conditions
Diazo coupling product
nitrogen double bond with two rings
Reductive amination
most general synthesis , capable of adding a primary or secondary alkyl group to an amine
Reductive Amination: 1° Amines
LiAlH4 or NaBH3 CN can be used to reduce the oxime
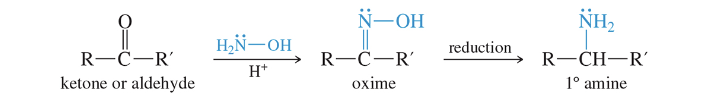
Reductive Amination: 2° Amines
LiAlH4 or NaBH3 CN can be used to reduce the oxime
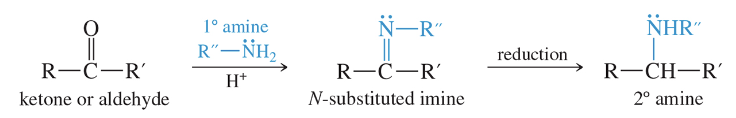
Reductive Amination: 3° Amines
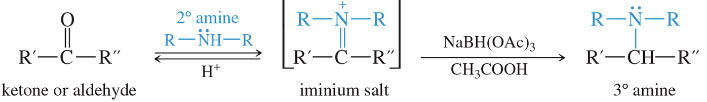
NaBH(OAc)3 CH3COOH is used to reduce the salt
reduction hydroxylamine to
primary amine
reduction of primary amine to
secondary amine
reduction of a secondary amine to
a tertiary amine
1° Amines by Acylation-reduction
acid chloride + ammonia
2° Amines by Acylation-reduction
acid chloride + primary amine
3° Amines by Acylation-reduction
acid chloride + secondary amine
Gabriel Synthesis
involves reacting a potassium phthalimide with an alkyl halide, followed by hydrolysis or hydrazinolysis to remove the phthaloyl group and yield the desired primary amine
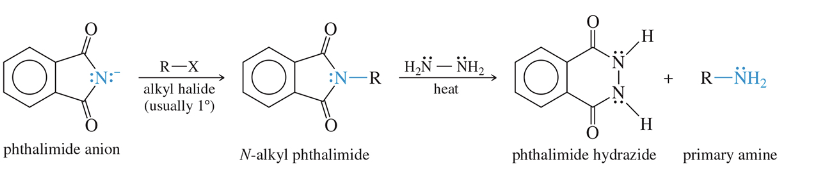
Reduction of Azides
React azide with unhindered 1° or 2° halide or tosylate (SN2) and with reduction yield a primary amine
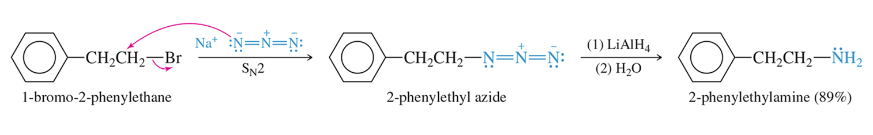
reduction of nitriles
React nitrile with unhindered 1° or 2° halide or tosylate (SN2) and with reduction yield a primary amine
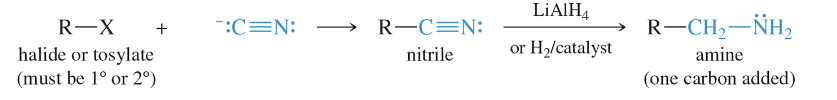
azide
Azide ion, –N 3 , is a good nucleophile