Field Botany (RNR 230R) Exam 2 Vocabulary UofA
1/206
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
207 Terms
germination
the development of a plant from a seed or spore after a period of dormancy
reproduction
the formation of new individuals; production of a new member of a population from existing members
meiosis
Sexual reproduction; cell division producing 4 cells with half the number of chromosomes as in a body cell
fertilization
the union of male and female gametes to produce a zygote (fertilized egg).... similar for both flowering plants (angiosperms) and seed-bearing plants (gymnosperms
mitosis
Asexual reproduction; the process through which a plant cell divides and creates two identical copies of itself, which are referred to as daughter cells
chromosomes
self reduplicating nuclear filaments endowed with hereditary (genetic) function; great importance in determining the phylogeny and taxonomy of the species
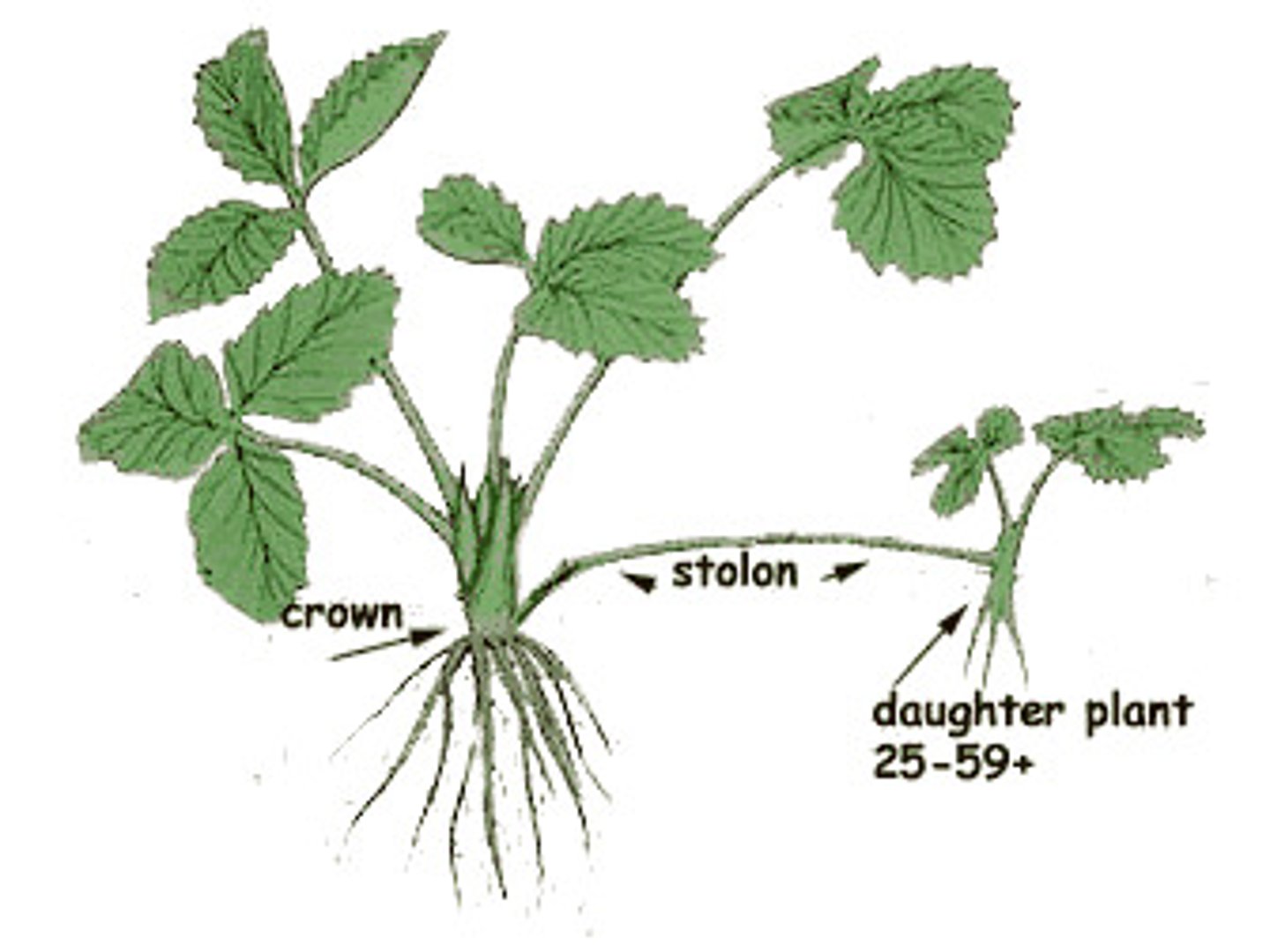
stolon
stems which grow at the soil surface or just below ground that form adventitious roots at the nodes, and new plants from the buds; often called runners
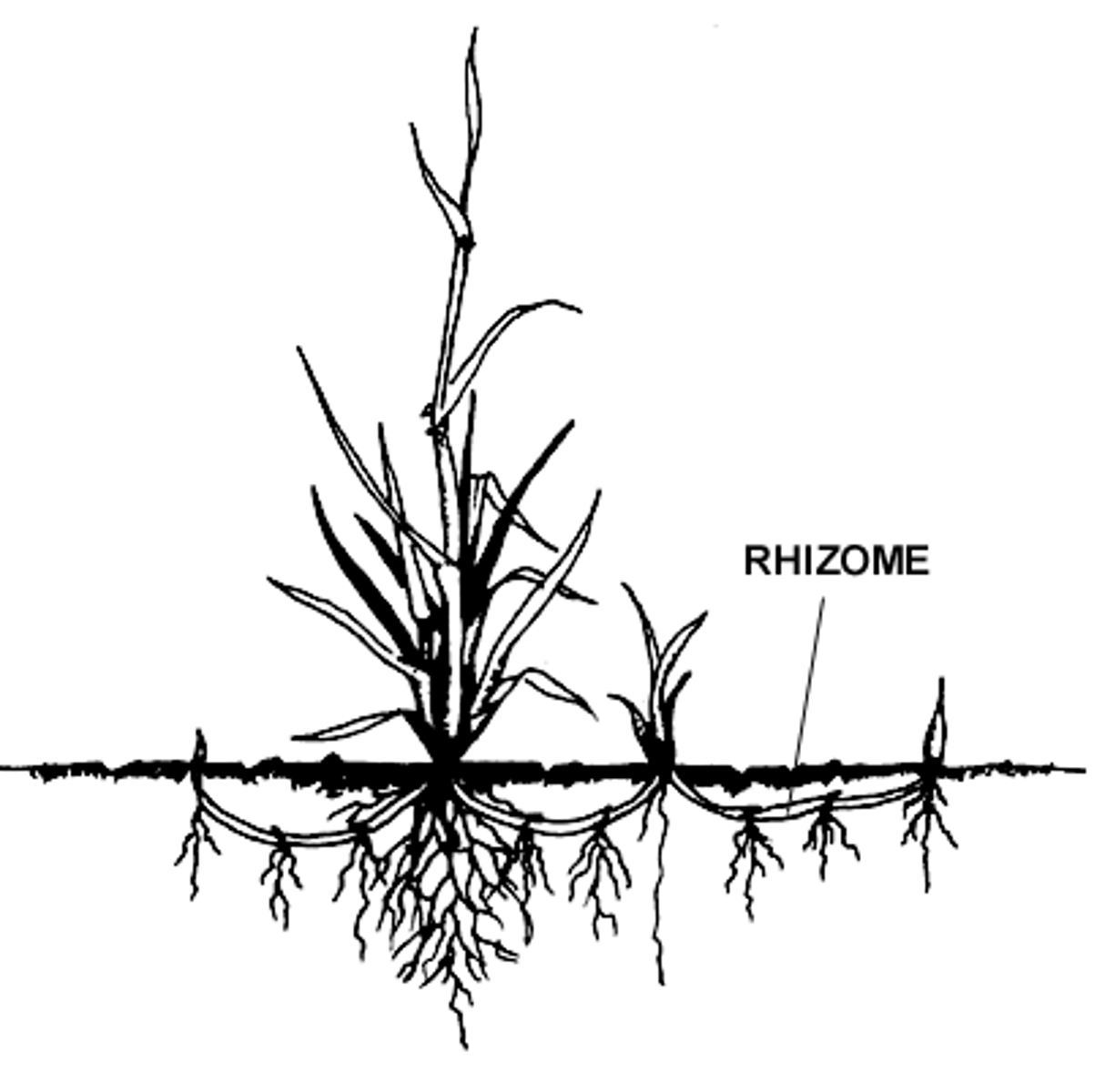
rhizome
horizontally growing below ground stem; may produce roots and shoots at nodes
spreading growth
The way a plant, or grass, grows and develops outward over a flat surface. Some plants choose to spread when growing while others are non-spreading, or grow upright
asexual reproduction
reproduction where an organism replicates itself without the involvement of meiosis or fertilization ; reproduction as budding, fission, or spore formation, not involving the union of gametes
caespitose
growing in small dense clumps or tufts
tiller
a plant shoot that springs from the root or bottom of the original stalk
ring formation
in a cross section of the stem of a woody plant; represent layers of cells produced by vascular cambium
basal bud
various types of shoots which grow from a bud at the base of a tree or shrub or from adventitious buds in its roots
tuber
thickened rhizome or stolon ; stem tissue ; a swollen, fleshy, usually underground outgrowth of the stem or rhizome of a plant, such as the potato, bearing buds from which new plant shoots arise
storage organ
a part of a plant specifically modified for storage of energy (generally in the form of carbohydrates) or water; often grow underground, where they are better protected from attack by herbivores
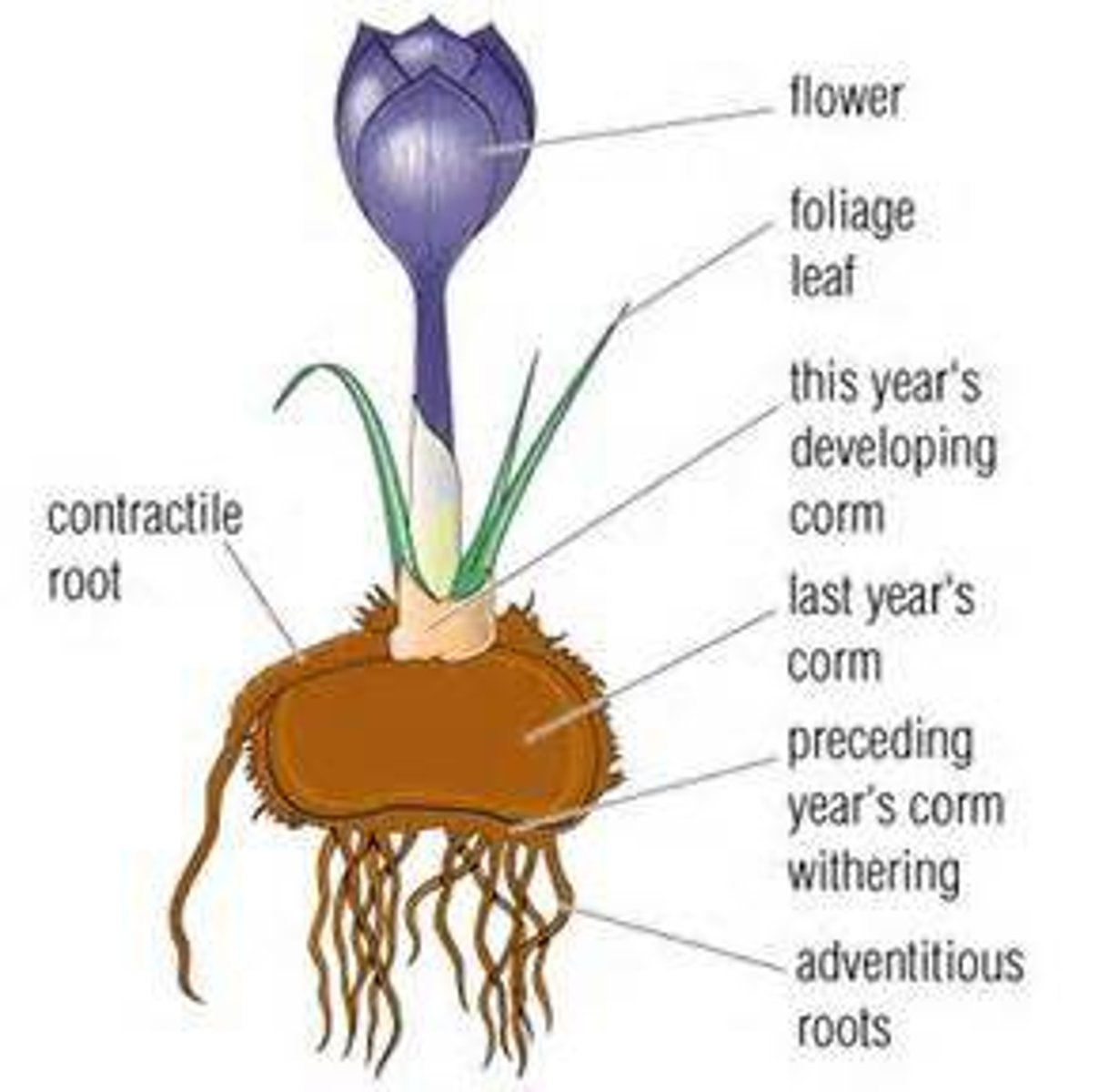
corm
short, vertical, thickened underground stem tissue
bulb
underground vertical shoot with overlapping leaves modified for energy storage; any plant that stores its complete life cycle in an underground storage structure; a resting stage of a plant
adventitious
roots that arise from an organ other than the root—usually a stem, sometimes a leaf

totipotency
the potential of a single cell to produce specialized cells of many different types or to create a new individual; Spores and zygotes are examples of totipotent cells
stem cutting
a piece of a plant that is used in horticulture for vegetative (asexual) propagation
plantlet
young or small plants
monocarpic
flower once then die; plants that flower, set seeds and then die
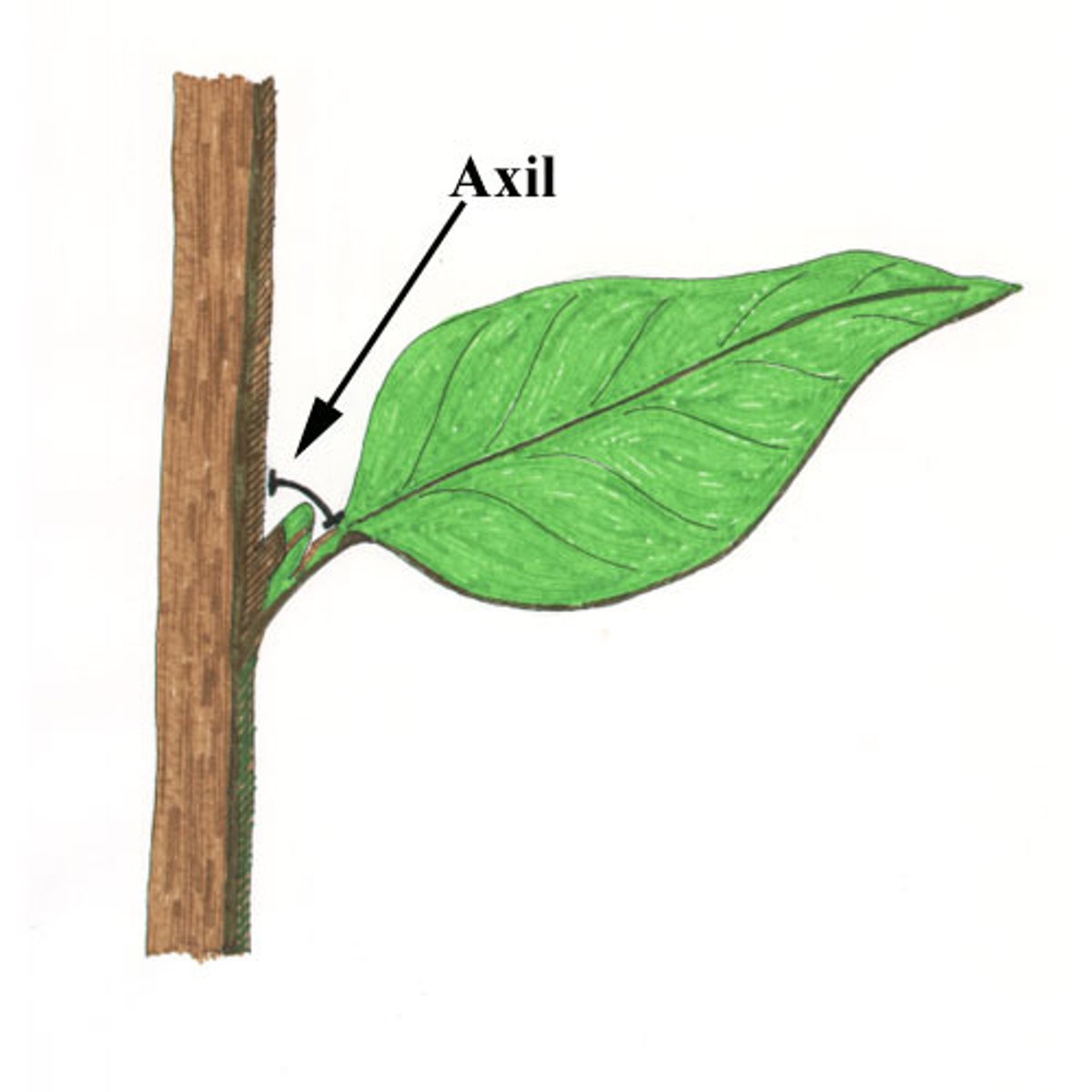
axil
the angle between the upper side of a leaf or stem and the supporting stem or branch
gametic meiosis
results in formation of haploid gametes; gametes fuze during fertilization and form diploid zygote i.e. having diplontic life cycle
diploid
having two similar complements of chromosomes
haploid
a cell or organism that has a single set of chromosomes that are not paired
zygote
fertilized egg
sperm
male gamete; such as a spermatozoon of an animal or one of the cells or nuclei produced by a pollen grain of a plant
egg
A female gamete; an ovum; consisting usually of an embryo surrounded by nutrient material and a protective covering
gametes
sex cells of plants; a haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that sexually reproduce
sporic meiosis
occurs during the process of sporogenesis and results in the formation of haploid spores. Spore divides to form gametophyte which eventually form gametes. A diploid sporophyte is formed as a result of fusion of those gametes.
sporophyte
plants that produce spores; the form of a plant in the alternation of generations that produces asexual spores
spore
A small, usually single-celled asexual or sexual reproductive body that is highly resistant to desiccation and heat and is capable of growing into a new organism, produced especially by certain bacteria, fungi, algae, and nonflowering plants
gametophyte
gamete producing plant ;
process involves a multicellular diploid generation called a sporophyte and a multicellular haploid generation called a gametophyte
carpel
composed of an ovary, a style, and a stigma; leaves (megasporophylls) that have evolved to enclose the ovules; the term pistil is sometimes used to refer to a single carpel or to several carpels fused together
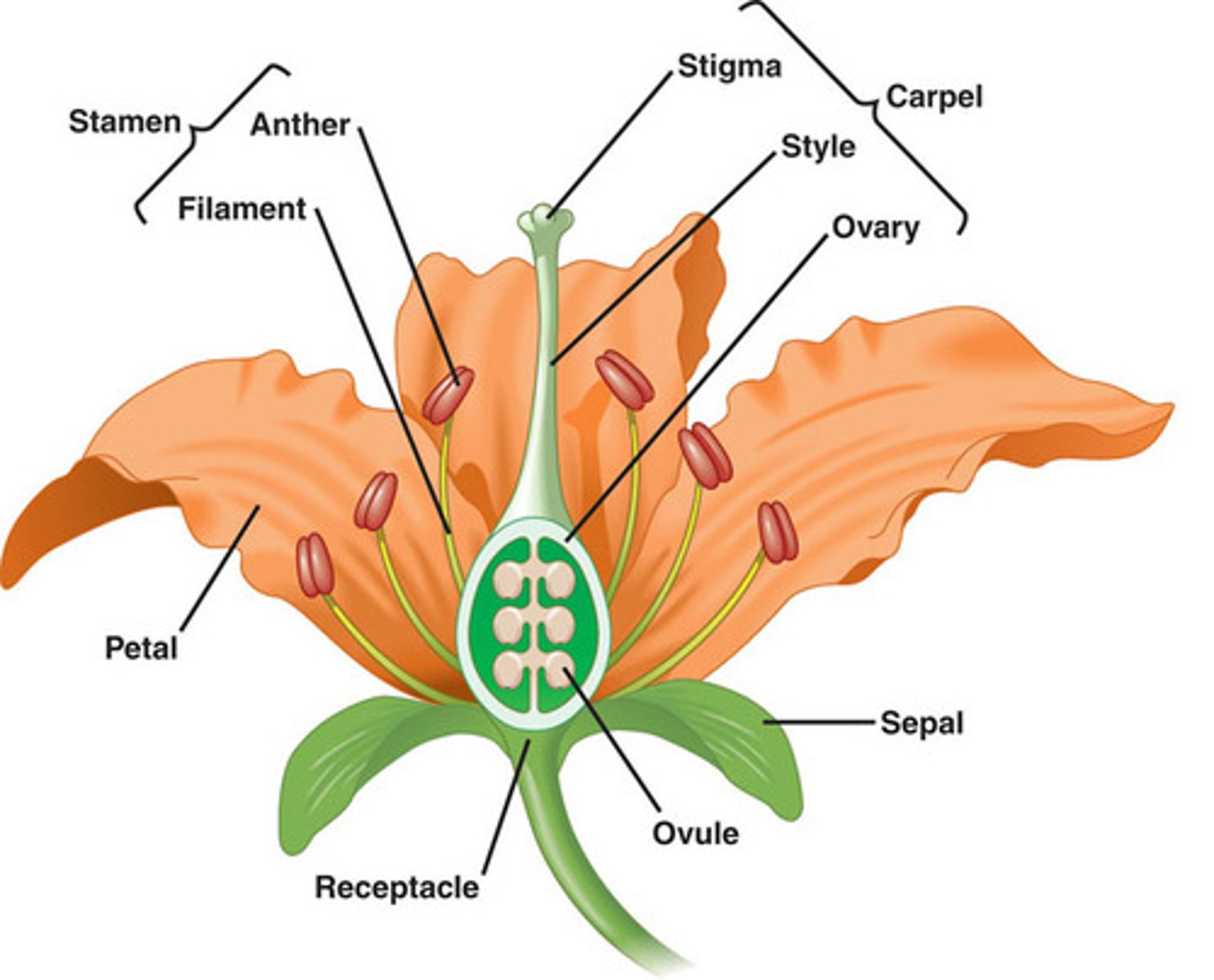
stigma
The tip of the pistil; where pollen grain germinates; sticky; adapted in various ways to catch and trap pollen with various hairs, flaps, or sculpturings
style
The narrow elongated part of the pistil between the ovary and the stigma; a long, slender stalk that connects the stigma and the ovary;a sticky platform where pollen is deposited
ovary
The rounded base of a pistil that contains one or more ovules
ovule
the plant part that contains the embryo sac/ female germ cell, which after fertilization develops into a seed
anther
The part of the stamen where pollen is produced
filament
support for the anther
stamen
male part of the flower, made up of anther and filament
microgametophyte
The male gametophyte that arises from a microspore of a heterosporous plant. In seed plants, the microgametophyte is contained in the pollen grain; The pollen grains of gymnosperms and angiosperms
microspore
land plant spores that develop into male gametophytes; a microspore refers to the spore produced by sporophytes. It is haploid and gives rise to a male gametophyte
pollen grain
A structure produced by plants containing the male haploid gamete to be used in reproduction; the male portion of the reproductive process in plants and trees
pollination
movement of pollen grains ; pollination is not fertilization
sperm cell
the male gamete or reproductive cell involved in sexual reproduction. It is produced by a male organism that unites with the egg of a female organism forming a zygote
tube cell
the cell in the pollen grain that develops into the pollen tube
megagametophyte
The female gametophyte that arises from a megaspore of a heterosporous plant. In angiosperms, "the blank... is the embryo sac"
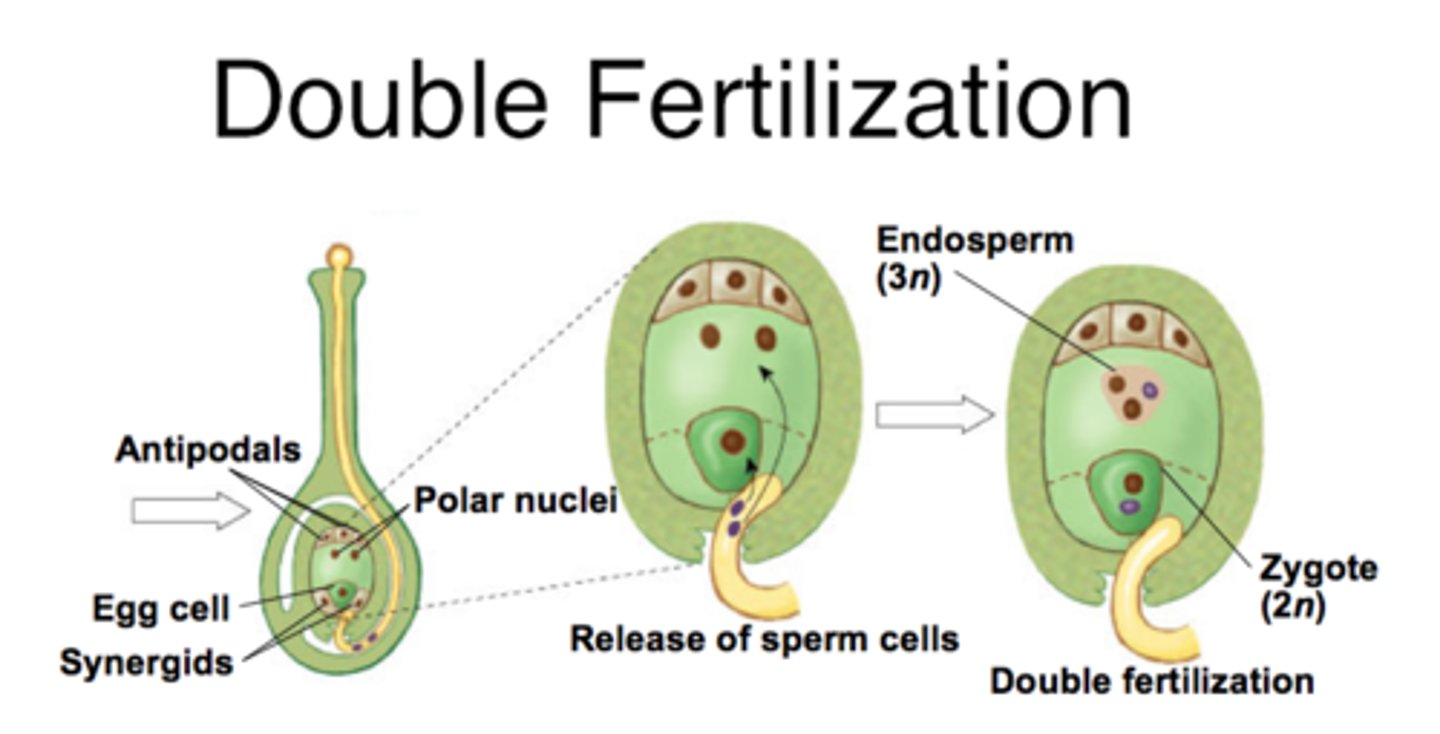
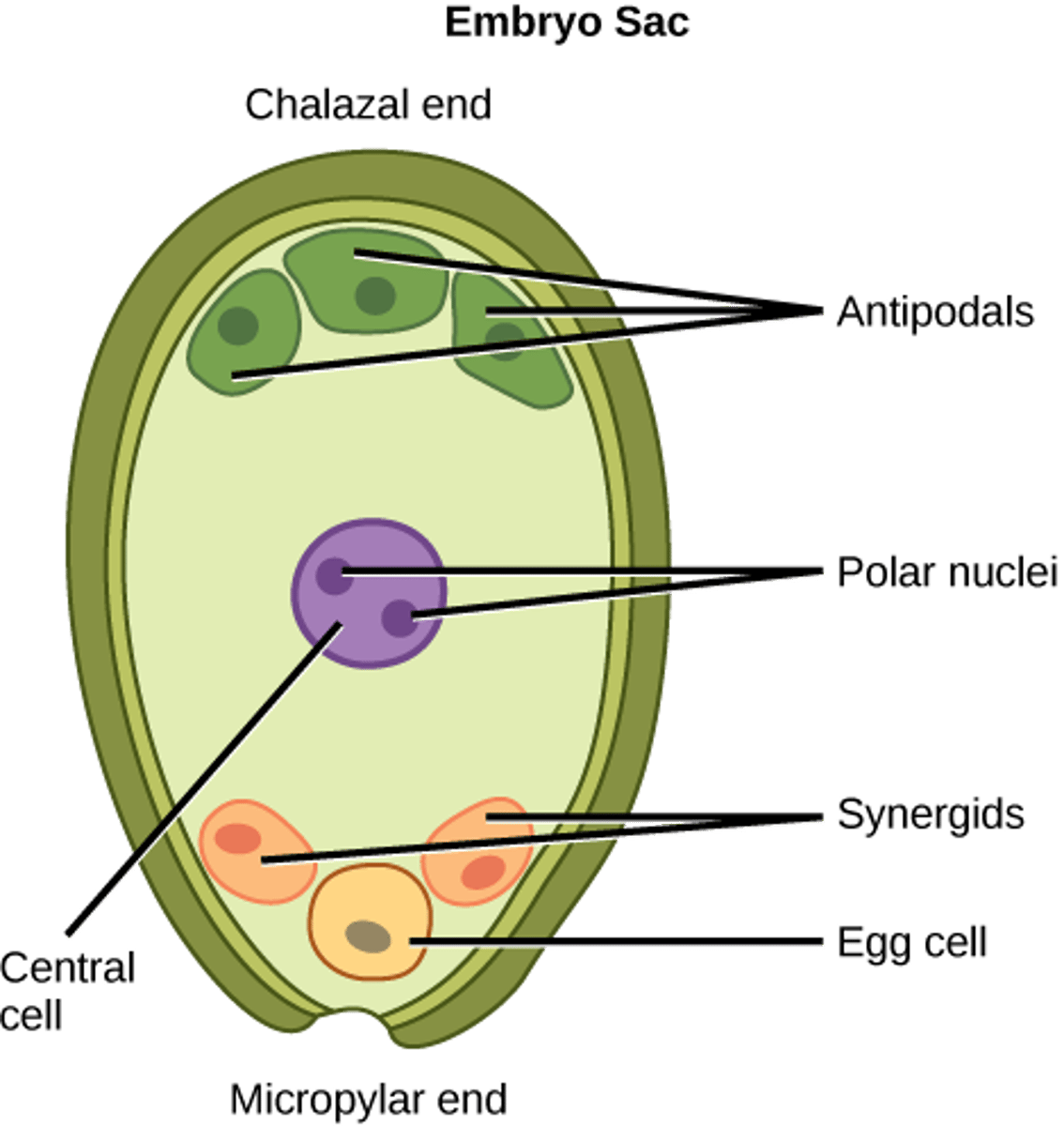
polar nuclei
Two haploid nuclei inside the mid-region of the embryo sac of a flowering plant which fuse with another nucleus (1 of 2 sperm nuclei) to form the triploid endosperm
antipodals
The three haploid cells in the mature embryo sac of flowering plants that are situated at the opposite end to the micropyle
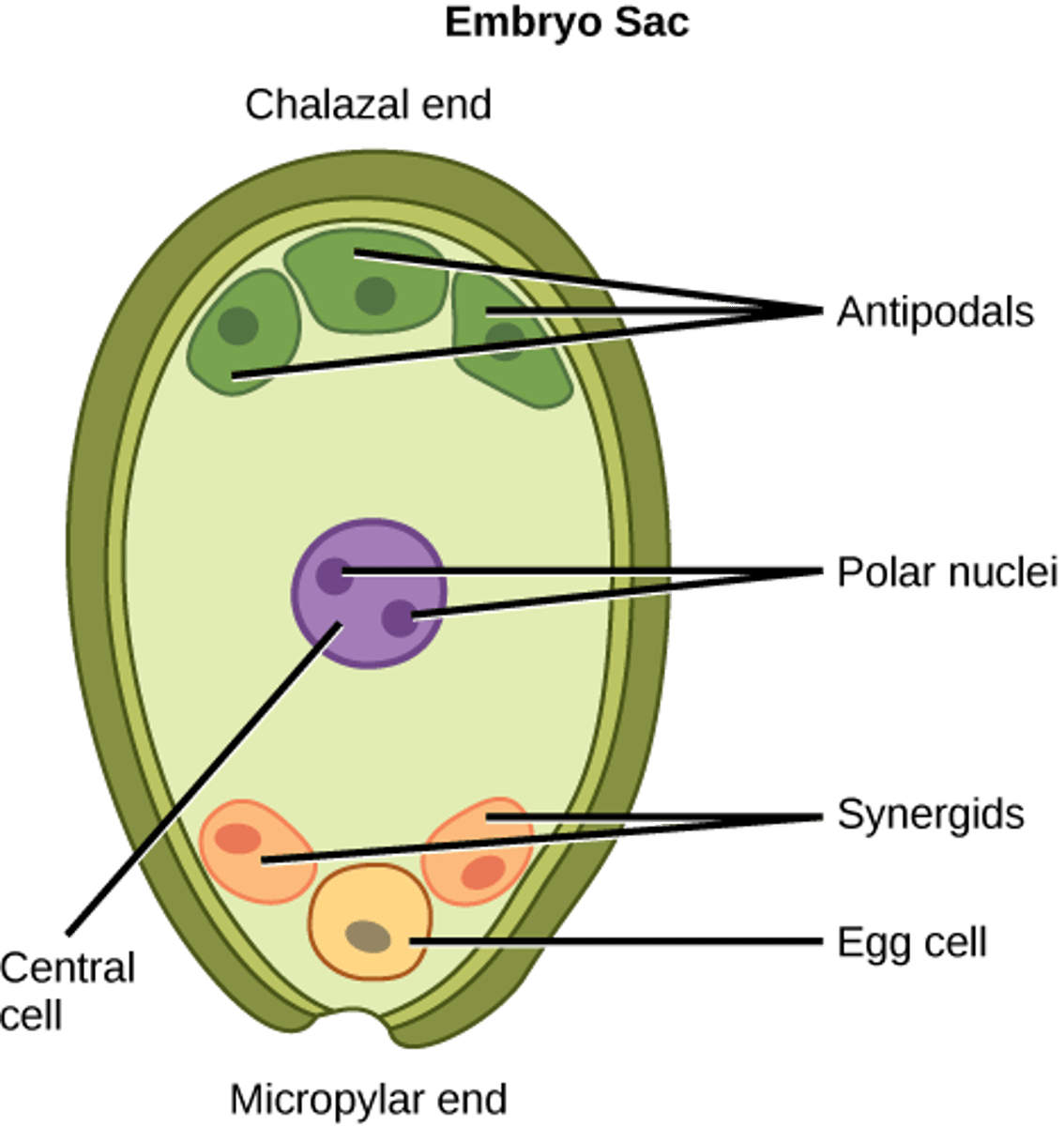
central cell
the cell in the center of the archegonium whose division produces the egg and usually also the ventral canal cell (as in cycads)
synergids
one of two small cells that lie inside the embryo sac of a flowering plant and nourish the ovum
embryo
the rudimentary plant usually contained in the seed; the zygote will begin to divide by mitosis to produce a multicellular organism
embryo sac
the megaspore of a seed-bearing plant, situated within the ovule, giving rise to the endosperm and forming the egg cell or nucleus from which the embryo plant develops after fertilization
ovule
a rudimentary seed;
the plant part that contains the embryo sac and hence the female germ cell, which after fertilization develops into a seed
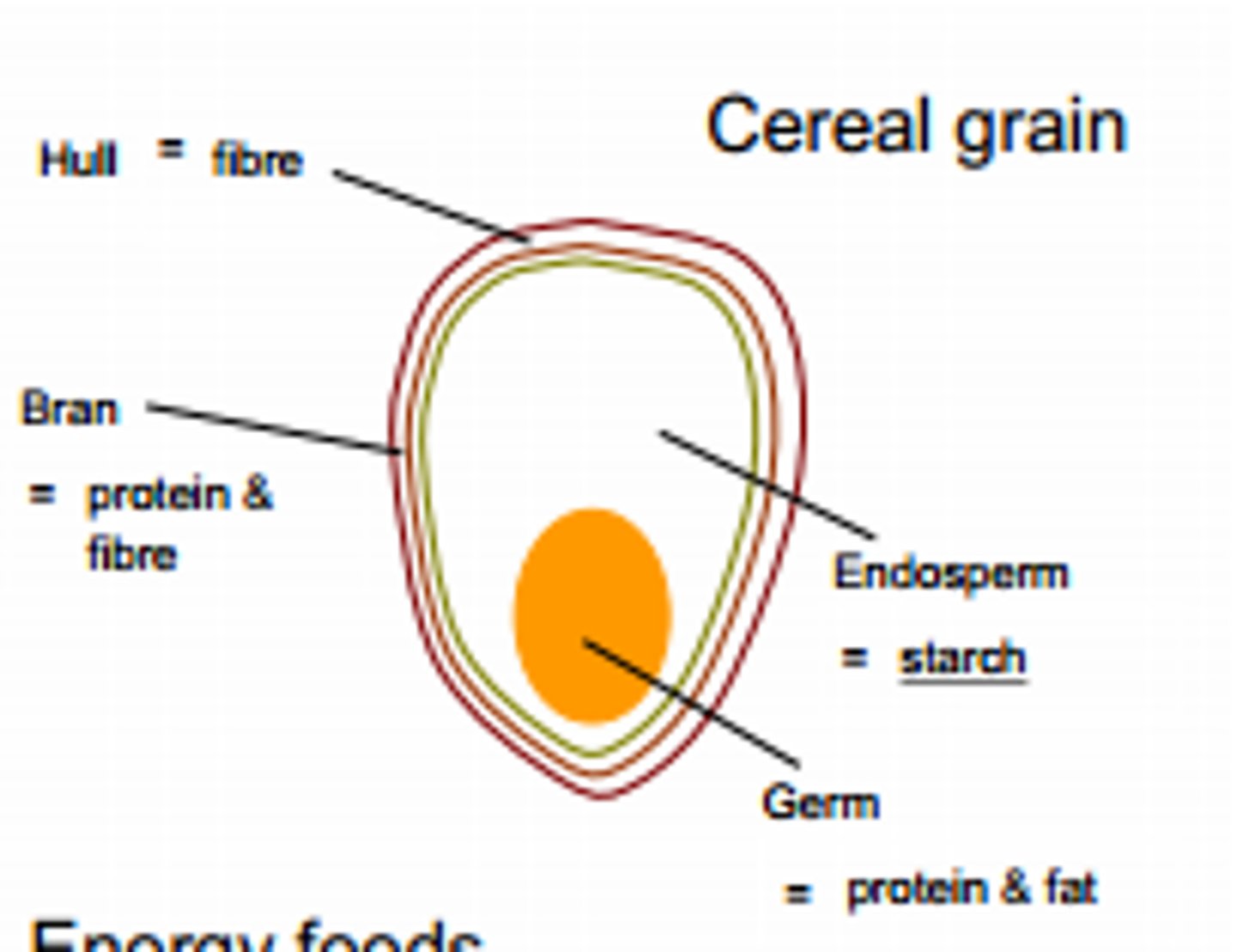
endosperm
the part of a seed that acts as a food storage for the developing plant embryo, usually containing starch with protein and other nutrients
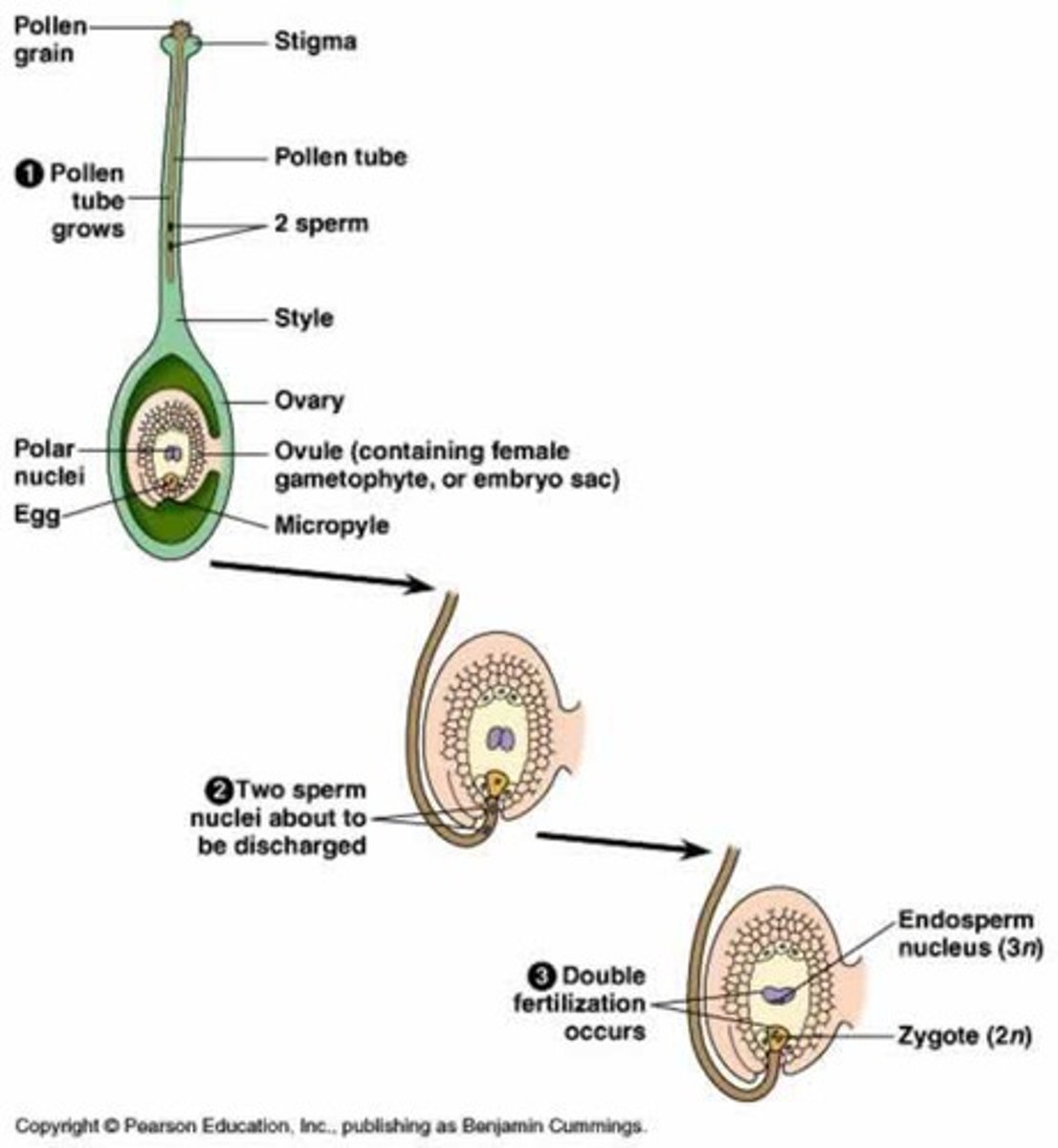
double fertilization
This process involves the joining of a female gametophyte with two male gametes ; the fertilization process characteristic of flowering plants, in which one sperm cell of a pollen grain fertilizes an egg cell while a second fuses with two polar nuclei to produce a triploid body that gives rise to the endosperm
seed
the fertilized, matured ovule of a flowering plant, containing an embryo or rudimentary plant
fruit
the developed ovary of a seed plant
indehiscent
not opening to release seeds; not splitting open to release the seeds when ripe
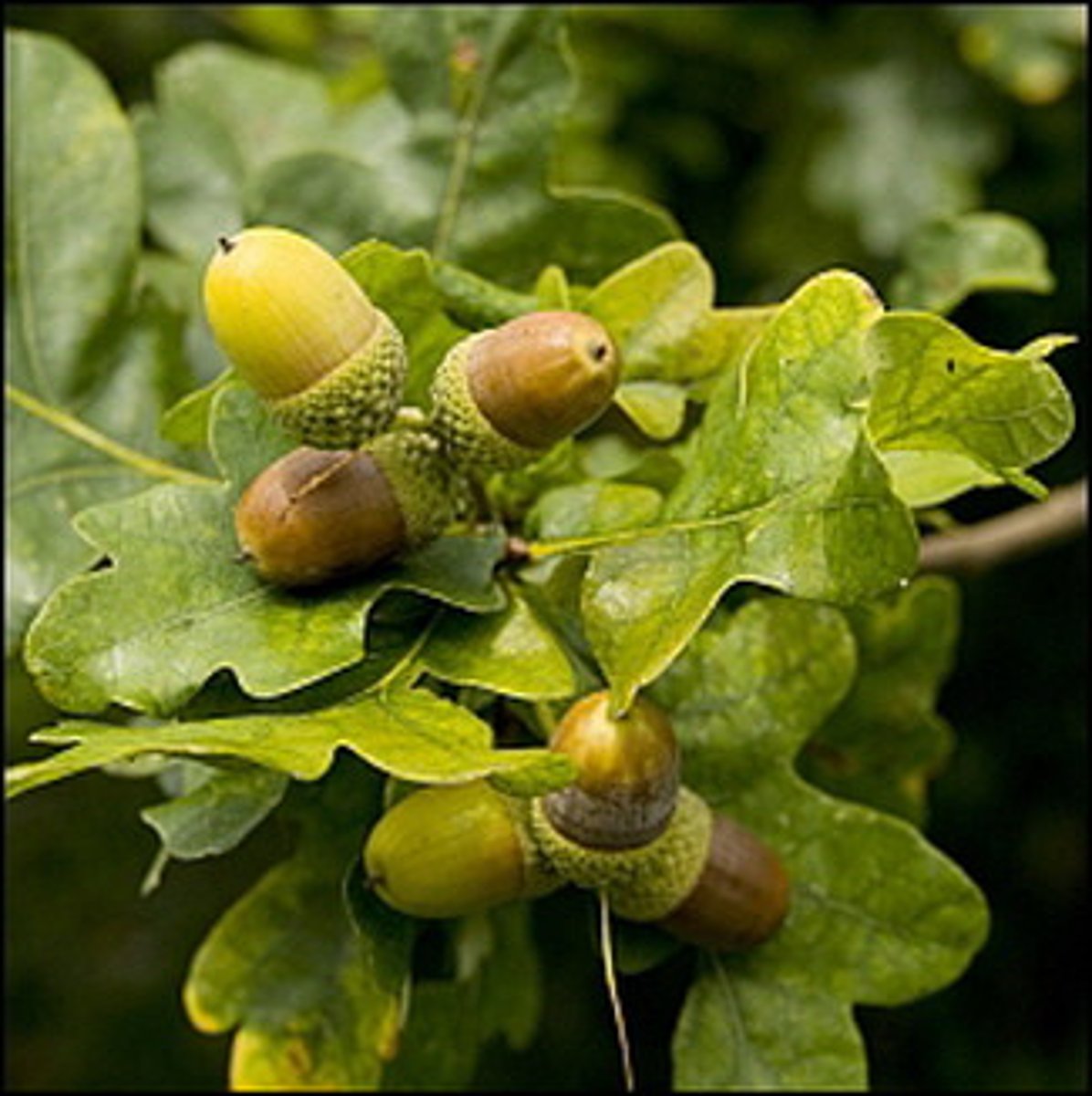

dehiscent
the natural bursting open of capsules, fruits, anthers, etc., for the discharge of their contents
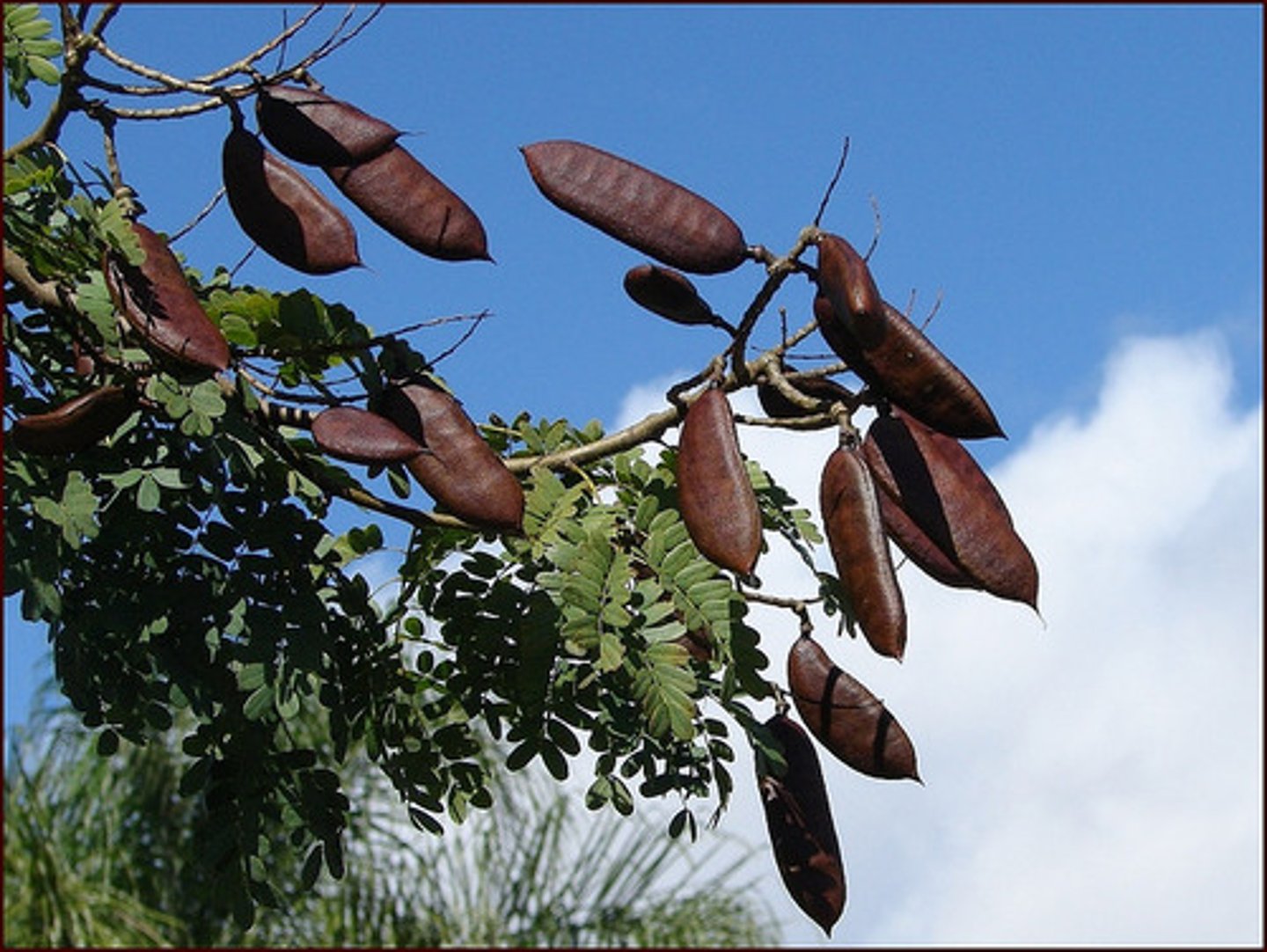

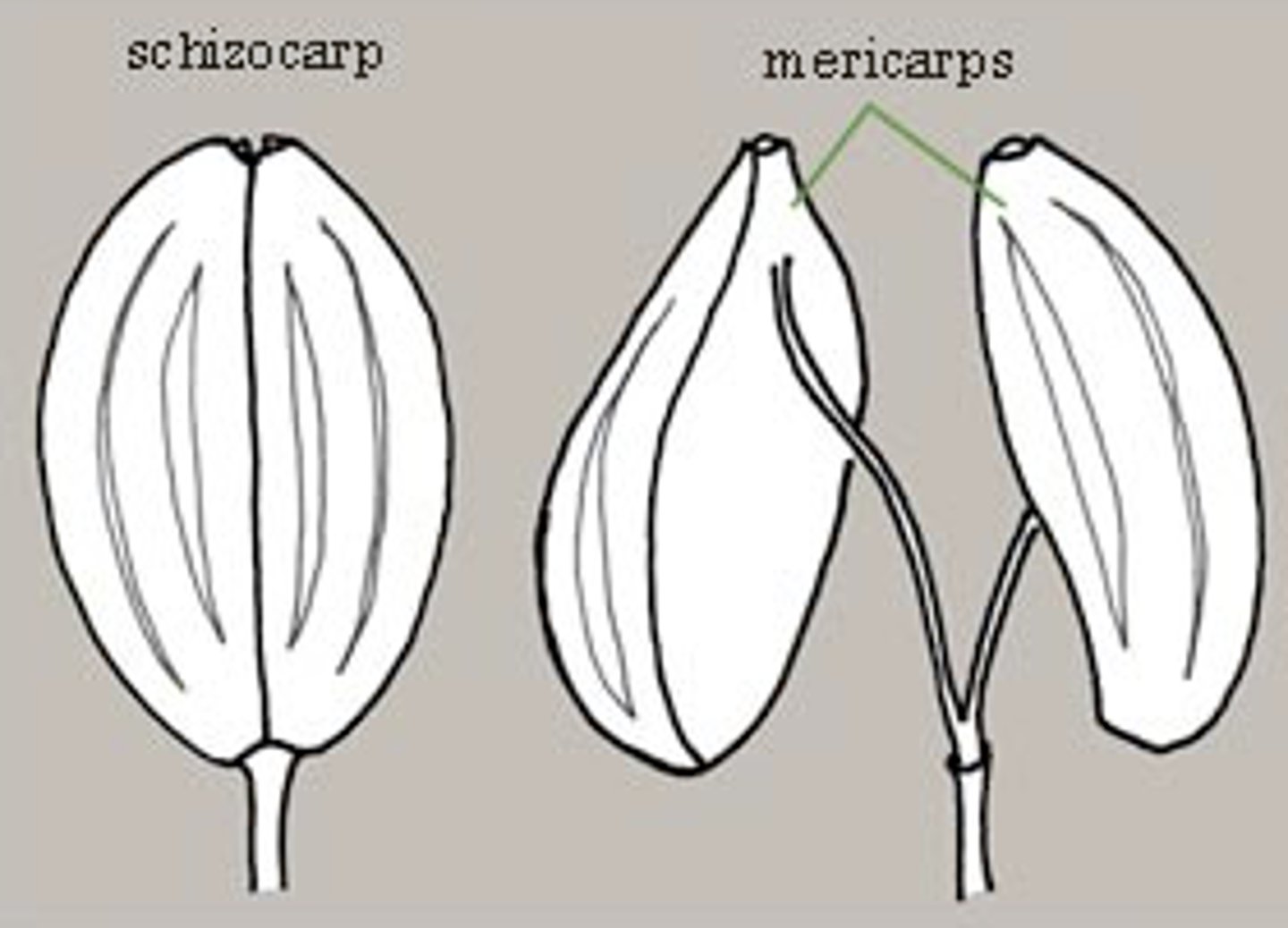
schizocarp
a dry, dehiscent fruit that at maturity splits into two or more one-seeded carpels
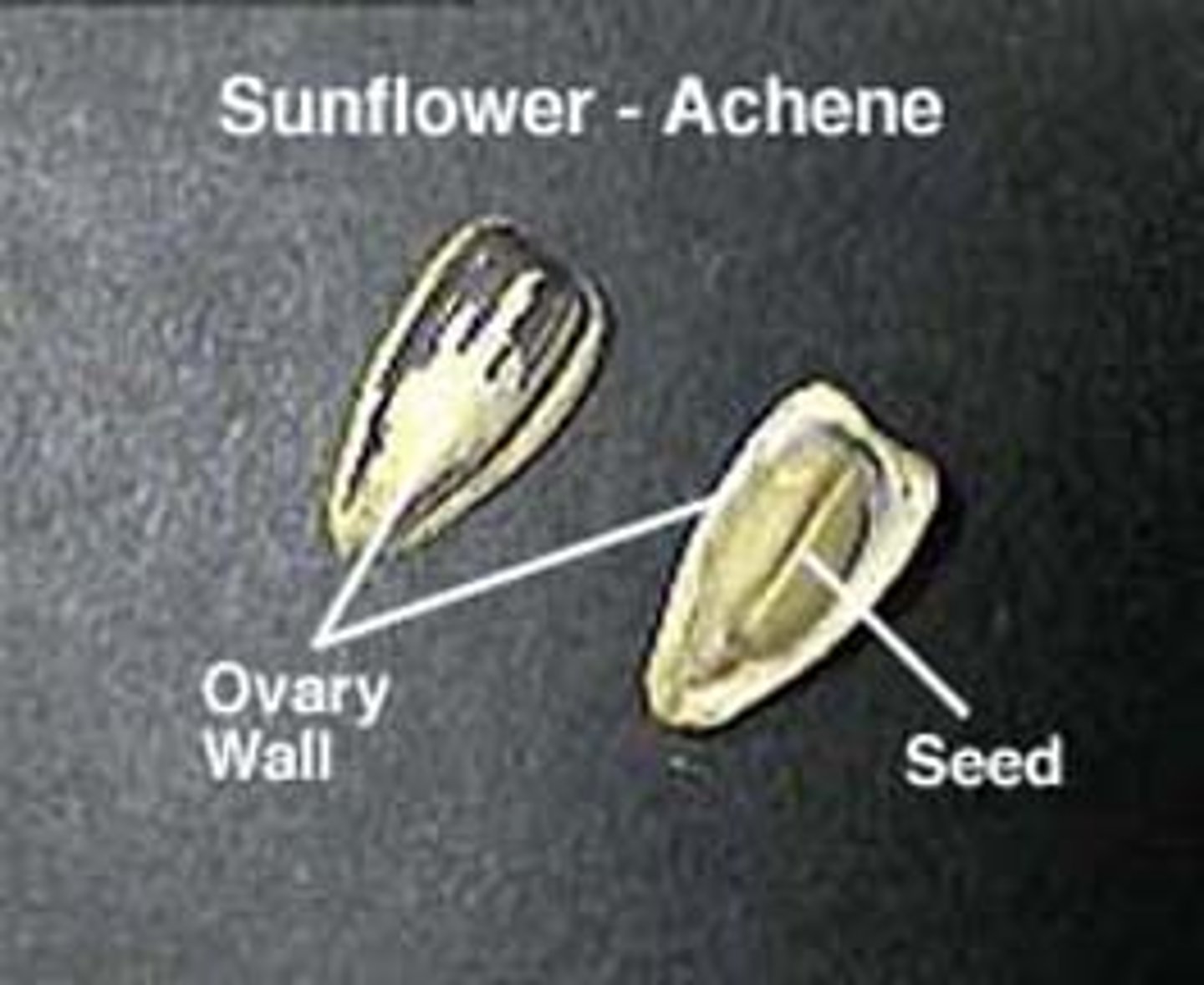
achene
a small, dry, one-seeded fruit that does not open to release the seed
dry fruit
is fruit from which the majority of the original water content has been removed either naturally, through sun drying; Fruits in which the coat becomes dry at maturity
fleshy fruit
a fruit consisting largely of soft succulent tissue; ex: drupe, berry, pome
nut
A dry one-seeded fruit which is indehiscent; a hard-shelled pod that contains both the fruit and seed of the plant
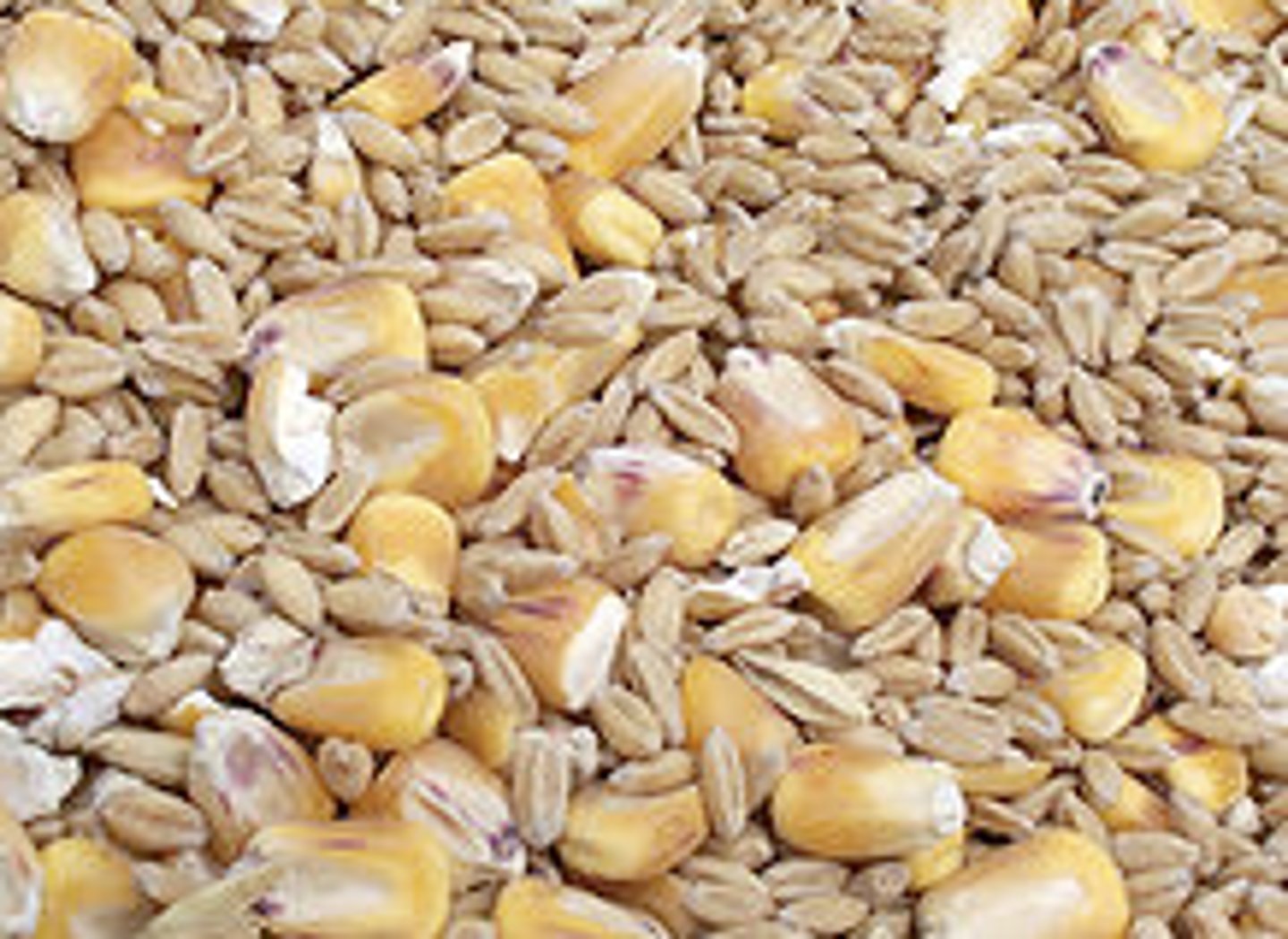
caryopsis
a dry one-seeded fruit in which the ovary wall is united with the seed coat, typical of grasses and cereals

silique
any dry fruit that separates at maturity into two or four segments called valves, leaving a persistent partition that bears the seeds
legume
a dry dehiscent one-celled fruit developed from a simple superior ovary and usually dehiscing into two valves with the seeds attached to the ventral suture; ex: pod; Peas, beans, and peanuts
capsule
a structure composed of two or more carpels; dry fruit that opens when ripe
fascial
a bundle of leaves or flowers growing crowded together; vascular tissues that supply organs with nutrients
berry
is a fleshy or pulpy indehiscent fruit developing form a single carpel withe several seeds
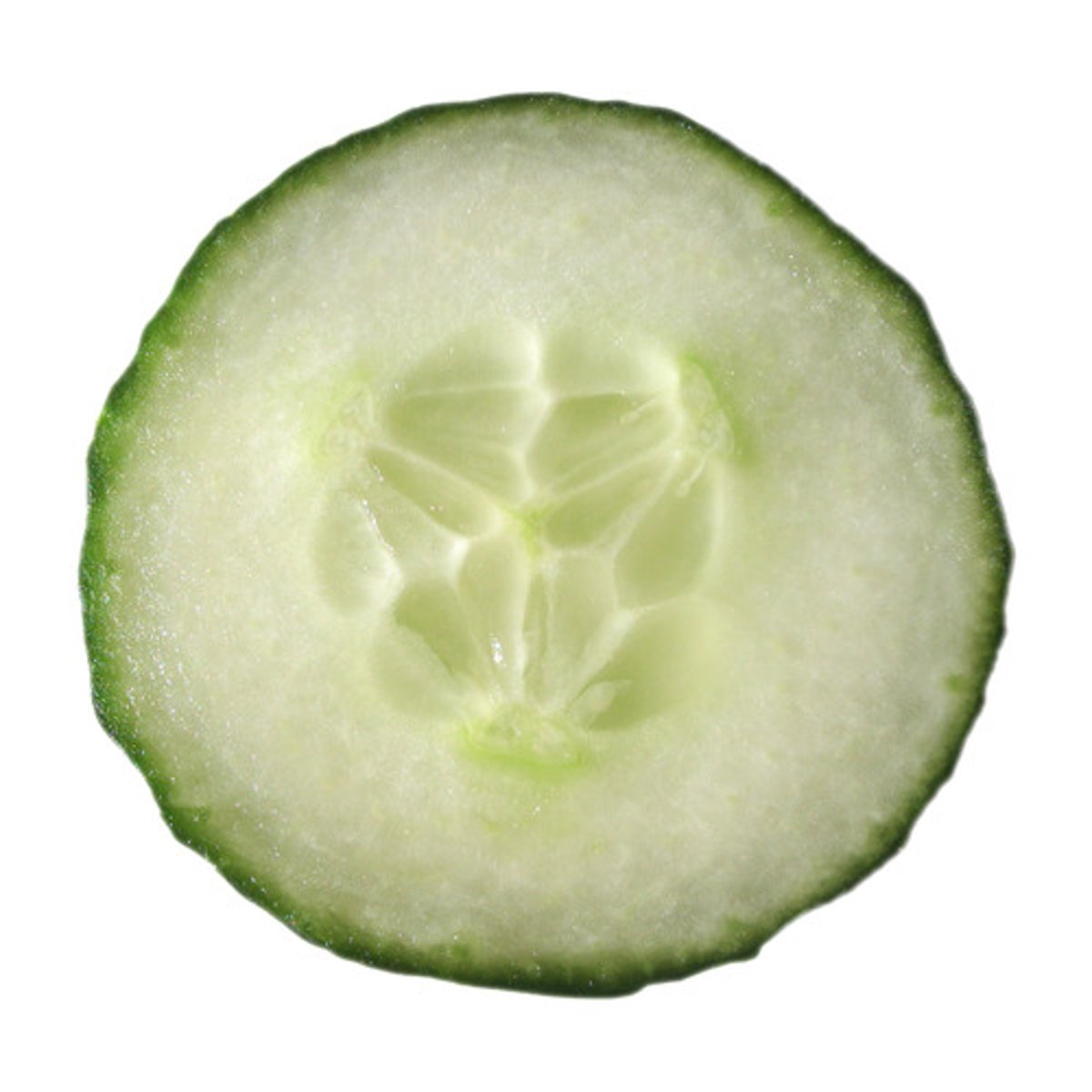
pepo
Any fleshy watery fruit of the melon or cucumber type, with numerous seeds and a firm rind

drupe
an indehiscent fruit in which an outer fleshy part (exocarp, or skin; and mesocarp, or flesh) surrounds a single shell (the pit, stone, or pyrene) of hardened endocarp with a seed (kernel) inside
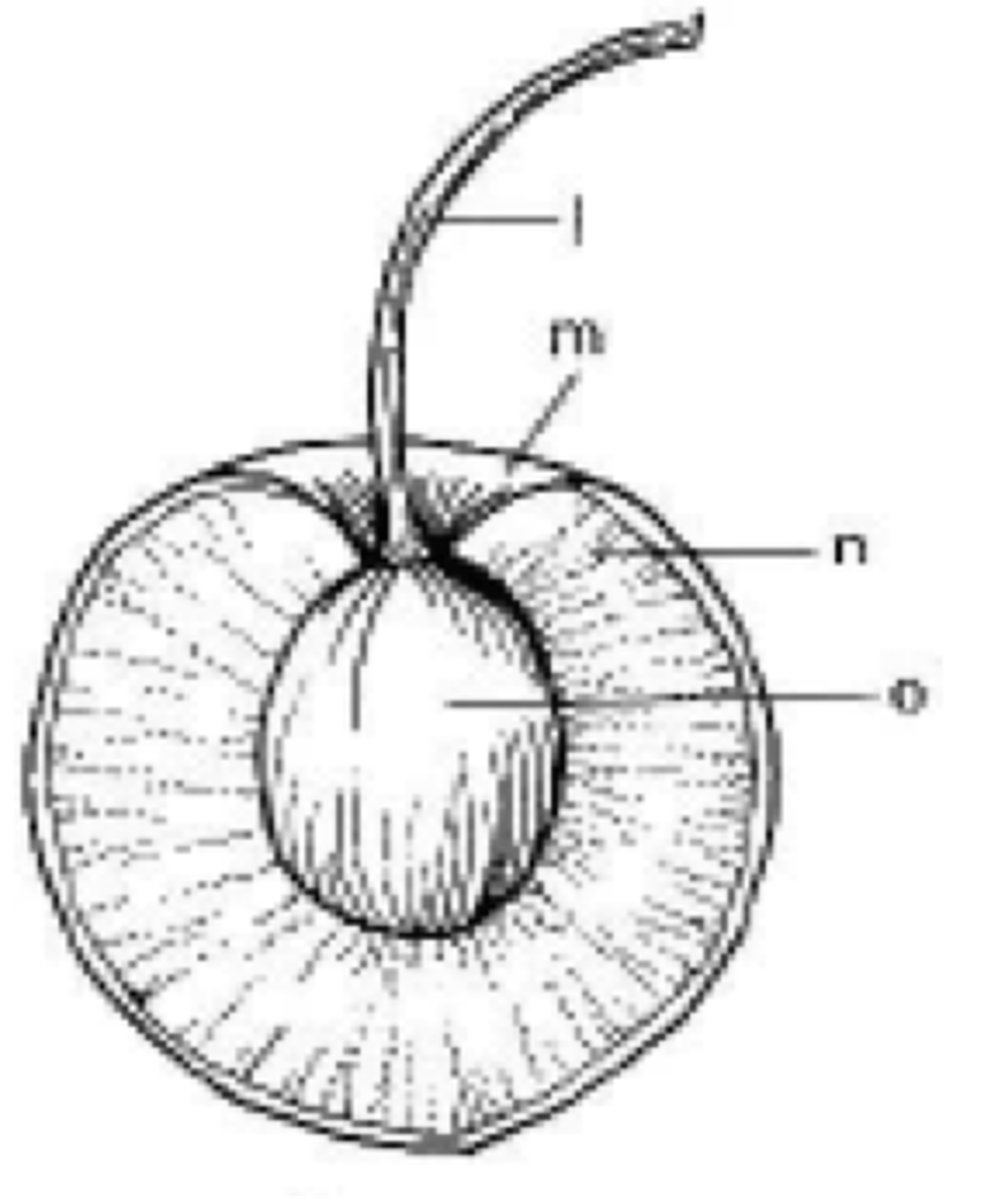
hybridization
the process of crossing two genetically different individuals to result in a third individual with a different, often preferred, set of traits
hybrid sterility
The inability of a hybrid to produce viable offspring; refers to the offspring of a successful primary cross, however the secondary cross would fail
interspecific hybridization
Hybrids between different species within the same genus
polyploidization
a doubling of the complete chromosome set
tetraploid
four times the regular number of chromosomes
hexaploid
having a chromosome number that is six times the haploid number
apomixis
any of several types of asexual reproduction
binomial
two parts; the genus name and the specific epithet. For example, Escherichia coli; a taxonomic name consisting of a generic and a specific term, used to designate species
class
a taxonomic group containing one or more closely related orders
order
taxonomic group containing one or more closely related families
family
a taxonomic group containing one or more genera
genus
species name is the basic unit of classification; The first word in the two-part naming system. It is always capitalized.
group of similar species that have similar features and are closely related
phylum
taxonomic group containing one or more closely related classes
gymnosperm
a plant that has seeds unprotected by an ovary or fruit; includes conifers, cycads, and ginkgo
cycads
a palmlike plant of tropical and subtropical regions, bearing large male or female cones; columnar trunk bearing a crown of large, leathery, pinnate leaves
Ginkgo biloba
one of the oldest trees on Earth, once part of the flora of the Mesozoic period; the only surviving species of its family
gnetophytes
any gymnosperm plant of the phylum Genetophyta, which includes three genera: Gnetum, consisting of small tropical trees and vines, Ephedra (see ephedra), and Welwitschia (see welwitschia); gymnospermous flowering plants; supposed link between conifers and angiosperms
conifer
a tree that bears cones and evergreen needlelike or scalelike leaves; a plant producing naked seeds in cones
cone
the dry fruit of a conifer, typically tapering to a rounded end and formed of a tight array of overlapping scales on a central axis that separate to release the seeds
dioecious
having the male and female reproductive organs in separate individuals
seed cone
megaosporangiate cones; remain on or beneath the tree for a longer period of time
pollen cone
microsporangiate cones; male cones that produce the pollen that is released to fertilize seed cones
cone scale
individual plates of a cone; each carry two ovules that eventually develop into seeds
pollination drop
A drop of sugary fluid that is secreted into the micropyle at the time of pollination in many gymnosperms, and which traps pollen grains that may then float up to the nucellus or be drawn there by the reabsorption of the drop