ch 6: serotonin
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
draw the serotonin synthesis pathway
tryptophan → 5-HTP (rate-limiting step) → 5-HT
synthesis can be triggered by tryptophan or 5-HT
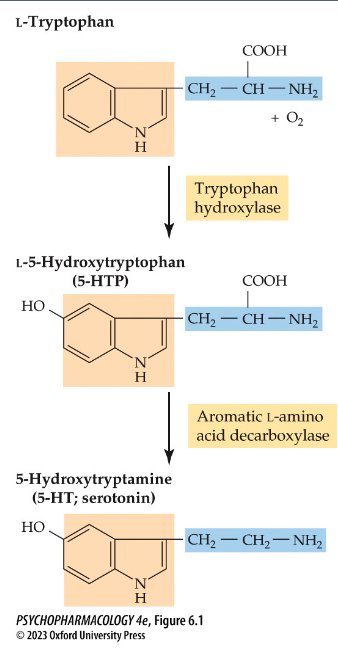
two forms of tryptophan hydroxylase (TPH)
TPH2: only in serotonergic neurons
TPH1: in non-neuronal cells in the gut + pineal gland
neuroendocrine tumors in the gut secrete ____ → elevated blood lvls cause _____ which can be treated w telotristat → a ______
5-HT
carcinoid syndrome
nonselective TPH inhibitor → does not cross the BBB → only blocks peripherally expressed TPH1
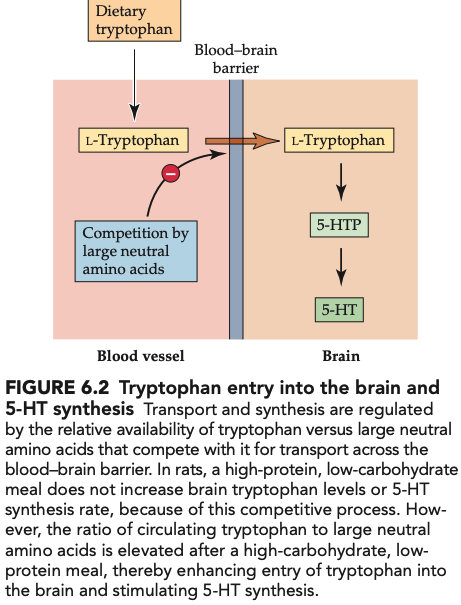
what effect does a high-protein meal vs low-protein meal have on tryptophan lvls in the blood vs brain (3)
a high-protein meal will not cause increase in tryptophan or 5-HT in the brain but lvls in blood do increase
A low-protein, high-carbohydrate meal will increase ratio of tryptophan to competing large neutral amino acids (LNAA) since insulin stimulates uptake of AAs except tryptophan
therefore: ratio of tryptophan to other AA competitors for transport across the BBB determines whether serotonin synthesis is stimulated or not
2 methods of 5-HT depletion to asses its role in bhvr:
para-chlorophenylalanine (PCPA): selectively blocks 5-HT synthesis by irreversibly inhibiting TPH
acute tryptophan depletion (ATD): large doses of amino acids minus tryptophan
impair memory consolidation of verbal info → little-no influence on WM or attention
reduced sleep duration + quality
what are methods of increasing tryptophan and why might this be important? (3)
tryptophan loading: administration of pure tryptophan
supplemented w alpha-lactalbumin or other high-tryptophan proteins
elevating tryptophan availability has been shown to enhance cognitive functions ie. memory, attention, elevate mood, improve sleep
___% of ingested tryptophan is metabolized to _____ rather than 5-HT which is then further metabolized to the kynirenine pathway → _____ and inflammation can _____. kyurenine metabolites have been implicated in several ___ and ____
95%
kynurenine
stress
stimulate enzymes involved
psychiatric disorders
neurodegenerative diseases
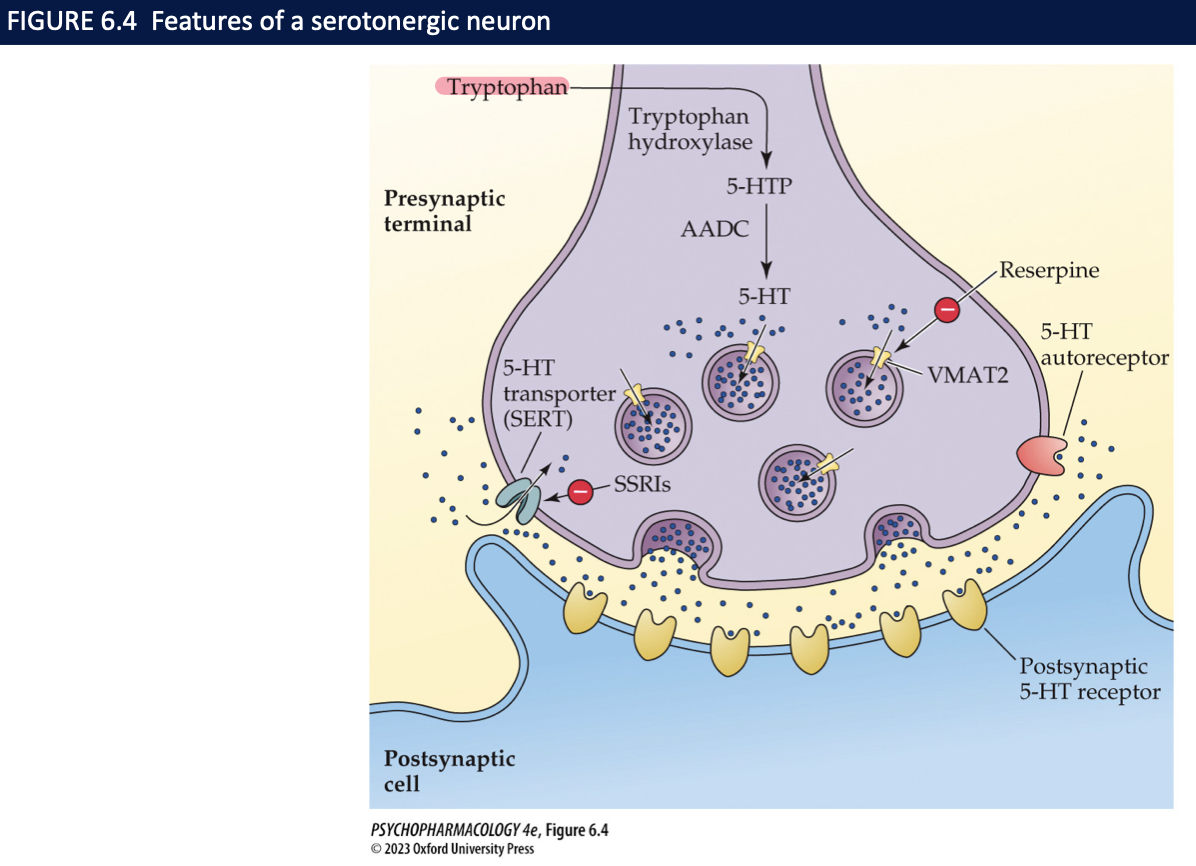
5-HT is transported into synaptic vesicles by ______ → ______ (a VMAT blocker) depletes 5-HT which is broken down when _____. _____ directly inhibit 5-HT release + ____ autoreceptors inhibit release by ____________
vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2)
reserpine
not protected in vesicles
terminal autoreceptors
somato-dendritic
slowing the rate of nerve firing
release of 5-HT can be stimulated by (2)
drugs that are based on the structure of amphetamine
ie. para-chloroamphetamine, fenfluramine, MDMA (ecstasy)
how does MDMA affect behaviour and what are its drawbacks? (4)
heightened arousal, euphoria, enhanced perceptual awareness, prosocial effect (an entactogen)
low + controlled doses: beneficial as an adjunct to psychotherapy in chronic PTSD
potential toxic effects → serotonin syndrome → can lead to death
↑ MDMA = 5-HT depletion in experimental animals + serotonergic deficits
how is serotonergic transmission terminated and how is it mediated? why is this protein important? (3)
transmission terminated by reuptake of 5-HT from the extracellular fluid
process mediated by 5-HT transporter
SERT is an important target for several antidepressant drugs (SSRIs) → ie. Prozac which inhibit 5-HT reuptake
serotonin is eventually broken down by ____ to form ____
MAO-A
5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA)
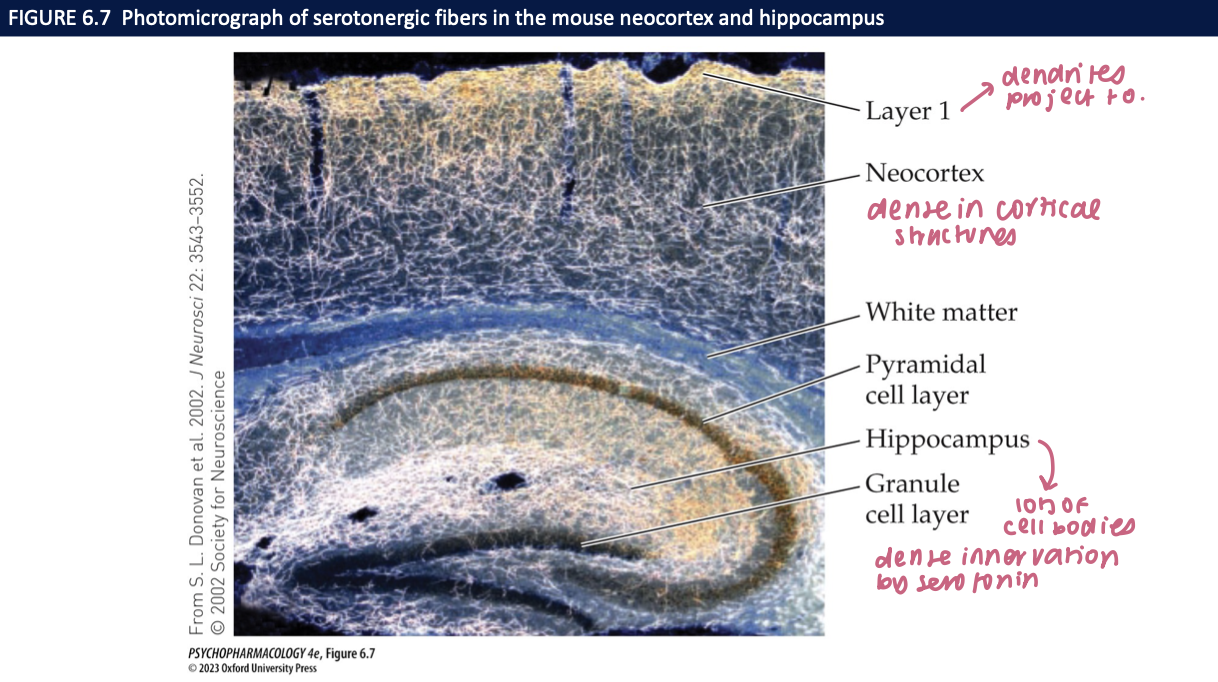
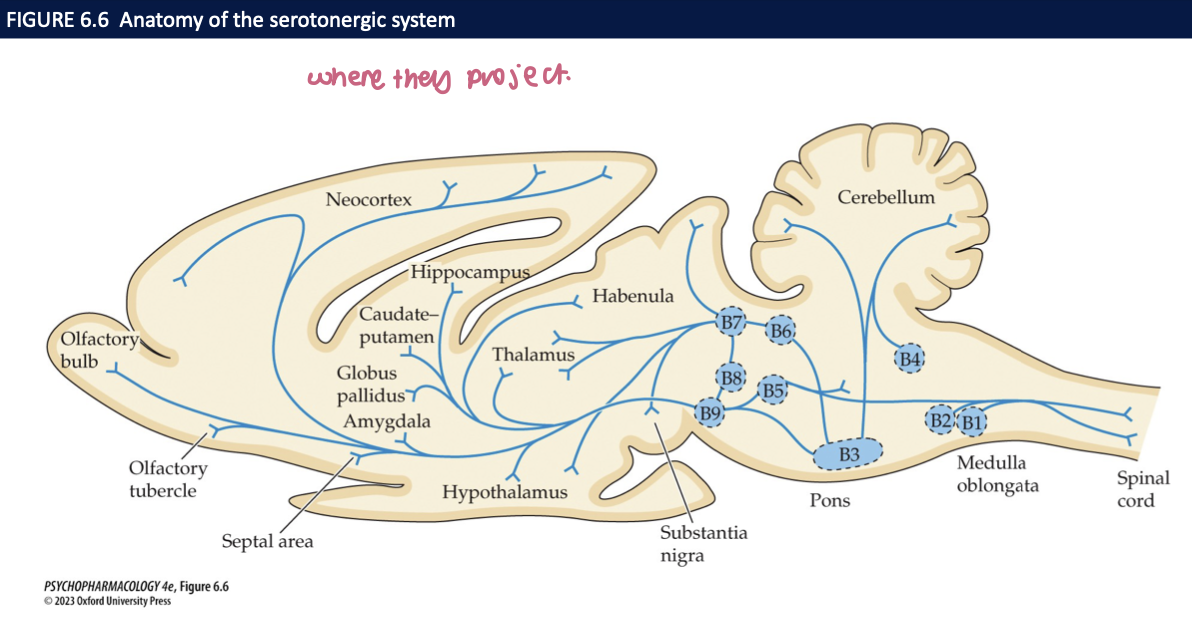
serotonin neurons in CNS are found along __1__ loosely associated with the _2_ → the __3__ raphe nucleus + __4__ raphe nucleus give rise to most of the serotonergic fibres in the__5__ → in the cortex, nerve fibers are _6_ at the surface which has a _7_ density of __8__ + __8__
midline of the brainstem (medulla, pons, midbrain)
raphe nuclei
dorsal raphe nucleus (DRN)
median raphe nucleus (MRN)
forebrain
dense
↑
dendrites + synaptic connections
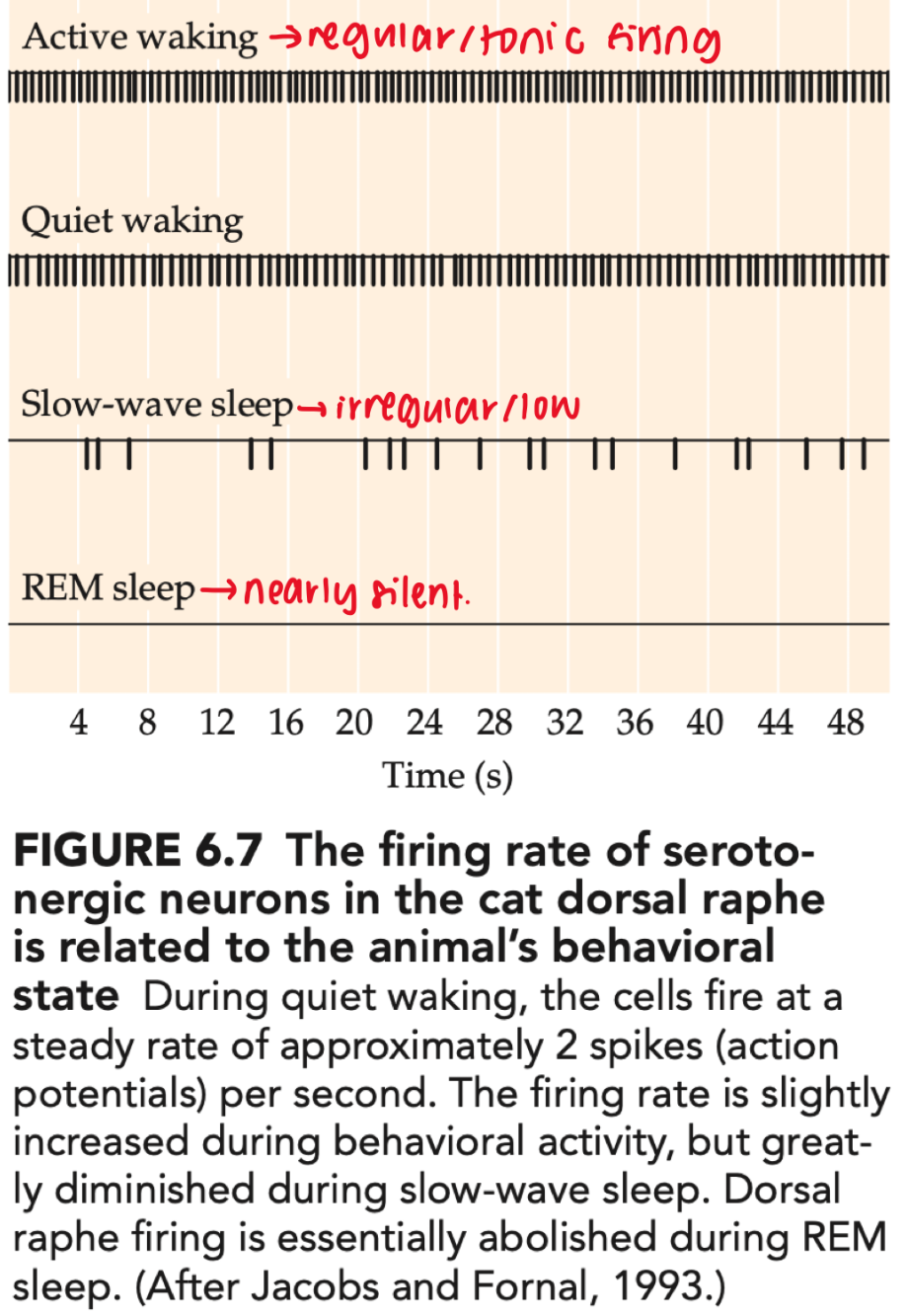
how does DRN serotonin neuron firing relate to sleep–wake state, and what do different patterns do? (3)
Natural states: awake = tonic/regular, SWS = reduced/irregular, REM = near-silent
cats: when awake = tonic firing (regular rate) → irregular w slow-wave sleep → stop firing during REM sleep
DRN/MRN KO mice: slow tonic 5-HT drive → promotes NREM sleep; burst/phasic drive → promotes wakefulness
🧠 Takeaway: DRN 5-HT controls arousal; rate + pattern determine sleep vs wake.
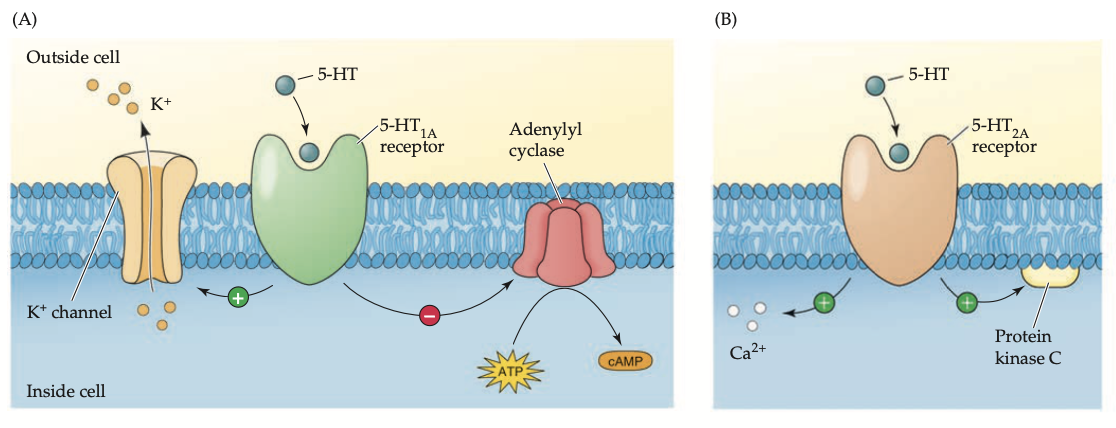
most 5-HT receptors are ___, except ___ which is _____.
metabotropic
5-HT3
excitatory ionotropic receptor
compare 5-HT1A to 5-HT2A receptor subtypes (5)
5-HT1A: in hippocampus, septal area, parts of amygdala, dorsal raphe nucleus
reduce cAMP synthesis by inhibiting adenylyl cyclase
↑sed opening of K+ channels + membrane hyperpolarization = ↓sed firing of either post-synaptic cell or the serotonergic cell itself
5-HT2A: in cerebral cortex: striatum, nucleus accumbens
activate the PIP2 messenger system = ↑sed Ca2+ lvls + activates PKC
what is the hypothesized connection btw serotonin + hallucinogenic drugs? how can this be useful when treating disease like schizophrenia? (3)
DOI: widely used 5-HT2A agonist
effects of LSD believed to stem from its ability to stimulate 5-HT2A receptors
blockade of 5-HT2A receptors + D2 antagonism leads to symptom improvement in patients with schizophrenia while minimizing the side effects associated w previous drugs
what receptor subtype is targeted by triptan drugs + what effect do they have? (2)
5-HT1B/1D: causes constriction of the blood vessels w/in the brain → providing relief from migraine symptoms
+ receptor agonist blocking of pain signals transmitted by the trigeminal nerve
how are 5-HT3 receptors related to chemotherapy-induced nausea + how can vomiting/nausea be counteracted (3)
5-HT3 receptors present on the peripheral terminals of the vagus nerve → induces activation of vomiting centre in the brainstem
5-HT3 antagonists can counteract the nausea/vomiting
ie. ondansetron (Zofran), granisetron (Kytril), palonosetron (Aloxi)
methodological approaches in human clinical research to assess serotonergic function (3)
comparing lvls of 5-HIAA in CSF or 5-HT + 5-HIAA in postmortem brain regions w bhvrl traits or neuropsychiatric disorders
assess responses to SSRIs or receptor agonists + antagonists
identify associations btw psychiatric disorders + polymorphisms in the genes for SERT or serotonergic receptors
pharmacological tools for probing the the serotonergic system specifically 5,7-DHT (5)
serotonergic neurotoxins → para-choloamphetamine, MDMA, 5,7-dihydroxytryptamine (5,7-DHT) → doesn’t readily cross BBB so has to be given directly into the brain
lesioning results in ∆s in hunger/eating bhvr, anxiety, pain sensitivity, learning/memory
causes massive damage to serotonergic axons + nerve terminals in the forebrain but in the raphe nuclei are usually spared
drug challenges w selective receptors agonists + antagonists
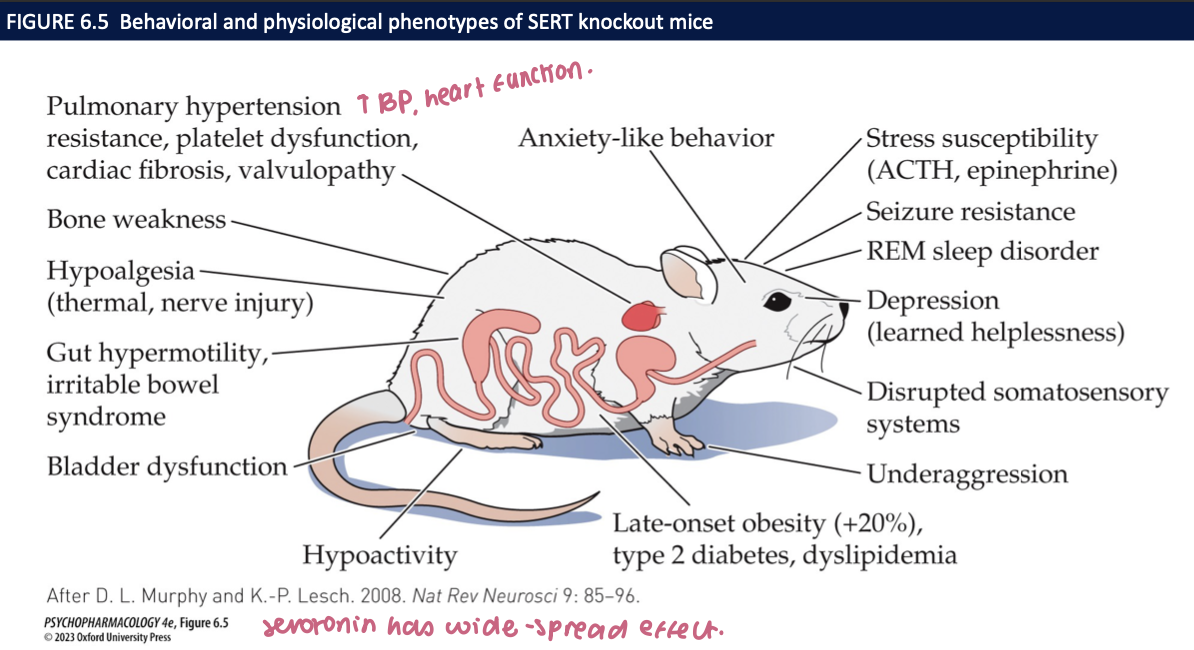
what do TPH2 knockout mice reveal about serotonin function (3)
TPH-2 KO mice have complete loss of 5-HT in the brain → preservation of lvls in bloodstream
helps regulate the development of its own fibre system
↓ 5-HT = large ↑ in aggressive bhvr
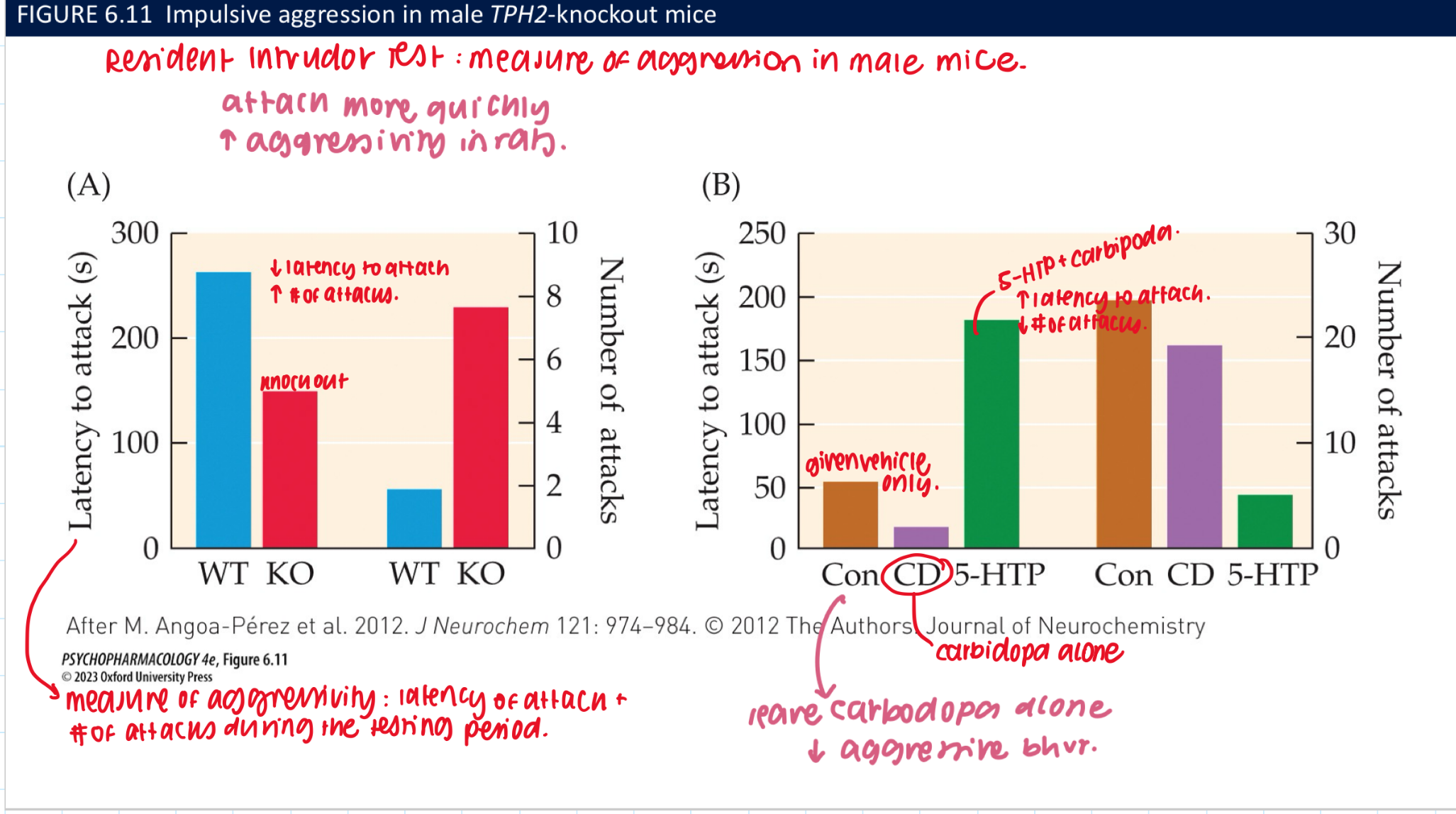
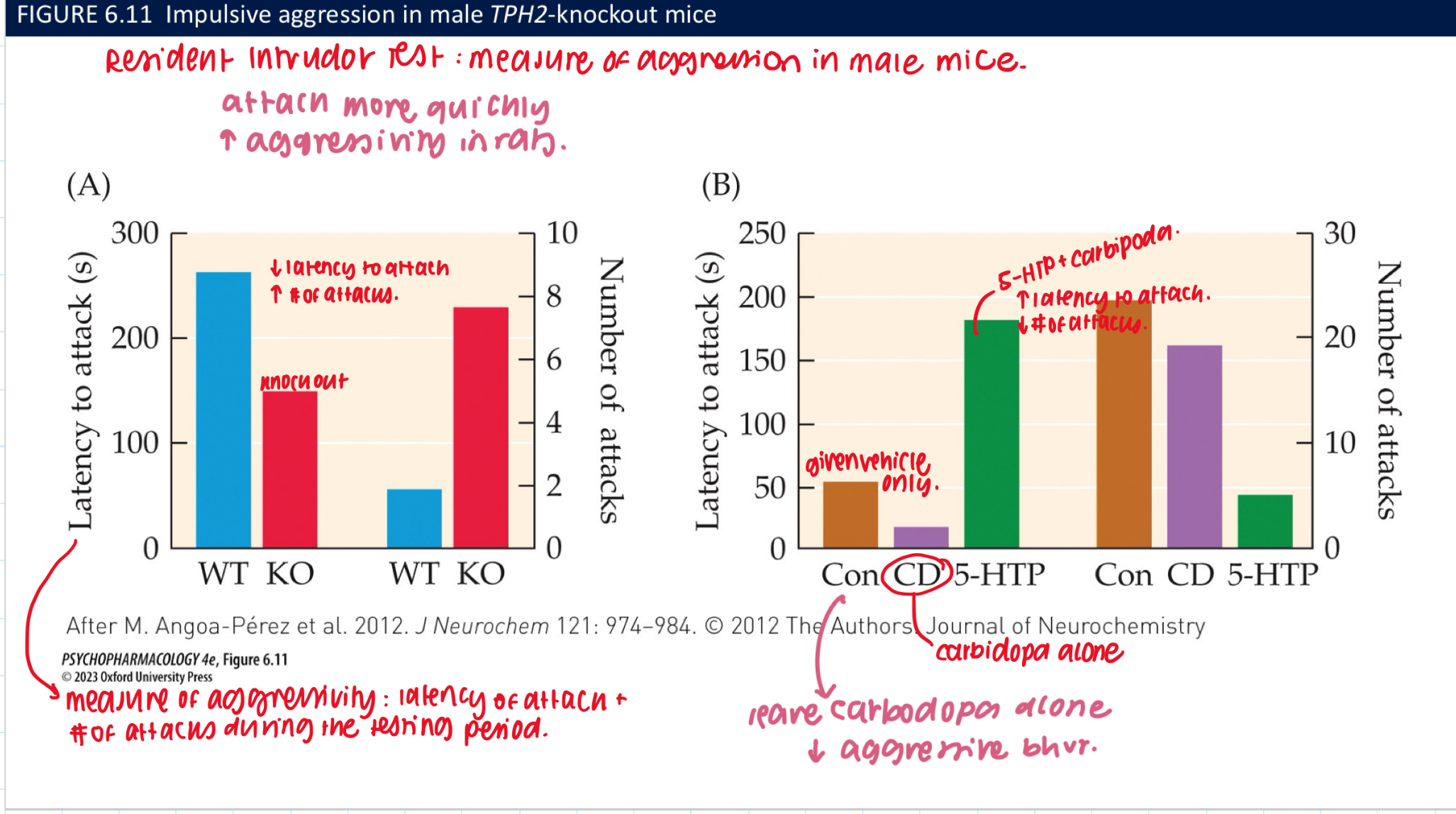
how can loss of 5-HT in the brain be restored? temporarily (3) vs fully rerstored (3)
temporarily restored w 5-HTP → bc newly synthesized NT is gradually metabolized by MAO-A + cannot be replenished in mutant mice
HT gets produced where its not supposed to
works bc 5-HTP is the product of the rxn catalyzed by TPH → bypasses the missing step in the biosynthetic pathway
fully restored by 5-HTP plus carbidopa → an AADC inhiitor that doesn’t cross the BBB
reverses ↑ lvls of aggressive bhvr in TPH2 KO males
blocks conversion of 5-HTP → 5-HT in peripheral + allows for ↑ 5-HTP availability to the brain + prevents adverse consequences of elevated peripheral 5-HT lvls
bhvrs of TPH2-KO mice + physiological deficits (4)
more impulsive + compulsive
less anxious → have poor social communication + social bhvrs including maternal deficit
poor thermoregulation
abnormal respiration including apnea
5-HT role in regulation of anxiety
SSRIs are used to treat anxiety disorders → target 5-HT1A receptors
Where are 5-HT₁A receptors and how do they affect anxiety? (3)
Autoreceptors (raphe soma/dendrites): ↓ firing → ↓ global 5-HT
Postsynaptic (hippocampus/mPFC/amygdala): activation reduces anxiety
🧠 Takeaway: Autoreceptor = brake; postsynaptic = anxiolysis.
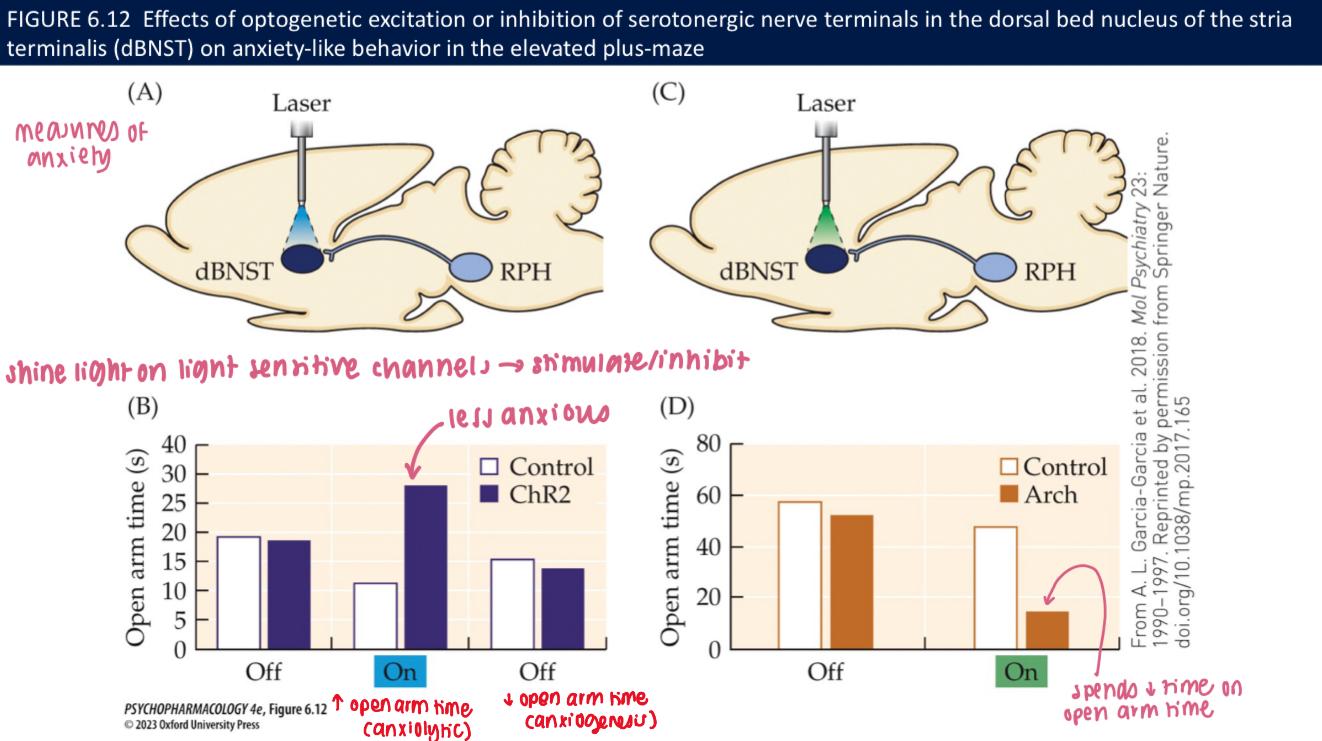
What do optogenetic studies show about 5-HT terminals in anxiety tests (EPM)? (3)
Excite 5-HT terminals → ↑ open-arm time (anxiolytic)
Inhibit terminals → ↓ open-arm time (anxiogenic)
🧠 Takeaway: Local 5-HT release in limbic targets calms anxiety circuits
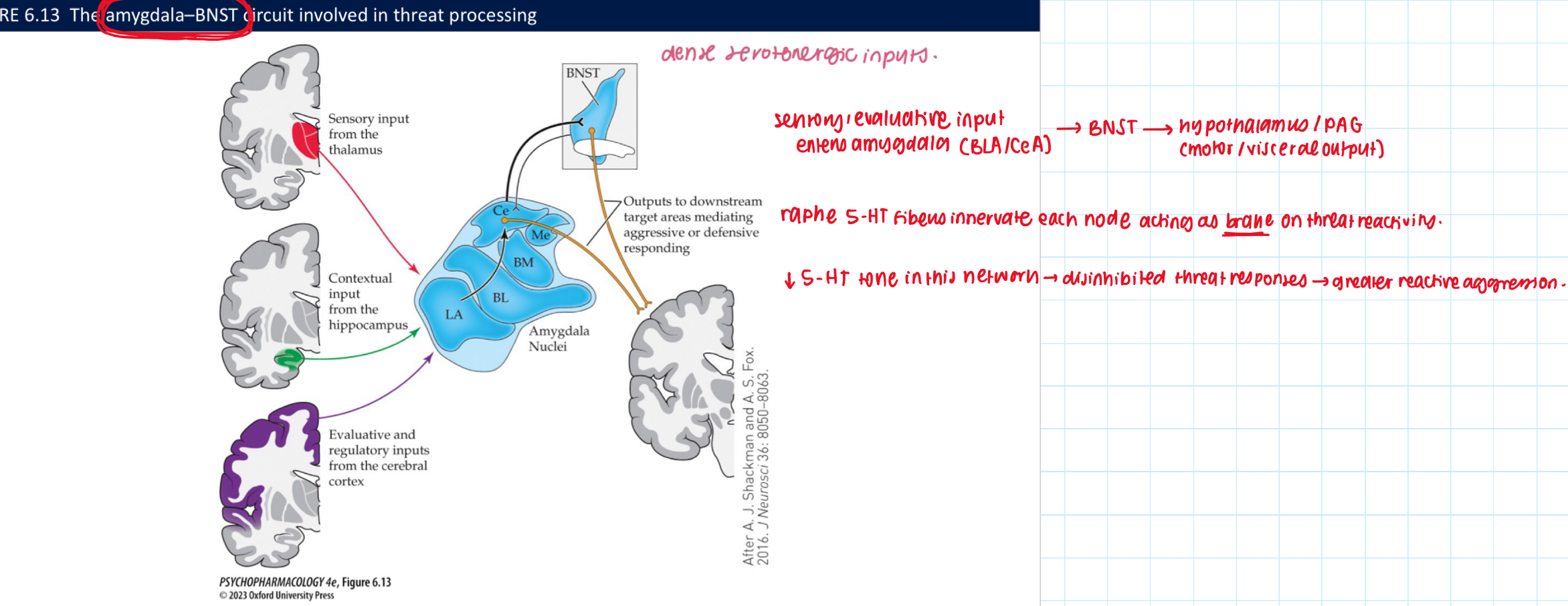
How does serotonin relate to aggression, and what circuit is involved? (3)
Low central 5-HT → ↑ reactive/impulsive aggression
Circuit: amygdala → BNST → hypothalamus → PAG (+ cortex/hipp/striatum) with raphe 5-HT inputs
🧠 Takeaway: 5-HT acts as a brake on the threat/reactivity network.
What’s the “5-HT deficiency” idea and clinical link? (3)
Many studies: low 5-HT/5-HIAA ↔ hyperaggressiveness/irritability
SSRIs (e.g., sertraline) can reduce anger/irritability in several disorders
🧠 Takeaway: Trend holds, but context/receptor subtype matters.
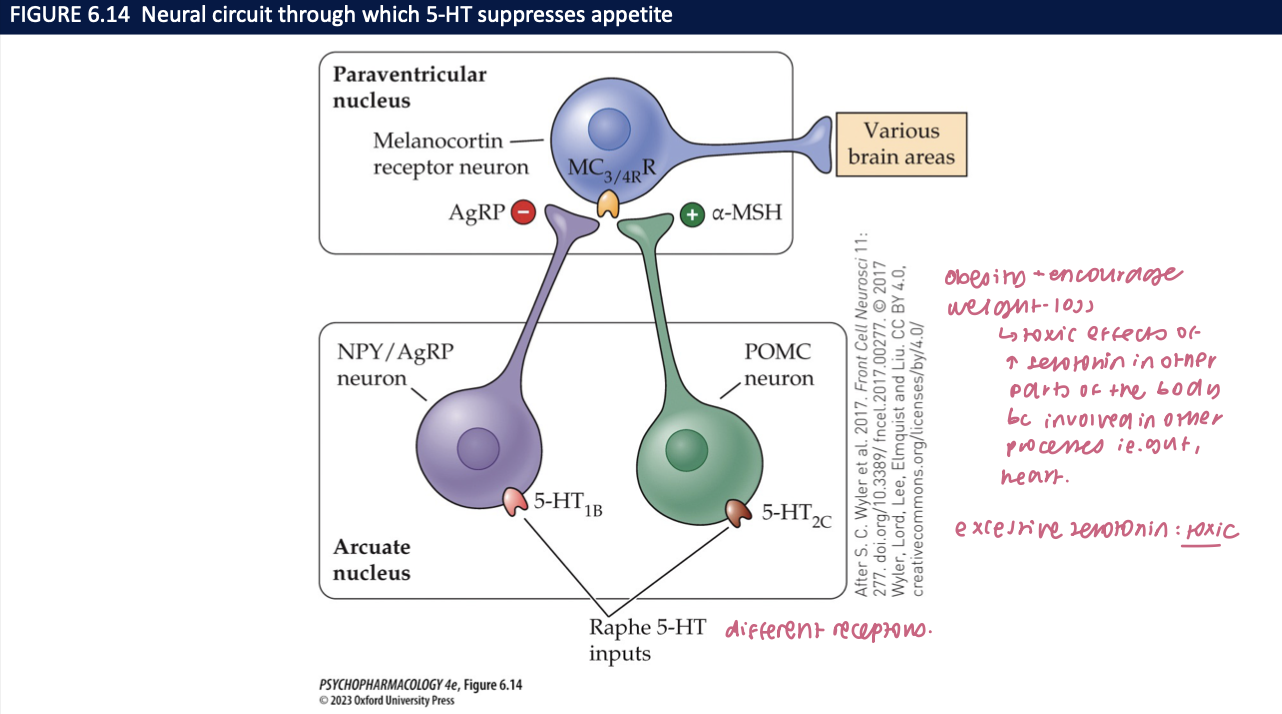
How does 5-HT suppress appetite via the arcuate nucleus (ARC)? (3)
5-HT₂C on POMC → ↑ α-MSH → MC4R (PVN) → ↓ feeding
5-HT₁B on NPY/AgRP → inhibits orexigenic neurons → ↓ feeding
🧠 Takeaway: 5-HT boosts POMC and brakes NPY/AgRP → MC4R-mediated satiety.
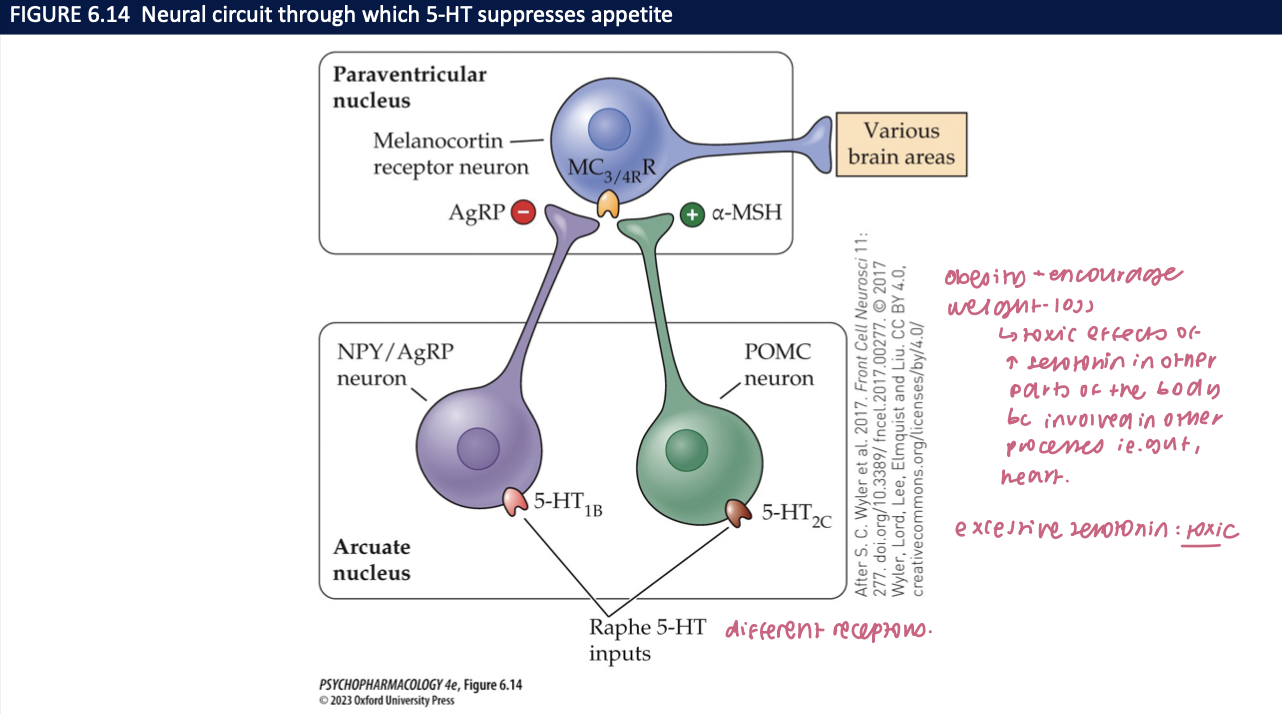
Put the appetite circuit together (flow) (3)
Raphe 5-HT → ARC (POMC ↑ via 5-HT₂C, NPY/AgRP ↓ via 5-HT₁B) → PVN MC4R → autonomic/endocrine outputs → reduced intake
Drug note: Lorcaserin = 5-HT₂C agonist (mechanistic example)
🧠 Takeaway: Raphe → ARC → PVN (MC4R) is the serotonergic satiety axis.
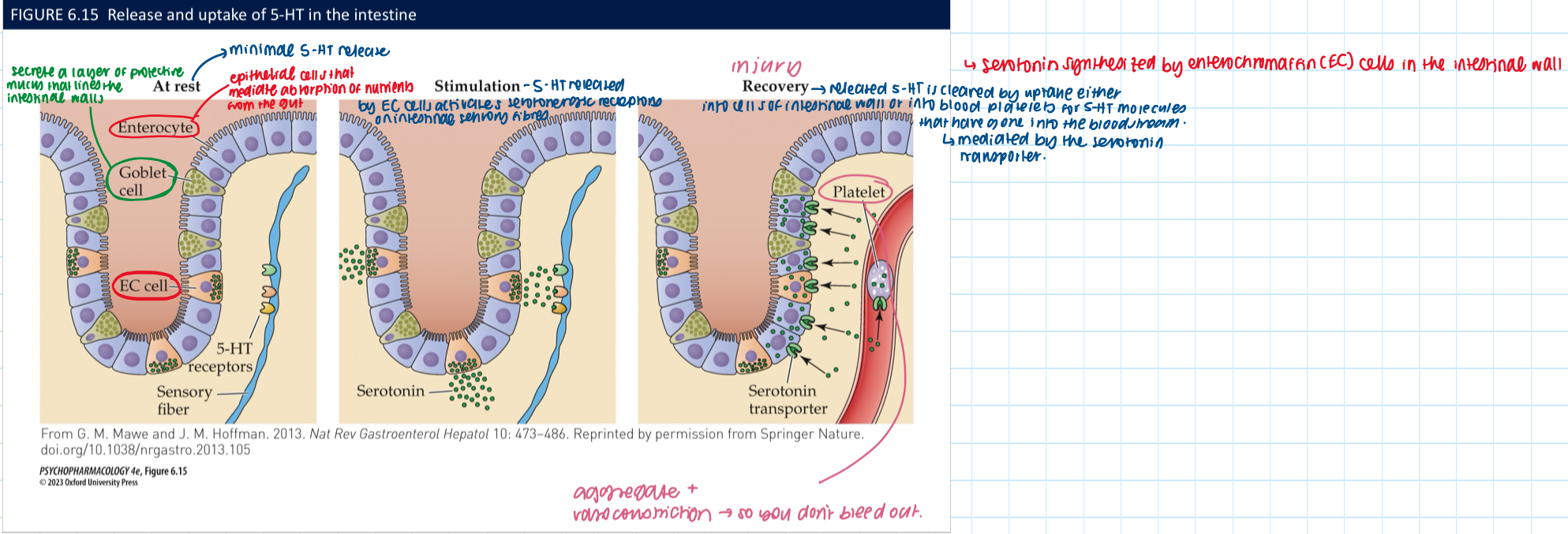
most of the body’s 5-HT is located in the _1_→ the _2_ NS + synthesized by _3_ cells using TPH1. 5-HT release is stimulated by __4__ which promotes secretion of _5_ + ↑ __6__
gut
enteric
enterochromaffin
food in the gut
metabolic hormones
peristaltic activity
5-HT and IBS + potential treatment (3)
↑ 5-HT = enhanced gut motility → IBS diarrhea
↓ 5-HT = constipation IBS
5-HT3 antagonist alosetron treating IBS but has potentially dangerous side effects