The Ankle and Foot Complex
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
How many bones are in the ankle and foot
28
How many joints are in the ankle and foot
33
How Many ligaments are in the ankle and foot
112
What are the joints of the ankle
Proximal and distal tibiofibular joints
Talocrural joint (the ankle joint)
Subtalar joint
Talocalcaneonavicular joint
Transverse tarsal joint
Tarsometatarsal joints
Metatarsophalangeal joints
Interphalangeal joint
Why does the ankle-foot complex have so many issues
Complex structure
Sustain large weight bearing stresses
Multiple and somewhat conflicting functions in stability and mobility
Stability demands of the ankle-foot
Stable base of support without unnecessary muscle activity
Rigid lever for propulsion during gait and balance control
What are the mobility demands of the ankle-foot complex
Conform to complex terrain
Absorb shock from weight bearing stresses
Accommodate rotation of the more proximal lower body joints
Explain the movements of the Distal Tibiofibular Joint
Allows for small amount of spread or accommodation at the talocrural joint.
The Distal Tibiofibular joint is supported by
Anterior tibiofibular ligament
Posterior tibiofibular ligament
Inferior transverse ligament
interosseous ligament
What kind of joint is the Talocrural joint?
How many DOF’s does it have?
Modified Hinge joint
1 primary DOF: Plantarflexion/ Dorsiflexion
20 degrees of dorsiflexion is checked mainly by what muscle
Triceps surae
30-50 degrees of plantarflexion is checked by which muscles
Tibialis anterior, extensor hallucis longus and extensor digitorum longus
During dorsiflexion the Talocrural goes through what arthrokinematics
Anterior rolling and posterior gliding of the described asymmetric talus on the tibia produces dorsiflexion and abduction
During plantarflexion The Talocrural joint goes through what arthrokinematics
Posterior rolling and anterior gliding of the talus produces plantarflexion and adduction.
What are the medial ligaments of the Talocrural joint
Medial Collateral Ligament
What are some characteristics of the Medial collateral ligament (Deltoid ligament)
Fan shaped
Very strong
Tibial malleolus to navicular, talus, calcaneus
Checks medial distraction and joint end range of motion
What are the Lateral Ligaments of the Talocrural joint
Anterior talofibular
Posterior talofibular
calcaneofibular ligaments
What is a difference between the MCL and LCL of the talocrural joint
Lateral ligaments are weaker and more injury prone than the MCL
The LCL checks what
Varus stress
Which Lateral ligament is the weakest an most commonly torn
Anterior talofibular
At the subtalar joint what movements are considered pronation
Calcaneal dorsiflexion
Abduction
Eversion
At the subtalar joint what movements are considered supination
Calcaneal plantarflexion
adduction
Inversion
What kind of joint is the subtalar joint
Modeled as a mitered hinge joint
Where do the interosseous talocalcaneal ligament and ligamentum cervicis lie?
In the tarsal canal
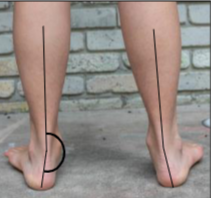
This image shows calcaneal valgus or varus?
Valgus
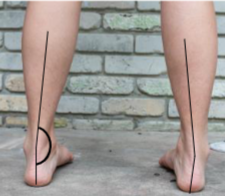
This image shows calcaneal valgus or varus?
Varus
At the subtalar joint what is the closed chain movement?
Calcaneus become fixed in the sagittal and transverse planes although must still invert and evert
Explain the movements of supination at the calcaneus, talus, and tibiofibular
Calcaneus: Inversion
Talus: Abduction and Dorsiflexion
Tibiofibular: Lateral Rotation
Explain the movements of pronation at the calcaneus, talus, and tibiofibular
Calcaneus: Eversion
Talus: Adduction and Plantar flexion
Tibiofibular: Medial Rotation
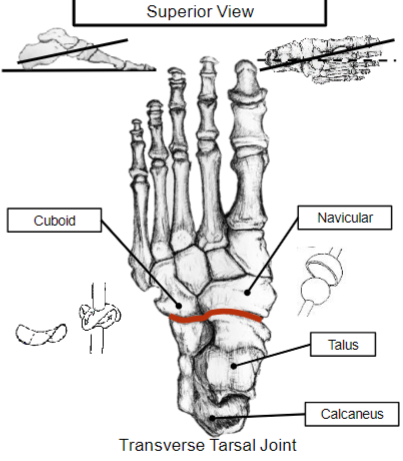
What are some characteristics of the Transverse Tarsal Joint
S- Shaped joint line that transects the foot
Divides hindfoot from the mid + forefoot
Comprised of the talonavicular and the calcaneocuboid joint
What is the function of the Transverse Tarsal Joint
Action permits the forefoot to remain in contact with the ground through hindfoot varus/valgus positions
Allows for accommodation of uneven terrain and/or absorption of rotation of the lower limb
With weight bearing tibial internal rotation and subsequent subtalar pronation, the TTJ joint may do what kind of movements?
Substantial Supination
What is the meaning of substantial supination
Maintain appropriate load bearing in forefoot on uneven terrain
With weight bearing tibial external rotation and subsequent subtalar supination, the TTJ joint may do what kind of movements?
Slight pronation
What does slight pronation mean?
Limited ability to pronate the forefoot to maintain a fixed position of the forefoot
What are some functions of the Tarsometatarsal joints
Unique but not fully independent motion
Each ray rotates about distinct axis
Almost all have triplanar movement
Allow for the cupping movement of the plantar surface of the foot
Explain the structure of the Metatarsophalangeal Joints
Condyloid joint
“toe joint”
Allow for hinging and the smaller base of the support in heel rise.
What kind of joint is the metatarsophalangeal joints? How many degrees of freedom are there?
Condyloid joint
2 DOF’s
What are typically movements of the metatarsophalangeal joints
Flexion/extension
Abduction/adduction
What are some functions of the metatarsophalangeal joints
Hinging axis during heel lift in weight bearing
Oblique axis through MTP joints of digits 2-5
More evenly distributes weight bearing across the toes
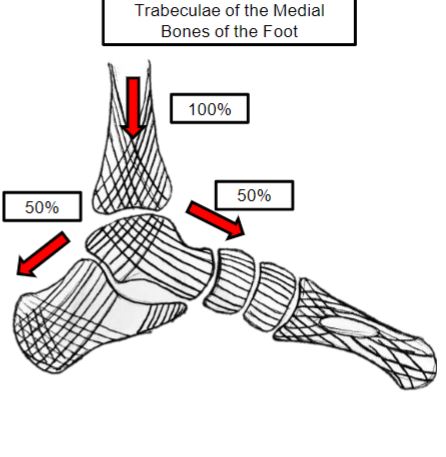
Where is the load transmitted posteriorly?
Through the calcaneus to heel contact
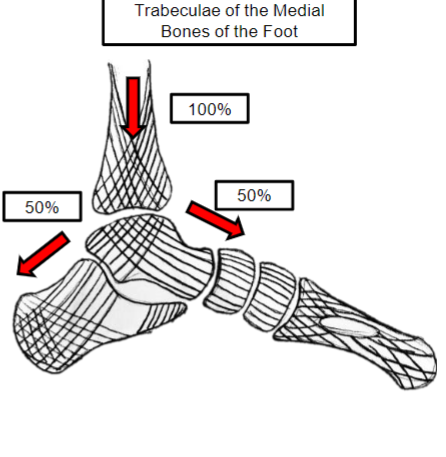
Where is the load transmitted anteriorly?
Through the talonavicular and calcaneocuboid joints
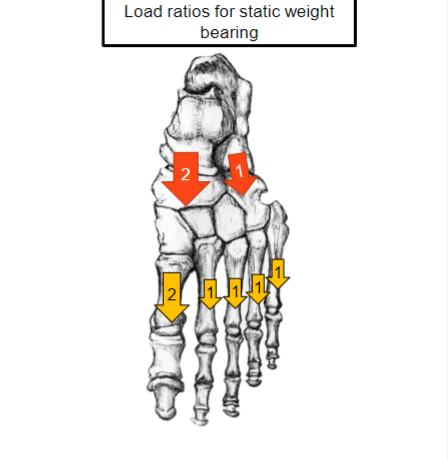
In this image is there more force on the medial or lateral position of the foot
Medial has more force than the lateral
In Plantar arches what is considered the “keystone”
Middle Cuneiform
In plantar arches where is the greatest amount of arch
Towards the medical border
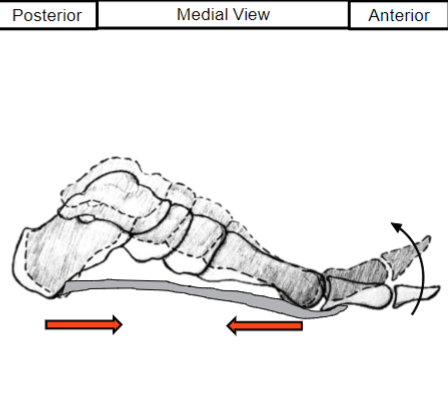
Explain the Plantar Aponeurosis Windlass Effect
Dense fascia running the length of the foot
Important for creating a rigid lever in gait
As the toe lifts up, the tendon compresses together causing an arch
What is the function of the Peroneus Longus
Tendon that supports transverse arch
What muscles cause plantar flexion
Triceps Surae
Flexor Hallucis Longus
Flexor Digitorum Longus
Tibialis Posterior
Peroneus Longus
Peroneus Brevis
What muscles cause DorsiFlexion
Tibialis anterior
Extensor Hallucis Longus
Peroneus Tertius
Extensor digitorum longus
What Muscles cause pronation
Peroneus tertius
Extensor Digitorum Longus
What muscles cause supination
Tibialis Anterior
Extensor Hallucis Longus