OCR A level Chemistry Practical techniques
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
MgSo4
CaSo4
Pear shaped flask
Condenser
Rubber tubing
Heat source
Clamp stand
Screw tap adaptor
Receiver adaptor
Still head
Thermometer
How does distillation work?
-The different liquids in the mixture will have different boiling points.
-The liquid with the lowest boiling point is the most volatile and will boil first.
-The vapour moves out of the flask up into the other parts of the apparatus, leaving behind the less volatile components of the mixture.
-When the vapours reach the cold condenser, they condense and become a liquid.
-This liquid then drips into the collecting flask.
-When preparing samples of organic liquid water may be obtained along side
-This will bring about the appearance of two liquid layers
-One will be organic one and one will be the aqueous one
-To identify which one is which you add some water to the mixture the larger that increases in size is the aqueous layer
-Ensure tap of separating funnel is closed
-Pour liquid mixture in separating funnel and place a stopper on the top of the funnel and invert the contents
-Add water to see which layer gets bigger and this one is the aqueous layer
-Place a conical flask under the separating funnel, remove stopper and open tap until the whole of the lower layer has left the funnel
-Place a second conical flask under the separating funnel to collect the other layer
-The layers are now separated in the flasks
-Label which is which
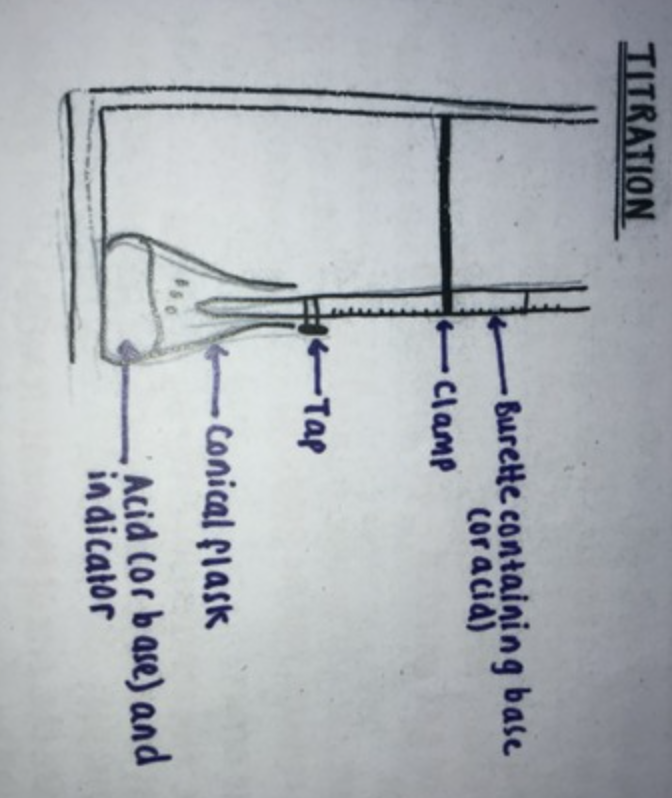
-Fill a burette with the acid of known concentration.
-Accurately measure an amount of the alkali using a calibrated pipette and pipette filler.
-Add the alkali to a conical flask with a few drops of a suitable indicator.
-Run in acid from the burette until the colour just changes showing that the solution in the conical flask is now neutral.
-Repeat the procedure adding the acid dropwise.
add aqueous sodium carbonate
shake
acid will react and release CO2
add solution to separating funnel
slowly open tap whilst holding separating funnel upside down
remove aqueous sodium carbonate layer
wash organic layer and run into a flask
Alkali turns pink
Acid turns colourless
Alkali turns yellow
Acid turns orange
End point turns orange
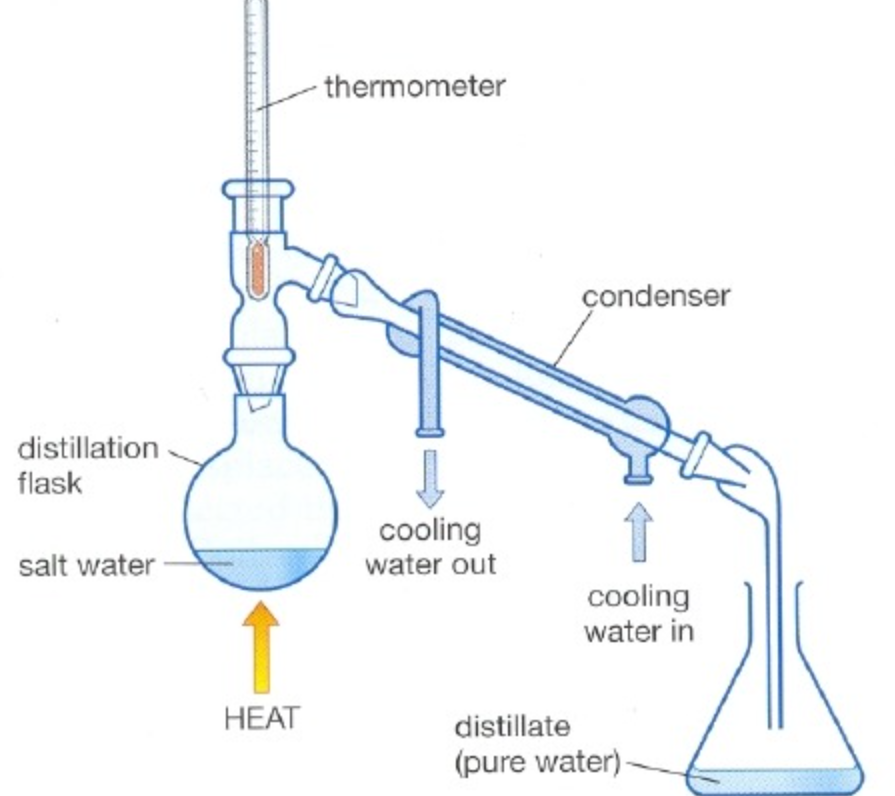
Include:- Liebig condenser.
- COLD water in (bottom right).
- COLD water out (top left)
- Pear-shaped flask.
- Anti-bumping granules.
- Open top.
- HEAT.

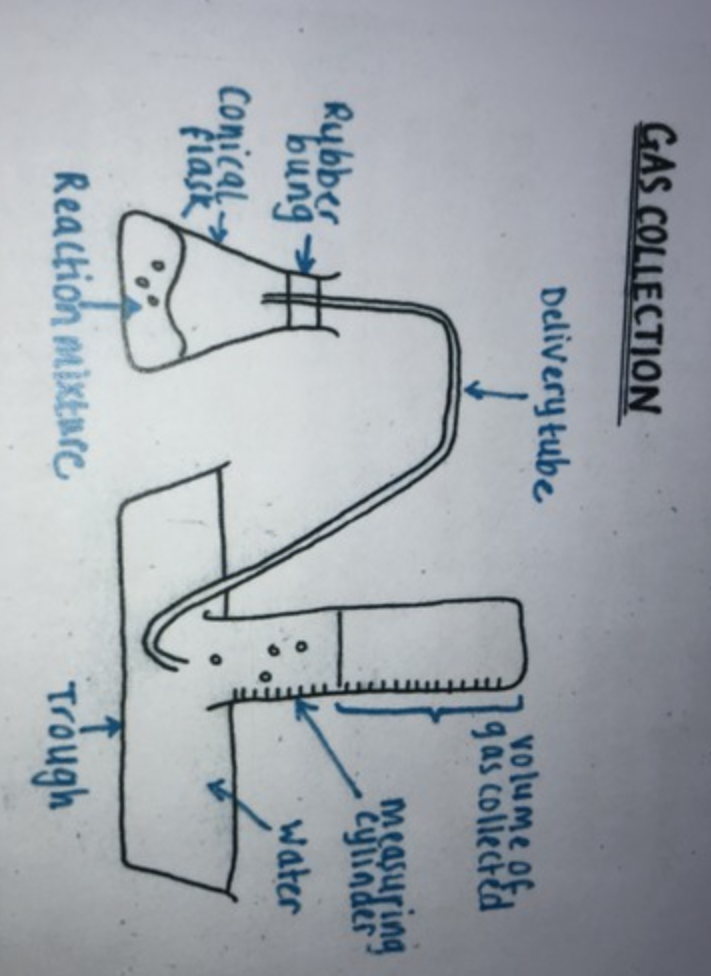
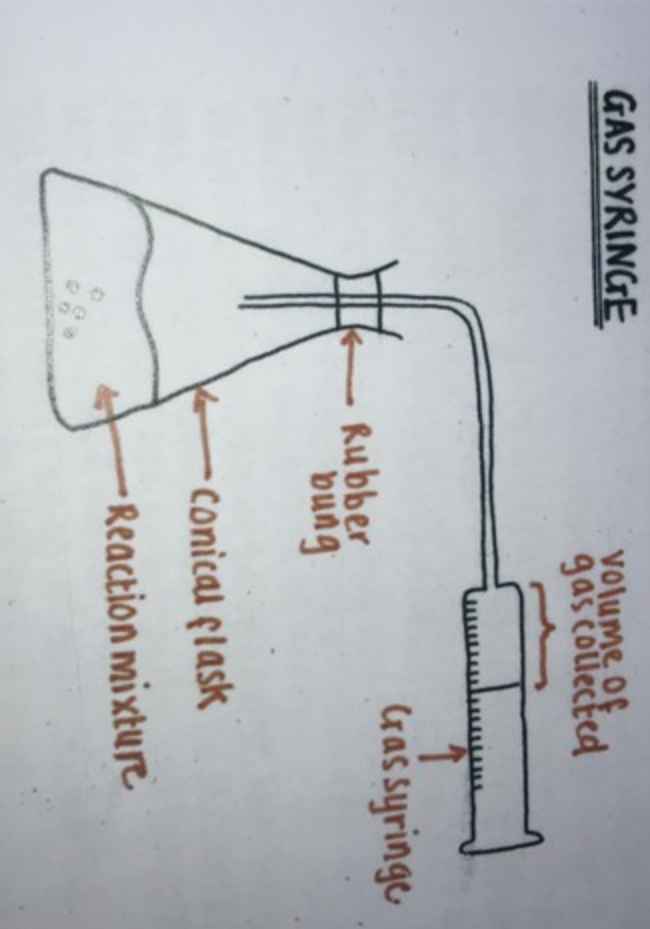
Draw the gas collection apparatus?
replace measuring cylinders with pipettes/ burettes as they are more precise
to reduce burette reading errors make the titre a larger volume
increase the volume and concentration of substance in conical flask
decrease the concentration of substance in burette
use more accurate balance
use larger mass
measure by difference
Minimize apparatus error
Make sure the gas syringe is large enough to collect predicted volume
Put metal in beaker, shake and tip to start reaction preventing gas leakage
Allow it to cool before measuring volume as gas expands when hot
Decrease uncertainty by using apparatus with finer scale divisions
Increase size of measurements made
CaCl2
CaSo4
MgSo4
-Add organic liquid to conical flask
-Use a spatula and add some drying agent to the liquid and gently swirl the contents to evenly distribute them
-Place a stopper on the flask to prevent your products from evaporating away
-If this solid has all stuck together in a lump this means water is present
-Add more drying agent until the solid on the solution is as fine powder
-Decant the liquid from the solid into a flask and it should be dry if it's clear
Reflux salicylic acid, ethanoic anhydride and glacial ethanoic acid using quick fit apparatus
Solid is formed which has to be separated before being purified
Alkaline hydrolysis
Quickfit apparatus
Reflux methyl benzoate with aqueous sodium hydroxide
Now carry out acidification
Solid is formed which has to be separated before being purified
Designed to be easily connected
Involves:
Round bottom flask
Pear shaped flask
Condenser
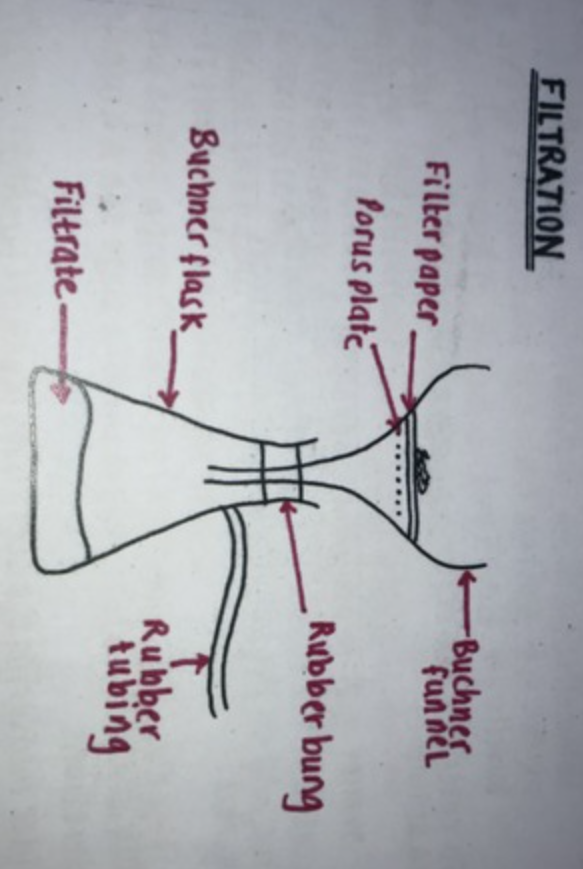
Büchner flask
Büchner funnel
Pressure tubing
Filter paper
Access to filter or vacuum pump
-connect one end of pressure tubing to vacuum outlet whilst attaching other end to Büchner flask
-fit Büchner funnel to flask ensuring tight fit
-switch on vacuum pump that is attached to filter pump
-place a filter paper inside funnel that is wet with the same solvent used to prepare solid
-filter sample by pouring mixture into centre of filter paper
-rinse beaker with solvent so all solid crystals collect into funnel
-rinse crystals into funnel with more solvent and leave them to dry
-pour solvent into conical flask
If the solvent is flammable, warm solvent over water bath
If solvent is water place flask on tripod and gauze over Bunsen paper
-put impure sample into a second flask
-slowly add solvent into impure sample until dissolved.
Add minimum required to dissolve
-allow solution to cool so crystals or desired product form
-after no more crystals form filter under reduced pressure to obtain dry solid
Impure compounds have have a wild melting range
Pure compounds have a very sharp melting range
-take glass capillary tube and hold one end to a flame and rotate until the end is sealed
-fill tube with crystals
-place tube into a sample hole of a melting point apparatus and place thermometer in thermometer hole
-using rapid heating settings heat up sample whilst observing it through magnifier
-once the solid starts to melt record melting point
-repeat
1. Dissolve impure compound in a minimum volume of hot solvent
2. Hot filter solution through filter paper
3. Cool filtered solution by placing the beaker in ice
4. Filter under pressure with bunched flask to separate crystals
5. Wash crystals with distilled water
6. Dry crystals on absorbent paper
Why dissolve in minimum volume of hot solvent ?
Must dissolve compound and impurities and be stable when cold // not dissolve
- crystals lost when filtering or washing
- products may remain in solution after recrystallisation
- other side products / reaction occurring