Overview - Human Body
1/80
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
What are the important function of the human body?
Support
Collection and evaluation of info,
transportation of oxygen and nutrients,
protection of internal organs
obtaining nutrients from food
maintenance of constant body temps
What helps with support?
endoskeleton
What helps with collection and evaluation of information?
nervous system
What type of system is the transportation of oxygen and nutrients? (i couldnt figure out how to word this question)
in a closed system
Whats a closed system?
In the context of the human body, a closed system refers to a system where matter doesn't enter or leave, but energy can be exchanged with the surroundings.
What helps with the protection of internal organs?
coelem
What is coelem?
fluid filled cavity that protects internal organs and allows muscles to contract w out harming internal organs
What does the body need to obtain?
nutrients from food
What does the body need to maintain
constant body temp
Organization of Body
cell —> tissue —> organ —> organ system
What are cells specialized for?
for a particular function
Totipotent
Totipotent refers to cells that have the potential to develop into a complete organism on their own.
Pluripotent
Pluripotent cells are stem cells that can turn into many different types of cells in the body, but not all types. able to produce many cell types
Multipotent stem cells
Multipotent stem cells are stem cells that can differentiate into a limited range of cell types within a specific tissue or organ.
Blastocyst
A blastocyst is an early stage of embryo development in mammals, including humans. It is a hollow sphere-like structure composed of a layer of cells surrounding a fluid-filled cavity. The blastocyst forms about 5-7 days after fertilization and is crucial for implantation into the uterus.
Inner cell mass (ICM)
This cluster of cells within the blastocyst will develop into the embryo itself, including all the different cell types of the body. (developing fetus)
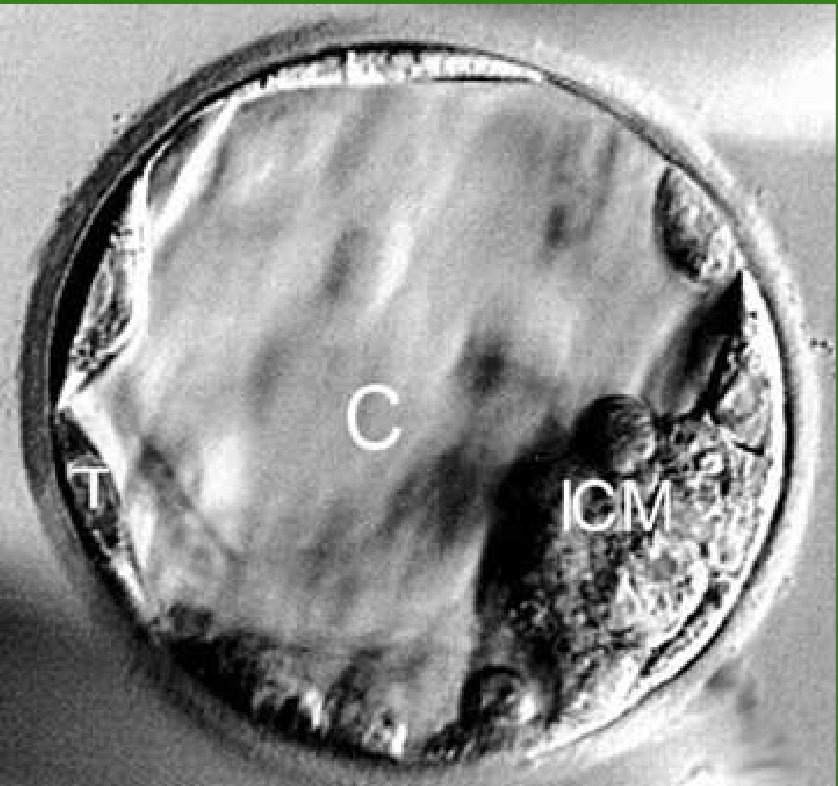
T- becomes placenta, C- is the cavity
Stem cells differentiate into ______
specialized cells
cultured stem cell —> 3 different culture conditions —→ 3 different types of differentiated cells
Ex of differentiated cells: liver cells, nerve cells, heart muscle cells
When researchers mention a regression of multipotent stem cells to pluripotent stem cells, they are typically describing a process where the stem cells, which were previously committed to developing into a limited range of cell types (multipotent), regain the ability to differentiate into a broader range of cell types (pluripotent).
“basically how to grow stem cells which are pluripotent from multipotent cells.. either through cloning where an unfertilized egg is used or they add genes to skin cell this allows for stem cells w out an embryo, precise genetic control, and makes embryonic cell work more unnecessary” - DANNYS WORDS
How many types of tissues are in the human body?
4
what are the types of tissues are in the human body?
Muscle tissue
nervous tissue
Epithelial tissue
connective tissue
epithelial tissue
epithelial tissue
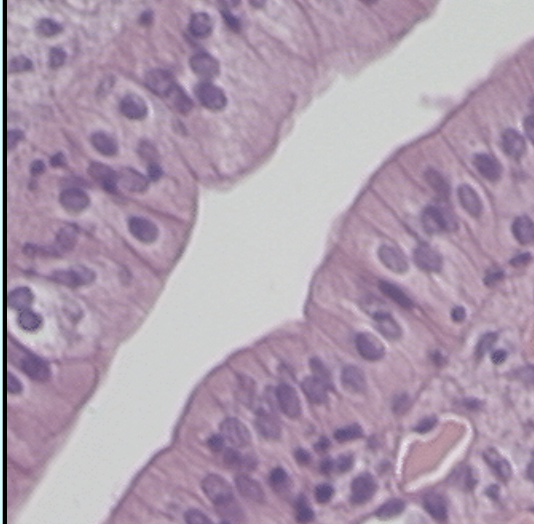
What does the epithelial tissue protect the body from?
protects from dehydration and physical damage
What does the epithelial tissue control?
controls what enters and leaves cells
Where are the glands and tissues on the epithelial tissue?
it is on the interior or exterior body surfaces
epithelial tissue has layers under it. how think can a layer be?
layer can be one or a few cells thick
epithelial tissue is very regenerative.
How many types of layers are there?
3 types attached to a basement membrane
what are the three types of layers?
simple
Stratified
Glandular
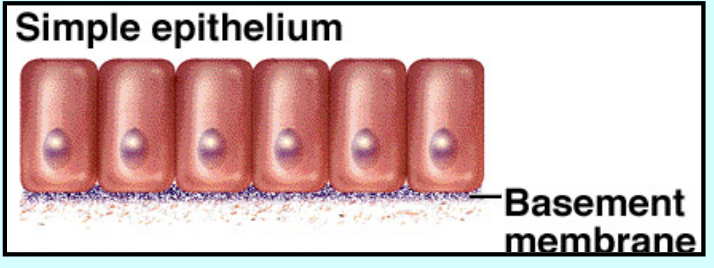
Simple - single layer
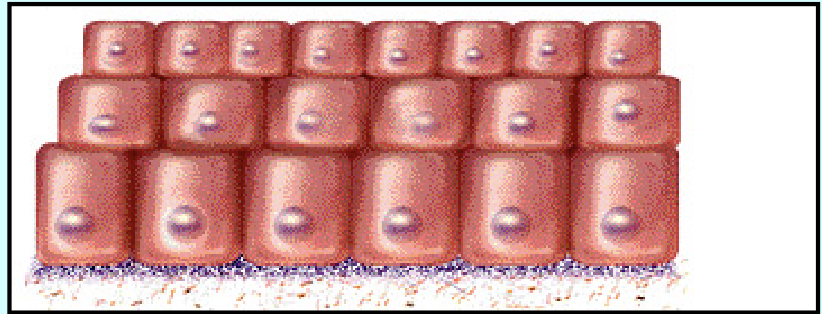
Stratified - multiple layers
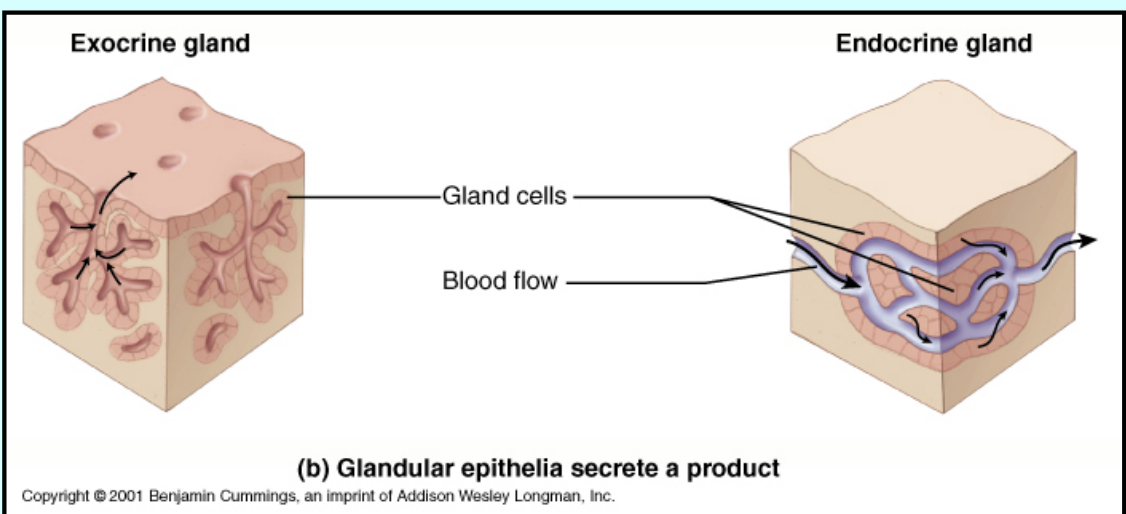
Glandular - secrete a product
"Glandular" refers to anything related to glands, including their structure, function, or the substances they produce and secrete. It can describe processes, tissues, or organs involved in the production and release of hormones, enzymes, or other essential substances in the body. These substances are then either secreted into the bloodstream or released into a cavity or onto a surface in the body to perform specific functions.
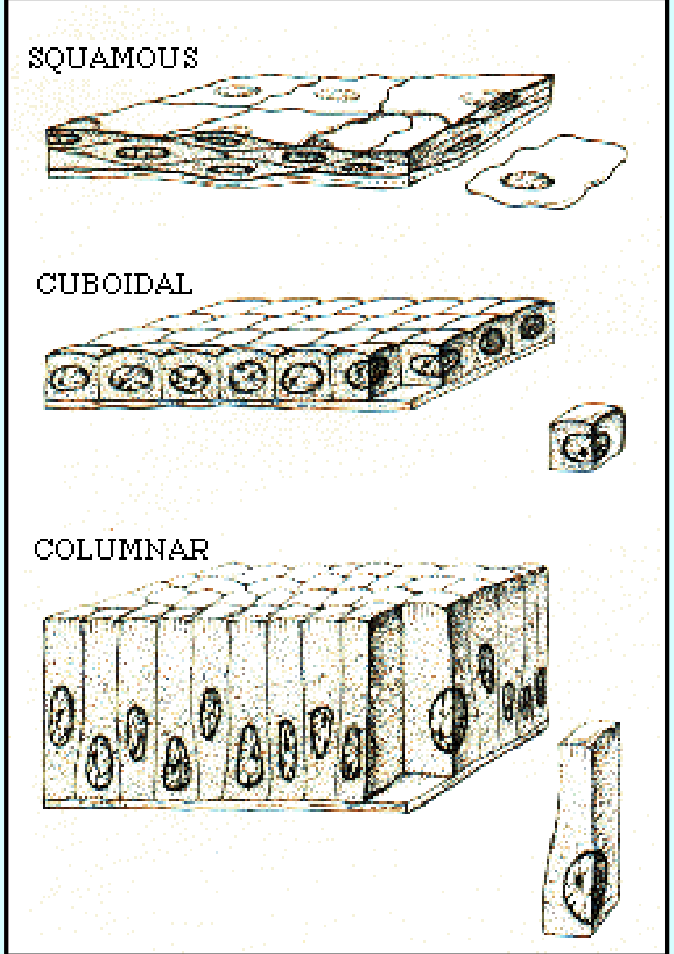
epithelial tissue is also classified by shape
Squamous - flat
cuboidal - square
columnar - column
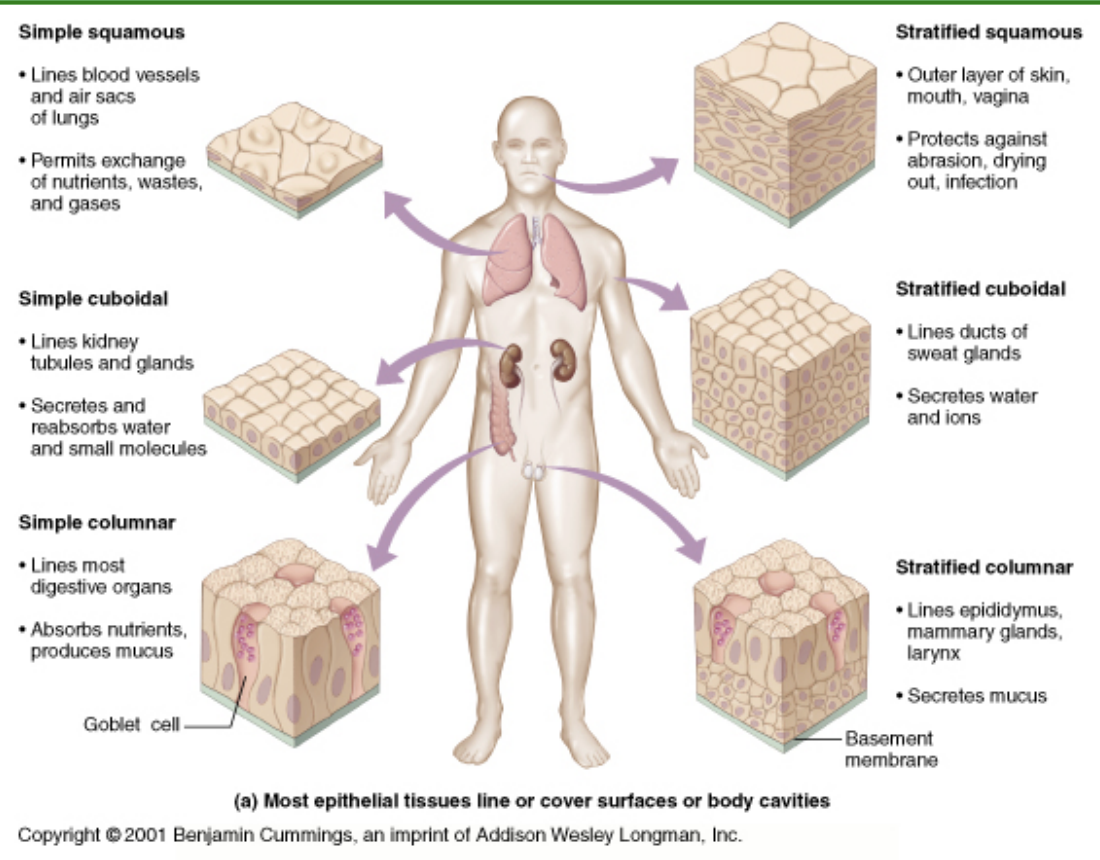
Connective tissue
A) What defends the body?
white blood cells
Types of white blood cells:
macrophages
lymphocytes
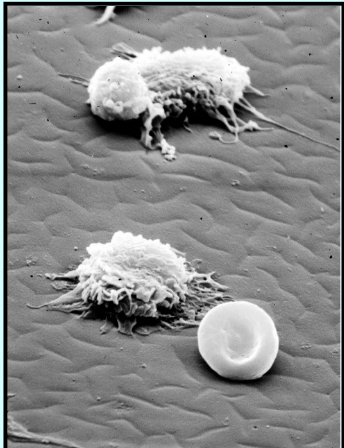
Macrophages - engulf and digest microbes
A type of white blood cell that surrounds and kills microorganisms, removes dead cells, and stimulates the action of other immune system cells
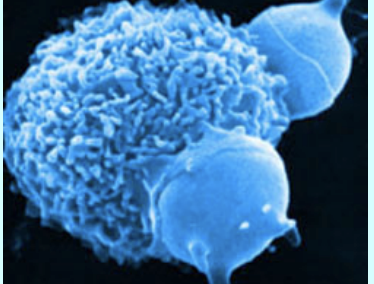
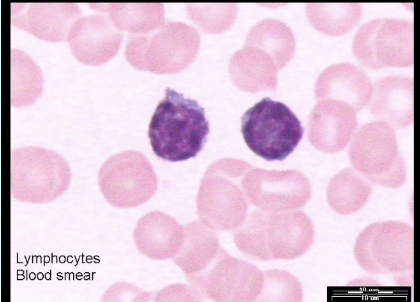
Lymphocytes - make antibodies, attack virus-infected cells and cancer cells
type of white blood cell that plays a crucial role in the body's immune system. They are produced in the bone marrow and mature in the lymphoid organs, such as the thymus and lymph nodes. Lymphocytes are responsible for recognizing and attacking foreign invaders like viruses, bacteria, and other pathogens, as well as for regulating immune responses to prevent autoimmune reactions.
B) What does the connective tissues do?
supports the body and connects parts
What is used to support body and connect parts?
cartilage and bone
C) the connective tissue accumulates and transports materials
Adipocytes - fat cells
Adipocytes are cells specialized in storing energy as fat. adipocytes can expand or shrink in response to changes in energy balance, such as calorie intake. They also produce hormones and signaling molecules that regulate metabolism
Leucocytes - white blood cells
also known as white blood cells, are a vital part of the body's immune system. They circulate in the blood and lymphatic system, defending the body against infections and foreign invaders such as bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens. Leucocytes can be further categorized into several types, including lymphocytes,
Erythrocyte - red blood cells
known as red blood cells, are specialized cells responsible for carrying oxygen from the lungs to the body's tissues and transporting carbon dioxide back to the lungs for exhalation. They contain hemoglobin, a protein that binds oxygen and gives blood its red color. Erythrocytes lack a nucleus and other organelles, maximizing space for hemoglobin and enhancing their oxygen-carrying capacity.
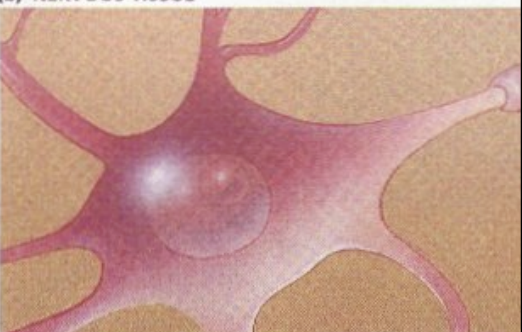
Nervous tissue
What does the nervous tissue do?
conducts signals rapidly
what does nervous tissue include?
neurons (nerve cells)
Muscle tissue
type of tissue that is responsible for movement in the body. Muscle tissue is made up of cells called muscle fibers, which contract when stimulate
What does the muscle tissue permit?
permits movement
How many types of muscles are there?
3
What kinds of muscles are there?
smooth
cardiac
skeletal
Skeletal muscle
attached to bones and allows for voluntary movement
Smooth muscle
found in the walls of organs and blood vessels, controlling involuntary movements such as digestion and blood vessel dilation
Cardiac muscle
which forms the heart and is responsible for pumping blood throughout the body
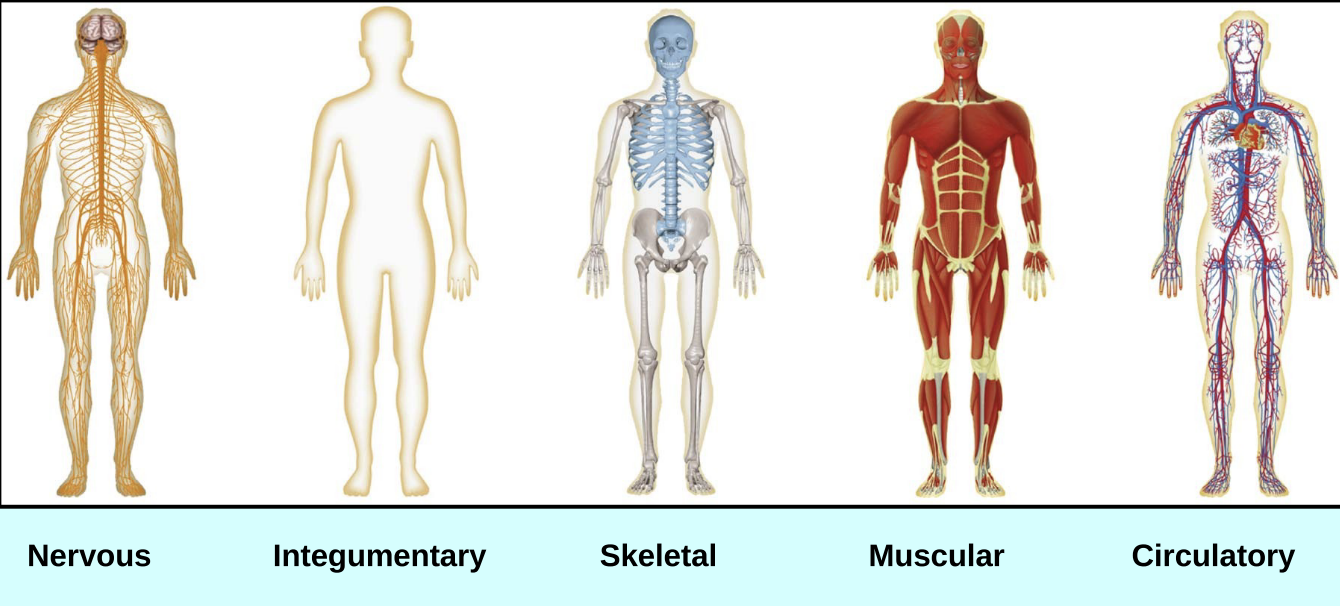
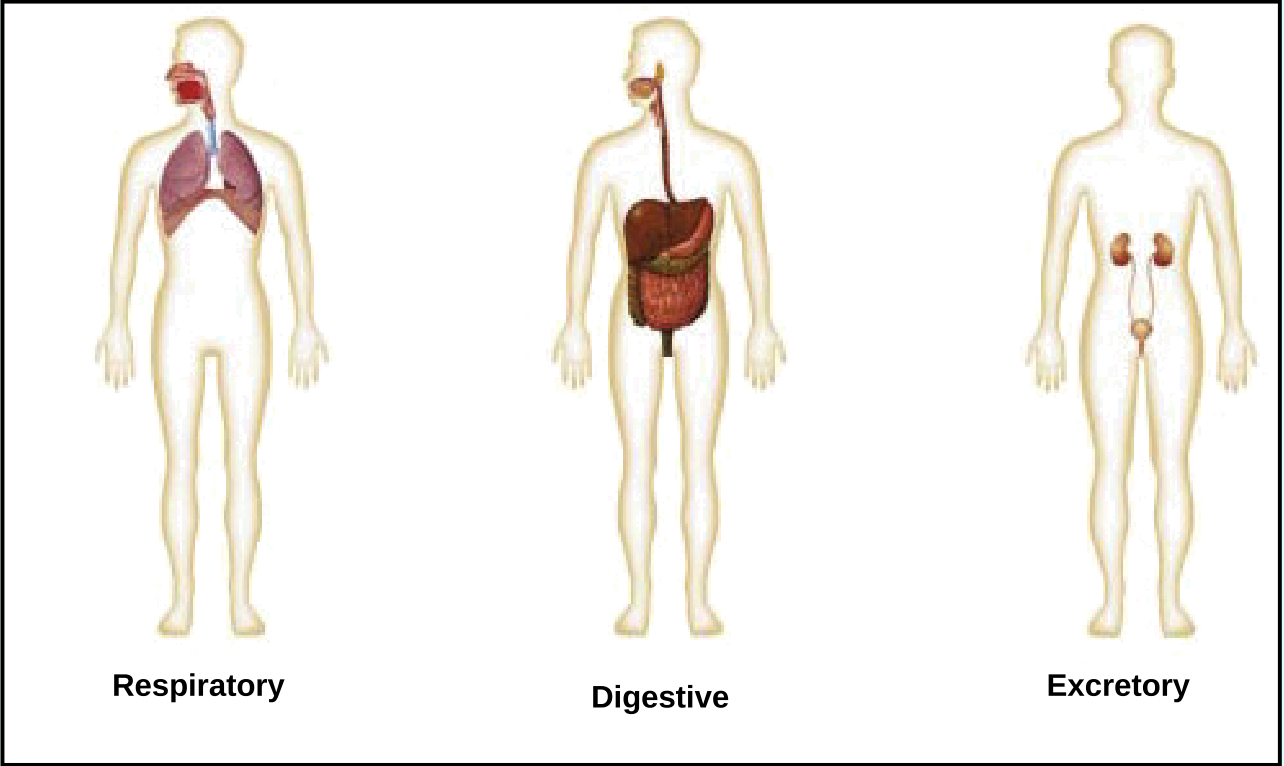
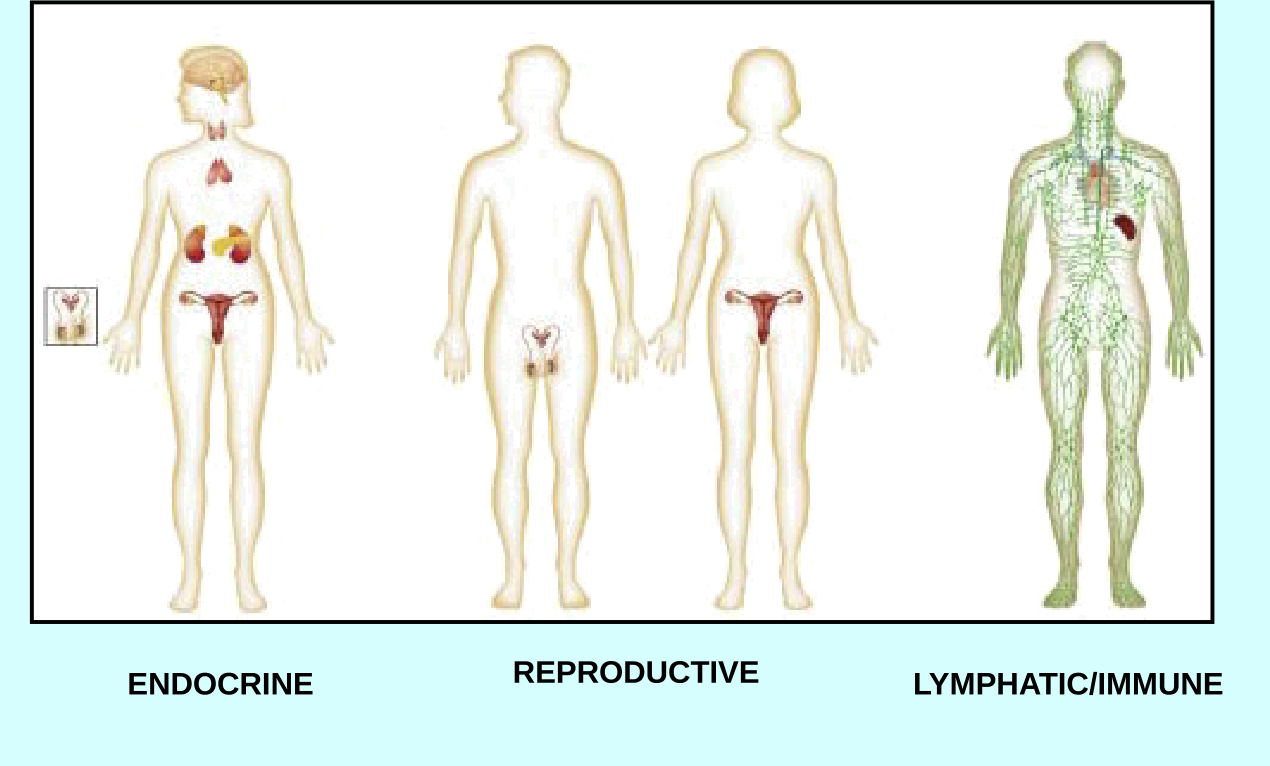
How many organ systems does the body have?
11 organ systems
What is the importance of homeostasis?
it provides stable environment so chemical reactions can occur
Feedback of information maintains homeostasis
What is the Hypothalmus in brain important for?
important in regulation
What are the two types of feedback loops?
negative feedback and positive feedback
A negative feedback loop is a regulatory mechanism in biological systems that works to maintain homeostasis, by counteracting changes from an ideal set point. In this process, when a change occurs that moves a system away from its set point, the feedback loop activates mechanisms to oppose or reverse that change, bringing the system back towards the set point. Once the system returns to its ideal state, the feedback loop reduces its activity. This self-regulating mechanism helps to maintain stability and balance
Negative feedback - prevents deviation from set point; not normal back to normal
ex: maintaining body temp, blood pressure
Positive feedback is a regulatory mechanism in biological systems where a change in a certain direction leads to an amplification or reinforcement of that change, rather than opposing it like in negative feedback. In positive feedback loops, the initial stimulus triggers a response that further increases the stimulus, leading to a continuous process of amplification until a specific endpoint is reached. This mechanism is often associated with processes that need rapid and decisive responses, such as blood clotting, childbirth, and some aspects of the nervous system.
Positive feedback - increases distance from initial value
ex: blood clotting, uterine contractions in childbirth, and breakdown of glycogen
glycogen
Glycogen is a form of stored energy made of many glucose molecules linked together.
Body signal systems
electrical
chemical
Electrical - neurons, fast communication
An electrical body signal refers to any form of electrical activity generated within the body, often associated with the nervous system or muscle activity.
Chemical- hormones and other chemicals, slower but longer lasting response
A chemical body signal refers to any form of communication within the body that involves the release and reception of chemical substances. For instance, hormones released by glands travel through the bloodstream to target tissues, where they exert specific effects on cellular activity and metabolism.
Organs and organ systems are made of a combination of how many types of tissue?
4 types
Functions of the organ systems:
cover, support or produce movement
integumentary, muscular, skeletal
regulate body functions
endocrine, nervous , reproductive
transport or protect
circulatory, immune
involved in metabolism or excretion
respiratory, digestive, urinary (excretory)