Rituals, Morality, and Well-Being in Religious Contexts
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
What are the defining features of rituals?
Rituals are rigid, repetitive, and redundant actions that do not have a clear goal but are essential features of religion.
What does it mean for a ritual to be 'causally opaque'?
It means that it is not clear how the actions of that ritual achieve a certain goal.
How do rituals differ from ordinary goal-directed actions?
Rituals can be performed repeatedly even when the preferred outcome is absent, and there is no clear mechanism for causality.
What are instrumental goals in ritual practices?
Instrumental goals help you acquire something or achieve a goal.
What are symbolic goals in ritual practices?
Symbolic goals provide meaning and significance to life.
What does 'high-fidelity imitation' mean?
High-fidelity imitation is when children and adults copy complex behaviors to identify with ingroups, especially when threatened by exclusion.
What cues lead people to imitate ritual actions more precisely?
Threats to social inclusion and social convention cues.
What are the key differences between doctrinal and imagistic modes of religiosity?
Doctrinal mode is characterized by frequently performed rituals with moderate to low emotional intensity, while imagistic mode features less frequent rituals with high emotional intensity.
What social context promotes doctrinal mode?
A social context where doctrine is valued and institutions follow a doctrine.
What social context promotes imagistic mode?
A social context where special events and transformative experiences are valued.
What key functions do rituals serve for individuals and groups?
Rituals serve to reduce anxiety, boost performance, and increase social cohesion.
How can rituals help reduce anxiety during uncertainty?
By drawing focus away from stressors, limiting overthinking.
How might ritual actions improve performance on challenging tasks?
They help individuals focus attention on a goal and reduce fear of failure.
How do rituals promote social cohesion?
Performing rituals with ingroup individuals fosters a sense of belonging and bonding.
What is 'collective effervescence'?
An intense emotional state experienced by individuals in a group setting, enhancing group bonding.
How do extreme or painful rituals create stronger social bonds?
They demonstrate commitment to group beliefs, fostering support and belonging.
What is the association between extreme rituals and wellbeing?
Extreme rituals encourage group fusion, enhancing individual well-being through a sense of belonging.
How do rituals during public tragedies contribute to attitudes?
They help people bond and provide a sense of control and explanation for events.
What is the social control hypothesis of human sacrifice?
It legitimizes class-based power through displays of authority and sanctified authority.
How can rituals reinforce authority and moral norms?
They increase social stratification and solidify moral norms within society.
What does it mean for ritual behavior to act as a costly signal of belief?
It signifies strong belief and commitment, as costly signals are hard to fake.
How do costly rituals promote cooperation and trust?
They signal trustworthy membership, enhancing group cohesion and survival.
What do CREDs stand for?
credibility enhancing displays that show commitment and true beliefs.
How do CREDs transmit belief more effectively than verbal testimony?
People trust actions more than words.
How does religious morality build upon universal human moral intuitions?
It encourages cooperative behavior and maintains justice beliefs.
What is the difference between self-report measures and behavioral measures in studying prosociality?
Self-reports can be biased, while behavioral measures observe actual prosocial behavior.
Why might self-report measures overestimate religiosity and prosocial behavior?
Due to social desirability bias and expectations of religious behavior.
What evidence shows reminders of God can increase prosocial behavior?
Studies show that priming with spiritual words makes religious people more prosocial.
When are the effects of religious priming strongest?
When the priming is done explicitly rather than implicitly.
What are meta-ethics?
Meta-ethics are explanations for where moral guidance comes from and the justification for moral principles.
How do religious and secular individuals differ in justifying moral principles?
Religious individuals justify moral principles based on what they believe God wants, while secular individuals use abstract principles.
What is the difference between deontology and utilitarianism in religious and secular morality?
Deontology is followed mostly by religious individuals who judge morality based on rightness, while secular morality focuses more on utilitarianism.
What are the five moral foundations?
Care/harm, Loyalty/betrayal, Fairness/cheating, Authority/subversion, Purity/degradation.
How do different cultures emphasize moral foundations?
Christian communities emphasize loyalty/authority and purity; secular liberal communities emphasize care and fairness.
How do Judaism and Christianity differ in their emphasis on moral thoughts vs. actions?
Christianity equates thoughts with actions, while Judaism focuses on behavior as a measure of morality.
How can religious beliefs affect environmental concern?
Less concern arises from beliefs in dominion over nature; more concern arises from stewardship beliefs.
What is ecospirituality?
Ecospirituality is the belief that spirituality and nature are interconnected, viewing nature as sacred.
What did Preston & Shin (2022) find about spirituality and environmental attitudes?
Higher spirituality predicts stronger environmental concern and pro-environmental behaviors.
What does it mean for religious morality to be parochial?
Parochial morality means being more prosocial towards members of one's religious group.
What is religious priming?
Religious priming is a method to manipulate thinking by providing religious ideas, either implicitly or explicitly.
What did Shariff & Norenzayan (2007) find about religious priming and generosity?
Religious cues can prime people to act more generously in economic games.
What distinguishes implicit and explicit religious primes?
Implicit primes are less reliable, while explicit primes produce more consistent effects.
How do situational and individual differences moderate priming effects?
Believers show increased morality from reminders of God compared to non-believers.
What is the 'Big Gods' hypothesis?
The hypothesis states that large-scale societies are more likely to be religious, aiding social coordination.
How do religious beliefs support cooperation in large-scale societies?
They help solve coordination problems and foster trust among strangers through the threat of supernatural punishment.
What did Purzycki et al. (2016) show about gods' moral concerns?
Small-scale religions have gods with limited concerns relevant to local cooperation dilemmas.
How do religious beliefs reflect adaptive responses to social challenges?
Beliefs in stewardship lead to environmental care, while beliefs in dominion can lead to neglect of ecological issues.
What does Allport's Paradox mean regarding religion and prejudice?
Religion can both increase prejudice through exclusion and decrease it through teachings of compassion.
What challenges exist in studying religion's role in prejudice and conflict?
Scientific study faces difficulties due to the complexity of religious beliefs and their social implications.
What challenges exist when studying religion's role in prejudice and conflict scientifically?
There are two main challenges: various conflicts between different religious groups with varying effects, and the coexistence of different religions in societies.
What is parochial prosociality?
Parochial prosociality is when socially beneficial behaviors are limited to ingroup members.
How does universal prosociality differ from parochial prosociality?
Universal prosociality involves prosocial behaviors performed regardless of ingroup or outgroup membership.
What are the potential benefits of extending prosocial behavior beyond the ingroup?
It can build trust, foster cooperation, and create alliances with outsiders.
What are the potential costs of extending prosocial behavior beyond the ingroup?
It carries risks such as being exploited by free-riders, losing resources, or weakening ingroup cohesion.
How do social identity processes create religious ingroups and outgroups?
Social identity is important; identifying with a group makes it the ingroup, while others are seen as outgroups.
What are realistic threats and how do they fuel intergroup conflict?
Realistic threats relate to resources like land or oil, leading to conflicts over these resources.
What are symbolic threats and how do they fuel intergroup conflict?
Symbolic threats undermine group values, leading to conflicts to protect those values.
How does religion relate to prejudice against Muslims, immigrants, gay people, and atheists?
Religion can elicit negative attitudes towards those conflicting with religious aspects, such as behavior, belonging, and beliefs.
What is Christian nationalism?
The belief that the United States should be explicitly Christian and governed by Christian values.
What is religious fundamentalism?
Rigid adherence to literal interpretations of sacred texts and belief in one true faith, often leading to intolerance.
What is authoritarianism in relation to intergroup hostility?
Preference for strict hierarchy and obedience, often linked to punitive measures against outgroups.
Why is distrust a central component of anti-atheist prejudice?
Religiosity is linked to trustworthiness; atheists are seen as untrustworthy due to lack of religious belief.
What are system-justifying beliefs associated with religiosity?
Beliefs include a just world, right-wing authoritarianism, a powerful God, and karma.
What are sacred values and how do they affect conflict resolution?
Sacred values are absolute core values that make negotiation or compromise difficult.
What did Ginges et al. (2007) find about sacred values and material incentives?
Palestinians and Israelis were less willing to trade sacred values for money, viewing it as taboo.
What is identity fusion?
Identity fusion is when personal and group identity blur, leading to extreme self-sacrificial behavior.
How do shared painful or emotional rituals increase group solidarity and willingness to fight for the group?
Shared painful or emotional rituals release certain hormones that promote social bonding and increase a sense of belonging.
How can exposure to conflict increase religiosity?
It increases the need for order, leading people to turn to religion for comfort and explanations.
How does heightened threat affect preferences for moral order?
It increases the psychological need for order and belief that following rules can provide safety.
How does thinking about God influence willingness to help ingroup vs. outgroup members?
It increases willingness to help both, especially ingroup members, but less so when conflict is salient.
What evidence suggests that religious practices can promote peace?
Practices like the Hajj foster empathy and cooperation among diverse participants.
How does thinking about God's perspective affect forgiveness of out-groups?
It prompts kindness and forgiveness, as believers think God wants peace.
How did the historical spread of Christianity influence Western societies?
It centralized authority, codified moral norms, and promoted prosocial behavior.
What is kinship intensity?
Kinship intensity refers to the strength of familial bonds and their influence on social behavior.
How did the historical spread of Christianity shape Western societies?
It centralized authority, codified moral norms, promoted prosocial behavior, and unified populations under shared beliefs.
How does kinship intensity relate to prosociality and fairness?
It reduces prosociality and fairness because it emphasizes loyalty and purity.
What is the association between religion and well-being?
There is a small but robust positive correlation; religion contributes to aspects of well-being.
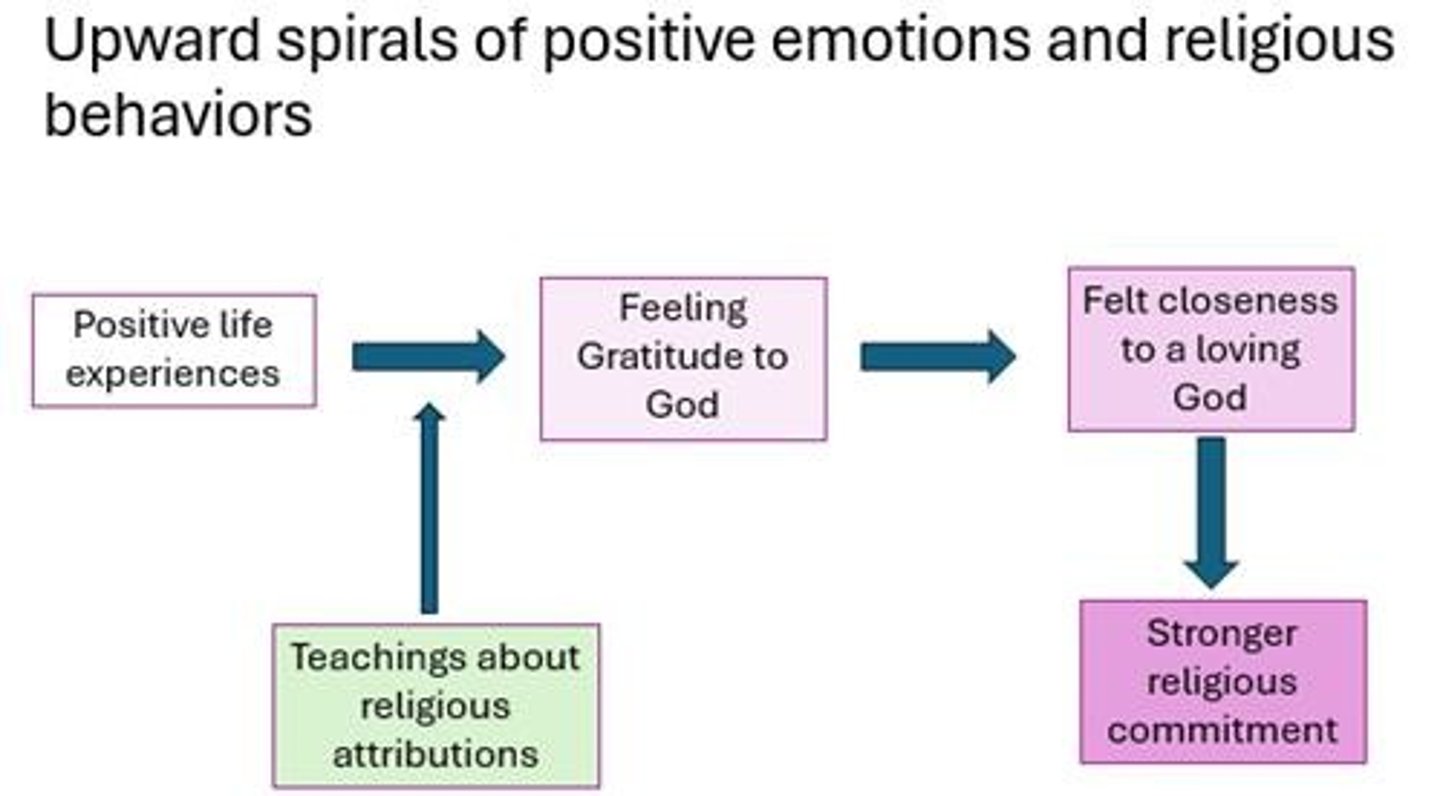
How does cultural context moderate the association between religiosity and well-being?
The positive correlation is seen in cultures that value religion.
What is the difference between ideal affect and actual affect?
Ideal affect is the emotions individuals wish to have, while actual affect is what they actually experience.
How do religious traditions differ in the types of positive emotions they value?
Christianity values high arousal positive emotions, while Buddhism values low arousal positive emotions.
What emotions are especially valued across religious traditions?
Awe, gratitude, compassion, meaning of life, and forgiveness.
How might religious practices increase cognitive reappraisal?
They encourage reappraisal of events, producing positive emotions and increasing life satisfaction.
What is positive religious coping?
It involves benevolent reappraisals of God, leading to better life satisfaction and well-being.
What is negative religious coping?
It involves malevolent reappraisals of God, leading to negative emotions and decreased well-being.
How does religion provide meaning in the face of suffering?
It offers comfort and helps maintain hope for better days.
Why do psychological disorders often include religious content?
Symptoms are drawn from everyday concepts, including religious beliefs.
What does it mean that behaviors considered abnormal in one culture may be normal in another?
Cultural norms vary, so what is normal in one culture may seem abnormal in another.
How do glossolalia and divine voices illustrate the cultural context of mental health?
They are seen as religious behaviors in some cultures but may be diagnosed as schizophrenia in others.
How can religious beliefs influence anxiety?
They can provide reassurance and calmness or heighten anxiety if spiritual understanding is lacking.
What features of religious teachings may contribute to OCD symptoms?
Teachings like thought-action fusion and scrupulosity can exacerbate OCD symptoms.
How are PTSD symptoms associated with religiosity?
Religion can provide communal support, helping reduce symptoms, but can also increase symptoms if victims are blamed.
How does belief in karma influence emotional outcomes?
It leads to internal attribution for events, eliciting positive emotions for good outcomes and negative emotions for bad outcomes.
Why are religious delusions common among people with psychosis?
Hallucinations and delusions often draw on cultural and personal religious beliefs.
What are the potential risks of addressing religion in therapy?
Language and cultural barriers, misdiagnosis, and mismatches between client and therapist worldviews.
Why might highly religious individuals be more concerned about mental health stigma?
Fear of judgment from the community and the belief that mental illness is punishment from God.
What are the potential benefits of incorporating religion into therapy?
Clients feel more understood, and treatments may be more effective.
Why is cultural humility important in therapy?
It prevents therapists' biases from overshadowing clients' needs.
What does it mean to be client-centered when addressing religion in therapy?
It means understanding how clients perceive their own experiences.