inc Ch 26: Toxic Granulation, WBC Anomalies, Leukemic Cells
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
INBORN ERRORS OF IMMUNITY
IEI meaning
Severe Combined Immune Deficiency
includes a group of IEIs associated with defects in both cellular and humoralimmunity.
Nearly all patients with SCID experience a marked
decrease in circulating T cells, poorly functioning B cells,
hypogammaglobulinemia, and symptoms during infancy
First 2 years
if left untreated, most patients with SCID die within _ in life from overwhelming bacterial, viral, and/or fungal infections
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Therapy/HSCT, Gene therapy
Potential curative options are ?
Common Gamma Chain Deficiency/X-linked SCID/T-B+ SCID
most common SCID
initiates from a mutation in IL2RG located at Xq13.1
Infants With this disease have no thymus, tonsils, or lymph nodes and experience severe life-threatening infections
IL2RG
normally encodes the gamma chain protein within receptor complexes that bind interleukin-2 (IL-2), IL-4, IL-7, IL-9, IL-15, and IL-21
mutation in this gene leads to truncated gamma chain proteins and faulty signal transduction that impairs T and NK cell development.
WBC, T & NK lymphocytes
in affected infants is decreased as a result of severely decreased and _. _ are generally adequate in number but are dysfunctional without T cell signaling
Adenosine deaminase deficiency (ADA-SCID)
T–B– SCID1 and represents 10% to 20% of SCID cases. It is an
autosomal recessive disorder caused by a mutation in the ADA
gene located at chromosome 20q13.12
there is intracellular and extracellular accumulation of toxic levels of adenosine and deoxyadenosine in lymphocytes, causing profound decreases in T , B, and NK cells
Symptoms: severe recurring, life-threatening bacterial, viral, and fungal infections beginning early in life. + skeletal abnormalities, neurologic deficits,and skin rashes
Adenosine deaminase
is a key component in the metabolic breakdown of adenosine
triphosphate (ATP) and RNA in all cells
Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome
classified as a combined immunodeficiency with associated or syndromic features.
rare X-linked disease caused by one of more than 450 mutations in that gene
Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (WASP)
controls RNA polymerase II–dependent transcription and has a critical role in actin cytoskeleton remodeling of hematopoietic cells
low amount if this an impact on the stability of the immunologic synapse, the site where T-cells and antigen-presenting cells interact
Gene therapy
promising approach most appropriate for patients with W AS who lack a matched donor
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Therapy
can be curative in patients with human leukocyte antigen (HLA)- matched donors
22q11.2 deletion syndrome/DiGeorge syndrome
a heterozygous microdeletion of 1.5 to 3 million base pairs on chromosome 22 at q11.2 resulting in a loss of over 100 genes and their encoded protein products
deletion breakpoint and genes lost in the deletion can differ among patients, contributing to the variable clinical phenotype.
Haploinsufficiency
caused by the loss of T-box transcription factor 1 gene (TBX1), DiGeorge Syndrome Critical Region 8 (DGCR8), and several microRNAs result in congenital malformations and other clinical manifestations in 22DS
Peroxidase-positive
Abnormal granules in phagocytes
Peroxidase-negative
Abnormal granules in lymphocytes
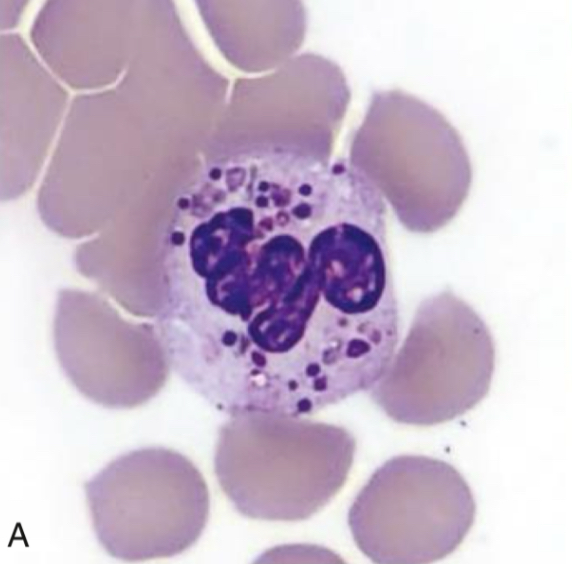
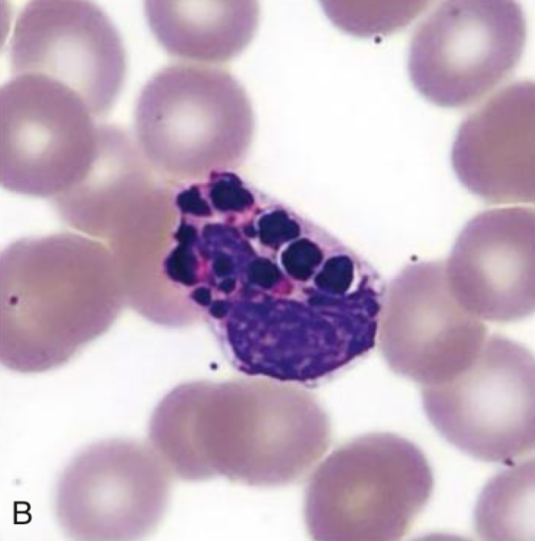
Chediak-Higashi Syndrome
Leukocyte Adhesion Disorder (LAD)
Characterized by the presence of giant fused cytoplasmic granules/inclusions in leukocytes (granulocytes, monocytes,
and lymphocytes (NK and cytotoxic T cells)
Manifestations:
partial albinism (due to abnormal packaging of melanosomes)
severe recurrent bacterial infections
mild bleeding
Easy bruising
Progressive neurological impairment
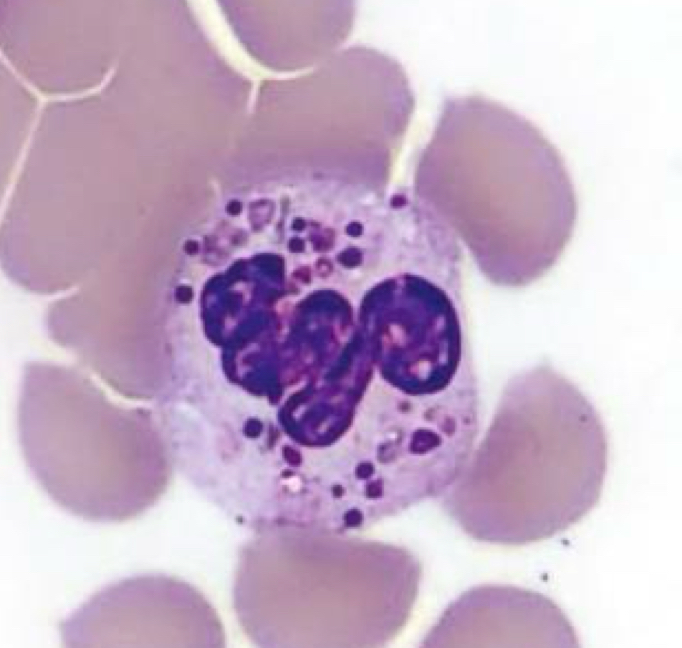
Neutrophil, Chediak-Higashi syndrome
Identify the cell and abnormality
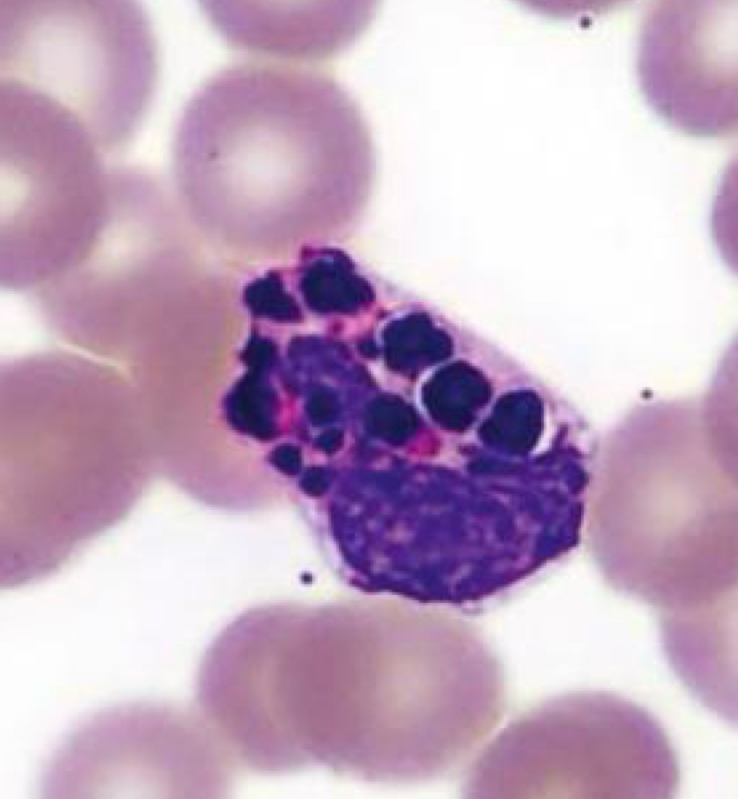
Basophil, Chediak-Higashi Syndrome
Identify cell and abnormality
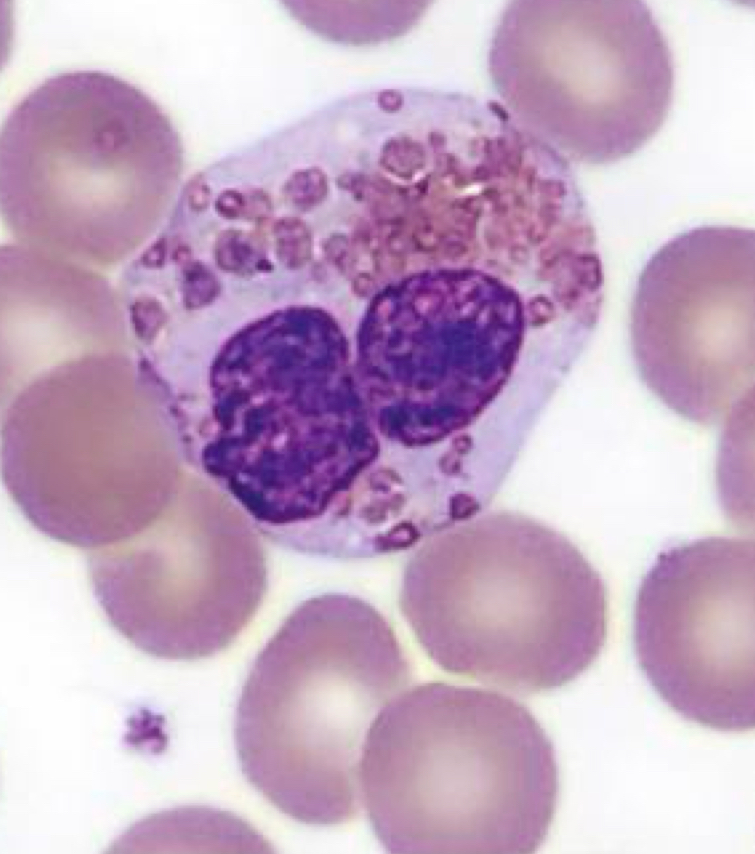
Eosinophil, Chediak Higashi Syndrome
Identify cell and abnormality
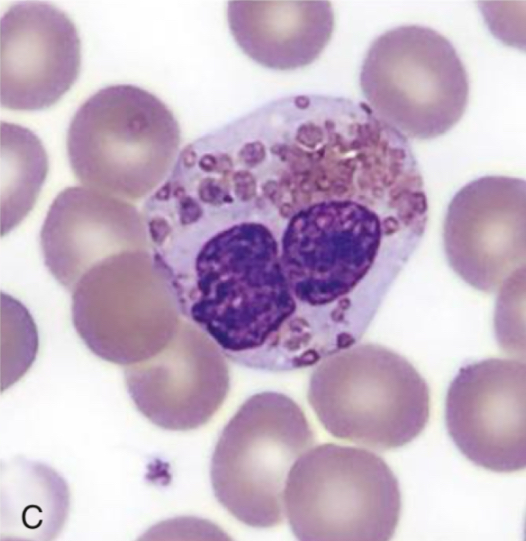
Leukocyte Adhesion Disorder/LAD
● Inability of neutrophils and monocytes to move from the peripheral circulation to sites of infections
● Manifestations:
○ recurrent infection
○ impaired wound healing
○ developmental abnormalities
○ increased bleeding risk
Leukocyte Adhesion Disorder Type 1
most common type
Nonneuropathic (-) cns disease
Neutrophils accumulate in peripheral circulation but cannot reach sites of infection in tissues due to adhesion problem
Life span: 6-80+yrs
Leukocyte Adhesion Disorder Type II
Decrease leukocyte adhesion to the vascular endothelium and impairs transmigration to sites of infection
From infancy
No skeletal abnormalities
acute neuropathic
Life span: <2yrs
Panerhnic
Leukocyte Adhesion Disorder Type III
Normal integrin expression but fail to respond to external
signals
subacute neuropathic
2-60yrs
Chronic Granulomatous Disease
Characterized by decreased ability of neutrophils, monocytes, macrophages, and eosinophils to kill phagocytized
bacteria and yeast
● Manifestations:
○ catalase-positive bacterial and fungal infections
○ colitis and granuloma formation in the GIT and GUT
● Screening test: dihydrorhodamine 123 or nitroblue tetrazolium test (NBTZ)
○ Positive: bite color (normal phagocyte function)
○ Negative: colorless (CGD)
● Confirmatory test: DNA sequencing
NADPH oxidase deficiency
Defect in the respiratory burst and production of antimicrobial superoxide anions and other reactive oxygen species
(H203, hypochlorous acid, etc.) = ?
dihydrorhodamine 123, nitroblue tetrazolium test
Screening tests for CGD
Myeloperoxidase Deficiency
● Most common inherited disorder of phagocytes
● Decreased MPO production
● Most individuals are asymptomatic
● Neutrophils has a normal morphology
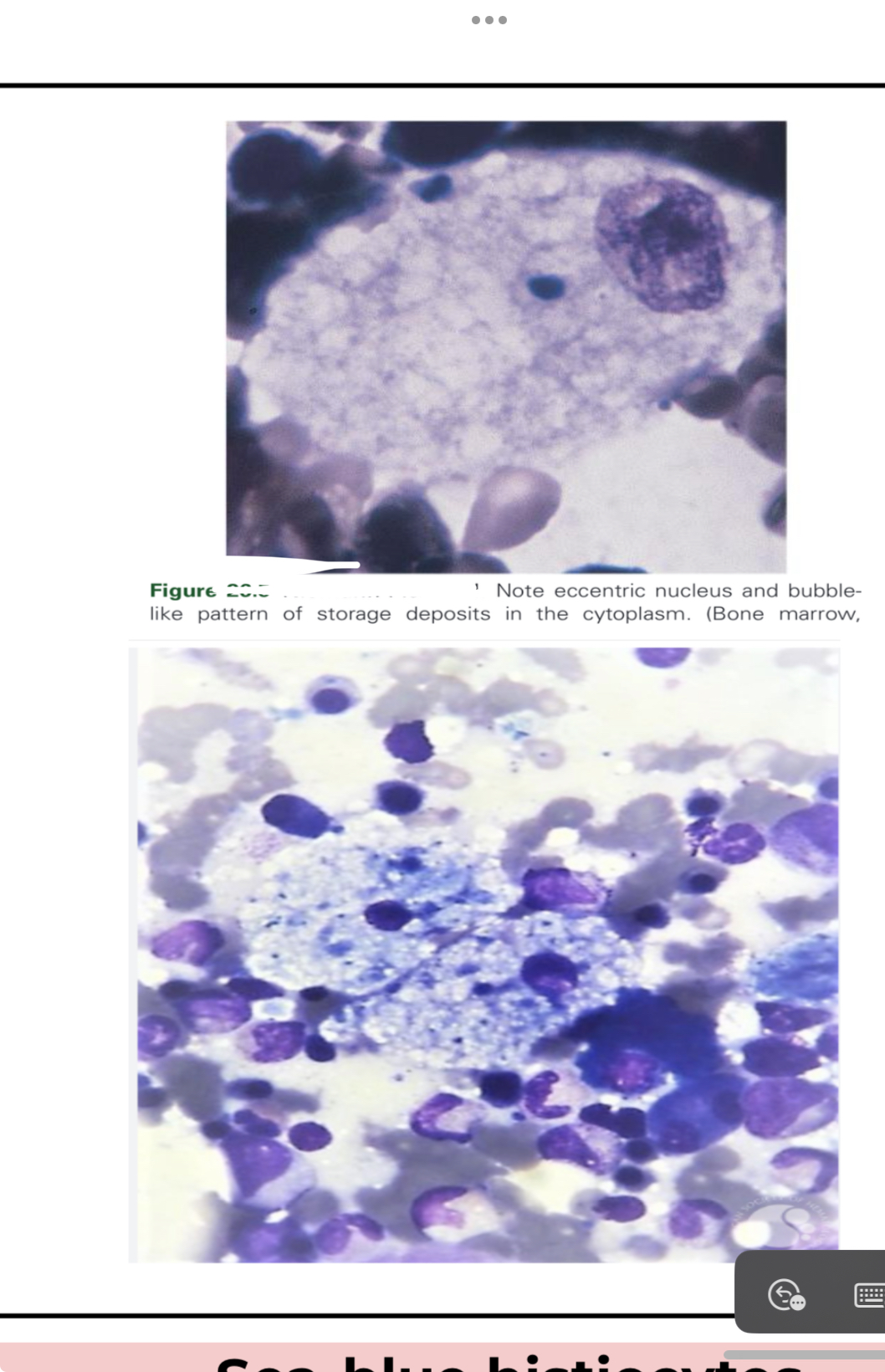
Gaucher Disease
● Most common lysosomal storage disorder
● Defect or deficiency in the catabolic enzyme
B-glucocerebrosidase (necessary for glycolipid
metabolism)
● Unmetabolized substrate sphingolipid
glucocerebrosidase accumulates in the lysosomes
of macrophages throughout the body, including
microglia (CNS) and osteoclast (bone)
● Found in:
○ Spleen
○ Liver
○ Bone marrow
● Lysosome-engorged macrophages with eccentric
nucleus
● Fibrillar blue-gray cytoplasm with a striated or
wrinkled appearance (onion skin-like or
crumpled tissue paper)
● Stain positive with:
○ PAS
○ ACP
○ trichrome
○ aldehyde fuchsin
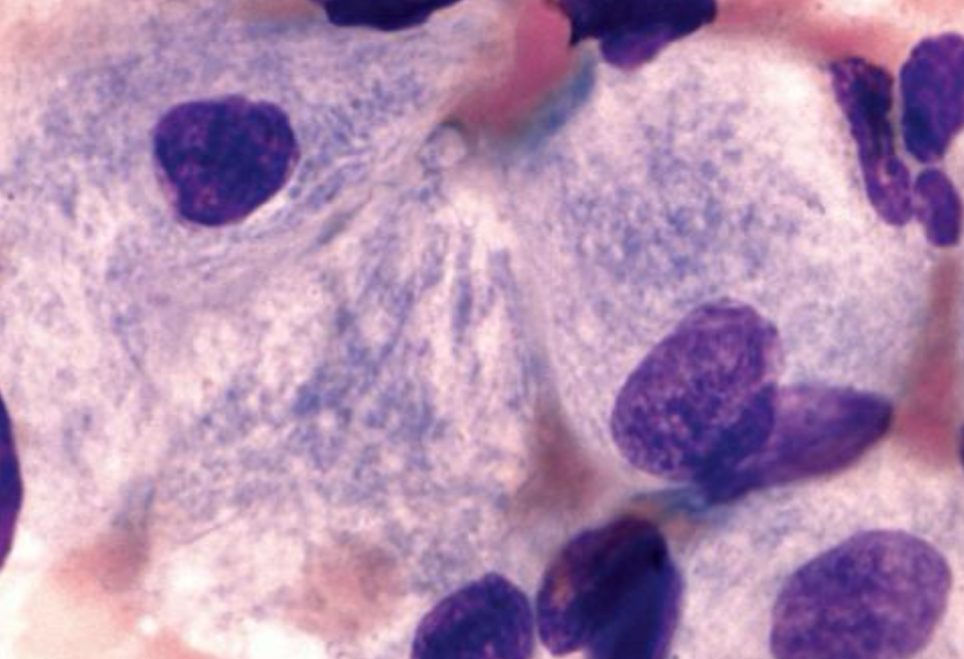
Pseudo-Gaucher cells
● Seen in patients with thalassemia, myeloid neoplasm,
ALL, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and plasma cell neoplasm
● Seen on cancer patients
● Composition: needle-like inclusion
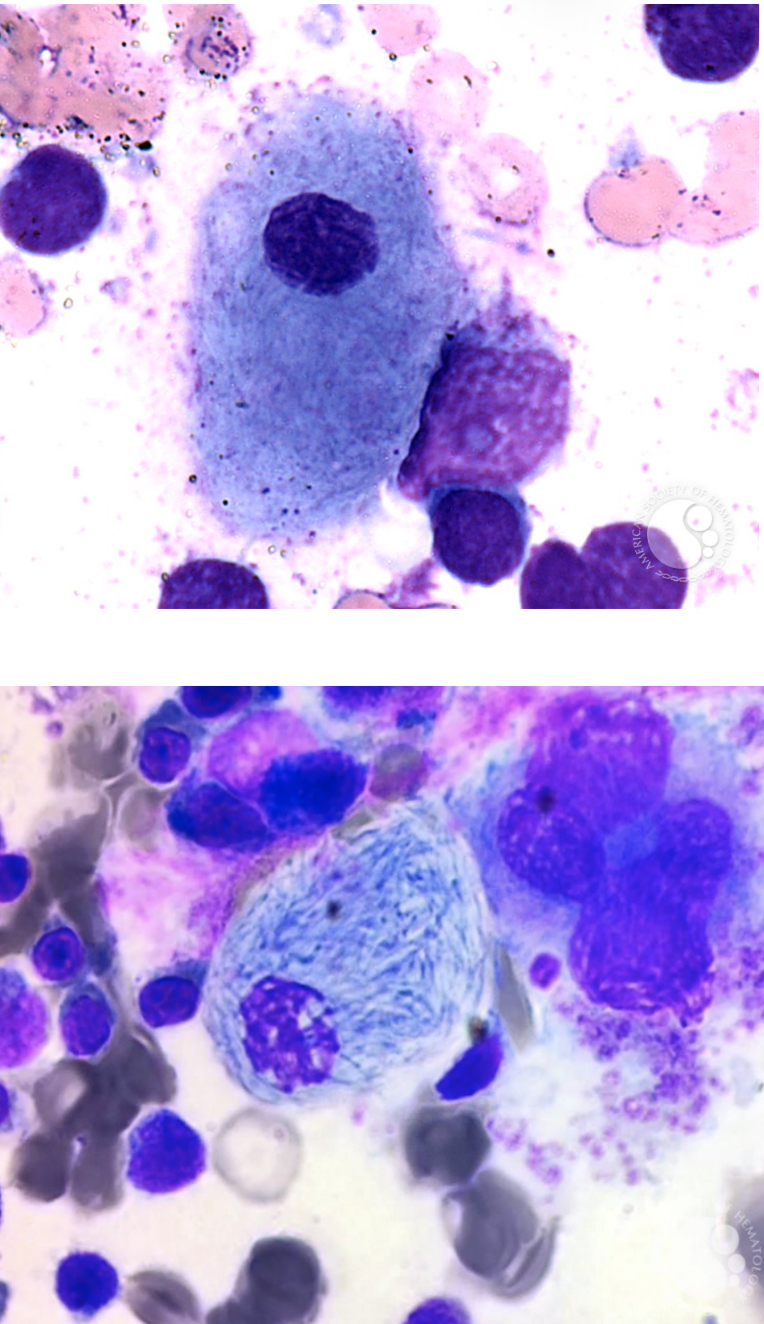
Niemann-Pick Disease
● Deficiency of lysosomal hydrolase enzyme acid
sphingomyelinase (ASM)
● Characterized by an accumulation of fat
(sphingomyelin) in cellular lysosomes of liver,
spleen, and lungs
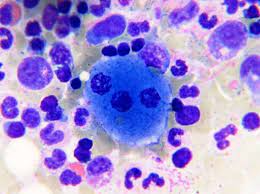
Foam cells
Macrophages with cytoplasm packed with lipid-filled lysosomes that appear as small vacuoles (foam)
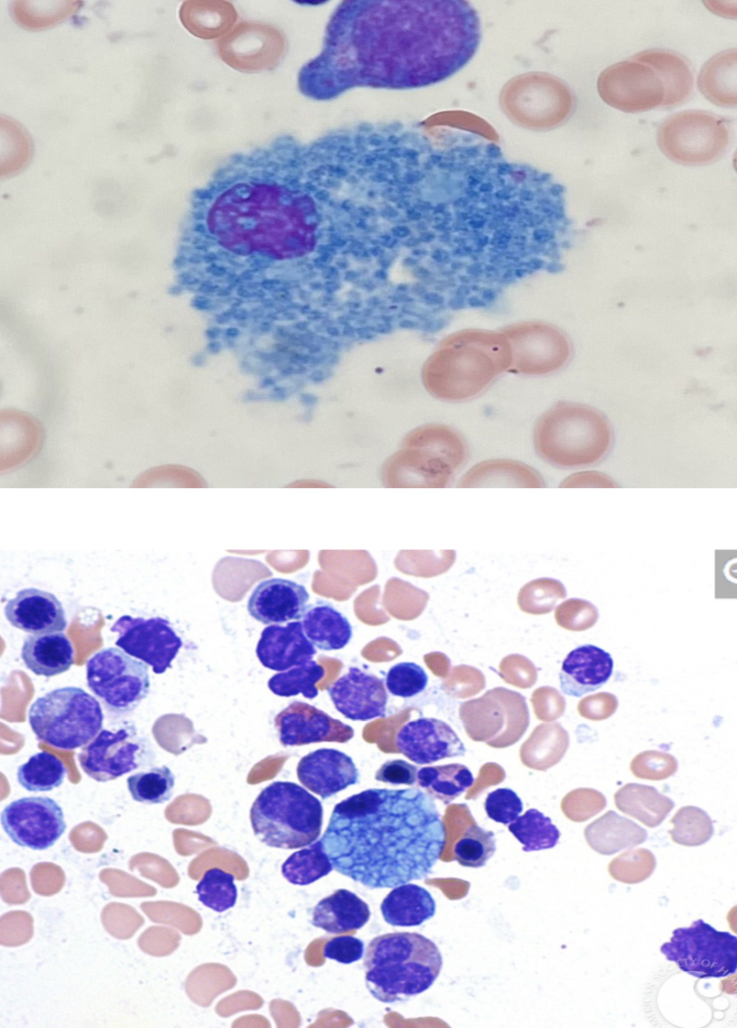
Sea-blue histiocytes
Macrophage filled with ceroid (of its cytoplasm) that appears blue on Romanowsky-type stain
Bruton Tyrosine Kinase Deficiency
caused by a mutation in the gene encoding BTK (Xq21.3-Xq22)
leads leads to marked reduction in B cells, Absent tonsils and adenoids, inability to produce plasma cells
Clinical manifestation after 3-18 weeks
Recurrent otitis, conjunctivitis, diarrhea, sinus, and skin infections
Chromosome 1q42.3
Caused by a mutation in lysosomal trafficking regulator (LYST) gene