7th grade review - Science TEKS
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
Unicellular
organisms that are made up of only one cell
Multicellular
organisms made up of many cells
Homeostasis/Equilibrium
the body's way of adjusting to different conditions and keeping the conditions balanced
Adaptations
genetic traits or behaviors that change to allow organisms to survive in the new environment (different types of beaks)
Extinction
the loss of an entire species

Chromosome
contains information for specific genetic traits
Inherited Trait
a characteristic passed on from a parent to an offspring like eye or fur color
Assexual reproduction
reproduction in which a single parent produces offspring that are genetically identical to the parent (bacteria)
Sexual reproduction
2 parents pass genes for traits from the sex cells on to their offspring. Half come from the male and half come from the female
Ecosystem
the living and nonliving parts of an environment

Population
group of individuals of the same species that live in the same area

Habitat
the specific place in which an organism makes its home

Biotic
the living organisms in an ecosystem
Abiotic
nonliving, physical features of the environment, including air, water, sunlight, soil, temperature, and climate
Producers
organisms that make their own food

Primary Consumers
animals that get their energy from eating plants

Secondary Consumers
animals that eat primary consumer animals

Herbivores
animals that eat only plants
Carnivores
animals that eat only other animals
Omnivores
animals that eat both plant and other animals

Decomposers
Organisms that feed on dead plants and animals and release the chemical energy and nutrients in the dead plants and animals back into the environment
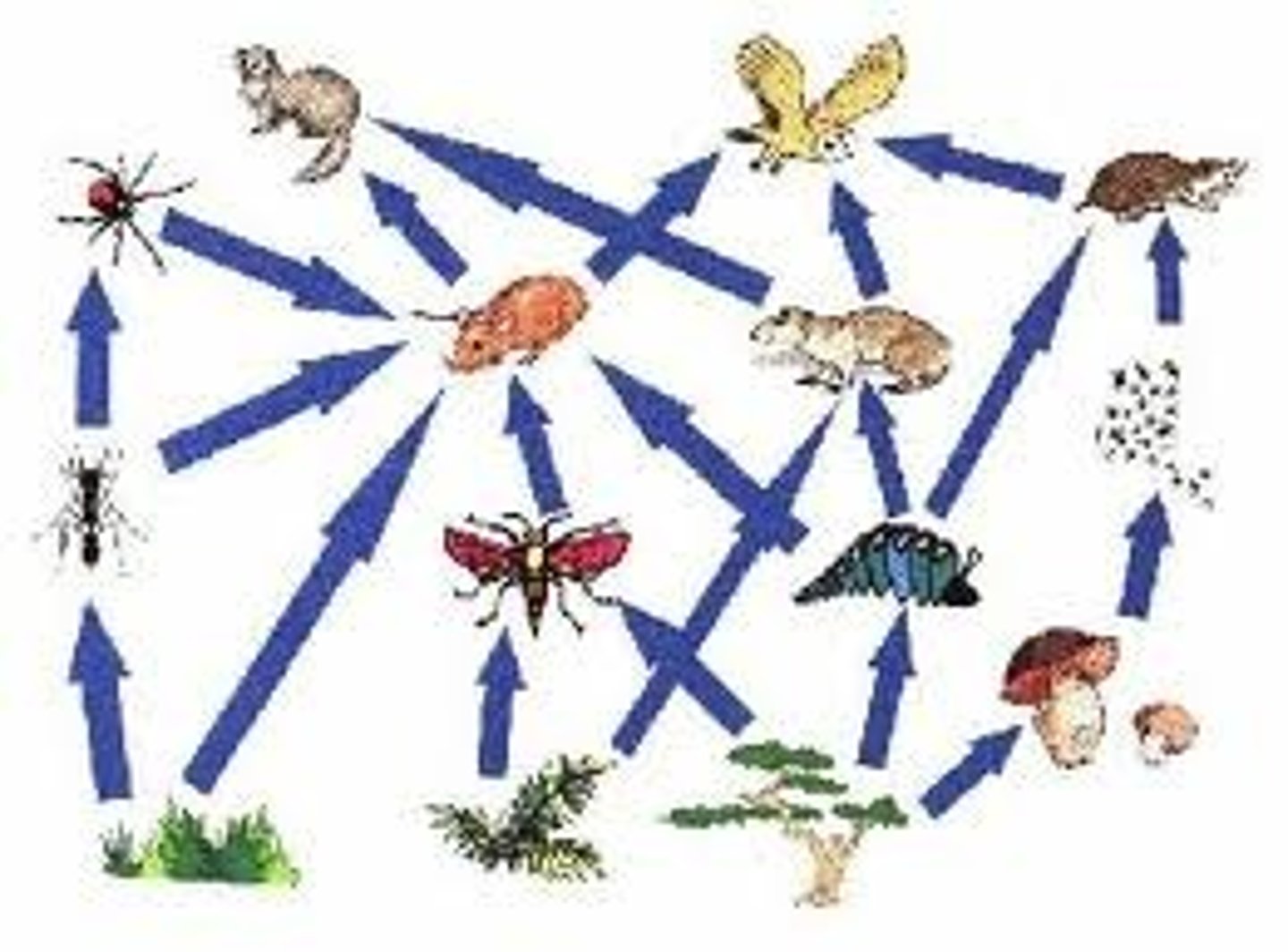
Food Chain
shows the flow of energy from one organism to another to yet another
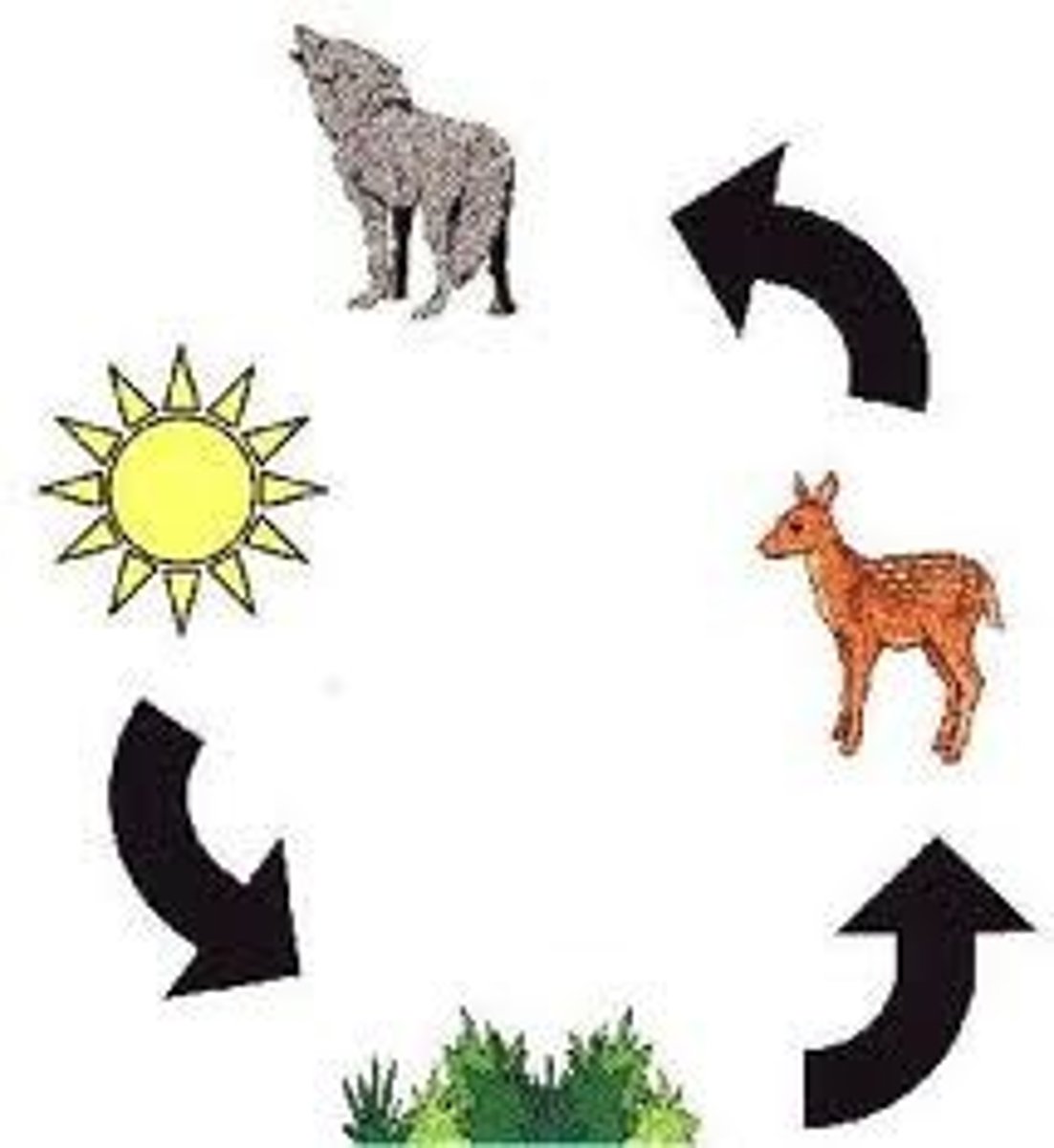
Food Web
A complex system of energy flow through overlapping food chains
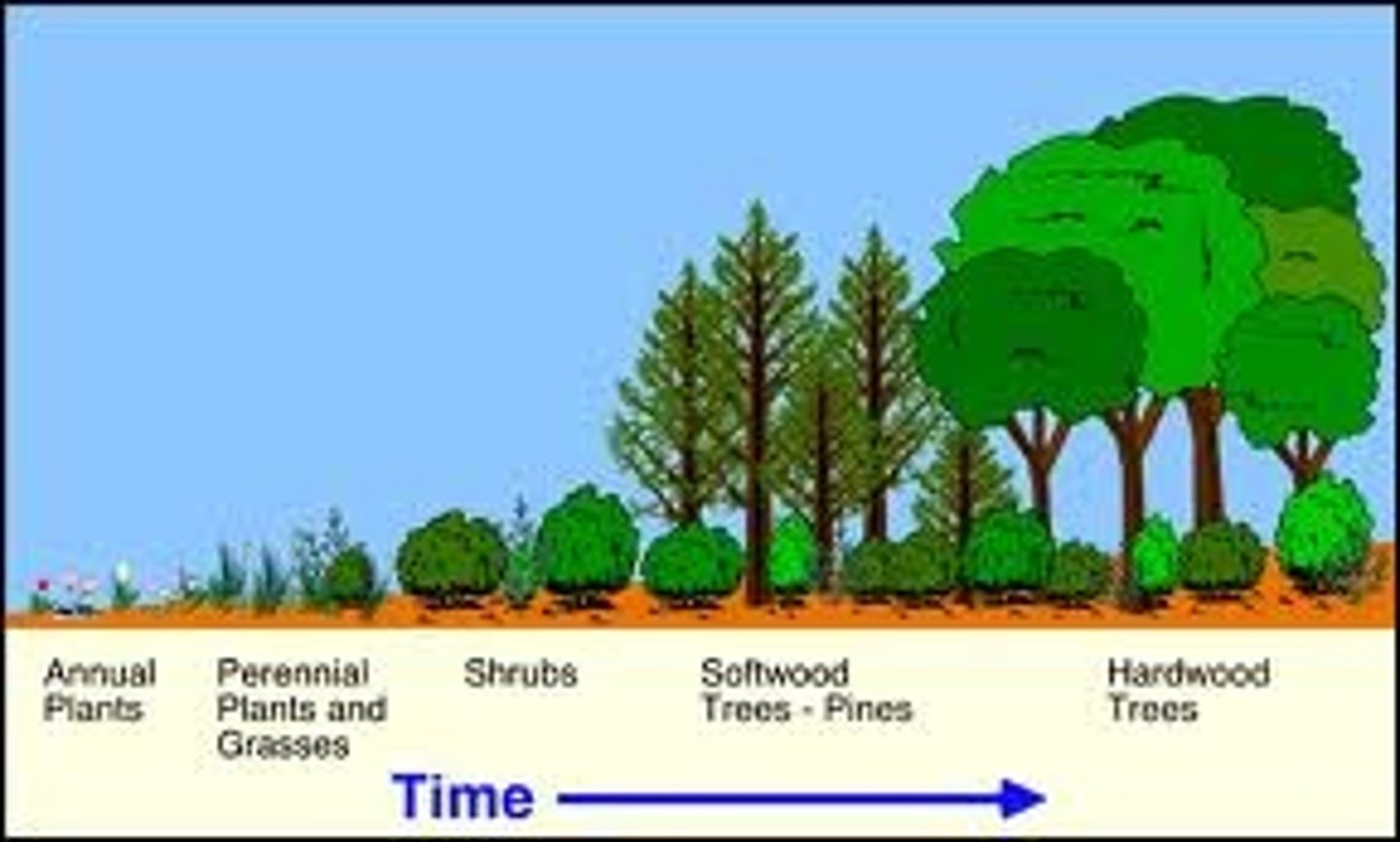
Succession
the rebuilding of populations in a community or ecosystem that has been changed due to events in the environment
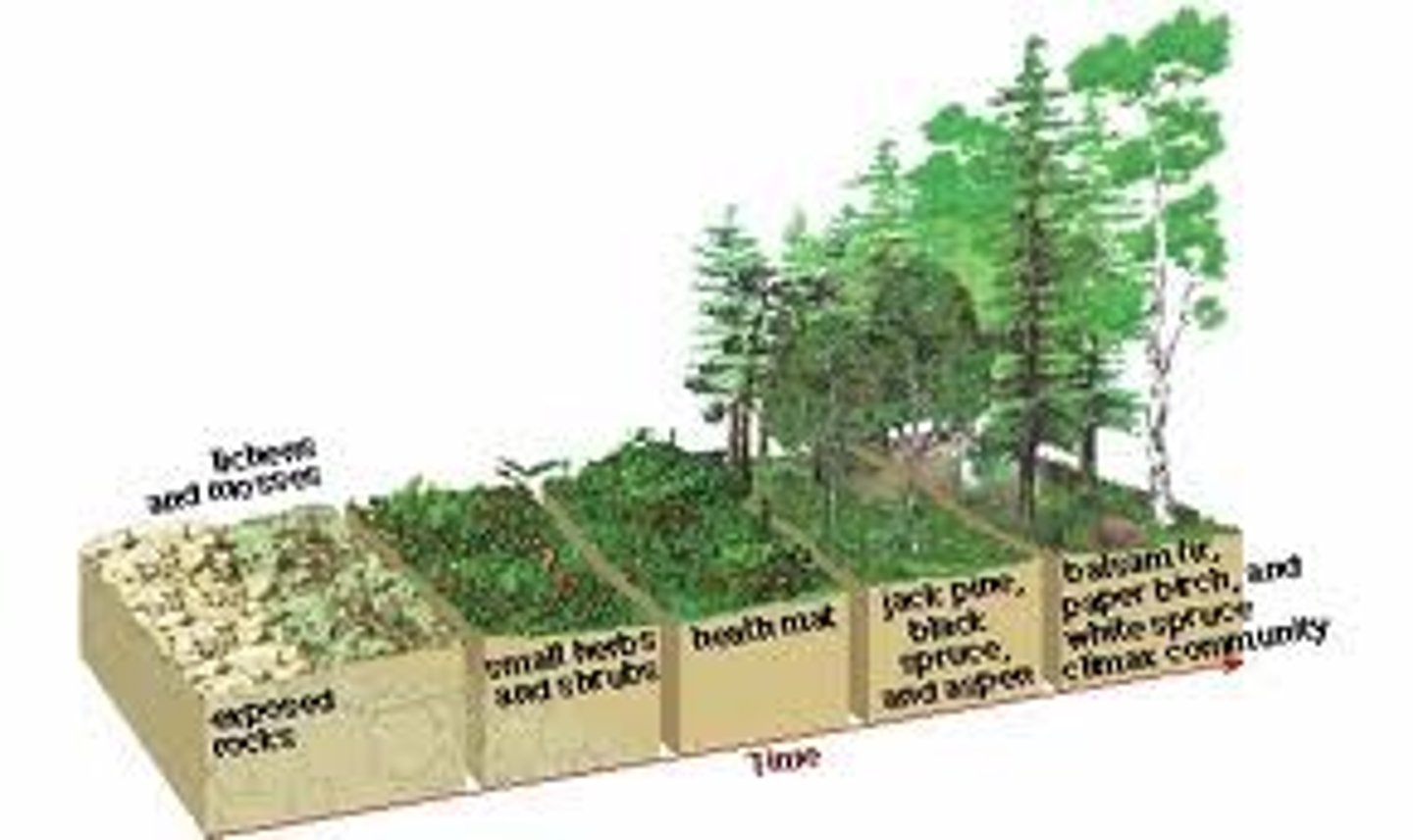
Primary Succession
succession that occurs on surfaces where no soil exists; lichens grow first on bare rock
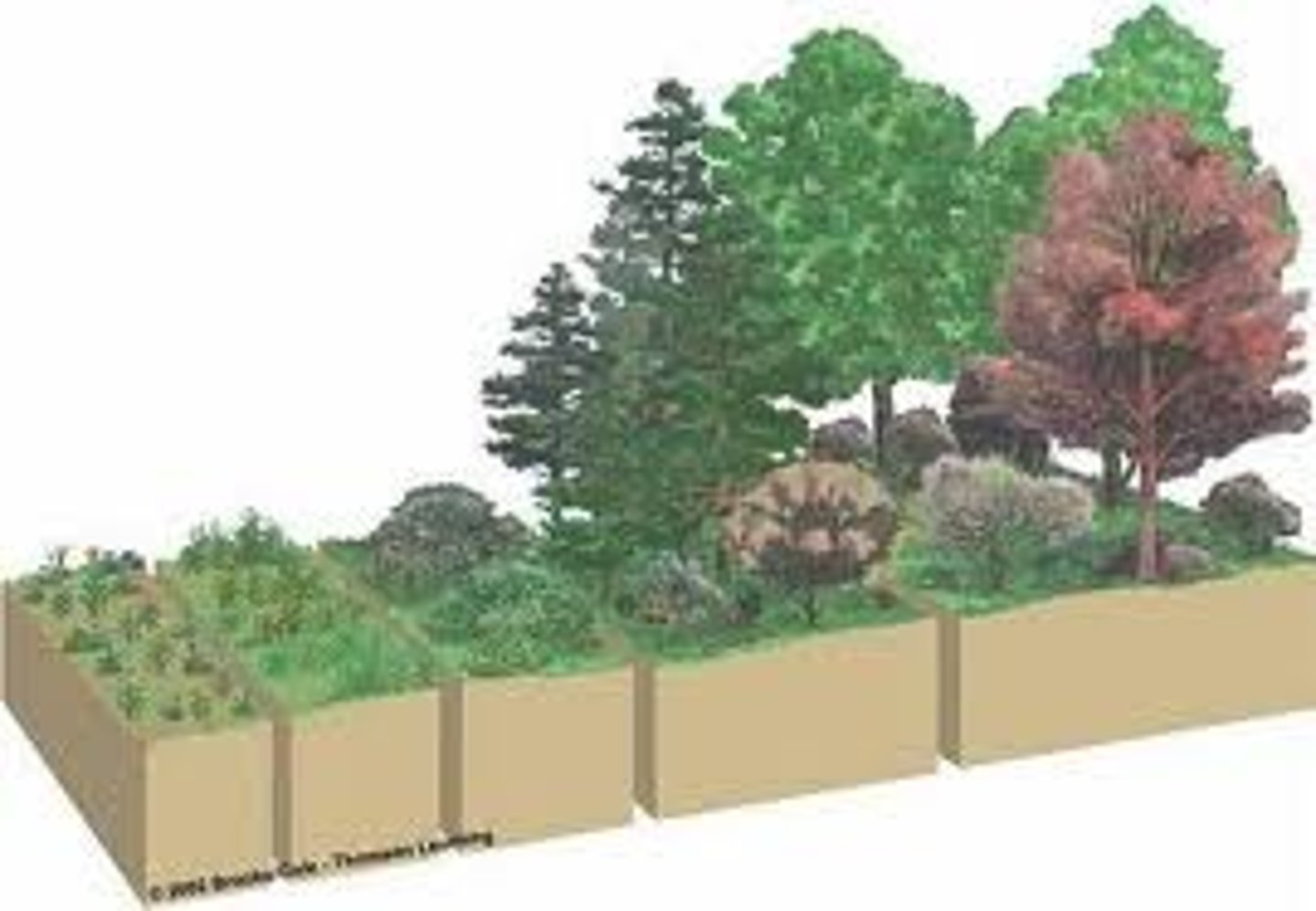
Secondary Succession
succession following a disturbance that destroys a community without destroying the soil
tissue
a group of similar cells that work together
Organ
made up of two or more tissues working together
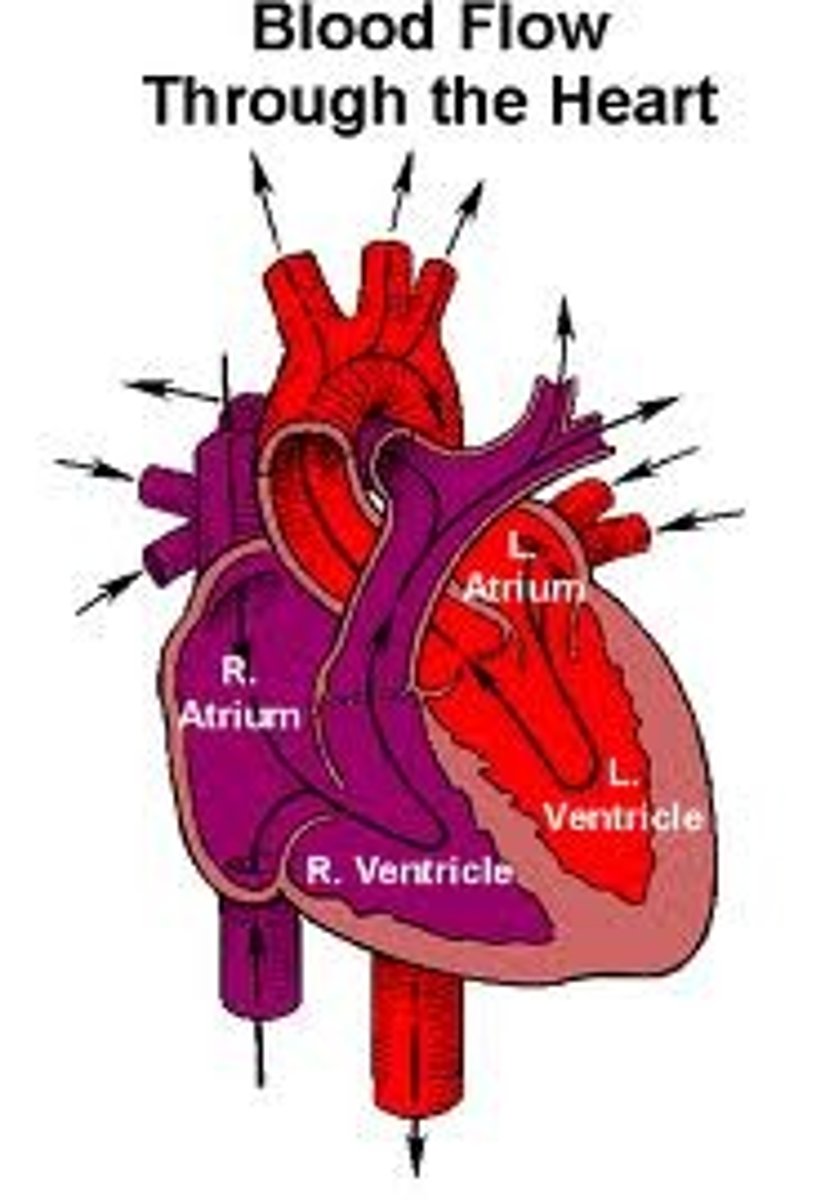
Organ system
a group of organs that working together to perform a specific function
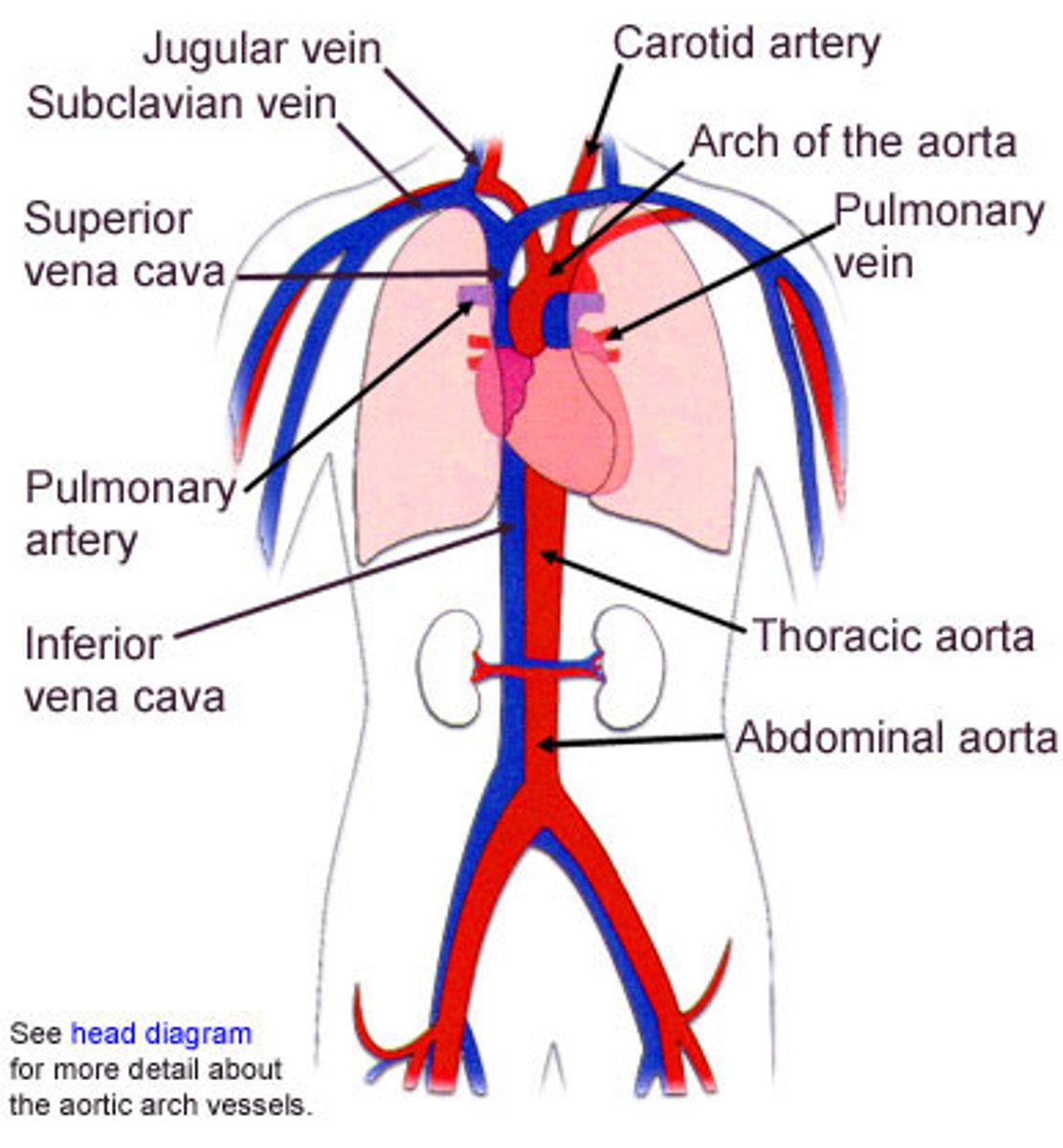
Organism
an individual living thing comprised of mutliple organ systems

Cells
basic unit of life that all organisms are made of
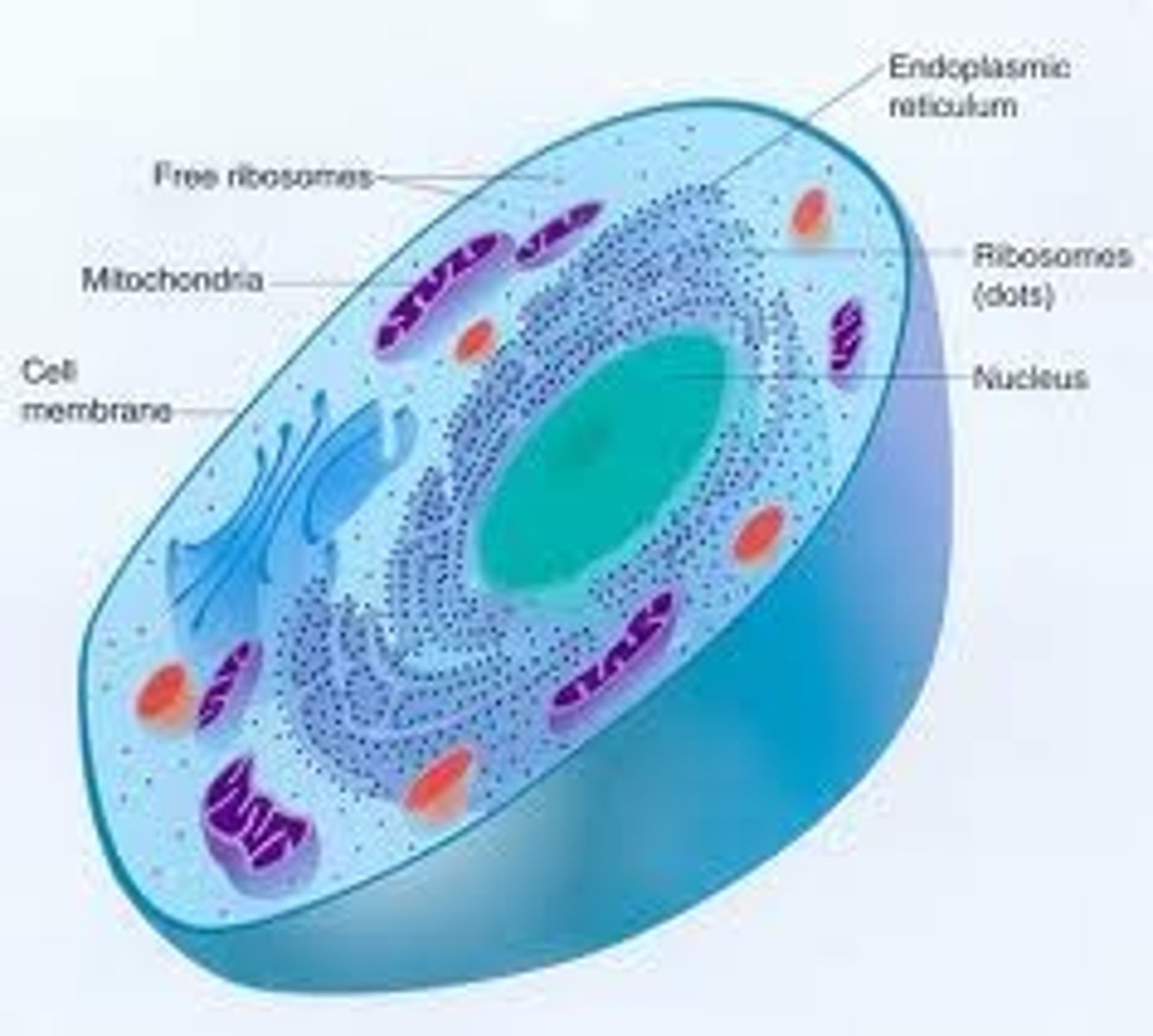
prokaryote
single-cell that does not have a nucleus (bacteria)
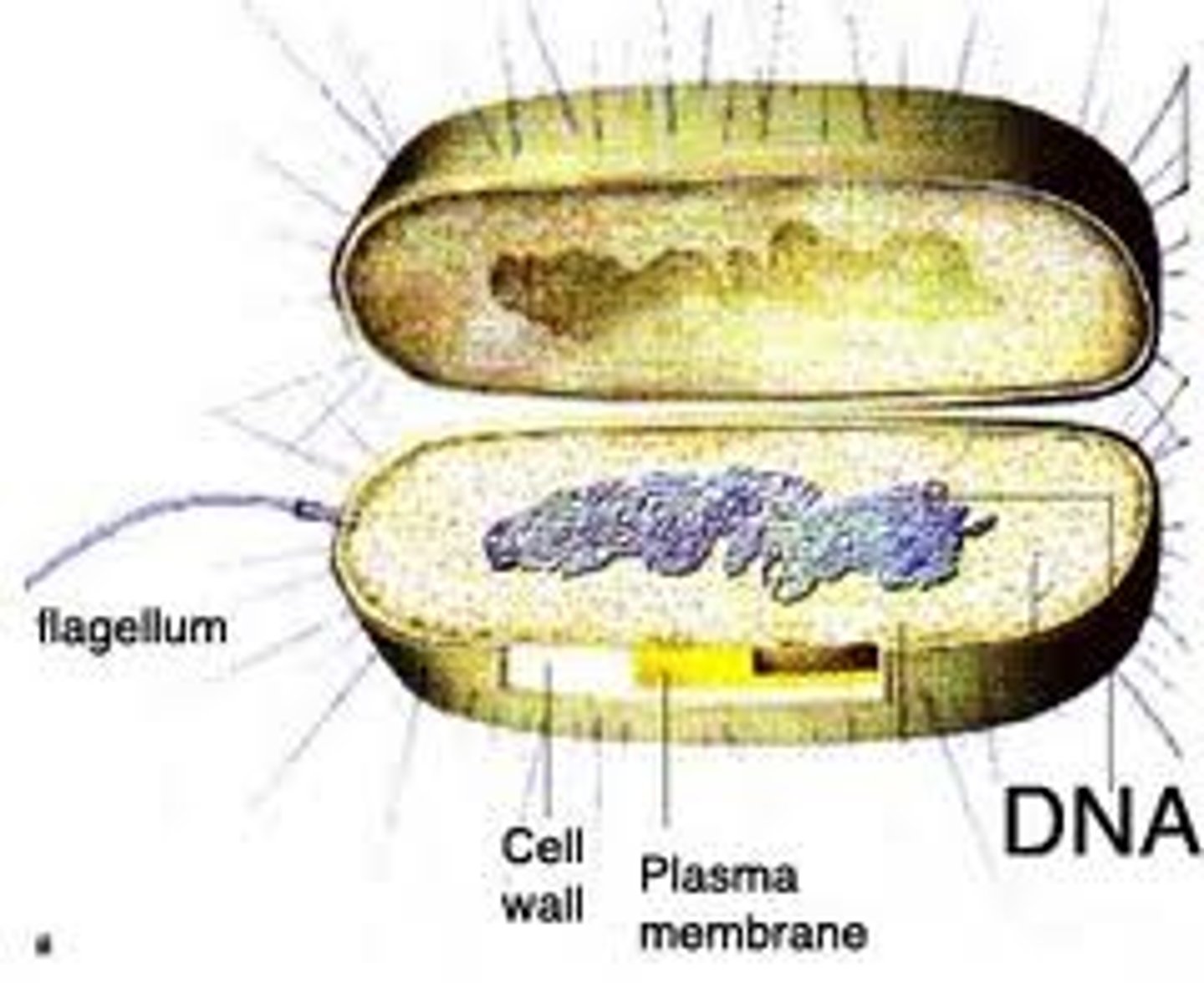
eukaryote
complex cell that contains a nucleus and organelles (humans and plants)
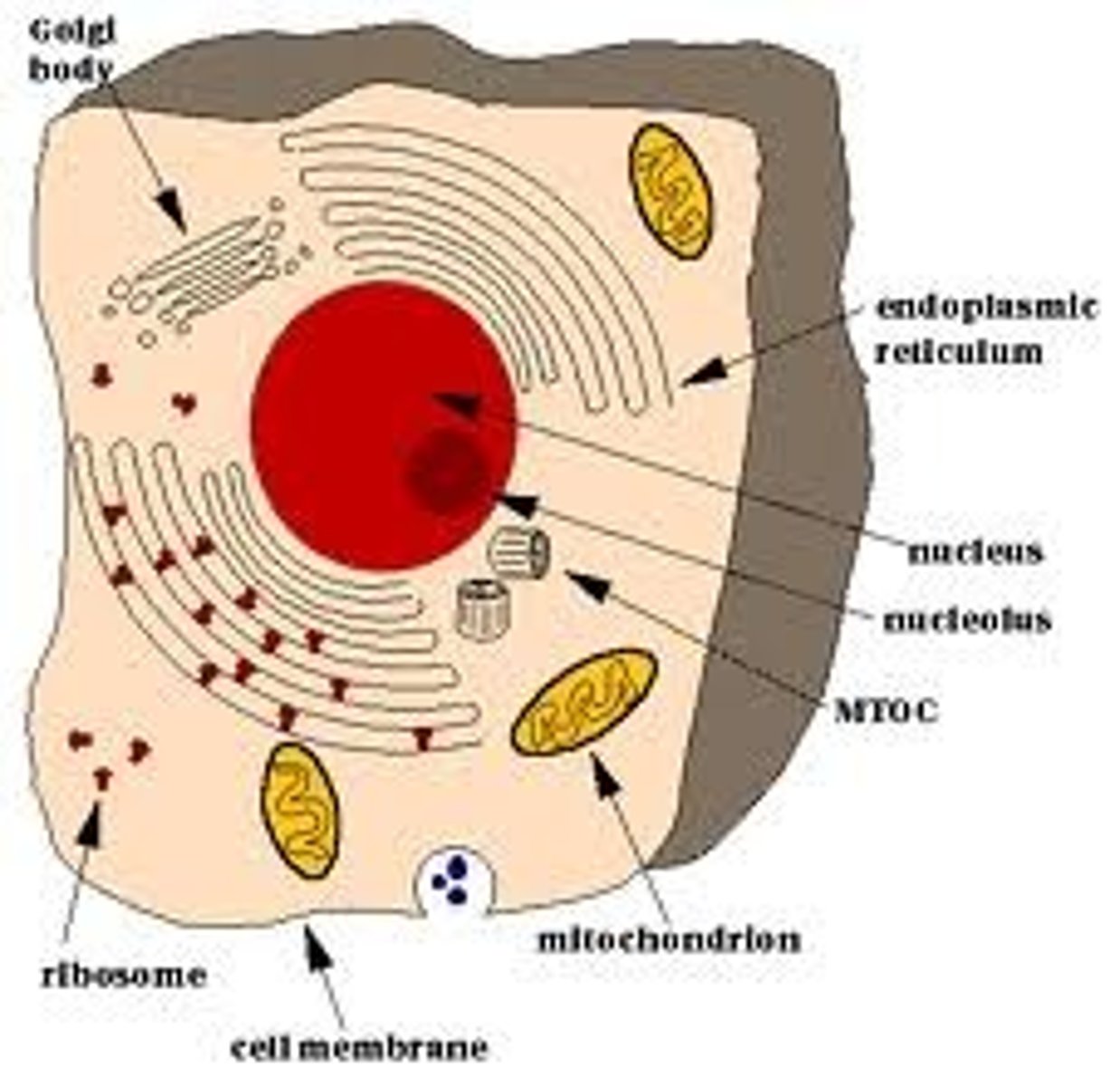
organelles
cell parts with a specialized functions
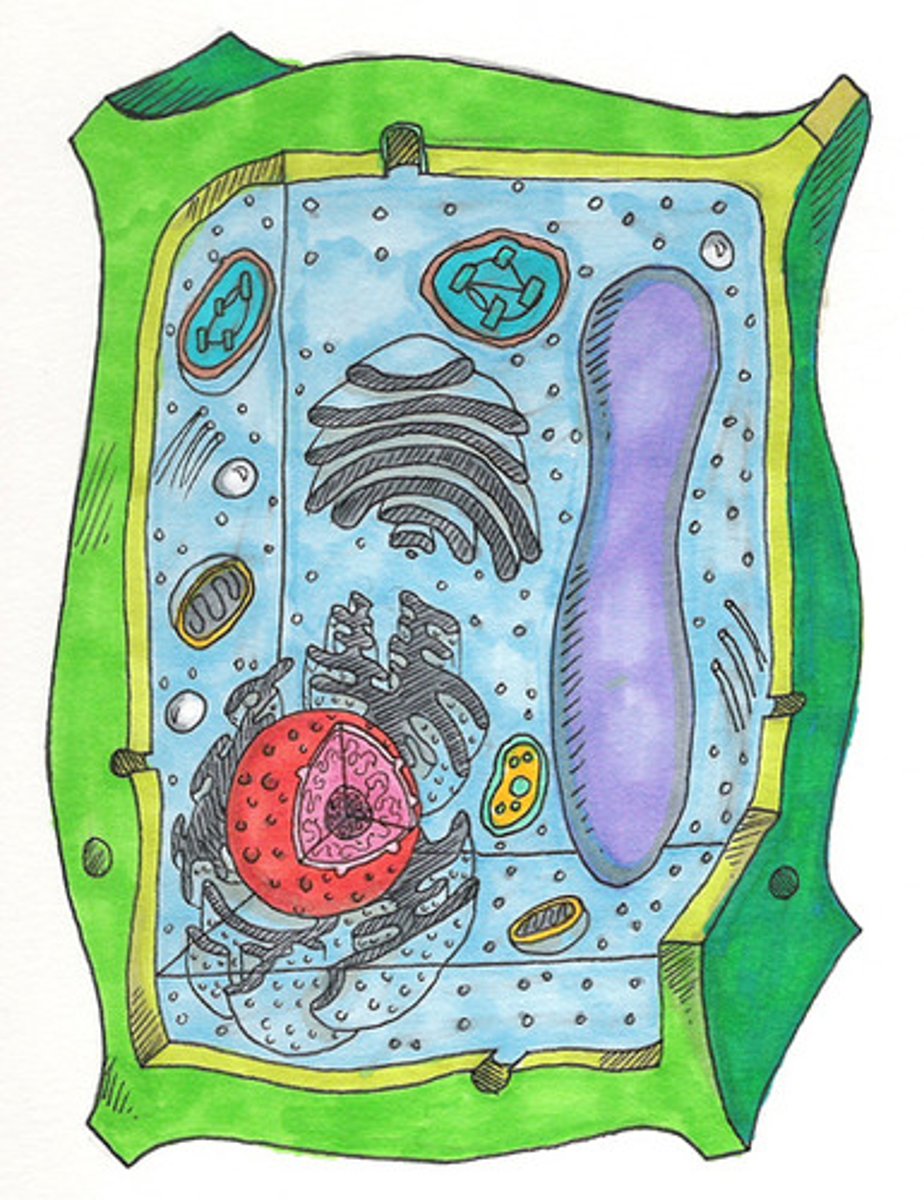
plant cell
contains a cell wall, chloroplast and large vacuole
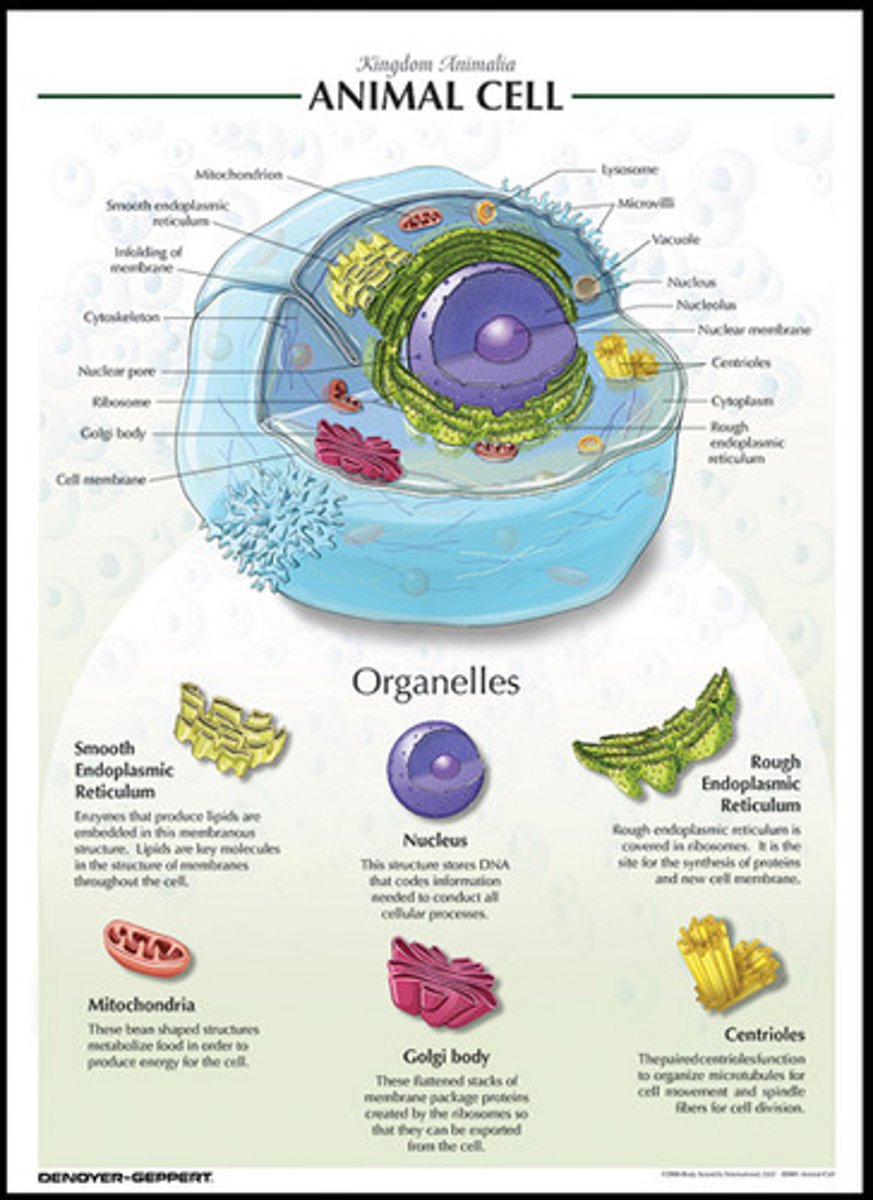
animal cell
does not have a cell wall or chloroplast but it does have a small vacuole
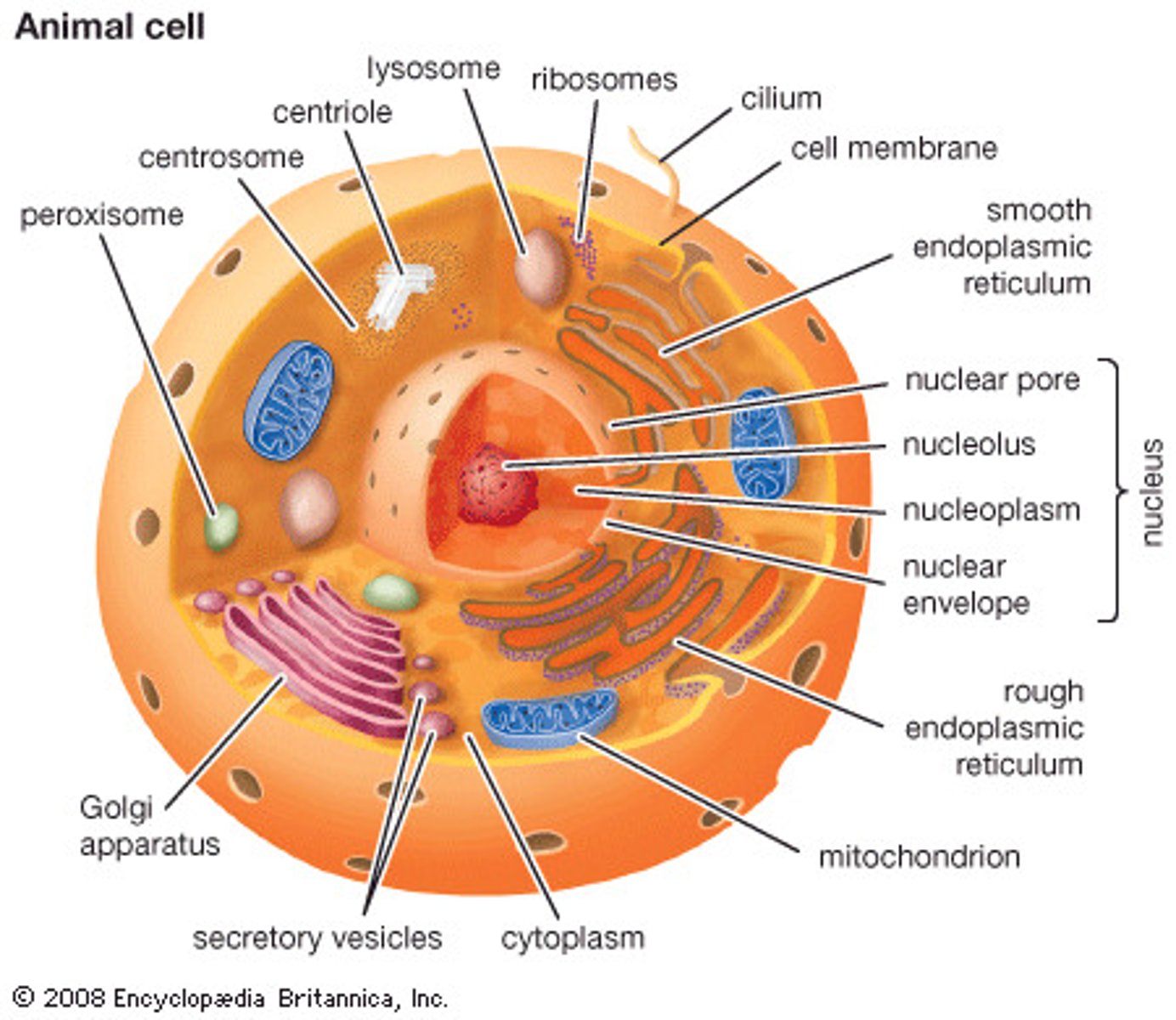
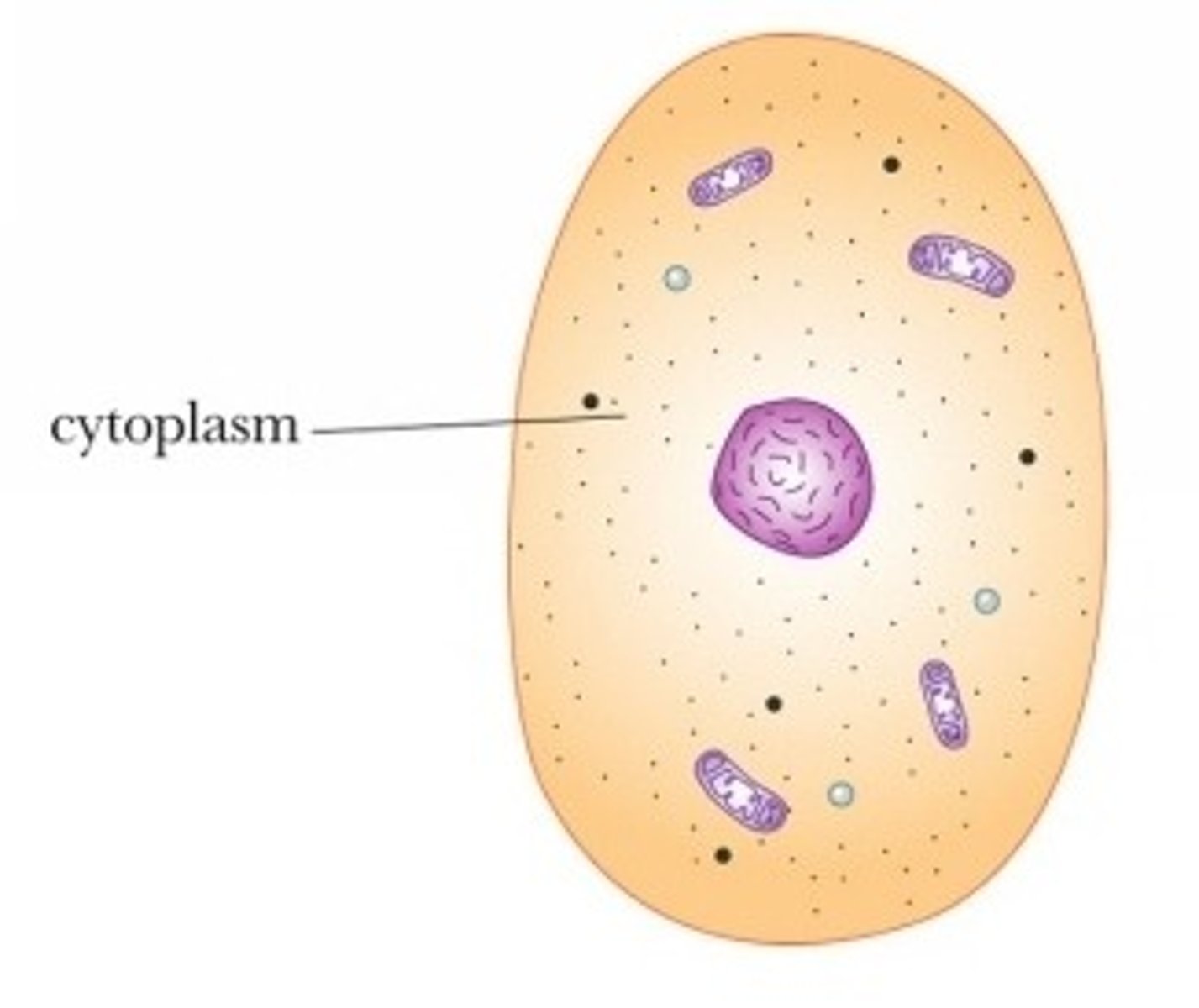
cytoplasm
jelly-like substance found in cells that the organelles float in
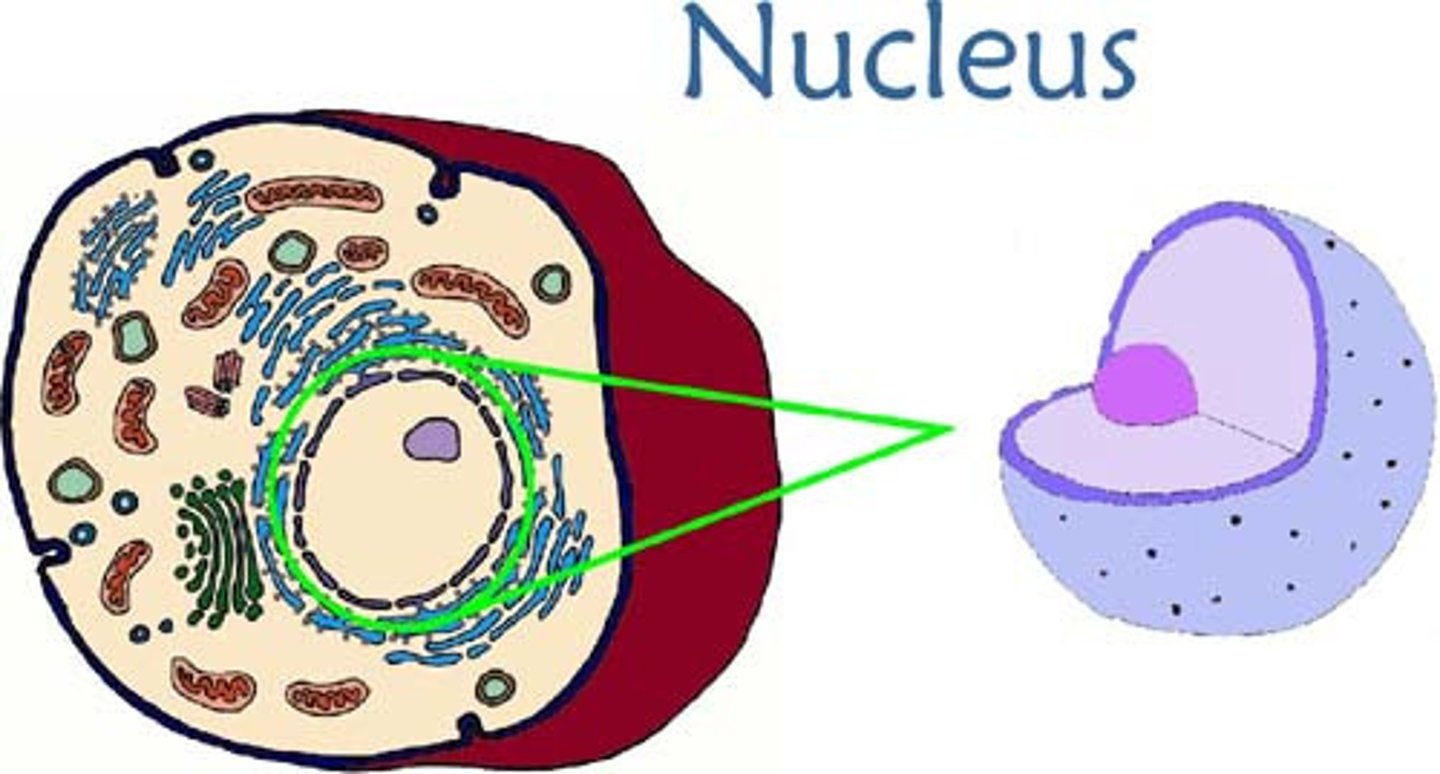
nucleus
organelle know as the control center of the cell; contains DNA
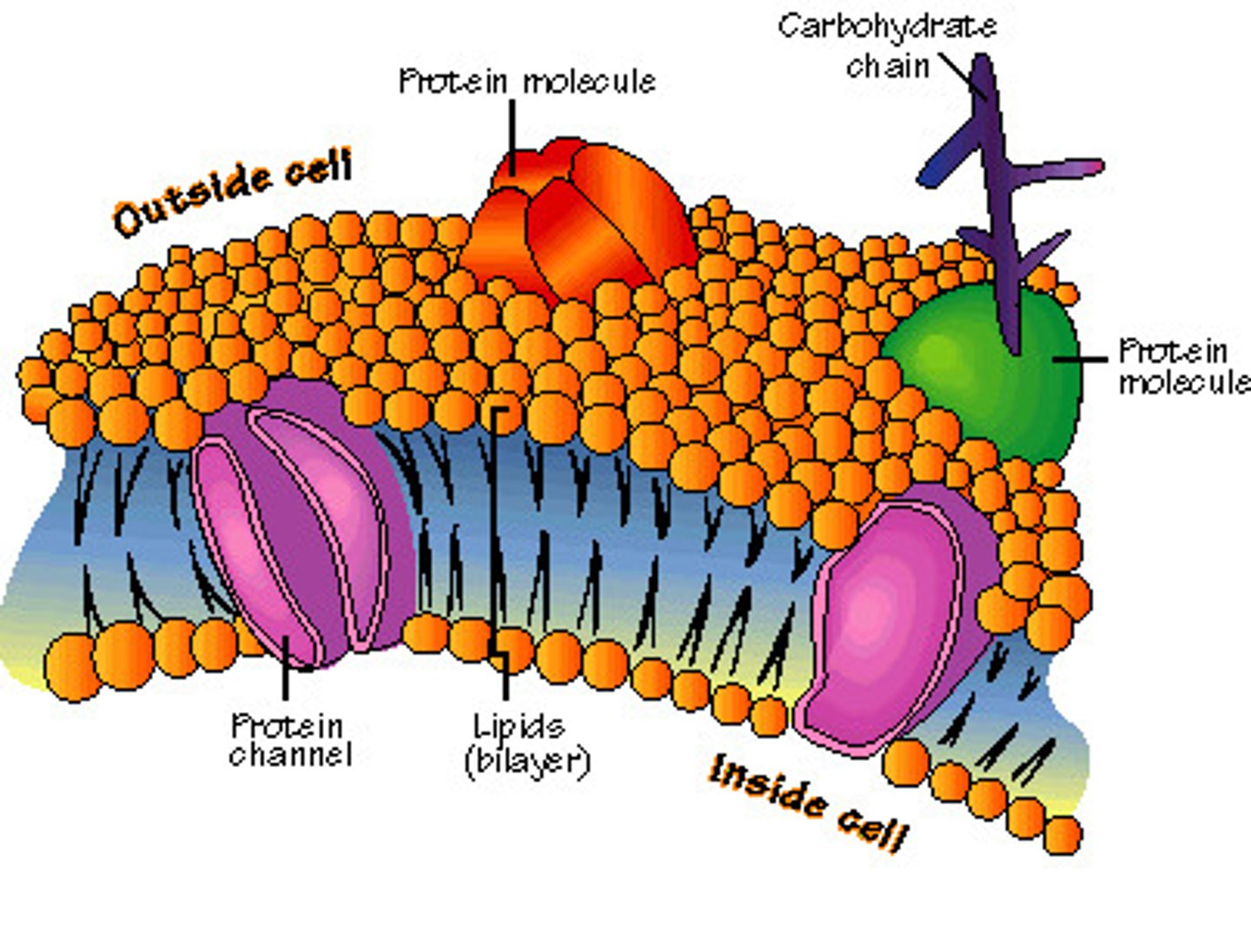
cell membrane
outer boundry of cell; protects and controls what can enter and leave
cell wall
provides support in plant cells
chloroplast
organelle where photosynethsis takes place in plant cells

mitochondria
organelle that produces energy in the cell
vacuole
organelle that stores water, nutrients and waste
circulatory system
transports nutrients, gases and wastes in blood
respiratory system
breathes in oxygen and removes carbon dioxide
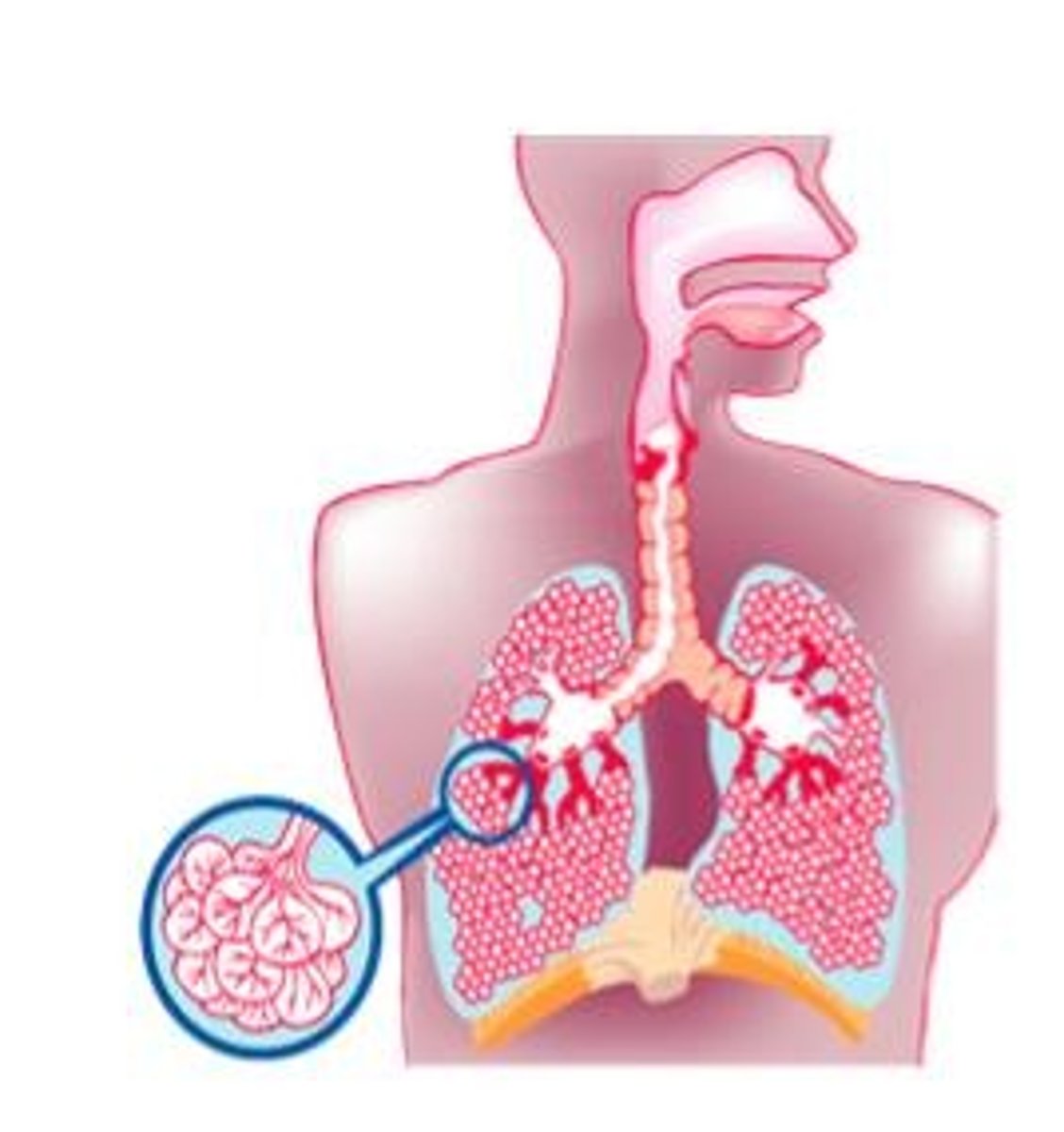
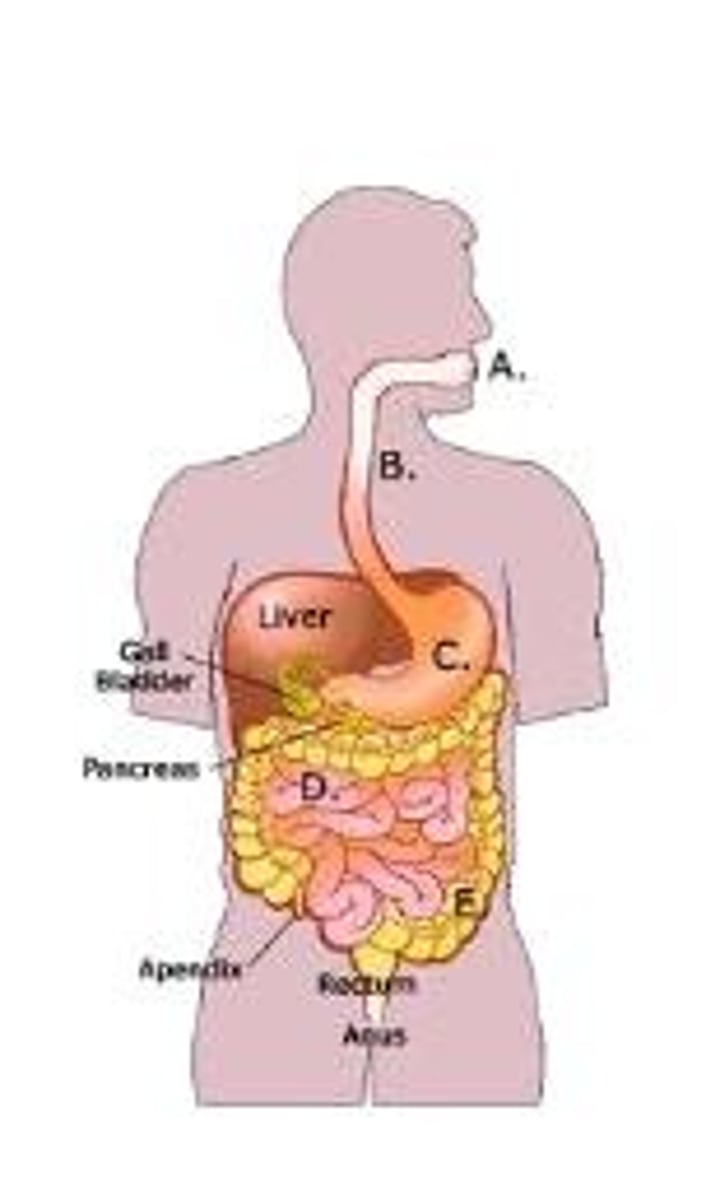
digestive system
breaks down food into units that can be absorbed by the body
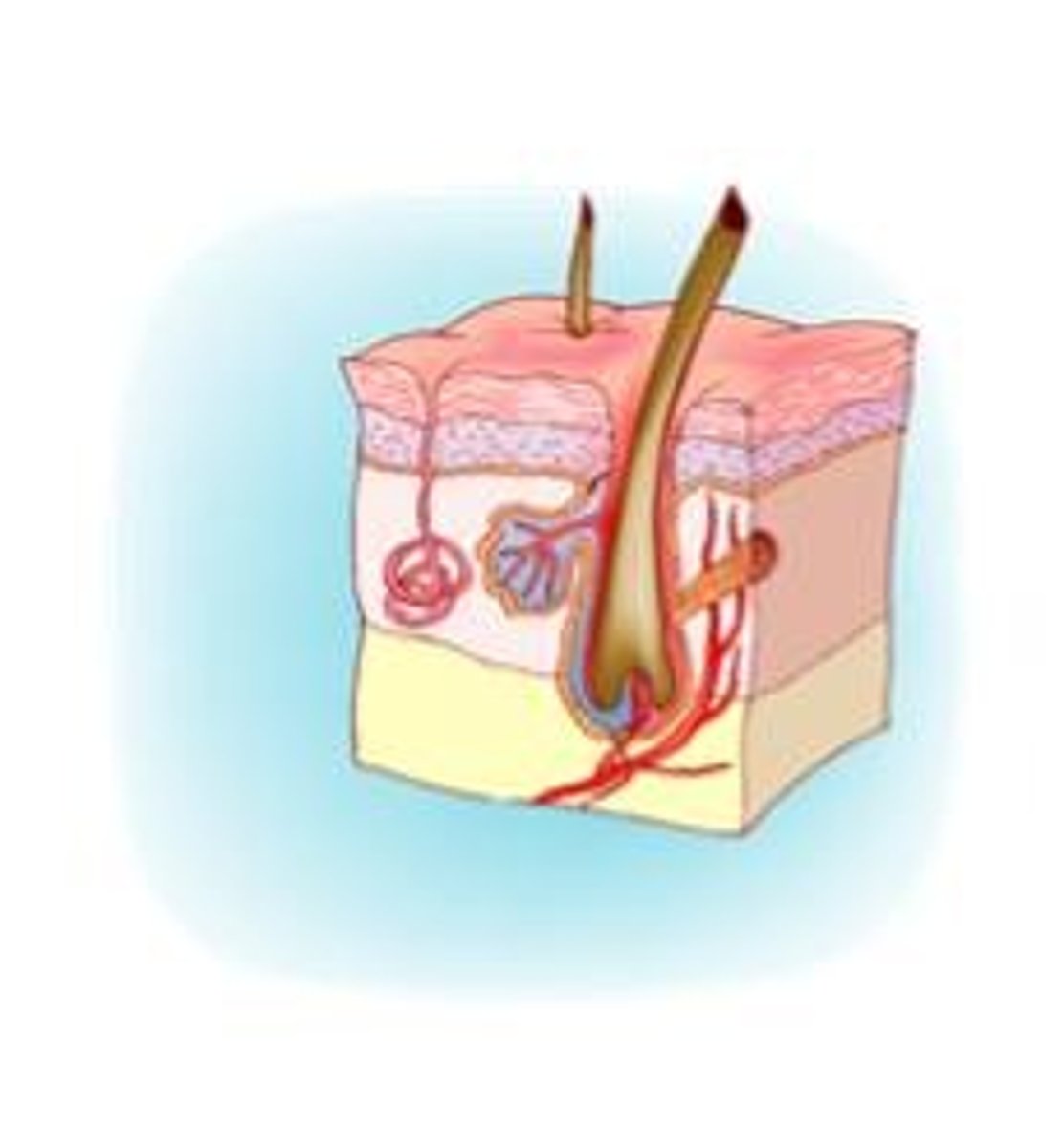
integumentary system
provides a protective barrier for the body
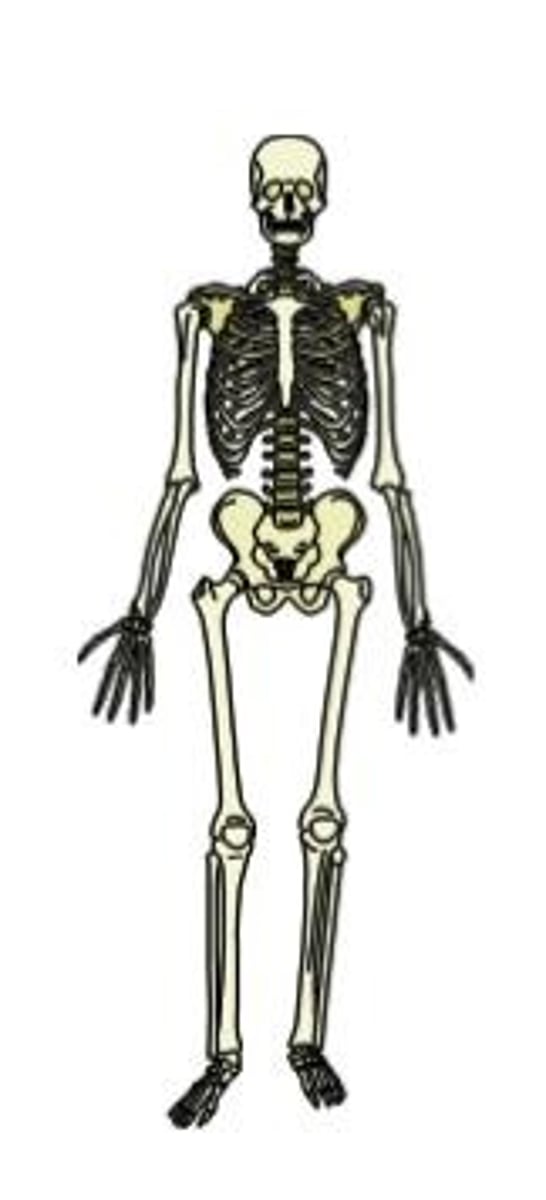
skeletal system
provides support for the body and protects major organs
muscular system
controls muscles and movements

nervous system
controls body activites with electrical signals
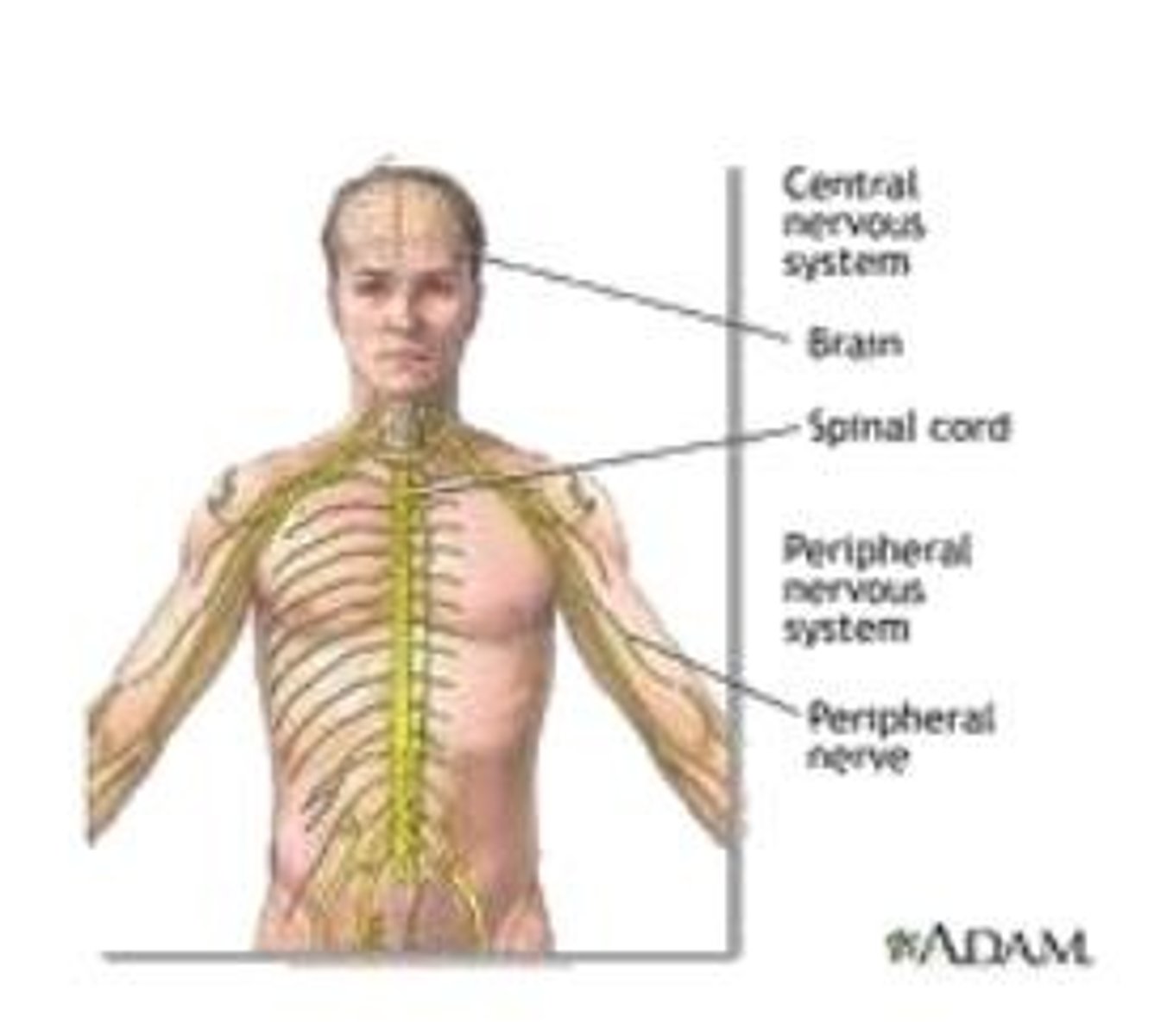
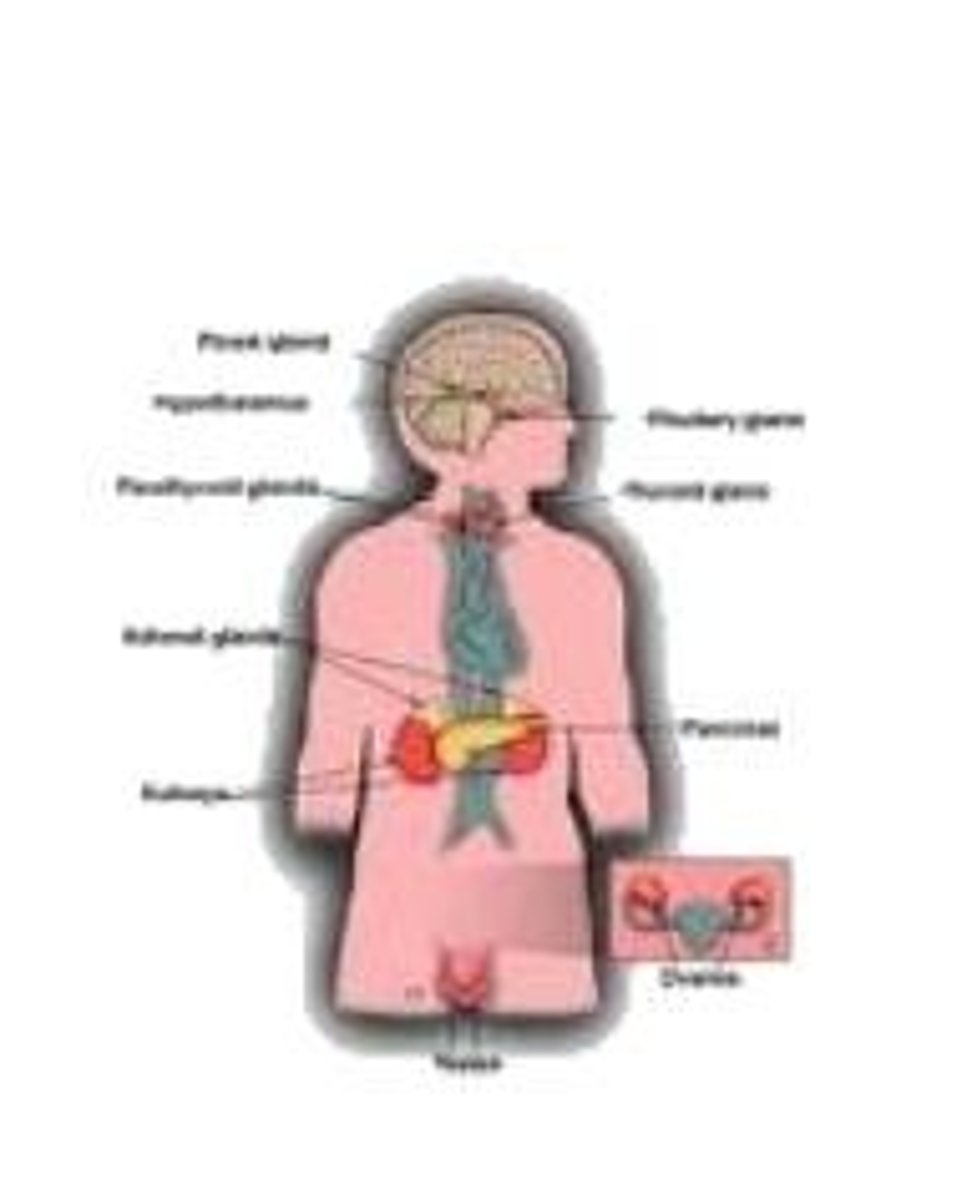
endocrine system
controls body activities with hormones
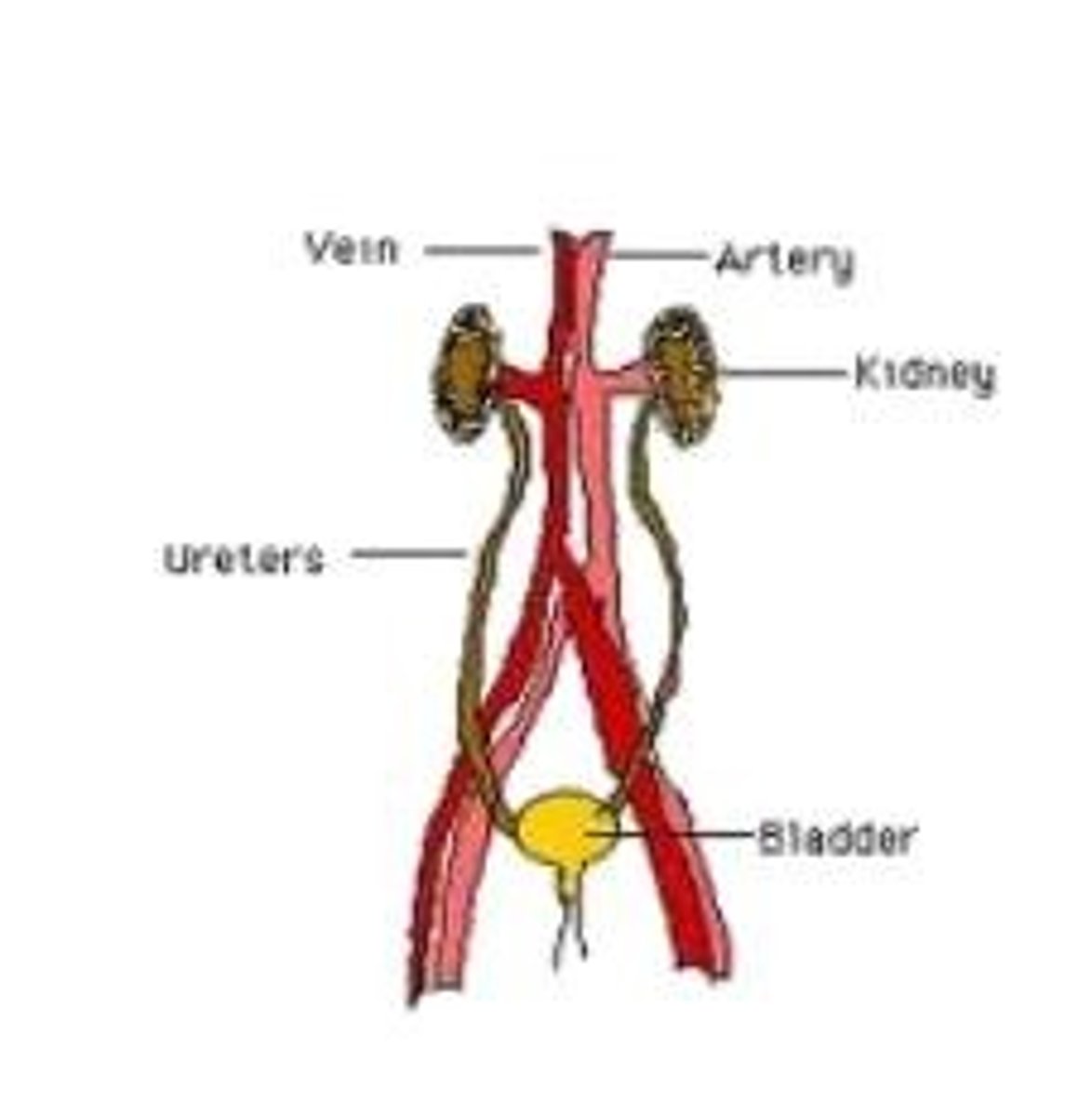
excretory system
removes waste from the body
Rainforest
a forest region located in the Tropical Zone with a heavy concentration of different species of broadleaf trees competing for sunlight

Marine Biome
covers 70% of earth's surface; largest biome; temperatures vary from region to region; algae and plankton form the base of the food chain

Predator
animal that hunts and eats other animals

Prey
animal hunted or caught for food

Parasite
an organism that lives on or in a host and causes it harm

Runoff
Water that flows across the land and enters rivers and streams. It eventually flows into lakes and the ocean

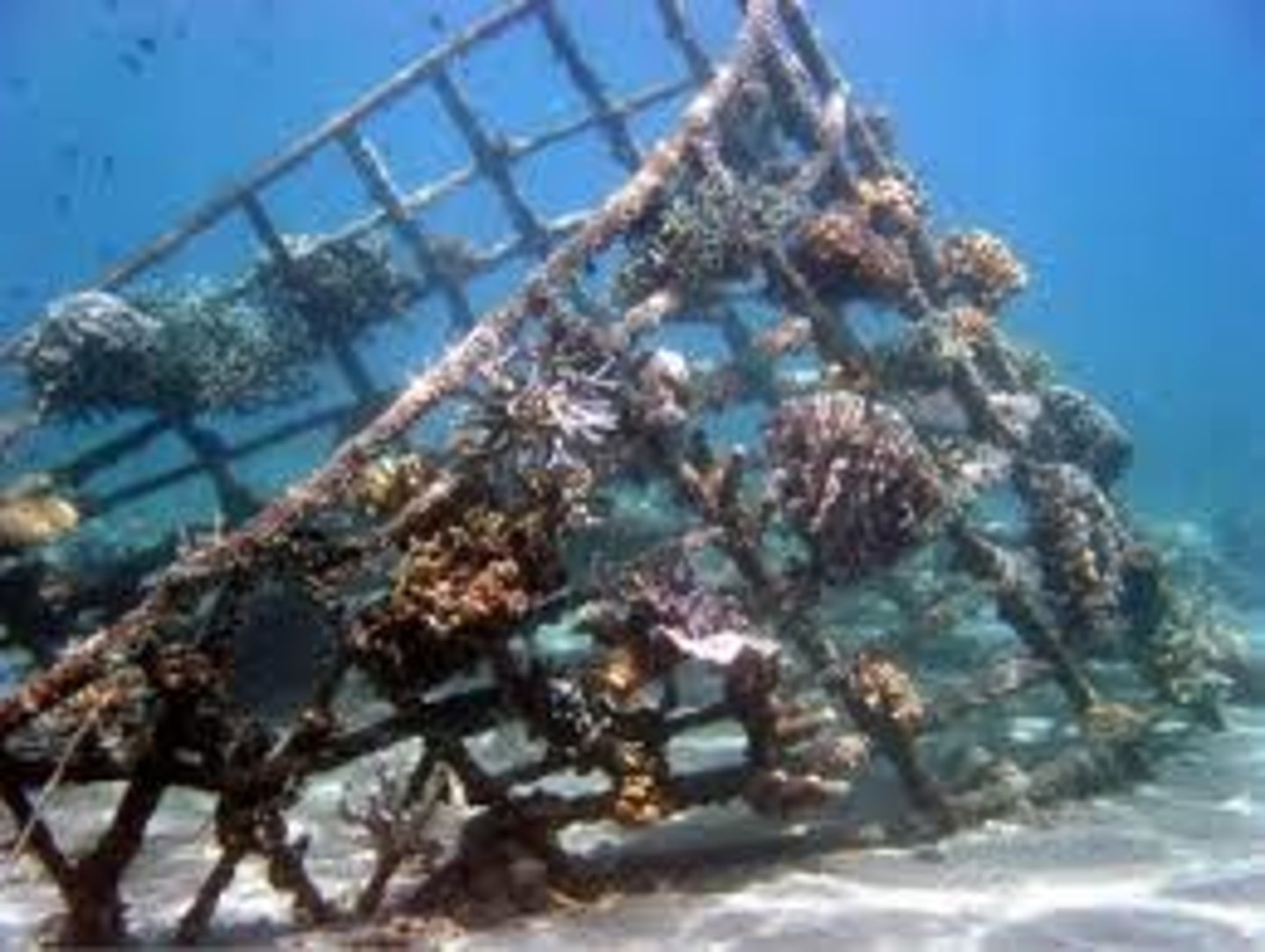
Artificial Reef
a man-made, underwater structure, typically built for the purpose of promoting marine life in areas of generally featureless bottom.

Overfishing
Removing more fish from the oceans than can be naturally produced

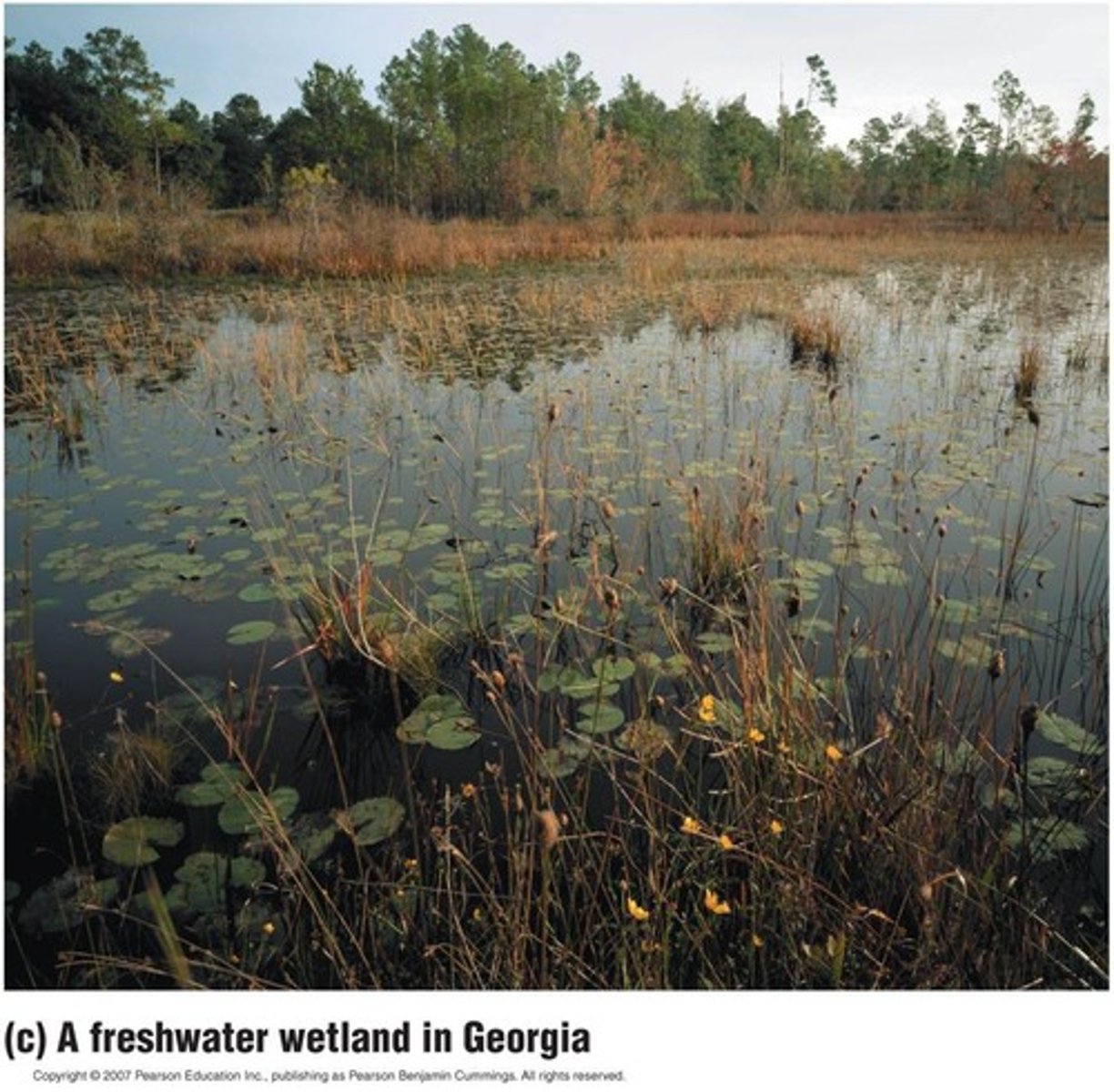
fresh water biome
made up of any of body of water that is made of freshwater such as lakes, ponds, streams, and rivers.

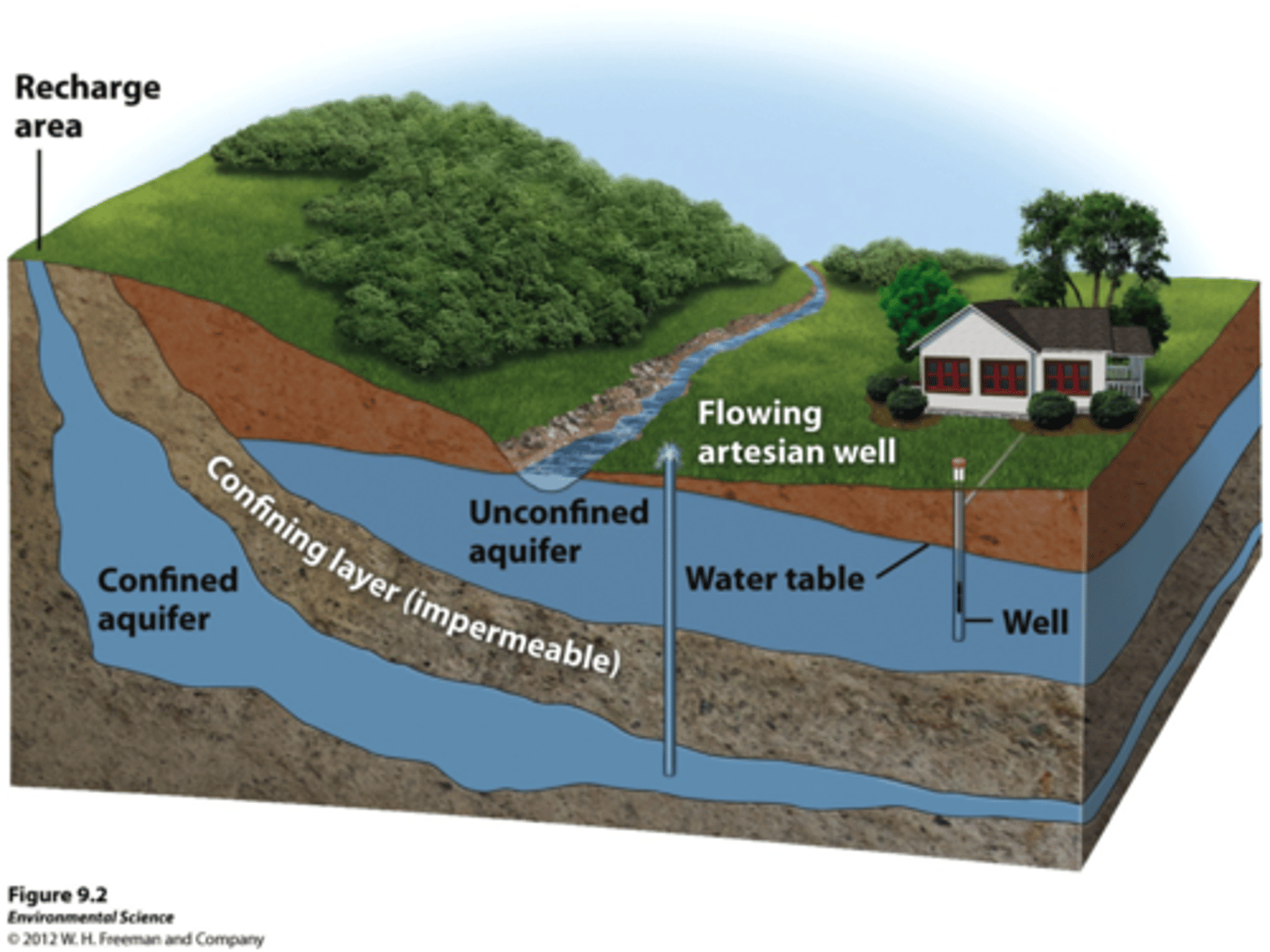
groundwater
water held underground in the soil or in pores and crevices in rock
Protista
unicellular, eukaryotic, moves with flagella and cilia
Archaebacteria
unicellular, prokaryotic, lives in extreme environments
Eubacteria
unicellular, prokaryotic, also known as true bacteria
Animalia
multi cellular, eukaryotic, reproduces mostly sexually, heterotrophic
Plantae
multi cellular, eukaryotic, autotrophic, can reproduce sexually or asexually
Fungi
mostly multi cellular, eukaryotic, heterotrophic