Biochemistry (Unit 3)
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Carbon and Carbon-bonding
Very reactive - 4 valence electrons
Each carbon can form 4 single covalent bonds
Carbon forms extensive networks (carbon skeletons)→ forms large mlc
Functional groups
A variety of functional groups added to carbon networks
Carbon sharing electrons with O, N, or other atoms in a particular region in organic compound
Group of atoms linked by strong covalent bonds and tending to function in chemical rxns as single unit
5 functional groups
Hydroxyl, carboxyl, amino, methyl, and phosphate
Monomers and polymers
Some organic macromolecules are called polymers and are made up of multiple copies of single units called monomers
Link together by covalent bonds to form large compounds - polymers through dehydration synthesis
Split into monomers by hydrolysis
Carbohydrates
Composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen (sugars)
(CH2O)n - lots of -OH groups
most carbohydrates, hydrogen and oxygen are found in the same two-to-one relationships that they are in water
Contains several hydroxyl groups - makes mlcs polar in nature
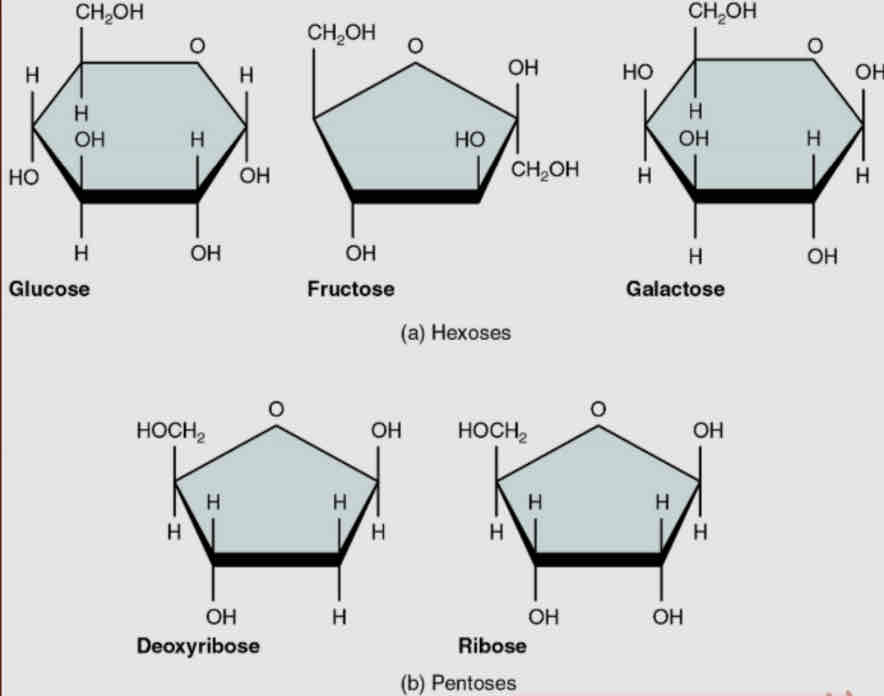
Monosaccharides
Simple sugars - called glucose
1 unit of sugar
Pentose - 5 carbon atoms
ribose
deoxyribose
genetic - (RNA + DNA + ATP)
Hexose - 6 carbon
glucose
fructose
galactose
nutritional
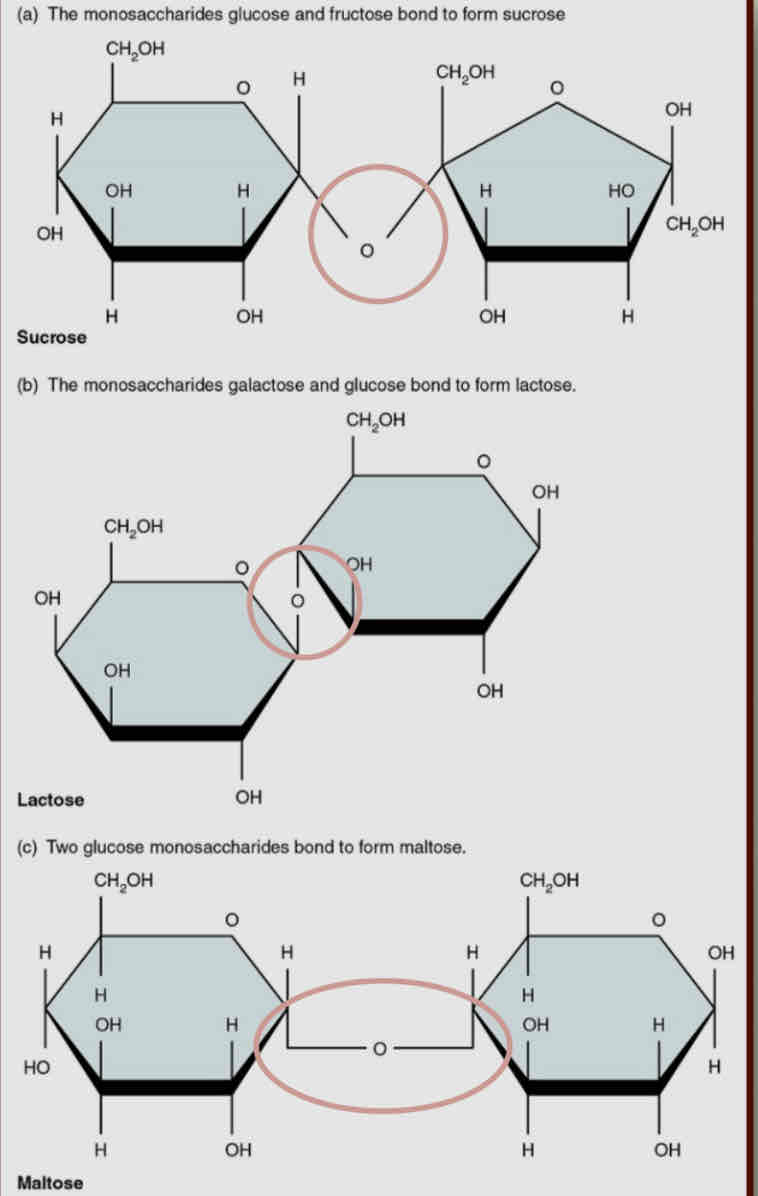
Disaccharides
2 unit sugars (2 monosaccharides joined tgt)
Sucrose - glucose + fructose
Maltose - glucose + glucose
Lactose - glucose + galactose
all nutritional
Polysaccharides
Many mono. linked tgt
a) Starch - storage, made by plants, amylose + amylopectin (nutritional)
b) Glycogen - storage, animal, human (nutritional)
c) Cellulose - structural, plants - made up of glucose subunits
Function of Carbs
Used for energy: plant-based foods
Polysaccharides (ex. starch), and various disaccharides and monosaccharides play a roles as a primary energy source - esp glucose
Short chains of carbs can be used for glycocalyx that surrounds most animal cells
Human body stores glucose as polysaccharide glycogen
Pentose sugars important for ATP and nucleotides make up DNA and RNA
Lipids
Have lots of (C-H), less oxygen, most are non-polar (hydrophobic)
Few oxygen atoms lipids do contain are often at the edge of the molecules and part of functional groups
Lipids form an emulsion - a mixture of solutions that do not mix well
due to the fats emulsifying, therefore, non-polar
Triglycerides (fats and oils)
Triglycerides consist of a glycerol molecule covalently bonded to 3 fatty acids
Glycerol - organic compound with 3 carbon atoms, while fatty acids have a long chain of hydrocarbons with an acidic carboxyl group on the end
Each fatty acid is covalently bonded to one of the 3 oxygen atoms of the glycerol mlc through dehydration syn. - produce 3 mlc of water
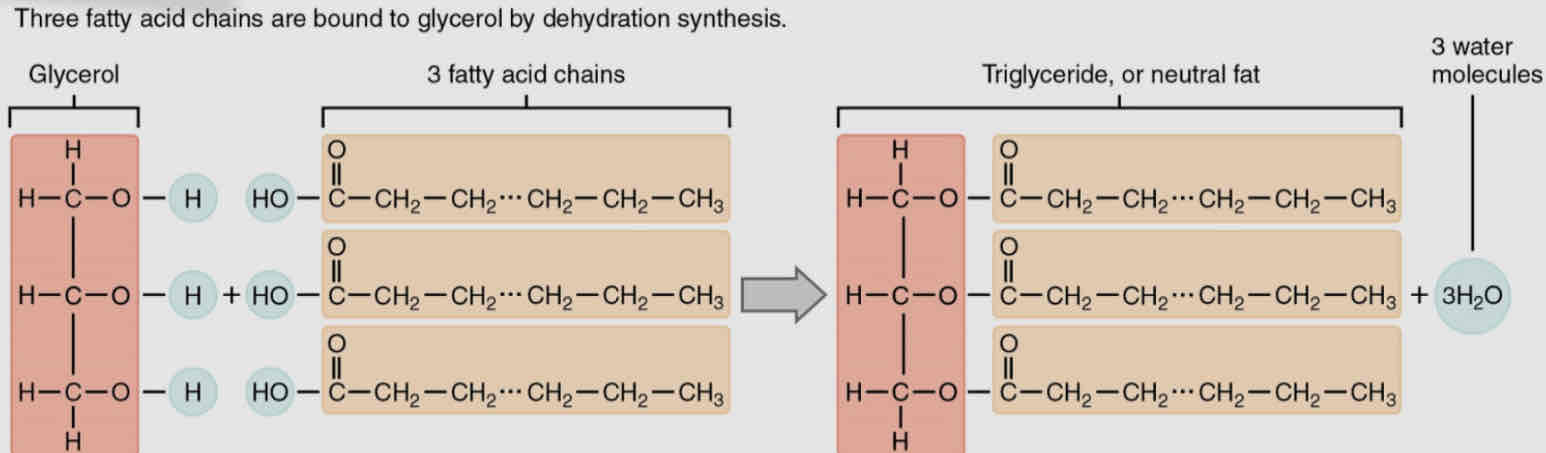
Triglycerides (Sat vs. Unsat)
Only saturated fatty acids = saturated fat
One of the fatty acids is unsaturated = unsaturated fat
Saturated - No C=C, more hydrogen
triglyceride w/ 3 saturated fatty acids
fats, solid, from animals
Unsaturated - at least one C=C, less H
triglyceride w/ at least one unsaturated fatty acid
oils, from plants, liquid
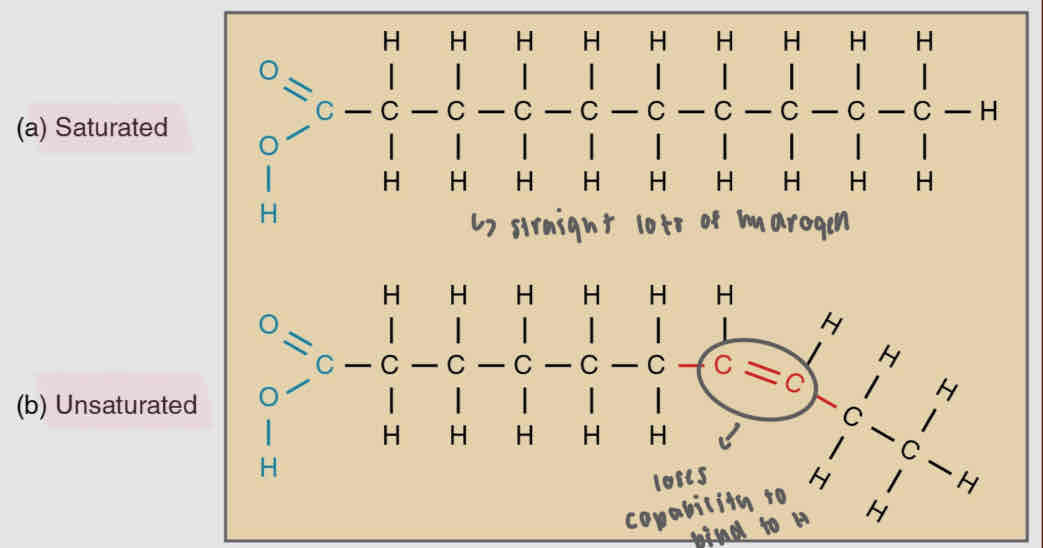
Sat vs. Unsat. fats
Unsat. fats - called oils, in plants and liquid at room temp.
Sat. fats - get packed tightly (no bends in the fatty acid chains), solid at room temp and in animals
Triglyceride functions
Major fuel source for the body
when glucose storages are low and fuel long - slow physical activities
Dietry fats assits the absorption of non-polar fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K)
Body fats protects and cushions the body’s bones and internal organs and acts as an insulation
Fatty acids are components of glycolipids - sugar-fat compounds found in the cell membrane
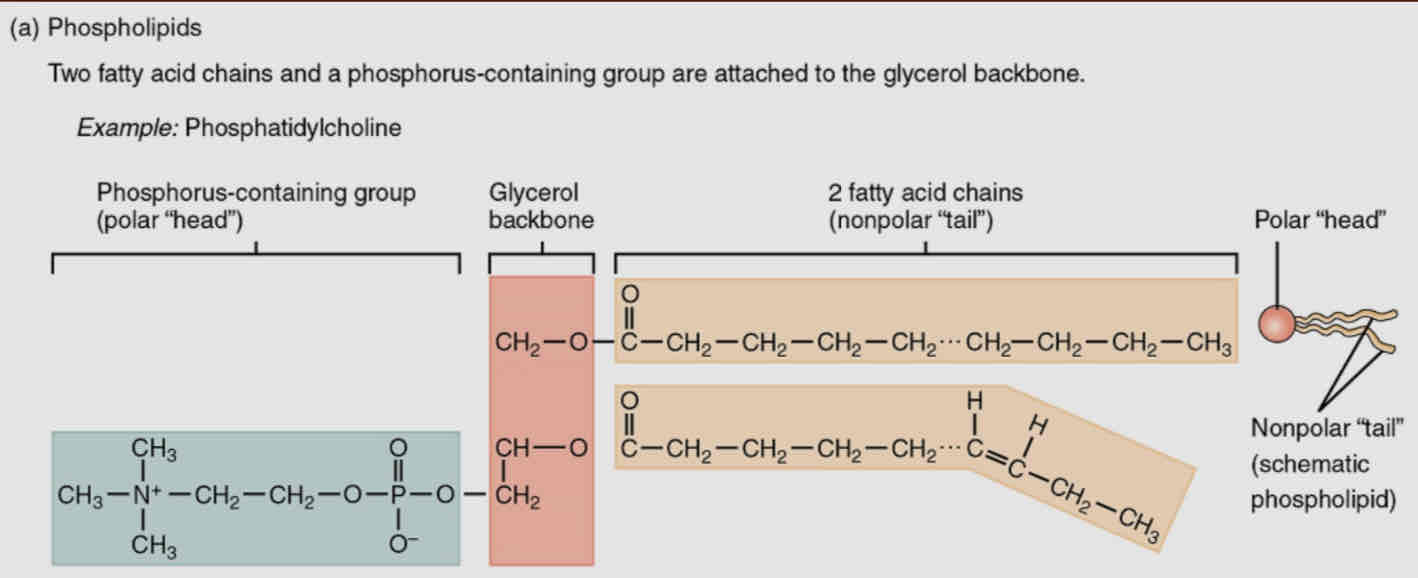
Phospholipids
Plasma membranes composed of a BILYAER of phospholipids
composed of glycerol covalently bound to 2 fatty acids and phosphate group
Has a region that attracts water (polar) - hydrophilic head where phosphate group is located
Has a hydrophobic tail - not attracted to water, where the fatty acid tail are located
Steroids
4 fused hydrogen rings and many have short hydrocarbon tail
Aka sterols are considered lipids because they are hydrophobic
Functions are hormones (testosterone and estradiol)
IMPORTANT - CHLOESTEROL
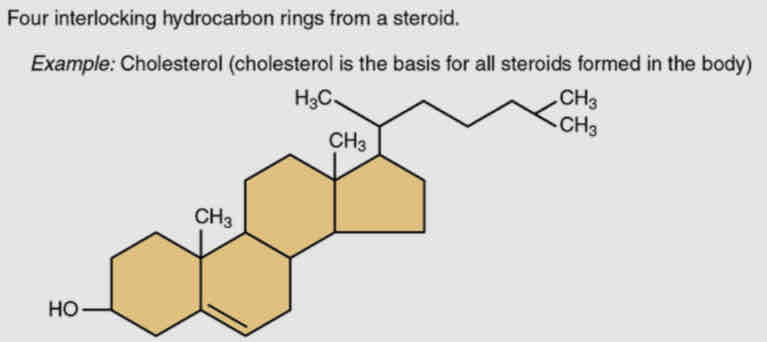
What is the contribution of cholesterol in steriods?
Synthesized by the liver and present in most animal-based foods
Important component of bile acids, compounds that help emulsify dietary fats
Building block of many hormones, signaling molecules that the body releases to regulate processes at distant sites
Protein
Important to all tissues and organs
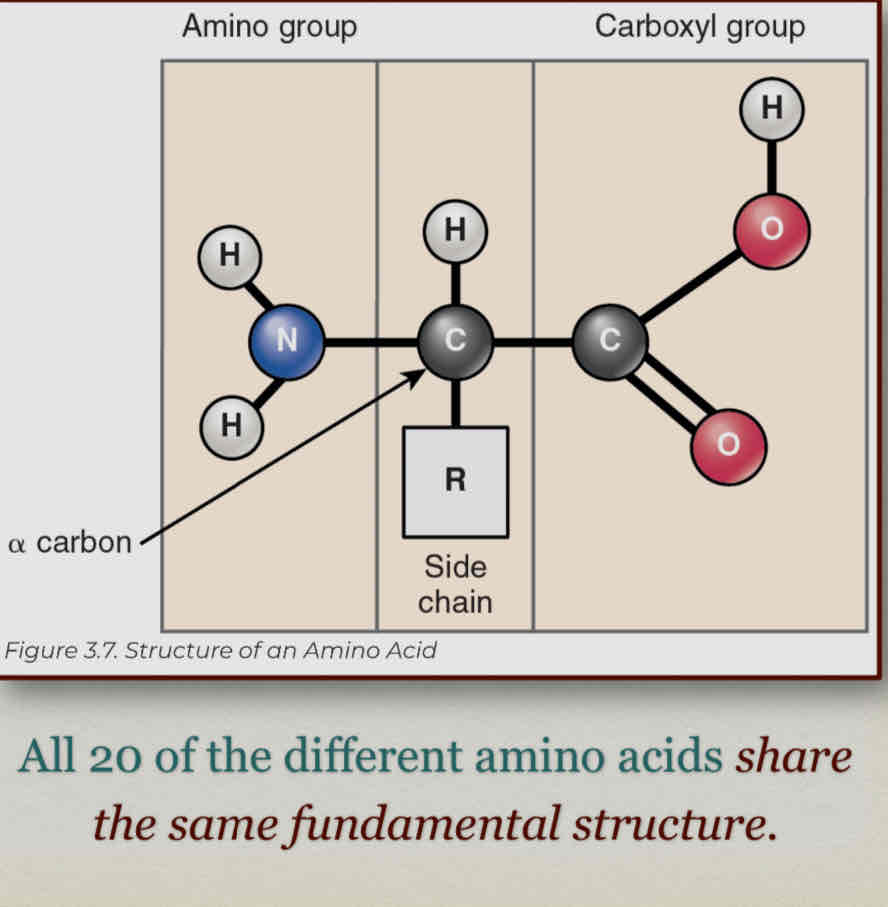
A large, globular macromolecule made of 1 or more chains of amino acids
Amino acid chains are called peptides.
Peptides twist + turn + bend into specific 3D shape (has 4 levels)
Always have nitrogen, many have sulfur
Amino acids - units that make up proteins
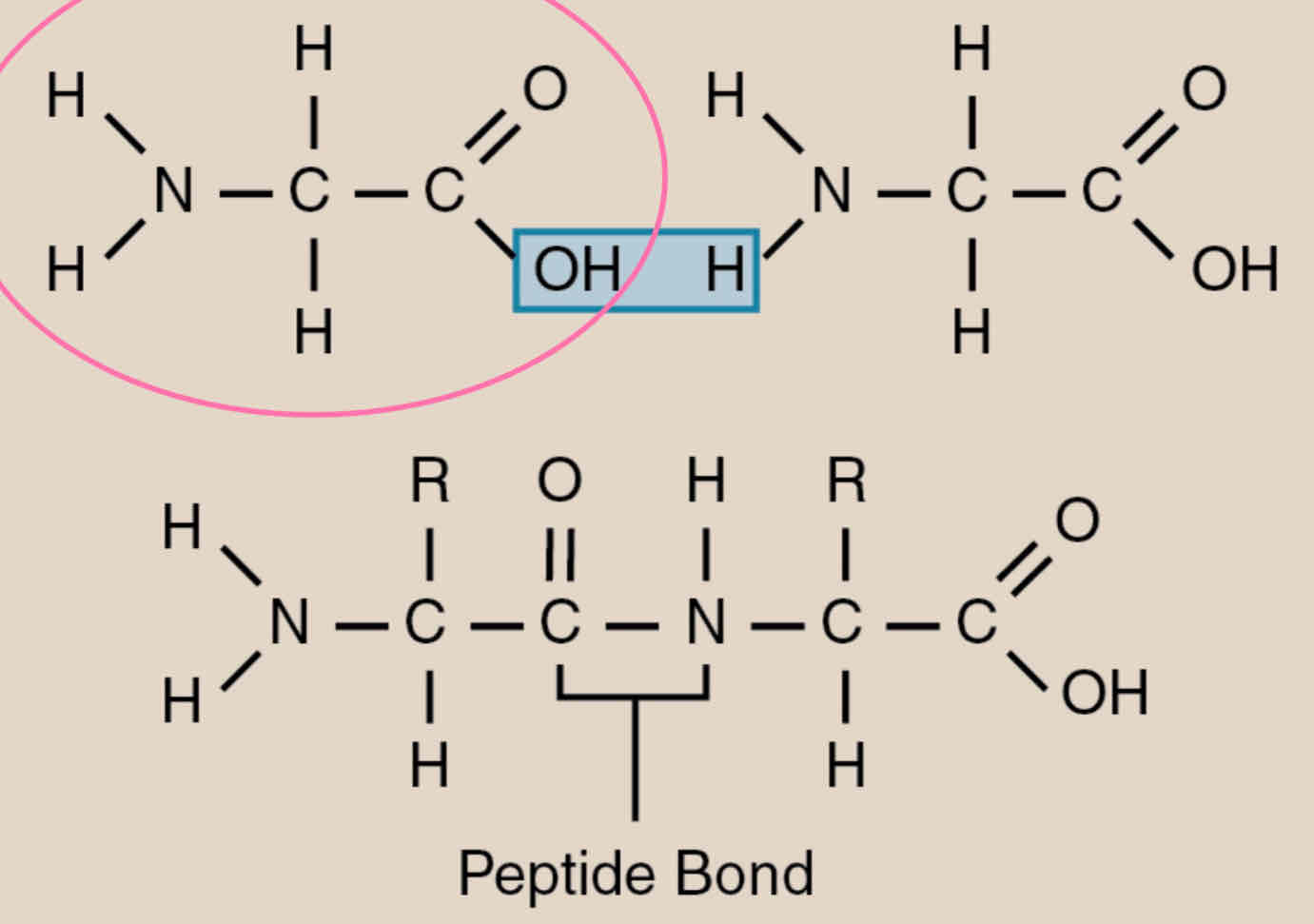
Peptide bonds
Two amino acids positioned so that the carboxyl group of one is adjacent to the amino group of the other
joined by dehydration reaction
Peptide bond forms between 2 amino acids
Protein structures
3-D are important for proper functioning
Primary structure - linear sequence of amino acids
Secondary structure - folding and coiling patterns resulting from hydrogen bonds between the R groups of amino aicds
Tertiary structure - produced by the folding of the already coiled and folded chain of amino acids
Quaternary structure - several polypeptides aka subnunits and the interaction of subunits create quaternary
Protein function

DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) - all nucleotides have deoxyribose as pentose sugars
stores genetic information (cellular blueprint molecules)
exists as two nucleic acids that coil around one another (double helix)
composed of 2 polymers and nucleotides (each a nucleic acid) formed with bonds between phosphate and sugar groups (sugar-phosphate backbone)
held by hydrogen bonds between nitrogen bases
RNA
Ribosenucelic acid (RNA) - all nucleotides have ribose as the pentose sugar
involved in producing proteins
exists as a single strand
Nucleicotides and nucleic acids
Nucleic acids (chains of nucleotides—phosphate grp, pentose sugar, nitrogen base) carry genetic blueprint of a cell and carry instructions for cell functioning
Adenosine triphopshate (ATP)
Nucleotide composed of a ribose sugar, an adenine base, and three phosphate groups
High energy compound - 2 covalent bonds linking its 3 phosphates store a significant amount of potential energy
Energy released from breaking bonds help fuel body
Breakdown of ATP → APD and AMP is reversible when AMP or ADP undergo phosphorylation