Lecture 22 (Ticks)
1/163
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
164 Terms
What is associated with Class Arachnida?
Ticks, Mites, Spiders
What is a common outdoor nuisance associated with pets and humans that play an important role in transmission of infectious disease?
Ticks
What can be caused by Ticks?
Tick Paralysis, Inflammation and infection at site of tick bite
Lyme Disease
Rocky Mtn. Spotted Fever
Canine Babesiosis
What are different Tick-borne Diseases?
Encephalitides & hemorrhagic fevers
Rocky Mtn. Spotted Fever
Boutonneuse Fever
Queensland Tick Typhus
Siberian Tick Typhus
Q Fever
Tick-borne Relapsing Fever
Lyme Disease
Tularemia (Rabbit Fever)
Babesiosis (Texas Cattle Fever)
What is associated with Ixodid or the Family Ixodidae?
Hard Ticks
Ticks are macroparasites meaning what?
They are visible without a microscope
Ticks have a fused 2-piece body plan including what?
Fused head/thorax (cephalothorax)
Abdomen (opisthosoma)
Is there constriction between the head and body in ticks?
No
How is the skeleton/appearance of a tick described?
Chitinous exoskeleton w/ hard scutum and have toothed hypostome
How many legs do adults and nymphs have?
8 legs
How many legs do larvae have?
6 legs
T or F: All ticks are parasitic in all lifecycle stages.
True
T or F: Not all ticks suck blood.
False
*All ticks suck blood
What type of feeders are all stages of ticks?
Obligate blood feeders
What type of life cycle do most ticks have?
A 3 host life cycle
What is there variable expression of among species of ticks?
Nest dwelling (nidicolous) and host seeking (questing)
T or F: Ticks are able to withstand starvation for long periods between hosts.
True
What plays an important role in the infectious disease transmission cycle of ticks?
Wildlife Reservoirs
What is the basic life cycle of the tick?
Eggs → Larva → Nymph → Adult (male/female) → Female acquires host and gets blood meal then lays cluster of eggs
What are the tick life cycle variations?
1 host - uses 1 host for entire lifecycle
2 host - uses 2 hosts to complete lifecycle (Not common in U.S.)
3 host - uses 3 hosts to complete lifecycle
What is the only reason a 1 host tick will leave?
A female will leave to lay her eggs
What does it mean to be a 1 host tick?
It completes the entire lifecycle on a single animal
Where are 1 host tick eggs deposited (oviposition)?
Off the host
Where do 1 host ticks molt to each life-stage (instar)?
On the host
T or F: 1 host ticks are highly susceptible to control efforts.
True
What is the only route of infectious disease transmission associated with 1 host ticks?
Trans-ovarial (Vertical transmission)
Trans-ovarial is the only mechanism for 1 host ticks to do what?
Vector disease
What occurs in Trans-ovarial transmission for 1 host ticks?
Infectious agent is passed to progeny through the ovaries
2 host ticks require 2 hosts for completion of the lifecycle - at what point does the host change?
Larvae and nymph feed on same host
Adults acquire new host
Where does oviposition of 2 host ticks occur?
Off the host
Where are 2 host ticks commonly found?
Africa
What is the only route of infectious disease transmission associated with 2 host ticks?
Interstadial
What occurs in interstadial transmission for 2 host ticks?
Infectious agent acquired by larvae/nymph from host and passed to adult stage
How many times does a 3 host tick acquire a new host?
3 times - larvae, nymph, adult
Where does oviposition occur?
Off of the host
How common is the 3 host tick lifestyle in North America tick species?
It is the most common
What is the only route of infectious disease transmission associated with 3 host ticks?
Interstadial
What occurs in Interstadial transmission for 3 host ticks?
Infectious agent acquired by larvae or nymph from host and passed to successive stages — larva to nymph or nymph to adult
What are the 3 primary tick species associated with zoonotic disease?
Ixodes scapularis
Amblyomma americanum
Dermacentor varriabilis
What disease is associated with Ixodes scapularis?
Lyme Disease
What disease is associated with Amblyomma americanum?
STARI
Ehrlichiosis
What disease is associated with Dermacentor varriabilis?
RMSF
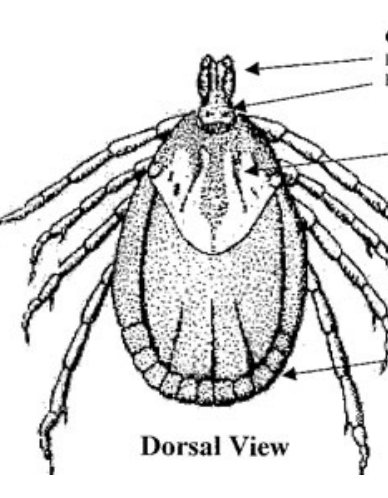
What is the top arrow?
Capitulum
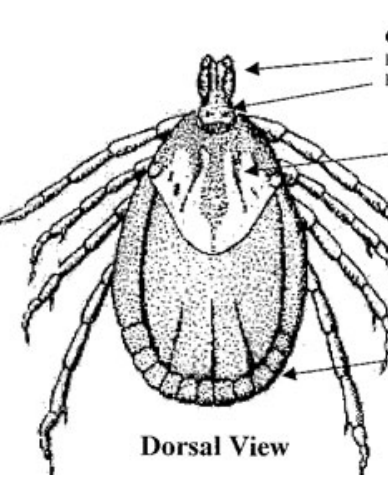
What is the middle arrow?
Scutum (Dorsal shield)
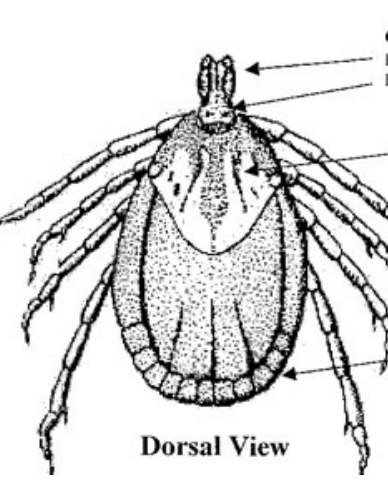
What is the bottom arrow?
Festoons
What ticks are included in the Dermacentor spp.?
D. varriabilis
D. albipictus
D. andersoni
D. occidentalis
D. nitens
What is Dermacentor varriabilis also known as?
American Dog Tick
What type of lifecycle does D. varriabilis have?
3 host lifecycle
Where are D. varriabilis adults found?
On larger vertebrates
What diseases are associated with D. varriabilis or the American Dog Tick?
RMSF
Tularemia
Q Fever
Tick Paralysis
Where is Dermacentor albipictus found?
Cananda, Northern US, Appalachian Mtns
What type of lifecycle does D. albipictus have?
1 host lifecycle
What species are D. albipictus typically associated with?
Deer
Elk
Moose
What impact does D. albipictus have on the host?
Hair loss/lose body condition in winter
What is Dermacentor albipictus also known as?
The “Winter Tick”
What is Dermacentor andersoni also known as?
Rocky Mtn Wood Tick
What type of lifecycle does D. andersoni have?
3 host lifecycle
Where are D. andersoni adults found?
On larger vertebrates
What is Dermacentor occidentalis also known as?
Pacific Coast TickW
What type of lifecycle does D. occidentalis have?
3 host life cycle
Where are D. occidentalis adults found?
On larger vertebrates
What diseases are associated with D. occidentalis or the Pacific Coast Tick?
Bovine Anaplasmosis
Tularemia
Q Fever
Tick Paralysis
Where is Dermacentor nitens found?
South Florida and Texas
What type of life cycle does D. nitens have?
1 host life cycle
What disease is associated with Dermacentor nitens?
Equine Babesiosis
What is an acute disease associated with Rickettsial infection by Dermacentor varriabilis?
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever
What are the initial signs associated with Rocky Mtn. Spotted Fever?
Non-specific muscle aches and fever
What occurs 2-5 days post tick exposure with Rocky Mtn. Spotted Fever?
Rash appears
When is Rocky Mtn. Spotted Fever typically seen?
April - September
How is Rocky Mtn. Spotted Fever treated?
Easily treated with antibiotics - But early diagnosis is key
This canine presented for a spay and a petechial rash was noticed on the abdomen. What does she most likely have?
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever
What is a tickborne disease associated with the neurotoxic salivary component of ticks?
Tick Paralysis
What can the rapid ascending paresis of tick paralysis lead to?
Respiratory and fatality if untreated
T or F: Tick paralysis can be caused by a single tick.
True
Although other species can be involved, what is tick paralysis often associated with?
Dermacentor varriabilis (American Dog Tick)
What is Amblyomma americanum also known as?
The Lonestar Tick
What are the characteristics that allows you to differentiate the lonestar tick or Amblyomma americanum?
Long mouthparts (Palps)
Prominent white spot (“Lonestar”) on dorsal scutum
Festoons along distal margin
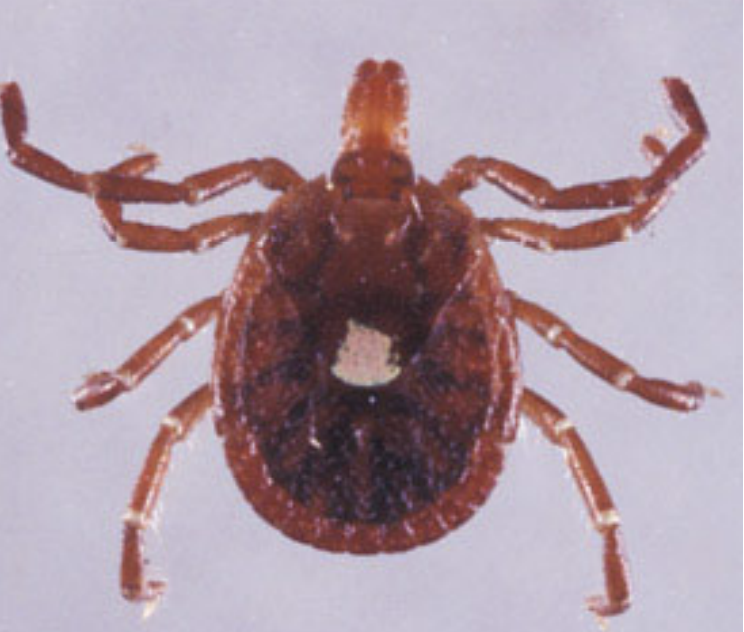

What tick is seen in the following image?
The “Lonestar” Tick - Amblyomma americanum
How can you differentiate a male and female Amblyomma americanum tick?
The scutum in the male is not obvious while the margin of the scutum in the female encircles a white “Lonestar”
What disease is associated with the bite of the Lonestar Tick?
STARI - Southern Tick Associated Rash Illness
Has the etiologic agent for STARI been isolated?
No
What is an acute disease of humans and animals where gram negative bacteria invade white blood cells leading to a low white blood cell count or low platelets?
Ehrlichiosis
What is the principle vector of Ehrlichiosis?
Amblyomma americanum
How many human cases of Ehrlichiosis are seen annually?
> 1200 cases
What is Rhipicephalus sanguineus also known as?
Brown Dog Tick
What type of lifecycle does Rhipicephalus sanguineus have?
3 host lifecycle
Rhipicephalus sanguineus have a tropical distribution including what?
Adapted to living indoors
Central heating offers optimal temperature and humidity
Semi-nidicolous behavior w/ eggs in bedding/residential environment
What does the rapid lifecycle of Rhipicephalus sanguineus facilitate?
The development of huge populations
Short as 2 months and may require household fumigation
What is Rhipicephalus sanguineus or the Brown Dog Tick a disease vector for?
Babesia canis, B. gibsoni
Hepatozoon canis
RMSF (Rickettsia rickettsii)
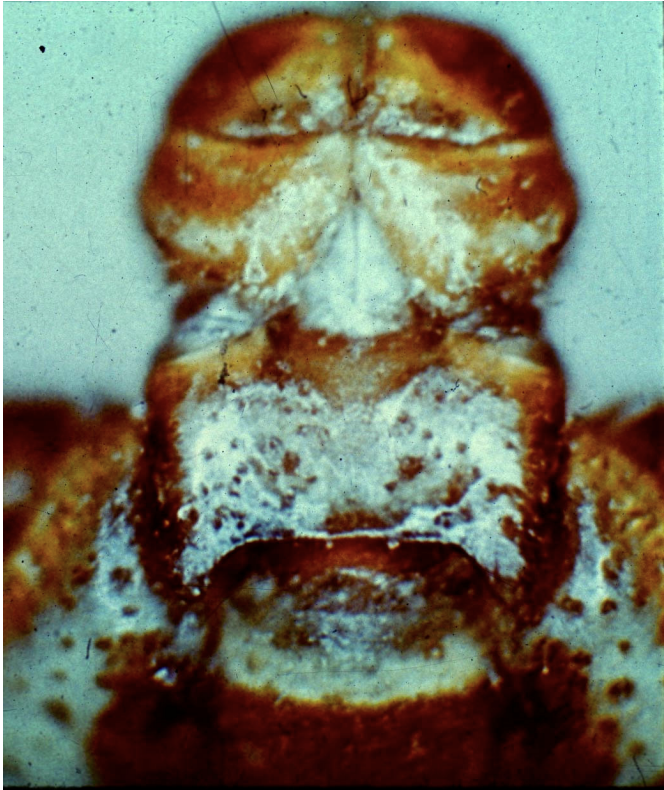
What species of tick is associated with the following image?
Dermacentor
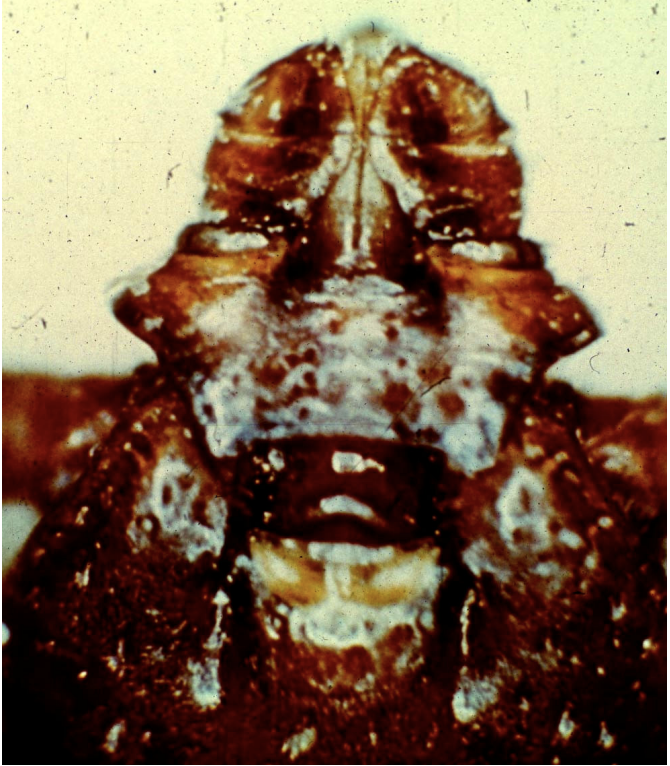

What species of tick is associated with the following image?
Rhipicephalus
How would you describe the “neck” of Dermacentor?
Rectangular shaped
How would you describe the “neck” of Rhipicephalus?
Diamond shaped
What is Haemaphysalis longicornus also known as?
The Longhorn Tick
What is an invasive 3 host tick species that is native to Eastern Asia with recent recognition in New Jersey (Aug. 2017) and has been in the U.S. since 2010?
The Longhorn Tick - Haemaphysalis longicornus
What significant vector potential does Haemaphysalis longicornus or the Longhorn Tick have?
Theileriosis
Babesiosis
Anaplasmosis
Ehrilichiosis
Lyme borreliosis
Various viral diseases
How do Haemaphysalis longicornus ticks reproduce?
Parthenogenically - males are rare and unnecessary
What should Haemaphysalis longicornus be differentiated from?
H. leporispalustris - native species on rabbits
T or F: Haemaphysalis longicornus is reportable to the State Vet/USDA.
True
Who is Haemaphysalis longicornus found on?
Cattle, Dogs or Cats