astro
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
how to find particle denisty
number of particles / volume
density / mass of particle
how to find number of particles
mass of universe/mass of particle
what is the composition of the universe
90% H, 10%He, 0.01% everything else
how to find number of molecular gas
density / (2 x mass of hydrogen)
how to find number of atomic gas
density / mass of hydrogen
how to find number of ionized gas
( 2 x density) / mass of hydrogen
what is the force of gravity
weak, attractive, radial force
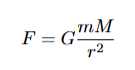
what is the total energy of an object
start energy + energy gained ( not linked to speed )
what is the work done due to energy
derived from integrating the gravitational force, as F is not constant with r
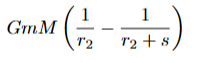
what is the escape velocity of an object
KE = gravitational
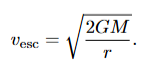
what is the orbital velocity of an object
gravitational = centripetal
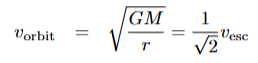
what is kepler’s first law
planets orbit in ellipses with sun at one focus not the centre
how to find eccentricity of an orbit
sqrt ( 1 - (b/a)² )

what is kepler’s second law
planets sweep out equal areas in equal times, as there is a conservation of angular momentum (m v r sintheta)
what is kepler’s third law
period² = r³
what is a binary system
centre of mass is stationary and shared, objects are on opposite sides to conserve momentum and have the same period
how to find the parallax of an object
distance to object / distance to sun
what is parallax
change in position due to motion of earthw
what is proper motion
velocity (km/s) = proper motion (arsec/yr) x 4.74 x d (pc)
what is a parsec
if parallax = 1arsec and distance is 1pc
how many arsecs is 1 degree
3600
what is the equatorial system
declination - 0 at equator +_ 90 at north/ south
right ascension - in hours
how to find right ascemsion in arsec
RA(sec) x 15 x cos
what is the equation for flux
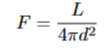
what is the equation for magnitude in terms of flux
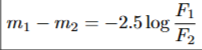
what is equation of magnitude in terms of distance

what is a Cepheid variable
strict periodicity, longer peirod = higher luminsity
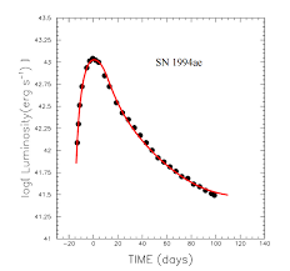
graph and peak for a supernova 1a
-19.3
what is the EM spectrum
gamma, xray, uv, visible, ir, micro, radio
what is radiation
object absorbs and emits photons of all wavelenghts with perfect efficiency
what is weins law
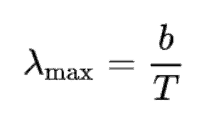
what is stefans law for flux

what is stefans law for power
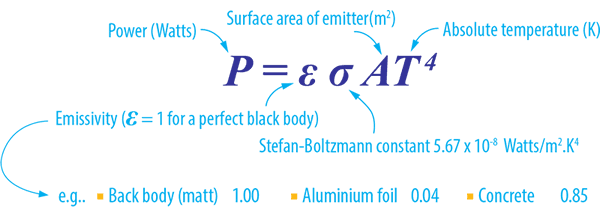
what is the equation for luminosity
surface area x flux
what is the emitted energy over time
luminosity x time
what is the most perfect blackbody
CMBR
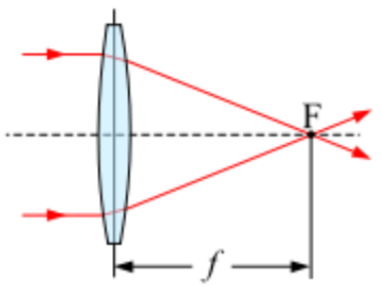
what a convex lens
converging
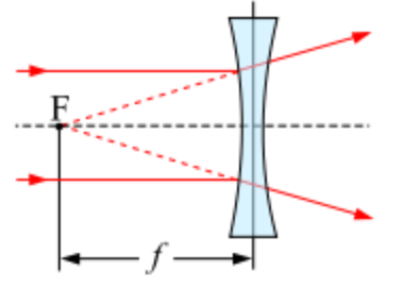
what is a concave lens
diverging
how to find power of a lens
1 / focal length
how to find distance of focal length
1/f = 1/distance from object and lens + 1/distance from lens and image
what are the images from a lens dependent on focal lenght

equation for magnification
objective/eyepiece
what is a refracting telescope
needs large objective focal lens, heavy - experiences chromatic aberration ( blurry/colourful images0
what is a reflecting telescope
mirrors, large, parabolic - spherical aberration ( not in focus)
what is the power of a lens
s = perpendicular distance between image and principle axid
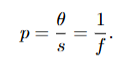
what is the focal ratio
smaller value = brighter image, less detail, wide fov
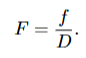
what is the diffraction limit
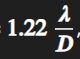
what is atmospheric turbulence
pockets of air at different temps causing differential refraction
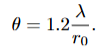
typical values for atmospheric turbulence
r0 - 5-30cm
t0- 1-100ms
what is an interferometry
combine line for N telescopes spread of distance d, with diameter D
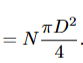
what is the resolution of a telescope
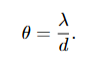
what is snell’s law
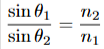
which light bend more
blue bends more than red
what is the diffraction grating equation
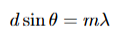
why are CCDs better than light
larger quantum efficiency - 70-80%
large charge transfer efficiency
large dynamic range - can count high number of electrons
how to CCDs work
convert photons to measurable light, photo electric effect, use silicon crystals
what is the equation for v from the doppler shift
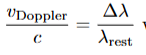
what is the equation for z

how to use doppler effect for exoplanet detection
wobble of star is large due to gravitational effect of planet
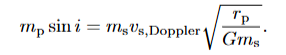
properties of low mass stars
cooler, smaller, fainter, higher density
properties of a stellar cluster
same age- found from main sequence turn off
luminosity of main sequence stasr

what is the equation for energy in a hydrigen nucleus
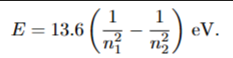
what is the equation for wavelength in any nucleus
x nucleus number²
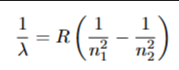
what are the hydrogen line series
n=1 - Lyman UV
n=2 - Balmer optical
n=3 - Paschen infrared
equation for dynamic timescale
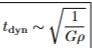
equation for hydrostatic equlibrium
negative pressure gradient
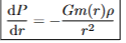
potential energy from constant density
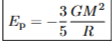
total momentum
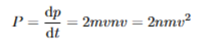
total velocity for constant velocities
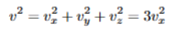
total velcity for random velocities
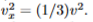
equation for thermal energy
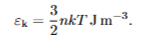
what does the virial theorem state
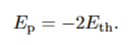
what is stellar nucleosynthesis
gravitational contraction- releases PE
nuclear fusion- produces right amount of energy needed
multiple reaction chains dependent on temp and density of star
what is the pp-cycle
energy release from fusion of 4 protons to 1 He nucleus as there is a mass deficit
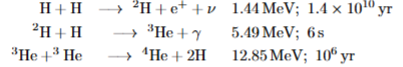
energy needed in a star synthesis
luminosity / mass
why are planets stellar thermostats
can self-regulate temp, by increasing radius so lower temp and decrease in energy production
how long can a star shine
efficiency factor x mass / luminosity
proportion of luminosity and mass in main sequence star
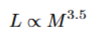
proportion of time and mass in a main sequence star
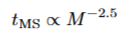
max nucleon binding energy
56Fe, fusion for lighter, fission for heavier
radius for a black hole
escape velocity = c
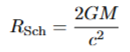
galaxy calssification system
hubble’s tuning fork
E- ellipitcal, S- spiral, SB- spiral bar, irregular
10^7 - 10^13 Molar masses

properties of spiral galaxies
central bulge or bar, rotating disk, spiral arms(stars form(, stellar halo (globular clusters), younger stars orbit centre, random velocities, 10^9 - 10^12 molar masses, mostyl dmoinated by dark matter
properties of elliptical galaxies
little structure, old stars, little gas/dust, no star formation, product of merger of glaxies, E0 -circular - E7 -flat
properties of irregular galaxies
no clear structure, gas rich and star forming, undergoing merges, small
properties of supermassive black holes
centre of massive galaxies, not stellar remnants, active accretion disk which fuels star formation, cannot be views, 10^6 - 10^10 solar masses
how does gas work in a galaxy
makes up 5-25^ of mass and extends out of disk, is observed through 21cm emission from H gas,
how is H gas viewed
spin of electrons and protons gives 2 energy states, transition between states rises 21cm emission line, experiences doppler shift which shows rotation
how to find M(R) and velocity of a planet
centripetal = gravitational
where masses are m and M(R)
why does velocity profile prove dark matter
mass increases linearly from centre of galaxy, must be in spherical halo that extends further than stars and gas
properties of dark matter
cannot interact electromagnetically only gravity, emits no light, not baryonic
properties of the universe
homogeneous(same at any location), isotropic(same in all directions), gallilean invariance (same laws of physics)
what is the hubble flow
H = 70, v = km s^-1 , D = Mpc
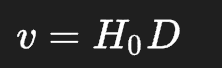
what is the hubble time and radius
expansion started at the same time for all galaxies, t = 1/H, radiues = H time x c
what is the distance ladder
parallax, cepheid, supernova 1a
what is look back time
galaxies are seen in the past, z=1, time = 8Gyr
what is the evidence for the age of the universe
radioactive decay of elements, must be older than earth
evidence of age of stars
radioactive decay, ratios of decay give age, oldest stars in milky way are in globular clusters
when is peak star formation for galaxies
z=2 (10Gyr), declined by factor of 10 now