Unit 2 Biology Quiz - Cells, Division, etc
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
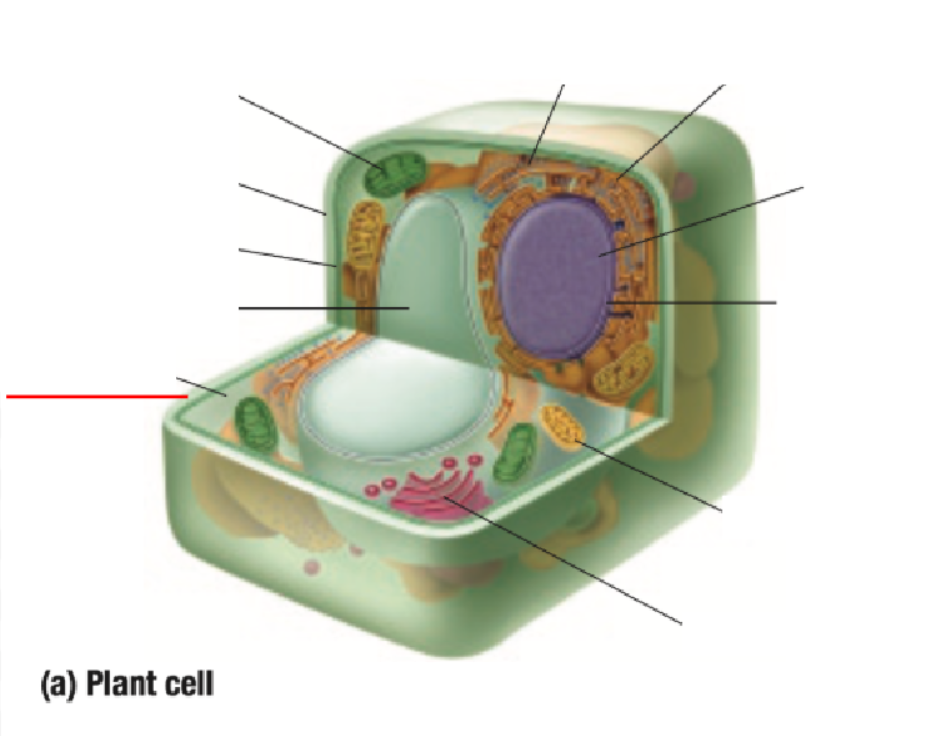
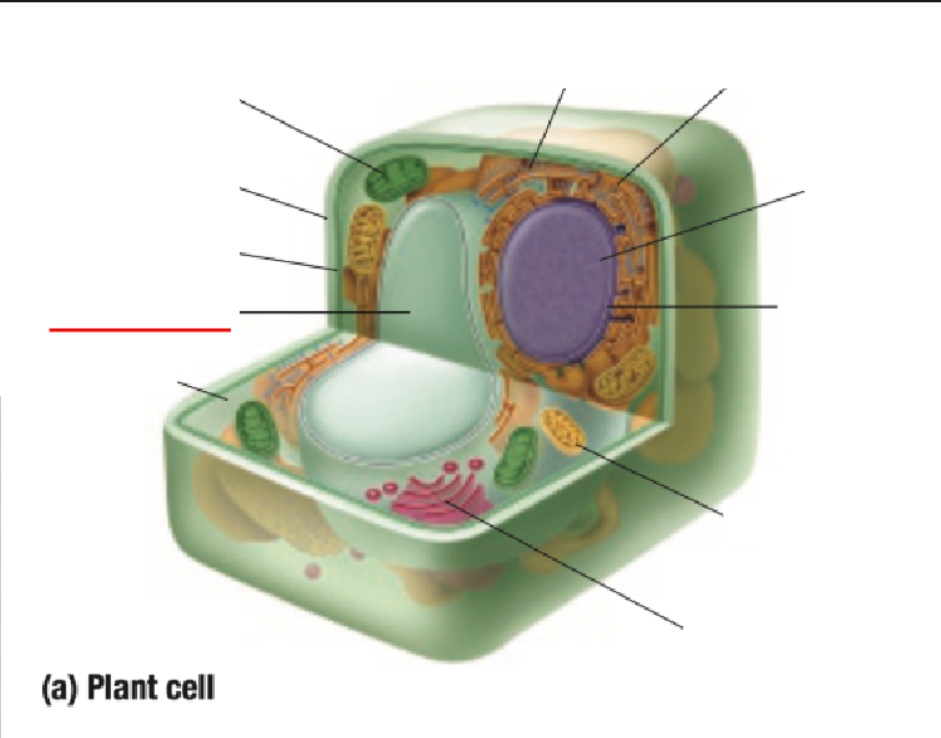
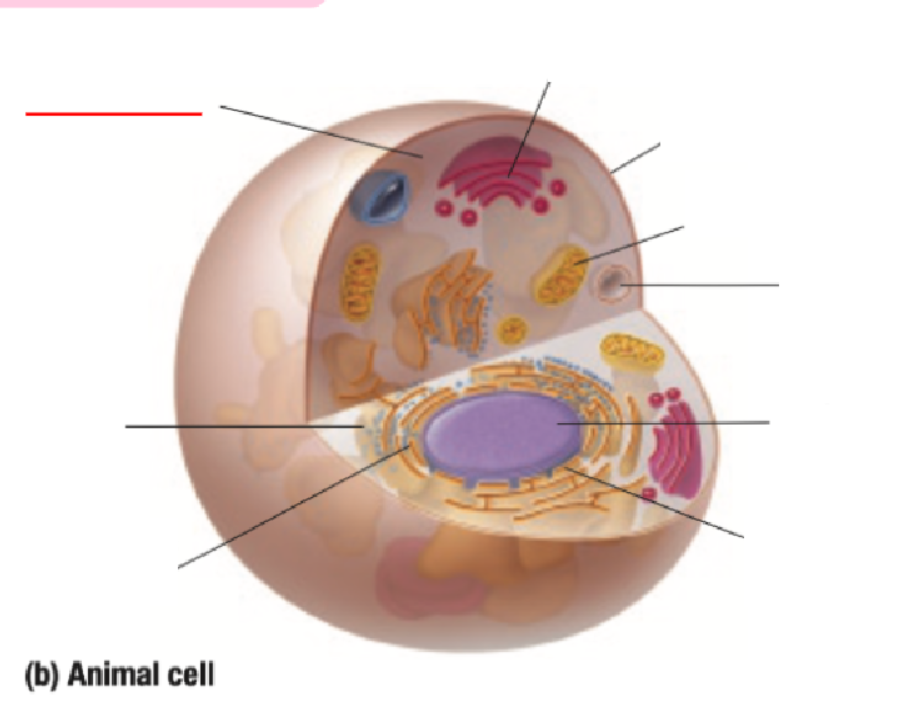
Cytoplasm
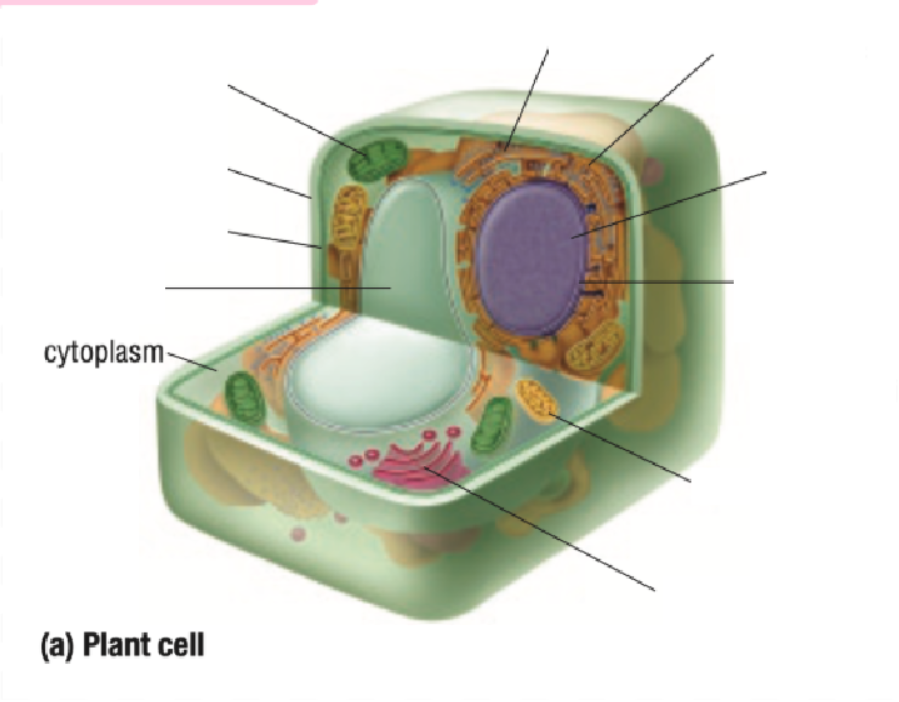
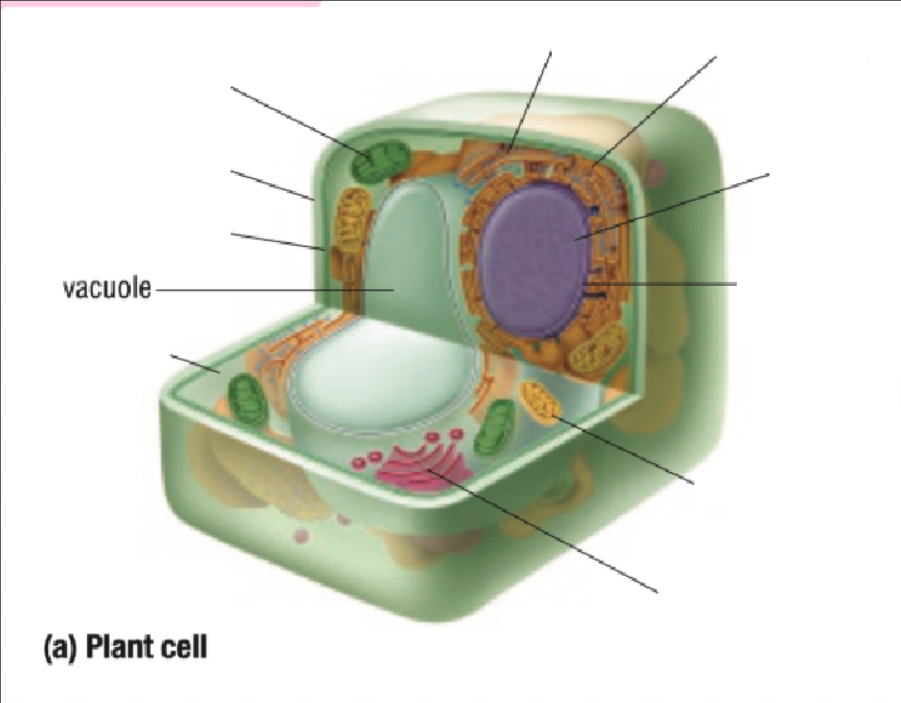
Vacuole
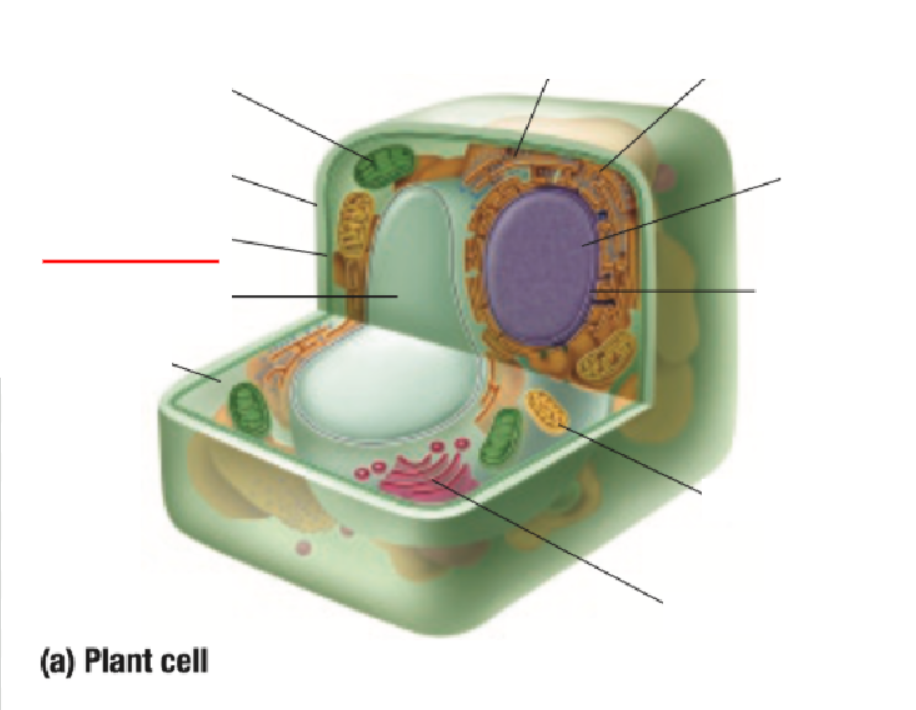
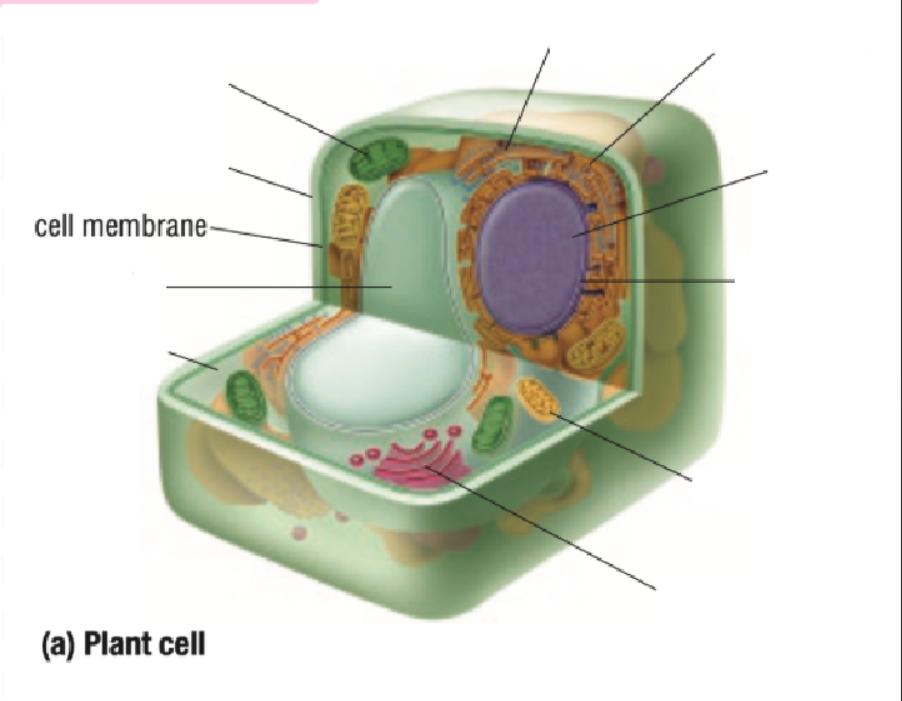
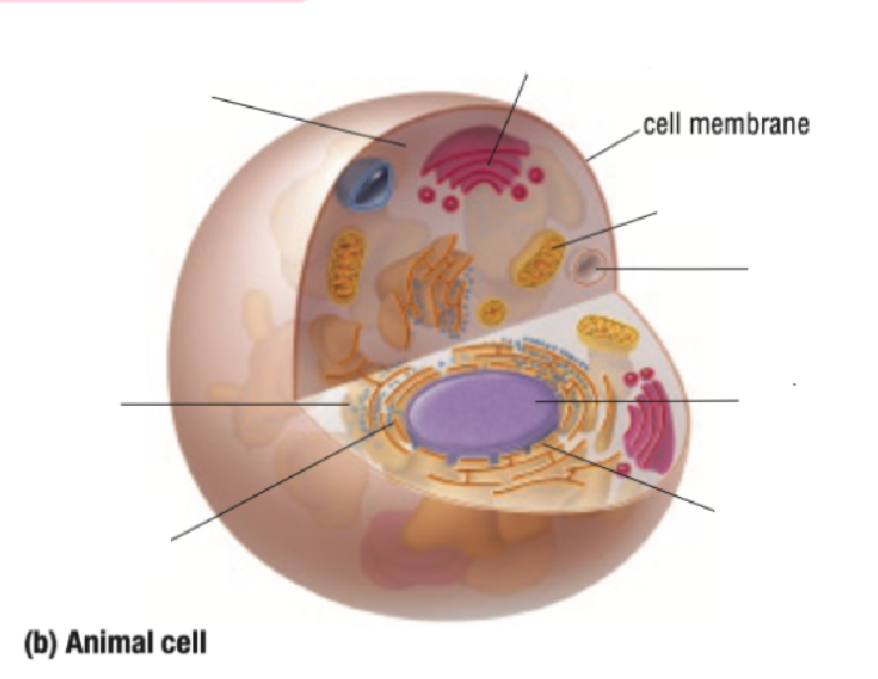
Cell Membrane
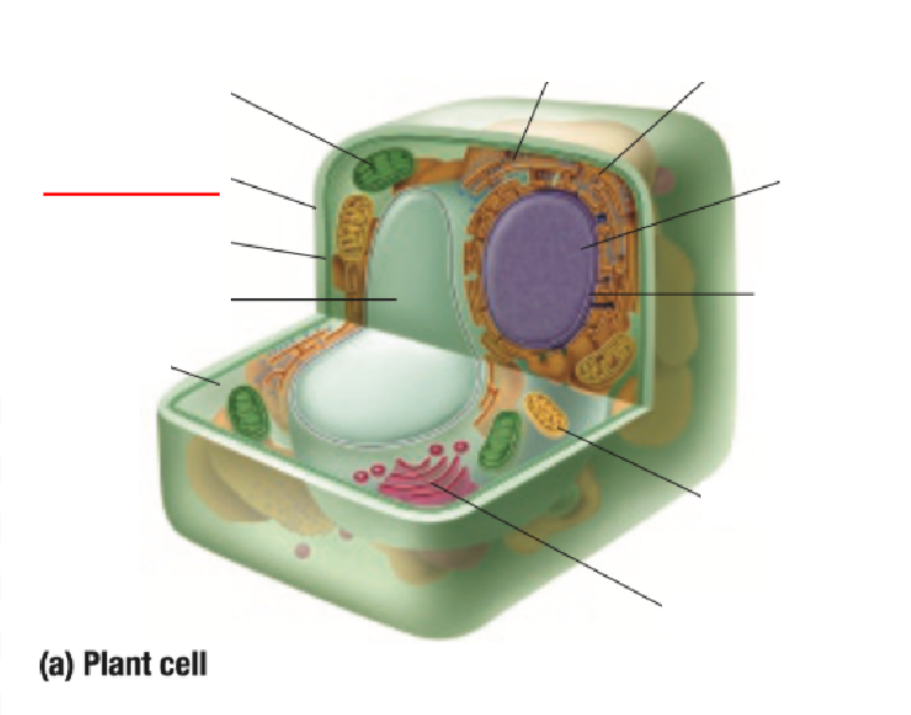
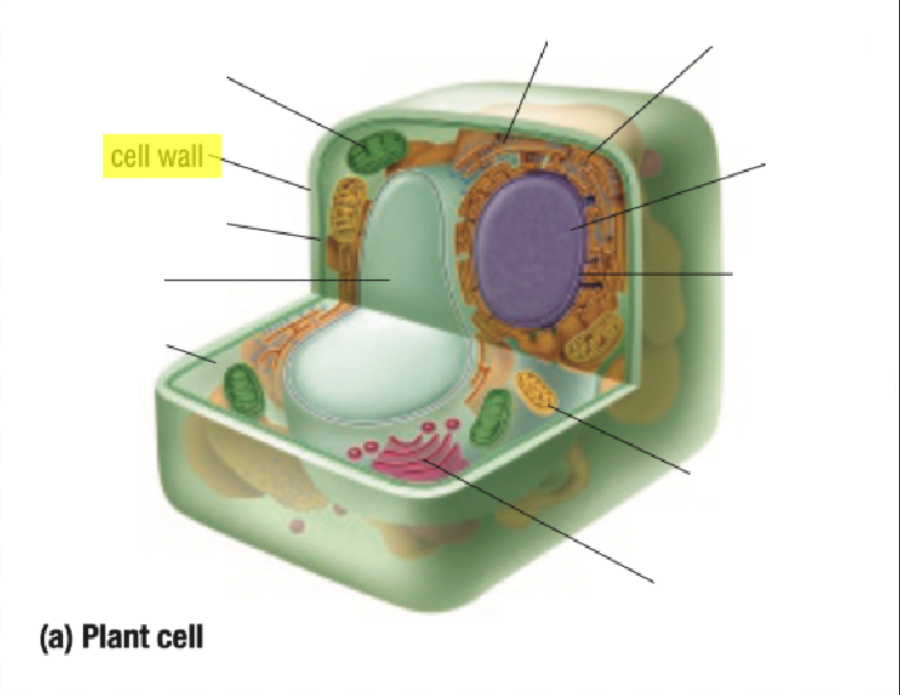
Cell Wall
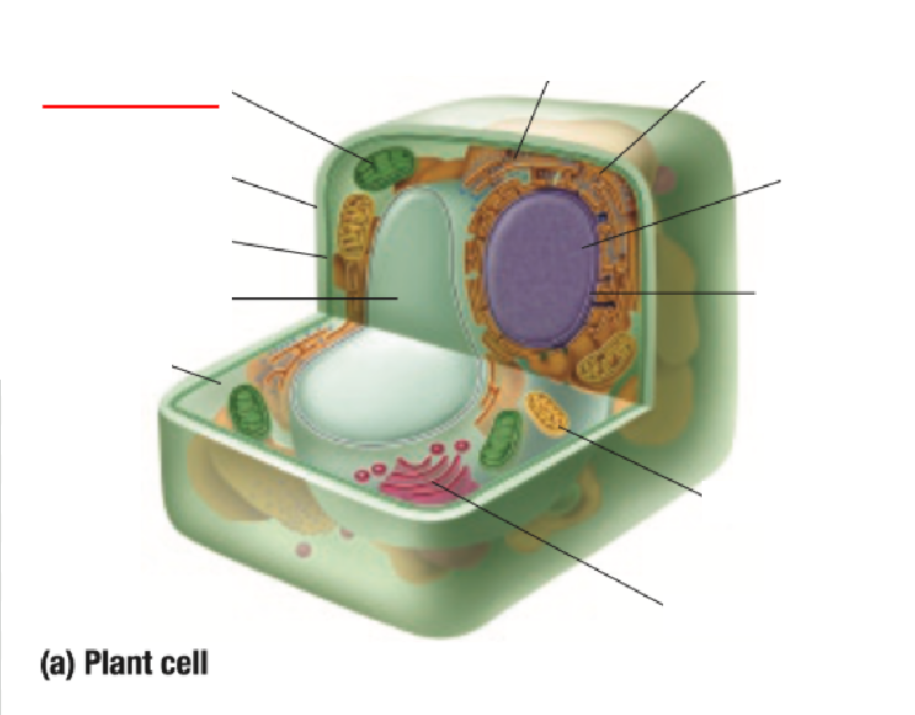
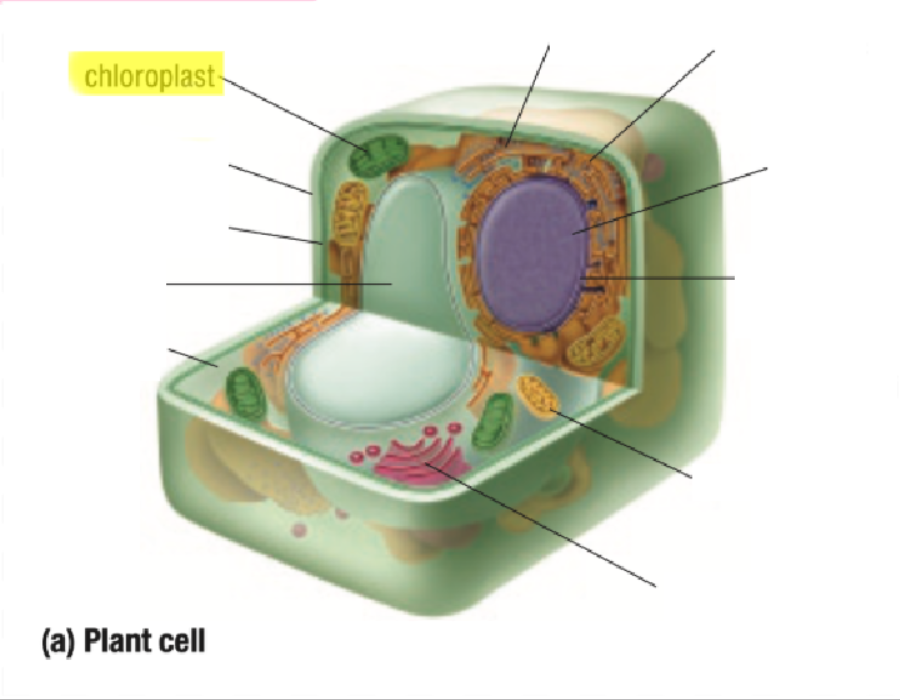
Chloroplast
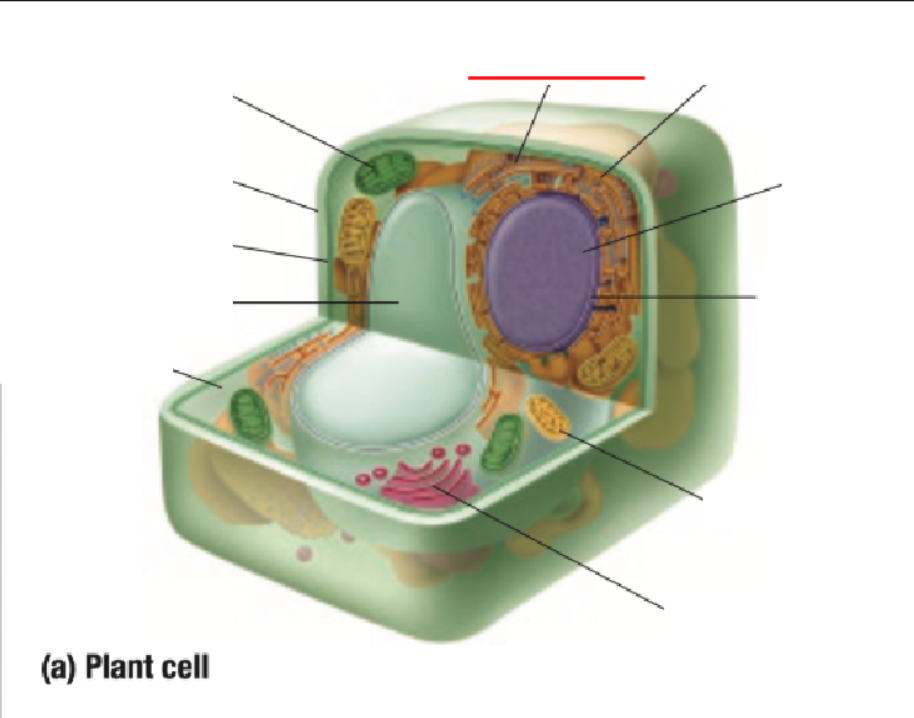
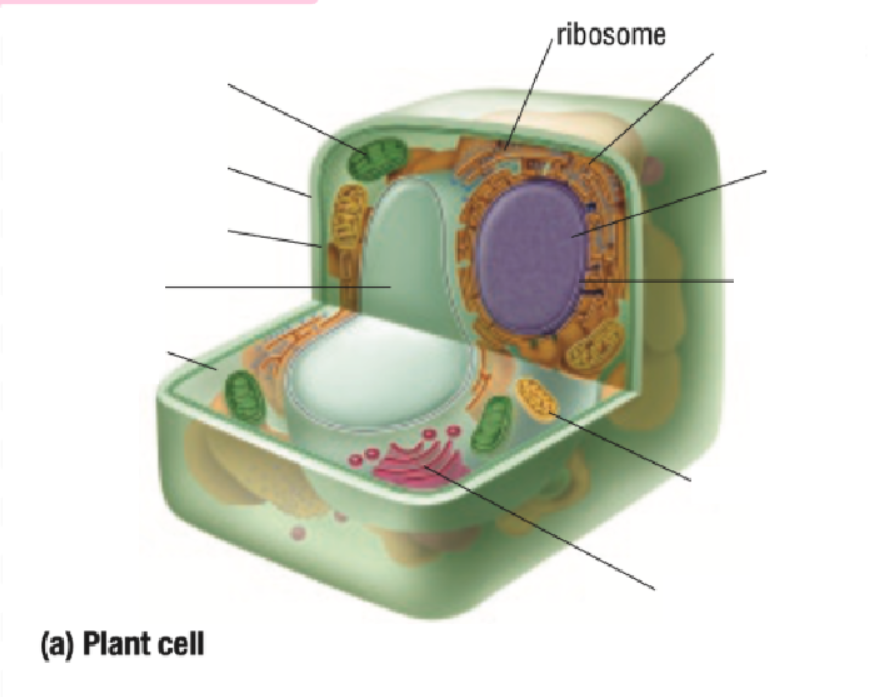
Ribosome
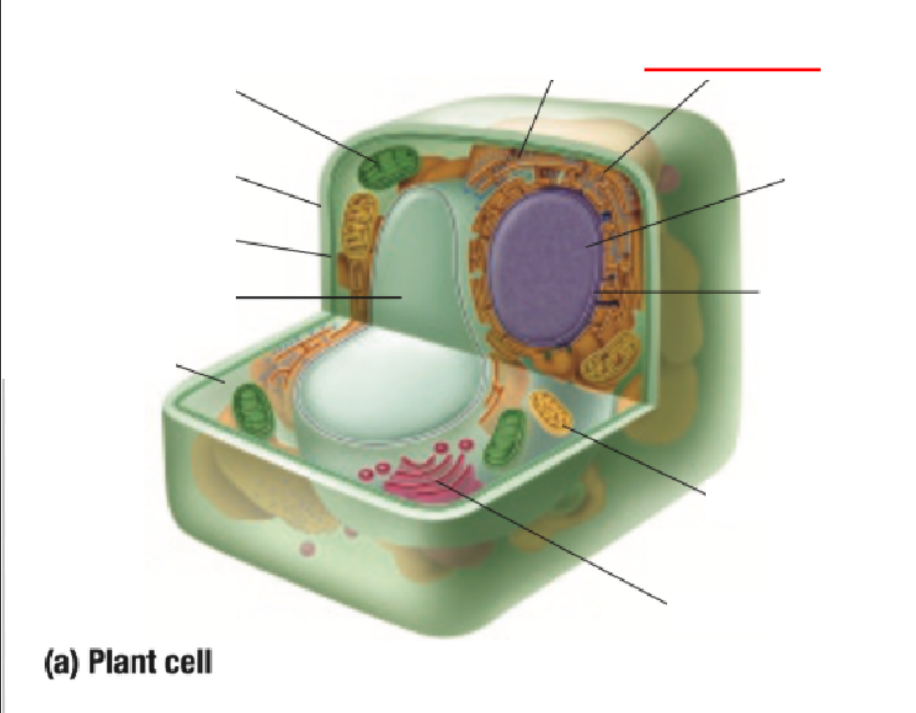
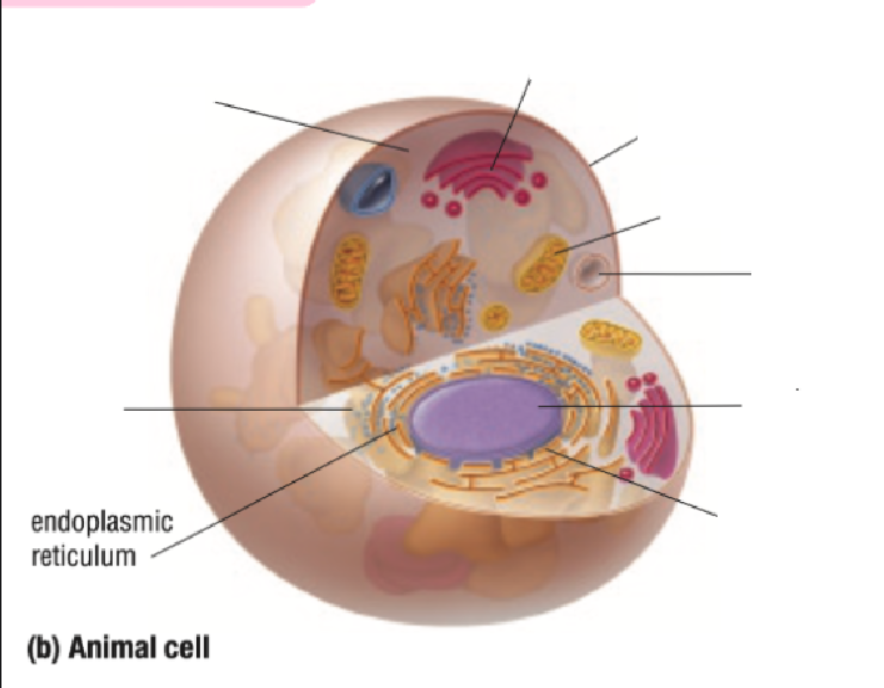
Endoplastic Recticulum
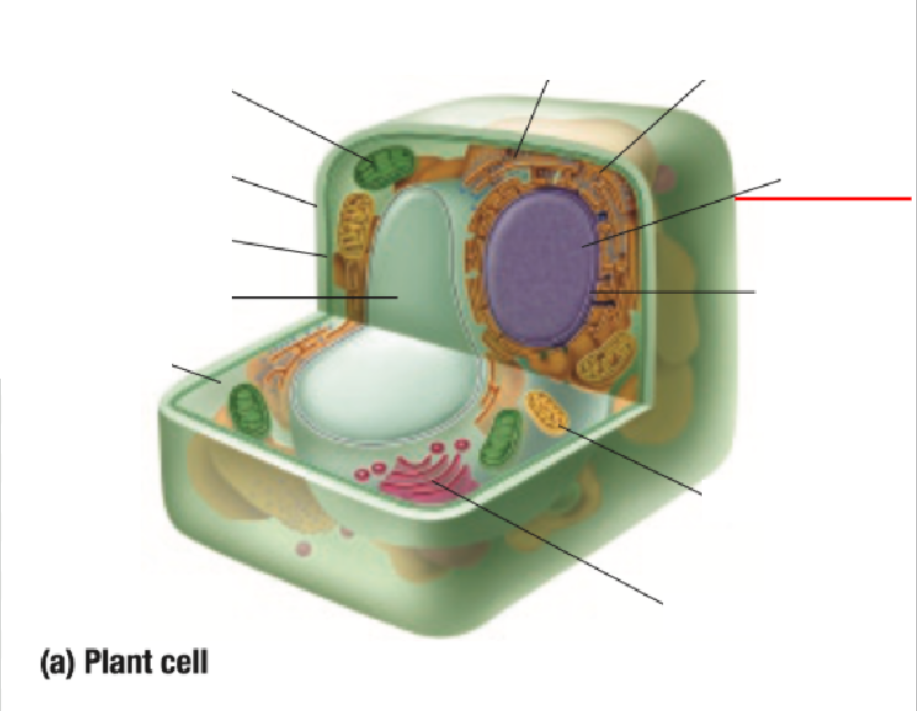
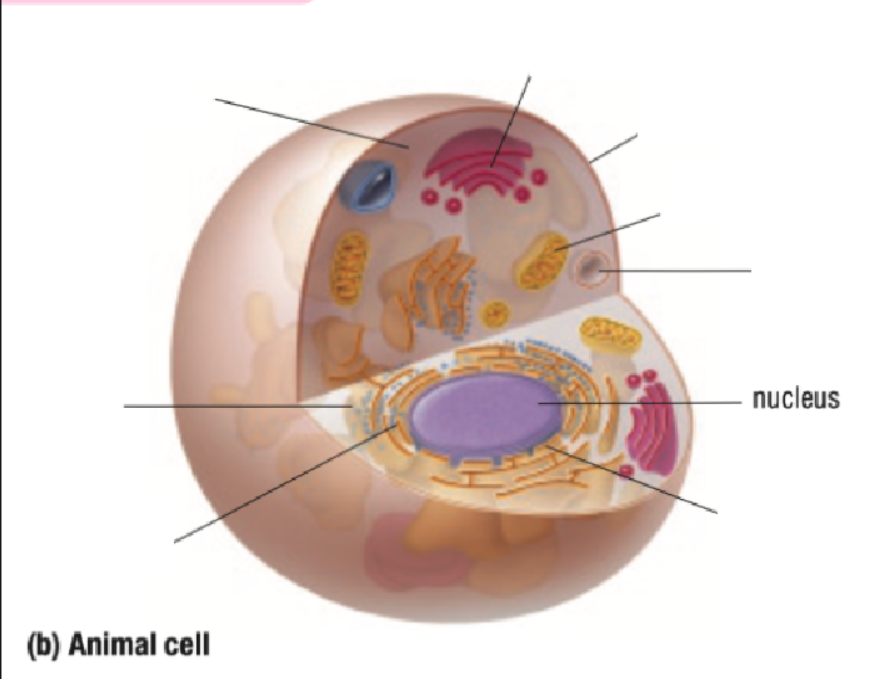
Nucleus
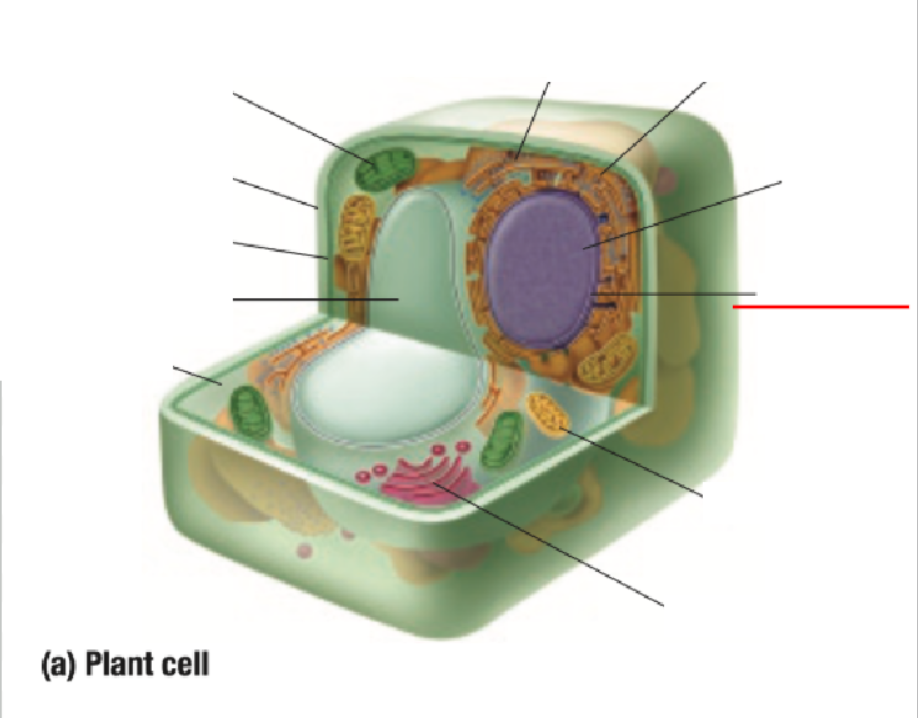
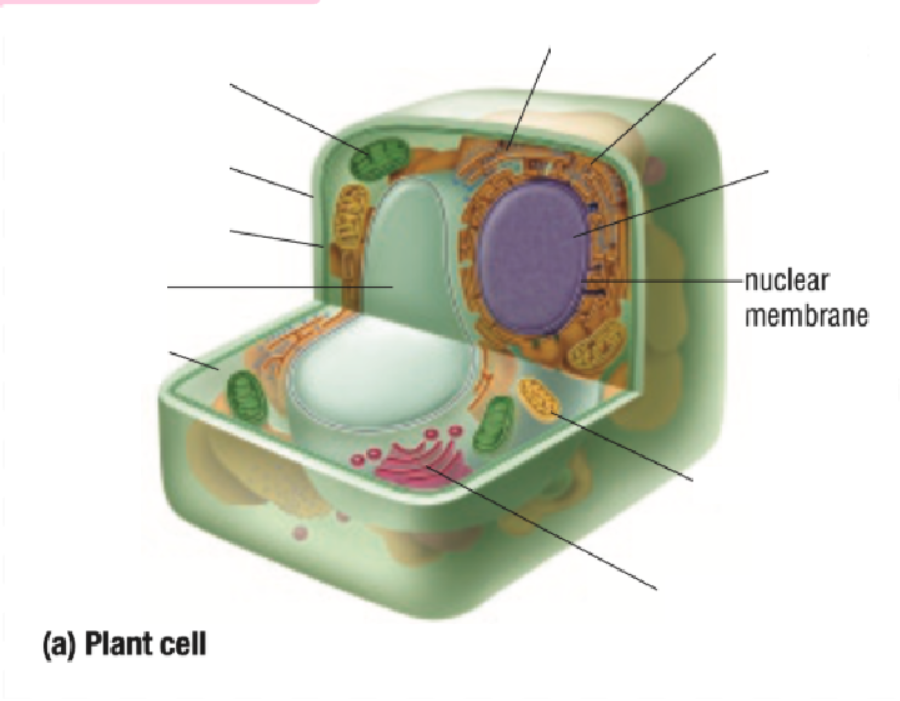
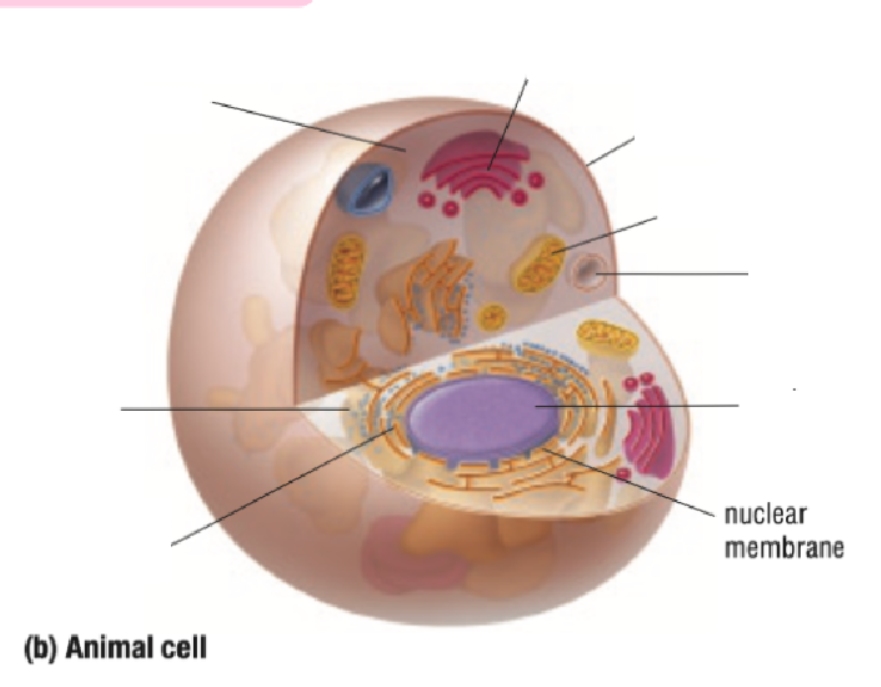
Nuclear Membrane
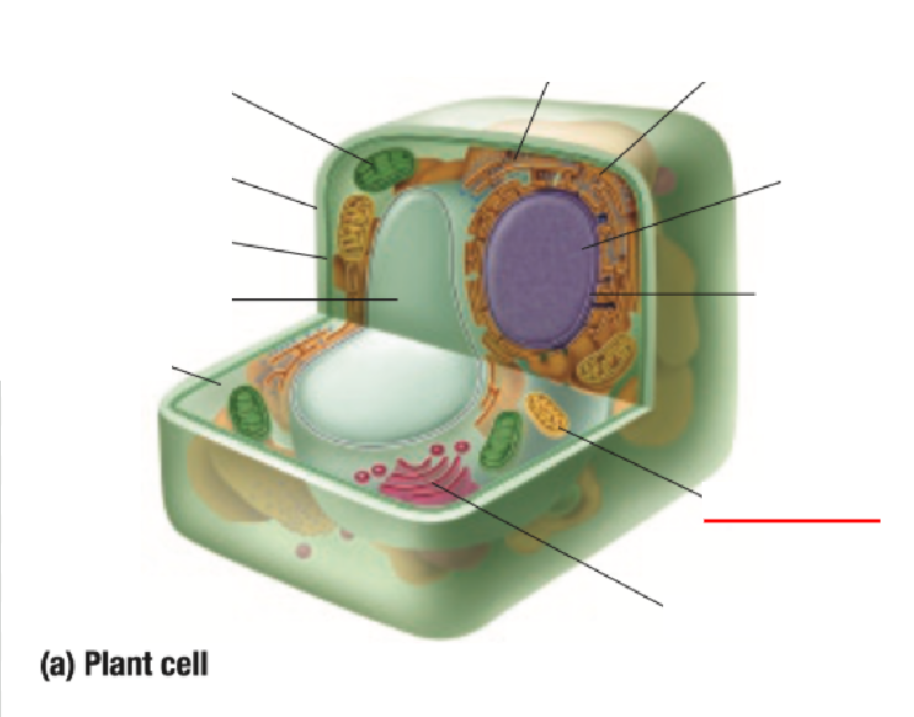
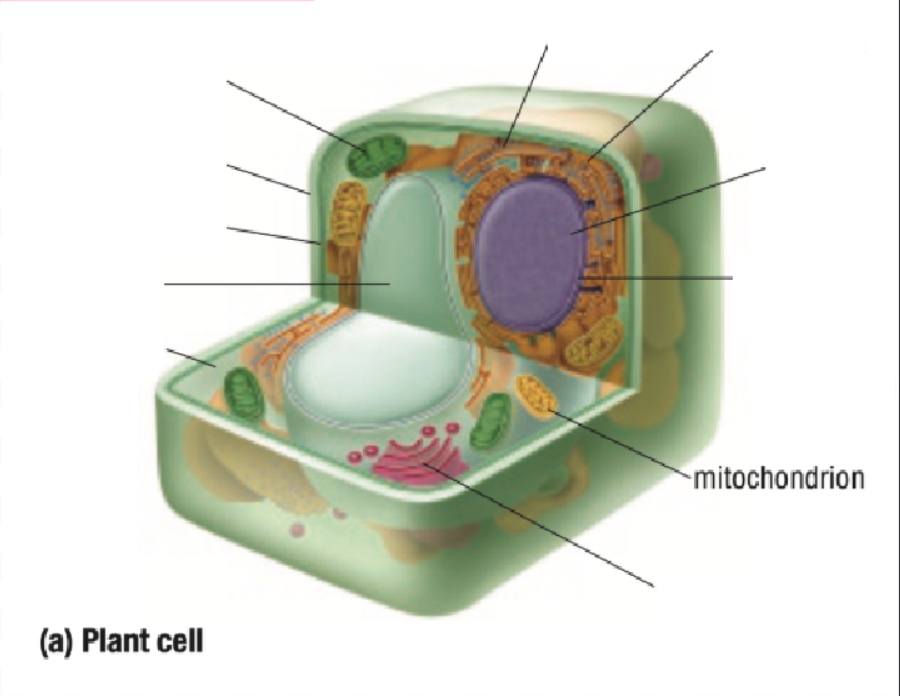
Mitochondria
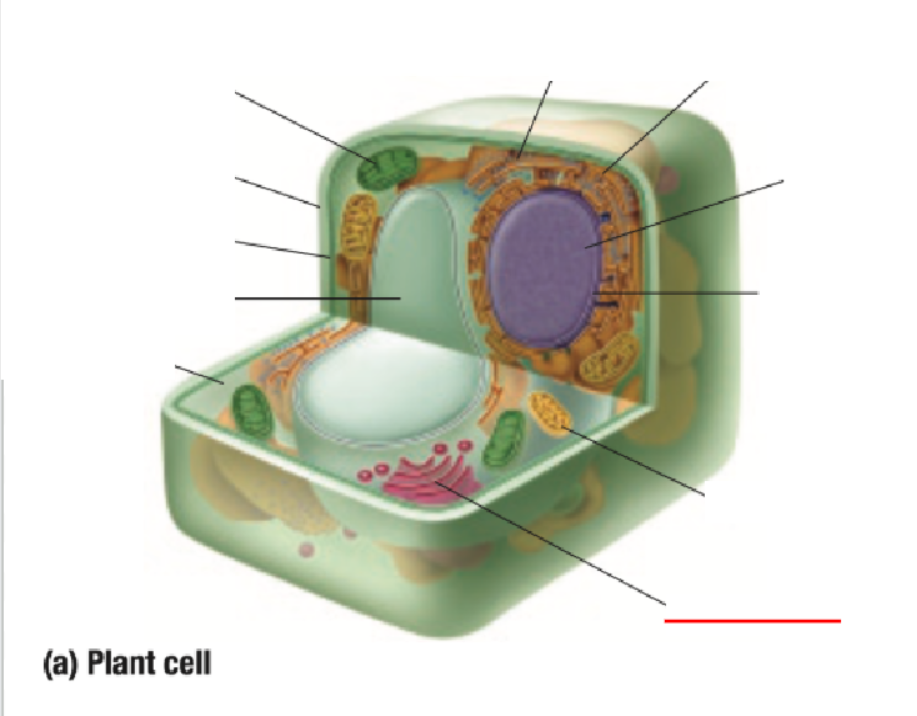
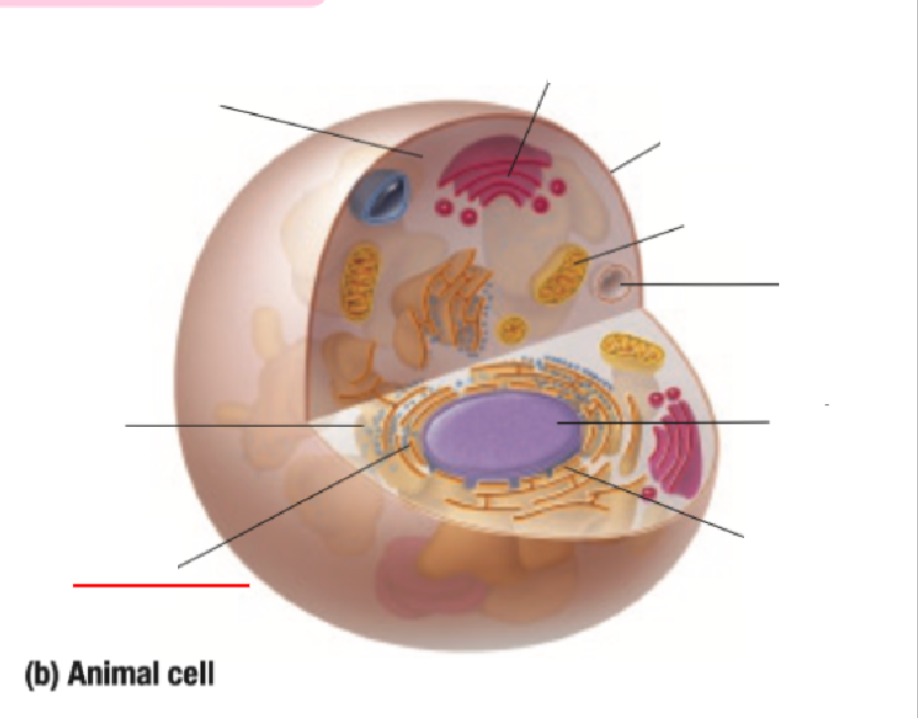
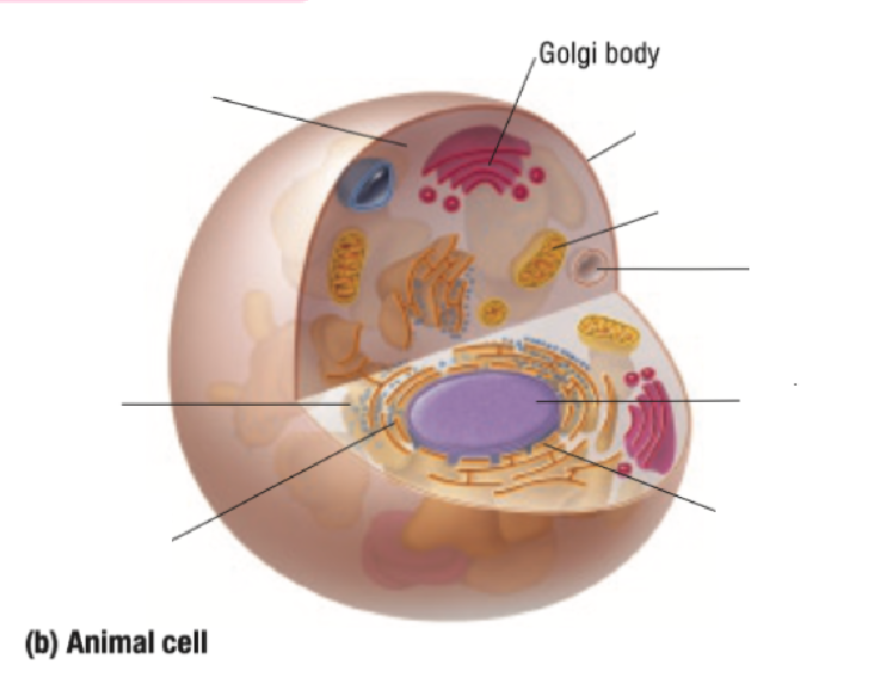
Golgi Body
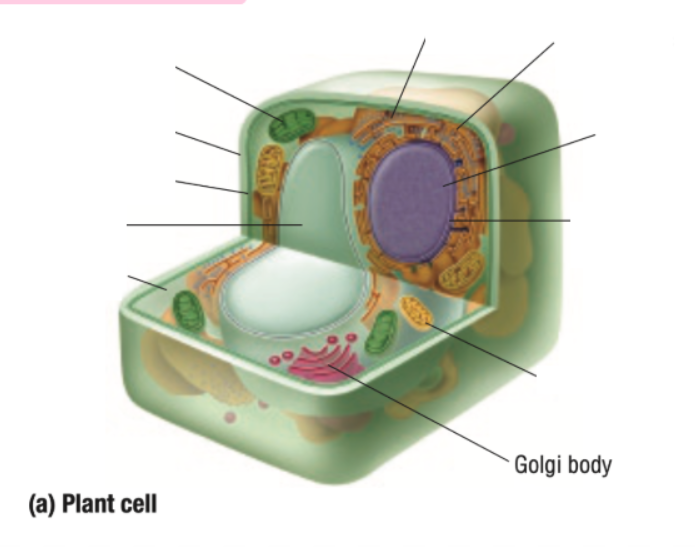
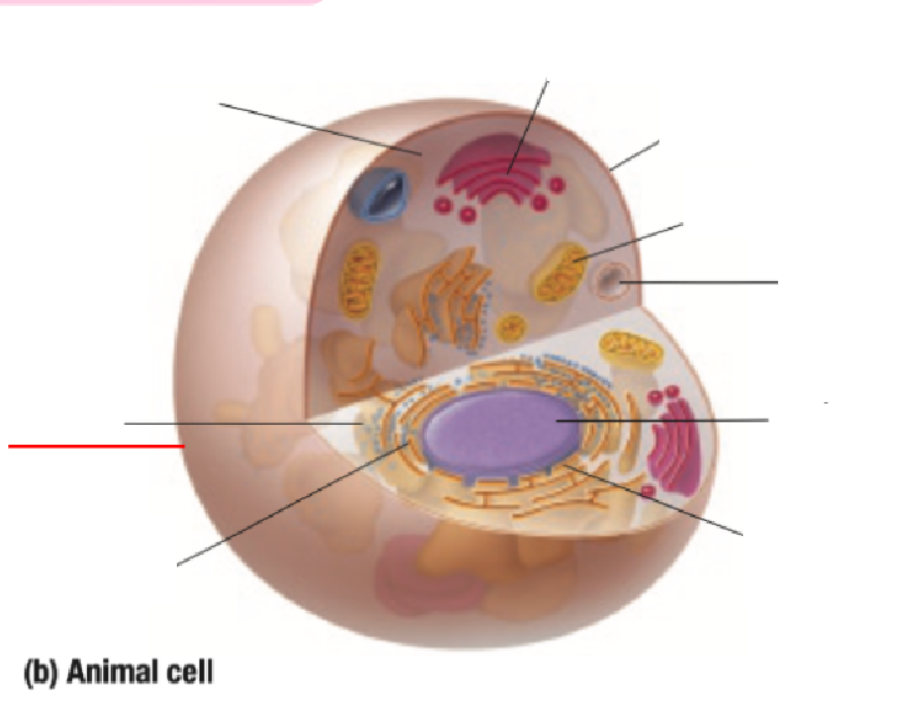
Cytoplasm
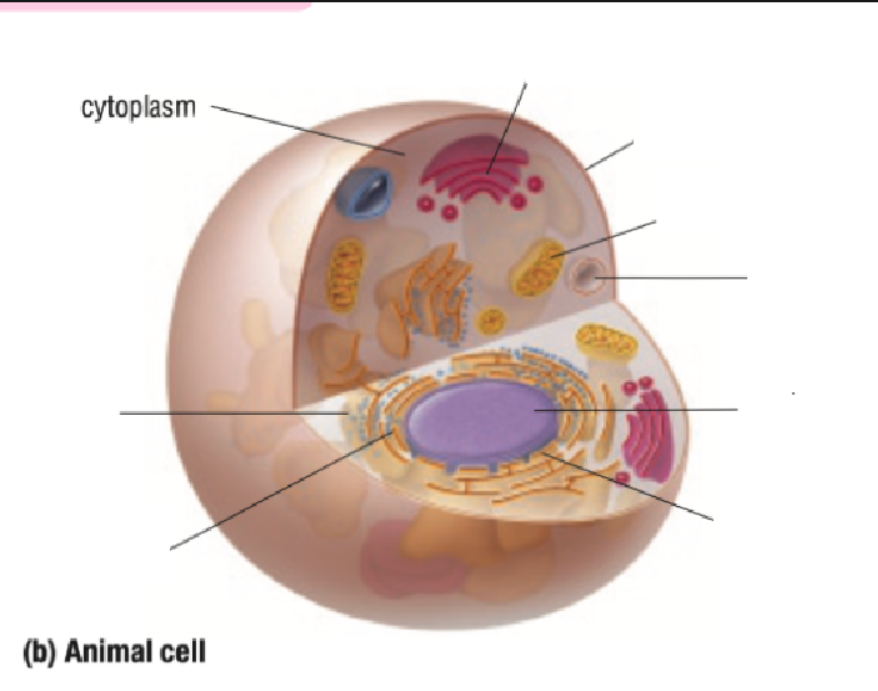
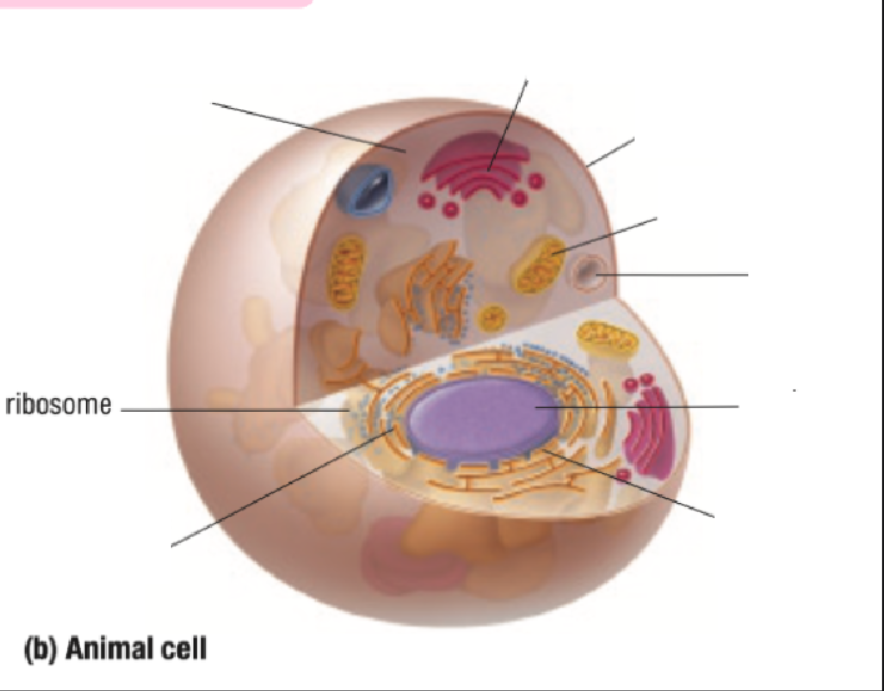
Ribosome
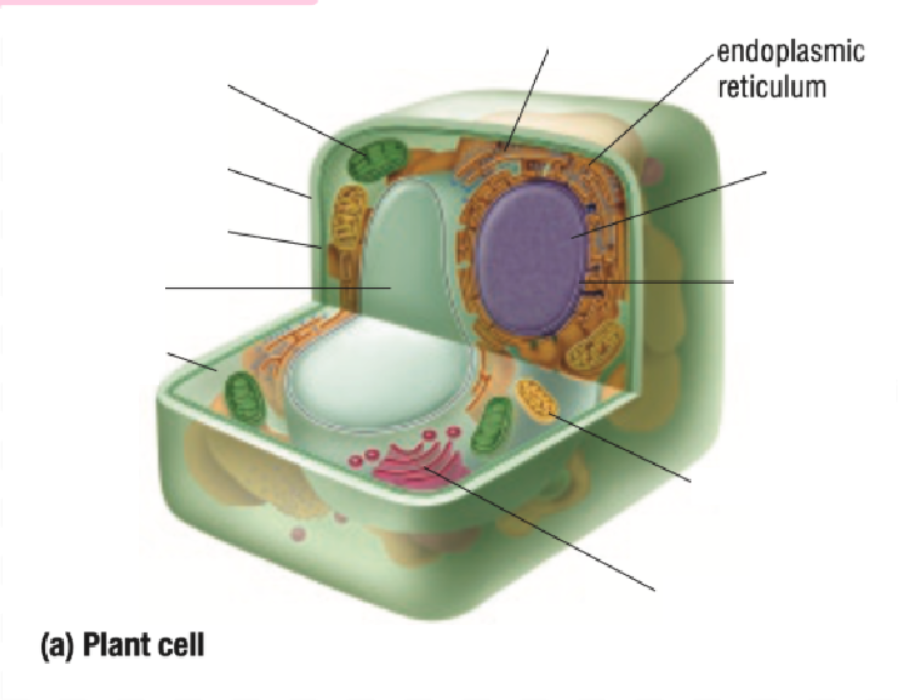
Endoplastic Recticulum
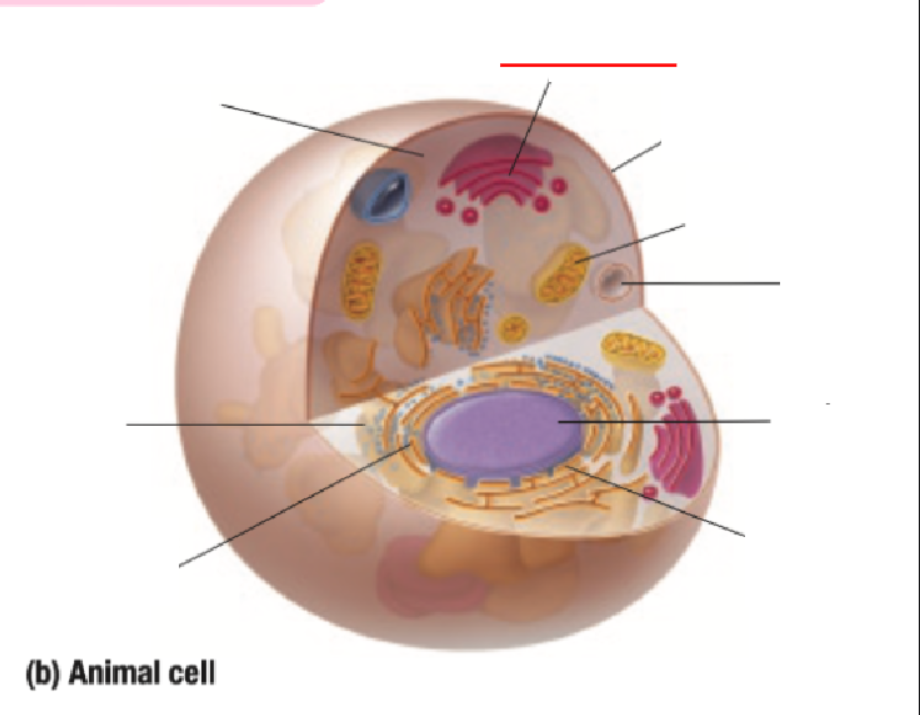
Golgi Body
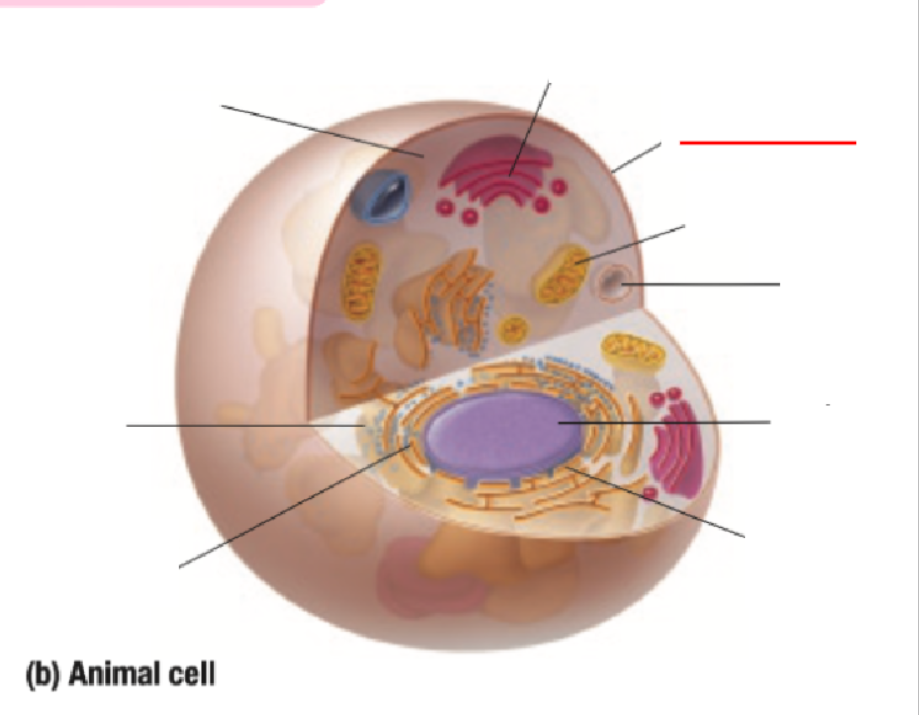
Cell Membrane
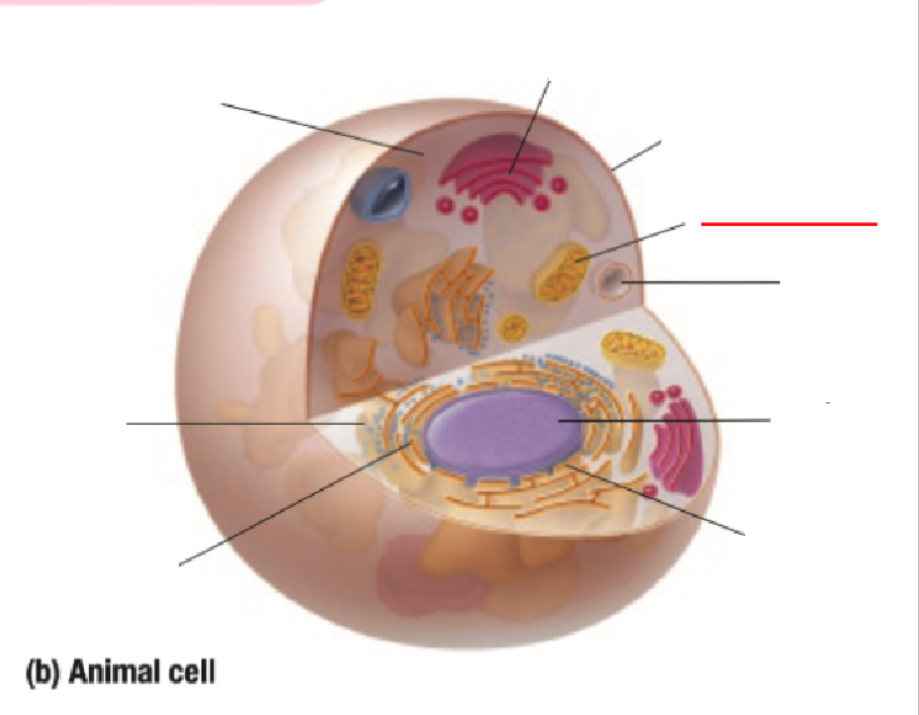
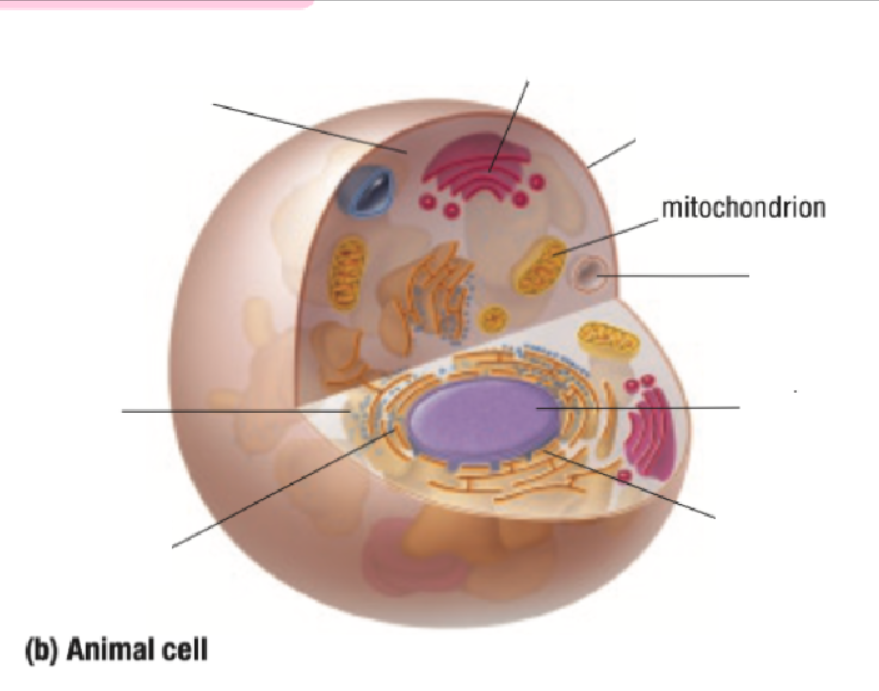
Mitochondria
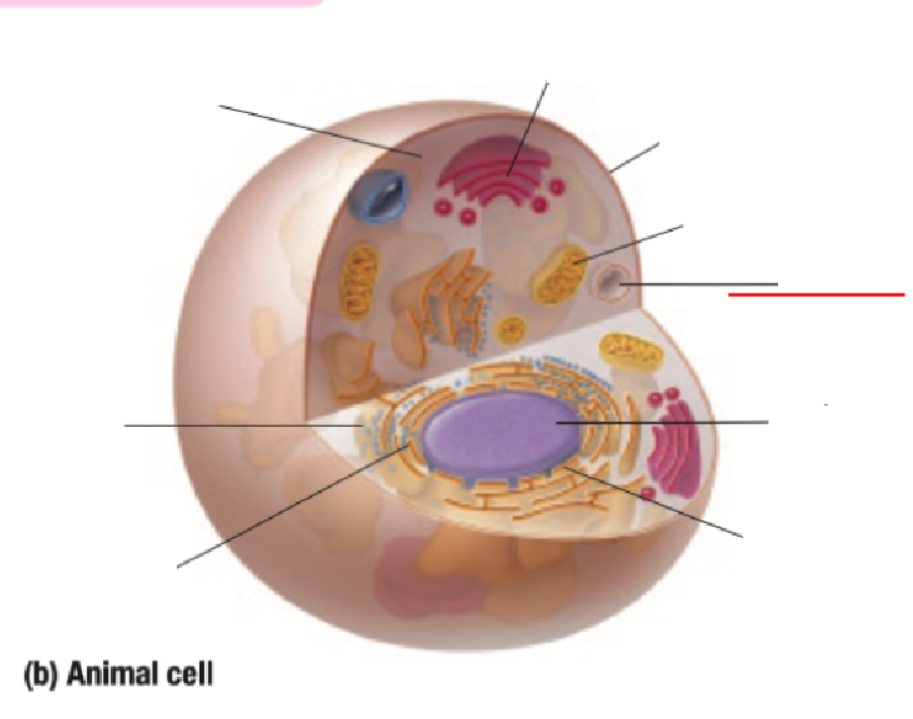
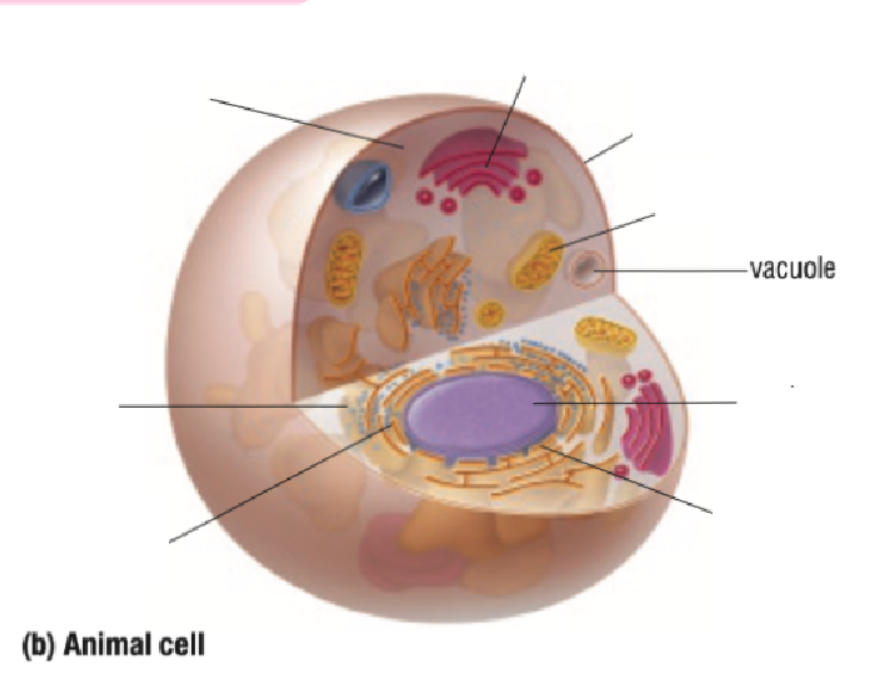
Vacuole
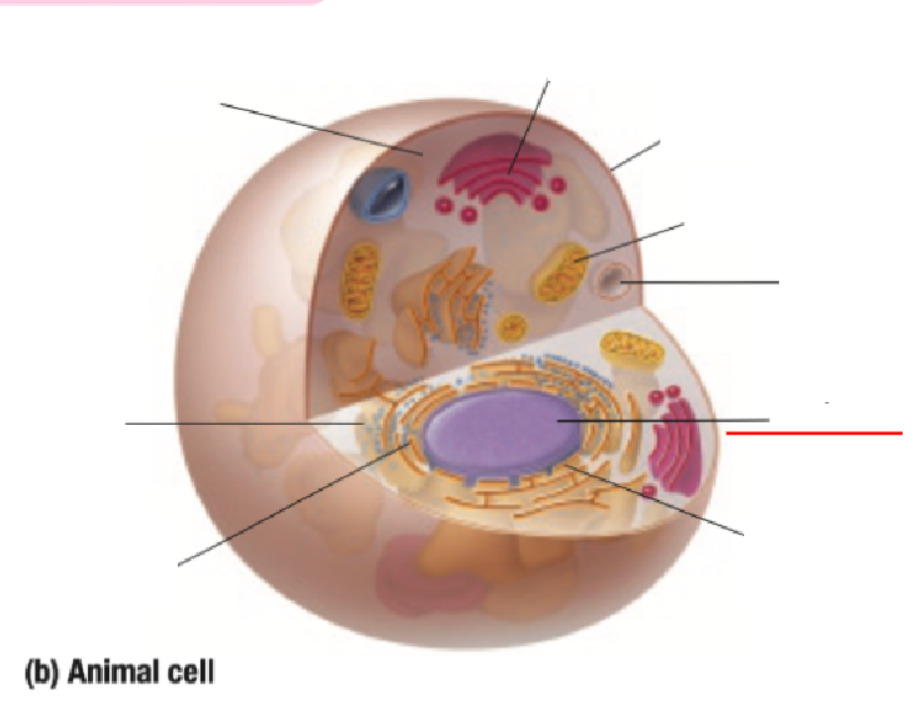
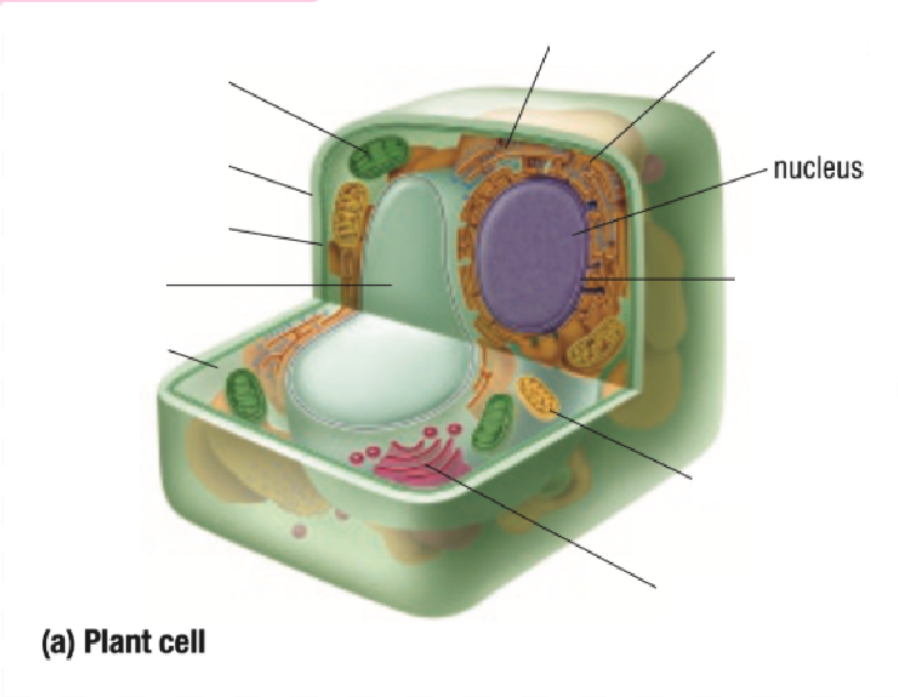
Nucleus
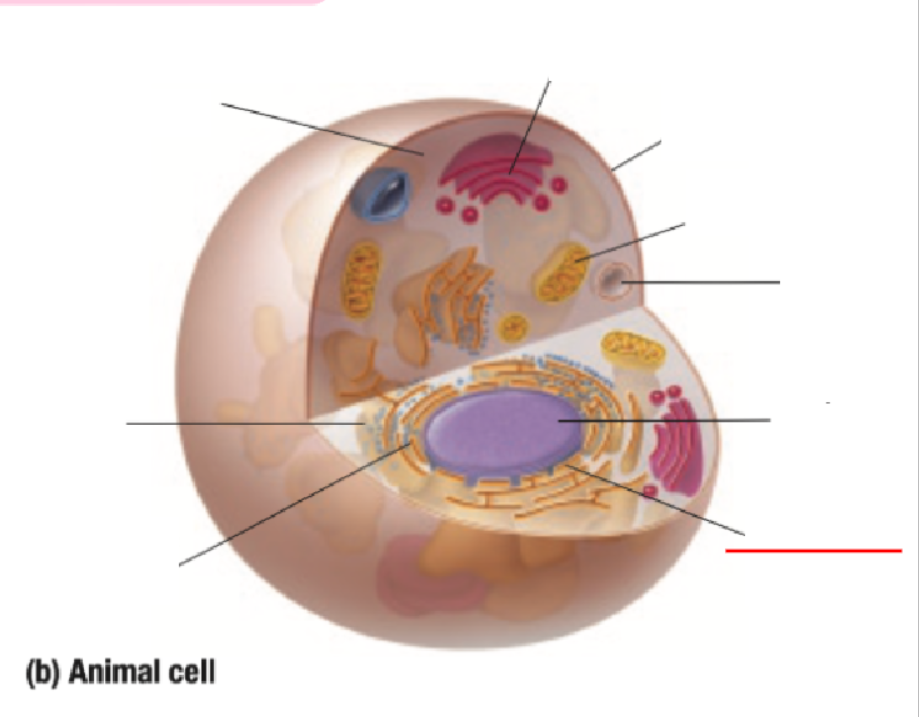
Nuclear Membrane
Cytoplasm Definition
All organelles are floating inside the cytoplasm
Made of mostly water, making it either jelly-like or liquid for organelles to move around inside of it
Endoplastic Reticulum Definition
Made of branching tubes and pockets
Continuous from the nuclear membrane to the cell membrane
Fluid-filled tubes transport materials through the cell
Ribosomes Definition
Protein Factory: Ribosomes are like tiny factories in a cell that make proteins. Proteins are important for the cell to work and grow
Ribosomes read the cell's DNA to know how to build the right proteins
You can find ribosomes floating in the cell’s cytoplasm or stuck on the endoplasmic reticulum.
Golgi Bodies Definition
Collect and process materials to be removed from the cell
Makes and secretes mucus
Vacuoles Definition
Single layer of membrane for a fluid-filled sac
Function depends on the type of cell
Some functions are:
containing some substances
removing unwanted substances from the cell
maintaining internal fluid pressure inside the cell
Takes up most space in plant cells
Cell Wall Definition
Outside the cell membrane of a plant cell
Made of cellulose
Gives support for cell shape
Protects cell from physical injury
Chloroplast
Contains chlorophyll pigment which gives leaves their green colour
Absorbs light energy to allow for photosynthesis
Photosynthesis: light energy from the Sun and carbon dioxide is used to make glucose (sugar) and oxygen
Prokaryotes
A cell that does NOT have a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles
Eukaryotes
A cell that HAS a nucleus and other organelles, each surrounded by a thin membrane
Diffusion
Movement of particles from high concentration to low concentration
Osmosis
Movement of water from high concentration to low concentration
Name the stages of Cell Division
Interphase
G1
S
G2
Mitosis:
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
Cytokinesis
What happens to a plant cell in cytokinesis?
In a plant cell, a plate forms that becomes a cell wall, sealing off the contents of the new cells from each other.
Apoptosis
When a cell is damaged, it is programmed to destroy itself through apoptosis
Tumor
Abnormal mass of cells that can harm tissues, organs, and systems. This can lead to cancer.
Cancer
When cells grow out of control and damage healthy organs and tissues
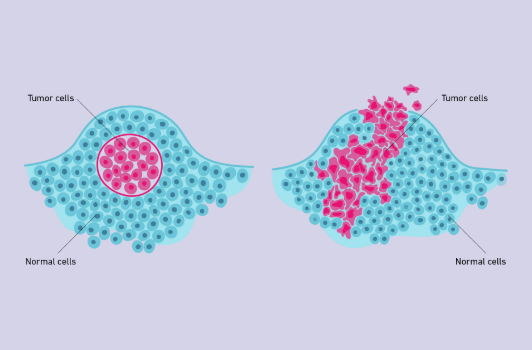
Benign Tumor
A tumor that does not affect surrounding tissues other than by physically crowding them (Left)
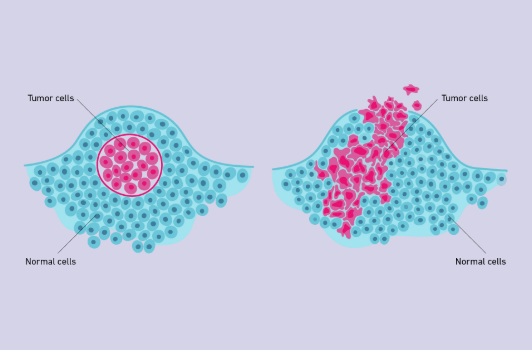
Malignant Tumor
A tumor that interferes with the functioning of surrounding cells; a cancerous tumor (Right)
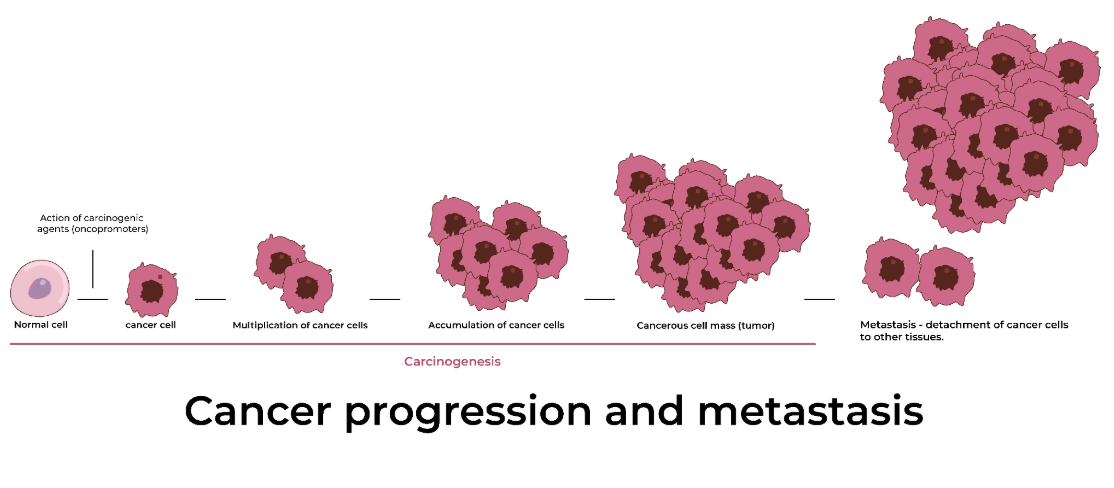
Metastasis
The process of cancer cells breaking away from the original (primary) tumor and establishing another (secondary) tumor elsewhere in the body
Cellular Differentiation
The process by which a cell (Unspecialized/Stem Cell) becomes specialized to perform a specific function
Stem Cell
An undifferentiated cell that can divide to form specialized cells
Embryonic Stem Cells
Can differentiate into any kind of cell
→ pluripotent: can transform into mostly any type of cell
Tissue Stem Cells:
Can differentiate into specific types of cells depending in what tissue it is in
→ multipotent: multipotent: can only transform into a limited number of cells