15 Greenhouse gases and the Carbon Cycle
Carbon Dioxide and Methane
- When shortwave radiation from the sun strikes the Earth's surface it is absorbed and re-emitted from the surface of the Earth as infrared radiation
- However much of the I.R. energy is trapped inside the Earth's atmosphere by Greenhouse gases which can absorb and hold the radiation
- Two such gases are carbon dioxide and methane
- Levels of carbon dioxide and methane in our atmosphere are increasing as a result of human activity
Carbon dioxide
- Sources: combustion of wood and fossil fuels, respiration of plants and animals, thermal decomposition of carbonate rocks and the effect of acids on carbonates
- Main reason for increasing levels: combustion of fossil fuels increasing to meet our demands
Methane
- Sources: digestive processes of animals, decomposition of vegetation, bacterial action in swamps, rice paddy fields and landfill sites
- Main reasons for increasing levels: increase in animal farming, number of paddy fields and landfill sites
The green house effect
Caused by the presence of greenhouse gases within our atmosphere, mainly methane and carbon dioxide
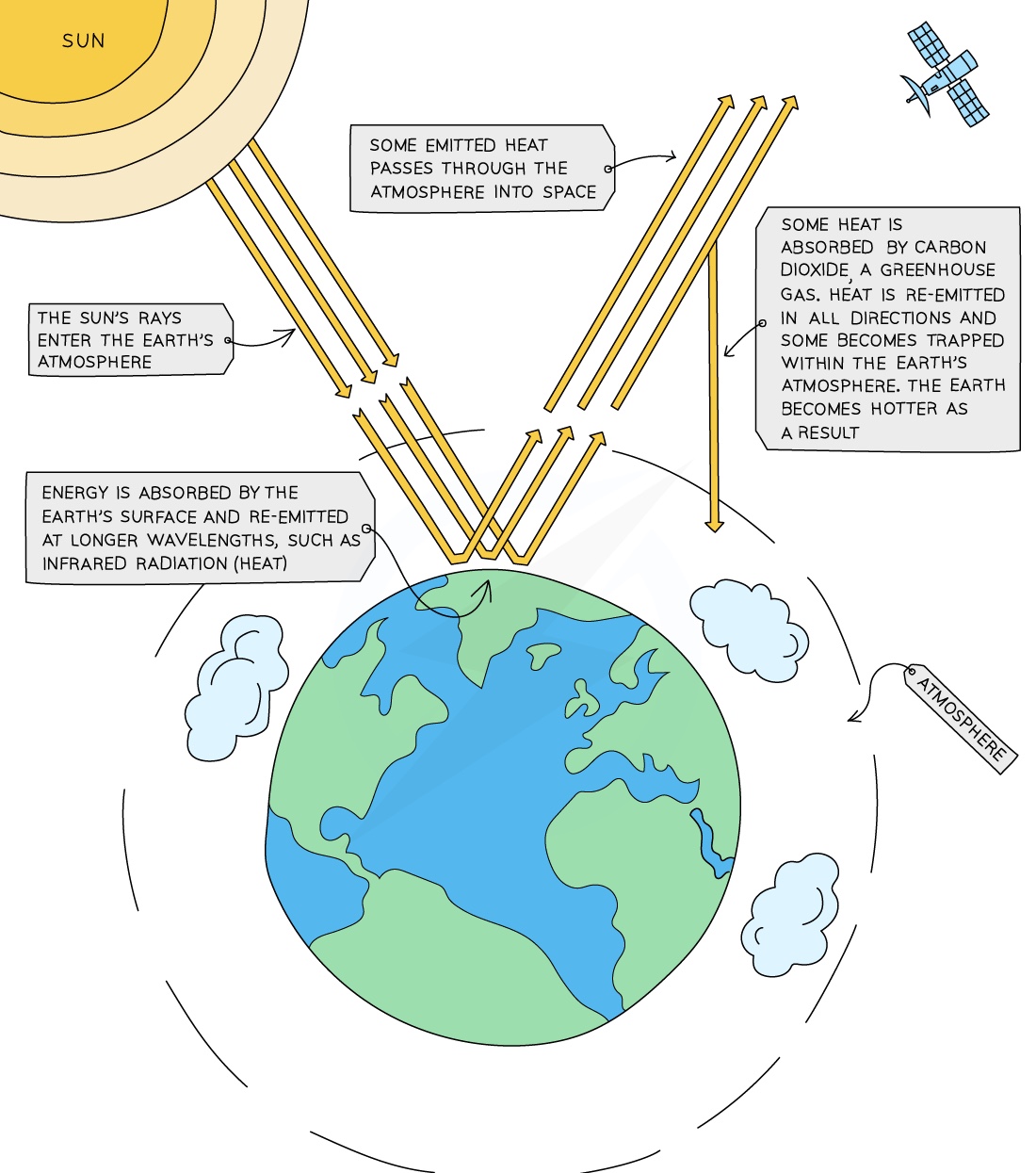
EXPLANATION
- The Sun emits rays that enter the Earth’s atmosphere
- The heat is absorbed and re-emitted back from the Earth’s surface
- Some heat is reflected back out into space
- But some heat is absorbed by greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane and is trapped within the Earth’s atmosphere, keeping the Earth warm
- As the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere increases due to human activity, more heat is trapped within the Earth's atmosphere causing the Earth’s average temperature to rise (global warming)
Consequences of global warming:
Climate change due to the increase in Earth’s temperature
Water levels will rise as glaciers melt because of high temperatures, causing flooding in low-lying countries
Extinction of species due to the destruction of natural habitats
Migration of species as they will move to areas that are more habitable (no droughts)
Spread of diseases caused by warmer climate
Loss of habitat due to climate change (animals that live on glaciers)
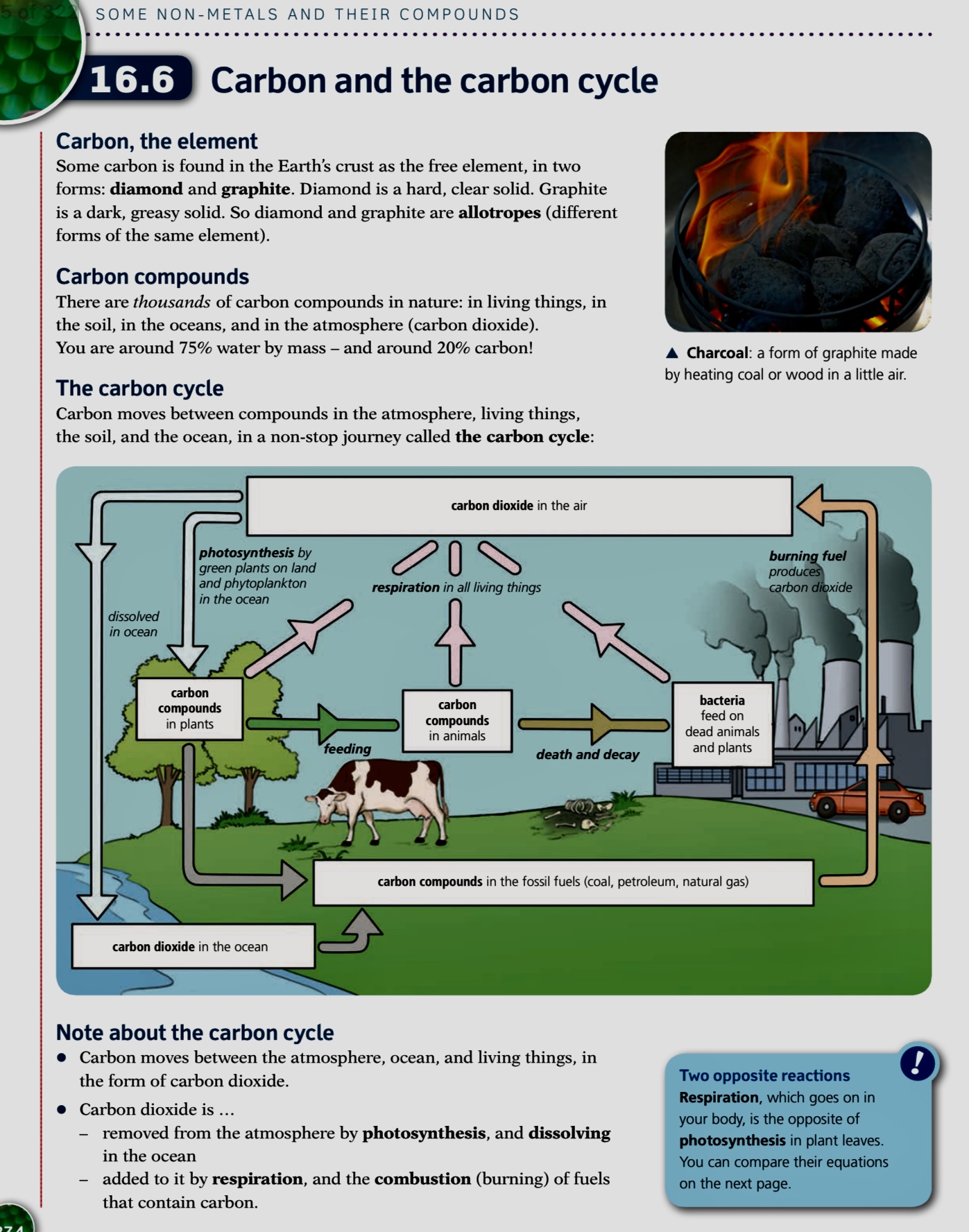

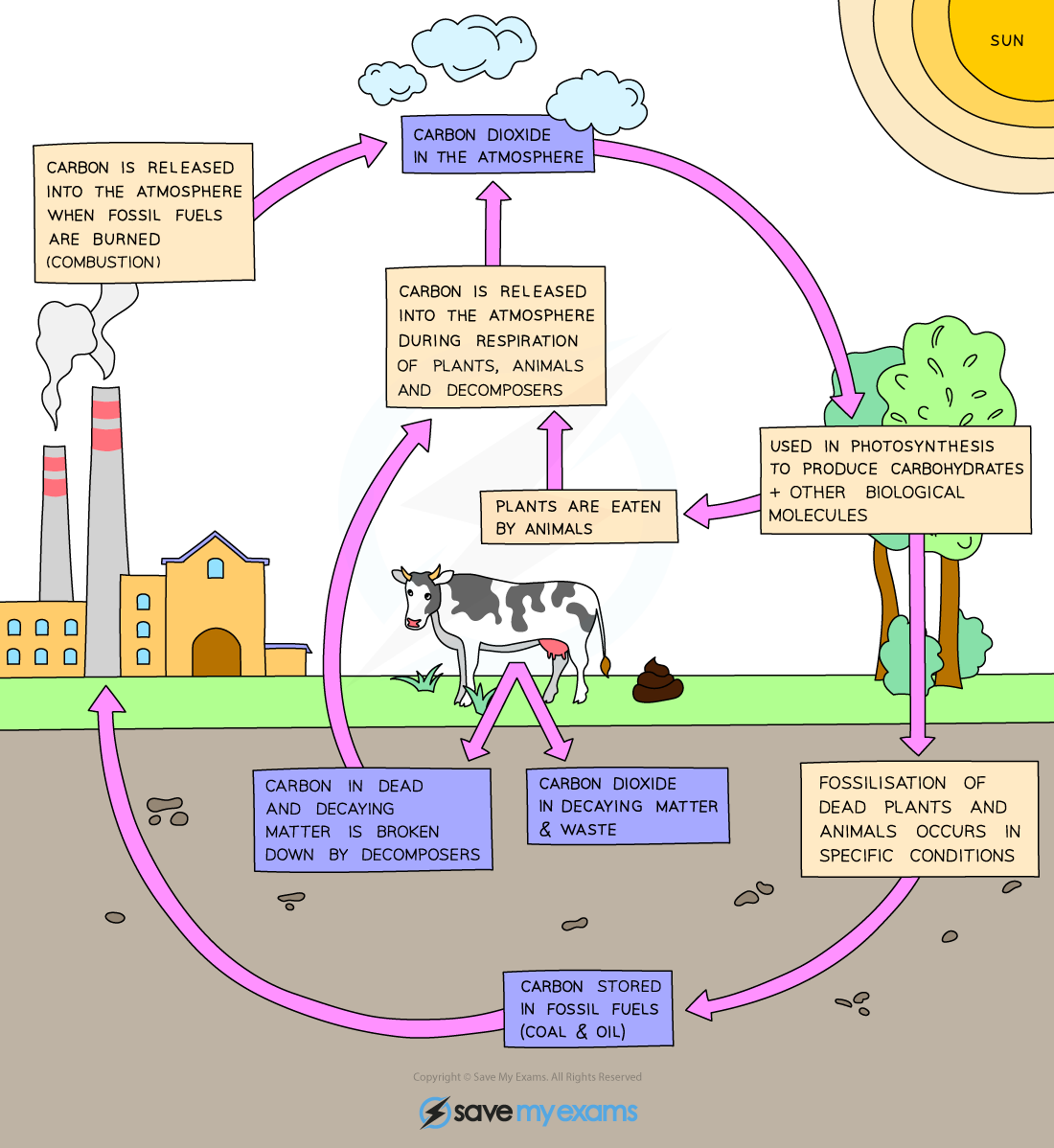
THE CARBON CYCLE
- The carbon cycle describes the movement of carbon between the seas, land and atmosphere
- In the atmosphere, the main source of carbon is carbon dioxide
Sources of CO2 in the atmosphere
- Combustion of fossil fuels, e.g: methane:
- CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + H2O
- Respiration: the production of energy in living things. The overall reaction of respiration is represented by the equation:
- C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O
- Decomposition of limestone
- CaCO3 → CaO + CO2
- Reactions of acids with carbonates
- CaCO3 + 2HCl → CaCl2 + H2O + CO2
Removal of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere
Photosynthesis: the process of producing glucose and oxygen from carbon dioxide and water in plants in the presence of chlorophyll and light:
- 6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Carbon dioxide dissolves in the water in seas and oceans and is removed by shellfish for making their calcium carbonate shells
Balancing the Carbon
Carbon as carbonate, carbon dioxide or organic carbon compounds is present in the sea, the air and under the Earth
There is a continuous cycle of these compounds between these sources called the carbon cycle
There is a constant amount of carbon compounds in the sea, atmosphere and under the Earth
As long as these are balanced, the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere remains constant
Scientists are worried that increasing the amounts of fossil fuels burned will increase global warming and unbalance the carbon cycle