1.10 streptococcus (s. pneumoniae)
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
what did fredrick griffith discover when experimenting with s. pneumoniae?
he discovered the "transforming principal" in which heat-killed virulent bacteria could transform non-virulent bacteria into a virulent
can the strain of s. pneumoniae without a "shiny" capsule kill mice subjects?
no
what do staph. aureus and strep. pyogenes have in common?
A. they both produce coagulase
B. they both secrete catalase
C. both can cause toxic shock syndrome
D. both have protein G that binds to antibodies
E. all of the above are shared properties
C
strep contains protein ___. while staph contains protein ____
G; A
strep. pneumonia is frequently isolated from the ____ _____ ____. what age group is a common carrier of strep. pneumonia ?
upper respiratory tract; pre-school aged children
strep. pneumonia is most often the cause of ____ ______
otitis media (ear infection)
strep. pneumonia is the major cause of community-acquired ________. and common cause of _______ and _________ at all ages
pneumonia; bacteremia; meningitis
strep. pneumonia meningitis is most commonly found in what age group?
adults
strep. pneumonia falls into which group on the streptococci "tree"? what other strep class belongs in this group?
mitis; S. oralis
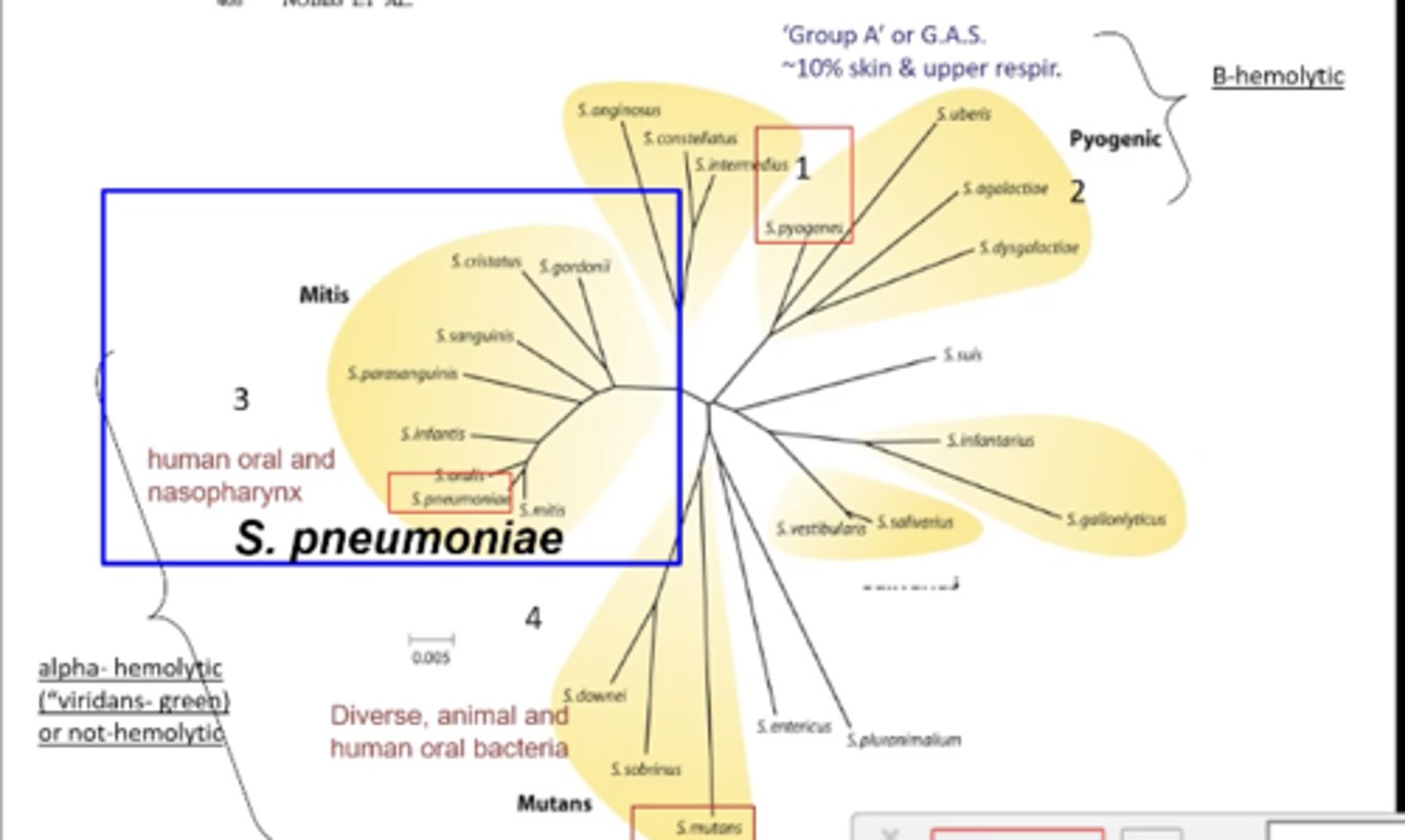
what type of hemolysis does strep. pneumonia present?
partial or no lysis of RBC's
what group of strep strains are more important clinically? (they can have a major effect on pts with endocarditis)
S. oralis, S. gordonii, S. sanguis, S. mitis
the viridans (or mitis group) is ______-hemolytic
alpha
what is the microscopic morphology of strep. pneumonia
gram + diplococci
what is the characteristic color of strep. pneumonia if a sputum sample is obtained?
red
similar to Staph. aureus, strep. pneumonia can travel through the blood stream leading to ________ and eventually _______ and ______ ________
bacteremia; endocarditis; septic arthritis
how would you diagnose strep. pneumonia?
gram stain, blood sample, sputum sample, CNS fluid
can you diagnose or obtain a sample via throat swab?
no
previously strep. pneumonia was very sensitive to _______ however resistance is increasing. What might be given instead?
penicillin; augmentin
what is the major virulance factor of strep. pneumonia
capsule
the polysaccharide capsule has multiple different _______ which allow it to have varying _________
serotypes; virulance
strep. pneumonia produces an exotoxin called _______.
pneumolysin
Pneumolysin is a _____-______ _____ that is only expressed in an _______ environment
oxygen-labile hemolysin; anaerobic
is strep. pneumonia catalase + or -
- (air is irrelevant)
how does strep. pneumonia interact with antibodies?
degrades IgA1 antibody
(IgA is the mucosal antibody)
does strep. pneumonia have vaccines?
yes
what is unique about strep. pneumonia vaccines?
it can include or vaccinate for multiple different capsule types
what was the main issue with the old strep. pneumonia vaccine?
it had little to no response in children under 2yr
how is the new strep. pneumonia vaccine different?
it protects against 7-13 most common capsule types via a conjugated protein