4- Endocrine Pharm
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
Endocrine pharmacology general function
• Replacement
• Increase hormonal effect
• Treat excessive endocrine function
• Regulate/manipulate normal endocrine function
4
What are the 4 types of insulin?
- rapid acting
- regular
- intermediate-acting
- long acting
Regular insulin
- Synthetic or pork
- Absorption slower than endogenous insulin released from the pancreatic beta cells
Rapid acting insulin
- Biosynthetic insulin that is slightly different than human insulin to allow rapid absorption
Intermediate-acting insulin
- Absorbed slower and have a prolonged effect
- Created by adding other agents to insulin
Long-acting insulin
Absorbed slower and has a prolonged effect
• Used when less stringent control of blood sugar is needed such as person controlling condition with diet & weight control
• May be used if person has problems with hypoglycemia overnight
Biosynthetic
A combination of insulin is used to
provide optimal control of blood sugar
Intensive insulin therapy goal
maintain blood glucose in the normal physiologic range
• Frequent monitoring of blood glucose level and self-administration of insulin
• Decreases long-term complications due to “tighter control”
Insulin therapy ADR
Immunologic reaction
– Allergic reaction (rash, wheezing, bronchoconstriction, etc)
– Usually associated with animal forms of insulin
Hypoglycemia
• Dose greater than patient’s needs
• Missed or delayed meal
• Exercise – accelerates the movement of glucose out of bloodstream into skeletal muscle
What are the initial s/s of Hypoglycemia?
- Headache
- Fatigue
- Hunger
- Tachycardia
- Sweaty/Clammy
- Pale
- Anxiety
- Confusion
What are the later s/s of Hypoglycemia?
- Loss of consciousness
- Seizures
- Death
What are the consideration of Insulin therapy?
• Insulin needs to be refrigerated
• Need sterile syringes
• Rotate sites (abdomen, upper thighs, upper arms, back, buttocks)
• Glucose monitoring
Oral antidiabetic drugs
Control blood glucose levels in type 2 DM
- increases the release of insulin from pancreatic beta cells
- increases sensitivity of peripheral tissues to insulin
What are the types of oral antidiabetic drugs?
- Sulfonylureas
- Biguanides
- Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors
- Thiazolidinediones
- Benzoic acid derivatives
Sulfonylureas MOA
- increase insulin release
- decrease hepatic glucose production
- variable efficacy and effects decrease with time
Sulfonylureas ADR
- Hypoglycemia (most common)
- GI disturbances
- Headache
Biguanides MOA
- decreases hepatic glucose production
- increase tissue sensitivity to insulin
*Metformin (Glucophage) is a
Biguanides
Biguanides ADR
- GI disturbances
- Lactic acidosis (rare, but can be fatal)
Sulfonylureas vs Metformin
• Sulfonylurea use associated with 21% increase in cardiovascular events (stroke, MI) & deaths
• Confirms use of metformin as first-line drug for treatment of diabetes
• Strengthens the evidence about the cardiovascular benefits of metformin
Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors MOA
Inhibit glucose absorption from the GI tract
• Inhibit enzymes that break down sugars in the GI tract which slows the entry of glucose into the bloodstream
Examples of alpha glucosidase inhibitors
- Acarbose (Precose)
- Miglitol (Glyset)
Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors ADR
- GI disturbances
Thiazolidinediones MOA
- decrease hepatic glucose production
- increase tissue sensitivity to insulin
Examples of Thiazolidinediones
- Pioglitazone (Actos)
- Rosiglitazone (Avandia)
Thiazolidinediones ADR
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Fatigue/weakness
- Back pain
- Hepatic toxicity (rare)
Benzoic acids MOA
- increase insulin release
Benzoic acids examples
- Repaglinide (Prandin)
- Nateglinide (Starlix)
Benzoic acids ADR
- Hypoglycemia
- Bronchitis
- Upper respiratory tract infections
- Joint & back pain
- GI disturbances
- Headache
Glucagon is used to manage Hypogycemia. It is used to
treat hypoglycemia associated with insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents
– Mobilizes release of glucose from liver: Sufficient glycogen needed in the liver to be effective
Glucagon ADR
nausea, vomiting, allergic reaction (skin rash, difficulty breathing)
Glucagon-like Peptide agonist (GLP-1)
hormone that is normally released from the GI tract after eating
• Stimulates insulin release from pancreas
• Decreases glucagon release, delays absorption of food, & reduces appetite
GLP-1 agonists
• Manage BS
• Lower A1C
• Weight loss
GLP-1 Agonists
• Exenatide (Byetta): Injected before morning and evening meals to prevent BS spikes
• Tirzepatide (Mounjaro): Once weekly injection
• Semaglutide
– Injection (Ozempic, Wegovy)
– Rybelsus
What are the side effects of GLP-1 agonists?
• GI symptoms: Nausea, Vomiting, Diarrhea
• Hypoglycemia
Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 (DPP-4) Inhibitors
- Inhibits enzyme that breaks down GLP-1 to prolong effects
- Example: Sitagliptin (Januvia), Vildagliptin (Galvus)
Immunosuppressants
- Used in Type 1 DM
- Limits beta cell destruction & decreases need for exogenous insulin
Immunosuppressants ADR
severe side effects when used at high doses for long time
What are rehab considerations for pts taking drugs for DM?
• Have foods containing glucose available in case of hypoglycemia
• Can patient or other person self-administer insulin appropriately?
• Insulin absorption affected by: Physical agents (heat, cold), Massage, Exercise
• Patient education: Diet, Exercise, Signs & symptoms of low blood sugar
• Ask patient about most recent blood sugar level
A 75 y/o patient is receiving outpatient physical therapy for gait & balance impairments. They come to PT at 9 am 2x/wk. They c/o feeling shaky and have a headache. Their pulse is 100 bpm. They are sweating and pale. PMH includes a h/o DM & hypertension. Meds: Humalog 75/25, Furosemide, Atenolol.
– What are considerations when working with this patient?
– What is your next step?
– Other considerations
- what their blood sugar
- vital signs
- dehydration (furosemide may cause this)
- atenolol is a beta blocker, monitor RPE
Antithyroid agents for hyperthyroidism
inhibit synthesis of thyroid hormones
- Temporary measure
- Examples: Propylthiouracil (Propyl-Thyracil), Methimazole (Tapazole)
Antithyroid ADR
skin rash, itching agranulocytosis (↓ WBC), aplastic anemia (↓ RBC), excessive inhibition will cause symptoms resembling hypothyroidism
Beta blockers for Hyperthyroidism
Used to treat symptoms of tachycardia, palpitations, etc
Iodide for hyperthyroidism
- Large doses to cause a rapid decrease in thyroid function
- Effects diminish ≈ 2 weeks of use
- May be used prior to thyroidectomy
- ADR: severe hypersensitivity (allergic) response
Radioactive iodine for hyperthyroidism
- Radioactive isotope selectively destroys thyroid tissue (follicle)
- Grave's Disease
- Ablates thyroid gland & need to have thyroid replacement therapy
Hormone replacement therapy for hypothyroidism
- Debate about whether to replace T4 only or both T3 & T4
- Used after thyroidectomy, pharmacologic ablation, treatment of goiter, other hypothyroidism
What are rehab considerations of thanking thyroid disorders
- monitor pt for s/s related to dosing
- differentiate between disease process and ADR
- watch for treatment interactions
- vital signs
hyperparathyroidism is usually managed with:
surgical resection
• Alternative pharmacological management of hypercalcemia: Biphophonates, Calcitonin
Pharm management for Hypoparathyroidism
Calcium supplements: used to ensure adequate calcium is present for physiologic processes and encourage bone formation
Signs of hypercalcemia
- Constipation
- Drowsiness
- Fatigue
- Headache
- Confusion
- Irritability
- Cardiac arrhythmias
- Hypertension
- Nausea & vomiting
- Skin rash
- Pain in bones & muscle
Vitamin D for hypoparathyroidism
Fat-soluble vitamin
Used to ↑ blood calcium & phosphate levels to enhance bone mineralization
• ↓ renal excretion of calcium & phosphate
• ↑ intestinal absorption of calcium & phosphate
Signs of vitamin D toxicity
- Headache
- Increased thirst
- Decreased appetite
- Metallic taste
- Fatigue
- GI disturbances (nausea, vomiting, constipation, diarrhea)
- Hypercalcemia
- Hypertension
- Cardiac arrhythmias
- Renal failure
- Mood changes
- Seizures
- Death due to cardiac & renal complications
What are rehab considerations for pts taking drugs for parathyroid disorders
• Monitor patient for signs & symptoms related to toxicity
• Weight bearing activities to stimulate bone formation
• Avoid stress to bones that may be weak
• UV light promotes endogenous Vitamin D synthesis & bone formation
Male and female hormone
*see pic
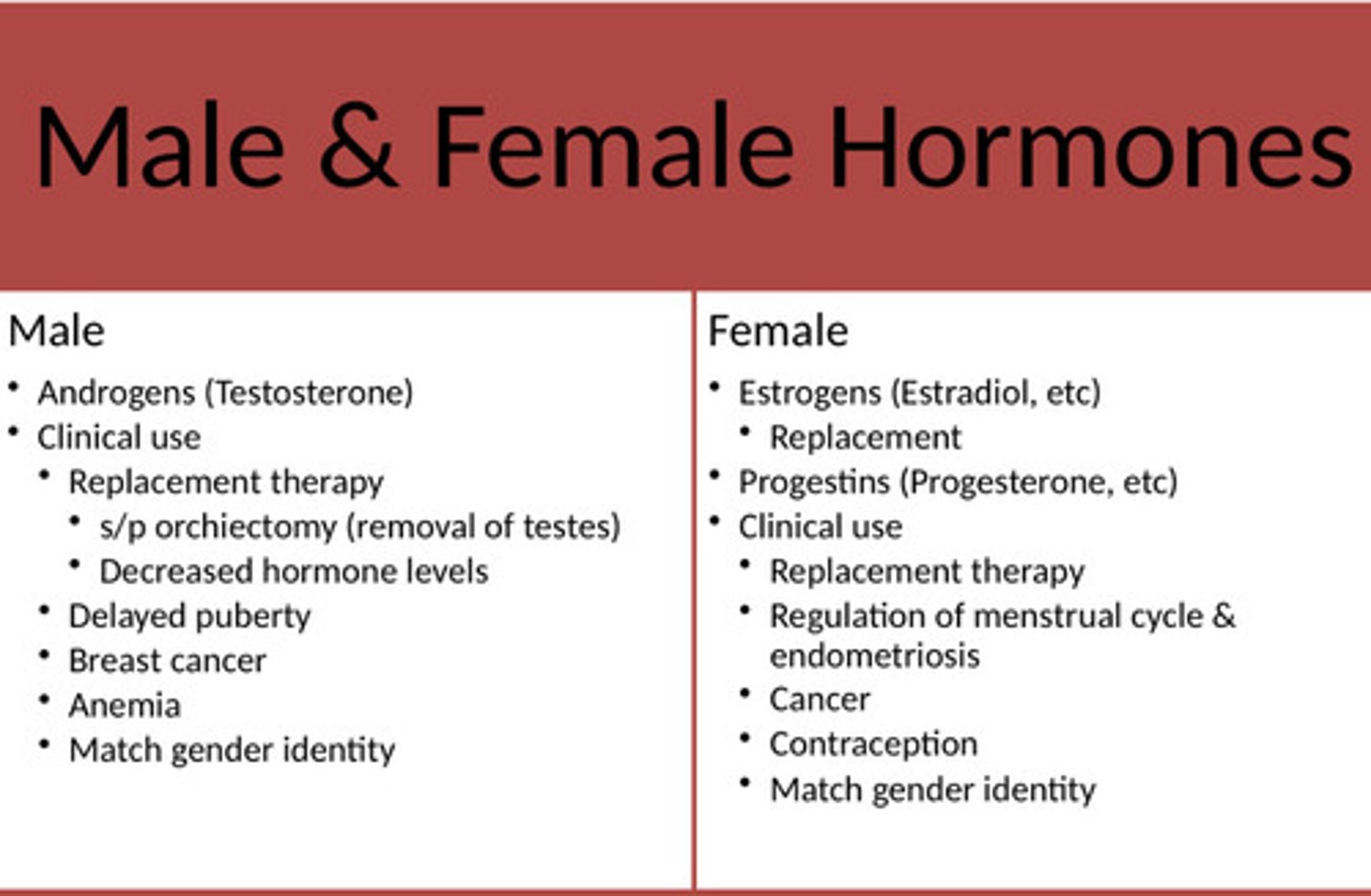
Androgens
Testosterone replacement: small doses to counteract effects of aging in men
Anabolic steroids
- Used to ↑ muscle size & strength
- Use several anabolic steroids together: Known as "stacking"
ADR associated with high doses of anabolic steroids
• Liver damage
• Cardiovascular disease
• Affect bone metabolism
- Accelerate closure of epiphyseal plates leading to impaired skeletal growth in children
- Avascular necrosis of femoral heads
• Aggression & severe mood swings
• Testicular atrophy & impaired sperm production
There are no problems if anabolic steroids taken at physiologic doses. T/F?
True
Hormonal contraceptives
Estrogen replacement therapy
Hormone therapy for persons with gender dysphoria
Rehab considerations for pts taking drugs male and female hormones
25 y/o patient is receiving outpatient PT for a whiplash injury during a motor vehicle accident. They smoke ½ pack per day & drink 3-4x/mo. Meds: Flexeril (muscle relaxant), oral contraceptive with Estrogen & Progesterone, Acetaminophen as needed.
- Today, the patient reports an increase in headaches. Additional questions reveal c/o a dull ache & tightness in the right calf. What are your concerns & why?
- How do you proceed?
- possible DVT: smoking and estrogen contraceptive
- refer, wells criteria to pass along to PCP