L&D ch. 11 - Maternal Adaptation During Pregnancy
1/138
Earn XP
Description and Tags
includes material from the Ricci textbook, canvas powerpoints, canvas quizzes, and supplemental material.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
139 Terms
a pregnancy is divided into 3 trimesters that are each _____ long.
13 weeks
signs and symptoms of a pregnancy are grouped into what 3 categories?
presumptive, probable, positive
which category of signs and symptoms of pregnancy do the following belong to?
ultrasound verification of embryo or fetus outline
fetal movement felt by an experienced clinician
auscultation of fetal heart tones
fetal heart rate seen on ultrasound
positive
the only signs that can determine a pregnancy with 100% accuracy are _____ signs.
positive
which category of signs and symptoms of pregnancy do the following belong to?
braxton hicks contractions
positive pregnancy test
hyperpigmentation of the skin
increased abdominal girth from uterine enlargement
ballottement
goodell sign
chadwick sign
hegar sign
palpable fetus outline
probable
which category of signs and symptoms of pregnancy do the following belong to?
amenorrhea
breast enlargement and tenderness
nausea and vomiting
urinary frequency without dysuria (pain when urinating)
excessive fatigue
fetal movements known as quickening
presumptive
at what point during pregnancy does fatigue (presumptive) typically occur?
12 weeks
at what point during pregnancy does breast tenderness (presumptive) typically occur?
3-4 weeks
at what point during pregnancy does nausea and vomiting (presumptive) typically occur?
4-14 weeks
at what point during pregnancy does urinary frequency (presumptive) typically occur?
6-12 weeks
at what point during pregnancy does hyperpigmentation of the skin (presumptive) typically occur?
16 weeks
at what point during pregnancy does uterine enlargement (presumptive) typically occur?
7-12 weeks
at what point during pregnancy does breast enlargement (presumptive) typically occur?
6 weeks
at what point during pregnancy does quickening (presumptive) typically occur?
16-20 weeks
at what point during pregnancy do braxton hicks contractions (probable) typically occur?
16-28 weeks
at what point during pregnancy does a positive serum hCG pregnancy test (probable) typically occur?
4-12 weeks
at what point during pregnancy does ballottement (probable) typically occur?
16-28 weeks
at what point during pregnancy does the goodell sign (probable) typically occur?
5 weeks
at what point during pregnancy does the chadwick sign (probable) typically occur?
6-8 weeks
at what point during pregnancy does the hegar sign (probable) typically occur?
about 16 weeks
at what point during pregnancy does abdominal enlargement (probable) typically occur?
14 weeks
at what point during pregnancy does fetal movement felt by an experienced clinician (positive) typically occur?
20 weeks
at what point during pregnancy can fetal heart tones via doppler ultrasound (positive) typically occur?
10-12 weeks
_____ (aka subjective) signs of pregnancy are s/s that suggest the possibility of pregnancy but aren't definitive proof, as these symptoms can also stem from stress, hormonal shifts, illness, or other conditions.
presumptive
_____ (aka objective) signs of pregnancy are s/s that can be detected on a physical examination by a healthcare provider, suggesting pregnancy is likely but still not confirmed.
probable
at what point during pregnancy can ultrasound verification of embryo or fetus (positive) typically occur?
4-6 weeks
_____ signs of pregnancy are s/s identified by a healthcare professional that can undeniably be directly attributed to a fetus, such as a fetal heartbeat. these signs confirm that a fetus is growing in the uterus with certainty.
positive
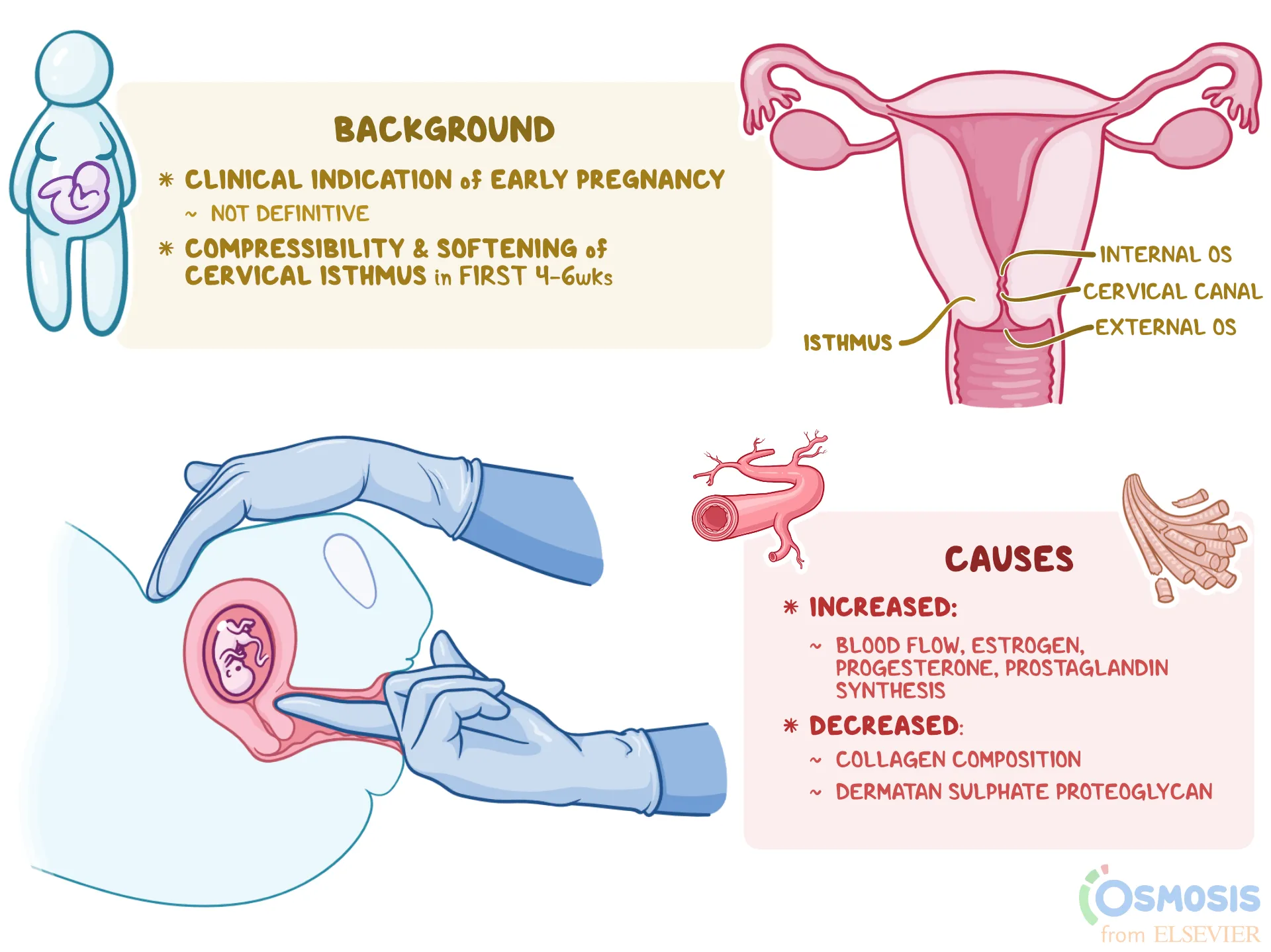
softening and compressibility of the lower uterine segment (aka isthmus) observed during a physical examination
hegar sign
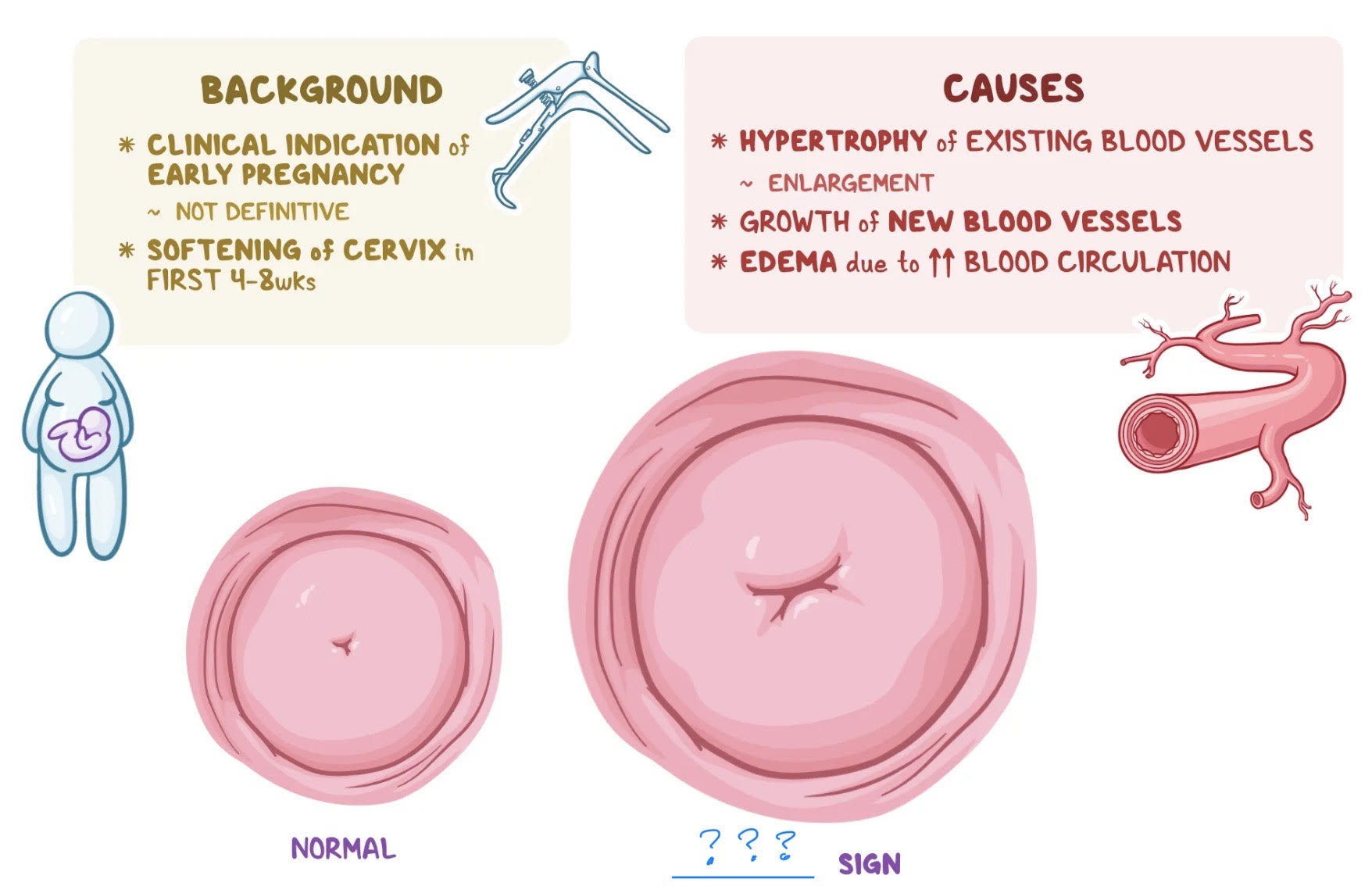
softening of the cervix due to increased blood flow and vascularization in early pregnancy observed during a physical examination
goodell sign
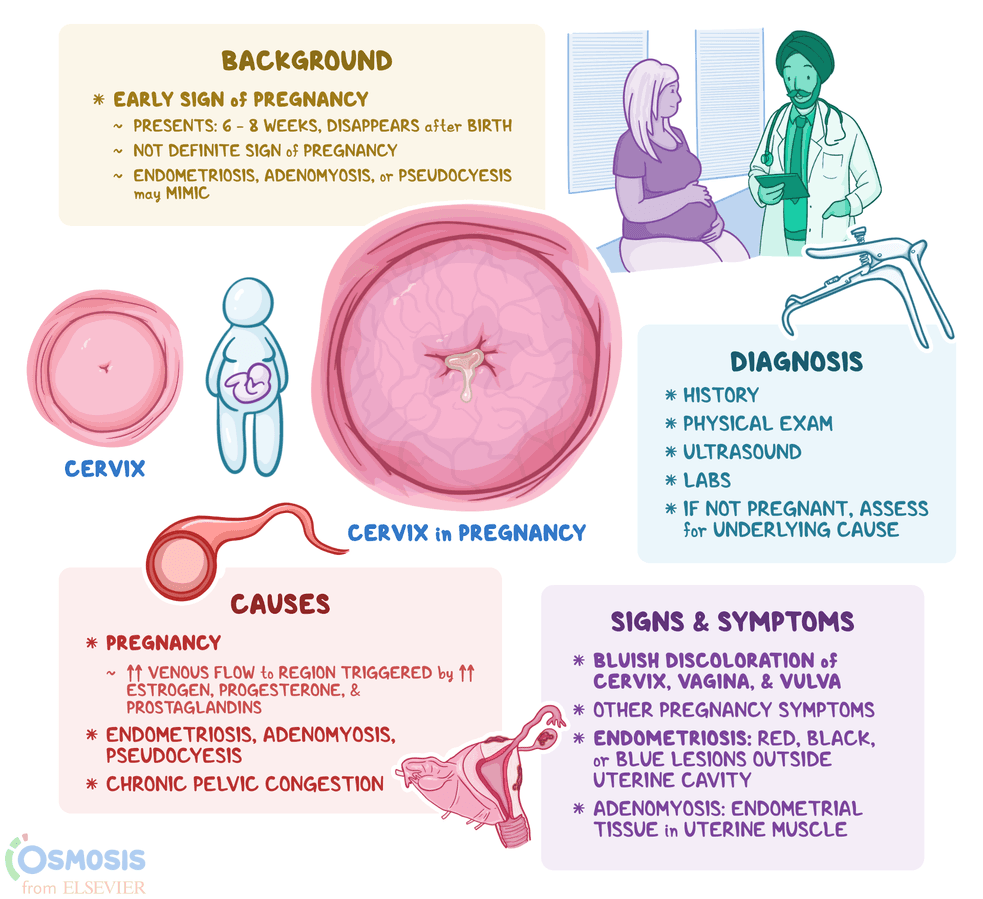
bluish-purple coloration of the vaginal mucosa and cervix due to increased blood flow and vascularization in early pregnancy observed during a physical examination
chadwick sign
irregularly spaced and infrequent contractions that are not typically painful, sometimes referred to as “practice” contractions. start in the first trimester and continue throughout pregnancy (especially within the last month) as the body prepares for labor, and usually subside with rest or change in position.
braxton hicks contractions
a medical examination where the physician applies pressure to the uterus (either internally or externally), causing the fetus to move away and then rebound back against the uterine wall.
ballottement
fetal movement described as feeling like a “fluttering” in the abdomen or uterus. typically occurs around 18-20 weeks and is a presumptive sign of pregnancy.
quickening
pregnancy tests: an hCG level lower than _____ is considered negative. An hCG level higher than _____ is considered positive.
5, 25
hCG levels during a normal pregnancy usually double every 29-53 hours during the first 30 days after implantation, and peak around 8-10 weeks gestation.
why is monitoring the doubling time of hCG levels important?
they can be used to differentiate if gestation is normal or abnormal
hCG levels during a normal pregnancy usually double every 29-53 hours during the first 30 days after implantation, and peak around 8-10 weeks gestation.
in regards to monitoring hCG doubling time, low levels are associated with _____
ectopic pregnancy
hCG levels during a normal pregnancy usually double every 29-53 hours during the first 30 days after implantation, and peak around 8-10 weeks gestation.
in regards to monitoring hCG doubling time, higher than normal levels may indicate _____
multiple gestation pregnancy
the elevation of hCG levels corresponds to the _____ period of approximately 6-12 weeks during early pregnancy
morning sickness
the non-pregnant uterus is typically _____ shaped & sized and contained within the pelvis.
pear
as pregnancy progresses, about _____ of uterine blood flow is directed towards the placenta, with the remainder distributed between the endometrium and myometrium.
80-90%
why is it not recommended for pregnant women to lie flat on their back (supine)?
compression of major blood vessels vena cava and aorta
by 20 weeks gestation the fundus (top of the uterus) is at what level & measurement?
umbilicus 20cm
fundal heigh in centimeters is measured monthly. this measurement correlates with _____ most accurately between the period of 18-32 weeks. note: certain conditions can interfere with the accuracy of this correlation.
gestational weeks
fundal height can be most accurately correlated with gestation weeks during which period? note: certain conditions can interfere with the accuracy of this correlation.
18-32 weeks
conditions such as obesity, hydramnios (excess amniotic fluid), and uterine fibroids can interfere with the accuracy of _____
correlating fundal height to gestational weeks
the fundus reaches its highest level at the xiphoid process at approximately _____.
36 weeks
between which period of gestation does the fundal height drop as the fetus begins to descend and engage into the pelvis?
38-40 weeks
the period by 40 weeks in which the fetal head begins to descend and engage into the pelvis is termed _____
lightening
in a person who is pregnant for the very first time, lightening typically occurs when?
2 weeks before the onset of labor
in a person who is pregnant for the second or subsequent time, lightening typically occurs when?
at the onset of labor
how is fundal height measured?
from the top of the pubic bone to the fundus
which hormone influences the following physiological changes during pregnancy:
a thick mucus plug is formed in the cervix to protect from bacterial entry
breast enlargement and tenderness + vascularization
decreased intestinal peristalsis
smooth muscle relaxation → delayed gastric emptying & relaxation of the LES → acid reflux/GERD
hyperventilation → hypocapnia
peripheral vasodilation → decreased peripheral veinous pressure
progesterone
most women experience an increase in whitish/yellowish vaginal discharge during the second trimester that is termed _____
leukorrhea
durgin pregnancy the vaginal pH increases, which raises the risk for developing what?
vaginal candidiasis
the increased blood supply to the ovaries causes them to enlarge until approx. _____ of gestation. after this point they are no longer palpable due to the uterus filling the pelvic cavity.
12-14 weeks
the presence of elevated levels of estrogen and progesterone block the hormones _____ from the anterior pituitary, stopping ovulation from occurring during pregnancy.
follicle stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone
the ovaries are active in hormone production to support a pregnancy from until about _____, after which the corpus luteum regresses and the placenta takes over major production of progesterone.
6-7 weeks
the ovaries are active in hormone production to support a pregnancy until about 6-7 weeks, after which the corpus luteum regresses and the _____
placenta takes over major production of progesterone
creamy yellowish fluid that is rich in antibodies - called _____ can be expressed from the breast by the third trimester (canvas slideshow says by 12 weeks, book says otherwise, idk). converts to mature breastmilk after delivery.
colostrum
excessive salivation due to excessive swallowing from nausea is termed _____, and is a normal/common s/s
ptyalism or sialorrhea
common s/s of _____ during pregnancy (normal - caused by increased estrogen) include dental problems such as swollen gums that tend to bleed, gingivitis, and periodontitis
hyperemia
during pregnancy, the combination of increased venous pressure, constipation, and pressure from the enlarged uterus all put the mother at risk of developing _____
hemorrhoids
during pregnancy, delayed gallbladder emptying + increased lithogenicity of bile put the mother at risk for developing _____
gallstones
nausea and vomiting affects what percentage of pregnant women?
90%
blood volume increases _____ during pregnancy
50%
during pregnancy, increased number of RBCs + increased levels of fibrinogen + increased levels of clotting factors all put the mother at risk for developing _____
DVT
what is the normal fluctuation of blood pressure during pregnancy?
slight decline until mid-pregnancy, then returns to normal
iron needs increase _____ during pregnancy
50%
what is the non pharmacologic treatment for a pregnant patient experiencing lightheadedness?
lie on their left side to decrease pressure on the vena cava
during pregnancy, plasma volume increases at a faster rate than the increase of RBCs causing hemodilution, which causes a condition termed _____. this is reflected by a lower hemoglobin and hematocrit level.
physiologic anemia
which major s/s during pregnancy can be attributed to the following physiologic changes:
increased body water
increased blood volume
increased capillary hydrostatic pressure
decreased serum albumin
swelling/edema
kidney activity increases when a pregnant patient is in which positions?
lying down or on their side
increased vascularity and edema of upper respiratory mucosa causes what common pregnancy s/s
nasal congestion, nose bleeds (epistaxis)
the following physiological changes put a pregnant patient at risk for what?:
increased blood flow to kidneys + increased GFR + increased kidney size
dilation of renal pelvis and ureters causing urinary stasis
UTI
during pregnancy the bladder mucosa is edematous and hyperemic, and sometimes there is incontinence of the vesicoureteral valve. this causes which common s/s
frequency, urgency, dysuria, nocturia, stress incontinence
during pregnancy oxygen consumption increases how much
10-20%
due to progesterone-induced hyperventilation → hypocapnia, pregnancy is considered a state of _____ with a lower partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PCO2) and a higher partial pressure of oxygen (PO2) compared to the nonpregnant state
compensated respiratory alkalosis
during pregnancy, the rise in blood volume correlates directly with _____, supporting the concept of the placenta as an arteriovenous shunt in the maternal vascular compartment
fetal weight
during pregnancy, maternal heart rate _____, a normal adaptation that lasts until term
increases by 10-30 bpm
due to _____ throughout pregnancy, high-impact or strenuous exercise not recommended during, as it can cause musculoskeletal disorders or injuries
progressive joint and ligament mobility and softening
which common pregnancy symptom can be attributed to the following factors:
ligaments holding the sacroiliac joints and the pubis symphysis in place soften and stretch to allow easier delivery
articulations between joints become wider and more moveable
increased swayback and upper spine extension
center of gravity shifts forward
increased lumbosacral curve (lordosis)
lower back pain
an increase in estrogen, progesterone, and melanocyte-stimulating hormone levels causes what common pregnancy symptom (75%)?
linea nigra, facial melasma, and hyperpigmentation of axilla, perineum, and nipples
what common s/s related to hair and nails to pregnant women typically experience?
brittle but fast-growing nails, decreased hair growth
high progesterone levels → smooth muscle relaxation → delayed gastric emptying and decreased peristalsis → food moves through the GI tract much slower → more water than normal is reabsorbed. this process is responsible for causing which common pregnancy s/s?
bloating and constipation
why do the kidneys increase in size and functioning during pregnancy?
to accommodate the increase in blood volume and increase in maternal and fetal waste
during pregnancy, the kidneys increase in size and functioning. what implications does this have for drugs that are renally excreted?
the patient may require a higher dose due to faster filtration rate
braxton hicks contractions vs true labor: these contractions are felt in the abdomen, are irregular in pattern, typically not painful and reside with rest.
braxton hicks contractions
braxton hicks contractions vs true labor: these contractions are felt in the lower back, get stronger and closer together as time goes on, do not subside with rest, and are typically painful.
true labor
progressive joint and ligament mobility and relaxation as pregnancy continues is caused by which hormone(s)?
progesterone and relaxin
the _____ slightly enlarges during pregnancy and increases in activity and hormone production, which causes an increase in basal metabolic rate (BMR)
thyroid gland
which maternal hormone that is passed to the fetus during the first trimester is responsible for fetal brain development and neurogenesis?
thyroid hormone
the _____ enlarges during pregnancy, increasing in production of prolactin and melanocyte stimulating hormone (MSH).
anterior pituitary
oxytocin and antidiuretic hormone are stored and released by which gland? (but produced by the hypothalamus)
posterior pituitary
oxytocin is responsible for what function(s)?
uterine contractions, milk ejection during breastfeeding, release of prostaglandins
during pregnancy, glucose is transported across the placenta for the fetus to utilize. what happens to maternal blood glucose levels because of this?
maternal blood glucose declines to a level that would be considered hypoglycemic in a nonpregnant person
in the second trimester, the placenta begins to produce hPL, a hormone which acts as an antagonist to maternal insulin. thus, insulin levels rise to combat this. this causes what?
maternal insulin resistance which increases the amount of glucose being transported to the fetus
insulin cannot do what during pregnancy?
cross the placenta, thus the fetus must produce its own
what do the adrenal glands do during pregnancy?
increased cortisol and aldosterone secretion
prostaglandin production increases at term, which functions to do what?
facilitates uterine contractions and myometrial oxytocin sensitivity
during pregnancy, the placenta functions as _____ - it can manufacture and secrete hormones.
an endocrine gland