Biology - DNA and RNA
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
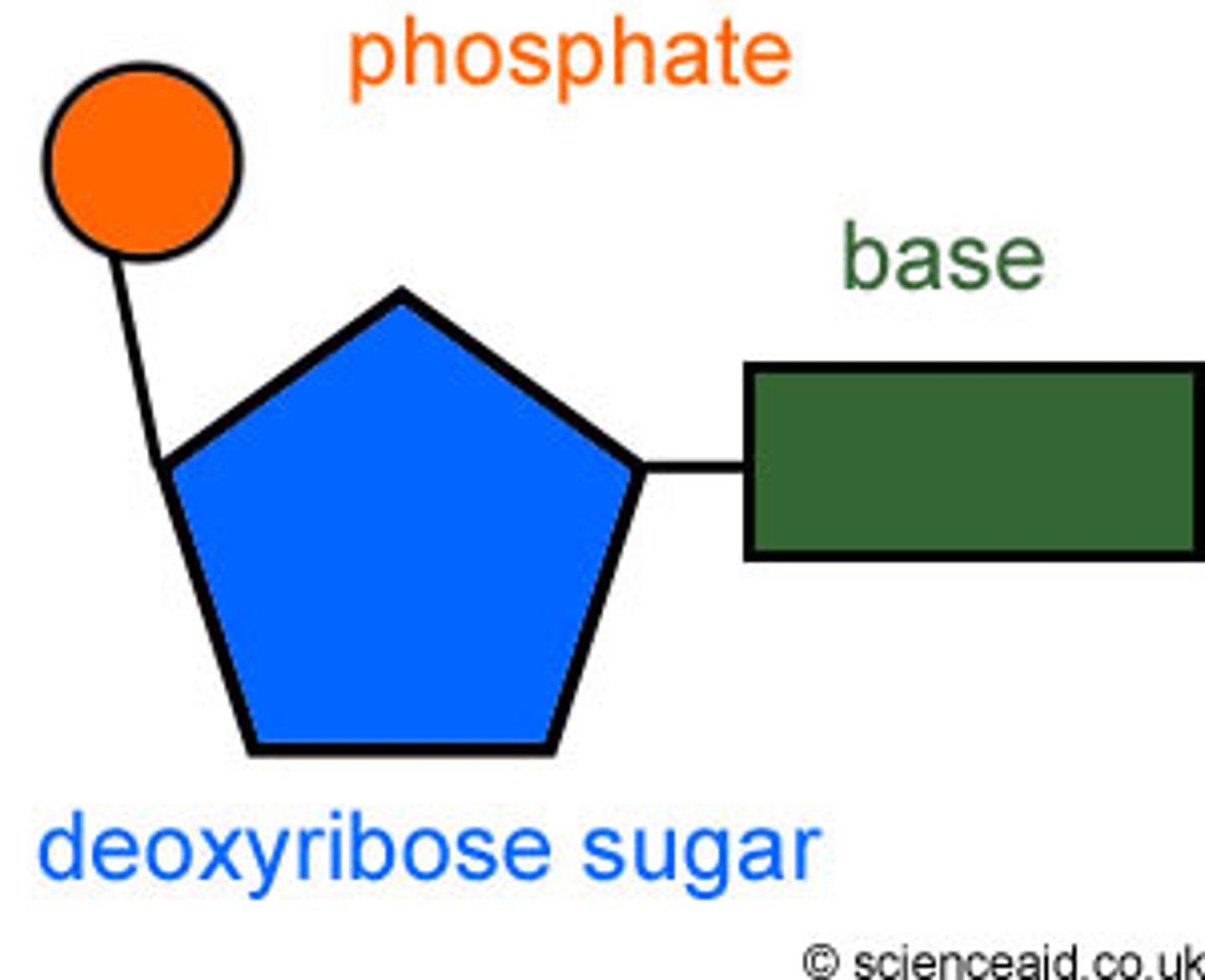
What are the 3 parts that make up a nucleotide?
Phosphate group, deoxyribose (sugar), base
What type of bond holds the nucleotide together and connects it to other nucleotides?
Covalent bond
What is the sugar phosphate?
The backbone between two molecules
What are the four examples for bases in the nucleotide?
Adenine, guanine, thymine, cytosine
What are the parts of the DNA molecule?
2 nucleotides bonded together with a hydrogen bond and a sugar phosphate backbone
What two bonds are used to make up a DNA molecule? Where are each of the them found?
Hydrogen bond - In between the nitrogen bases bonding them together
Covalent bond - in between the phosphate group, sugar, and attaching the base to the sugar. But most importantly, holding the sets of nucleotides together (horizontally)
What is the Chargaff Rule with base pairing?
Adenine - Thymine
Guanine - Cytosine
How many hydrogen bonds does each nitrogen base pair share?
G/C = 3
A/T = 2
What are the steps of DNA replication?
1. Helicase unzips DNA (breaks base pairs)
2. RNA primase adds RNA at the beginning so DNA polymerase knows where to starts
3. DNA polyermase helps the new nucleotides attach and proof reads for any mistakes
4. DNA lygase glues fragments together
What is DNA helicase?
Unzips the DNA strands, and forms the replication fork by breaking hydrogen bonds
What is DNA primase?
Shows the DNA polymerase knows where to starts attaching nucleotide.
Generates RNA primers. (short RNA molecules that act as templates for the starting point of DNA replication)
What is DNA polymerase?
Attaches nucleotides to new strands and proof reads the DNA to check for mistakes
What is DNA ligase?
Glues DNA fragments together by forming phosphodiester bonds between nucleotides
What is topoisomerase?
It corrects any mistakes the helicase may have made when unwinding the DNA. "Unwinding double helix"
Review the diagram from your DNA Replication digital assignment for the parts of DNA replication
how to make a complementary strand of DNA from a DNA template strand
Attach the proper nucleotide to its pair. (Adenine - Thymine
Guanine - Cytosine)
What is the difference between a leading and lagging strand?
Leading - 3' to 5'
Lagging - 5' to 3'
What direction does replication move in?
5' to 3' (which makes it easier to replicate the leading strand)(it pairs with it's opposite 5-3 and 3-5)
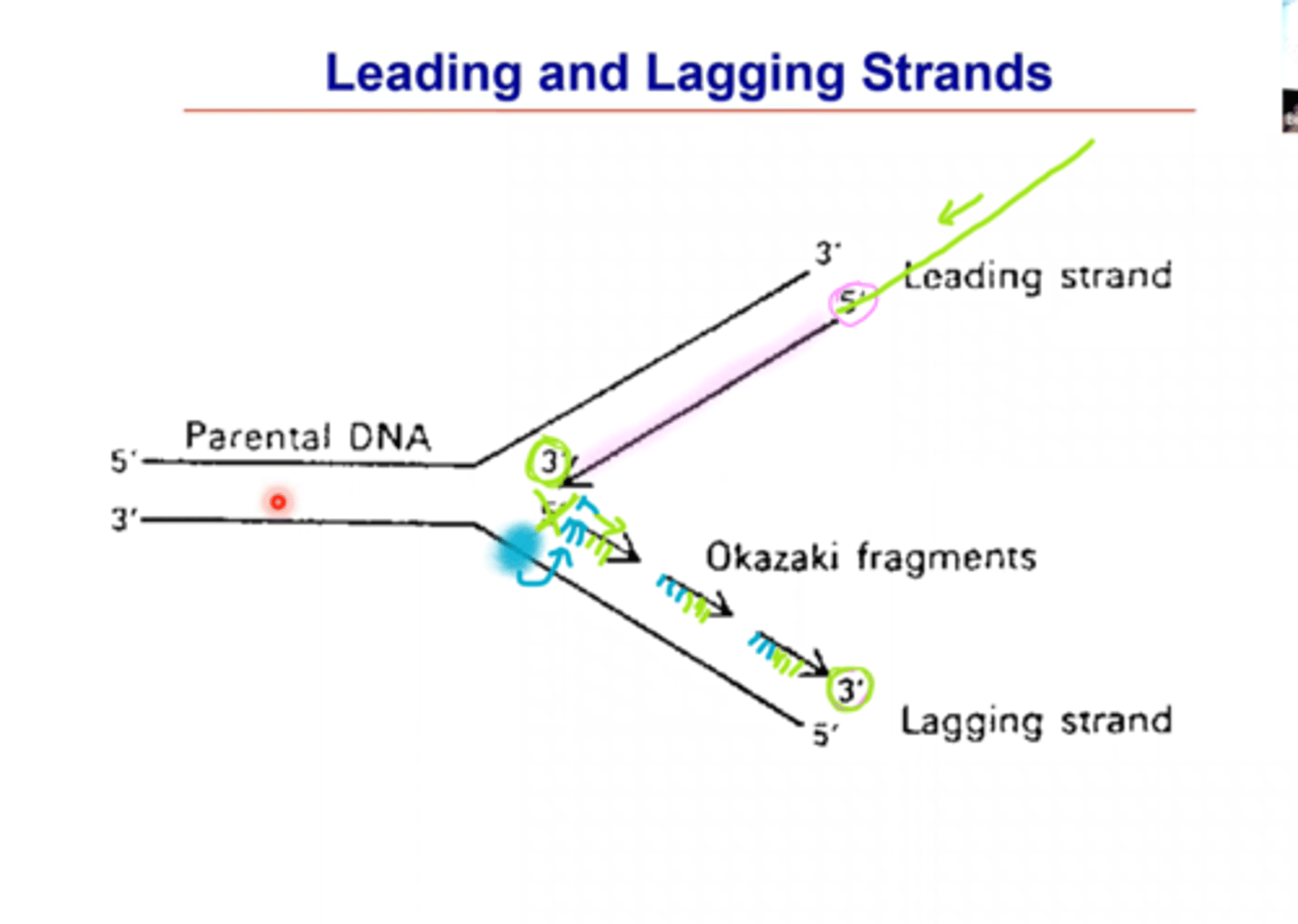
What is an Okazaki fragment?
The discontinuous replication of DNA. In lagging strand
What direction does the lagging strand replication move in?
Often not necessarily towards the fork
What is semi-conservation DNA?
old DNA strand is used as a template to make the new DNA strand
What are the differences between DNA and RNA? What is the same?
DNA - deoxyribose sugar, double stranded/double helix, has the nitrogen base Thymine
RNA - ribose sugar, single strand, nitrogen base Uracil (U) instead of T
Both - A, C, G
What is the central dogma of biology?
DNA -> RNA -> Protein
What are the 3 types of RNA?
mRNA, tRNA, rRNA
What does mRNA do in protein synthesis?
Messenger RNA. A copy of the portion of the DNA that will be used to make protein. Made in the nucleus and travels to the cytoplasm, the cite of photosynthesis. (can leave the nucleus)
What does tRNA do in protein synthesis?
Transfer RNA. Carries amino acids to make proteins. Carries amino acids from the cytoplasm, to mRNA when it enters the ribose
What does rRNA do in protein synthesis?
Ribosomal RNA. Help make up ribosomes. This is the place mRNA is read
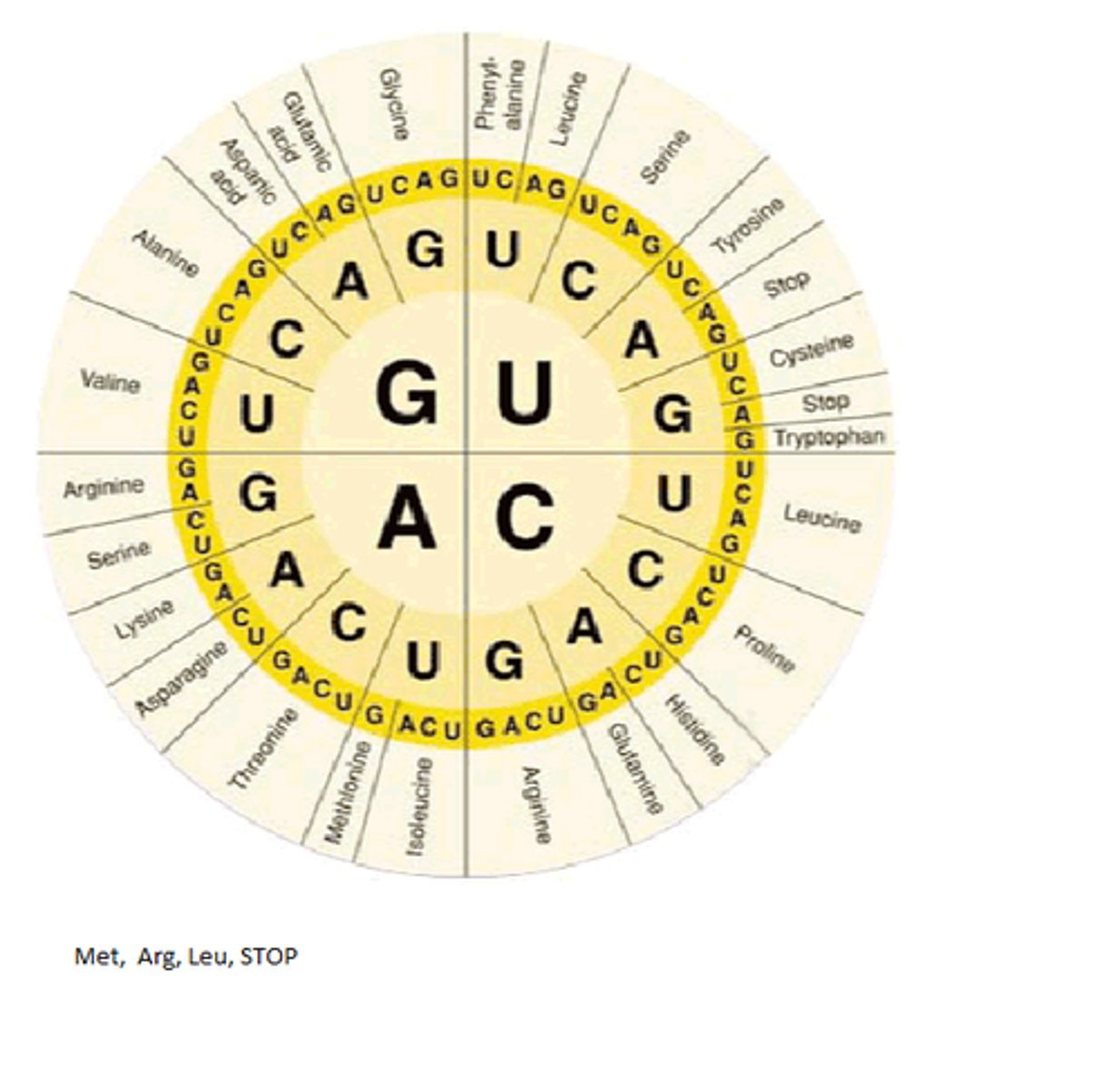
What is a codon?
Groups of 3 nucleotide bases that make up the genetic code. Read as 3 letter codes when translating
What is an anticodon?
3 nucleotides on tRNA that compliment mRNA codon
Know how to use circular codon chart
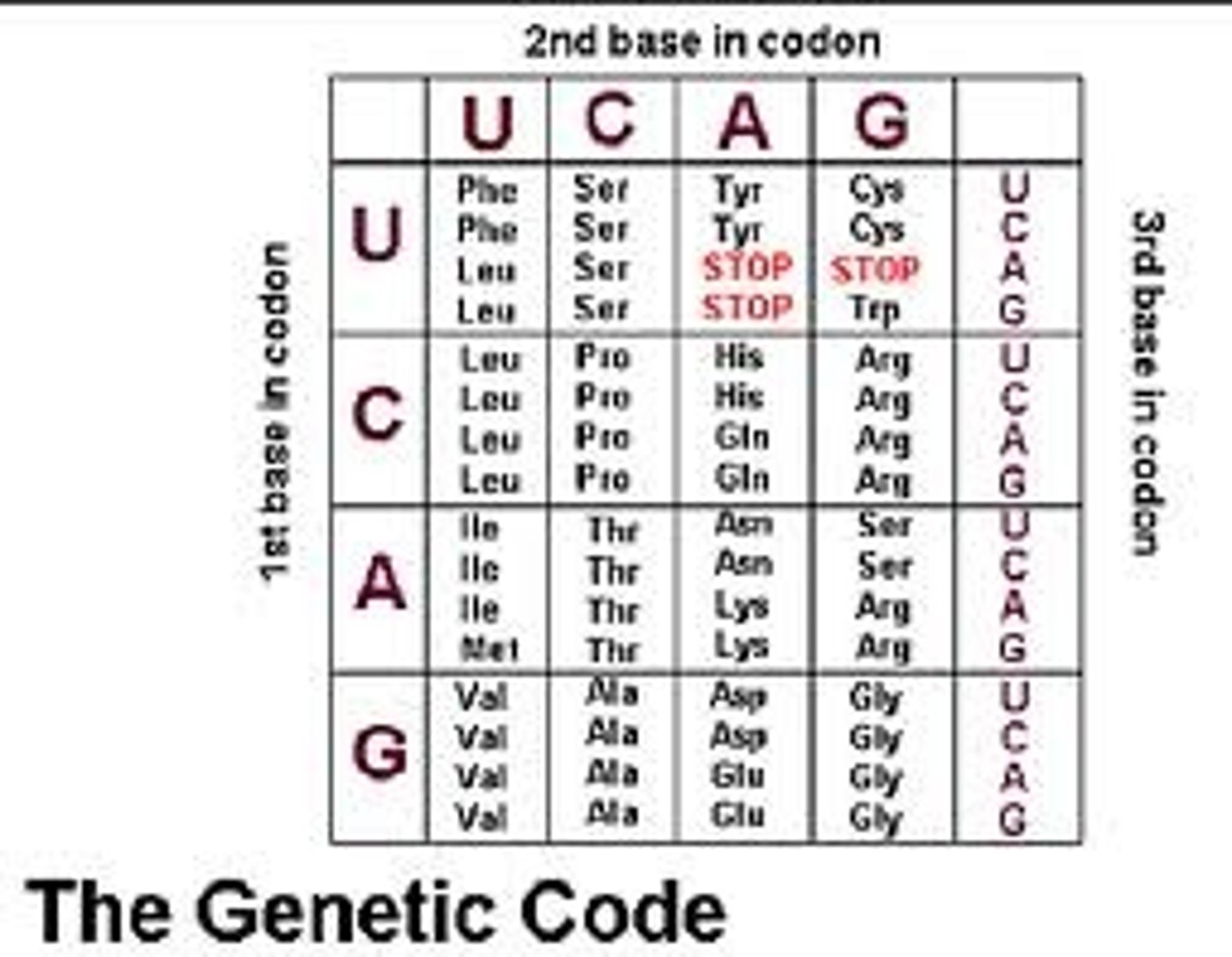
Know how to use square codon chart
How to transcribe DNA in RNA
C - G
G - C
A - U
T - A
What is the monomer of nucleic acids
nucleotides
What is the monomer of proteins
amino acids
What is the start protein?
AUG, met
What is a silent point mut?
A nucleotide is changed but it doesn't change the amino acid
What is a missense mut?
One Amino acid is changed
What is a nonsense mut?
the amino acid is changed into a stop protein
What is an addtion vs. deletion mut?
One nulceotide is added/removed and it shifts everything up or down and changes the whole protein
What is a point vs. frameshift mutation?
Only one codon affected vs the whole sequence is affected