PSYC1030 Quiz 3 Measurement and Intelligence
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
What is required to confirm a tests legitimacy
-Standardised
-Reliable
-Valid
-Not biased
what is ‘s’ factor
specific intellectual abilities. Unique individual abilities on a particular task
what is test bias
extent to which everyone has the same chance at doing well on test
Ppl from the culture of development have more of a bias towards doing well bc test is more likely to reflect culture
how do we compare people in a normal distribution
convert raw score to standardised score.
standard score= (score-mean)/SD
68% of scores are within 1 SD, 95% within 2 SDs, and nearly all within 3 SDs
4 ways intelligence is measured
aptitude (what someone may be able to do in the future)
achievement (what someone can do now)
intelligence (lvl of cognitive ability)
personality
What does standardised tests tell us
-Average: mean levle
-Variation: standard deviation
To ensure test standardisation what is required
-Large population
-Representative sample
-Relevance
What are the easiest groups/types of people to gather data on and study
-Uni students
-Western culture
What techniques evaluate the reliability of tests
-Alternate forms
-Split half reliability
-Test retest reliability
Alternate forms reliability
-Evaluation of two different versions of the same test.
-comparison of performance between both tests
-Positive correlation
Split half reliability
-Split one test into 2 parts (not versions)
-Evaluation of perfomance on both tests
-Assumption that both halves are testing the same thing. Addressed by splitting in ways which is not necessarily top half/bottom half
-Money/time constants
Problem with split half reliability
-Two halves could be measuring different things
Test retest reliability
-Getting same people to re do the test twice at diff time points
- correlation between diff time points looked at
-assumes thing being measured is stable and changes in performance aren’t due to exposure
What are the 3 types of validity
-Predictive validity
-Criterion validity
-Construct validity
Predictive validity
Whether or not scores on test match later outcomes
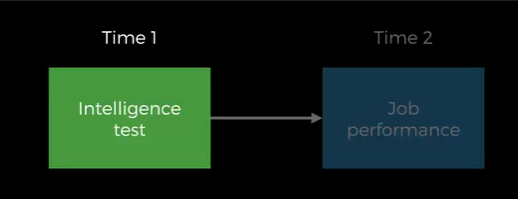
Criterion validity
Match scores on test with some other measure:
-Previous measure or
-Concurrent measure of same thing
Example of criterion validity
-Are your grades in this course a valid measure of academic performance
-Compare grades from high school
Construct validity
-An idea not a test
-How well a test maps onto the underlying theory with regard to the thing we are measuring
e.g. personality test measuring 3 factors. 3 factors must be tested
What's the first systematic measurement of intelligence
-The binet-simone scale
-Intelligence measurement
-Standardised across ages
-Mental age based on age-normed questions passed
Who introduced IQ and define it
-Lewis Terman
-Translated binet-simone's intellegence scale into english
-IQ: Ratio mental age with chronological age
-Mental age/Chronological age x100
-Name Stanford-Binet scale
-IQ scores have mean of 100 and SD of 15
Problem with Stanford-Binet scale
-Age normed items goes up to age 16
-At 16 IQ starts decreasing because chronological age keeps increasing
How do we measure IQ
-Compare IQ to standardized data
Weschler created several different intelligence scales name them
-Weschler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS)
-Weschler Intelligence Scale for Children (WISC) (very young)
-Weschler Preschool and Primary Scale of Intelligence (WPPSI)
Describe the Weschler Intelligence Scales
-Different questions for different ages
-Different tests standardized
-Performance compared to standardized information
What is the current level of the Weschler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS)
WAIS-IV (4)
The WAIS is broken down into separate components
-Verbal IQ: Verbal comprehension index, Working memory index
-Performance IQ: Perceptual organisation index, Processing speed index
WAIS Verbal comprehension index components
-Vocabulary
-Similarity
-Information
-Comprehension
WAIS Working memory index components
-Arithmetic
-Digit span
-Letter number sequencing
WAIS Perceptual organisation index components
-Picture completion
-Block design
-Matrix reasoning
WAIS Processing speed index components
-Digit symbol coding
-Symbol search
What intelligence measure model is WAIS and why is this so
-General intelligence model
-Measures a lot of things
-It assumes IQ is a function of all of the properties (if ur good at one thing you’ll be good at others)
What do psychologists generally agree they are measuring with intelligence
-Ability to learn and remember information
-Ability to recognize concepts and their relations
-Ability to apply the information to their own behaviour in an adaptive way,
Regarding the nature of intelligence and how it works what are two methods
-General intelligence
-Multiple intelligences
what were the subskills of intelligence proposed by Howard Gardner
-Linguistic
-Musical
-Logical/mathematical
-Spatial
-Bodily/Kinaesthetic
-Intra-Personal
-Inter-Personal
Howard Gardner's theory about intelligence
-No general intelligence underlying everything
-Can be good at some of these not others
-Independent abilities
-Unrelated abilities
multiple intelligence theory
Spearman's Two factor theory
-Systematic testing of performance on tests which is a function of:
-General intelligence factor
-Specific intellectual abilities
-We all have G but S varies from person to person on a particular task
Spearman's Two factor theory: 3 subcategories of G factor
-Apprehension of experience
-Education of relations
-Education of correlates
Requires individual to think through and provide reasoning for answer
Ravens Progressive Matrices
-A test designed to assess General intelligence factor of Spearman's Two factor theory
-Non verbal test
-Measures peoples ability to comprehend their perceptions
-Application to novel stimuli to work out missing bits
-Different tests for different ages
-Often used in military or job selection
-Test not reliant on high level education background
In 1938, Thurstone conducted a factor analysis to determine the nature of intelligence how many factors and tests?
-Seven factors from 56 tests.
Thurstone's factors underlying intelligence
-Verbal comprehension
-Verbal fluency
-Number
-Spatial visualization,
-Memory
-Reasoning
-Perception speed
Factor analysis
-Statistical analysis on how many factors best describe the data
How do you know when youre adequately describing the data with Factor Analysis
When variation around those factors reduced to a statistical minimum
Horn and Cattell performed factor analysis on Thurstone's seven factors how many factors did they find
-Two higher order factors that described performance across those seven factors.
-Both needed to describe test performance
-Fluid intelligence or (Gf)
-Crystallized intelligence (Gc)
What's Fluid intelligence
-Performance on culture-free tasks
Example: Raven's Progressive Matrices
Gf
Crystallized intelligence
Tasks requiring some sort of prior information
Example: Capital of France
Gc
Best way to assess intelligence without cultural bias
-Horn and Cattell
-Fluid intelligence
-Raven's Progressive Matrices
Test-Retest Reliability of intelligence tests and definition
-Correlation between scores received on intelligence tests at two different times
-Correlation of 0.85
What's the criterion validity correlation
Correlation between 0.4 and 0.75