Review: Science Exam
5.0(3)
Card Sorting
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:01 PM on 12/5/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
1
New cards
Radio Waves, Microwave, IR Radiation, Visible Light, UV Radiation, X-rays, Gamma-rays
Correct order of EM Radiation with increasing frequency
2
New cards
Transverse
Electromagnetic waves are _____
3
New cards
Television, infrared, visible light, X-rays
Which of the following correctly lists electromagnetic waves in order from longest to shortest wavelength?
4
New cards
Gamma rays have greater energy than visible light for penetrating matter
Why are high-frequency gamma rays more dangerous to humans than visible light?
5
New cards
Gamma ray
Which type of EM radiation has the shortest wavelengths?
6
New cards
Global Positioning System
By using ______, you can determine your exact position and altitude on Earth.
7
New cards
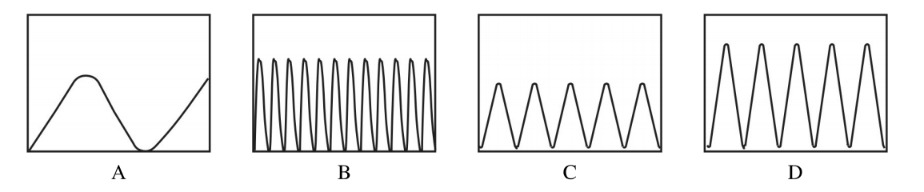
Letter B
Which diagram represents electromagnetic energy with the shortest wavelength?
8
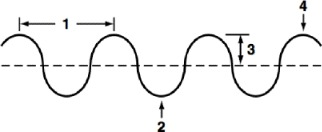
New cards
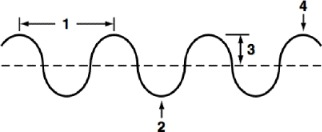
Wavelength
What part of a wave is shown at point 1
9
New cards
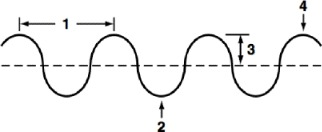
Trough
What part of a wave is shown at point 2
10
New cards
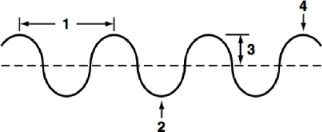
Amplitude
What part of a wave is shown at point 3
11
New cards
Crest
What part of a wave is shown at point 4
12
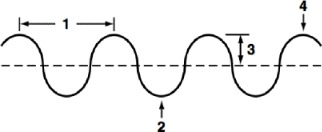
New cards
EM or Transverse Wave
What kind of wave is represented by this diagram?
13
New cards
Increases
As the frequency of a wave ____ the wavelength becomes smaller
14
New cards
Visible Light
____ has a shorter wavelength and higher frequency than infrared rays.
15
New cards
X rays
_____ shorter wavelength and higher frequency than UV-rays. It carries a great amount of energy
16
New cards
Photons
Light is made of little particles called _____
17
New cards
Straight path
Light can travel in a
18
New cards
Light
Is a form of EM Wave that is propagated perpendicular to the source of energy
19
New cards
Absorption
Of light energy is converted into some other form, such as thermal or heat energy
20
New cards
Refracted
Light when passes from one medium into another, it changes direction slightly this is called ______
21
New cards
Transmitted
Light can be _____, sometimes it passes through a certain matter.
22
New cards
Equal
Angle of incidence is to the angle of reflection
23
New cards
Bends away from normal
A ray of light when passing from glass to air, ________
24
New cards
lower speed
Light travels at a _____ in water than in air
25
New cards
same straight-line path
Light travels in the _______ while passing through different media.
26
New cards
Reflected rays
_______ are formed when light strikes the surface of an object
27
New cards
transmitted light
The ________ is the difference if incident light and absorbed light
28
New cards
Index of Refraction (n)
______ is the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum and the speed of light in the material
29
New cards
Always greater than 1
The indices of refraction of different materials are always ______
30
New cards
Wavelengths
White light is actually a combination of several different ____ of light traveling together.
31
New cards
Red
Which has the longest wavelength?
32
New cards
Violet
Which has the shortest wavelength?
33
New cards
White Light
All the colors in the visible spectrum put together will form
34
New cards
Rays
Light travels in straight paths called ___.
35
New cards
Wave-particles
Sir Issac Newton describe light as ___.
36
New cards
Dispersion, Refraction, Reflection
The particle theory of light can explain the following phenomena ______.
37
New cards
Refraction
Light beam changes its direction when it strikes a boundary between air and water.
38
New cards
Frequency
When light crosses a boundary between air and water, the following quantity of light remains the same _____
39
New cards
Red
Sun rays fall on a grass prism. What light ray will be refracted the least?
40
New cards
Reflected
Light that bounces off an object is
41
New cards
Disappears
A student conducts an investigation to determine the focal length of a convex lens. She holds the lens in front of her and looks through it at a distant object. She slowly moves the lens towards her eye. She knows she is holding it at the focal length when the image
42
New cards
Diverging
A lens is used to produce a virtual image that is smaller than the object the lens must be a _ lens
43
New cards
Convex mirror and concave lens.
Identify the list below that contains items that diverge light rays.
44
New cards
Total Internal Reflection
also the principle behind fiber optics.
45
New cards
ROYGBIV
Is a way of remembering the colors of the visible spectrum.
46
New cards
A Concave Lens (diverging)
thinner in the middle than at the edges and spreads the light passing through it.
47
New cards
transmitted, reflected, or absorbed
When light or sound waves hit an object, they can be _______, _______ and _______
48
New cards
Light travels to you faster than sound.
Why do you see lightning before hearing thunder
49
New cards
A Convex Lens (converging)
is thicker in the middle than at the edges and focuses the light passing through it.
50
New cards
Speed, Direction. The change in speed causes it to bend.
When light changes ___, it also changes ____.
51
New cards
300,000 km/s
All electromagnetic waves travel at ________ through a vacuum.
52
New cards
look identical to images formed by flat mirrors.
Images formed by spherical mirrors will ___
53
New cards
bends
* Light ____ when it travels from air into water (Slower)
* Bending of light depends on the medium and the density of the medium
* Bending of light depends on the medium and the density of the medium
54
New cards
color of light it reflects.
The color of an object is really the ___
55
New cards
Electromagnetic waves
are made by vibrating electrical charges that can travel
through matter.
through matter.
56
New cards
same electric charge
Particles with the _____ repels each other
57
New cards
opposite charge
Particles with the _____ attract each other
58
New cards
vibrating electrical charges that can travel through matter.
Electromagnetic waves are made by ________