Gen Chem Ch. 5 Pearson Questions
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Of the following elements, which has the highest electronegativity?
P
Si
Ca
Ge
Answer: P
Explanation: electronegativity increases up and to the right
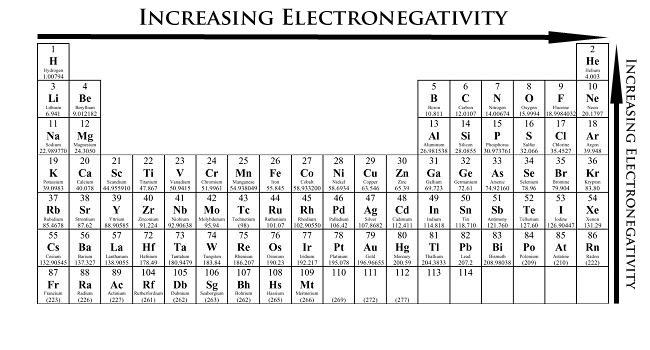
Of the following elements, which has the lowest electronegativity?
I
Sr
Ca
Br
Answer: Sr
Explanation: electronegativity increases up and to the right
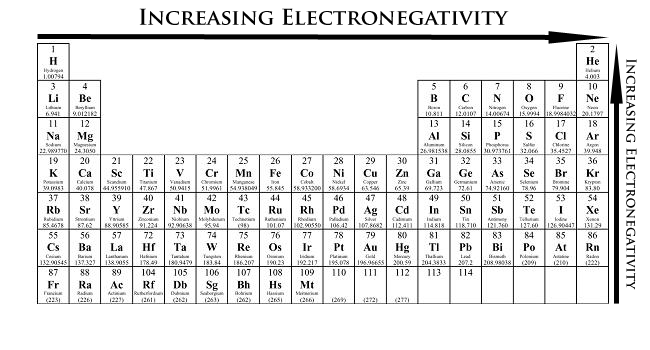
Choose the bond below that is most polar.
H-Cl
H-I
H-Br
C-H
H-F
Answer: H-F
Explanation: Florine is the most electronegative element. The most polar means the greatest difference in electronegativity between the two elements.
Find the two elements that are furthest apart using the increasing electronegativity rule.
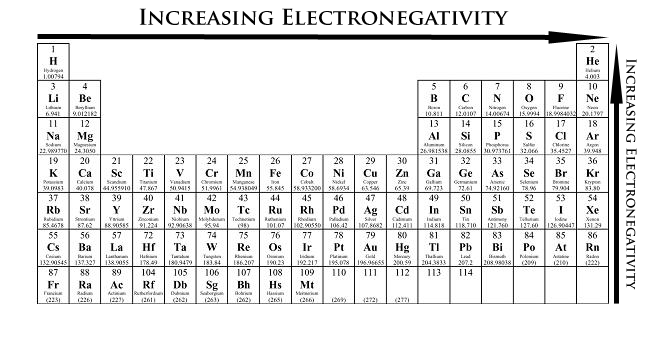
Using periodic trends, place the following bonds in order of increasing ionic character.
Si-P Si-Cl Si-S
Si-P < Si-Cl < Si-S
Si-P < Si-S < Si-Cl
Si-Cl < Si-P < Si-S
Si-S < Si-Cl < Si-P
Si-Cl < Si-S < Si-P
Answer: Si-P < Si-S < Si-Cl
Explanation: Find the two elements that are furthest apart using the increasing electronegativity rule.
Choose the bond below that is least polar.
P-F
C-F
C-I
C-Cl
C-Br
Answer: C-I
Explanation: C-I is least polar because the difference in electronegativity is the least
Place the following elements in order of increasing electronegativity.
Li Fr P
Fr < Li < P
Fr < P < Li
P < Li < Fr
P < Fr < Li
Li < P < Fr
Answer: Fr < Li < P
Explanation: increasting electronegativity = up and to the right
Place the following elements in order of decreasing electronegativity.
S F Te
S > F > Te
Te > F > S
F > S > Te
Te > S > F
F > Te > S
Answer: F > S > Te
Explanation: increasting electronegativity = up and to the right
List the following compounds in decreasing electronegativity difference.
Br2 HBr KBr
HBr > KBr > Br2
KBr > Br2 > HBr
KBr > HBr > Br2
Br2 > HBr > KBr
Answer:
Explanation:
find the electronegativities of each compound
use the relative distances between the compound’s elements coupled with the “up and to the right” electronegativity trend
Br2 = Br to Br = 0 (meaning nonpolar)
HBr = H to Br = very long distance (polar)
KBr = K to Br = on opposite ends of the same row
This would mean the order is: KBr > HBr >Br2
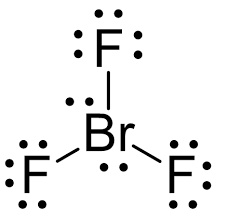
Give the number of valence electrons for SCl4
30
34
32
28
Answer: 34
Explanation: 6 + 7×4 = 34
Give the number of pairs of valence electrons for BBr3.
8
12
14
10
16
Answer: 12
Explanation: 3 + 3×7 = 24 valence / 2 = 12 pairs of valence
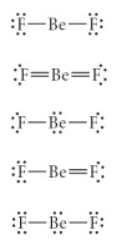
Choose the best Lewis structure for BeF2.
see attached image for answer choices
Answer: see attached image for correct answer
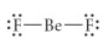
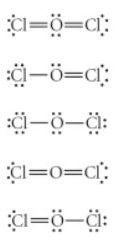
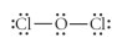
Choose the best Lewis structure for OCl2.
see attached image for answer options
Answer: see attached image for correct answer
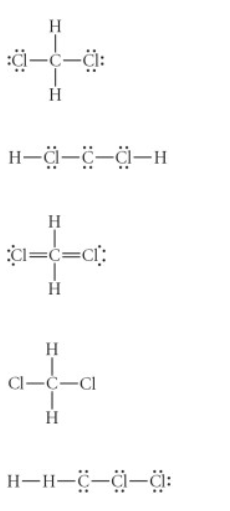
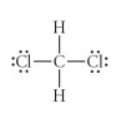
Choose the best Lewis structure for CH2Cl2
see attached image for answer options
Answer: see attached image for correct answer
Give the number of valence electrons for CH2Cl2.
16
12
18
20
22
Answer: 20
C = 4
H = 1
Cl = 7
1×4 + 2×1 + 2×7 = 20 valence electrons
Give the number of valence electrons for XeI2.
22
18
24
16
20
Answer: 22
Xe = 8
I = 7
1×8 + 2×7 = 22 valence electrons
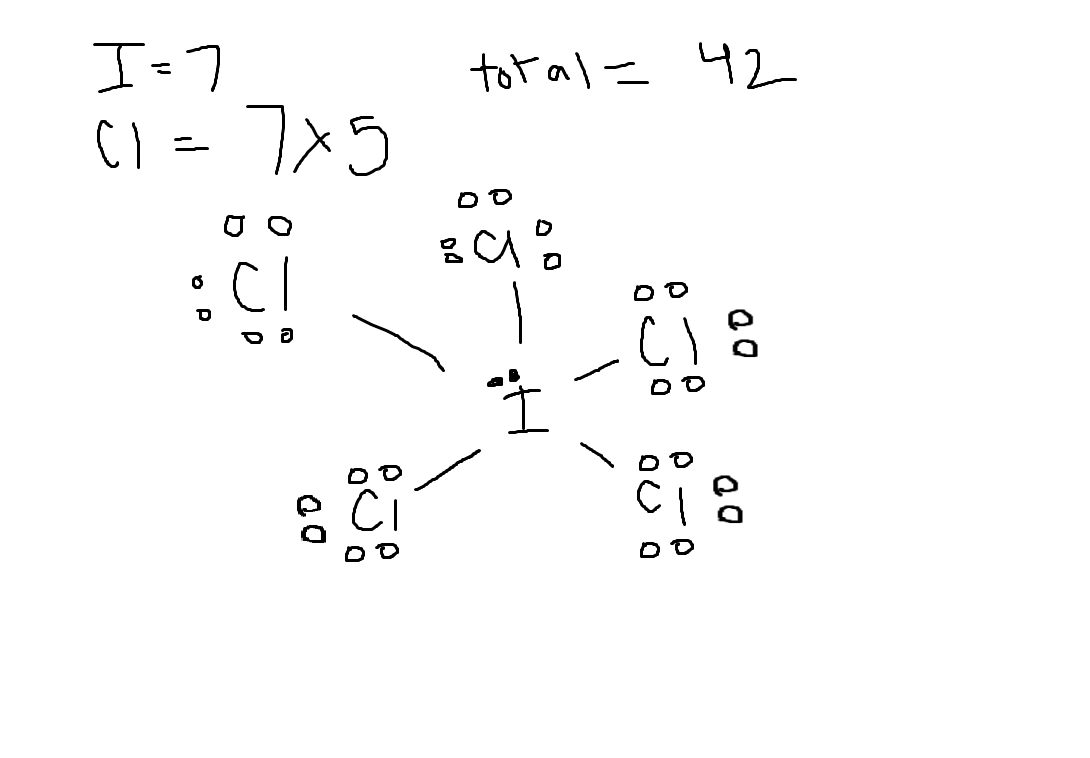
Give the number of valence electrons for ICl5.
36
40
44
46
42
Answer: 42
Explanation:
I = 7
Cl = 7
1×7 + 5×7 = 42 valence electrons
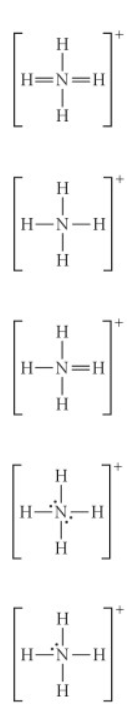
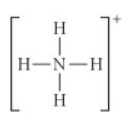
Choose the best Lewis structure for NH4+
See attached image for answer choices
Answer: see attached image for correct answer
Explanation:
when a compound is positively charged we subtract 1 from the total electron count. This allows us to form an octet by subtracting 1 from nitrogen in this case.
Identify the number of bonding pairs and lone pairs of electrons in Br2.
2 bonding pairs and 1 lone pair
4 bonding pair and 2 lone pairs
2 bonding pairs and 3 lone pairs
6 bonding pair and 1 lone pair
1 bonding pairs and 6 lone pairs
Answer: 1 bonding pairs and 6 lone pairs
Explanation:
a bonding pair is a connection between the elements in a molecule. An electron pair is the count of bonding pairs + the count of lone pairs.
Draw a Lewis structure for the following molecule.
NF3
Answer: see attached image
explanation:
NF3 has 26 valence electrons since nitrogen atoms have 5 valence electrons and fluorine atoms have 7 valence electrons. Connecting the nitrogen atom to each fluorine atom with a single bond and then distributing the remaining 20 electrons as lone pairs across the atoms allows for each atom to have a completed octet
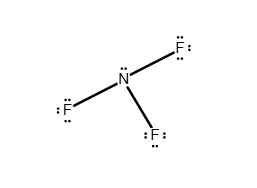
Draw a Lewis structure for the following molecule.
HBr
Answer: see attached image
Explanation:
Hydrogen has a valence shell that can only hold two electrons. Since a H atom has one electron, it only needs one more to complete its shell. However, bromine has seven valence electrons and only needs one to complete its octet. Thus, in HBr bromine and hydrogen share a single electron pair to satisfy both of their valence shells. The remaining six electrons exist as lone pairs on the Br atom.
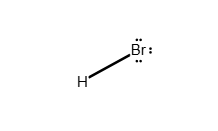
Draw a Lewis structure for the following molecule.
SBr2
Answer: see attached image
Explanation:
The sulfur shares a single electron pair with each bromine atom to satisfy the octet rule. Although sulfur can have an expanded octet, the most stable and likely conformation is the formation of a single covalent bond between the sulfur atom and each bromine atom. The remaining electrons exist as lone pairs on each atom.
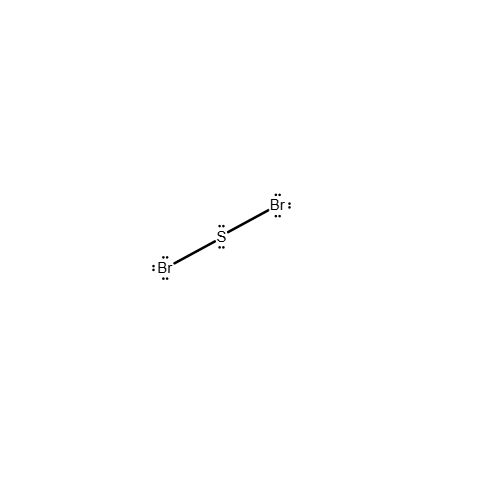
Draw a Lewis structure for the following molecule.
CCl4
Answer: see attached image
explanation:
Carbon has enough valence electrons (four) to share one electron with each chlorine atom to complete the octets of all five atoms in CCl4. In the correct Lewis structure, carbon shares a pair of electrons with each chlorine atom to form four covalent bonds, and the remaining 24 electrons exist as lone pairs on the chlorine atoms.
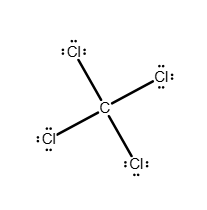
Write a Lewis structure for the molecule or ion.
N2H2
Answer: see attached image
Explanation: Each nitrogen atom contributes 5 valence electrons, and each hydrogen atom contributes 1. The correct structure of this molecule utilizes 12 valence electrons and allows each nitrogen atom to have a full octet of electrons (bonding and nonbonding) while minimizing the formal charge. A double bond between nitrogen atoms allows for every atom to have a formal charge of 0.
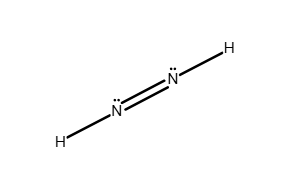
Write a Lewis structure for the molecule or ion.
N2H4
Answer: see attached image:
Explanation:
The total number of valence electrons is 14 (5 from each nitrogen atom and 1 from each hydrogen atom). Each atom has a full octet (or duet in the case of hydrogen). Elements in the second period are unable to have expanded octets because there are only four orbitals at the valence level (n=2).
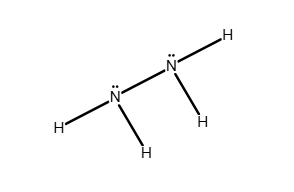
Write a Lewis structure for the molecule or ion.
C2H2
Answer: see attached image
Explanation:
Carbon can form up to four single bonds, but, when bonded with fewer atoms, a triple bond is possible.
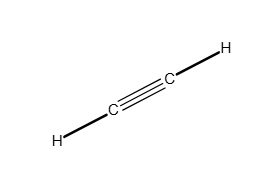
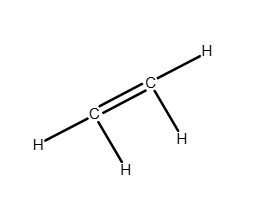
Write a Lewis structure for the molecule or ion.
C2H4
Answer: see attached image
Explanation:
Carbon can form single bonds, double bonds, and triple bonds as long as the octet rule is satisfied.
How many lone pairs of electrons are on the As atom in AsF3?
0
1
2
3
Answer: 1
Explanation: draw the lewis structure for the compound and then identify which
Which element can expand its valence shell to accommodate more than eight electrons?
He
O
P
C
Answer: P (phosphorus)
Explanation: Because phosphorus is a third row element, it can be expanded to accommodate more than eight electrons (has access to 3d orbitals)
Which of the following contains an atom that does not obey the octet rule?
NaCl
BrF
BrF3
SiO2
Answer: BrF3
Explanation: Draw the lewis structures for each and determine if it is an octet or not
NaCl - ionic bonding meaning electrons are transferred NOT shared
metal + nonmetal = ionic bond
Na+ Bonds with Cl- to create octet
BrF - covalent bonding (two nonmetals) electrons shared
Br shares one electron with flourine, Flourine shares one electron with Br
This creates an octet for each of the elements
BrF3 - covalent bonding electrons shared
Br forms 3 covalent bonds with 3 Fs
This means there are 2 lone pairs
Total electrons around Br = 6 bonding electrons + 4 nonbonding electrons = 10 electrons around Br
This violates octet rule which needs 8 electrons around Br (expanded octet is possible because its a 3rd row element those elements on rows 3+ can expand octet while those on rows 1 or 2 cannot
SiO2 - Si forms double bonds with O to obey octet rule
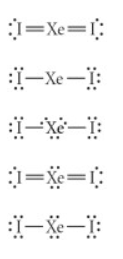
Choose the best Lewis structure for XeI2.
See attached image for correct answer
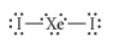
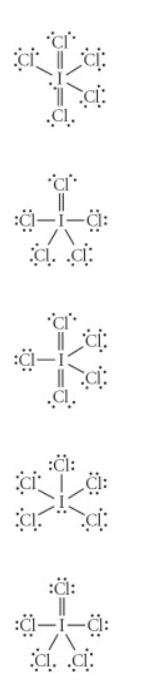
Choose the best lewis structure for ICl5
See attached image for correct answer
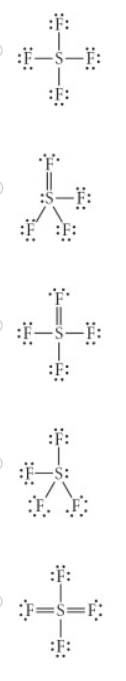
Choose the best Lewis structure for SF4.
Answer shown in attached image
Note the answer does not reflect the exact form of the correct answer but structurally it is the same
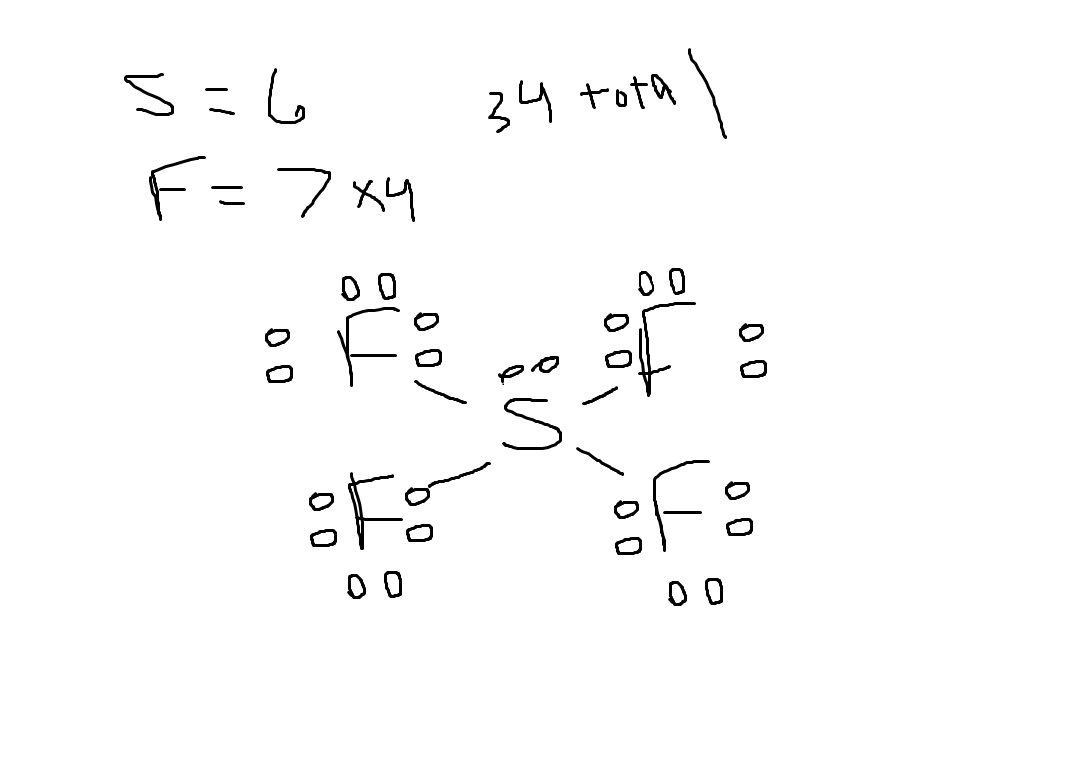
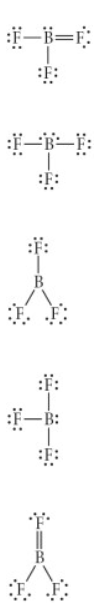
Choose the best Lewis structure for BF3
Asnwer shown in attached image
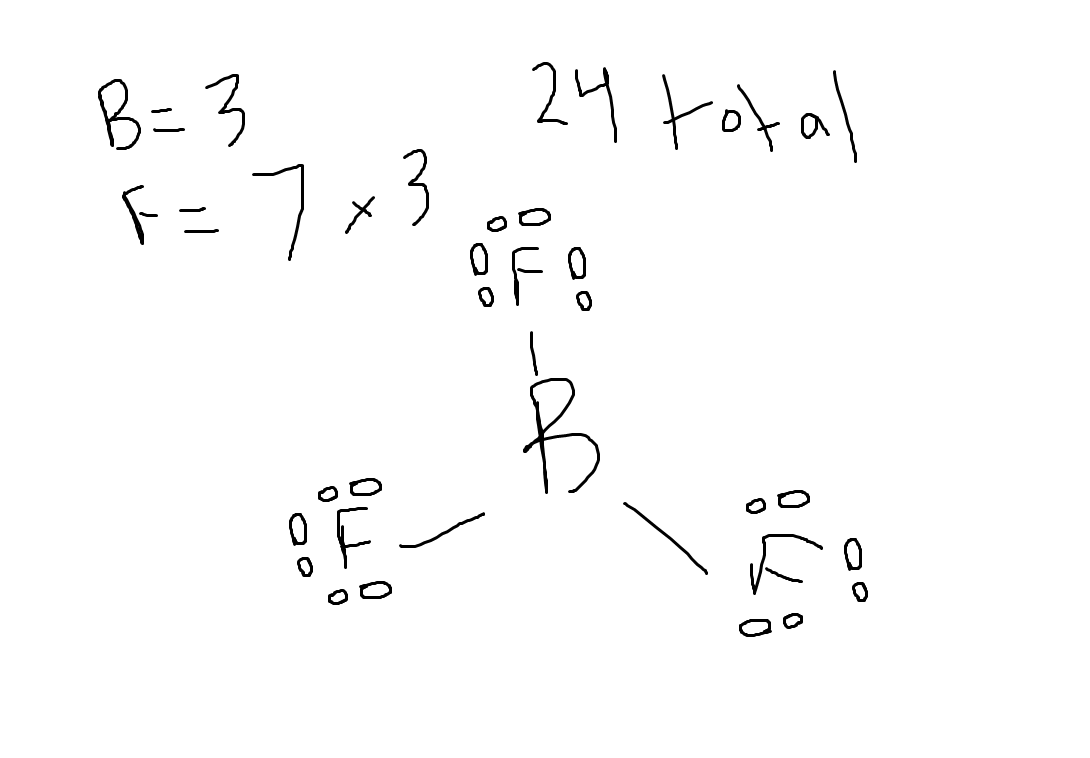
Which compound has the longest carbon-carbon bond length?
CH2CH2
HCCH
CH3CH3
all bond lengths are the same
Answer:
explanation:
Single bonds are longest
Double bonds are shorter
Triple bonds are even shorter
CH2H2: contains a double carbon-carbon bond
H H
\ /
C = C
/ \
H H
HCCH: contains a triple carbon-carbon bond
H – C ≡ C – H
CH3CH3: contains a single carbon-carbon bond
H H
\ /
H – C – C – H
/ \
H H
Therefore CH3CH3 has the longest carbon-carbon bond length
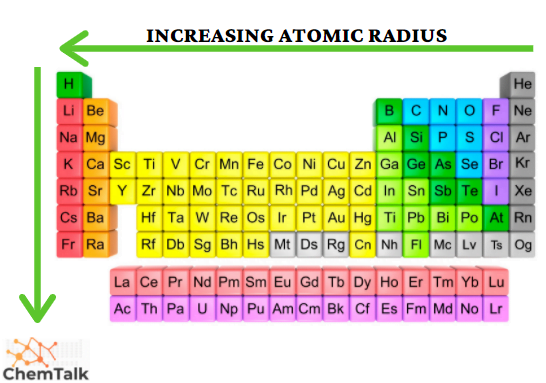
Place the following in order of increasing bond length.
C-F, C-S, C-Cl
C-S < C-Cl < C-F
C-F < C-S < C-Cl
C-S < C-F < C-Cl
C-Cl < C-F < C-S
C-F < C-Cl < C-S
Answer: C-F < C-Cl < C-S
Explanation:
Bond length is influenced by:
Atomic radius — larger atoms form longer bonds
Bond order — more bonds (e.g., double/triple) = shorter bond (not relevant here since all are single bonds)
Electronegativity and orbital overlap — more effective overlap = shorter bond
Therefore, we can identify the longest bond length for this question by finding the element with the largest atomic radius (use attached image for reference)
F < Cl < S
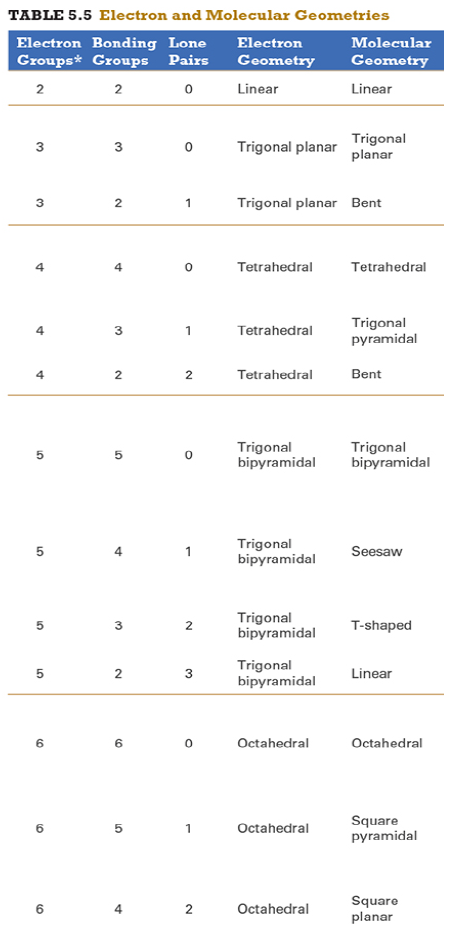
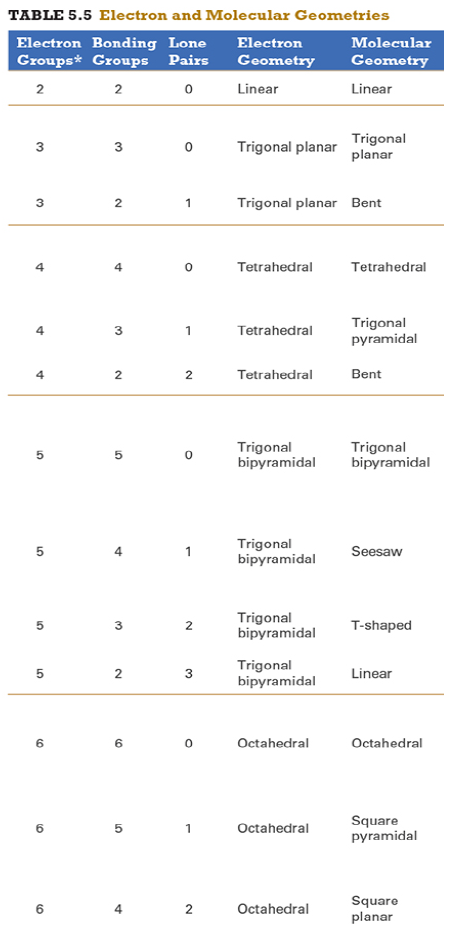
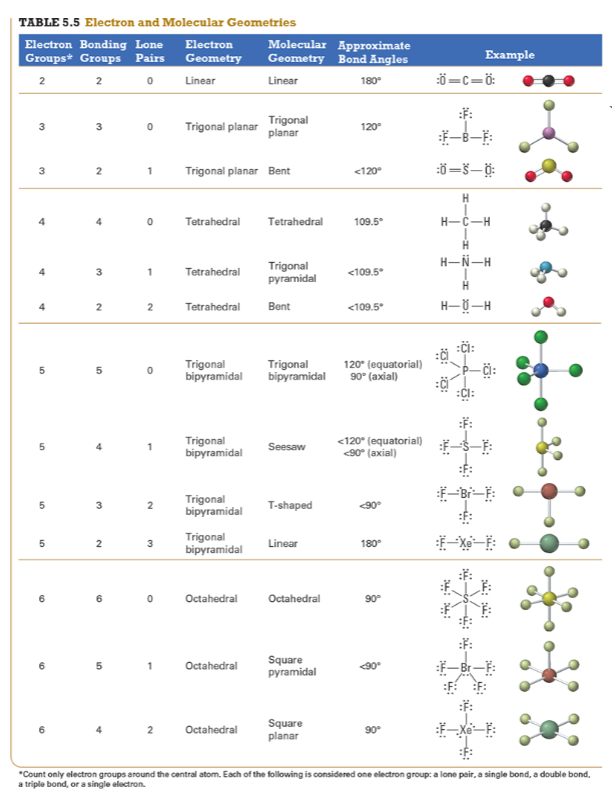
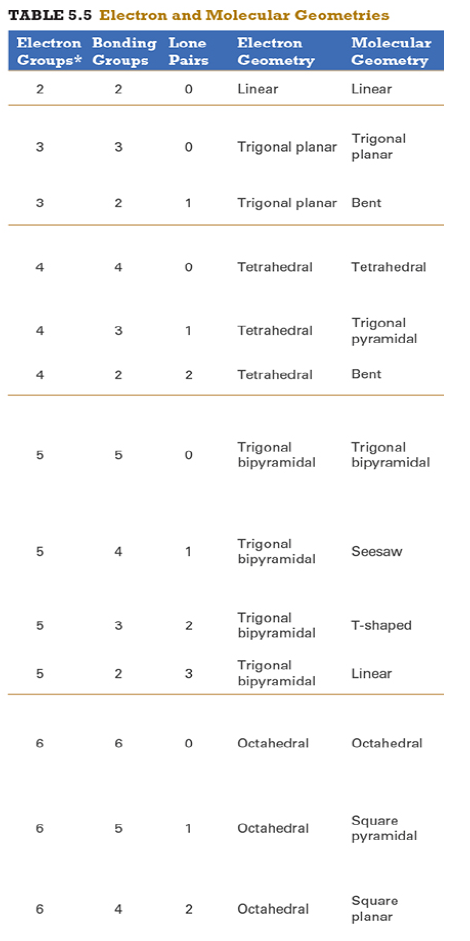
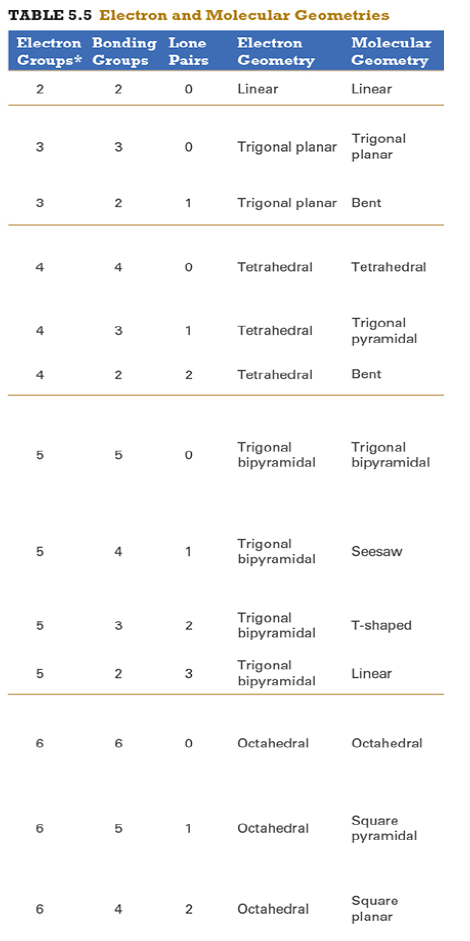
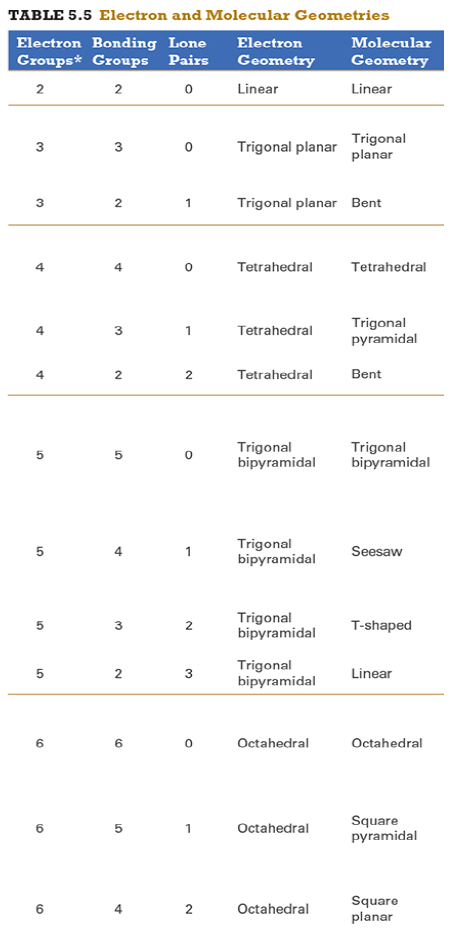
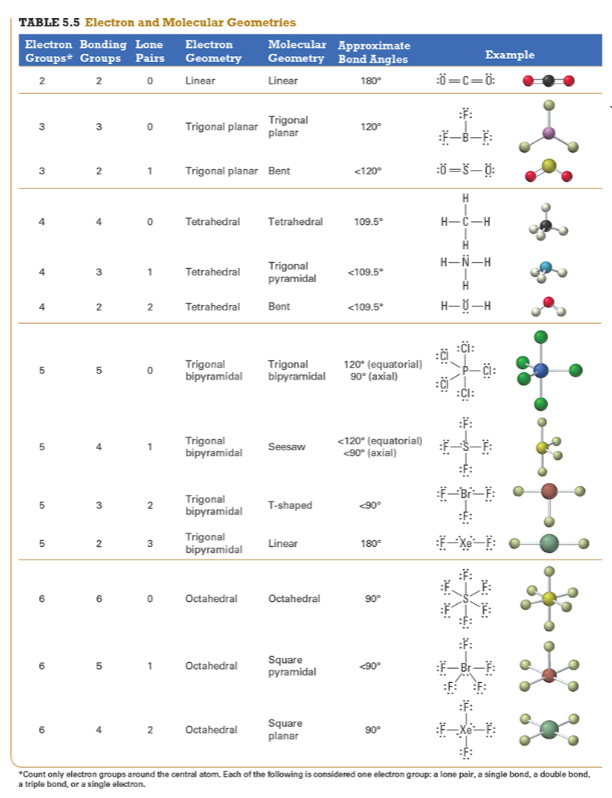
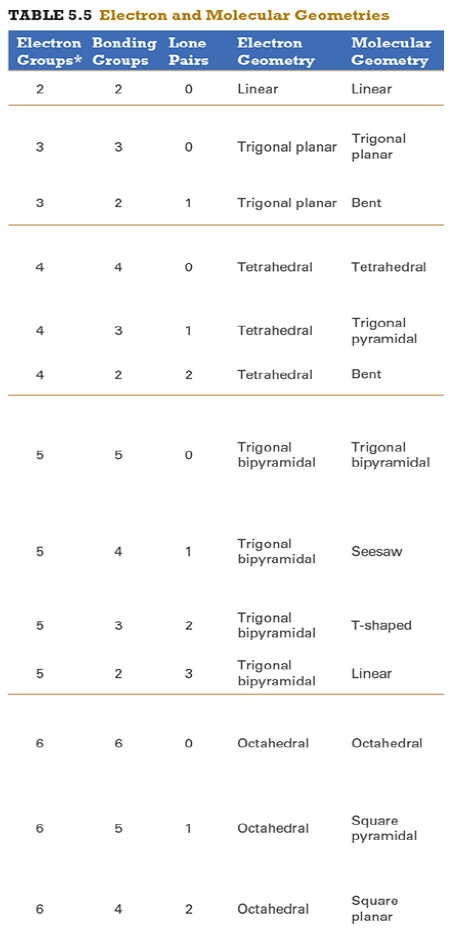
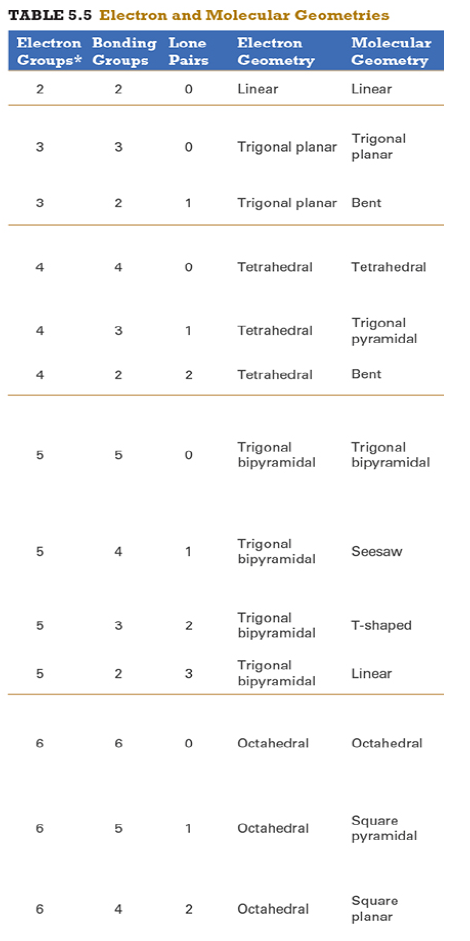
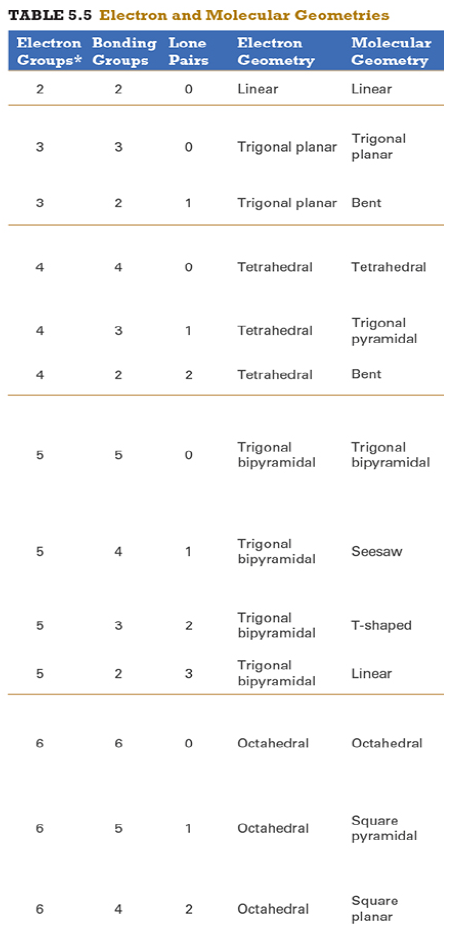
Give the approximate bond angle for a molecule with an octahedral shape.
120°
180°
90°, 180°
109.5°
105°
Answer: 90°, 180°
explanation:
You need to memorize the table attached.
Octahedral meaning 6 electron groups
Know the angle associated with the geometric shape
90° between atoms in adjacent positions
180° between atoms directly opposite each other (linear across the central atom)
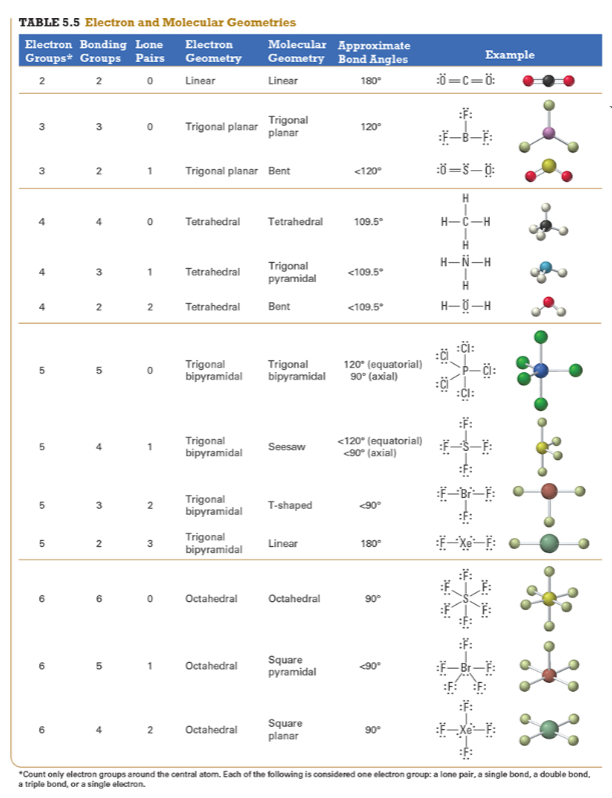
Determine the electron geometry (eg) and molecular geometry (mg) of CH3+1.
eg=tetrahedral, mg=trigonal pyramidal
eg=trigonal planar, mg=bent
eg=tetrahedral, mg=trigonal planar
eg=trigonal planar, mg=trigonal planar
eg=tetrahedral, mg=tetrahedral
Answer: eg=trigonal planar, mg=trigonal planar
Explanation: draw lewis structure
C = 4
H = 1 × 3 = 3 total
Because it is positively ionized we subtract 1 from sum total valence meaning 6 total valence
H
|
C
/ \
H H
Normally C woudl have 4 valence but positively charged so lose an electron
3 EG, 3 BG , 0 LP
Points to trig planar and trig planar for EG and BG (see attached table)
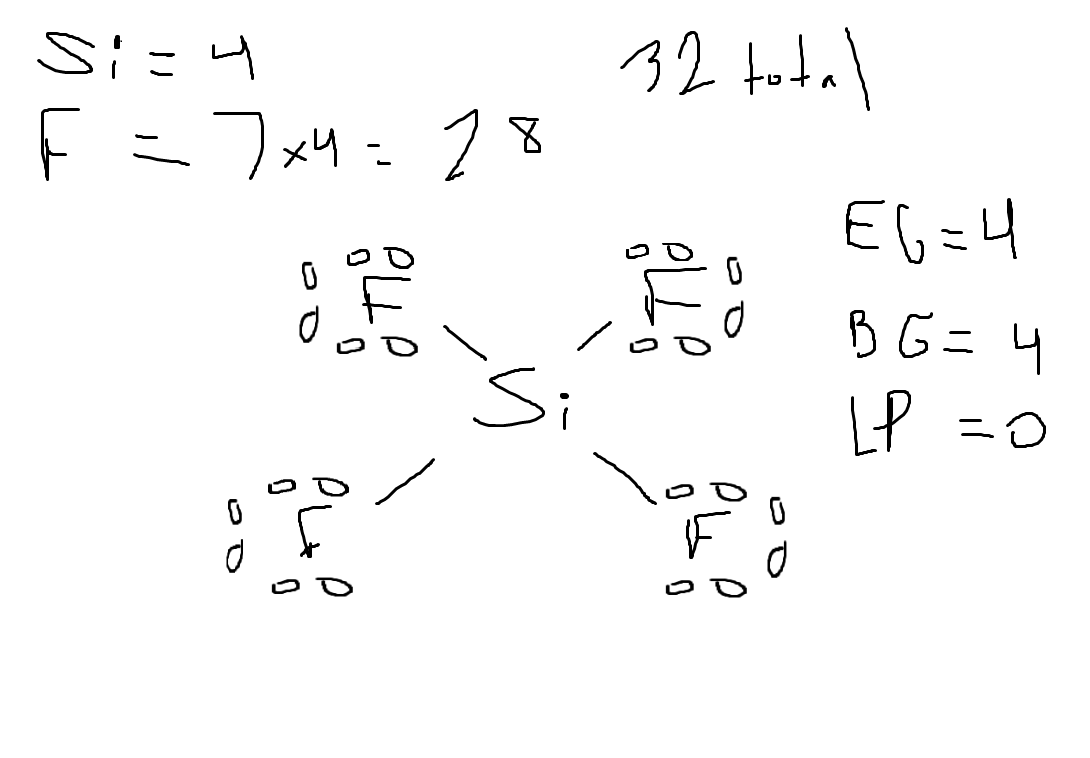
Determine the electron geometry (eg) and molecular geometry (mg) of SiF4.
eg=trigonal bipyramidal, mg=trigonal pyramidal
eg=tetrahedral, mg=tetrahedral
eg=tetrahedral, mg=bent
eg=octahedral, mg=square planar
eg=tetrahedral, mg=trigonal pyramidal
Answer:eg=tetrahedral, mg=tetrahedral
explanation:
Draw lewis structure
Determine EG, BG, and LP
Then determine geometry with VESPR table
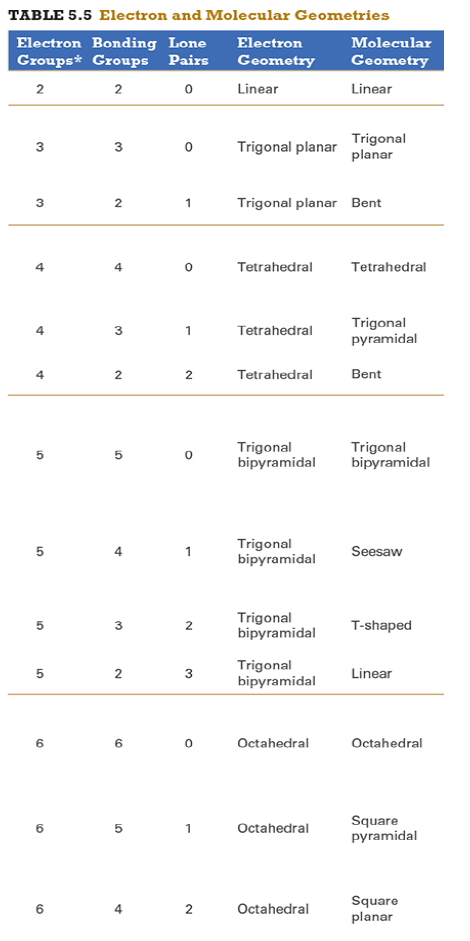
Determine the electron geometry (eg) and molecular geometry (mg) of PF5.
eg=trigonal bipyramidal, mg=trigonal bipyramidal
eg=octahedral, mg=octahedral
eg=trigonal planar, mg=octahedral
eg=trigonal bipyramidal, mg=tetrahedral
eg=tetrahedral, mg=trigonal pyramidal
Answer: eg=trigonal bipyramidal, mg=trigonal bipyramidal
Explanation:
Draw lewis structure
Determine EG, BG, and LP
Then determine geometry with VESPR table
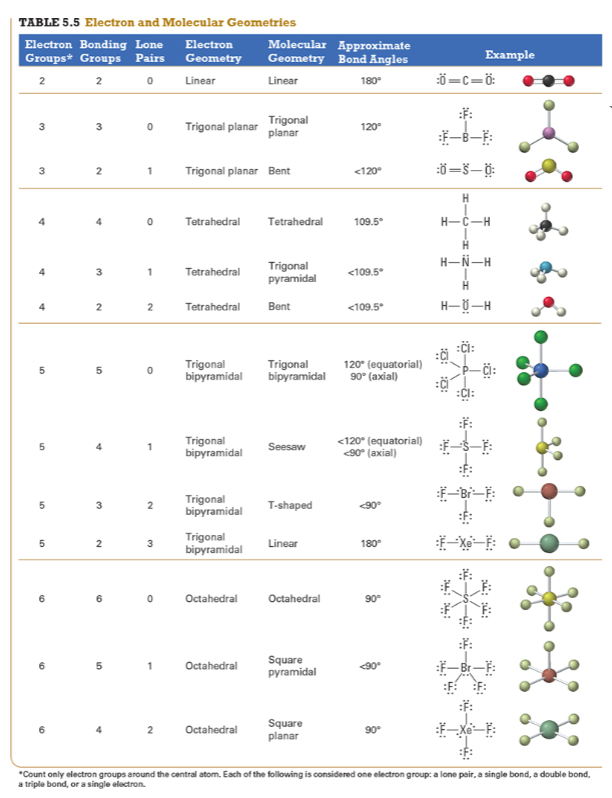
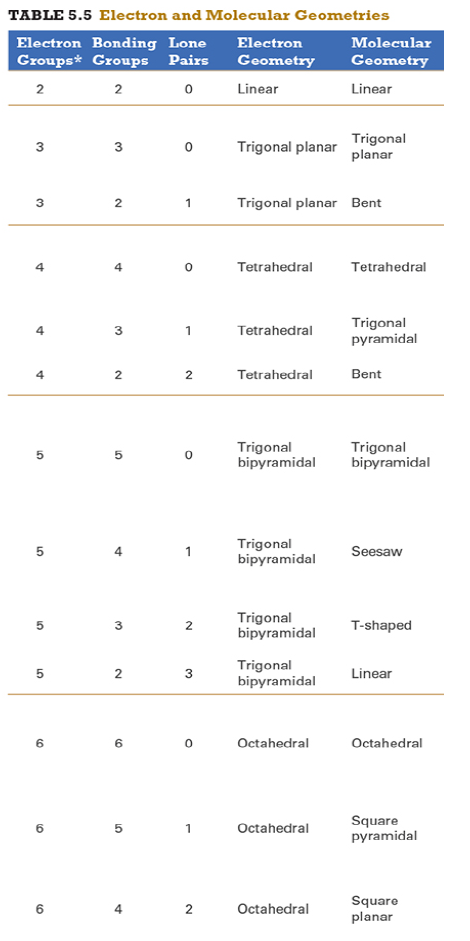
Determine the electron geometry (eg) and molecular geometry (mg) of CO2.
eg=trigonal planar, mg=trigonal planar
eg=linear, mg=linear
eg=linear, mg=trigonal planar
eg=trigonal planar, mg=bent
eg=tetrahedral, mg=tetrahedral
Answer: eg=linear, mg=linear
Explanation:
Draw lewis structure
Determine EG, BG, and LP
Then determine geometry with VESPR table
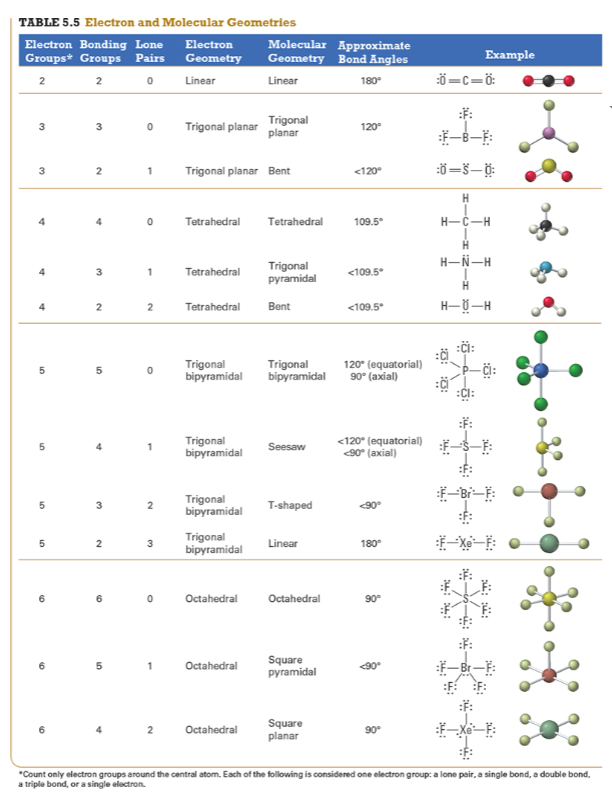
Determine the electron geometry (eg) and molecular geometry (mg) of the underlined carbon in CH3CN.
eg = linear, mg = bent
eg = bent, mg = tetrahedral
eg = linear, mg = linear
eg = tetrahedral, mg = bent
eg = trigonal planar, mg = tetrahedral
Answer: eg = linear, mg = linear
Explanation:
Draw lewis structure
Determine EG, BG, and LP
Then determine geometry of underlined carbon with VESPR table
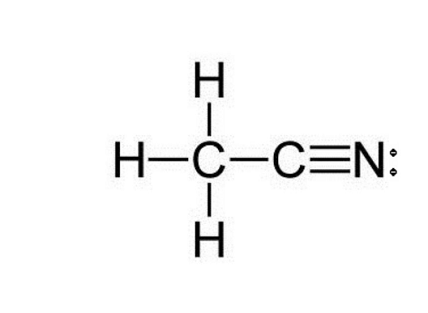
When a central atom has an expanded octet, what geometric shape might the species exhibit?
Hint: An expanded octet would require more than four electron pairs around the central atom.
Equatorial
Trigonal planar
Tetrahedral
Seesaw
Answer: Seesaw
Explanation:
Equatorial - not even a geometry
Trigonal planar - involves 3 electron groups
Tetrahedral - involves 4 electron groups
Seesaw - involves 5 electron groups
Since seesaw is the only option with electron groups > 4 it is the correct answer
According to VSEPR theory, what determines the geometry of a molecule?
the repulsions between electron groups on interior atoms of a molecule
the repulsions between electron groups and the nucleus of an interior atom in a molecule
the attractions between electron groups and the nucleus of an interior atom in a molecule
the attractions between electron groups on interior atoms of a molecule
Answer:
the repulsions between electron groups on interior atoms of a molecule
Explanation:
this is a definition
The bond angle in NH3 is
120°
104.5°
109.5°
107°
95°
Answer:
ExplanationIdeal tetrahedral angle = 109.5°
Lone pairs repel more strongly than bonding pairs, so they compress the bond angle slightly.
Draw the Lewis structure of H2O. Include any nonbonding electron pairs.
What is the electron geometry of H2O?
Answer: See attached image
Electron geometry = tetrahedral because there are 4 electron groups
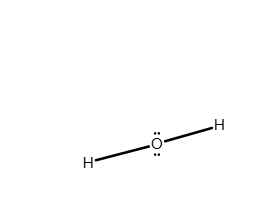
What is the electron geometry of SBr4?
Answer: trigonal bipyramidal
Explanation: It has 5 electron groups
What is the electron geometry of BI3?
Answer: trigonal planar
Explanation it has 3 electron groups
Determine the electron geometry (eg) and molecular geometry (mg) of BCl3.
eg=tetrahedral, mg=trigonal pyramidal
eg=tetrahedral, mg=trigonal planar
eg=trigonal planar, mg=bent
eg=trigonal bipyramidal, mg= trigonal bipyramidal
eg=trigonal planar, mg=trigonal planar
Answer: eg=trigonal planar, mg=trigonal planar
Explanation:
Draw lewis structure
Determine EG, BG, and LP
Then determine geometry with VESPR table
Determine the electron geometry (eg) and molecular geometry (mg) of NCl3.
eg=tetrahedral, mg=trigonal pyramidal
eg=tetrahedral, mg=tetrahedral
eg=linear, mg=trigonal planar
eg=linear, mg=linear
eg=trigonal planar, mg=bent
Answer: eg=tetrahedral, mg=trigonal pyramidal
explanation:
Draw lewis structure
Determine EG, BG, and LP
Then determine geometry with VESPR table
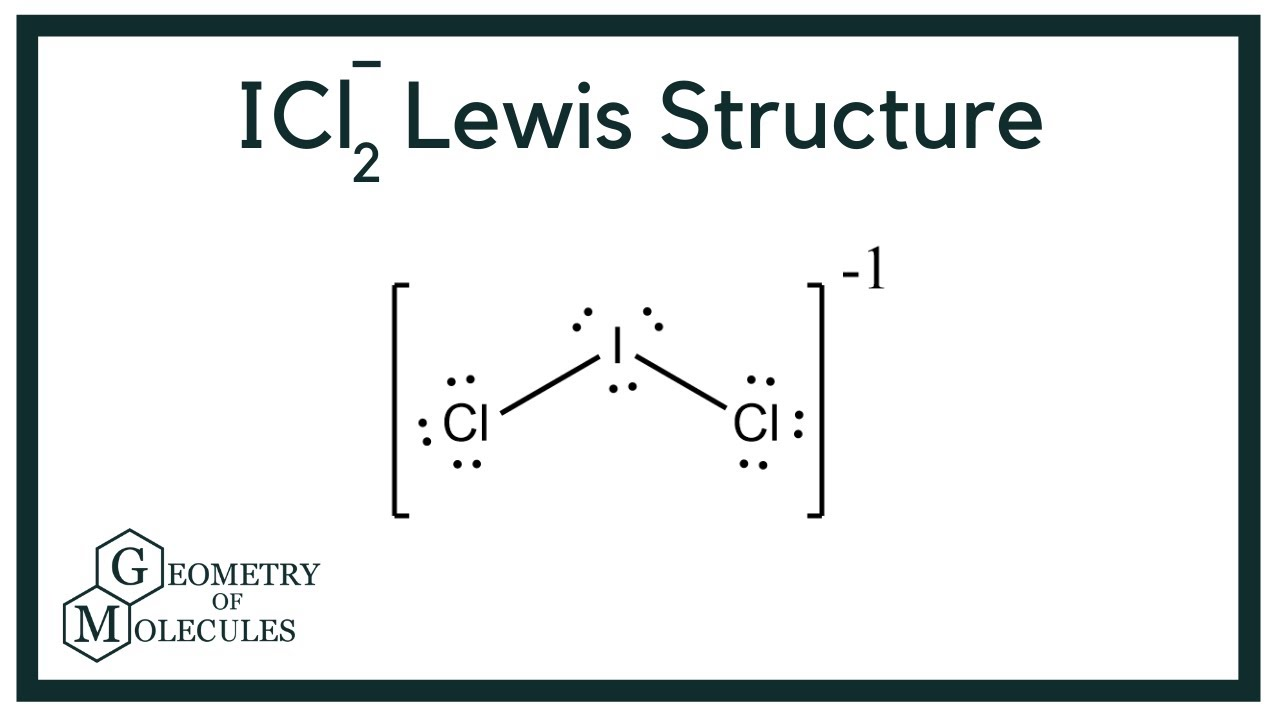
Determine the electron geometry (eg) and molecular geometry (mg) of ICl2-.
eg=tetrahedral, mg=trigonal pyramidal
eg=octahedral, mg=linear
eg=trigonal bipyramidal, mg=linear
eg=trigonal bipyramidal, mg=trigonal planar
eg=tetrahedral, mg=bent
Answer: eg=trigonal bipyramidal, mg=linear
explanation:
Draw lewis structure
Determine EG, BG, and LP
Then determine geometry with VESPR table
Determine the electron geometry (eg) and molecular geometry (mg) of XeF2.
eg=tetrahedral, mg=linear
eg=tetrahedral, mg=bent
eg=trigonal bipyramidal, mg=linear
eg=linear, mg=linear
eg=trigonal bipyramidal, mg=bent
Answer:eg=trigonal bipyramidal, mg=linear
Explanation:
Draw lewis structure
Determine EG, BG, and LP
Then determine geometry with VESPR table
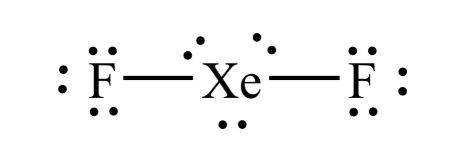
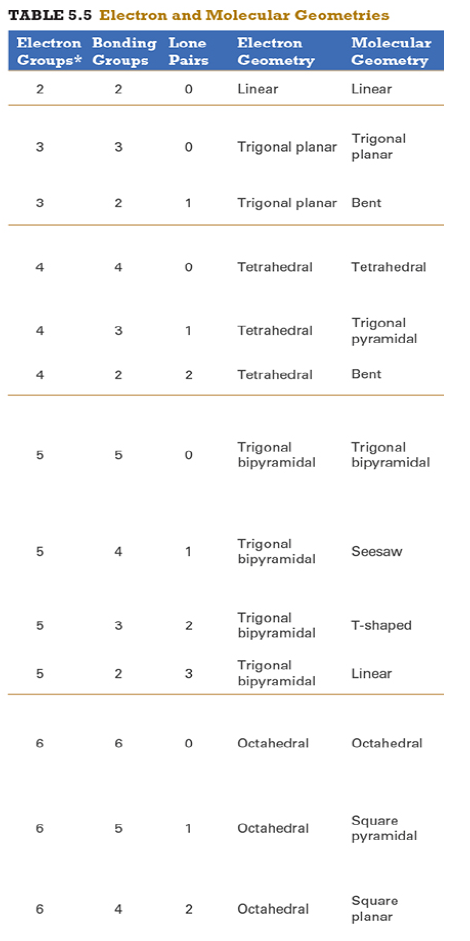
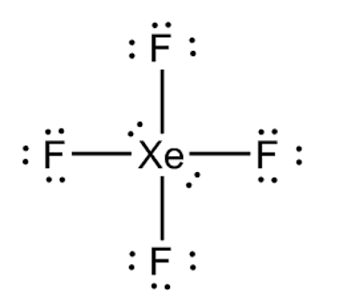
Determine the electron geometry (eg) and molecular geometry (mg) of XeF4.
eg=tetrahedral, mg=bent
eg=linear, eg=linear
eg=tetrahedral, mg=tetrahedral
eg=octahedral, mg=square planar
eg=trigonal bipyramidal, mg=tetrahedral
Answer: eg=octahedral, mg=square planar
explanation:
Draw lewis structure
Determine EG, BG, and LP
Then determine geometry with VESPR table
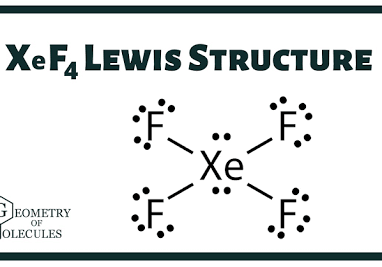
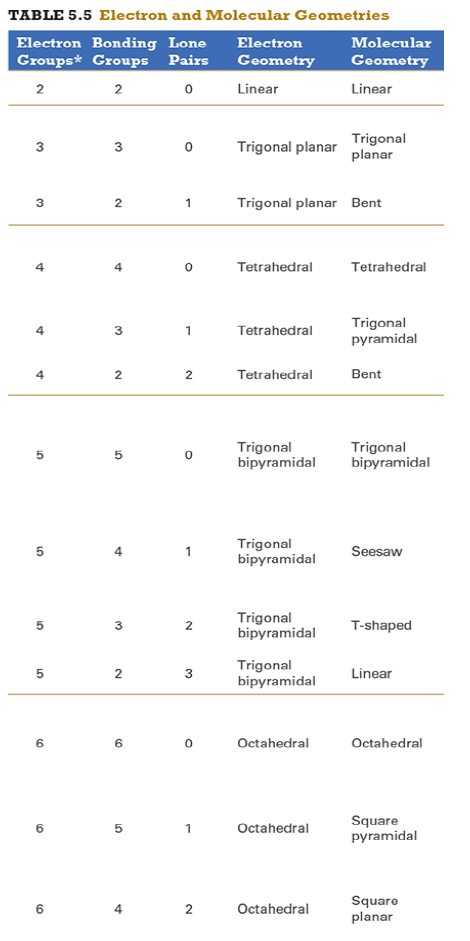
Determine the electron geometry (eg) and molecular geometry (mg) of the underlined atom CH3OCH3.
eg=tetrahedral, mg=bent
eg=tetrahedral, mg=tetrahedral
eg=trigonal bipyramidal, mg=tetrahedral
eg=linear, eg=linear
eg=octahedral, mg=square planar
Answer: eg=tetrahedral, mg=bent
explanation:
Draw lewis structure
Determine EG, BG, and LP
Then determine geometry with VESPR table
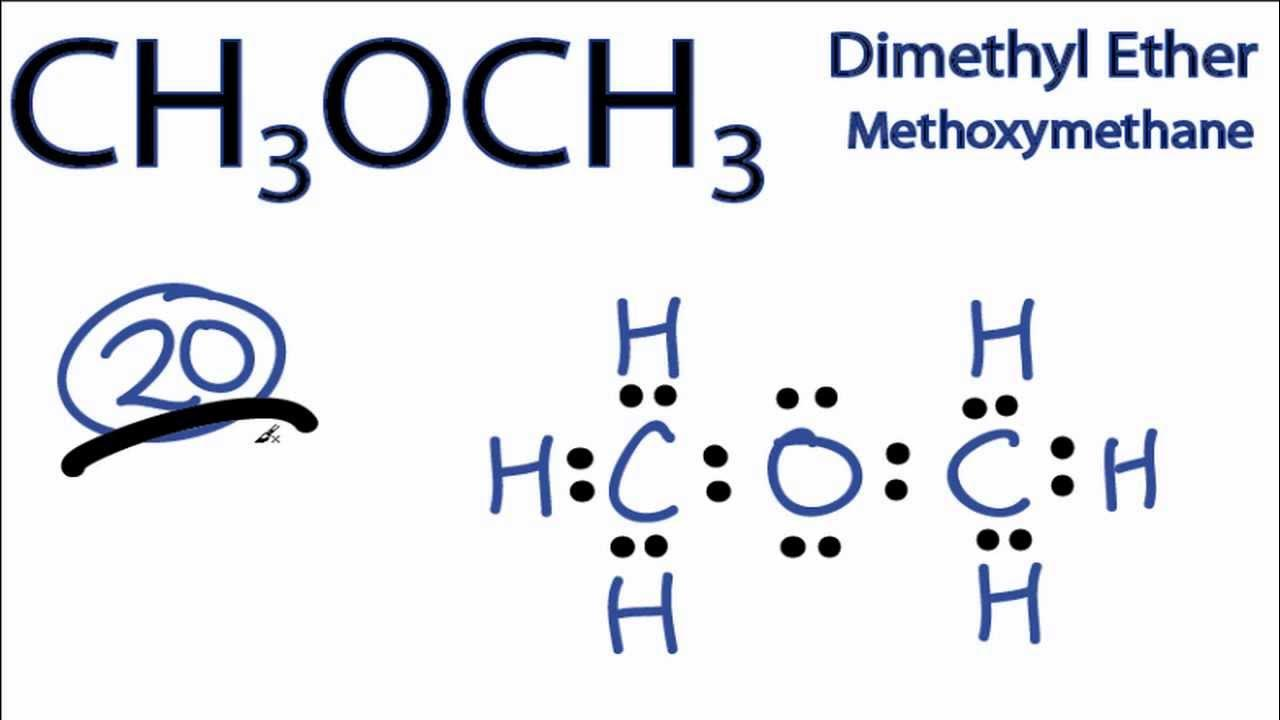
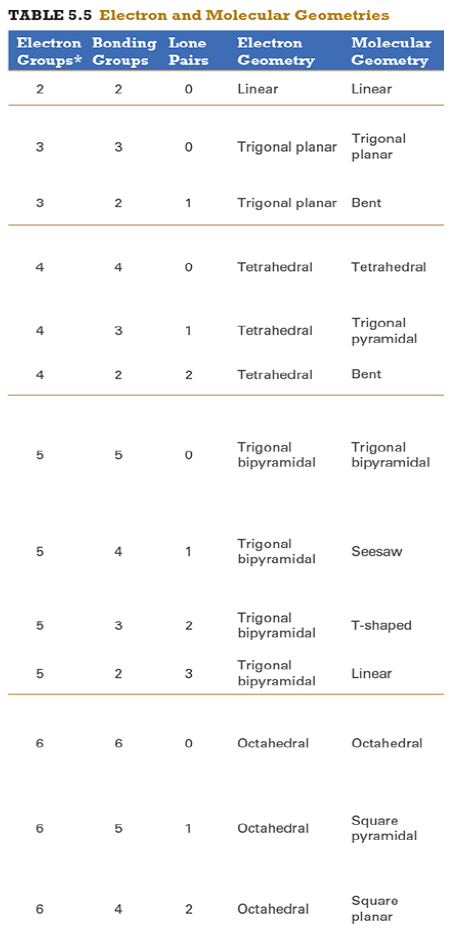
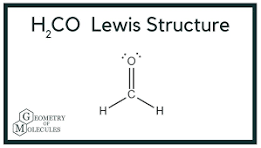
Determine the electron geometry (eg) and molecular geometry (mg) of the underlined atom H2CO.
eg=trigonal bipyramidal, mg=tetrahedral
eg=trigonal planar, eg=trigonal planar
eg=tetrahedral, mg=tetrahedral
eg=octahedral, mg=square planar
eg=tetrahedral, mg=bent
Answer: eg=trigonal planar, eg=trigonal planar
Explanation:
Draw lewis structure
Determine EG, BG, and LP
Then determine geometry with VESPR table
What is molecular geometry of XeF4?
Octahedral
Seesaw
Square planar
Tetrahedral
Answer: Square planar
Explanation:
Draw lewis structure
Determine EG, BG, and LP
Then determine geometry with VESPR table
How many of the following molecules are polar?
PCl5, COS, XeO3, SeBr2
2
1
3
4
0
Answer: 3
explanation:
use geometry to
PCl5 is nonpolar
COS is polar
XeO3 is polar
SeBr2 is polar
Determine the electron geometry (eg), molecular geometry (mg), and polarity of SO2.
eg=linear, mg=linear, nonpolar
eg=tetrahedral, mg=tetrahedral, nonpolar
eg=tetrahedral, mg=bent, polar
eg=trigonal planar, mg=bent, polar
eg=trigonal pyramidal, mg=trigonal pyramidal, polar
Answer: eg=trigonal planar, mg=bent, polar
Explanation:
Draw lewis structure
Determine EG, BG, and LP
Then determine geometry with VESPR table
use geometry and bond angles to determine polarity