Adrenoreceptors and Ligand-Gated Ion Channels Overview
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
how many types of adrenoreceptors
Nine types including α and β subtypes.
β1 Receptors
found in the heart
increase heart rate and force of contraction
gs coupled
β2 Receptors
found in bonchial smooth muscle
involved in bronchodilation and vasodilation
gs coupled
pLGICs
pentameric channels with five subunits in a ring
second transmembrane domain from each subunit forms part of the channel lining
4 transmembrane domains
large n terminal extracellular domain
Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors
pGLIC
cation channels permeable to Na+, K+, and Ca2+
16 different subunits
5 classes of subunit
pharmacological importance of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
blocking neuromuscular transmission
used as relaxant in surgery
GABA-A Receptors
pGLIC
Chloride channels that hyperpolarize cells
physiological importance of GABA-A receptors
main inhibitory neurotransmitter
GABA-A are responsible for fast synaptic inhibition
general anaesthetic
GABA-B vs GABA-A
gpcr
slower inhibition than GABA-A
ionotropic Glutamate Receptors families
NMDA, AMPA and kainate
NMDA Receptors are permeable to which ion
Highly permeable to calcium ions.
Structure of nAChRs
pentameric ligand gated ion channel with cys loop
structure of tyrosine kinase receptors
single transmembrane domain
present as dimers
intracellular domain w tyrosine kinase domain
steps for tyrosine kinase receptor
once agonist binds tyrosine kinase receptor dimerises
tyrosine kinase domain becomes activaated
phosphorylation of residues
binds to intracellular adapter proteins and activates them
physiological importance of tyrosine kinase receptors
regulation of growth and metabolism
insulin receptor
her2 receptor
what is function of her2 receptor
regulation of epithelial cell division and differentiation
used in breast cancer therapeutics
pharmacological importance of tyrosine kinase receptors
synthetic insulin and insulin analogues
target in therapeutics in cancer therapy (her2 receptor)
nuclear receptors function
bind lipophilic agonists that pass through membrane
purpose of companion chaperone proteins
bound to nuclear receptors
helps them fold and remain stable
steps for binding to nuclear receptor
once agonist is bound, chaperone protein disassociates
receptor forms dimer that responds to specific sequences
moves through nuclear pore
influences transcription rate
transactivation or transrepression
structure of nuclear hormone receptor
dna binding domain
linked to ligand binding domain
by hinge region
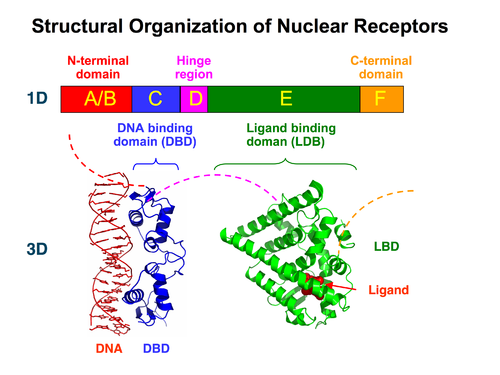
physiological importance of nuclear receptors
regulate basic functions
hormones - steroid sex hormones
examples of nuclear hormone receptors
glucocorticoid
mineralocorticoid
thyroid hormone
main agonist to glucocorticoid receptors (nuclear hormone receptor)
cortisol
function and agonist of mineralocorticoid receptor
regulate salt and water balance
control bp
aldosterone is main hormone
pharmacological importance of nuclear hormone receptors
steroid sex hormone receptors - target for drugs that modulate reproductive system eg oral contraceptive
glucocorticoid receptors - anti-inflammatory agents
mineralocorticoid receptors - target for cardiovascular conditions
thyroid hormone receptors - main treatment for hypothyroidism