cardiac & non-cardiac muscle enzymes- diagnostics
1/66
Earn XP
Description and Tags
diagnostics 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
cardiac laboratory tests are used to
confirm our clinical suspicion of heart disease rather than to establish the diagnosis
cardiac enzymes measure the level of
enzymes that are linked with injury of heart muscles
cardiac enzymes
cardiac troponin
creatinine kinase
lactic dehydrogenase
myoglobin
CK
creatinine kinase
CK with different subtypes
CK isoenzyme CK-MB specific to the heart
LDH
lactate dehydrogenase
cardiac troponins
troponin I
troponin T
both troponin I and T are found in
heart muscles and are released into the blood stream when cardiac cells are damaged
troponin I
TnI
TnI
found only in the heart muscle, more sensitive for diagnosing acute MI
binds to actin in think myofilaments
troponin T
TnT
TnT
found in heart muscle and small amounts in other muscles
binds to tropomyosin
poor renal clearance (pt w/ CKD/ESRD or AKI) can cause decreased
clearance of troponin
in CKD pts, what should you be aware of in relation to troponin?
troponin levels lack specificity in pts with CKD
troponin elevations are mostly related to
ischemic myocyte injury due to acute coronary syndrome (Type I MI)
what is the first line test for evaluation pts with suspected acute MI? why?
cardiac troponin
bc troponin has the highest sensitivity and specificity for myocardial injury
We use high sensitivity troponin I in hospital to detect
troponin at much lower concentrations than what the conventional troponin tests can detect
allows for more rapid diagnosis in pts in the hospital suspected to have acute MI
Troponin T and I are more sensitive and specific for. . .
myocardial injury than CK-MB
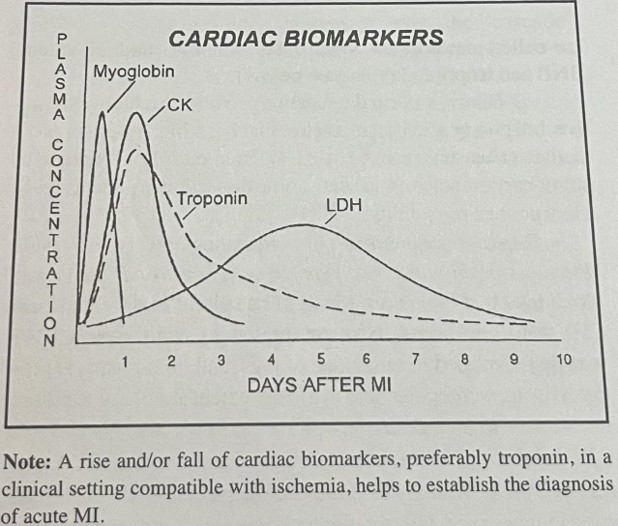
troponin is detectable in serum
3-6 hours after an acute MI begins
troponin reaches 95-99% sensitivity and specificity by
10 hours
troponin peaks at
24-48 hours→ peak level correlates with size of infarct
troponin remains detectable in serum for
10-14 days after the acute events (4x longer than CK levels) → allows for dx of an acute MI even more than a week after onset
cardiac troponins can detect. . .
lesser degrees of myocardial necrosis and is useful to diagnosis microinfarcts in CK-MB negative pts with ACS
troponin is used to r/o . . .
false positive CK-MB suspected acute MI
dx of acute MI
needs to be a rise and/or fall in cardiac troponin levels along with a clinical picture consistent with ACS
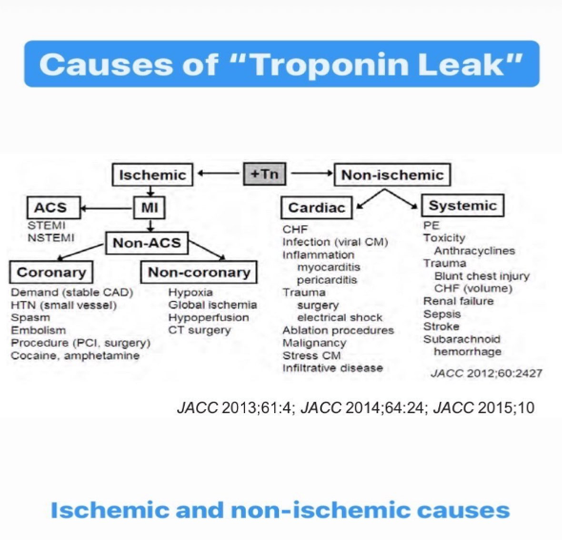
causes of troponin leak
cardiac biomarkers
troponins can be elated in conditions that
result in supply-demand ischemic mismatch (type II MI)
things that can cause troponin leaks
anemia, tachyarrhythmias, hypotension, hypertension, myocarditis, PE d/t RV ischemia, acute CHF, renal failure (CKD/AKI/ESRD), catheter ablation procedure, electrical cardioversions/defibrillators, CPR, PCI and CABG, post surgery, vigorous exercise, sepsis, critical illness
elevated serum troponin levels in pts with ACS may reflect
watershed injury or minor degrees of myocardial necrosis that result from microembolic from an unstable coronary atherosclerotic plaque
troponin levels may not rise until . . . . . after the onset of symptoms
6 hours
SO measurements need to be repeated if initial troponin levels are negative at < 6 hrs from onset of chest pain
serial troponins are crucial in the . . .
diagnosis (rise and/or fall)
CK is found in
the tissues of the heart, skeletal muscle, CNS, lungs
CK subtypes
CK-BB
CK-MB
CK-MM
CK-BB
brain tissue and smooth muscle
CK-MB
mostly in the heart muscle, but small amounts in skeletal muscles
CK-MM
skeletal muscle
CK rises for . . . . after the acute event and peaks at . . . .
several hours and peaks at 24 hrs
CK returns to baseline within
48-72 hrs
CK can be elevated from
non-cardiac sources; less specific to the heart
skeletal muscle injury
trauma
surgery
IM injections
myopathy or myositis
secondary to statins
rhabdomyolysis
hypothyroidism
renal disease (less affected by renal function compared to troponins)
CK-MB is the . . .
most specific CK isoenzyme to the heart
CK-MB is less sensitive and specific for
myocardial injury than troponin I or T
CK-MB is only marginally specific for . . .
acute MI and not a reliable lab value by itself to r/o acute MI
1/3rd of ACS pts have
elevated troponin levels but negative CK-MB
CK-MB is useful for clarifying the etiology of
myocardial injury in addition to troponin levels when diagnosis is not clear
CK-MB is used at times when the provider. . .
cannot discern chest pain etiology and do not have a reason for troponin elevation
CK-MB can be useful for diagnosing
reinfarction given it returns to baseline faster than troponin levels (which can persist for days)
LDH is found in
almost all body tissues but highest concentrations in the muscle, liver, kidneys, and RBCs
how many isoenzymes of LDH?
5 separate isoenzymes
LDH can be found in the heart, but . . .
elevation is very non-specific for cardiac cause
not used in cardiology often
LDH-1
for myocardial injury
LDH serum levels rise more gradually 24-48 hrs after acute MI and peak at 3-5 days after the acute event
returns to baseline around 5-10 days
LHD-5
in liver injury
LDH-2 and LDH-3
in lung injuries and disease
if all LDH levels are elevated
suggests multi-system organ disease
LDH is falsely positive if
hemolysis occurs, strenuous exercise, drugs (EtOH, aspirin, narcotics)
myoglobin
heme protein that is rapidly released from damaged tissue in the bloodstream
myoglobin is found in high concentrations within
skeletal muscle and heart tissue
smaller molecule detected in the serum earlier than CK-MB or troponins but LESS specific for myocardial necrosis
myoglobin
myoglobin is the
first to appear, first to peak, first to decline
myoglobin may be detected . . .
as early as 2 hrs after the onset of myocardial necrosis→ HOWEVER not cardiac specific
myoglobin peaks
within 4-12 hrs and then immediately returns to baseline levels
myoglobin is excreted in the
urine and can be elevated d/t poor renal clearance
myoglobin has ________ sensitivity
HIGH
negative myoglobin within the first several hours after the onset of chest pain can be useful in r/o an acute MI
myoglobinuria is not used in
the diagnosis of ACS
if myoglobinuria is positive it suggests
non-cardiac source
myoglobinuria can be ________ after fevers, infections, trauma
falsely elevated
myoglobinuria→ urine test
urine test that is measured at rest and after exertion
indicated to r/o rhabdomyolysis, metabolic disorders, mitochondrial disorders