Animal Health Management and Disease Prevention
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Mortality
death loss - obvious economic loss
Morbidity
sickness - lower production and higher production costs; even more of an economic loss
Noninfectious disease
results from injury, genetic abnormalities, poor nutrition, etc.
Infectious disease
caused by microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, and protozoa
Contagious
if it spreads rapidly from one animal to another
Immunity
process by which particles foreign to the body are identified and destroyed or metabolized
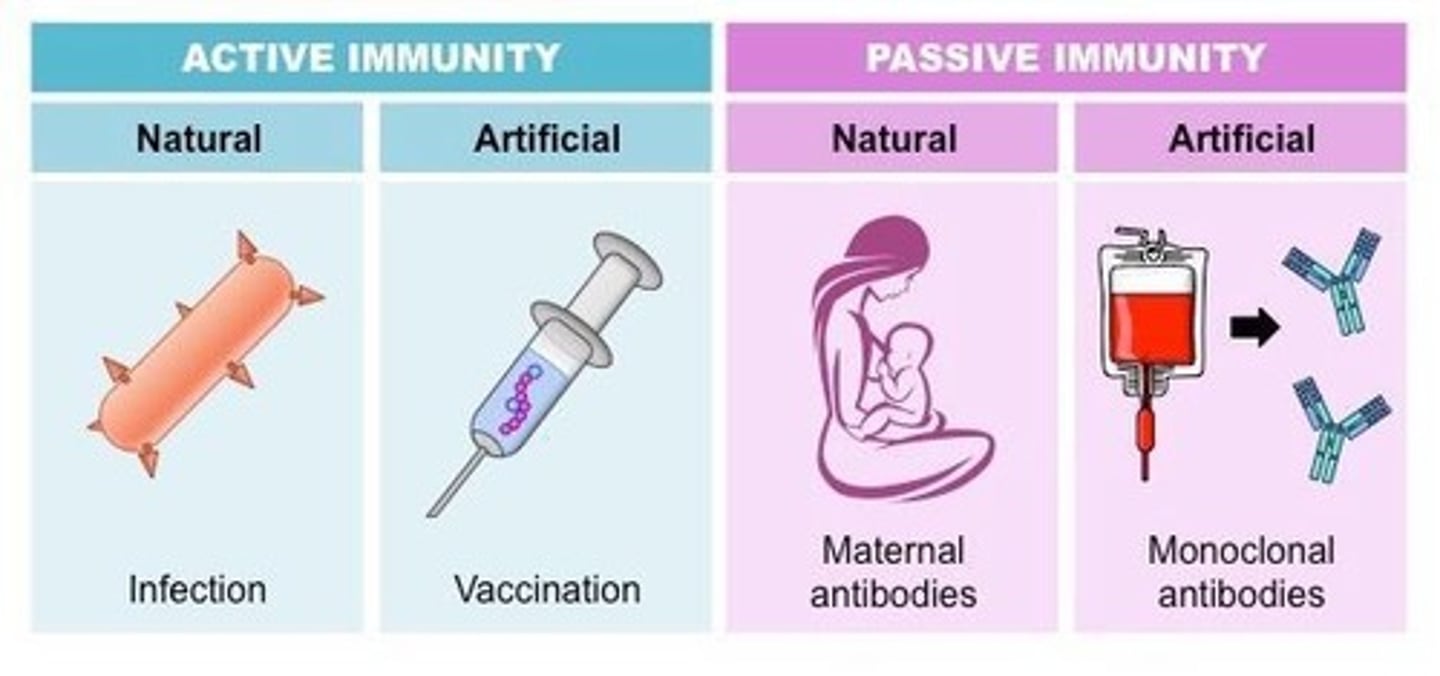
Natural (native) immunity
present at birth (skin, secretions, acidic stomach)
Acquired resistance
activated when body encounters foreign substances, involves lymphocytes
Passive immunity
receive from colostrum
Active immunity
attained when the individual can initiate its own antibody production against specific invasive antigens
Whole herd management
necessary for prevention of health-related losses
Veterinarian-assisted planning
vets help plan and implement the health-management program
Sanitation
can reduce exposure to pathogens and affect severity and susceptibility
Sound nutritional management
important for maintaining strong immune systems and reducing vulnerability to microorganisms
Record analysis
keeping a record of diseases caught from an outbreak, and medication given at the time
Biosecurity
measures taken to protect livestock from disease
Proper use of biologics and pharmaceuticals
ensures effective treatment and prevention of diseases
Minimization of stress
important for maintaining animal health
Personnel training
ensures staff are knowledgeable about health management practices
Disease incidences
Records of occurrences of diseases in animals.
Mortality rates
The rate at which animals die in a given population over a specific time period.
Morbidity rates
The rate at which animals become ill in a given population over a specific time period.
Vaccination records
Documentation of vaccinations administered to animals.
Treatment records
Records that include animal ID, date of treatment, product administered, withdrawal dates, dose, route of administration, and site of administration.
Facilities cleanliness
The necessity to maintain clean facilities to prevent harm and disease spread.
Physical facilities
Structures that can cause physical injury or stress to animals and may spread pathogens.
Source of livestock
The origin from which animals are purchased, emphasizing reliability to reduce disease transmission.
Herd health-management programs
Effective programs that manage the health of animal herds to prevent disease.
Cross contamination
The transfer of pathogens from one source to another, often through human actions or vehicles.
Biosecurity
Measures taken to protect animal health by preventing the introduction and spread of diseases.
Serological testing
Testing for antibodies in the blood to determine immune response.
Pharmaceuticals
Substances used mainly to treat diseases in animals.
Biologicals
Substances used primarily to prevent diseases in animals.
Vaccines
Biologics used to stimulate active immunity in animals.
Passive immunity
Immunity that is transferred from a vaccinated dam to her offspring.
Killed vaccines
Vaccines made from inactivated pathogens.
Modified live vaccines
Vaccines made from live pathogens that have been altered to not cause disease.
Chemically attenuated vaccines
Vaccines made from pathogens that have been weakened through chemical processes.
Isolation facilities
Areas designated for isolating animals to observe for disease symptoms.
Monitoring incidence of disease
The process of tracking and recording occurrences of diseases in a population.
Employee protocols
Guidelines for employees interacting with animals to ensure biosecurity.
Topical
Applied to the skin.
Oral
Administered through the mouth by feeding, drenching, using a balling gun.

Injection
Administered via a needle and syringe.
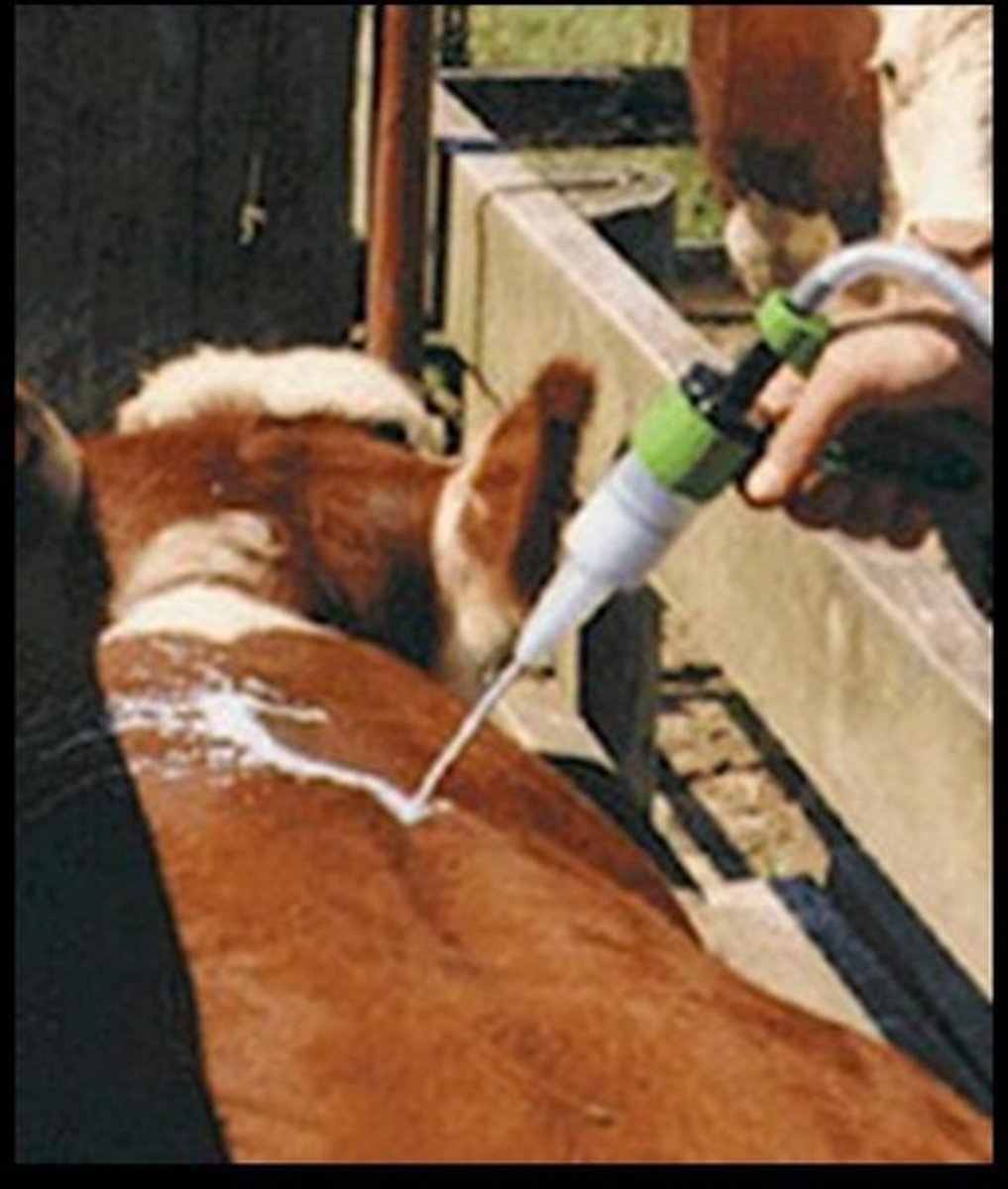

Subcutaneous
Administered under the skin.
Intramuscular
Administered into muscle.
Intravenous
Administered into a vein.
Intramammary
Administered through the teat canal.
Intraperitoneal
Administered into the body cavity.
Intrauterine
Administered through the cervix and into the uterus.
Intranasal
Administered via inspired air.
Stress
Any environmental factor that can cause a significant change in the animal's physiological processes.
Prolonged stress
Can impair the immune system.
Visual detection
Usually the first step in detecting unhealthy animals.
Vital signs
Indicators such as body temperature, respiration rate, heart rate, gut sounds, ease of respiration, capillary refill rates, and coloration of the eye.
Quality assurance programs
Designed by professionals to help producers improve management practices, record keeping, and personnel training.
Best practices
A series of approved protocols designed to assure wholesome and safe products.
Client-patient relationship
A valid relationship with a veterinarian is required for quality assurance.
Herd health plan
An effective plan focusing on prevention.
Antimicrobials
Responsible use of substances including antibiotics is required.
Record keeping
A system for animal ID and health records is necessary.
Employee training
Certification and accountability of employees is essential.
Humane animal handling
Providing appropriate animal care is a requirement.
Environmental stewardship
Responsible management of environmental resources is necessary.
Continuous improvement
Ongoing enhancement of practices is required.
Disease
Any deviation from normal health with marked physiological, anatomical, or chemical changes.
Mortality and morbidity rates
Minimized in an excellent herd health management program.