Waves 1
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Made with help from @beanny3004's flashcards: https://knowt.com/flashcards/7e598737-637e-4f97-ac54-0b748931397a
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Progressive wave
A wave in which oscillations (or peaks & troughs / compressions & rarefactions) move through the medium as energy is transferred
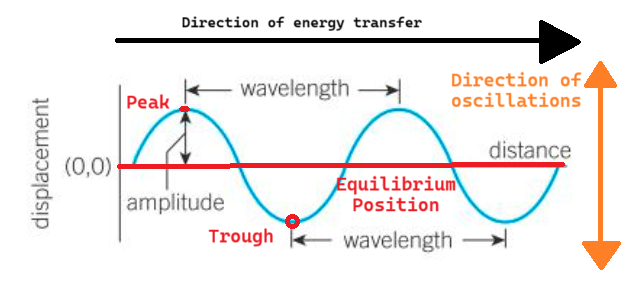
Displacement
distance from the equilibrium position in a particular direction; a vector, so it can have either a positive or a negative value
Amplitude
Maximum displacement from the equilibrium position (can be positive or negative)
Wavelength
minimum distance between two points in phase on adjacent waves, for example, the distance from one peak to the next or from one compression to the next
Period of oscillation (time period)
The time taken for one oscillation
Frequency
The number of oscillations per unit time
Wave speed
the distance travelled by the wave per unit time
Wave speed equation
v = fλ
wave speed = frequency x wavelength
Releationship between frequency and time period
f = 1/T
Phase
The position of a certain point on a wave cycle, (units are radians, degrees or fractions of a cycle)
Phase difference
How far ‘out of step’ the oscillations at two points on the same wave or two points on similar waves are from each other
Difference is normally measured in degrees/radians, but sometimes in fractions of a cylce or wavelength
Transverse wave sketch (include the direction of oscillations, the direction of energy transfer, equilibrium position, wavelength, amplitude and peak & trough)
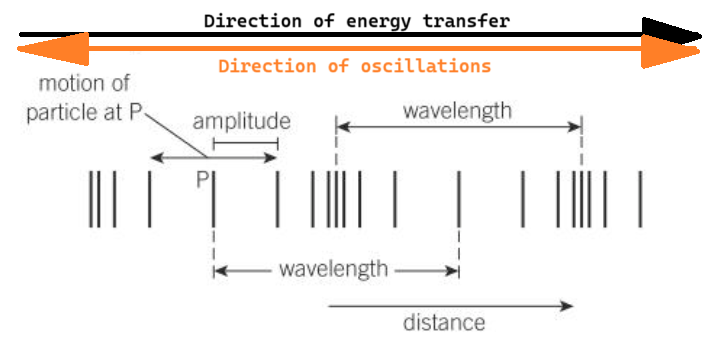
Longitudinal wave sketch (include the direction of oscillations, the direction of energy transfer, wavelength, amplitude and compressions & rarefactions)
Transverse wave
A wave in which oscillations (of medium particles) are perpendicular to the direction of energy transfer
Longitudinal wave
A wave in which oscillations of the medium particles are parallel to the direction of energy transfer
Describe the difference between longitudinal and transverse waves.
In a transverse wave oscillations are perpendicular to the direction energy transfer
In a longitudinal wave oscillations are parallel the direction of energy transfer
Range of wavelengths of radio waves
10-1 to >106 metres
Range of wavelegnths of microwaves
10-3 to 10-1 metres
Range of wavelengths of infrared radiation
7×10-7 to 10-3 metres
Range of wavelengths of visible light
4×10-7 to 7×10-7 metres
Range of wavelengths of ultraviolet
10-8 to 4×10-7 metres
Range of wavelengths of x-rays
10-13 to 10-8 metres
Range of wavelengths of gamma rays
<10-16 to 10-10 metres
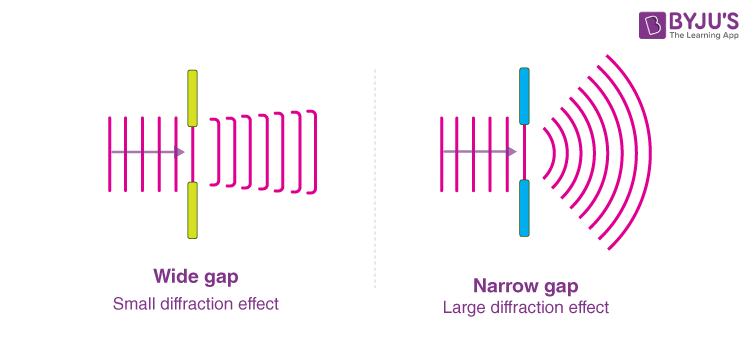
Diffraction
The spreading out of a wave front as it passes through a gap or around an obstacle. Maximum diffraction will occur when the gap the wave passes through is the same size as the wavelength of the incident wave
Reflection
When a wave changes direction at a boundary between two different media so that the wave remains in the original medium
Law of reflection
The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection
Refraction
The change in direction of a wave when it passes from one medium to another
Law of refraction
n1sin(θ1)=n2sin(θ2)
Snell’s law
n sin(θ) = k
where n is the refractive index of material, θ is the angle between the normal and the incident ray, and k is a constant
In phase
When particles are oscillating perfectly in step - they have 0 phase difference
In anti-phase
When particles are oscillating completely out of step - they have a phase difference of πc / 180o
Refractive index
The ratio of the speed of light through a vacuum to the speed of light through the material
It has no units as it is a ratio
n = c/v
Critical angle
The angle of incidence at the boundary between two media that will produce an angle of refraction of 90°
Sin(C)=1/n
Total internal reflection
The reflection of all light hitting a boundary between two media back into the original medium when the light is travelling through the medium with the higher refractive index and the angle of incidence at the boundary is greater than the critical angle
Conditions required for TIR
The light must be travelling through a medium with a higher refractive index as it strikes the boundary with a medium with a lower refractive index.
The angle of incidence must be above the critical angle. This angle depends on the refractive index of the medium.
Intensity
The power transmitted per unit area
Intensity = power / area = P / A
Has unit Wm-2
What is the relationship between intensity and amplitude?
Intensity is proportional to amplitude2: I ∝ A2
Electromagnetic wave
Transverse wave with oscillating electric and magnetic field components at right angles to each other
They don’t need a medium to propogate
They have a speed of 3×108ms-1 in a vacuum
Electromagnetic spectrum
full range of frequencies of EM waves, from gamma rays to radio waves
Wave profile
displacement-distance graph of a wave (‘snapshot’ of the wave)
Unpolarised wave
Transverse wave in which the oscillations occur in many planes
Partially polarised wave
Transverse wave in which there are more oscillations in one particular plane, but the wave is not completely plane polarised
This occurs when transverse waves reflect off a surface
Plane polarised wave
A transverse wave in which the oscillations are limited to only one plane - the convention is to use the electric field
Polarisation (transmission) axis
The axis (direction) which waves are allowed through a polarising filter
How a polarising filter works
Contains many long chain molecules that are aligned in the same direction
The molecules absorb light aligned in that direction
Therefore the orientation of the molecules is PERPENDICULAR to the polarisation axis. Diagrams usually show the polarisation axis - DO NOT CONFUSE THE TWO
Describe how you can use a polarising filter to determine if a beam of light is polarised. State clearly what you should observe.
Rotate the polarising filter and look for dim and bright light alternating every 90°
How does changing the wavelength affect diffraction
Assuming the wavelength is still comparable to the size of the gap:
Shorter wavelength means less diffraction
Longer wavelength means more diffraction, until the wavelength is greater than or equal to the gap. After this it diffracts the same amount
How does the movement of air molecules creates compressions and rarefactions in a sound wave travelling through air?
The air molecules oscillate parallel to the direction of the energy transfer.
This creates areas of high and low pressure which are compressions and rarefactions respectively