Image Processing Techniques in Ultrasound Imaging
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
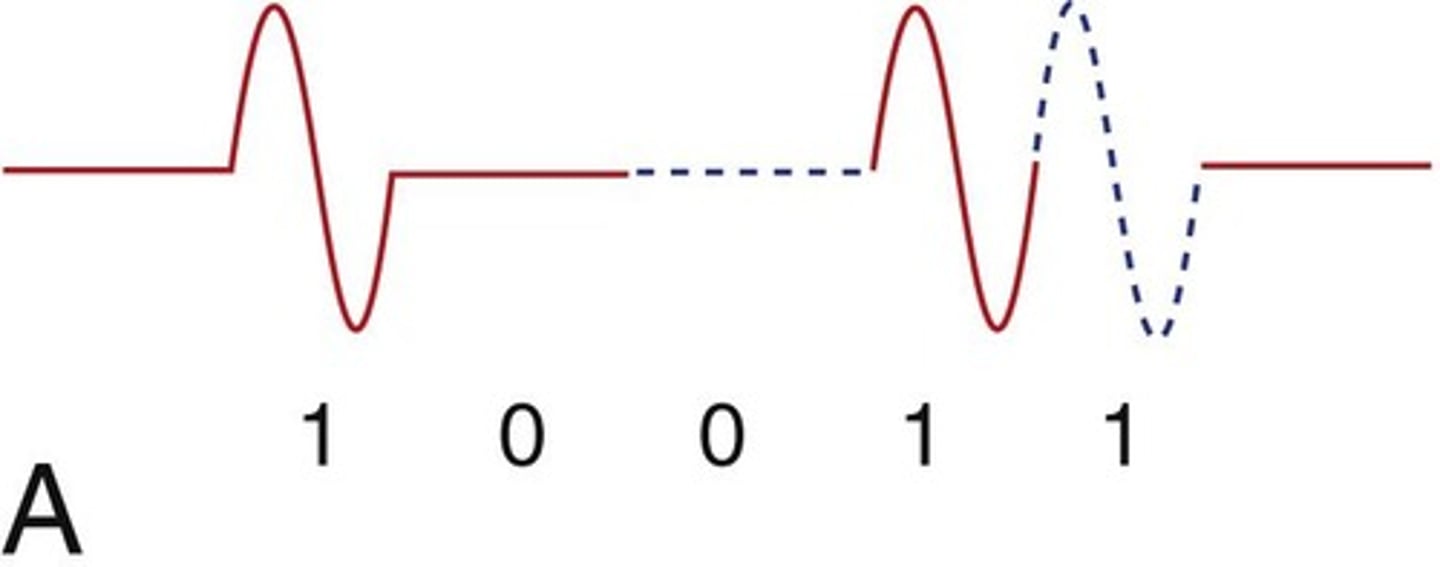
Code Excitation
Uses pulses and gaps for signal transmission.
Higher SNR
Increased signal-to-noise ratio enhances image quality.
Spatial Compounding
Reduces artifacts and improves spatial resolution.
Frequency Compounding
Combines frequency ranges for better image quality.
Preprocessing
Image processing before storing in memory.
Edge Enhancement
Sharpens image boundaries for better detection.
Pixel Interpolation
Fills missing pixels using adjacent pixel averages.
Persistence
Averages frames to reduce noise and smooth images.
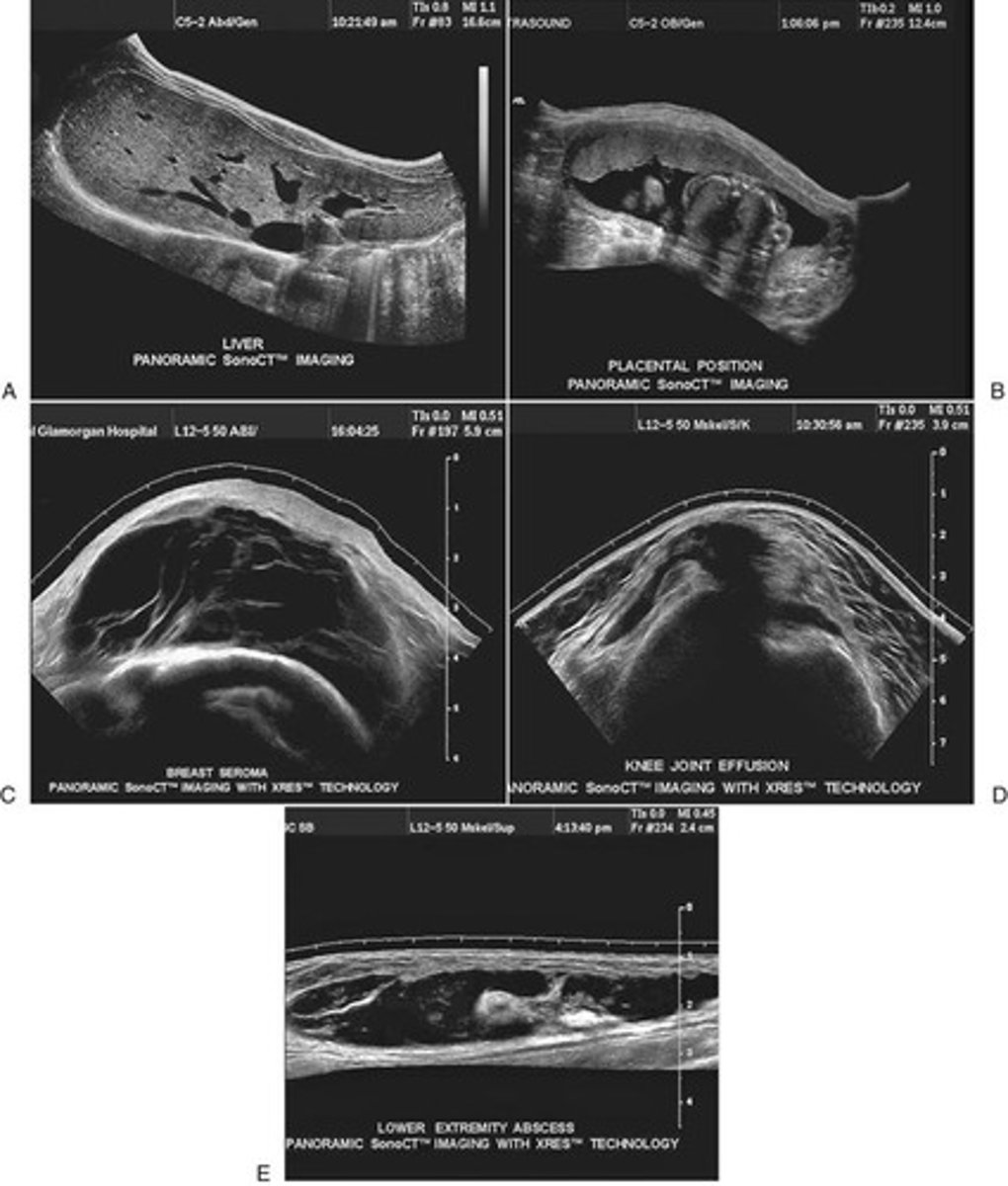
Panoramic Imaging
Extends field of view by combining frames.
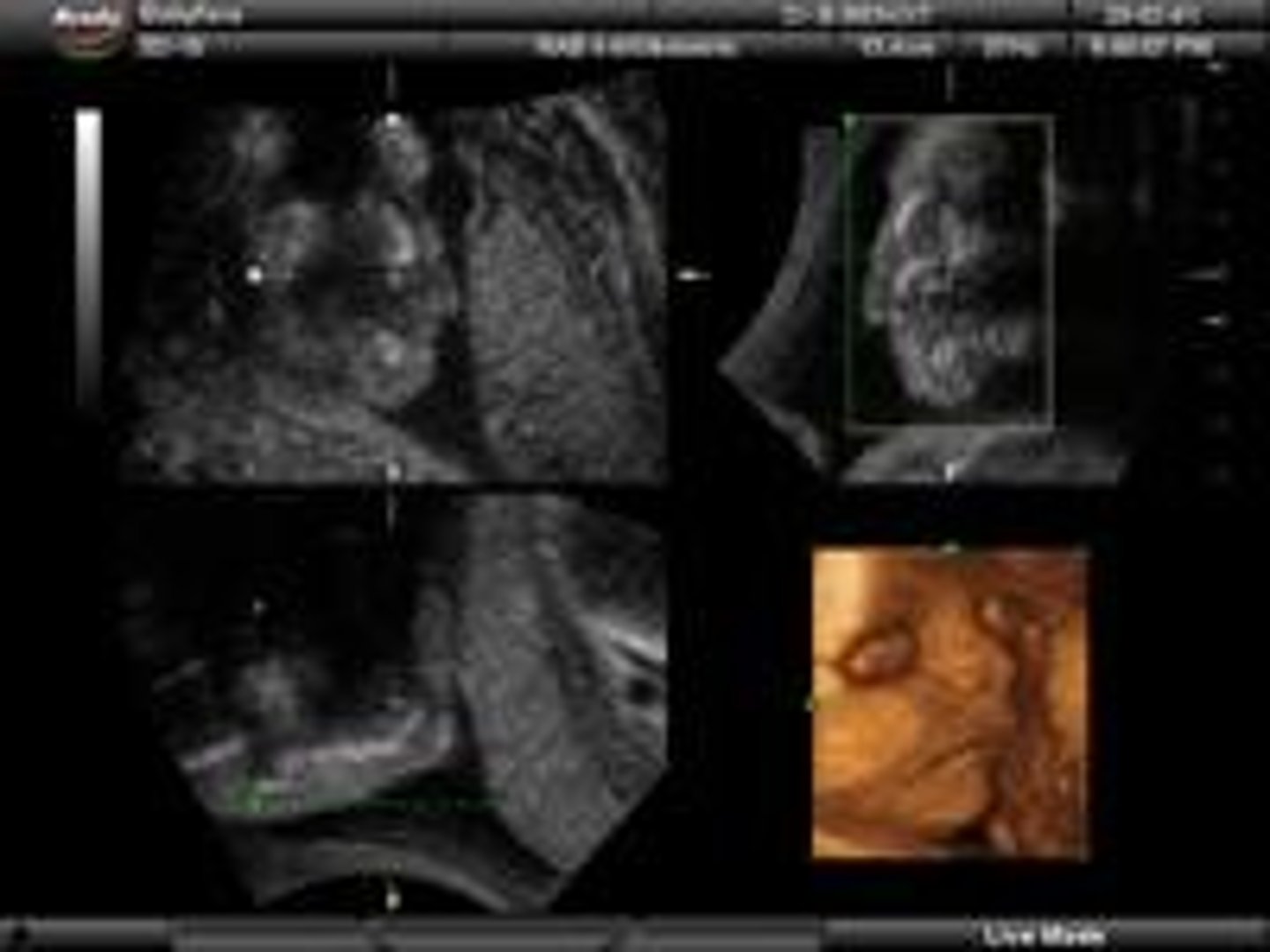
3D Imaging
Creates 3D images from multiple 2D scans.
Write Zoom
Improves spatial resolution by rescanning ROI.
Image Memory
Stores image frames for display and retrieval.
Pixels
Smallest unit of a digital image.
Pixel Density
Number of pixels per inch in an image.
Bits
Smallest unit of computer memory.
Byte
Group of 8 bits in computer memory.
Gray Shades
Determined by bits assigned to each pixel.
Binary Numbers
Use digits 0 and 1 for data representation.
Postprocessing
Image processing after echoes are stored.
Read Zoom
Zooms ROI after data collection.
B Color
Assigns colors to improve contrast resolution.
Harmonic Imaging
Improves image quality by reducing artifacts.
Cine Loop
Stores last frames before freezing the image.
Matrix
Arrangement of pixels in rows and columns.
Dynamic Range
Range of brightness levels in an image.
Grating Lobes
Unwanted signals affecting image quality.